Abstract
Background
Metastasis is a leading cause of death among cancer patients. In the tumor microenvironment, altered levels of extracellular matrix proteins, such as collagens, can facilitate the first steps of cancer cell metastasis, including invasion into surrounding tissue and intravasation into the blood stream. However, the degree of misexpression of collagen genes in tumors remains understudied, even though this knowledge could greatly facilitate the development of cancer treatment options aimed at preventing metastasis.
Methods
We systematically evaluate the expression of all 44 collagen genes in breast cancer and assess whether their misexpression provides clinical prognostic significance. We use immunohistochemistry on 150 ductal breast cancers and 361 cervical cancers and study DNA methylation in various epithelial cancers.
Results
In breast cancer, various tests show that COL4A1 and COL4A2 overexpression and COL17A1 (BP180, BPAG2) underexpression provide independent prognostic strength (HR = 1.25, 95% CI = 1.17–1.34, p = 3.03 × 10−10; HR = 1.18, 95% CI = 1.11–1.25, p = 8.11 × 10−10; HR = 0.86, 95% CI = 0.81–0.92, p = 4.57 × 10−6; respectively). Immunohistochemistry on ductal breast cancers confirmed that the COL17A1 protein product, collagen XVII, is underexpressed. This strongly correlates with advanced stage, increased invasion, and postmenopausal status. In contrast, immunohistochemistry on cervical tumors showed that collagen XVII is overexpressed in cervical cancer and this is associated with increased local dissemination. Interestingly, consistent with the opposed direction of misexpression in these cancers, the COL17A1 promoter is hypermethylated in breast cancer and hypomethylated in cervical cancer. We also find that the COL17A1 promoter is hypomethylated in head and neck squamous cell carcinoma, lung squamous cell carcinoma, and lung adenocarcinoma, in all of which collagen XVII overexpression has previously been shown.
Conclusions
Paradoxically, collagen XVII is underexpressed in breast cancer and overexpressed in cervical and other epithelial cancers. However, the COL17A1 promoter methylation status accurately predicts both the direction of misexpression and the increased invasive nature for five out of five epithelial cancers. This implies that aberrant epigenetic control is a key driver of COL17A1 gene misexpression and tumor cell invasion. These findings have significant clinical implications, suggesting that the COL17A1 promoter methylation status can be used to predict patient outcome. Moreover, epigenetic targeting of COL17A1 could represent a novel strategy to prevent metastasis in patients.
Similar content being viewed by others
Background
Metastasis, the spread of cancer cells to distant organs, is one of the leading causes of death among cancer patients. To be able to disseminate, cancer cells need to overcome a number of barriers. In epithelia, cell-cell interactions and a basement membrane initially constitute major obstacles. In addition, once local invasion through the basement membrane has occurred, tumor cells need to be able to survive in the very different environment of the stroma [1].
The stroma consists of fibroblasts and extracellular matrix (ECM). The ECM is composed of polysaccharides, water, and stromal cell-secreted proteins, as well as soluble growth factors sequestered by matrix components [2]. Two types of macromolecules in the ECM, proteoglycans and fibrous proteins, influence cell growth, migration, attachment, and differentiation [3]. Collagens are fibrous proteins, which, with their high abundance in the ECM, contribute substantially to these processes [4]. In humans, a total of 44 collagen genes encode 28 varieties of collagen proteins [5].
While initially regarded as a physical barrier to tumor cell migration, recent studies have shown that collagens also support tumor progression depending on the stage of cancer development [6]. Associations between aberrant expression of collagens and tumor progression and metastasis are well established. For instance, increased density of collagen type I in lymph nodes is a clinical marker for breast cancer invasion [7]. Collagen I is also differentially expressed during colorectal tumorigenesis [8]. High levels of collagen type VI promote epithelial to mesenchymal transition, angiogenesis, inflammation, and chemotherapy resistance [9]. Collagen XI is expressed at high levels in human gliomas, colorectal cancer, and metastatic ovarian carcinoma, and at low levels in breast cancer [10–13]. Hence, collagen levels in the tumor stroma represent a valuable diagnostic parameter to differentiate between normal tissue, low-grade tumors, and metastatic cancer.
In contrast to other collagens, collagen types XIII, XVII, XXIII, and XXV are transmembrane proteins, characterized by an N-terminal cytoplasmic domain and an extracellular C-terminus that contains 3 to 15 collagenous domains [14]. Most research involving collagen XVII has focused on its role in healthy and diseased skin. Collagen XVII is a hemidesmosomal adhesion protein, whose expression in normal skin is limited to the basal keratinocytes, which are anchored to the basement membrane via collagen XVII [15]. However, it is overexpressed in squamous cell carcinoma (SCC) of the skin and in melanoma [15, 16].
Here, we systematically study the expression of all 44 collagen genes in breast cancer. We find that reduced expression of COL17A1, the gene that encodes collagen XVII, is most significantly associated with poor patient prognosis. Consistently, collagen XVII levels are reduced in breast tumors and this is strongly associated with tumor stage, invasion, and menopausal status. Conversely, collagen XVII levels are elevated in cervical cancer and this is associated with increased local metastasis. Interestingly, the COL17A1 promoter methylation status correctly predicts the direction of collagen XVII misexpression in multiple types of epithelial cancers, including breast and cervical cancer.
Results
Underexpression of COL17A1 is a marker for poor prognosis in breast cancer
To identify collagens whose misexpression may contribute to breast cancer development, and in particular metastasis, we systematically evaluated expression levels of all 44 collagen genes. By combining microarray expression data from 26 previously published datasets, Cox proportional hazard analyses were performed based on expression level and distant metastasis-free survival (see the “Methods” section). For 18 of the 44 collagen genes, increased or decreased expression was significantly associated with poor patient outcome (HR with 95% CI <> 1, p < 0.05, 1052 < n < 4177; Additional file 1: Table S1).
