Abstract
Chemotherapy, radiotherapy, targeted therapy, and immunotherapy are established cancer treatment modalities that are widely used due to their demonstrated efficacy against tumors and favorable safety profiles or tolerability. Nevertheless, treatment resistance continues to be one of the most pressing unsolved conundrums in cancer treatment. Hypoxia-inducible factors (HIFs) are a family of transcription factors that regulate cellular responses to hypoxia by activating genes involved in various adaptations, including erythropoiesis, glucose metabolism, angiogenesis, cell proliferation, and apoptosis. Despite this critical function, overexpression of HIFs has been observed in numerous cancers, leading to resistance to therapy and disease progression. In recent years, much effort has been poured into developing innovative cancer treatments that target the HIF pathway. Combining HIF inhibitors with current cancer therapies to increase anti-tumor activity and diminish treatment resistance is one strategy for combating therapeutic resistance. This review focuses on how HIF inhibitors could be applied in conjunction with current cancer treatments, including those now being evaluated in clinical trials, to usher in a new era of cancer therapy.
Similar content being viewed by others
Background
Hypoxia is a frequent phenomenon in cancer growth and progression that is linked to adverse outcomes [1]. Due to rapid proliferation in an enlarging tumor mass and aberrant microvessel architecture, cells in solid tumors are prone to oxygen deficiency. As most solid tumors contain heterogeneously dispersed regions of chronic or acute hypoxia, hypoxia has been identified as one of the intrinsic features of solid tumors [2]. In cancer biology, hypoxia confers increased propensity of chemoresistance, radioresistance, disease relapse, and potentiates cancer metastasis [3]. This phenomenon is well established by evidence from as early as the 1950s, when Gray et al. first described the negative association between hypoxia and the success of radiotherapy [4].
The key players behind these unfavorable effects are the hypoxia-inducible factors (HIFs), a family of transcription factors that drive cellular adaptation to hypoxia. Under hypoxic conditions, HIFs have the ability to activate hundreds of genes responsible for genetic instability, cell proliferation, angiogenesis, metastasis, glucose metabolism, growth factor signaling, immunosuppression, and the development of therapeutic resistance [5, 6]. Consistently, overexpression of HIFs is associated with resistance to cancer treatment, metastasis, and poor prognosis in patients [7].
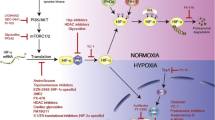
Given the fact that cancer cells inhabit a unique hypoxic microenvironment that is often much more extreme than normal tissues and that hypoxia plays a major role in cancer progression and treatment resistance, it is only rational to utilize this characteristic to develop novel treatment modalities against cancer. Various strategies have been attempted to target hypoxia, including genetically engineered anerobic bacteria [8] and bioreductive prodrugs [9], which are activated in hypoxic environments. Among these approaches, the HIF pathway is a compelling target for pharmacologic inhibition due to its central role in hypoxic adaptative programs, versatility of effects, and selective induction under hypoxia. The correlation between HIF overexpression and poor treatment response has been demonstrated in an extensive range of cancers, including liver, ovarian, breast, cervical, pancreatic, colorectal, gastric cancer, and melanoma [6]. The co-administration of HIF inhibitors on top of current treatment modalities counteracts resistance and improves treatment response. This effect has been widely corroborated in chemotherapy [10], radiotherapy [11, 12], targeted therapy [13], and metabolic therapy [14], in various types of cancer, by preclinical studies and clinical trials. While numerous studies have demonstrated the efficacy of co-administering HIF inhibitors with existing cancer treatment modalities to overcome resistance and improve response rates, there remains a gap between the evidence in the literature and clinical practice, as current treatment guidelines do not yet incorporate this approach. Therefore, we herein propose that integrating HIF inhibitors into cancer treatment regimens represents a promising yet underutilized strategy for improving patient outcomes (Fig. 1).
Targeting HIF in conjunction with current therapies. Resistance to chemotherapy, radiotherapy and immunotherapy is associated with the activation of HIF and its downstream. To improve anti-tumor effect and diminish treatment resistance, HIF inhibitors together with cancer therapies would be a good solution for patients with resistant cancer. Abbreviations: HIF = hypoxia inducible factor
Nevertheless, the development of HIF inhibitors has also faced various challenges and obstacles. Adverse drug-drug interactions and toxicity are major challenges when pursuing this line of research. This review summarizes the current progress of HIF inhibitor development and discusses the potential of combining HIF inhibitors with current treatment modalities as a novel cancer treatment approach.
The functions and roles of HIFs in cancer biology
HIFs are highly conserved transcriptional factors. The HIF-1 transcriptional complex is heterodimeric, composed of an alpha and a beta subunit, named HIF-1α and HIF-1β, respectively. Each subunit of HIF-1 consists of three isoforms, namely HIF-1α, HIF-2α, and HIF-3α, along with HIF-1β, HIF-2β, and HIF-3β. All are involved in cancer progression, HIF-1α regulates the response to acute hypoxia, while HIF-2α and HIF-3α are dominant in the chronic hypoxia response [2, 15]. In animal and clinical studies, HIF-1α and HIF-2α have been reported to participate in tumor growth, angiogenesis, and metastasis [15, 16] (Fig. 2). Although some inconsistent findings exist, most studies found that increased HIF-1α or HIF-2α expression is linked to a worse prognosis, and that HIF expression could be a potential biomarker for cancer therapy response [15, 17].
