Abstract
Introduction
Matrix metalloproteinase-8 (MMP-8; neutrophil collagenase) is an important regulator of innate immunity that has oncosuppressive actions in numerous tumor types.
Methods
We have intercrossed Mmp8-null mice with the Polyoma virus middle T oncogene-driven (MMTV-PyMT) mouse model of mammary cancer to explore the effects of loss of MMP-8 on the incidence and progression of mammary carcinomas.
Results
In this aggressive mouse model of breast cancer, loss of MMP-8 accelerated tumor onset even further, such that 90% of MMTV-PyMT; Mmp8-null female mice were tumor-bearing at the time of weaning. Throughout the 14 weeks of the model, tumor burden increased in homozygous Mmp8-null mice compared to Mmp8-wild-type and -heterozygote animals. Likewise, lung metastasis dramatically increased in the MMTV-PyMT; Mmp8-null mice. Immunohistochemistry revealed that tumors in wild-type, Mmp8-heterozygotes and -null animals had similar vascular density at 8 weeks, but at 10 weeks Mmp8-wild-type tumors had a lower vascularity than their heterozygote and null counterparts. No differences in macrophage infiltration were apparent throughout primary tumor development, though at 10 weeks a drop in neutrophil infiltrates was observed in Mmp8-wild-type tumors. Using quantitative real-time RT-PCR, we tracked the expression of the entire Mmp and Timp gene families, observing a significant decrease in Mmp3 expression in Mmp8-null tumors compared to wild-type and heterozygotes throughout the time course of the model, which was confirmed at the protein level.
Conclusions
These findings provide novel insight into the suppressive action of MMP-8 on mammary tumorigenesis and metastasis, and indicate that the loss of MMP-8 likely has pleiotropic effects on innate immunity and angiogenesis that are reflected in changes in the protease web.
Similar content being viewed by others
Introduction
The matrix metalloproteinase (MMP) family of secreted Zn-dependent endopeptidases play important roles in physiological processes and disease states via their effects on the structure and content of the extracellular environment. In cancer they have been identified as key regulators of cell proliferation, apoptosis, migration, invasion, angiogenesis and the immune system [1]. In humans, the MMP family consists of 24 enzymes that can be categorized based on their structural similarities and substrate specificities into collagenases, gelatinases, matrilysins, stromelysins, membrane-bound MMPs and others. It was originally thought that MMPs acted en masse to promote tumorigenesis and progression via extracellular matrix (ECM) degradation that permitted cancer cell invasion, which led to the development of broad-spectrum synthetic inhibitors as anti-cancer therapies. However, these agents subsequently proved disappointing in the clinic, contributing to the recognition that the roles of the MMPs are much more complex than originally believed [2,3]. Recent evidence has demonstrated that MMP family members exhibit both pro- and anti-tumorigenic/metastatic functions and thus their inhibition can have adverse consequences [4,5]. One of the first MMPs to emerge as an anti-target due to its anti-tumorigenic and anti-metastatic functions was MMP-8.
MMP-8, otherwise known as neutrophil collagenase thanks to its abundant expression in neutrophil granules, can be expressed by a wide variety of cell types including epithelial cells, fibroblasts, endothelial cells, macrophages and neutrophils [6]. We, and others, have demonstrated that MMP-8 exerts tumorigenic and/or metastasis suppressive roles. Human correlation studies have shown that positive MMP-8 expression is linked to a lower risk of cancer incidence and metastasis, and to prolonged disease-free and overall survival [7-12]. Using a carcinogen-induced skin tumorigenesis mouse model, Balbin et al. reported in 2003 that the absence of MMP-8 dramatically increased the incidence of skin papillomas in male Mmp8-null mice, while a similar observation for tongue squamous carcinomas was made by Korpi et al. a few years later [10,13]. Xenograft models with breast cancer and melanoma cells have also demonstrated the anti-metastatic ability of MMP-8 [9,14,15]. Analysis of a pair of breast tumor cell lines, originating from the same breast tumor but with opposite metastatic capabilities, revealed increased expression of MMP-8 in the non-metastatic cell line and corresponding xenograft [16]. Furthermore, downregulation of MMP-8 in the non-metastatic cell line led to increased invasion through Matrigel [16] and enhanced lung metastasis [17]. Enhanced expression of MMP-8 by melanoma cells was found to decrease their invasion and migration by enhancing their adhesion to the ECM [9]. A recent breast cancer xenograft study has provided insight into potential molecular mechanisms behind this anti-metastatic behavior, indicating that MMP-8 cleavage of decorin from the ECM leads to downregulation of active transforming growth factor beta (TGF-β) and consequent suppression of miR-21 expression [15]. Furthermore, MMP-8 has a range of extracellular substrates including cytokines, chemokines, growth factors, ECM proteins, proteases and protease inhibitors [6,17]. There is accumulating evidence that MMP-8 regulates the innate immune system in vivo via the cleavage of chemokines and cytokines. MMP-8 has been implicated in the acute immune response in a number of experimental models of inflammatory diseases where it can either act to promote or hinder the inflammatory response [18]. We recently reported that enhanced production of MMP-8 by breast cancer cells induced the expression of the proinflammatory mediators interleukin-6 (IL-6) and IL-8 [19]. Thus, MMP-8 may participate in and orchestrate multiple events in the tumor microenvironment during the stages of tumor progression.
In the present study, we have explored the effects of constitutional loss of MMP-8 on mammary oncogenesis and metastasis in the mouse mammary tumor virus-Polyoma virus middle T-antigen (MMTV-PyMT) mouse, which is a rapid and robust model of human luminal breast cancer [20]. These mice develop pre-malignant epithelial hyperplasia as early as 4 weeks, which progresses to overt carcinoma by 12 weeks at which time essentially all of the mice show metastasis to the lung and lymph nodes [21-23]. This work represents the first study exploring the role of MMP-8 in a spontaneous cancer mouse model. We show here that in the absence of MMP-8, the oncogenic program in MMTV-PyMT mice is further accelerated as tumor latency is decreased and the resulting lesions grow larger, generating increased numbers of lung macrometastases. Increased malignancy was also evident from changes in tumor vascularity and immune cell infiltration in Mmp8-deficient mice that became apparent at later stages of the model. We also found that the complete absence of MMP-8 had repercussions for other MMP family members, with MMP-3 in particular showing reduced expression throughout the time course of the model. This suggests that the position of MMP-8 in the interconnected ‘protease web’ may have extensive downstream consequences [24]. Together these findings confirm the anti-tumorigenic and anti-metastatic functions of MMP-8 in a spontaneous mouse mammary cancer model and highlight its impact on multiple components, including angiogenesis and inflammatory cell involvement.