We more stringently tested how well the misexpression of these genes might provide independent prognostic strength by including various other clinical parameters, such as lymph node status, tumor size, and menopausal status, all of which are included in Adjuvant! Online and the Nottingham Prognostic Index (NPI) [17, 18]. This reduced the number of significant associations from 18 to 8 collagen genes that passed all three tests with p < 0.05 (HR with 95% CI <> 1, 1052 < n < 4177) (Additional file 1: Table S1).
We also assessed whether patient survival significantly differed between patients whose tumors expressed low and high levels of these genes. This further reduced the number of genes to three, with overexpression of COL4A1 and COL4A2 and underexpression of COL17A1 correlating with poor distant metastasis-free patient survival (p = 1.71 × 10−5, n = 3925; p = 0.0098, n = 4177; and p = 0.0001, n = 3925, respectively, log-rank test; Additional file 1: Table S1).
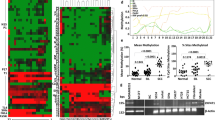
In an effort to independently validate these results, we used a combination of 28 other microarray datasets, as described [19, 20]. However, this showed that COL4A1 expression did not significantly change (1.15-fold increase, p = 0.2574, t test, n = 1137) and that COL4A2 expression was significantly reduced (1.53-fold decrease, p = 7.97 × 10−10, n = 2830), rather than increased (Fig. 1a). Only COL17A1 misexpression was validated, as it consistently decreased in all analyses, the latter showing a 3.70-fold decrease (p = 4.93 × 10−11, n = 3004; Fig. 1a). Analysis of COL17A1 levels using RNAseq data from The Cancer Genome Atlas (TCGA) [21, 22] also showed a significant downregulation (p < 0.0001, n = 1075; Fig. 1b). We therefore hereafter focus on COL17A1.
Reduced COL17A1 expression correlates with poor breast cancer patient prognosis. a Fold change in normalized COL4A1, COL4A2 (4A2), and COL17A1 (17A1) expression using 28 combined previously published datasets. p values: t test. b Fold change in normalized COL17A1 expression using the TCGA breast cancer RNAseq dataset. p value: Mann-Whitney U test. c–e Distant metastasis-free survival (c), recurrence-free survival (d), and overall survival (e) for breast cancer patients whose tumors express high (green) or low (red) COL17A1 levels. Patients were split in low and high expression groups using the median expression level as the cut-off [23]. p values: log-rank test. p value summaries: n/s not significant; ****p < 0.0001
In addition to the above survival analyses (Additional file 1: Table S1), we investigated whether reduced COL17A1 expression is associated with poor distant metastasis-free survival, recurrence-free survival, and overall patient survival, as previously described [23]. This confirmed significant correlations between these parameters (p = 0.0044, n = 1601; p = 6.58 × 10−10, n = 3524; p = 0.0341, n = 1115, respectively, log-rank test; Fig. 1c–e).
Underexpression of collagen XVII is a marker for advanced stage, increased invasion, and postmenopausal status in breast cancer
Focusing on protein-level expression of collagen XVII, the product of the COL17A1 gene, we next performed immunohistochemistry (IHC) using a previously well-characterized antibody [15, 16]. We used tissue microarrays with a total of 227 tissue samples, including 57 normal control breast samples, 20 hyperplastic breast samples, and 150 ductal breast carcinomas. The staining intensity ranged from negative to moderate in the normal and hyperplastic samples and from negative to strong in the tumor samples (Fig. 2). The corresponding H&E-stained images are available in Additional file 1: Figure S1. The increase in the fraction of strongly stained sections between normal and tumor samples (from 0% (0/56) to 4% (6/150), Fig. 2) was not statistically significant (p = 0.1908, Fisher’s exact test). Neither was the decrease in the fraction of moderately stained sections (from 9% (5/57) to 3% (4/150), p = 0.1185; Fig. 2). We therefore hereafter analyzed differences only based on whether staining was negative or positive.
Collagen XVII is underexpressed in breast cancer. Tissue microarrays with a total of 57 normal breast tissues, 20 hyperplastic breast tissues, and 150 breast ductal carcinomas were stained with an anti-collagen XVII antibody [15, 16]. Numbers of samples in each category, as well as the total number of samples, are indicated. Percentages indicate frequencies of observations per row. Scale bar, 50 μm
Consistent with our above prognostic analyses, the ductal breast carcinomas stained positive for collagen XVII significantly less frequently that normal control tissue (22% (33/150) vs 42% (24/57), p = 0.0038, Fisher’s exact test; Table 1). The frequency in hyperplastic mammary epithelium, potentially a precursor of mammary carcinoma, did not significantly differ (55% (11/20) vs 42% (24/57), p = 0.2308).
