Abstract
We discuss the dynamical properties of a SIRS computer virus propagation model with impulsive detoxication and saturation effect. By the Internet, new antivirus software can be released immediately and take effect quickly after it is running. This leads to the circumstance that many infected computers can be cured in a short time. So impulsive detoxication is a vitally important way for prohibiting the spread of network viruses. The theoretical results show that: (a) the virus-free equilibrium is globally stable when the basic reproduction ratio (BRR) is less than unity, (b) the system is uniformly permanent when BRR exceeds unity, and (c) a supercritical bifurcation occurs when BRR equals unity. Several numerical examples also clearly display the results obtained. Finally, some feasible strategies of eradicating electronic viruses are advised.
Similar content being viewed by others
1 Introduction
While the popularized communication networks have brought great convenience to our daily work and life, they also provide a fast channel for the spread of computer viruses. During the last decades, massive outbreaks of network viruses have caused enormous financial losses.
For the purpose of effectively controlling virus diffusion, it is of practical importance to understand the way that malicious codes propagate over the Internet. Due to the compelling analogy between electronic viruses and their biological counterparts [1, 2], a multitude of computer virus epidemic models, ranging from SIS models [3, 4], SIR models [5, 6], SIRS models [7], SEIR models [8], SEIRS model [9], SLBS models [10–12], SLAS model [13], SIPS model [14], to delayed models [7, 15] and stochastic models [16, 17], have been proposed. In our opinion, these models can help us better understand how the viruses diffuse on networks.
In the classical epidemic models, the incidence rate β, which is the probability of transmission per contact, is assumed to be bilinear with respect to the numbers of susceptible and infected individuals [18]. To the best of our knowledge, in most of previous computer virus models, the incidence rate β is also simply supposed to be unvaried [19, 20]. However, in reality, when the population are aware of the existence of computer viruses on networks, they will reduce the number of communication contacts per unit time to avoid being infected, the more infectious computers being reported, the less contact with other computers, which is called the saturation effect. In an attempt to capture the saturation effect, Yuan et al. [21] proposed a nonlinear incidence rate. As the transmission details of computer infections are quite complicated, their results have only limited applications. Recently, Yang and Yang [22] also suggested a nonlinear incidence rate. However, its description of saturation effect is not clear. Based on a large number of numerical examples, we use \(1/(1+\alpha I(t))\) (α is a positive constant and \(I(t)\) represents the percentage of infected internal computers at time t, respectively) to denote the saturation effect [23], namely, use \(\frac{\beta}{1+\alpha I(t)}\) to replace β. This seems reasonable.
In the prevalence of infectious diseases, it is impossible to rapidly disseminate the new remedy to a great many patients, and it often takes a lot of time to finish one or several courses of the remedy [24–26]. On the contrary, as new antivirus software can be released immediately via the Internet and takes effect quickly after it started running, many of the infected computers can be cured in a short time [20]. To understand how impulsive detoxication [16] and saturation effects prohibit virus spread on networks, a novel impulsive computer virus propagation model is established in this paper. We theoretically analyze that the virus-free equilibrium is globally asymptotically stable when BRR is less than unity. It is shown that the system is uniformly permanent when BRR exceeds unity. In addition, by bifurcation theory we see that a supercritical bifurcation occurs when BRR equals unity. Both theoretical predictions and numerical examples show that impulsive detoxication can control virus diffusion effectively. Finally, considering the influence of varying model parameters on BRR, we propose some feasible strategies of deracinating malicious viruses. One should emphasize that there are few computer virus propagation models in the literature that consider the combined impact of impulsive detoxication and saturation effects.
The remainder of this paper is organized as follows: the new model is elaborated in Section 2; it is theoretically studied in Sections 3, 4, and 5; the influence of model parameters is discussed in Section 6; finally, this work is summarized in Section 7.