Materials and methods
Mice and genotyping
The Mmp8-null mice were previously described [9,13]. MMTV-PyMT mice (Charles River Laboratories, Margate, UK) were on the FVB/n genetic background and Mmp8-null mice were backcrossed onto the FVB/n genetic background for more than eight generations. Both mouse strains were intercrossed and male MMTV-PyMT offspring were used to establish sibling cohorts of MMTV-PyMT; Mmp8-wild-type (WT), MMTV-PyMT; Mmp8-heterozygote (HET) and MMTV-PyMT; Mmp8-null (KO) females. Mouse husbandry and animal experiments were conducted under Home Office project license PPL 80/2288 in accordance with the Animals (Scientific Procedures) Act 1986, with the approval of the University of East Anglia Ethics Review Committee.
Genotyping of ear snips was performed using PyMT-3p primer 5′- CGG CGG AGC GAG GAA CTG AGG AGA G −3′ and PyMT-4 m primer 5′-TCA GAA GAC TCG GCA GTC TTA GGC G – 3′ for detection of the PyMT transgene; and Mmp8-Anchor primer 5′- AGC CCT TAA ACC GCT AAG GA – 3′, Mmp8-WT primer 5′- TCG TCT CAA GAG GTA GGC TCA– 3′ and Mmp8-Neo primer 5′- GCC AGA GGC CAC TTG TGT AG −3′ for detection of Mmp8.
Tumor growth and lung metastasis
Tumor growth was assessed by biweekly palpations of all 10 mammary glands from day 21 to day 98. Tumor size was categorized into four groups: 0 cm, <0.5 cm, 0.5 to 1 cm, >1 cm. Tumor onset was recorded as the first day when tumors could be detected by palpation.
At 14 weeks of age, mice were sacrificed and lungs were injected intratracheally with 15% India ink. Lungs were excised, washed in Carnoy’s fix and surface metastases were imaged and counted using a Lumar Stereoscope (Carl Zeiss, Jena, Germany).
Quantitative real-time RT-PCR
Snap-frozen tumor tissue was homogenized in RNA-Bee (Amsbio, Rockville, MD, USA) using a tissueLyser at 50Hz for 2 to 3 min and 7 mm stainless steel balls. RNA was isolated from the homogenized tissue using a chloroform extraction method followed by a column purification step (Promega, Madison, WI, USA). RNA quantity and purity was assessed by A260/A280 and A260/A230 absorbance ratios using a Nanodrop system (Thermo Fisher Scientific, Frederick, MD, USA). Reverse transcription of 1 μg was performed using MMLV-Superscript (Sigma-Aldrich, St Louis, MO, USA) resulting in a final concentration of 50 ng/μl. Quantitative real-time polymerase chain reaction (qRT-PCR) was conducted using 5 ng cDNA for all genes of interest and 1 ng cDNA for 18S rRNA and the cycle conditions were as following: 2 min at 50°C, 10 min at 95°C, followed by 40 cycles of 15 sec at 90°C and 1 min at 60°C. Expression of IL-6, CXCL5 and CD68 was quantified using specific 5′FAM-3′TAMRA Taqman gene expression primer/probe sets (Mm00446190_m1, Mm00436451_g1, Mm03047340_m1, Life Technologies, Carlsbad, CA, USA). Expression levels were normalized to 18S rRNA using forward primer 5′-GCCGCTAGAGGTGAAATTCTTG-3′, reverse primer 5′-CATTCTTGGCAAATGCTTTC G-3′ and probe 5′-FAM-ACCGGCGCAAGACGGA-TAMRA-3′. Specific primers and 5′FAM-TAMRA-3′ probes were designed for all MMPs and tissue inhibitor of metalloproteinases (TIMPs), and synthesized by Sigma-Aldrich (Sigma-Aldrich, St Louis, MO, USA). The sequences for the primers and probes are given in Table 1.
Western blotting
Snap-frozen tumor tissue was homogenized in RIPA lysis buffer (500 mM NaCl, 1% Triton-X100, 0.1% sodium dodecylsulphate, 50 mM Tris pH 7.4) with complete EDTA-free protease inhibitor cocktail mix (Roche Applied Science, Penzberg, Germany) using a tissueLyser at 50Hz for 2 to 3 min and 7 mm stainless steel balls. Tissue lysates were centrifuged for 10 min at 10,000 rpm, supernatants were harvested and protein content was determined using a BCA protein assay (Thermo Fisher Scientific, Frederick, MD, USA). Tumor lysates were reduced and denatured in Laemmli sample buffer (containing 4% b2-mercaptoethanol) and equal amounts of total protein were loaded onto a 10% SDS-PAGE gel. Proteins were transferred onto polyvinylidene fluoride membrane (EMD Millipore, Billerica, MA, USA), blocked in Tris-buffered saline (TBS)/0.1% Tween-20/2.5% non-fat dried milk and incubated overnight at 4°C with sheep anti-mouse MMP-3 (the kind gift of Dr G. Murphy [25]) or mouse heat shock protein-70 (sc-7298, Santa Cruz Biotechnology, Santa Cruz, CA, USA), diluted in TBS/ 0.1% Tween-20/2.5% non-fat dried milk. The next day the membranes were washed three times with TBS/0.1% Tween-20 for 5 min and incubated in horseradish peroxidase (HRP)-labeled secondary antibody (Jackson ImmunoResearch Laboratories, West Grove, PA, USA) for 1 hr. Finally, the membranes were washed with TBS and imaged using ECL chemiluminescence (Thermo Fisher Scientific, Frederick, MD, USA) and Fujifilm LAS-3000 Imager (FujiFilm, Tokyo, Japan). Densitometry was performed using Fiji software [26].
Gelatin zymography
Tumor lysates were harvested and processed as for western blotting, with the omission of protease inhibitors in the lysis buffer. The samples were diluted in non-reducing Laemmli sample buffer and loaded in equal amounts on a 7% gelatin-PAGE gel. Following electrophoresis, the gels were washed twice with 2.5% Triton-X100 for 15 min, briefly rinsed in water, followed by incubation in assay buffer (100 mM Tris, 30 mM CaCl2, 0.02% NaN3) at 37°C overnight. The next day the gel was stained in 0.25% Coomassie Brilliant Blue G250 and destained using 30% methanol/1% acetic acid until clear bands of enzymatic activity were visible. Imaging and quantification were performed using the Licor Odyssey (Licor, Lincoln, NE, USA).