We next assessed whether the reduced frequency of collagen XVII-positive staining in the tumors was specifically associated with tumor grade and markers used for diagnosis and determining the most effective treatment regimen. We did not observe any remarkable differences between tumors with differential estrogen receptor (ER), progesterone receptor (PR), or HER2 amplification status (Table 1). However, the already significant reduction in collagen XVII positivity from 42% (24/57) in normal samples to 26% (29/111) in early stage tumors (stage I/II; p = 0.0273) was further reduced significantly to 10% (4/39) in late stage cancers (stages III/IV; p = 0.0005 compared to normal, p = 0.0287 compared to stages I/II). The fractions of tumors that stained positive also significantly declined as tumors become more invasive, from 28% (27/97) in tumors that only locally invaded the submucosa and/or muscle (T1/2) to 11% (6/53) in tumors that invaded through underlying muscle and/or into other organs (T3/4) (p = 0.0143). Only 8% (2/25) of the most invasive cancers stained positive (p = 0.0015 compared to 42% (24/57) in normal tissue). Collagen XVII positivity also reduced with an increase in the number of positive lymph nodes and metastasis. Yet, this trend was not statistically significant (Table 1). Finally, with positive staining of 30% (21/71) of premenopausal carcinomas and 14% (4/42) of postmenopausal samples, menopausal status had a strong impact on collagen XVII expression (p = 0.0263; Table 1). Taken together, we conclude that the frequency of collagen XVII-positive tumors declines with advanced stage, increased invasion, and postmenopause.
Collagen XVII is overexpressed in cervical cancer
Our interest in women’s cancers prompted us to also assess collagen XVII expression in cervical cancer. In contrast to breast tumors, cervical cancers show a significant twofold increase in COL17A1 mRNA level compared to normal control tissue (p = 0.0046, Mann-Whitney U test, n = 185; Fig. 3a). We next performed IHC on tissue microarrays with 31 normal control tissues, 331 squamous cell carcinomas (SCC), 27 adenocarcinomas, and 3 adenosquamous carcinomas. Normal cervix typically stains weakly positive for collagen XVII (Fig. 3b). In contrast, among cervical SCCs, collagen XVII staining ranges from negative to strong. In addition, when positive, collagen XVII expression is observed in a much larger proportion of the cells as compared to normal tissue (Fig. 3c). In comparison to normal cervix, a significantly higher fraction of SCCs stains positive (68% (21/31) and 82% (273/331), respectively; p = 0.0442, Fisher’s exact test), moderately to strongly positive (23% (7/31) and 44% (146/331), respectively; p = 0.0146), or strongly positive (0% (0/31) and 20% (65/331), respectively; p = 0.0016) (Table 2). Among cervical adenocarcinomas and adenosquamous carcinomas, the fractions of positive and strongly positive samples were also increased, respectively. However, these increases were not statistically significant (Table 2).
Collagen XVII is overexpressed in cervical cancer. a COL17A1 is overexpressed twofold in the TCGA cervical cancer dataset. p values: t test. b, c Tissue microarrays with 31 normal control cervical tissue samples (b) and 331 cervical squamous cell carcinomas, 27 cervical adenocarcinomas, and 3 cervical adenosquamous carcinomas (c) were stained with an anti-collagen XVII antibody. Numbers of samples in each category, as well as the total number of samples, are indicated. Percentages indicate frequencies of observations per row. Scale bar, 50 μm
Collagen XVII overexpression is a marker for local metastasis in cervical cancer
We also investigated collagen XVII staining in relation to lymph node status and distant metastasis. Only two of the patients were diagnosed with distant metastasis, thus preventing us from evaluating this parameter. However, among the three cancer types, the fraction of tumors that stained positive for collagen XVII in lymph node-positive cervical cancers was consistently higher than that fraction in lymph node-negative tumors (Table 3). Overall, increased collagen XVII expression is significantly associated with an increase in local metastasis (81% (258/320) vs 94% (33/35); p = 0.0293, Fisher’s exact test; Table 3).
In breast cancer, the COL17A1 promoter is hypermethylated and this correlates with reduced gene expression
The misexpression of collagen XVII in breast and cervical cancers in opposite directions, both at mRNA and at protein levels, prompted us to investigate whether changes in allelic copy numbers could provide an explanation for this. We used SNP array GISTIC copy number data and RNAseq data from the respective TCGA studies [21, 22]. While the majority of the breast cancers (61% (657/1075)) had retained two copies of the COL17A1 locus, nearly a third, 31% (329/1075), lost one or both alleles. This led to a significant reduction of COL17A1 mRNA levels compared to diploid tumors (p < 0.0001, Mann-Whitney U test), whose levels were already significantly lower than in normal breast tissue (n = 112; p < 0.0001; Fig. 4a). Interestingly, despite the fact that the remaining 8.3% (89/1075) of the tumors had gained extra copies of the COL17A1 locus, their mRNA levels were significantly lower than those in diploid cancers (p = 0.0218).
The COL17A1 promoter methylation status predicts the direction of misexpression in breast and cervical cancer. a COL17A1 allelic copy number gains and losses in relation to normalized COL17A1 expression level. Data are extracted from TCGA breast cancer RNAseq V2 RSEM and SNP6 array GISTIC copy number datasets. Error bars represent standard error of the mean. p values: Mann-Whitney U test. b Heat map of the degree of promoter methylation based on β values for each indicated probe. Each three-probe column corresponds to a sample. Data were extracted from the TCGA Illumina Infinium HumanMethylation450 breast cancer dataset [21, 22]. c Box plot for COL17A1 promoter methylation comparing normal samples to all samples, as well as to samples with indicated allelic copy numbers. Whiskers represent 10–90 percentiles of the data. p values: Mann-Whitney U test. d Scatter plot of COL17A1 promoter methylation compared to normalized COL17A1 gene expression. p value for linear regression line: Spearman correlation. e–h Graphs as in (a–d), respectively, for cervical cancer. Data were derived from the TCGA cervical dataset. p value summaries: n/s not significant; *p < 0.05; **p < 0.01; ****p < 0.0001
The observation that copy number changes do not have a major impact on COL17A1 expression levels in breast cancer suggests that additional mechanisms regulate this gene’s expression. Tumor cells may silence gene expression through promoter hypermethylation [24]. Hence, we compared the COL17A1 promoter methylation status in normal breast and breast cancer samples using TCGA DNA methylation data [21, 22] (Additional file 1: Figure S2 and Additional file 2). This revealed that the COL17A1 promoter is indeed hypermethylated in breast tumors (n = 735 tumors, n = 92 normal samples; p < 0.0001, Mann-Whitney U test; Fig. 4b, c) and this hypermethylation is independent of COL17A1 allelic copy number variations (p < 0.0001; Fig. 4c). In addition, there is a strong negative correlation between COL17A1 promoter methylation and gene expression (Spearman p < 0.0001; Fig. 4d). Taken together, these analyses suggest that reduced COL17A1 expression in breast cancer is caused by hypermethylation of the COL17A1 promoter.