2 Model formulation
In this section, we will formulate a computer virus propagation model with impulsive detoxication and saturation effects. As usual, we shall simply assume that every computer is in one of three states: susceptible, infected, and recovered. Both susceptible computers and recovered computers are uninfected, however, the former has no immunity, while the latter has temporary immunity. Let \(S(t)\), \(I(t)\), and \(R(t)\) denote the percentages of susceptible, infected, and recovered internal computers at time t, respectively, then \(S(t)+I(t)+R(t)\equiv1\).
For simplicity, in this paper, we do not consider the situation where the susceptible computers get recovered.
Considering the above discussions, we establish a mathematical model with the following assumptions:
-
(H1)
All newly accessed computer are susceptible. Furthermore, susceptible computers are accessed to the Internet at the constant rate \(\mu>0\). And every computer on the Internet leaves the network with constant probability \(\mu>0\).
-
(H2)
By contact with infected internal computers, at time t, every susceptible internal computer gets infected with probability \(\frac{\beta I(t)}{1+\alpha I(t)}\), where \(\beta>0\) and \(\alpha>0\) are constants.
-
(H3)
By running of previous antivirus software, every infected internal computer gets recovered with constant probability \(\gamma>0\).
-
(H4)
Every recovered internal computer loses immunity with constant probability \(\delta>0\).
Moreover, the following additional hypotheses are raised.
-
(H5)
The latest antivirus software is disseminated at \(t = kT\), \(k \in\mathbb{N}\), where \(\mathbb{N}=\{1,2,3,\ldots\}\), \(T > 0\), is a constant.
-
(H6)
For dissemination of the latest antivirus software, a q fraction of infected internal computers get recovered at time instant kT, where \(0< q< 1\), and q is a constant.
From these assumptions, one has a novel computer virus propagation model, which can be represented by means of the impulsive differential equations
with initial condition \((S(0^{+}),I(0^{+}),R(0^{+})) \in\{(S,I,R) \in R_{+}^{3}:S+I+R=1\}\).
Since \(S(t)+I(t)+R(t)\equiv1\), system (1) can be rewritten as
with initial condition \((S(0^{+}),I(0^{+})) \in\Omega\), where
Obviously, Ω is positively invariant for system (2). The right-hand side of system (2) ensures the existence, uniqueness, and piecewise continuity of its solution [27].
3 Virus-free equilibrium and its stability
In this section, we shall prove the existence and global stability of the infection-free equilibrium under certain conditions.
First, we show the existence of the infection-free equilibrium, in which infectious computers are entirely absent from the internal computers permanently, i.e., \(I(t)\equiv0\), \(t\geq0\). In this situation, the growth of the removed computers \(R(t)\) simplifies to
Solving system (3), we get \(R(t)=R(0)\exp(-(\mu+\delta)t)\). Obviously, \(R(t)\geq0\) for \(t\geq0\), and \(\lim_{t\rightarrow+\infty }R(t)=0\). So we have the following.
Theorem 1
System (2) has a unique virus-free equilibrium \((0, 0)\).
Clearly, we have the following.
Theorem 2
System (1) has a unique virus-free equilibrium \((1, 0, 0)\).
Next, we explore the global asymptotically stability of the virus-free equilibrium to system (2). Let us define
Theorem 3
If \(\Re_{0}<1\), the virus-free equilibrium \((0, 0)\) of system (2) is locally asymptotically stable.
Proof
The linearized system of system (2) at \((0, 0)\) is
Denote
We get the monodromy matrix M of the linearized equation:
it is not necessary to calculate the exact form of (∗). Then the eigenvalues of (M), denoted by \(\lambda_{1}\) and \(\lambda_{2}\), are the following:
\(\lambda_{2}<1\) if \(\Re_{0}<1\). According to Floquet theory [28], it is easy to see that \((0,0)\) is locally asymptotically stable if \(\Re_{0}<1\). The proof is thus completed. □
To prove the main result of this section, we first show a lemma.