Immunofluorescence
Tumor tissue was harvested in 4% paraformaldehyde overnight, paraffin-embedded and sectioned at 6 μm. Detection of macrophages and neutrophils was achieved after trypsin antigen retrieval using a primary antibody targeted against respectively F4/80 clone Cl:A3-1 (MCA497R, AbD Serotec, Kidlington, UK) and Ly6B2 clone7/4 (MCA771G, AbD Serotec, Kidlington, UK) at a dilution of 1:100 in phosphate-buffered saline (PBS)/0.1% Tween. Blood vessels were detected using an antibody against Endomucin clone V.7C7 (sc-65495, Santa Cruz Biotechnology, Dallas, TX, USA) at a dilution of 1:500 in PBS/0.1% Tween-20. Unspecific binding of primary antibody was prevented by blocking the sections in PBS/0.1% Tween-20 with 10% normal donkey serum. Visualization was obtained using a donkey-anti-rat Alexa594-labeled secondary antibody at 1:500 dilution in PBS/0.1% Tween-20. Sections were mounted using Prolong Gold Antifade with DAPI solution (Invitrogen, Carlsbad, CA, USA). The whole section on a slide was imaged at 10x magnification using automated slide scanning and the Zeiss Axiovision plugin MosaiX (Carl Zeiss, Jena, Germany) to stitch the images together, followed by image processing in Fiji and analysis on Volocity.
Statistics
Data were analyzed using the two-tailed unpaired t test or the chi-square test and are represented as mean ± standard error of the mean (SEM) unless stated otherwise.
Results
Accelerated tumor onset and progression in MMP-8-deficient PyMT mice
The effect of MMP-8 ablation on tumor onset and growth was investigated in cohorts of Mmp8-wild-type, heterozygote and null female PyMT littermates [27]. All 10 mammary glands were palpated biweekly for the presence of tumors. In MMTV-PyMT; Mmp8-null mice (KO; n = 10), tumors were first detected at the age of 25 days compared to 32 days in wild-type (WT; n = 17, P <0.01) and heterozygote mice (HET; n = 30, P <0.05) (Figure 1A). All MMTV-PyMT; Mmp8-null mice (n = 21) were tumor-bearing at the age of 40 days, whereas full penetrance in heterozygote (n = 34) and wild-type (n = 26) mice was not observed until 50 and 55 days respectively (Figure 1B). No difference in tumor multiplicity was found (data not shown).
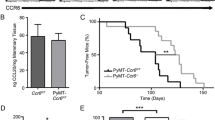
Loss of MMP-8 accelerates tumor onset; promotes progression, tumor size and lung macrometastases in the MMTV-PyMT model. (A) Detection of first palpable tumors of MMTV-PyMT; Mmp8-wild-type (WT, n = 17), MMTV-PyMT; Mmp8-heterozygote (HET, n = 30) and MMTV-PyMT; Mmp8-null (KO, n = 10) mice. Mean ± SEM, two-tailed unpaired t test; * P <0.05; ** P <0.01. (B) Tumor progression determined by palpation of all 10 mammary glands from day 21 to day 98 for MMTV-PyMT; Mmp8-wild-type (WT, n = 26), −heterozygote (HET, n = 34) and -null (KO, n = 21) mice. (C) Tumor size distribution (0, <0.5, 0.5 to 1, >1 cm) at 10 weeks of age for MMTV-PyMT; Mmp8-wild-type (WT, n = 26), MMTV-PyMT; Mmp8-heterozygote (HET, n = 34) and MMTV-PyMT; Mmp8-null (KO, n = 21) mice; and at 14 weeks of age for MMTV-PyMT; Mmp8-wild-type (WT, n = 22), MMTV-PyMT; Mmp8-heterozygote (HET, n = 30) and MMTV-PyMT; Mmp8-null (KO, n = 16) mice. chi-square test, * P <0.01. (D) Number of lung macrometastases assessed at 14 weeks of age for MMTV-PyMT; Mmp8-wild-type (WT, n = 4), MMTV-PyMT; Mmp8-heterozygote (HET, n = 4) and MMTV-PyMT; Mmp8-null (KO, n = 2) mice. Left panel of representative pictures depicts the top and bottom of all lung lobes (one lobe of the left lung, four lobes of the right lung). Black solid arrows = smaller macrometastases, white solid arrows = larger macrometastases. Mean ± SEM, two-tailed unpaired t test; ** P <0.01. MMP, matrix metalloproteinase; MMTV, mouse mammary tumor virus; PyMT, Polyoma virus middle T-antigen; SEM, standard error of the mean.
Tumor progression was assessed by biweekly palpation from day 21 to day 98 and tumors were categorized according to their size (0, <0.5, 0.5 to 1, >1 cm) as presented in Figure 1C. At 10 weeks of age, MMTV-PyMT; Mmp8-wild-type (n = 26) and heterozygote (n = 34) mice showed similar tumor size distribution patterns with the majority of tumors being between 0.5 to 1 cm. The Mmp8-null mice (n = 21) overall presented with bigger tumors, with a remarkable doubling of very large tumors (>1 cm, P <0.01) compared to their wild-type or heterozygous littermates. At 14 weeks of age, again no difference in tumor size could be observed between wild-type (n = 22) and heterozygote (n = 30) mice with the majority of tumors being larger than 1 cm. In line with the observations at 10 weeks, Mmp8-null mice (n = 16) had a significantly greater proportion of very large tumors (P <0.01).
Induction of lung surface metastases in MMP-8-deficient PyMT mice
PyMT transgenic mice are prone to the formation of lung metastases so we assessed the impact of MMP-8 deficiency on the spread of the disease to this site (Figure 1D) [27]. At 14 weeks of age, 100% of female PyMT mice had lung metastases. Although on a limited cohort, Mmp8-null PyMT mice had a significant 11.8-fold increase in the number of lung surface metastases (520 ± 55) compared to wild-type or heterozygote PyMT mice (44 ± 5).
Changes in angiogenesis in MMP-8-deficient PyMT mice
Changes in blood vessel formation were investigated by immunohistochemical analysis of endomucin at different time points (Figure 2) [28]. Endomucin staining was high in tumors in all of the genotypes at 8 weeks. In contrast, at 10 weeks of age there was a significant drop (P <0.04) in vascularity in MMTV-PyMT; Mmp8-wild-type tumors compared to those in Mmp8-heterozygote or -null animals, which remained at the higher levels seen at the 8-week stage.