In cervical cancer, the COL17A1 promoter is hypomethylated and this correlates with increased gene expression
In cervical cancer, the COL17A1 locus was less frequently subject to copy number changes than in breast cancer (Fig. 4e). When copy number alterations did occur, this did not affect its expression (Fig. 4e). In contrast, the COL17A1 promoter was considerably hypomethylated compared to normal tissue (n = 189 tumors, n = 3 normal samples; p < 0.0001, Mann-Whitney U test; Fig. 4f, g). This occurred irrespective of allelic copy number changes (p ≤ 0.0035; Fig. 4g), and COL17A1 expression strongly correlated inversely with the degree of methylation of its promoter (Spearman p < 0.0001; Fig. 4h). These data strongly suggest that increased COL17A1 expression in cervical cancer is caused by hypomethylation of the COL17A1 promoter.
The COL17A1 promoter methylation status accurately predicts the direction of misexpression in epithelial cancers
Interestingly, collagen XVII overexpression is observed by IHC in various other cancers, including skin SCC, melanoma, non-small cell lung cancer, lung adenocarcinoma, lung SCC, and head and neck SCC [15, 16, 25–28]. This led us to also investigate the promoter methylation status for these cancers. For the former three, TCGA data were either not available or the low number of normal samples (n = 2) precluded accurate analysis. For the remaining cancers, we find that the degree of COL17A1 promoter methylation is significantly reduced in the tumor samples (n = 516, n = 435, n = 361, respectively) compared to normal control samples (n = 50, n = 29, n = 41, respectively; p ≤ 0.0002, Mann-Whitney U test; Fig. 5a–c). In addition, similar to breast and cervical cancer (Fig. 4d, h), the degree of promoter methylation highly significantly correlates inversely with gene expression for these cancers (p ≤ 0.0008, Spearman correlation; Fig. 5d–f). Thus, the COL17A1 promoter methylation status accurately predicts the direction of the misexpression of collagen XVII in five out of five cancer types. This indicates that the differential COL17A1 promoter methylation dictates whether collagen XVII is under- or overexpressed in these epithelial cancers (p = 0.0313, binomial test).
The COL17A1 promoter is hypomethylated in head and neck and lung cancers. a–c Methylation status of the COL17A1 promoter in head and neck squamous cell carcinoma (SCC), lung adenocarcinoma, and lung SCC using the respective TCGA datasets [41–43], as in Fig. 4c. p values: Mann-Whitney U test. d–f Scatter plots of COL17A1 promoter methylation compared to normalized gene expression for indicated cancer types, as in Fig. 4d. p values: Spearman correlation for linear regression. g Box plot comparing the absolute COL17A1 mRNA levels in five epithelial tumor types and their respective matched normal control tissues. Data were extracted from TCGA RNAseq datasets [21, 22, 41–43]. N normal tissues, T tumor tissues. Sample numbers are indicated below each box. p values: Mann-Whitney U tests. p value summaries: **p < 0.01; ***p < 0.001; ****p < 0.0001
Absolute levels of COL17A1 expression differ between normal and tumor tissues of different origin
We observed that COL17A1 is underexpressed in breast cancer and overexpressed in cervical and other epithelial cancers. This raises the possibility that the absolute COL17A1 levels are similar in different cancers while the basal COL17A1 levels are high in normal breast tissue and low in other normal epithelia. To test this hypothesis, we directly compared the absolute COL17A1 mRNA levels in the five tumor types and the respective matched normal control tissues investigated above (Fig. 5g). This scenario seemed to apply when we compared breast to lung. Specifically, COL17A1 levels in breast carcinomas and lung adenocarcinomas are similar, while the COL17A1 levels are highest in normal breast tissue and lowest in normal lung tissue (Fig. 5g). Generally, however, this is not the case. For instance, head and neck SCCs express significantly higher levels than normal breast tissue (p < 0.0001, Mann-Whitney U test; n = 497 and n = 112, respectively). Also, in normal cervix, COL17A1 levels do not significantly differ from those in breast carcinoma (p = 0.1417, Mann-Whitney U test; n = 3 and n = 1041, respectively), whereas the levels in normal cervix are significantly lower than in normal breast tissue (p = 0.0027, Mann-Whitney U test; n = 3 and n = 112, respectively; Fig. 5g). Thus, while COL17A1 misexpression is common in epithelial cancers, the absolute COL17A1 levels vary widely between and among tumors and matched normal samples of different tissue origin.