Lemma 1
Consider the following impulsive differential equation:
where m is a positive constant. Then there exists a unique positive periodic solution of system (6)
which is globally asymptotically stable.
Proof
Let us solve the first equation in system (6), then
Let \(g_{k}=g(kT^{+})\), we get the stroboscopic mapping F for system (6) as follows:
Obviously, the mapping F has only one (positive) fixed point
which implies that \(\bar{g}(t)\) is unique T-period solution to system (6). As
\(g_{*}\) is globally asymptotically stable for equation (9). The global asymptotical stability of \(\bar{g}(t)\) holds without doubt. □
Theorem 4
The virus-free equilibrium \((0, 0)\) of system (2) is globally asymptotically stable if \(\Re_{0}<1\).
Proof
Let \((I(t), R(t))\) be a solution to system (2). By Theorem 3, it suffices to prove that
\(\Re_{0}<1\) can be rewritten as
let \(\sigma=(1-q)\exp((\beta-\mu-\gamma)T)\), then \(\Re_{0}<1\), equivalently, \(\sigma<1\).
Via system (2), we have
Let us consider the comparison system
with initial condition \(v(0^{+})=I(0^{+})\). Then \(v(T^{+})=I(0^{+})\sigma\), \(v(nT^{+})=I(0^{+})\sigma^{n}\), which implies that \(\lim_{n\rightarrow\infty }v(nT^{+})=0\). Moreover, if \(nT< t\leq(n+1)T\), then
implying that \(\lim_{t\rightarrow+\infty}v(t)=0\). By the comparison theorem in impulsive differential equations [27], we get \(\lim_{t\rightarrow+\infty}I(t)=0\). Thus, there is \(T_{1}>0\) such that \(I(t)<\varepsilon\) for \(t\geq T_{1}\). Substituting this equation into system (2), we have
Let \(N_{1}=[\frac{T_{1}}{T}]\), we assume for the comparison system:
with initial condition \(w(N_{1}T^{+})=R(N_{1}T^{+})\). According to Lemma 1, it has a globally stable periodic solution
By the comparison theorem [27], there exists \(T_{2}>T_{1}\) such that
Considering the arbitrariness of ε, \(R(t)\geq0\), and noting that \(\lim_{\varepsilon\rightarrow0^{+}}\bar{w}(t)=0\), we get \(\lim_{t\rightarrow+\infty}R(t)=0\). The proof is complete. □
Via Theorem 4, we have the following.
Theorem 5
The virus-free equilibrium \((1, 0, 0)\) of system (1) is globally asymptotically stable if \(\Re_{0}<1\).
Example 1
Consider system (1) with the parameter values \((\mu ,\beta,\gamma,\delta,\alpha, q,T)=(0.09, 0.08, 0.06, 0.15, 0.05, 0.2, 3)\), we have \(\Re_{0}=0.3565<1\). Figure 1 depicts three typical orbits.
Phase portrait for the system given in Example 1 .
Example 2
For system (1) with the parameter values \((\mu ,\beta,\gamma,\delta,\alpha,q,T) =(0.08, 0.15, 0.06, 0.15, 0.05, 0.2, 5)\), we get \(\Re_{0}=0.8124<1\). Figure 2 displays three typical orbits.
Phase portrait for the system given in Example 2 .
From Figures 1 and 2, we can see that the state of system (1) is approaching the virus-free equilibrium, as fits the theoretical prediction. In other words, the computer viruses will be eradicated in these situations.
4 Permanence
In the following, we study uniform permanence of system (2) and system (1). First we give two definitions.
Definition 1
System (2) is said to be virus permanent in Ω, if for every solution \((I (t), R(t))\) to system (2) with \(I (0^{+} ) > 0\), there is \(m > 0\) such that \(I (t)\geq m\) for all large t.