Altered MMTV-PyMT tumor vascularity in Mmp8- null mice. Vascular density of tumors in early- and late-stage tumors as determined by Endomucin staining. The number of mice used for analyses were as following: 8 weeks; MMTV-PyMT; Mmp8 wild-type (WT, n = 4), MMTV-PyMT; Mmp8 heterozygote (HET, n = 5), MMTV-PyMT; Mmp8 null (KO, n = 5), and 10 weeks; MMTV-PyMT; Mmp8 wild-type (WT, n = 4), MMTV-PyMT; Mmp8 heterozygote (HET, n = 6) and MMTV-PyMT; Mmp8 null (KO, n = 4). Representative pictures of 10-week tumors are shown.* P <0.05, ** P <0.01. MMP, matrix metalloproteinase; MMTV, mouse mammary tumor virus; PyMT, Polyoma virus middle T-antigen.
Changes in immune cell infiltrates and proinflammatory mediators in MMP-8-deficient PyMT mice
We investigated the effect of MMP-8 deficiency on macrophage and neutrophil cell infiltrates during disease progression using F4/80 and Ly6B2 for immunohistochemistry analysis and CD68 for RNA profiling [29]. No substantial or significant difference in the number of macrophages was found between the various Mmp8 genotypes throughout the time course of disease (Figure 3). Though image quantification showed an apparently statistically significant increased level of macrophage staining at 6 weeks in Mmp8-null mice, this was based on only two Mmp8-null mice and should be interpreted with caution. Macrophage staining in all genotypes peaked at 8 weeks, which is also reflected in CD68 mRNA levels. On the other hand, expression of the proinflammatory mediators IL-6 and the murine IL-8 ortholog CXCL-5/LIX rose from early- (6 weeks) to later-stage disease (10 to 14 weeks) and were generally somewhat higher in MMP-8-deficient animals (both Mmp8-heterozyote and -null) than wild-type (Figure 3B).
Loss of MMP-8 affects MMTV-PyMT neutrophil, but not macrophage, infiltration and expression of proinflammatory mediators. (A) Number of macrophages/mm2 and neutrophils/mm2 in early- and late-stage tumors as determined by staining for F4/80 and Ly6B.2, respectively. The number of mice used for analyses of macrophage and neutrophil infiltration respectively were at 6 weeks: Mmp8 wild-type (WT, n = 5, 5), heterozygote (HET, n = 4, 3) and null (KO, n = 2, 3); 8 weeks: Mmp8 wild-type (WT, n = 4, 5), heterozygote (HET, n = 6, 5), null (KO, n = 4, 5) and at 10 weeks: Mmp8 wild-type (WT, n = 5, 5), heterozygote (HET, n = 5, 5) and null (KO, n = 4, 4).* P <0.05, ** P <0.01. One representative image of macrophage and neutrophil staining is shown for each genotype at 10 weeks of age. (B) Relative RNA expression of macrophage marker CD68, IL-6 and CXCL5/LIX, normalized to 18S rRNA, throughout disease progression (6 to 14 weeks of age). IL, interleukin; MMP, matrix metalloproteinase; MMTV, mouse mammary tumor virus; PyMT, Polyoma virus middle T-antigen.
Looking at neutrophil infiltration, no significant differences were apparent between genotypes at early time points (Figure 3A). However, at 10 weeks significantly lower numbers of neutrophils were observed in tumors in wild-type mice compared to heterozygote (P = 0.008) and Mmp8-null mice (P = 0.02).
Perturbation of the MMP and TIMP families in MMP-8-deficient PyMT mice
The consequences of MMP-8 ablation on the protease web were assessed through a comprehensive real-time qRT-PCR profiling of the MMP and TIMP families (Figure 4A) in end-stage (14 week) tumors [30]. The highest overall expression levels were shown by Mmp15 and Timp2, with several genes showing very low expression in tumors (including Mcol-a/b, Mmp7, Mmp10, Mmp20 and Timp4). A more in-depth RNA analysis in the form of a time-course profile (6 to 8 to 10 to 14 weeks; Figure 4C) was performed for all MMPs/TIMPs with a significant 50% change (+1.5- or −2.0-fold change) in Mmp8-null mice compared to wild-type mice (shaded grey in Figure 4B). Due to the very low expression levels of Mcol-a and Mcol-b, further analysis was not pursued. Several genes showed progressive increases during tumor growth, including Mmp2, Mmp3, Mmp13 and Mmp16, whereas Timp2 and Mmp27 showed more dynamic fluctuations in expression. Protein expression of a select number of candidate altered genes (MMP-3, MMP-13, TIMP-2) was performed based on the availability of antibodies for western blot analysis. While the changes observed at the RNA level could not be confirmed at the protein level for MMP-13 and TIMP-2 (data not shown), the decrease in MMP-3 expression in Mmp8-null mice was clearly apparent (Figure 5A). Zymography analysis of tumor homogenates showed no changes in overall expression levels of the gelatinases MMP-2 and MMP-9, though there was a slight reduction in the ratio of active MMP-2/pro-MMP-2 in heterozygote and null mice compared to their wild-type littermates at end-stage disease or 14 weeks of age (Figure 5B).
MMP-8 ablation perturbs the tumor protease web at the RNA level. (A) qRT-PCR profiling of MMP and TIMP RNA expression at 14 weeks of age with expression levels classified as very high (CT <25), high (CT = 26 to 30), moderate (CT = 31 to 35), low (CT = 36 to 39) or not detected (CT = 39 to 40). (B) MMPs and TIMPs with a significant change in expression in PyMT knockout (KO) or heterozygote (HET) mice compared to wild-type (WT) littermates at 14 weeks of age. Genes with significant 50% up- (FC +1.5) or down-regulated (FC −2.0) expression in null mice compared to wild-type littermates are highlighted in grey. FC, fold change. (C) RNA time course of selected MMPs and TIMPs (highlighted in grey in Figure 4B). Expression data was normalized to 18S rRNA, throughout disease progression (6 to 14 weeks of age) and expressed as arbitrary units. MMP, matrix metalloproteinase; PyMT, Polyoma virus middle T-antigen; qRT-PCR, quantitative real-time polymerase chain reaction; TIMP, tissue inhibitor of metalloproteinases.