HIF-1a and HIF-2a upstream and downstream pathways promoting cancer. HIF-1a expression varies with oxygen level in the cellular environment while HIF-2a is constitutively expressed and has some known oncogenic effects. Under normal oxygen conditions, both HIF-1a and HIF-2a are degraded through ubiquitination pathway by proteasome. Under hypoxia (low oxygen) conditions, HIF-1a translocates into the nucleus and forms HIF complex with HIF-1b and p300, leading to many cancer-promoting outcomes, including metabolic adaptation, cell survival, invasion and metastasis, angiogenesis and vascular tone, cellular proliferation, and apoptosis. Abbreviations: ADM = adrenomedullin; ALD = adrenoleukodystrophy protein; ANF = atrial natriuretic factor; Ang2 = Angiopoietin 2; ANGPT = Angiopoietin-related protein; ANP = Atrial natriuretic peptide; BCL-2 = B-cell lymphoma 2; BNIP3 = BCL2/adenovirus E1B 19 kDa interacting protein 3; CATHD = Cathepsin D; c-MET = mesenchymal-epithelial transition factor; C-MYC = Cellular myelocytomatosis oncogene; COS4 = ; EDN1 = Endothelin 1 gene; EGF = Epidermal growth factor; EG-VEGF = endocrine gland derived vascular endothelial growth factor; ENG = Endoglin; ENO = Enolase; EPO = Erythropoietin; ET1 = Endothelin 1; Flt-1 = Fms Related Receptor Tyrosine Kinase 1; FN1 = soluble plasma fibronectin; GAPDH = Glyceraldehyde 3-phosphate dehydrogenase; GPI = Glycosylphosphatidylinositol; HIF = hypoxia inducible factor; HK = Hexokinase; HRE = Hypoxia-response element; HSP90 = Heat shock protein 90; ID2 = Inhibitor Of DNA binding 2; IGF2 = Insulin like growth factor 2; IGF-BP = Insulin-like growth factor-binding protein; iNOS = Inducible nitric oxide synthases; KL = Klotho; KRT = Keratin; LDH-A = Lactate Dehydrogenase A; LEP = Leptin; LRP = Low-density lipoprotein (LDL)-related protein; MMPs = Matrix metalloproteinases; mTORC = mechanistic target of rapamycin complex; NOS = nitric oxide synthases; OH = Hydroxyl group; P4HS = Prolyl 4-hydroxylase; PDGF-B = platelet derived growth factor; PDK1 = Pyruvate Dehydrogenase Kinase 1; PFK2 = Phosphofructokinase 2; PFKFB3 = 6-phosphofructo-2-kinase/fructose-2,6-bisphosphatase 3; PFKL = ATP-dependent 6-phosphofructokinase, liver type; PGF = Placenta growth factor; PGK1 = Phosphoglycerate Kinase 1; PGM = phosphoglucomutase; PHD = HIF prolyl hydroxylase; PKM2 = Pyruvate kinase isozymes M2; POK1 = Phragmoplast orienting kinesin 1; pVHL = Von Hippel–Lindau tumor suppressor; RTP801 = HIF responsive protein; S6K1 = Ribosomal protein S6 kinase beta-1; TGF = Transforming growth factor; TIMP = Tissue Inhibitor of Metalloproteinase; TPI = Triosephosphate isomerase; Ub = Ubiquitin; uPAR = urokinase plasminogen activator surface receptor; PAI-1 = plasminogen activator inhibitor 1; PI3K = Phosphoinositide-3-kinase; VEGF = Vascular endothelial growth factor; VEGFR2 = Vascular endothelial growth factor receptor 2; VIM = Vimentin; WAF-1 = Wild type p53 activated protein-1
Molecular functions of HIFs
Under normal oxygen conditions, HIF-1α subunit undergoes rapid proteasomal degradation due to hydroxylation by HIF prolyl-hydroxylases, allowing its recognition and labeling by the von Hippel-Lindau (VHL) E3 ubiquitin ligase [18]. Under hypoxia, HIF-1α is stabilized by its N-terminal transactivation domain and translocated into the nucleus, where it dimerizes with HIF-1β to form the HIF-1 complex [2]. The HIF-1 transcriptional complex subsequently activates a substantial number of cancer-related genes by binding to gene promoters containing hypoxia responsive elements (HRE) [1, 2, 15-17]. The HIF-1 regulated- genes include angiopoietin, vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF), and erythropoietin, which promote angiogenesis and red blood cell production [1], glucose transporters (GLUTs) and glycolytic enzymes, which promote glycolysis [16], and genes involved in immune checkpoints [19], cell proliferation [20], autophagy [21], and DNA damage [22]. The discovery of HIF-1’s fundamental mechanism of oxygen sensing and adaptation was awarded the Nobel Prize in 2019 [23].
HIF-2α and HIF-3α are homologues of HIF-1α, bearing closely similar structures. Despite HIF-1α and HIF-2α sharing similar abilities to dimerize with HIF-β, bind to genes whose promoters containing the HRE motif, and activate downstream expression of hypoxia-inducible genes, they differ in expression levels during different timings in cancer progression [24]. Studies have shown that the expression of HIF-1α is more prominent in the early stages of cancer, during which tumorigenesis, cellular proliferation, and survival are major events, while HIF-2α-mediated cancer pathways are more active during the later stages, when metastasis and chemoresistance take place [25]. Various factors were suggested be involved in the signal switch from HIF-1α to HIF-2α, including prolonged hypoxia [26], pseudohypoxia [27], accumulation of Krebs cycle intermediates [28], onco-miRNAs [29], cytokines, and chemokines [30]. Upregulation of HIF-2α-mediated cancer pathways was reported to associate with advanced stage features such as malignant transformation, epithelial-mesenchymal transition, and VEGF resistance in a variety of cancers, especially gastric cancer [31], clear cell renal cell cancer (ccRCC) [32], and pancreatic cancer [33].
Targeting HIFs in cancer
Because of the importance of HIF-1 and HIF-2 in cancer progression, substantial research has focused on developing compounds that suppress their effects [16, 34]. The inhibition of HIF presents a challenging target for pharmacological inhibition as transcription factors are intracellular protein complex without easily accessible active sites typically used for drug binding [35]. Until recently, most HIF inhibitors developed were indirect inhibitors that targeted different stages of HIF-1 pathway, such as mRNA expression, protein translation, degradation, DNA binding, and transcriptional activity. However, some small-molecule inhibitors have been identified that directly target the key protein–protein interactions involved in HIF-1 activation and downstream gene regulation [36]. Examples of indirect HIF inhibitors include EZN-2968, a synthetic antisense oligonucleotide that targets HIF-1α mRNA and leads to decreased HIF-1α protein expression [37], and PX-478, a prodrug that inhibits HIF-1α translation by blocking its interaction with ribosomes [38]. Direct HIF inhibitors, such as acriflavine and chetomin, offer exciting possibilities for drug discovery. Acriflavine is a small molecule dereived from natural compounds that disrupts the interaction between HIF-1α and its binding partner p300, preventing the transcriptional activation of downstream genes [39]. Chetomin, on the other hand, binds to the HIF-1α/ARNT heterodimer and inhibits its DNA binding activity [40]. Interestingly, many HIF inhibitors are repurposed drugs that were originally developed for other purposes, such as metformin, a widely used drug for diabetes that has been shown to inhibit HIF-1α expression [41]. This suggests that drug repurposing could also be a cost-effective and efficient way to identify new HIF inhibitors for cancer therapy.
Combination therapies that incorporate HIF-1 inhibitors with other cancer therapies have considerable potential to improve treatment efficacy, ameliorate side effects, and reduce drug doses [16]. In the next section, we reviewed current research on the synergistic effects of HIF-1 inhibitors with different categories of cancer therapy, such as chemotherapy, targeted therapy, radiotherapy, immunotherapy, and metabolic therapy.
Chemotherapy or targeted therapy with HIF inhibitors
Chemotherapy resistance
HIF-1 activation causes the transcription of multiple genes implicated in chemoresistance, such as genes augmenting DNA repair ability, blocking apoptosis, and promoting drug efflux and cellular metabolism [6, 42, 43]. For example, P-glycoprotein (P-gp), a membrane efflux pump encoded by the multidrug resistant protein 1 (MDR1) gene, is recognized as one of the major elements of chemoresistance for its ability to regulate intracellular drug concentration [44]. The upregulation of P-gp was attributed to HIF-1 expression and was linked to adverse clinical outcomes [45]. Consistently, HIF-1 inhibition was demonstrated to overcome chemoresistance by downregulating MDR1/P-gp expression in colon cancer cells [46]. Moreover, HIF-1-mediated signaling is also indicated in the transition of cancer cells from oxidative phosphorylation to glycolysis. Under hypoxia, the HIF-1-dependent expression of GLUT1 and carbonic anhydrase IX is increased. This metabolic reprogramming was recognized to favor cancer progression, treatment resistance, and immune evasion [47]. Similarly, a recent study proved that HIF-1α-induced glucose metabolic reprogramming contributes to 5-Fluorouracil (5-FU) resistance in colorectal carcinoma through activation of the PI3K/Akt pathway and upregulation of nuclear β-catenin [48]. Further studies demonstrated that HIF-1 pathways are associated with increased stem-cell like features, which confers an increased risk of clinical relapse following chemotherapy. HIF-1α was shown to synergize with Transforming growth factor-2 released by cancer-associated fibroblasts to promote GLI family zinc finger 2 expression in colorectal cancer stem cells (CSCs), resulting in enhanced stemness, dedifferentiation, and chemotherapy resistance [49]. This evidence highlights that targeting HIF-1 in cancer and cancer stem cells has a significant potential to efficiently counteract chemotherapy resistance [6, 43].