Discussion
We systematically assessed the potential involvement of all 44 collagens in breast cancer progression and metastasis. This analysis identified overexpression of COL4A1 and COL4A2 as strong independent markers. However, independent assessment using TCGA RNAseq data did not validate this observation. At the protein level, a number of collagens, including collagens I, III, IV-α1, IV-α2, and V, are differentially expressed in breast cancer [29, 30]. This seeming discrepancy could be explained by the fact that our assessment is based on mRNA rather than on protein levels. Alternatively, sample-averaged mRNA levels could mask important differences in the local distribution of collagens within tumors, as observed for collagens IV, XV, and XIX in invasive ductal carcinomas [31]. Nevertheless, our approach led us to identify reduced COL17A1 mRNA levels as a strong independent prognostic marker in breast cancer development and this was not only sustained at the protein level, but it was also strongly associated with advanced stage, increased invasion, and postmenopausal status.
We find that collagen XVII is underexpressed in breast cancer, while it is overexpressed in various other cancers, including cervical cancer, as we show here, and skin SCC, melanoma, head and neck SCC, non-small cell lung cancer, lung adenocarcinoma, and lung SCC, as previously described [15, 16, 25–28]. The cancer type-specific misexpression in opposing directions is not unique for collagen XVII. Collagen XI is expressed at high levels in human gliomas [10], colorectal cancer [11], and ovarian carcinoma [12] but at low levels in breast cancer [13]. Also, collagen XI protein-level expression positively correlates with ovarian cancer metastasis, but it inversely correlates with breast cancer metastasis [12, 13].
It is well established that differential DNA methylation in promoter regions causes misexpression of genes in cancer [32]. Collagen gene expression is altered in this manner in various cancer types [33–35]. However, to our knowledge, this is the first study that links the cancer type-specific, opposed direction of the misexpression of any collagen gene to cancer type-specific epigenetic alterations. It would be interesting to see if differential promoter methylation of other collagen genes, such as those encoding collagens XI-α1 and XI-α2 [10–13], could similarly explain opposed misexpression in distinct cancer types.
While consistent with epigenetic alterations, it remains paradoxical that both reduced collagen XVII expression in breast cancer and increased collagen XVII expression in other cancers are associated with increased tumor cell invasion and metastasis [15, 16, 25–28]. We investigated the possibility that the absolute COL17A1 levels are similar in different cancers while the normal COL17A1 levels are high in normal breast tissue and low in other normal epithelia. However, the absolute COL17A1 levels vary widely between various tumor types, as well as between various normal tissues. The different ratios between the numbers of basal and non-basal cells in different tissue types could partly account for that. Alternatively, or additionally, changes in the expression of one particular collagen gene could be compensated for by changes in the expression of other collagen genes.
In any case, our observations suggest that the expression of collagen XVII needs to be maintained at a tissue and cell type-specific normal level to prevent invasion. This thesis is supported by several previous observations. In keratinocytes, complete loss of Col17a1 expression increases cell motility [36] and partial reduction of COL17A1 levels promotes undirected motility [37]. Conversely, collagen XVII expression is increased at the leading edge during wound healing [38] and at the invasive front of carcinomas [15], suggesting that it promotes motility. Consistently, COL17A1 supports directed migration by stabilizing actin bundles, which generates traction forces [37]. Together, this suggests that cancer cells may increase the invasive potential by either up- or downregulating collagen XVII expression.
Conclusions
In conclusion, we identify breast cancer as the first type of cancer in which collagen XVII expression is underexpressed. We also find that the promoter methylation status correctly predicts whether collagen XVII is over- or underexpressed in various epithelial cancers. The underexpression in breast cancer is associated with increased invasion, while overexpression in other cancer types is also associated with increased invasion and metastasis. Functional studies are needed to mechanistically explain how collagen XVII overexpression affects cell motility, and its direction, and promotes tumor cell invasion and metastasis. However, our study has significant clinical implications, as it suggests that epigenetic targeting of COL17A1 could represent a novel strategy to prevent metastasis in patients.
Methods
Clinical prognostic analyses
Data from 26 previously published breast cancer datasets were used to study the potential association between expression of each of the 44 collagen genes and distant metastasis-free survival, as described [23, 39]. Briefly, datasets were combined and statistical significance was determined according to a Cox proportional hazard model with 95% confidence interval (CI). Additional tests, according to Adjuvant! and the Nottingham Prognostic Index, were performed as described [17, 18]. Survival analyses were performed using a single clinical feature at a time, i.e., distant metastasis-free survival, recurrence-free survival, or overall survival, and by splitting the gene expression in tumors into below (low) and above (high) the median expression level, as described [19, 39]. Statistical analyses were performed using log-rank Mantel-Cox tests.
Validation analyses
Validation analyses for COL4A1, COL4A2, and COL17A1 gene expression in breast cancer were performed using 28 datasets, as previously described [19, 20]. In addition, the TCGA (The Cancer Genome Atlas) breast cancer and cervical cancer Illumina HiSeq RNA Seq V2 (RSEM-analyzed) datasets [21, 22] were used to compare COL17A1 expression levels in matched normal control to breast and cervical cancer samples. Statistical analyses were carried out using t tests. Validation analyses for patient survival (distant metastasis-free survival, recurrence-free survival, and overall survival) were performed using probe 204636_at and the median as the cut-off between low and high expression, as described [23]. Log-rank tests were used to assess statistical significance.