Definition 2
System (2) is said to be uniformly permanent in Ω, if there is a constant \(c> 0\) (independent of the initial data), such that every solution \((I(t),R(t))\) with initial condition \((I(0^{+}),R(0^{+})) \in\Omega\) of system (2) satisfies
Theorem 6
If \(\Re_{0}>1\), then there exists a positive constant \(m_{3}\), such that any positive solution of system (2) satisfies \(I(t)\geq m_{3}\), for t large enough. That is, system (2) is virus permanent.
Proof
As \(\Re_{0}>1\), we can say that there exist a small \(m_{1}\) (\(0< m_{1}<1\)) and \(\varepsilon>0\) (sufficiently small), such that
for the exact form of \(\bar{u}(t)\), we can see (16).
We claim that for any \(t_{0}>0\), \(I(t)< m_{1}\), is impossible for all \(t\geq t_{0}\). In contrast, there exists a \(t_{0}>0\), such that \(I(t)< m_{1}\) for \(t\geq t_{0}\). Then we have
Assume for the comparison system
with initial condition \(u(0^{+})=R(0^{+})\). Via Lemma 1, it has a globally stable periodic solution
According to the comparison theorem [27], there is \(t_{1}\geq t_{0}\) such that
Plugging into system (2), we get
Letting \(N_{2}=[\frac{t_{1}}{T}]\), integrating the first equation in system (18) on \((kT,(k+1)T]\), \(k\geq N_{2}\), and noting \(I(kT^{+})=(1-q)I(kT)\), we get
Hence, \(I(kT)\geq I(N_{2}T)\sigma^{k-N_{2}}\) for \(k\geq N_{2}\). Noting that \(I(N_{2}T)>0\), we have \(\lim_{k\rightarrow+\infty}I(kT)=+\infty\). It contradicts the fact that \(I(t)\leq1\). So there exists a \(t_{2}>t_{1}\), such that \(I(t_{2})\geq m_{1}\).
If \(I(t)\geq m_{1}\) for all \(t\geq t_{2}\), the claimed result has been obtained. Now, assume \(I(t) < m_{1}\) for some \(t>t_{2}\). Let
There are two cases here.
Case 1. \(t_{3}= kT\), without loss of generality, let \(t_{3}=K_{1}T\) (\(K_{1}\) is a positive integer). Then \(I(t)\geq m_{1}\) for \(t\in [t_{2},t_{3})\), and \(I(t)\) is continuous, so we have \(I(t_{3})=m_{1}\), and \(I(t_{3}^{+})=(1-q)I(t_{3})< m_{1}\). By induction, we claim that there exists a \(t_{4}\in(K_{1}T,(K_{1}+1)T]\), such that \(I(t_{4})\geq m_{1}\), otherwise, \(I(t)< m_{1}\) for \(t\in (K_{1}T,(K_{1}+1)T]\), evidently, (17) and (18) holds on this interval. So we get \(I((K_{1}+1)T)\geq I(K_{1}T)\sigma>m_{1}\), which is a contradiction. Let
Then \(t_{4}\in(K_{1}T,(K_{1}+1)T]\), \(I(t_{4})=m_{1}\), and \(I(t)< m_{1}\) for \(t\in(t_{3},t_{4})\).
From the first equation and the third equation of system (2), we have
Repeatedly integrating the first equation in system (19) and plugging the second equation in system (19) into the resulting equation, we get, for all \(t_{3}< t< t_{4}\),
Via alternatively repeating arguments similar to the previous discussions, we get \(I(t)\geq m_{2}\) for all \(t>t_{3}\).