Targeted therapy resistance
Mammalian target of rapamycin (mTOR) and VEGF inhibition are frequently adopted targeted therapy strategies that can yield considerable therapeutic efficacy. On the other hand, resistance to these therapies is attributed to changes in the tumor microenvironment that allow tumor growth by reducing reliance on VEGF [50]. It has been proven that HIF-1 and protein kinase B (AKT) are factors upstream of target blockage and are capable of driving tumor growth despite mTOR and VEGF inhibition [49]. HIF-1 neovascularization can also be initiated by cell-autonomous endothelial checkpoints independent of VEGF and become resistant to angiogenesis inhibitors [51]. Another mechanism of VEGF tyrosine kinase inhibitor resistance is through direct selection of cell subpopulations that can rapidly upregulate alternative proangiogenic pathways and have intrinsic hypoxia resistance [52]. Several studies of renal cell carcinoma and hepatocellular carcinoma treated with VEGF tyrosine kinase inhibitors sunitinib [53] and sorafenib [54] found that downregulation of HIF-1α and upregulation of HIF-2α with treatment can further stimulate the production of pro-angiogenic factors and cytokines to foster vascular endothelial cell proliferation.
In addition, hypoxia constitutes a significant mechanism that drives resistance to epidermal growth factor receptor (EGFR) inhibitors [55]. In non-small cell lung cancer, hypoxia promotes the expression of fibroblast growth factor receptor 1 (FGFR1), which, in turn, sustains EGFR signal through the MAPK pathway. This finding is substantiated by the restoration of sensitivity to EGFR inhibitors following the blockade of FGFR1 or MAPK by selective inhibitors [55]. Furthermore, another study reported that under hypoxic conditions, HIF-1α induces the expression and secretion of hepatocyte growth factor in pancreatic stellate cell, which in turn activates Met and the PI3K-AKT pathway, leading to resistance to EGFR inhibitor in pancreatic cancer [56]. Together, the above evidence suggests that HIF-mediated pathways contribute to an important part of targeted therapy resistance. By this token, inhibition of HIF pathways could potentially improve the efficacy of current targeted therapies.
Synergistic effects of HIF inhibitors in different types of cancer
Chemotherapy combined with HIF inhibitors has a synergistic effect by reducing VEGF to constrain angiogenesis and endothelial proliferation, downregulating MDR1 expression to retain drug, inducing apoptosis, and redirecting glycolysis to oxidative phosphorylation, which leads to an increase in reactive oxygen species (ROS) production. The combined therapy in cell and xenograft models for different types of cancer was summarized in Table 1 and Fig. 3.
Inhibition of HIF-1α and HIF-2α in combination with chemotherapy, radiotherapy, and targeted therapy. Chemotherapy such as Cisplatin and 5-FU can cause DNA damage and cancer cell apoptosis. Radiotherapy can increase the level of ROS and lead to cancer cell apoptosis. However, during hypoxia, tumor cell HIF-1 pathway will be activated and result in therapy resistance. For chemotherapy resistance induced by HIF pathway, cancer cell can promote chemo-drug pump out, undergo DNA repairment, inhibit cell apoptosis and shift cell metabolism. And radiotherapy resistance is made by angiogenesis and more blood supply which promote cancer cell survival. Therefore, many synergistic effects by the combination therapy of HIF inhibitor and chemo, radio and targeted therapy through reversing the resistance by HIF pathway. The effects are seen in vivo and in vitro of varied cancer cell type. • Chemotherapy includes cisplatin, carboplatin, oxaliplatin, 5-FU, doxorubicin, irinotecan. • HIF-1 pathway inhibitor includes erlotinib (EGFR inhibitor); HS-173 (PI3K inhibitor); everolimus/sirolimus (m-TOR inhibitor); Panobinostat (HDAC inhibitor); EZN-2698, PX-478, 2ME2, Camptothecin (HIF-1α translation inhibitor); Acriflavine (HIF-1α dimerization inhibitor); Echinomycin and Anthracycline (HIF-1α DNA-binding inhibitor). • HIF-2 pathway inhibitor includes PT-2385 and PT-2977. • The impact of cancer therapy (White words with blue background). • The effect of activated HIF-1 pathway (White words with green background). If given HIF inhibitor, the downstream mechanism of HIF would decrease (Dotted lines). Abbreviations: PI3K = Phosphoinositide-3-kinase; Akt = protein kinase B; mTOR = mechanistic target of rapamycin VEGF = Vascular endothelial growth factor; VEGFR = Vascular endothelial growth factor receptor; EGF = Epidermal growth factor; IGF-1 = Insulin like growth factor-1; GLUT = Glucose transporter; BCL-2 = B-cell lymphoma 2; EPO = Erythropoietin; HIF = hypoxia inducible factor; HRE = Hypoxia-response element; HSP90 = Heat shock protein 90; ROS = Reactive oxygen species; TOP1 = Topoisomerase1
SN38, a metabolite of irinotecan, which is both an HIF-1 inhibitor and a chemotherapy drug, was assessed in glioma cell models [57]. In another study, in comparison to monotherapy, temozolomide, an alkylating agent, can have a synergistic effect in the presence of HIF-1 knockdown [58]. There are no synergistic effects when HIF-1 knockdown glioblastoma cells are treated with cytotoxic chemotherapy; however, HIF-1 inhibition can led to oxygen-independent cytotoxicity and p53-independent apoptosis [59]. In another study, IDF-11774, a HIF-1α inhibitor, demonstrated a comparable ability to inhibit HIF-1α activity as HIF1A knock-down in vivo. Further investigation using a patient-derived xenograft murine model revealed that the combination of 5-FU and IDF-11774 successfully inhibited tumor growth in 5-FU-resistant rectal cancer. These results suggest that IDF-11774 has the potential to restore 5-FU sensitivity in treatment-resistant patients [48]. Erlotinib, an epidermal growth factor receptor inhibitor, can also suppress HIF-1 expression. A study showed that erlotinib combined with cisplatin can dampen tumor growth in a synergistic manner in head and neck squamous cancer cell and xenograft models [60].