MMP-8 ablation perturbs the tumor protease web at the protein level. (A) MMP-3 protein expression in tumor tissue at 14 weeks of age as determined by western blotting. Quantification of three biological replicates per genotype, normalized to Hsc70 and compared to PyMT wild-type (WT). Two-tailed unpaired t test, mean ± SEM. (B) Tumor expression of MMP-2 and MMP-9 forms by gelatin zymography at 10 and 14 weeks of age. two-tailed unpaired t test; AU, arbitrary unit; FC, fold change; MMP, matrix metalloproteinase; ns, non-significant; PyMT, Polyoma virus middle T-antigen; SEM, standard error of the mean.
Discussion
Matrix metalloproteinase-8 has emerged as a key tumor-suppressive enzyme and thus an anti-target for MMP-directed therapies [4,31,32]. The current study provides the first evidence from a spontaneous mouse tumor model for the tumor- and metastasis-suppressive functions of MMP-8. Despite the already aggressive nature of the MMTV-PyMT model, which leads to rapid, multifocal tumor formation in the mammary gland and a high frequency of lung metastasis [22,33], homozygous loss of MMP-8 further accelerated tumor onset, progression and lung surface metastasis formation. In the later stages of tumor development (10 weeks of age), we found that while vascularization and neutrophil infiltration in tumors in wild-type animals had decreased overall compared to earlier lesions at 8 weeks, these parameters remained elevated in MMP-8 deficient animals. Moreover, loss of MMP-8 led to changes in the expression or activation of other MMPs, particularly MMP-3. Thus, the absence of MMP-8 has multiple consequences for angiogenesis, innate immune responses and metastasis that conspire to promote tumor growth and malignancy, and which may involve systemic disturbance of the protease web.
Our observations in the MMTV-PyMT mouse mammary cancer model concur with observations of a suppressive role for host-derived MMP-8 in carcinogen-induced skin tumorigenesis. Male Mmp8-null mice have been shown to have enhanced formation of skin papillomas, which could be rescued by transfer of bone marrow from wild-type mice, suggesting that neutrophils (as the main source of MMP-8) are protective in the early stages of lesion formation [13]. A similar protective role for host neutrophil-derived MMP-8 was observed in spontaneous and experimental metastasis experiments with syngeneic Lewis lung carcinoma and B16F10 melanoma cells in C57Bl6 Mmp8-null mice [9]. However, tumor cell-expressed MMP-8 is also suppressive, so it is likely that the presence of MMP-8 in the tumor microenvironment, rather than its source, is the critical factor [9,15,16,34]. Expression of MMP-8 by tumor cells reduces invasion and increases adhesion to type-I collagen and laminin matrices [9]. Interestingly, an RNA interference screen has identified MMP-8 as a protein that interacts with and modifies the activity of β1 integrin, which may be the basis for its effects on tumor cell adhesion [35].
Although Mmp8-null mice have no overt phenotype without challenge (and of particular relevance for the present study we have seen no abnormalities in early mammary gland morphogenesis by whole mount staining, data not shown), they show altered inflammatory responses in several disease or pathology models, which can result in either exacerbation or protection depending on the context. In skin carcinogenesis or excisional wound repair, Mmp8-null mice show delayed neutrophil recruitment at early stages, but there is persistent neutrophil accumulation at later times, leading to a chronic inflammatory milieu that enhances tumor formation and impairs wound repair [9,36]. This is also apparent in models of periodontitis and lipopolysaccharide (LPS)-induced corneal inflammation [37-39]. In all of these scenarios, the initial recruitment of neutrophils is an important factor in orchestrating the inflammatory response to allow its subsequent resolution when the source of the inflammation is eliminated or tissue damage is repaired. In the MMTV-PyMT model we found no deficit in neutrophil accumulation at early-mid stages of tumor development (6 and 8 weeks), but by 10 weeks the neutrophil count in sections of wild-type tumors had declined, whereas levels remained elevated for tumors in both Mmp8-null and -heterozygote mice. The highly aggressive nature of the MMTV-PyMT model may be linked with the intrinsically high level of neutrophils in these tumors, similar to the previously observed relationship between increased metastatic potential of these transgenic mice and macrophage infiltration [40,41]. Reflecting this, F4/80-positive macrophage infiltration was unaffected by Mmp8 genotype throughout lesion development and progression. However, the absence of MMP-8 led to persistence of neutrophils in MMTV-PyMT lesions at the later stages (10 weeks) of tumor development. Along with the sustained high neutrophils levels in Mmp8-null mice, we observed that vascular density in 10-week tumors remained at the high levels seen in 8-week lesions, while it decreased in tumors in wild-type mice. This reduced angiogenesis in wild-type tumors is surprising given that the tumors are still growing up to the end point of the model. However, there is widespread necrosis at later stages of tumor growth (from 10 weeks onwards), potentially as a result of growth outstripping vascularization. Since we quantify all vessels across the entire tumor section, and not only the vessels near the proliferative margins, the increase in necrotic area likely contributes to the decreased vascular density observed in wild-type tumors at 10 weeks compared to the 8-week time point. Both neutrophil accumulation and vascular density may contribute directly to the enhanced growth and metastatic spread of tumors that we have observed in the Mmp8-null mice. Indeed the reduction in tumor-associated neutrophils in tumors in wild-type mice could be directly responsible for the diminished vascular density due to reduced release of pro-angiogenic factors [42-46]. However, since neutrophils may be of the anti-tumorigenic ‘N1-phenotype’ or the pro-tumorigenic ‘N2’ variety, with TGF-β directing the accumulation of the latter [47], it will be important to investigate further the nature of the neutrophils present in tumors in wild-type mice versus those in Mmp8-null and heterozygotes. This is particularly relevant given the recent links between MMP-8 and inhibition of TGF-β signaling [15,19]. It is also important to note that we found evidence of a sustained inflammatory milieu in lesions in Mmp8-null and Mmp8-heterozygote mice, resulting in higher expression of proinflammatory mediators IL-6 and LIX/CXCL-5 at the end stage of the MMTV-PyMT model, which may also contribute to enhanced malignant potential.