Immunohistochemistry
Paraffin-embedded breast cancer and cervical tissue microarrays (TMAs) were obtained from US Biomax Inc. (MD, USA). Samples were obtained under the Health Insurance Portability and Accountability Act (HIPAA)-approved protocols, in accordance with the approved guidelines and with informed consent from the donors. For the breast cancer analysis, only patients with ductal carcinoma pathology were included. However, no inclusion or exclusion criteria were applied based on treatments received. Cores were 5 μm thick and had a 1 mm diameter. TMAs were sectioned and stored at 4 °C until use. TMA slides were baked at 60 °C for 30 min, incubated in 100% xylene for 10 min for de-paraffinization, and incubated in ethanol series (100, 90, and 70%) and milliQ water for 10 min each for rehydration. For antigen retrieval using sodium citrate buffer (10 mM sodium citrate, 0.05% Tween-20, pH 6.0), slides were placed in a water bath, microwaved for 5 min (at P100/high), cooled for 5 min at room temperature (RT), and microwaved for 5 min. Slides were then cooled under tap water for 6 min, washed 2 × 5 min with PBS, and permeabilized in PBS/0.01% Triton-X for 10 min. Following 2 × 10 min PBS washes and 1 h incubation in blocking buffer (PBS/10% FBS), slides were incubated in blocking buffer with primary anti-collagen XVII antibody (clone 9G2, 1:100 dilution) [15] overnight at 4 °C, incubated at RT for 20 min, washed 2 × 5 min with PBS, blocked for endogenous peroxide in PBS/0.3% H2O2 for 10 min, washed 2 × 5 min with PBS, incubated with HRP-conjugated goat anti-mouse IgG (H + L) secondary antibody (Invitrogen, 62-6520) in blocking buffer for 1 h, followed by 2 × 10 min PBS washes. TMAs were then stained with 3,3′-diaminobenzidine (DAB) reagent (DBC859, Biocare Medical) and counter-stained with hematoxylin. Stepwise dehydration occurred in an ethanol series (70, 90, and 100%; 2 min each), followed by 9 min baking at 60 °C and incubation in 100% xylene for 2 min. Slides were mounted using Permount and dried overnight. Slides were imaged using Olympus Slide scanner VS120 (rm4026) and OlyVia software. Tissue sections were excluded from the analyses if chronic mastitis (breast), chronic inflammation/cervicitis, or cataplasia (cervix) was diagnosed or if more than 70% of the section was missing. Slides were independently scored by two individuals and in a blinded fashion. Clinical endpoints examined included pathology, age, grade, stage, tumor invasion, lymph node status, metastasis and estrogen (ER), progesterone (PR), and HER2 receptor status. Fisher’s exact tests were used for statistical analyses. In addition, we controlled for multiple testing by subjecting our analyses to a false discovery rate (FDR) of 5%, as previously described [40]. Where clinical data were missing for individual samples, these were excluded from the analyses involving the missing data, but included in analyses of other variables for which data were present. The clinicopathological details and standard prognostic variables of all patient samples subjected to immunohistochemistry are included in Additional file 1: Tables S2 and S3 for breast ductal carcinoma and cervical cancers, respectively.
Allelic copy number variation and RNAseq analysis
Putative COL17A1 allelic copy numbers were determined using Affymetrix Genome-Wide SNP6.0 Array datasets and GISTIC 2.0. RNAseq data, obtained from the TCGA breast cancer, cervical cancer, head and neck SCC, lung adenocarcinoma, and lung SCC Illumina HiSeq RNA Seq V2 (RSEM) datasets [21, 22, 41–43]. For each patient, copy number data and gene expression were combined and expression levels were plotted for each copy number category. Nonparametric Mann-Whitney U tests were used to compare differences.
Promoter methylation analyses
For COL17A1 promoter methylation analyses, Illumina Infinium HumanMethylation450 platform level 3 data were used from the respective TCGA cancer datasets [21, 22, 41–43]. For each sample, β values for all probes in the region from 400 bp upstream to 400 bp downstream of the COL17A1 transcription start site (chromosome 10/hg19 genomic coordinate 105845638) were used (Additional file 2). These probes were: cg13553455 (10/105846002), cg08509991 (10/105845720), and cg13448625 (10/105845238). The probes are located at positions −364, −82, and +400 relative to the COL17A1 transcription start site (TSS; see also Additional file 1: Figure S2). For each sample, the average of the β values was calculated and used. Data were not normally distributed, as determined by the D’Agostino and Pearson omnibus normality test p < 0.05. Therefore, nonparametric Mann-Whitney U tests were used to compare differences. RNAseq data from the respective TCGA datasets, as described above, were used to compare promoter methylation to gene expression. For linear regression, Spearman correlation analyses were used.
Abbreviations
- CI:
-
Confidence interval
- ECM:
-
Extracellular matrix
- ER:
-
Estrogen receptor
- FDR:
-
False discovery rate
- HR:
-
Hazard ratio
- IHC:
-
Immunohistochemistry
- PR:
-
Progesterone receptor
- SCC:
-
Squamous cell carcinoma
- TCGA:
-
The Cancer Genome Atlas
References
Cheung KJ, Ewald AJ. A collective route to metastasis: seeding by tumor cell clusters. Science. 2016;352:167–9.
Frantz C, Stewart KM, Weaver VM. The extracellular matrix at a glance. J Cell Sci. 2010;123:4195–200.
Jarvelainen H, Sainio A, Koulu M, Wight TN, Penttinen R. Extracellular matrix molecules: potential targets in pharmacotherapy. Pharmacol Rev. 2009;61:198–223.
Daley WP, Peters SB, Larsen M. Extracellular matrix dynamics in development and regenerative medicine. J Cell Sci. 2008;121:255–64.
Chu M-L. Structural proteins: Genes for collagen. eLS. 2011
Fang M, Yuan J, Peng C, Li Y. Collagen as a double-edged sword in tumor progression. Tumour Biol. 2014;35:2871–82.
Rizwan A, Bulte C, Kalaichelvan A, Cheng M, Krishnamachary B, Bhujwalla ZM, Jiang L, Glunde K. Metastatic breast cancer cells in lymph nodes increase nodal collagen density. Sci Rep. 2015;5:10002.