NVP-ADW742 inhibits insulin-like growth factor-I-mediated VEGF and HIF-1α and can further boost sensitivity to etoposide and carboplatin in small cell lung cancer cell lines[61]. As for non-small cell lung cancer, acriflavine, which inhibits the development of HIF-1α/β dimers [63], panobinostat, which degrades HIF-1α and histone deacetylase 4 (HDAC4) [62], and oroxylin A, which binds directly to the HIF-1α bHLH-PAS domain [64], can reduce hypoxia-induced cisplatin resistance. Besides that, in ovarian cancer cells, cisplatin (CDDP) can better demonstrate its therapeutic potential when combined with NSC606985, a camptothecin analog that inhibits the accumulation of HIF-1α [65], noscapine, which results in the degradation of cobalt-stabilized HIF-1α [67], or RAD001 (everolimus), an mTOR inhibitor that suppresses the expression of HIF-1α [66]. Acriflavine, the most efficacious HIF-1 inhibitors [68], or l-carnosine, which reduces HIF-1α and MDR1-pg expression [69], can have synergistic effects with doxorubicin or 5-fluorouracil in colorectal cancer cells. Endostar, a customized recombinant human endostatin, can reduce HIF-2α and C-X-C motif chemokine receptor 4 (CXCR4) levels to overcome oxaliplatin-resistance [70]. Melatonin can inhibit the mTORC1/p70S6K/RP-S6 pathway to downregulate HIF-1α protein production and diminish cytoprotective HIF-1α-mitophagy expression in hepatocellular carcinoma, hence increasing sorafenib sensitivity [71]. Sorafenib blocks HIF-1α production, enabling the hypoxic response to shift from HIF-1α to HIF-2α-dependent pathways, allowing tumors to grow more aggressively [54]. 2-Methoxyestradiol can disturb the expression of HIF-1α and HIF-2α when combined with sorafenib [72]. PT-2385, a compelling HIF-2α inhibitor, can also improve sorafenib’s effectiveness and mitigate its undesirable side effects [73].
Palbociclib, a CDK4/6 inhibitor, can suppress HIF-1α and GLUT1 expression, and the combination with BYL719, BKM120, and BEZ235 (PI3K/mTOR inhibitors) can boost synergistic anti-proliferative and pro-apoptotic effects in breast cancer cells and a mouse model [13]. Additionally, the combination of palbociclib and paclitaxel can decrease cell growth more effectively than either therapy alone [74]. The combination of the HIF1 inhibitor zoledronic acid with fulvestrant decreases tumor development in vivo and in vitro [75]. In addition, the combination of CRLX101, a dual inhibitor of topoisomerase-1 and HIF-1, with bevacizumab results in enhanced tumor shrinkage and delayed tumor recurrence [76]. Under gemcitabine therapy, the addition of either PX-478, an HIF-1 inhibitor [77] or FRAX597, a PAK1 selective inhibitor [78] augments the antitumor efficacy and stifles pancreatic cancer cell proliferation and migration. Synergistically, the combination of HS-173 with sorafenib decreases cell viability, triggers G2/M arrest, and facilitates apoptosis with the loss of mitochondrial membrane potential [79].
As nanotechnology advances, there is growing interest in targeting the hypoxic tumor environment with nanoconstructs that exploit the controlled-release and site-specific properties of nanoparticles, as well as their capacity to serve as drug delivery platforms. A recent study proposed a calcium peroxide-modified magnetic nanoparticle (CaO2-MNPs) which releases oxygen at tumor sites and induces ubiquitin-mediated degradation of HIF-1α. In chemoresistant triple-negative breast cancer, combination of CaO2-MNPs with doxorubicin significantly inhibited tumor growth and induced apoptosis both in vitro and in orthotopic murine models [80]. On the other hand, another group of researchers coenstructed a chitosan-based nanoplatform that releases hematoporphyrin and oxygen-storing agent perfluorooctyl bromide which alters hypoxia tumor microenvironment. This drug delivery system demonstrated a synergistic effect with Erlotinib and sonodynamic treatment in three-dimensional tumor spheroids culture of non-small cell lung cancer cell lines through increasing the production of ROS and downregulating EGFR and HIF-1α [81].
Radiotherapy with HIF inhibitors
The mechanism of radiotherapy to eradicate tumor cells is through either direct DNA damage or, more commonly, indirect damage by the induction of ROS [82]. Oxygen plays a crucial role in the success of radiotherapy since it affects the amount of ROS generated and the fixation of DNA damage via oxygen-free radical interaction [83]. In hypoxic conditions, radioresistance is increased due to reduced amounts of ROS and fixed DNA damage, which leads to a greater propensity for tumor cells to recover from DNA damage. Moreover, the reoxygenation of hypoxic tumor cells produces oxidative stress and leads to the upregulation of HIF-1, which stimulates the expression of VEGF and other pro-angiogenic factors that protect tumor cells from radiologic insults [84, 85]. Similarly, it has been demonstrated that the adaptive revascularization of tumors after radiation is dependent on the HIF-1-mediated pathway [86]. These studies suggest HIF-1 to be a major determinant of tumor survival after radiation and that disruption of the HIF-1 pathways is warranted in tumors that have developed radioresistance due to adaptive vascular recovery [87].
Increased radiotherapy efficacy via HIF-1 pathway inhibition
Numerous studies have examined the efficacy of radiotherapy alone vs. combined therapy (Fig. 3 and Table 2). For example, Erlotinib followed by radiation can decrease tumor regrowth [60]. Acriflavine can increase radiosensitivity and decompose endogenous H2O2 to O2. This HIF-1 inhibitor can further reduce hypoxia and boost ROS generation, resulting in DNA double-strand breakage and tumor cell apoptosis [88]. The diminished production of VEGF and matrix metalloproteinase 9 (MMP-9) further reduces the incidence of tumor dissemination [88]. Furthermore, in colorectal cancer cells, SN-38 may suppress HIF-1α and VEGF to cause cell cycle arrest in the S and G2/M phases, which elevates radiosensitivity [89]. Vitexin, a HIF-1 inhibitor, can increase the susceptibility of human glioma CSCs to hyperbaric oxygen when exposed to radiation [90]. Under hypoxic circumstances, the combined effect of sorafenib and radiation demonstrates synergistic cytotoxicity in breast CSCs by eliciting G2/M cell cycle arrest and inhibiting metastasis via reduction of HIF-1α and MMP-2 [91].
The majority of radiation combination treatment studies focused on squamous cell carcinoma of the head and neck (HNSCC) and non-small cell lung cancer cell lines. During transient hypoxic stress, HIF-1 knockdown in the xenograft model promotes hypoxia and boosts responsiveness to radiotherapy in HNSCC [92]. Cell lines treated with rapamycin and cetuximab can block the mTOR/HIF-1α axis. However, the increased expression of HIF-2α following the combination treatment increases the incidence of tumor recurrence [93]. Moreover, nelfinavir, an Human Immunodeficiency Virus protease inhibitor, reduces HIF-1α/VEGF expression in lung cancer cells, which can reverse radiation resistance [94]. When combined with radiation, endostar inhibits angiogenesis and tumor growth [95]. Another study proposed that upregulation of Notch pathway by radiation confers to radioresistance in non-small cell lung cancer cell lines through the activation of HIF-1α. The researchers showed that the radiation-induced upregulation of the Notch pathway and HIF-1α protein could be effectively suppressed by the HIF inhibitor YC-1, resulting in a synergistic antitumor effect when combined with radiotherapy under hypoxic conditions. Further combination of gamma-secretase inhibitor and YC-1 demonstrated the greatest radiosensitivity in vivo, suggesting a potential therapeutic strategy for future treatment [96]. Moreover, chrysin, a natural compound that has HIF1α and VEGF inhibiting capacity was also reported to act as a radiosensitizer in triple-negative breast cancer cell lines. When combined with radiotherapy, chrysin potentiates the effect of radiation by enhancing radiation-induced apoptosis and inhibiting STAT3 and cyclin D1 expression [97].