It had been previously thought that the key driver for the role of MMP-8 in neutrophil migration was its ability to cleave and activate the chemokine IL-8 or its murine counterpart LIX/CXCL-5 [17]. Cleavage of IL-8/LIX by MMP-8 released from neutrophils was argued to provide a feed-forward mechanism to drive rapid initial neutrophil recruitment, with loss of MMP-8 leading to impaired neutrophil migration. However, recent studies indicate that the in vivo inflammatory phenotypes resulting from loss of MMP-8 are indirect, and relate to its long-recognized ability to cleave and inactivate the abundant plasma serine protease inhibitor, α1-proteinase inhibitor (α1-PI), which regulates the activity of neutrophil elastase [48,49]. Thus, neutrophil elastase activates IL-8/LIX, and its activity is influenced by MMP-8 via α1-PI [49]. This is an example of the interconnectedness of the ‘protease web’, whereby the consequences of in vivo genetic inactivation of a particular proteolytic enzyme can have major repercussions for the activities or expression of other proteases, including other protease classes operating in distant tissue locations [50]. We have seen evidence of this from profiling the expression of the entire MMP and TIMP families in the MMTV-PyMT tumors in Mmp8-null mice, where we observed altered expression of Mmp2, 3, 13, 16, 27 and Timp2 transcripts, and we confirmed reduced expression of MMP-3 at the protein level. The reduction in MMP-3 expression may itself contribute to the enhanced tumor and metastatic capability of MMTV-PyMT tumors in the Mmp8-null background. Transgenic mice overexpressing MMP-3 in their mammary glands show reduced carcinogen-induced mammary tumors as a result of increased epithelial cell apoptosis [51]. A protective role for MMP-3 has also been seen in skin squamous cell carcinoma [52]. The increased expression of Timp2 transcripts that we observed in tumors of Mmp8-null mice might also contribute to localized effects on MT1-MMP-mediated activation of pro-MMP-2, leading to enhanced invasion and metastasis. It is likely that such changes in the protease web may also contribute to the different vascularization of tumors in Mmp8-wild-type, −heterozygote and -null mice. With the recent link that has been forged between MMP-8 and miR-21 [15], and recognition of the impact of microRNAs on the expression of several key degradome players, for example MMP-3, MMP-13 and TIMP-2, the effects of MMP-8 ablation on miRNA expression might be an interesting avenue for future research [53-61].
Conclusions
This study demonstrates that the suppressive effects of MMP-8 on tumorigenesis and metastasis are apparent even in an aggressive spontaneous model of mammary carcinoma, and that loss of MMP-8 function has pleiotropic effects on angiogenesis and inflammatory cell involvement, accompanied by changes within proteolytic networks operating within tumors.
Availability of supporting data
The data set(s) supporting the results of this article are available in the Figshare repository, http://dx.doi.org/10.6084/m9.figshare.1162505, http://dx.doi.org/10.6084/m9.figshare.1162507, http://dx.doi.org/10.6084/m9.figshare.1162499, http://dx.doi.org/10.6084/m9.figshare.1162492.
Abbreviations
- α1-PI:
-
α1-proteinase inhibitor
- ECM:
-
extracellular matrix
- HET:
-
heterozygote
- HRP:
-
horseradish peroxidase
- IL:
-
interleukin
- KO:
-
knockout
- LPS:
-
lipopolysaccharide
- MMP:
-
matrix metalloproteinase
- MMTV:
-
mouse mammary tumor virus
- PBS:
-
phosphate-buffered saline
- PyMT:
-
Polyoma virus middle T-antigen
- qRT-PCR:
-
quantitative real-time polymerase chain reaction
- TBS:
-
Tris-buffered saline
- TGF-β:
-
transforming growth factor beta
- TIMP:
-
tissue inhibitor of metalloproteinases
- WT:
-
wild-type
References
Egeblad M, Werb Z. New functions for the matrix metalloproteinases in cancer progression. Nat Rev Cancer. 2002;2:161–74.
Fingleton B. MMP inhibitor clinical trials – the past, present, and future. In: Edwards D, Høyer-Hansen G, Blasi F, Sloane BF, editors. The cancer degradome. New York: Springer; 2008. p. 759–85.
Fingleton B. MMPs as therapeutic targets – still a viable option? Semin Cell Dev Biol. 2008;19:61–8.
Decock J, Thirkettle S, Wagstaff L, Edwards DR. Matrix metalloproteinases: protective roles in cancer. J Cell Mol Med. 2011;15:1254–65.
Decock J, Roghi C, Edwards DR. Matrix metalloproteinases: a dual role in breast cancer? Breast Cancer Manag. 2013;2:353–6.
Van Lint P, Libert C. Matrix metalloproteinase-8: cleavage can be decisive. Cytokine Growth Factor Rev. 2006;17:217–23.
Decock J, Long JR, Laxton RC, Shu XO, Hodgkinson C, Hendrickx W, et al. Association of matrix metalloproteinase-8 gene variation with breast cancer prognosis. Cancer Res. 2007;67:10214–21.
Decock J, Hendrickx W, Vanleeuw U, Belle VV, Huffel SV, Christiaens M-R, et al. Plasma MMP1 and MMP8 expression in breast cancer: Protective role of MMP8 against lymph node metastasis. BMC Cancer. 2008;8:77.
Gutiérrez-Fernández A, Fueyo A, Folgueras AR, Garabaya C, Pennington CJ, Pilgrim S, et al. Matrix metalloproteinase-8 functions as a metastasis suppressor through modulation of tumor cell adhesion and invasion. Cancer Res. 2008;68:2755–63.
Korpi JT, Kervinen V, Mäklin H, Väänänen A, Lahtinen M, Läärä E, et al. Collagenase-2 (matrix metalloproteinase-8) plays a protective role in tongue cancer. Br J Cancer. 2008;98:766–75.
Korpi JT, Hagström J, Lehtonen N, Parkkinen J, Sorsa T, Salo T, et al. Expression of matrix metalloproteinases-2, −8, −13, −26, and tissue inhibitors of metalloproteinase-1 in human osteosarcoma. Surg Oncol. 2011;20:e18–22.
Väyrynen JP, Vornanen J, Tervahartiala T, Sorsa T, Bloigu R, Salo T, et al. Serum MMP-8 levels increase in colorectal cancer and correlate with disease course and inflammatory properties of primary tumors. Int J Cancer. 2012;131:E463–74.
Balbin M, Fueyo A, Tester AM, Pendas AM, Pitiot AS, Astudillo A, et al. Loss of collagenase-2 confers increased skin tumor susceptibility to male mice. Nat Genet. 2003;35:252–7.
Palavalli LH, Prickett TD, Wunderlich JR, Wei X, Burrell AS, Porter-Gill P, et al. Analysis of the matrix metalloproteinase family reveals that MMP8 is often mutated in melanoma. Nat Genet. 2009;41:518–20.