Zou X, Feng B, Dong T, Yan G, Tan B, Shen H, Huang A, Zhang X, Zhang M, Yang P, et al. Up-regulation of type I collagen during tumorigenesis of colorectal cancer revealed by quantitative proteomic analysis. J Proteomics. 2013;94:473–85.
Chen P, Cescon M, Bonaldo P. Collagen VI in cancer and its biological mechanisms. Trends Mol Med. 2013;19:410–7.
An JH, Lee SY, Jeon JY, Cho KG, Kim SU, Lee MA. Identification of gliotropic factors that induce human stem cell migration to malignant tumor. J Proteome Res. 2009;8:2873–81.
Fischer H, Salahshor S, Stenling R, Bjork J, Lindmark G, Iselius L, Rubio C, Lindblom A. COL11A1 in FAP polyps and in sporadic colorectal tumors. BMC Cancer. 2001;1:17.
Cheon DJ, Tong Y, Sim MS, Dering J, Berel D, Cui X, Lester J, Beach JA, Tighiouart M, Walts AE, et al. A collagen-remodeling gene signature regulated by TGF-beta signaling is associated with metastasis and poor survival in serous ovarian cancer. Clin Cancer Res. 2014;20:711–23.
Halsted KC, Bowen KB, Bond L, Luman SE, Jorcyk CL, Fyffe WE, Kronz JD, Oxford JT. Collagen alpha1(XI) in normal and malignant breast tissue. Mod Pathol. 2008;21:1246–54.
Franzke CW, Bruckner P, Bruckner-Tuderman L. Collagenous transmembrane proteins: recent insights into biology and pathology. J Biol Chem. 2005;280:4005–8.
Stelkovics E, Korom I, Marczinovits I, Molnar J, Rasky K, Raso E, Ficsor L, Molnar B, Kopper L, Krenacs T. Collagen XVII/BP180 protein expression in squamous cell carcinoma of the skin detected with novel monoclonal antibodies in archived tissues using tissue microarrays and digital microscopy. Appl Immunohistochem Mol Morphol. 2008;16:433–41.
Krenacs T, Kiszner G, Stelkovics E, Balla P, Teleki I, Nemeth I, Varga E, Korom I, Barbai T, Plotar V, et al. Collagen XVII is expressed in malignant but not in benign melanocytic tumors and it can mediate antibody induced melanoma apoptosis. Histochem Cell Biol. 2012;138:653–67.
Ravdin PM, Siminoff LA, Davis GJ, Mercer MB, Hewlett J, Gerson N, Parker HL. Computer program to assist in making decisions about adjuvant therapy for women with early breast cancer. J Clin Oncol. 2001;19:980–91.
Galea MH, Blamey RW, Elston CE, Ellis IO. The Nottingham Prognostic Index in primary breast cancer. Breast Cancer Res Treat. 1992;22:207–19.
Vaidyanathan S, Thangavelu PU, Duijf PH. Overexpression of Ran GTPase components regulating nuclear export, but not mitotic spindle assembly, marks chromosome instability and poor prognosis in breast cancer. Target Oncol. 2016;11:677–86.
Rhodes DR, Kalyana-Sundaram S, Mahavisno V, Varambally R, Yu J, Briggs BB, Barrette TR, Anstet MJ, Kincead-Beal C, Kulkarni P, et al. Oncomine 3.0: genes, pathways, and networks in a collection of 18,000 cancer gene expression profiles. Neoplasia. 2007;9:166–80.
Cancer Genome Atlas N. Comprehensive molecular portraits of human breast tumours. Nature. 2012;490:61–70.
Ciriello G, Gatza ML, Beck AH, Wilkerson MD, Rhie SK, Pastore A, Zhang H, McLellan M, Yau C, Kandoth C, et al. Comprehensive molecular portraits of invasive lobular breast cancer. Cell. 2015;163:506–19.
Gyorffy B, Lanczky A, Eklund AC, Denkert C, Budczies J, Li Q, Szallasi Z. An online survival analysis tool to rapidly assess the effect of 22,277 genes on breast cancer prognosis using microarray data of 1,809 patients. Breast Cancer Res Treat. 2010;123:725–31.
Jones PA, Baylin SB. The epigenomics of cancer. Cell. 2007;128:683–92.
Parikka M, Kainulainen T, Tasanen K, Vaananen A, Bruckner-Tuderman L, Salo T. Alterations of collagen XVII expression during transformation of oral epithelium to dysplasia and carcinoma. J Histochem Cytochem. 2003;51:921–9.
Tamas L, Szentkuti G, Eros M, Danos K, Brauswetter D, Szende B, Zsakovics I, Krenacs T. Differential biomarker expression in head and neck cancer correlates with anatomical localization. Pathol Oncol Res. 2011;17:721–7.
Papay J, Krenacs T, Moldvay J, Stelkovics E, Furak J, Molnar B, Kopper L. Immunophenotypic profiling of nonsmall cell lung cancer progression using the tissue microarray approach. Appl Immunohistochem Mol Morphol. 2007;15:19–30.
Fabian K, Nemeth Z, Furak J, Tiszlavicz L, Papay J, Krenacs T, Timar J, Moldvay J. Protein expression differences between lung adenocarcinoma and squamous cell carcinoma with brain metastasis. Anticancer Res. 2014;34:5593–7.