Immunotherapy with HIF inhibitors
Even though the early responses of immune checkpoint blockade have been uplifting in various types of cancer, clinical data shows that most patients relapse in a short period of time, and the overall benefit of the therapy is far from fulfillment [98]. Hypoxic tumor microenvironment has been recognized as an attributor of the suboptimal results of immunotherapies [99, 100]. For instance, via HIF-1α and HIF-2α, hypoxia upregulates the expression of immune checkpoints to develop an immunosuppressive tumor microenvironment and facilitate tumor phagocytosis escape [98]. In the same vein, HIF-mediated induction of cancer cell glycolysis under hypoxia is a common contributor to immune checkpoint inhibitor resistance [101]. As anti-tumoral immune cells such as T cells and natural killer (NK) cells usually have a high glucose demand for their cytotoxicity, the glucose-deprived tumor microenvironment significantly compromises the effect of immunotherapies [101, 102]. Moreover, autophagy induced by hypoxia renders tumor cells less susceptible to NK cell-mediated cytotoxicity and cytotoxic T lymphocyte-mediated lysis [103]. According to HIF-1’s ability to bind HREs on HLA-G (human leukocyte antigen-G), hypoxia upregulates the expression of the non-classical and immunosuppressive major histocompatibility complex (MHC) Class I [104]. The above evidence infers that reducing hypoxia in tumors could attenuate immunosuppressive factors and block the activity of immunosuppressive cells while simultaneously increasing the number of cytotoxic T cells and lead to a general improvement of anticancer immunotherapy (Fig. 4). However, the combination of a HIF inhibitor and immunotherapy remains theoretical at this moment. Further preclinical and clinical studies are urgently needed to test the feasibility and effectiveness of combining HIF inhibitors with immunotherapy. The following section lists applications of HIF pathways in immunotherapies that could serve as the focus of combination therapy in future studies (Table 3).
Combination therapy with immunotherapy or metabolic therapy. Combining blockage of HIF-1α or HIF-2α with immunotherapy (left). PD-1/PD-L1/CTLA-4, the immune checkpoint proteins on T cells which often transmit “immune switch off” signal, is correlated with HIF pathway, and tumor hypoxic status usually leads to the failure of immunotherapy. Therefore, by combining HIF/hypoxia inhibitors with PD-1/PD-L1/CTLA-4 inhibitors, it has been proved to significantly raise T cell immune activity, reducing the amount and malignant potential of tumors. • Immunotherapies: PD-1 inhibitor, PD-L1 inhibitor, CTLA-4 inhibitor. • HIF-1 pathway inhibitors: POG, X4-136, POM-1, ARL67156, Ganetespib. • HIF-2 pathway inhibitors: PT2385, PT2399. Combining blockage of HIF-1α or HIF-2α with metabolic therapy (right). Pyruvate flux through TCA cycle is downregulated in cancer cells. Glycolysis sustains the high proliferative rate of cancer cells. Targeting of HIF-1α may be a prerequisite for cancer metabolism targeted therapy. • Metabolic therapies: D-allose, dichloroacetate and vitamin C. • HIF-1 pathway inhibitors: polydatin, LY294002 and BAY872243. • Metabolic and HIF-1 pathway inhibitors: 2-DG, cardamonin and metformin. Abbreviation: IGF-1 = Insulin like growth factor-1; PI3K = Phosphoinositide-3-kinase; Akt = protein kinase B; mTOR = mechanistic target of rapamycin; mTORC2 = Mammalian Target of Rapamycin Complex 2; HIF = hypoxia inducible factor; HRE = Hypoxia-response element; PHD2 = prolyl hydroxylase domain protein 2; PP2A = Protein phosphatase 2A; HSP90 = Heat shock protein 90; CXCR4 = chemokine receptor type 4; COX2 = Cyclooxygenase-2; PGE2 = prostaglandin E2; MAPK = mitogen-activated protein kinase; ENTPD2 = Ectonucleoside Triphosphate Diphosphohydrolase 2; MDSC = Myeloid Derived Suppressor Cell; PD-1 = Programmed death-1; PD-L1 = Programmed death-ligand 1; CTLA-4 = cytotoxic T-lymphocyte-associated protein 4; CD80/86 = Cluster of differentiation 80/86; APC = Antigen-presenting cell; LDHA = Lactate dehydrogenase A; TCA = tricarboxylic acid
HIF-1α inhibitors improve immunotherapy efficacy
In human hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC), entonucleoside triphosphate diphosphohydrolase 2 (ENTPD2), a direct transcriptional target of HIF-1α, is predominantly upregulated in hypoxia [111]. It accelerates the development of HCC tumors and the formation of myeloid-derived suppressor cells (MDSC), allowing tumor cells to evade immune checkpoints and immunosuppressive activities [118]. Inhibition of ENTPD2 by ARL67156 and POM-1 reduces tumor growth and improves the effectiveness of immune checkpoint inhibitors of programmed death-1 (PD-1) (clone RMP1-14) and cytotoxic T-lymphocyte-associated protein-4 (CTLA-4) (clone 9D9), implying that ENTPD2 is a prospective cancer treatment target [111]. Similarly, the HIF-1α inhibitor IDF-11774 was found to enhance the efficacy of anti-PD-1 treatment in murine prostate cancer xenograft models [106]. Further analysis revealed that the combination of IDF-11774 with an anti-PD-1 antibody reduced the presence of immunosuppressive cells such as M2 macrophages and myeloid-derived suppressor cells, while increasing the number of effector T cells in the tumor microenvironment [106].
The expression of receptor activator of nuclear factor kappa B ligand (RANKL) is driven by HIF-1α and serves as a poor prognostic indicator in various types of malignancies [119-121]. It has been demonstrated that RANKL activation induces HIF-1 protein expression reciprocally [110]. There is evidence that RANKL inhibition with denosumab bolstered the effectiveness of the anti-CTLA4 monoclonal antibody (UC10-4F10) against solid tumors and metastases. The combination augments clusters of differentiation 8 (CD8), T-cell influx, and T-cell cytokine secretion, thereby inhibiting subcutaneous tumor growth [110].
Heat shock protein-90 (Hsp90) is a molecular chaperone involved in cell cycle regulation, hormone signaling, and cellular stress response [122]. HIF-1α is the downstream protein product of Hsp90; blocking Hsp90 will trigger the degradation of HIF-1α. Researchers have revealed that the Hsp90 inhibitor ganetespib effectively suppresses tumor growth in colorectal cancer, breast cancer, and esophageal cancer [123-125]. Furthermore, ganetespib has demonstrated a significant synergistic effect when used with immunotherapy agents for melanoma. The combination of ganetespib with anti-PD-1 (clone: 29 F.1A12, 135,204) and ganetespib with anti-CTLA4 (9H10) improved T-cell anti-tumor response and survival. Besides, a considerable increase in CD8 T-cells is found in the ganetespib and CTLA4 antibody (9H10) group [112, 113].
Celecoxib, a cyclooxygenase-2 (COX-2) inhibitor, has been demonstrated to have anti-tumor effects through impairing HIF-1α [126, 127]. Interleukin-1β (IL-1β) plays a vital role in the transformation between inflammation and cancer in lung adenocarcinoma via the IL-1β/NF-κB/COX-2/HIF-1α axis. The concurrent inhibition of IL-1β/miR-144-3p/WT1D by a miR-144-3p mimic and IL-1β/NF-κB/COX-2/HIF-1α by celecoxib suppresses lung adenocarcinoma cell growth with a synergistic effect [117].