Soria-Valles C, Gutiérrez-Fernández A, Guiu M, Mari B, Fueyo A, Gomis RR, et al. The anti-metastatic activity of collagenase-2 in breast cancer cells is mediated by a signaling pathway involving decorin and miR-21. Oncogene. 2013;33:3054–63.
Agarwal D, Goodison S, Nicholson B, Tarin D, Urquidi V. Expression of matrix metalloproteinase 8 (MMP-8) and tyrosinase-related protein-1 (TYRP-1) correlates with the absence of metastasis in an isogenic human breast cancer model. Differentiation. 2003;71:114–25.
Tester AM, Cox JH, Connor AR, Starr AE, Dean RA, Puente XS, et al. LPS responsiveness and neutrophil chemotaxis in vivo require PMN MMP-8 activity. PLoS One. 2007;2:e312.
Dejonckheere E, Vandenbroucke RE, Libert C. Matrix metalloproteinase8 has a central role in inflammatory disorders and cancer progression. Cytokine Growth Factor Rev. 2011;22:73–81.
Thirkettle S, Decock J, Arnold H, Pennington CJ, Jaworski DM, Edwards DR. Matrix metalloproteinase-8 (collagenase-2) induces the expression of interleukins-6 and −8 in breast cancer cells. J Biol Chem. 2013;288:16282–94.
Guy CT, Cardiff RD, Muller WJ. Induction of mammary tumors by expression of polyomavirus middle T oncogene: a transgenic mouse model for metastatic disease. Mol Cell Biol. 1992;12:954–61.
Maglione JE, Moghanaki D, Young LJT, Manner CK, Ellies LG, Joseph SO, et al. Transgenic polyoma middle-T mice model premalignant mammary disease. Cancer Res. 2001;61:8298–305.
Lin EY, Jones JG, Li P, Zhu L, Whitney KD, Muller WJ, et al. Progression to malignancy in the polyoma middle T oncoprotein mouse breast cancer model provides a reliable model for human diseases. Am J Pathol. 2003;163:2113–26.
Sevenich L, Werner F, Gajda M, Schurigt U, Sieber C, Müller S, et al. Transgenic expression of human cathepsin B promotes progression and metastasis of polyoma-middle-T-induced breast cancer in mice. Oncogene. 2010;30:54–64.
Overall CM, Kleifeld O. Tumour microenvironment - opinion: validating matrix metalloproteinases as drug targets and anti-targets for cancer therapy. Nat Rev Cancer. 2006;6:227–39.
Dew G, Murphy G, Stanton H, Vallon R, Angel P, Reynolds JJ, et al. Localisation of matrix metalloproteinases and TIMP-2 in resorbing mouse bone. Cell Tissue Res. 2000;299:385–94.
Schindelin J, Arganda-Carreras I, Frise E, Kaynig V, Longair M, Pietzsch T, et al. Fiji: an open-source platform for biological-image analysis. Nat Methods. 2012;9:676–82.
Decock J, Hendrickx W, Thirkettle S, Gutiérrez-Fernández A, Robinson S, Edwards D. MMP-8 and tumor onset; progression and size; and lung macrometastases in the MMTV-PyMT model. Figshare. 2014. http://dx.doi.org/10.6084/m9.figshare.1162505.
Decock J, Hendrickx W, Thirkettle S, Gutiérrez-Fernández A, Robinson S, Edwards D. MMP-8 and tumor vascularity in MMTV-PyMT mice. Figshare. 2014. http://dx.doi.org/10.6084/m9.figshare.1162507.
Decock J, Hendrickx W, Thirkettle S, Gutiérrez-Fernández A, Robinson S, Edwards D. MMP-8 and immune cell infiltrates in MMTV-PyMT mice. Figshare. 2014. http://dx.doi.org/10.6084/m9.figshare.1162499.
Decock J, Hendrickx W, Thirkettle S, Gutiérrez-Fernández A, Robinson S, Edwards D. MMP-8 and tumour protease web in the MMTV-PyMT model. Figshare. 2014. http://dx.doi.org/10.6084/m9.figshare.1162492.
Dufour A, Overall CM. Missing the target: matrix metalloproteinase antitargets in inflammation and cancer. Trends Pharmacol Sci. 2013;34:233–42.
López-Otín C, Matrisian LM. Emerging roles of proteases in tumour suppression. Nat Rev Cancer. 2007;7:800–8.
Almholt K, Nielsen BS, Frandsen TL, Brünner N, Danø K, Johnsen M. Metastasis of transgenic breast cancer in plasminogen activator inhibitor-1 gene-deficient mice. Oncogene. 2003;22:4389–97.
Montel V, Kleeman J, Agarwal D, Spinella D, Kawai K, Tarin D. Altered metastatic behavior of human breast cancer cells after experimental manipulation of matrix metalloproteinase 8 gene expression. Cancer Res. 2004;64:1687–94.
Pellinen T, Rantala JK, Arjonen A, Mpindi J-P, Kallioniemi O, Ivaska J. A functional genetic screen reveals new regulators of β1-integrin activity. J Cell Sci. 2012;125:649–61.
Gutierrez-Fernandez A, Inada M, Balbin M, Fueyo A, Pitiot AS, Astudillo A, et al. Increased inflammation delays wound healing in mice deficient in collagenase-2 (MMP-8). FASEB J. 2007;21:2580–91.
Gueders MM, Foidart JM, Noel A, Cataldo DD. Matrix metalloproteinases (MMPs) and tissue inhibitors of MMPs in the respiratory tract: potential implications in asthma and other lung diseases. Eur J Pharmacol. 2006;533:133–44.
Hernández M, Gamonal J, Salo T, Tervahartiala T, Hukkanen M, Tjäderhane L, et al. Reduced expression of lipopolysaccharide-induced CXC chemokine in Porphyromonas gingivalis-induced experimental periodontitis in matrix metalloproteinase-8 null mice. J Periodontal Res. 2011;46:58–66.
Lin M, Jackson P, Tester AM, Diaconu E, Overall CM, Blalock JE, et al. Matrix Metalloproteinase-8 facilitates neutrophil migration through the corneal stromal matrix by collagen degradation and production of the chemotactic peptide Pro-Gly-Pro. Am J Pathol. 2008;173:144–53.
Lin EY, Nguyen AV, Russell RG, Pollard JW. Colony-stimulating factor 1 promotes progression of mammary tumors to malignancy. J Exp Med. 2001;193:727–40.
Wyckoff J, Wang W, Lin EY, Wang Y, Pixley F, Stanley ER, et al. A paracrine loop between tumor cells and macrophages is required for tumor cell migration in mammary tumors. Cancer Res. 2004;64:7022–9.