Case 2. \(t_{3}\neq kT\). Then \(I(t)\geq m_{1}\) for \(t\in [t_{2},t_{3})\), and \(I(t)\) is continuous, \(I(t_{3})=m_{1}\). Now, without loss of generality, assume \(t_{3}\in(K_{2}T,(K_{2}+1)T]\) (\(K_{2}\) is a positive integer), let
By induction, we claim that there is a \(t_{5}\in(t_{4},(K_{2}+K_{3}+1)T]\), such that \(I(t_{5})\geq m_{1}\), otherwise, \(I(t)< m_{1}\) for \(t\in (t_{4},(K_{2}+K_{3}+1)T]\), obviously, (17) and (18) hold on this interval. So we have
A contradiction occurs. Let
Then \(I(t_{5})=m_{1}\), and \(I(t)< m_{1}\) for \(t\in(t_{3},t_{5})\). By (19) and the previous discussions, we get, for all \(t_{3}< t< t_{5}\),
Again, via alternatively repeating the discussions, we get \(I(t)\geq m_{3}\) for all \(t>t_{3}\). Evidently, \(m_{2}>m_{3}\).
By the above discussions, we have \(I(t)\geq m_{3}\) for all \(t>t_{3}\). The proof is complete. □
From Theorem 6, we get the following.
Corollary 1
System (1) is virus permanent if \(\Re_{0}>1\).
Theorem 7
System (2) is uniformly permanent if \(\Re_{0}>1\).
Proof
From the second equation and the fourth equation of system (2), we get
Then we consider the comparison system
with initial condition \(h(t_{3})=R(t_{3})\). Via Lemma 1, for system (21) there exists a positive unique periodic solution
which is globally asymptotically stable.
According to the comparison theorem [27], there is \(t_{6}\geq t_{3}\) such that
Let \(c=\min\{m_{3},m_{4}\}\). From Theorem 6 and the above discussion, system (2) is uniformly permanent. □
As a direct consequence of Corollary 1 and Theorem 7, we have the following.
Corollary 2
If \(\Re_{0}>1\), any positive solution of system (1) satisfies \(I(t)\geq m_{3}\) and \(R(t)\geq m_{4}\), for t large enough.
From the first equation and the fourth equation of system (1) and using Corollary 2, we have \(\frac{dS(t)}{dt} >\mu+ \delta m_{4} - (\mu+ \beta) S(t)\), \(t\geq t_{6}\); furthermore, we get \(\lim_{t\rightarrow\infty}S(t)\geq\frac{\mu+ \delta m_{4}}{\mu+ \beta}\). For a sufficiently small \(\varepsilon_{3}>0\), let \(m_{5}=\frac{\mu+ \delta m_{4}}{\mu+ \beta }-\varepsilon_{3}>0\), there exists a \(t^{\prime}>t_{6}\), such that \(S(t)>m_{5}\) for \(t>t^{\prime}\).
By combining Corollary 2 and the above discussions, we get the following.
Theorem 8
System (1) is uniformly permanent if \(\Re_{0}>1\).
Example 3
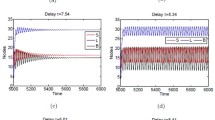
For system (1) with the parameter values \((\mu ,\beta,\gamma,\delta,\alpha,q,T) =(0.08, 0.23, 0.06, 0.1, 0.1, 0.15, 5)\), we have \(\Re_{0}=1.3333>1\). Figures 3-6 demonstrate the time plots of \(S(t)\), \(I (t)\), and \(R(t)\) and the phase portrait for the system with initial condition \((S(0), I (0), R(0)) = (0.5, 0.2, 0.3)\), respectively. We can see without difficulty that it conforms to the theoretical prediction. In other words, the computer viruses cannot be eradicated in this situation.
Time plot of \(\pmb{S(t)}\) for the system given in Example 3 .
Time plot of \(\pmb{I(t)}\) for the system given in Example 3 .
Time plot of \(\pmb{R(t)}\) for the system given in Example 3 .
Phase portrait for the system given in Example 3 .