Inflammatory signals initiate the recruitment of activated myeloid-derived suppressor cells (MDSCs) to tumor regions. MDSCs induce HIF-1α to express an immense amount of PD-L1 and ultimately suppress T cell activation [128]. Prim-O-glucosyl cimifugin (POG), a traditional Chinese medicine saposhnikovia root extract, impedes PMN-MDSC proliferation and metabolism by modulating arginine metabolism and the tricarboxylic acid cycle in order to target their immunosuppressive capabilities. Furthermore, when combined with immunotherapy, POG boosts the anticancer efficacy of the PD-1 inhibitor (clone RMP1–14) in mouse tumor models, intensifies CD8+ T-lymphocyte infiltration in tumors, and demonstrates a novel targeted approach for the PD-1 pathway [105].
CXCR4 was discovered to be overexpressed in a variety of cancer cells in response to hypoxia, hence contributing to cancer metastases. CXCR4 stimulates the accumulation of HIF-1α in the nucleus, hence urging the production of HIF-1α downstream genes. Nuclear HIF-1α increases CXCR4 transcription reciprocally to establish a positive feedback loop [116]. A growing body of evidence indicates that the CXCR4 inhibitor X4-136 inhibits the growth of murine B16/OVA melanoma tumors, diminishes immune-regulatory cell populations in the melanoma microenvironment, and also impairs the growth of renal cell carcinoma in Renca-DM syngeneic models [129]. Different levels of synergistic effects were observed when combining X4-136 with anti-PD-1, anti-PD-L1, or anti-CXCR4, including retardation of tumor growth, decline in regulatory T cells and infiltration of CD8+ cell, implying X4-136 is a pertinent agent to immune checkpoint inhibitors [129].
HIF-2α inhibitors improve immunotherapy effectiveness
In ccRCC, the loss of the tumor suppressor VHL is a common oncogenic factor. Although both HIF-1α and HIF-2α can be activated by the loss of VHL, mounting evidence suggests that HIF-2α plays a more central role than HIF-1α in ccRCC [130]. Multiple studies suggest that, unlike in other cancers, HIF-2α is oncogenic while HIF-1α is tumor suppressive in ccRCC [131]. This concept is supported by the observation that HIF-2α expression is proportional to the degree of dysplasia, while HIF-1α levels are inversely related to dysplasia [132]. In vitro and animal models of ccRCC have also shown that HIF-2α blockage with small interfering RNA (siRNA) is sufficient to inhibit the transformation of VHL-/- RCC cells [133]. Moreover, several studies have indicated that PD-L1 expression in ccRCC is primarily regulated by the pVHL/ HIF-2α axis instead of HIF-1α [134]. The ability of this axis to induce PD-L1 expression in ccRCC highlights the potential of combining immunotherapy and HIF-2 inhibition. Ongoing clinical trials are evaluating this strategy by combining selective HIF-2α antagonist PT2385 with the anti-PD-1 nivolumab (NCT02293980), as well as assessing the combination of non-specific HIF inhibitors, such as Hsp90 inhibitor vorinostat (NCT02619253), with immunotherapy in early phase clinical trials.
Metabolic therapy with HIF inhibitors
Most cancer cells produce energy by depending largely on glycolytic metabolism despite the presence of adequate oxygen. This unique metabolic reprogramming, referred to as the “Warburg effect,” not only provides essential cellular energy that sustains cancer cell growth but also generates a constellation of metabolic intermediates that are involved in the proliferation, adhesion, and invasion of cancer [135]. In addition to the Warburg effect, a hybrid metabolic state was observed in some aggressive cancer cell types, with coexisting glycolysis and oxidative phosphorylation (OXPHOS) that enhance the adaptation to environmental stress, invasiveness, and metastasis [136, 137]. With growing insight into cancer metabolism, metabolic therapy has become a promising therapeutic approach by targeting the distinctive energy metabolism, either upregulated glycolytic pathways or the hybrid phenotype, of cancer [137]. However, resistance to metabolic therapies has been reported due to upregulation of HIF-1 [138]. As a major regulator of tumor adaptation, HIF-1 promotes the expression of GLUT and glycolytic enzymes, thereby counteracting the effect of antiglycolytic agents. In support of this, a study demonstrated that the combination of dichloroacetate, a glycolysis inhibitor, and metformin, a mitochondrial electron transport chain inhibitor, synergistically increases cancer cell death in lung and breast cancer cell lines. However, this effect can be compromised by the up-regulation of the HIF-1α pathway, which induces the expression of glycolytic enzymes and leads to resistance to dichloroacetate/metformin therapy [139]. Moreover, HIF-1 activates the activity of pyruvate dehydrogenase kinase 1, which inhibits pyruvate dehydrogenase and suppresses the cell from undergoing mitochondrial metabolism [140]. These results challenge the utilization of metabolic therapy as a monotherapy for cancer and make targeting HIF-1α a prerequisite for cancer metabolic interventions. With this insight, increasing investigations have been looking into the combination of HIF-1 inhibitors and metabolic treatment, which may have a synergistic effect on suppressing cancer cell growth (Fig. 4). Although most studies are still in the preliminary stage, current preclinical results provide promising evidence for the potential of this novel treatment.
Glycolysis inhibitors targeting the HIF pathway
HIF-1α protects mitochondria from the hexokinase 2 (HK2) inhibitor 3-bromopyruvate-induced damage. 3-bromopyruvate and the glucose analog 2-Deoxy-D-glucose (2-DG), when used together, have greater anticancer effects in pancreatic cancer cells, as they inhibit glycolysis as well as HIF-1α [141]. Using SB202190, a MAPK inhibitor, reduces the accumulation of HIF-1α protein. Pre-treatment with SB202190 renders the tumor more sensitive to PARP cleavage, which is mediated by the glucose analogs 2-DG and D-allose and induces apoptosis in pancreatic cancer cells [142]. Combining polydatin, a natural precursor of resveratrol, with 2-DG in MCF-7 and 4T1 breast cell lines can stimulate cancer cell apoptosis and restrict cell proliferation by inhibiting the ROS/PI3K/AKT/HIF-1α/ hexokinase 2 signaling axis [143]. Cardamonin inhibits glycolysis and the mTOR/p70S6K pathway by downregulating HIF-1α; this accelerates mitochondrial oxidative phosphorylation and ROS production, ultimately impeding the survival of the triple-negative breast cancer cell line MDA-MB-231 [144] (Table 4).
OXPHOS inhibitors that target the HIF pathway
Metformin, one of the OXPHOS inhibitors, dampens the transcription of the mitochondrial respiratory chain (complex I) and HIF-1α [146, 147]. Several investigations have demonstrated that combining metformin with chemotherapy or immunotherapy has synergistic effects in the treatment of cancer. Metformin may render oral squamous cell carcinoma (OSCC) cells more sensitive to cisplatin; the expressions of GLUT1 and BCL-2, which are target genes of HIF-1α, are decreased as a result of the inhibition of the NF-κB/HIF-1α signaling pathway [148]. Metformin modulates the AMPK/mTOR/HIF-1/P-gp and MRP1 pathways. It also has a synergistic anti-proliferative activity with 5-FU, which boosts apoptosis and provokes cell cycle arrest to reverse multidrug resistance in hepatocellular carcinoma [149]. Treatment of OSCC with metformin and 5-FU results in significant reductions in HIF-1α and mTOR and an increase in AMPKα [150]. Doxorubicin-metformin liposomes inhibit HIF-1α and tumor growth in multiresistant breast cancer cells, suggesting that this combination has the potential to revert HIF-1α-induced treatment resistance [151]. Furthermore, the effect of metformin combined with bevacizumab was also evaluated [152]. Although bevacizumab is typically ineffective in treating ovarian cancer, as it has the potential to worsen hypoxia in the tumor microenvironment, thus sustaining CSCs and promoting metastasis, a recent study showed promising results with the use of metformin in combination with bevacizumab. This combination, with or without cisplatin, successfully offset the increased HIF-1α and CSC population seen in bevacizumab monotherapy and suppressed the growth of ovarian cancer [152] (Table 5).