Nakano S, Iyama K, Ogawa M, Yoshioka H, Sado Y, Oohashi T, Ninomiya Y. Differential tissular expression and localization of type IV collagen alpha1(IV), alpha2(IV), alpha5(IV), and alpha6(IV) chains and their mRNA in normal breast and in benign and malignant breast tumors. Lab Investig. 1999;79:281–92.
Oskarsson T. Extracellular matrix components in breast cancer progression and metastasis. Breast. 2013;22 Suppl 2:S66–72.
Amenta PS, Hadad S, Lee MT, Barnard N, Li D, Myers JC. Loss of types XV and XIX collagen precedes basement membrane invasion in ductal carcinoma of the female breast. J Pathol. 2003;199:298–308.
Ehrlich M. DNA methylation in cancer: too much, but also too little. Oncogene. 2002;21:5400–13.
Maekawa R, Sato S, Yamagata Y, Asada H, Tamura I, Lee L, Okada M, Tamura H, Takaki E, Nakai A, et al. Genome-wide DNA methylation analysis reveals a potential mechanism for the pathogenesis and development of uterine leiomyomas. PLoS ONE. 2013;8, e66632.
Hayashi M, Nomoto S, Hishida M, Inokawa Y, Kanda M, Okamura Y, Nishikawa Y, Tanaka C, Kobayashi D, Yamada S, et al. Identification of the collagen type 1 alpha 1 gene (COL1A1) as a candidate survival-related factor associated with hepatocellular carcinoma. BMC Cancer. 2014;14:108.
Cardenas H, Vieth E, Lee J, Segar M, Liu Y, Nephew KP, Matei D. TGF-beta induces global changes in DNA methylation during the epithelial-to-mesenchymal transition in ovarian cancer cells. Epigenetics. 2014;9:1461–72.
Loffek S, Hurskainen T, Jackow J, Sigloch FC, Schilling O, Tasanen K, Bruckner-Tuderman L, Franzke CW. Transmembrane collagen XVII modulates integrin dependent keratinocyte migration via PI3K/Rac1 signaling. PLoS ONE. 2014;9, e87263.
Hiroyasu S, Colburn ZT, Jones JC. A hemidesmosomal protein regulates actin dynamics and traction forces in motile keratinocytes. FASEB J. 2016;30:2298–310.
Jackow J, Schlosser A, Sormunen R, Nystrom A, Sitaru C, Tasanen K, Bruckner-Tuderman L, Franzke CW. Generation of a functional non-shedding collagen XVII mouse model: relevance of collagen XVII shedding in wound healing. J Invest Dermatol. 2016;136:516–25.
Vaidyanathan S, Cato K, Tang L, Pavey S, Haass NK, Gabrielli BG, Duijf PH. In vivo overexpression of Emi1 promotes chromosome instability and tumorigenesis. Oncogene. 2016;35:5446–55.
Benjamini Y, Hochberg Y. Controlling the false discovery rate: a practical and powerful approach to multiple testing. J R Stat Soc Ser B-Stat Methodol. 1995;57:289–300.
Cancer Genome Atlas N. Comprehensive genomic characterization of head and neck squamous cell carcinomas. Nature. 2015;517:576–82.
Cancer Genome Atlas N. Comprehensive molecular profiling of lung adenocarcinoma. Nature. 2014;511:1–7.
Cancer Genome Atlas Research N. Comprehensive genomic characterization of squamous cell lung cancers. Nature. 2012;489:519–25.
Acknowledgements
Not applicable.
Funding
This work was supported by University of Queensland (UQ) International and UQ Diamantina Institute scholarships (to PUT), Career Development Fellowships from the National Breast Cancer Foundation (to ED, PHGD), and grants from UQ Diamantina Institute and UQ (to PHGD). The funding bodies were not involved in the design of the study; in the collection, analysis, or interpretation of the data; or in writing of the manuscript.
Availability of data and materials
The datasets analyzed during the current study are available from The Cancer Genome Atlas (TCGA) Data Portal in the Genomic Data Commons, https://gdc.cancer.gov.
Authors’ contributions
P.U.T. performed experiments, analyzed the data, and wrote parts of the manuscript. T.K. provided reagents and protocols and discussed results. E.D. analyzed data and discussed results. P.H.G.D. conceived, designed, and supervised the study; performed analyses; and wrote parts of the manuscript. All authors read and approved the final manuscript.
Competing interests
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Consent for publication
Not applicable.
Ethics approval and consent to participate
Not applicable.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional files
Additional file 1:
Supplementary Material containing Table S1 (Prognostic strength of misexpression of collagen genes in breast cancer), Table S2 (Clinicopathological features of the breast cancer patients analyzed by immunohistochemistry), Table S3 (Clinicopathological features of the cervical cancer patients analyzed by immunohistochemistry), Figure S1 (H&E stained sections of corresponding samples shown in Fig. 2), Figure S2 (Schematic of the promoter and 5’ end of the COL17A1 gene), and Supplementary References. (PDF 1136 kb)
Additional file 2:
COL17A1 promoter methylation levels (β-values, TCGA Illumina Infinium Human Methylation 450). (XLSX 231 kb)
Rights and permissions
Open Access This article is distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/), which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided you give appropriate credit to the original author(s) and the source, provide a link to the Creative Commons license, and indicate if changes were made. The Creative Commons Public Domain Dedication waiver (http://creativecommons.org/publicdomain/zero/1.0/) applies to the data made available in this article, unless otherwise stated.
About this article
Cite this article
Thangavelu, P.U., Krenács, T., Dray, E. et al. In epithelial cancers, aberrant COL17A1 promoter methylation predicts its misexpression and increased invasion. Clin Epigenet 8, 120 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1186/s13148-016-0290-6
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1186/s13148-016-0290-6