Example 4
Consider system (1) with the parameter values \((\mu ,\beta,\gamma,\delta,\alpha, q,T)=(0.06, 0.28, 0.04, 0.12, 0.05, 0.15, 10)\). Then \(\Re_{0}=2.4086>1\). Figures 7 and 8 display the time plots of \(I(t)\) and the phase portrait for the system with initial condition \((S(0), I (0), R(0)) = (0.5, 0.2, 0.3)\), respectively, again it meets the theoretical prediction. In fact, the viral prevalence is quite high in this situation.
Time plot of \(\pmb{I(t)}\) for the system given in Example 4 .
Phase portrait for the system given in Example 4 .
One can easily find the limit cycle in Figures 6 and 8, respectively.
Based on many numerical examples, we speculate that system (1) has a stable viral periodic solution if \(\Re_{0}>1\).
5 Bifurcation analysis
Now, we investigate the existence of a viral periodic solution by means of the impulsive bifurcation theory in [29]. First, we present it as follows.
Consider the system
where \(f_{1}\), \(f_{2}\), \(\theta_{1}\), and \(\theta_{2}\) are sufficiently smooth, \(f_{2}(x_{1}(t),0)\equiv\theta_{2}(x_{1}(t),0)\equiv0\). Suppose
has a stable T-periodic solution denoted \(x_{e}(t)\). Thus, \(\zeta (t)=(x_{e}(t),0)^{T}\) is a trivial periodic solution to system (23). We will use bifurcation theory [29] to discuss the existence of viral periodic solution to system (2). Let \(\Phi(t)=(\phi_{1}(t),\phi_{2}(t))\) be the flow associated with system (23). We get \(X(t)=(x_{1}(t),x_{2}(t))^{T}=\Phi(t,X_{0})\), \(0< t\leq T\), where \(X_{0}=X(0)\).
We list the following notations [29]:
In the following, we quote without proof an important result from [29], which is indispensable for the proof of Theorem 9.
Lemma 2
Consider system (23) with \(0 < a_{0} < 2\).
-
(a)
If \(BC < 0\), a supercritical bifurcation occurs at \(d_{0} = 0\).
-
(b)
If \(BC > 0\), a subcritical bifurcation occurs at \(d_{0} = 0\).
-
(c)
If \(BC = 0\), there is an undetermined case.
Theorem 9
For system (2), a supercritical bifurcation occurs at \(\Re_{0}=1\). System (2) has a stable viral periodic solution which bifurcates from the virus-free equilibrium when \(\Re_{0}\) increasingly goes across unity.
Proof
Consider system (2). We change \(R(t)\), \(I(t)\) into \((x_{1}(t),x_{2}(t))\), respectively, thus
where \(x_{e}(t)=0\) can be looked upon as a trivial periodic solution of system (24).
Direct calculations yield
Since
we have
\(\Re_{0}=1\) implies \(d_{0}=0\) and \(\beta-\mu- \gamma>0\), so we get \(B<0\), then \(BC<0\). Clearly, \(0 < a_{0} < 2\). Therefore, the claimed result follows from Lemma 2. □
6 Discussions
By the previous discussions, some practicable and effective strategies should be followed to lower \(\Re_{0}\) below unity for deracinating network viruses. For that purpose, in the following, we study the effects of the changing model parameters on \(\Re_{0}\).
Theorem 10
\(\Re_{0}\) drops with increasing μ, γ and q, and \(\Re_{0}\) rises with increasing β and T.
One can easily see this result from (4).
Remark 1
In the real situations, β, μ, and γ can be looked upon as constants, while T and q are easily manipulated. We consider the following two situations:
-
Case 1.
\(\beta<\mu+\gamma\). Then \(\Re_{0}<1\) via (4), the computer viruses can also be deracinated without impulsive detoxication.
-
Case 2.
\(\beta\geq\mu+\gamma\). By (4), we have \(\Re_{0}<1\) if
$$ \frac{1}{T}\ln\frac{1}{1-q}>\beta-(\mu+\gamma). $$(25)
So we must manipulate T and q to meet (25) for eradicating computer viruses in this situation.