As for the combination of metformin with immunotherapy, it has been demonstrated that metformin not only reduces overall tumor hypoxia but also boosts antitumor cytotoxic T lymphocyte immunity by obstructing the PD-L1/PD-1 axis [155, 157]. The combination of metformin and PD-1 antibody (clone J43) elevates intra-tumoral T-cell activity and accelerates tumor clearance [155]. The combination of metformin with anti-CTLA-4 (clone 9D9) showed a substantial improvement in tumor shrinkage and cytotoxic T lymphocyte activity in 4T1 breast cancer, B16F10 melanoma, and CT26 colon cancer without significant body weight changes or observable damage in the kidneys or liver [156].
Clinical trials
In addition to preclinical studies of HIF signaling pathways and combination effects with HIF inhibitors, several combinations have been employed in clinical trials during the past few years. There are several strategies for impeding HIF activity, including targeting HIF-1α protein synthesis, stability, dimerization, and interactions with other proteins [158]. For example, Everolimus (RAD001) is a kind of indirect HIF inhibitor that is frequently utilized in clinical studies [159]. Camptothecin and its analogs, including SN-38, topotecan, and irinotecan, are topoisomerase 1 inhibitors that also cause HIF-1α downregulation [160]. Moreover, Ganetespib, a Hsp90 inhibitor, has been shown to be capable of inhibiting HIF-1α activity [161]. HIF-2α inhibitors such as PT2385, PT2977 and DFF332 are further options [107]. Combination therapy with HIF inhibitors in clinical trials will be summarized in the following section (Table 6).
Everolimus
Everolimus, also known as RAD001, suppresses the accumulation and transcription of HIF-1α [173]. In a phase I/II clinical trial, RAD001 was administered with mFOLFOX-6 and bevacizumab for the treatment of metastatic colorectal cancer. In phase I, the maximum tolerated dosage (MTD) of RAD001 with mFOLFOX6 + bevacizumab was 10 mg daily. In phase II, 25 patients were daily administered 10 mg of everolimus. At MTD, the objective response rate was 53% and progression-free survival (PFS) was 96%. Accordingly, the combination of everolimus, mFOLFOX-6, and bevacizumab is tolerated and efficacious for the treatment of metastatic colorectal cancer [163]. Another ongoing phase I study (NCT03324373) is seeking to see if the combination of lenvatinib and RAD001 can render surgically unresectable metastatic renal cell carcinoma resectable. The primary objective was to examine surgical complications, and 15 patients were included. Another phase I/II study, which was supposed to investigate the use of sorafenib coupled with RAD001 in advanced solid tumors based on molecular targets, was suspended early due to toxicity (NCT01226056). The primary outcome of this phase I study was MTD, and progression-free survival at 6 months was for phase II. The other phase I trial (NCT01332279) investigated the optimal dose of RAD001, erlotinib, in conjunction with radiotherapy for the treatment of recurrent head and neck cancer. However, this research was discontinued due to a lack of funding.
Camptothecin and analogues
Camptothecin, SN-38, topotecan, and irinotecan can lead to decreased accumulation and translation of HIF-1 because TOP1 plays a role as an upstream regulator in the HIF-1 pathway [160]. One phase II study investigated pegylated SN-38 or irinotecan plus cetuximab in patients with advanced colorectal cancer. The regimen was well tolerated for patients with refractory colorectal cancer, and overall survival and progression-free survival were similar in the cetuximab plus irinotecan arm and the SN-38 arm [167]. Another phase II trial evaluates the treatment effects of topotecan and cisplatin together with bevacizumab in recurrent or persistent cervical carcinoma. 6-month PFS was 59%, the median PFS was 7.1 months, and the median overall survival (OS) was 13.2 months. The results show the combination is an active but highly toxic regimen [163]. Another phase II trial investigates the FOLFIRI (leucovorin, 5-fluorouracil, irinotecan, and oxaliplatin) regimen combined with aflibercept in metastatic colorectal cancer patients. 73 patients were enrolled in the study, the median follow-up was 24.5 months, the 12-month PFS rate was 21.9%, median OS was 20.9 months, and the median PFS was 8.4 months. The combination regimen is tolerable; however, it did not improve the treatment efficacy in patients with metastatic colorectal carcinoma [164]. Another phase II trial (NCT01652079) investigated treatment of camptothecin and bevacizumab given in recurrent ovarian, tubal, and peritoneal cancer, the combination group received camptothecin 15 mg/m2 with Avastin 10 mg/kg which showed increased antitumor effect with PFS-6 56% compared to 27% in monotherapy group [168]. One phase I study (NCT00117013) is designed to explore the inhibition of HIF-1α expression and angiogenesis by topotecan in patients with metastatic solid tumors overexpressing HIF-1α. Topotecan was administered orally daily at a dose of 1.2 mg/m2 for 2 weeks, 16 patients were included in the study. Although the study was completed, the results are still pending.
Ganetespib
A phase Ib/II trial evaluates the efficacy of the combination of ganetespib and doxorubicin in relapsed small cell lung cancer. Eleven patients were included: nine in the phase Ib dose escalation and two in the phase II expansion. The response rate was 25%, and the median duration of response was 137 days. The combination was well tolerated [165]. Another phase I trial studied ganetespib combined with Ziv-Aflibercept, a VEGF-A and VEGF-B inhibitor. Frequent grade 2 adverse events (50%) were observed with ganetespib 100 mg/m2 + Ziv-Aflibercept 4 mg/kg; however, with ganetespib 100 mg/m2 + Ziv-Aflibercept 3 mg/kg, decreased grade 2 adverse events were discovered. Thus, the MTD was not established yet owing to the toxicity [169]. The other phase I/II trial investigated ganetespib and paclitaxel in patients with platinum-resistant ovarian cancer, 10 patients were included: four patients were given paclitaxel and ganetespib 100 mg/m2, whereas paclitaxel and ganetespib 150 mg/m2 were given to six patients; no dose-Limiting toxicities was found in either group. Two patients achieved a partial response, and four patients had a 60% disease control rate. The median PFS was 2.9 months. The combination was tolerated without dose-Limiting toxicities [166]. Another phase I study investigated the side effects of ganetespib combined with paclitaxel, carboplatin, and radiotherapy in stage II-III esophageal cancer patients. The study enrolled three participants to determine the MTD, and it was completed but pending final results (NCT02389751).