Christoffersson G, Vågesjö E, Vandooren J, Lidén M, Massena S, Reinert RB, et al. VEGF-A recruits a proangiogenic MMP-9-delivering neutrophil subset that induces angiogenesis in transplanted hypoxic tissue. Blood. 2012;120:4653–62.
Deryugina EI, Zajac E, Juncker-Jensen A, Kupriyanova TA, Welter L, Quigley JP. Tissue-infiltrating neutrophils constitute the major in vivo source of angiogenesis-inducing MMP-9 in the tumor microenvironment. Neoplasia N Y N. 2014;16:771–88.
Bekes EM, Schweighofer B, Kupriyanova TA, Zajac E, Ardi VC, Quigley JP, et al. Tumor-recruited neutrophils and neutrophil TIMP-free MMP-9 regulate coordinately the levels of tumor angiogenesis and efficiency of malignant cell intravasation. Am J Pathol. 2011;179:1455–70.
Nozawa H, Chiu C, Hanahan D. Infiltrating neutrophils mediate the initial angiogenic switch in a mouse model of multistage carcinogenesis. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2006;103:12493–8.
Tazzyman S, Lewis CE, Murdoch C. Neutrophils: key mediators of tumour angiogenesis. Int J Exp Pathol. 2009;90:222–31.
Fridlender ZG, Sun J, Kim S, Kapoor V, Cheng G, Ling L, et al. Polarization of tumor-associated neutrophil (TAN) phenotype by TGF-β: ‘N1’ versus ‘N2’ TAN. Cancer Cell. 2009;16:183–94.
Knäuper V, Reinke H, Tschesche H. Inactivation of human plasma alpha 1-proteinase inhibitor by human PMN leucocyte collagenase. FEBS Lett. 1990;263:355–7.
Fortelny N, Cox JH, Kappelhoff R, Starr AE, Lange PF, Pavlidis P, et al. Network analyses reveal pervasive functional regulation between proteases in the human protease web. PLoS Biol. 2014;12:e1001869.
Krüger A, Kates RE, Edwards DR. Avoiding spam in the proteolytic internet: future strategies for anti-metastatic MMP inhibition. Biochim Biophys Acta. 2010;1803:95–102.
Witty JP, Wright JH, Matrisian LM. Matrix metalloproteinases are expressed during ductal and alveolar mammary morphogenesis, and misregulation of stromelysin-1 in transgenic mice induces unscheduled alveolar development. Mol Biol Cell. 1995;6:1287–303.
McCawley LJ, Crawford HC, King LE, Mudgett J, Matrisian LM. A protective role for matrix metalloproteinase-3 in squamous cell carcinoma. Cancer Res. 2004;64:6965–72.
Zhao Z-G, Jin J-Y, Zhang A-M, Zhang L-P, Wang X-X, Sun J-G, et al. MicroRNA profile of tumorigenic cells during carcinogenesis of lung adenocarcinoma. J Cell Biochem. 2015;116:458–66.
Wang W, Lin H, Zhou L, Zhu Q, Gao S, Xie H, et al. MicroRNA-30a-3p inhibits tumor proliferation, invasiveness and metastasis and is downregulated in hepatocellular carcinoma. Eur J Surg Oncol. 2014;40:1586–94.
Lin Y-H, Liao C-J, Huang Y-H, Wu M-H, Chi H-C, Wu S-M, et al. Thyroid hormone receptor represses miR-17 expression to enhance tumor metastasis in human hepatoma cells. Oncogene. 2013;32:4509–18.
Xu N, Zhang L, Meisgen F, Harada M, Heilborn J, Homey B, et al. MicroRNA-125b down-regulates matrix metallopeptidase 13 and inhibits cutaneous squamous cell carcinoma cell proliferation, migration, and invasion. J Biol Chem. 2012;287:29899–908.
Yang Z, Zhang Y, Wang L. A feedback inhibition between miRNA-127 and TGFβ/c-Jun cascade in HCC cell migration via MMP13. PLoS One. 2013;8:e65256.
Lang Y, Xu S, Ma J, Wu J, Jin S, Cao S, et al. MicroRNA-429 induces tumorigenesis of human non-small cell lung cancer cells and targets multiple tumor suppressor genes. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2014;450:154–9.
Zhu M, Zhang N, He S, Lui Y, Lu G, Zhao L. MicroRNA-106a targets TIMP2 to regulate invasion and metastasis of gastric cancer. FEBS Lett. 2014;588:600–7.
Wu T-Y, Zhang T-H, Qu L-M, Feng J-P, Tian L-L, Zhang B-H, et al. MiR-19a is correlated with prognosis and apoptosis of laryngeal squamous cell carcinoma by regulating TIMP-2 expression. Int J Clin Exp Pathol. 2014;7:56–63.
Li P, Xu Q, Zhang D, Li X, Han L, Lei J, et al. Upregulated miR-106a plays an oncogenic role in pancreatic cancer. FEBS Lett. 2014;588:705–12.
Acknowledgements
We thank Carlos López-Otín for helpful comments. This work was supported by project grants from Cancer Research UK, the European Union Framework Programme 7 (SaveMe, MicroEnviMet) and the Ministry of Economy and Competitiveness (Spain).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Additional information
Competing interests
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Authors’ contributions
JD participated in the design of the study, designed and carried out experiments, analyzed data and drafted the manuscript. WH carried out experiments, designed the method for imaging analyses, analyzed data and helped edit the manuscript. ST analyzed data and helped edit the manuscript. AGF provided the Mmp8-null c57Bl6 mouse strain and critically evaluated data and the intellectual content of the manuscript. SDR participated in the lung metastases studies, imaging analyses, analyzed data and helped edit the manuscript. DRE conceived the study, participated in the design and coordination, analyzed data and drafted the manuscript. All authors read and approved the final manuscript.
Rights and permissions
This article is published under an open access license. Please check the 'Copyright Information' section either on this page or in the PDF for details of this license and what re-use is permitted. If your intended use exceeds what is permitted by the license or if you are unable to locate the licence and re-use information, please contact the Rights and Permissions team.
About this article
Cite this article
Decock, J., Hendrickx, W., Thirkettle, S. et al. Pleiotropic functions of the tumor- and metastasis-suppressing matrix metalloproteinase-8 in mammary cancer in MMTV-PyMT transgenic mice. Breast Cancer Res 17, 38 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1186/s13058-015-0545-8
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1186/s13058-015-0545-8