Remark 2
We notice that δ and α are not in (4), yet we know that they have significant impact on the spread of computer viruses. It ought to be considered as a demerit of the model, and we shall improve the model in the next research.
On the basis of the previous analysis, some practical and effective measures for containing the virus prevalence is presented below.
-
(1)
Strengthening the research of antivirus software and shortening the development cycle are conducive to reduce the impulsive detoxication period T and to enhance the impulsive detoxication rate q and the recovery rate γ.
-
(2)
The people must be often reminded to install antivirus software, so that the impulsive detoxication rate q and the recovery rate γ are raised.
-
(3)
Let your computer leave the Internet when unnecessary, so that the recruitment rate μ is increased, the incidence rate β is minimized.
7 Conclusions
Taking into account impulsive detoxication and saturation effects in the conventional SIRS model, a novel computer viruses propagation model has been established. The dynamical properties of this model have been investigated theoretically, and the results obtained have also been demonstrated by several numerical examples. Based on an analysis of the impact of varying model parameters on BRR, some effective measures for controlling electronic virus diffusion have been advised.
Recently, Yang et al. [30, 31] analyzed the impact of the structure of the propagation network on the spread of computer virus, and they proposed a node-based epidemic model, which can help us better understand how the electronic viruses diffuse on networks. The final goal is not only to understand epidemic processes and predict their behavior, but also to control their dynamics [32]. Our future work is to research the impact of impulsive detoxication on the spread of computer viruses in different structures of the propagation network.
References
Cohen, F: Computer viruses: theory and experiments. Comput. Secur. 6(1), 22-35 (1987)
Murray, WH: The application of epidemiology to computer viruses. Comput. Secur. 7(2), 130-150 (1988)
Kephart, JO, White, SR: Directed-graph epidemiological models of computer viruses. In: IEEE Computer Society Symposium on Research in Security and Privacy, pp. 343-359 (1991)
Kephart, JO, White, SR: Measuring and modeling computer virus prevalence. In: IEEE Computer Society Symposium on Research in Security and Privacy, pp. 2-15 (1993)
McCluskey, CC: Complete global stability for an SIR epidemic model with delay-distributed or discrete. Nonlinear Anal., Real World Appl. 11, 55-59 (2010)
Hattaf, K, Lashari, AA, Louartassi, Y, Yousfi, N: A delayed SIR epidemic model with general incidence rate. Electron. J. Qual. Theory Differ. Equ. 2013, 3 (2013)
Muroya, Y, Enatsu, Y, Li, H: Global stability of a delayed SIRS computer virus propagation model. Int. J. Comput. Math. 91(3), 347-367 (2014)
Yuan, H, Chen, G: Network virus-epidemic model with the point-to-group information propagation. Appl. Math. Comput. 206(1), 357-367 (2008)
Mishra, BK, Pandey, SK: Dynamic model of worms with vertical transmission in computer network. Appl. Math. Comput. 217(21), 8438-8446 (2011)
Yang, L-X, Yang, X, Zhu, Q, Wen, L: A computer virus model with graded cure rates. Nonlinear Anal., Real World Appl. 14(1), 414-422 (2013)
Yang, L-X, Yang, X: A new epidemic model of computer viruses. Commun. Nonlinear Sci. Numer. Simul. 19, 1935-1944 (2014)
Chen, L, Hattaf, K, Sun, J: Optimal control of a delayed SLBS computer virus model. Physica A 427, 244-250 (2015)
Muroya, Y, Kuniya, T: Global stability of nonresident computer virus models. Math. Methods Appl. Sci. 38, 281-295 (2015)
Yang, L-X, Yang, X: A novel virus-patch dynamic model. PLoS ONE (2015). doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0137858
Feng, L, Liao, X, Li, H, Han, Q: Hopf bifurcation analysis of a delayed viral infection model in computer networks. Math. Comput. Model. 56(7-8), 167-179 (2012)
Yang, X, Yang, L-X: Towards the epidemiological modeling of computer viruses. Discrete Dyn. Nat. Soc. 2012, Article ID 259671 (2012)
Zhang, C, Zhao, Y, Wu, Y, Deng, S: A stochastic dynamic model of computer viruses. Discrete Dyn. Nat. Soc. 2012, Article ID 264874 (2012)
Anderson, RM, May, RM: Infectious Diseases of Humans: Dynamics and Control. Oxford University Press, Oxford (1991)
Zhang, C, Zhao, Y, Wu, Y: An impulse model for computer viruses. Discrete Dyn. Nat. Soc. 2012, Article ID 260962 (2012)
Yang, L-X, Yang, X: The pulse treatment of computer viruses: a modeling study. Nonlinear Dyn. 76(2), 1379-1393 (2014)
Yuan, H, Guan, L, Guan, C: On modeling the crowding and psychological effects in network-virus prevalence with nonlinear epidemic model. Appl. Math. Comput. 219, 2387-2397 (2012)
Yang, L-X, Yang, X: The impact of nonlinear infection rate on the spread of computer virus. Nonlinear Dyn. 82(1), 85-95 (2015)
Capasso, V, Serio, G: A generalization of the Kermack-McKendrick deterministic epidemic model. Math. Biosci. 42(1-2), 43-61 (1978)
Sabin, A: Measles, killer of millions in developing countries: strategies of elimination and continuing control. Eur. J. Epidemiol. 7(1), 1-22 (1991)
Agur, Z, Cojocaru, L, Mazor, G, Anderson, R, Danon, Y: Pulse mass measles vaccination across age cohorts. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 90(24), 11698-11702 (1993)
Meng, X, Chen, L, Wu, B: A delay SIR epidemic model with pulse vaccination and incubation times. Nonlinear Anal., Real World Appl. 11(1), 88-98 (2010)
Lakshmikantham, V, Bainov, DD, Simeonov, PS: Theory of Impulsive Differential Equations. World Scientific, Singapore (1989)
Bainov, DD, Simeonov, PS: Impulsive Differential Equations: Periodic Solutions and Applications. Longman, New York (1993)
Lakmeche, A, Arino, O: Bifurcation of nontrivial periodic solutions of impulsive differential equations arising chemotherapeutic treatment. Dyn. Contin. Discrete Impuls. Syst. 7(2), 265-287 (2000)
Yang, L-X, Draief, M, Yang, X: The impact of the network topology on the viral prevalence: a node-based approach. PLoS ONE (2015). doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0134507
Yang, L-X, Draief, M, Yang, X: Heterogeneous virus propagation in networks: a theoretical study. Math. Methods Appl. Sci. (2016). doi:10.1002/mma.4061
Romualdo, P-S, Claudio, C, Piet, VM, Alessandro, V: Epidemic processes in complex networks. Rev. Mod. Phys. (2015). doi:10.1103/RevModPhys.87.925
Acknowledgements
This research is supported by the Natural Science Foundation of China (No. 61374078), NPRP grant # NPRP 4-1162-1-181 from the Qatar National Research Fund (a member of Qatar Foundation), Science and technology fund of Guizhou Province (LH [2015] No. 7612), China, and Chongqing Research Program of Basic Research and Frontier Technology (No. cstc2015jcyjBX0052), China.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Competing interests
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Authors’ contributions
XZ conceived and designed the experiments. XZ performed the experiments. XZ, CL, and TH wrote the paper. All authors read and approved the final manuscript.
Rights and permissions
Open Access This article is distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/), which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided you give appropriate credit to the original author(s) and the source, provide a link to the Creative Commons license, and indicate if changes were made.
About this article
Cite this article
Zhang, X., Li, C. & Huang, T. Impact of impulsive detoxication on the spread of computer virus. Adv Differ Equ 2016, 218 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1186/s13662-016-0944-x
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1186/s13662-016-0944-x