HIF-2α inhibitors
PT2385, a HIF-2α antagonist, can inhibit HIF-2α dimerization and its binding to DNA. In a phase I clinical trial (NCT02293980), PT2385 is given with nivolumab and cabozantinib to patients with metastatic renal cell carcinoma. The 50 patients were included in the expansion cohort of this clinical trial. The combination of PT2385 and nivolumab was tolerated, the objective response rate was 22%, and the median PFS of patients treated with PT2385 was 10.0 months [171]. PT2977, a second-generation HIF-2α inhibitor, has a similar mechanism to PT2385. However, PT2977 is more potent and has superior pharmacokinetics than PT2385. In a phase II clinical trial (NCT03634540) [170] investigating belzutifan plus cabozantinib for patients with advanced ccRCC, objective response rate was 22%, and disease control rate was 90%. The median PFS was 16.8 months, and the PFS rate and OS rate at 12 months were 65% and 81%, respectively. The study showed the combination had manageable safety and promising antitumor activity in patients with advanced ccRCC. Another phase I study (NCT04627064) aimed at assessing the safety and activity of abemaciclib and MK-6482 in patients with advanced refractory clear cell renal cell carcinoma. Moreover, another phase I study (NCT04895748) first used DFF332, a small molecule that targeted HIF-2α, in combination with Spartalizumab (anti-PD-1) plus Taminadenant (adenosine A2A receptor antagonist), in patients with advanced clear-cell renal cell carcinoma.
Metformin
Metformin is not only a famous type 2 diabetes treatment to improve metabolic dysregulation but also a HIF-1α inhibitor to decrease hypoxia-induced HIF-1α accumulation [146, 147]. A phase II trial was launched in 2019 to study the efficacy and safety of the combination of the PD-1inhibitor sintilimab and metformin (NCT03994744) [172]. This trial included patients with extensive-stage small cell lung cancer who were resistant to or relapsed after standard chemotherapy. The trial is currently ongoing, and so far, no adverse events have been observed in the recruited cases.
Future perspectives
In this review, we performed an extensive review of the literature on combination therapies involving HIF inhibitors. The synergistic impact of HIF-1α inhibitors with chemotherapy, targeted radiation, and immune therapy has been examined in cell lines and animal models with several promising results. In contrast, metabolic therapy has received less attention, and most results are still preliminary. Among the studied treatment combinations, some have proceeded to clinical trials, but they were mostly in phase I or phase II. Indirect HIF-1 inhibition is the most employed strategy. Recently, clinical trials on HIF-2α inhibitors such as PT-2385 and PT-2977 have been conducted; however, these trials were limited to clear cell renal carcinoma. Previous trials demonstrated a tolerable and effective outcome.
It is evident that the quantity and emphasis of preclinical and clinical trials investigating the synergistic impact of HIF inhibitors and cancer therapeutic drugs are escalating. However, several issues are to be addressed when perusing this line of research in the future. Firstly, since most currently adopted HIF inhibitors are repurposed drugs, their selectivity is often suboptimal. Off-target effects are major concerns of HIF inhibitors, but they could also be exploitable as inhibition of other HIF-mediated pathways may provide opportunities for additional antitumor effects. Second, in addition to evaluating synergistic effects in drug combinations, drug-drug interaction and toxicity are essential considerations when choosing HIF inhibitors. Third, HIF inhibitors-metabolic therapy combinations and applications of HIF-2 inhibitors are less investigated but are both potentially promising targets of research that are worth further attention. Lastly, more large-scale clinical trials are implicated in order to demonstrate the applicability of combined therapies in clinical settings.
Conclusions
The HIF pathway plays a crucial role in the etiology of several malignancies. In addition to promoting cell proliferation and tumor invasion, HIFs are also essential for cancer therapeutic resistance. It has been proven that overexpression of HIFs contributes to poor treatment responses in an extensive range of malignancies. The addition of HIF inhibitors has the capacity to counteract resistance, and a synergistic effect was found in combination with chemotherapy, radiotherapy, targeted therapy, immune therapy, and metabolic therapy in preclinical studies. Several clinical trials have demonstrated that combination therapies are well tolerated and effective and that progression-free survival is improved relative to monotherapy. Overall, while further large-scale clinical trials are warranted, the addition of HIF inhibitors to cancer treatment regimens could become the new rationale for future cancer therapeutics.
Availability of data and materials
The data used to support the findings of this study are included within the article.
Abbreviations
- 2-DG:
-
2-Deoxy-D-glucose
- 5-FU:
-
5-Fluorouracil
- AKT:
-
Protein kinase B
- CaO2-MNPs:
-
Calcium peroxide-modified magnetic nanoparticles
- CSCs:
-
Cancer stem cells
- CAIX:
-
Carbonic anhydrase IX
- ccRCC:
-
Clear cell renal cell cancer
- CD:
-
Cluster of differentiation
- COX-2:
-
Cyclooxygenase-2
- CTLA-4:
-
Cytotoxic T-lymphocyte-associated protein-4
- CXCR4:
-
C-X-C motif chemokine receptor 4
- ENTPD2:
-
Entonucleoside triphosphate diphosphohydrolase 2
- EGFR:
-
Epidermal growth factor receptor
- FGFR1:
-
Fibroblast growth factor receptor 1
- GLUTs:
-
Glucose transporters
- GSI:
-
Gamma-secretase inhibitor
- HCC:
-
Hepatocellular carcinoma
- HDAC4:
-
Histone deacetylase 4
- HIFs:
-
Hypoxia-inducible factors
- HLA-G:
-
Human leukocyte antigen-G
- HNSCC:
-
Squamous cell carcinoma of the head and neck
- HRE:
-
Hypoxia responsive element
- Hsp90:
-
Heat shock protein-90
- ICB:
-
Immune checkpoint blockade
- IL-1β:
-
Interleukin-1β
- MDR1:
-
Multidrug resistant protein 1
- MDSC:
-
Myeloid-derived suppressor cells
- MHC:
-
Major histocompatibility complex
- MMP:
-
Matrix metalloproteinase
- MTD:
-
Maximum tolerated dose
- mTOR:
-
Mammalian target of rapamycin
- NK:
-
Natural killer
- OS:
-
Overall survival
- OSCC:
-
Oral squamous cell carcinoma
- OXPHOS:
-
Glycolysis and oxidative phosphorylation
- P-gp:
-
P-glycoprotein
- POG:
-
Prim-O-glucosyl cimifugin
- PD-1:
-
Programmed death 1
- PD-L1:
-
Programmed death ligand 1
- PFS:
-
Progression-free survival
- RANKL:
-
Receptor activator of nuclear factor kappa B ligand
- ROS:
-
Reactive oxygen species
- siRNA:
-
Small interfering RNA
- VEGF:
-
Vascular endothelial growth factor
- VHL:
-
Von Hippel-Lindau
References
Semenza GL. Defining the role of hypoxia-inducible factor 1 in cancer biology and therapeutics. Oncogene. 2010;29(5):625–34.
Yu T, Tang B, Sun X. Development of Inhibitors Targeting Hypoxia-Inducible Factor 1 and 2 for Cancer Therapy. Yonsei Med J. 2017;58(3):489–96.
Wilson WR, Hay MP. Targeting hypoxia in cancer therapy. Nat Rev Cancer. 2011;11(6):393–410.
Gray LH, Conger AD, Ebert M, Hornsey S, Scott OC. The concentration of oxygen dissolved in tissues at the time of irradiation as a factor in radiotherapy. Br J Radiol. 1953;26(312):638–48.
Mennerich D, Kubaichuk K, Kietzmann T. DUBs, Hypoxia, and Cancer. Trends Cancer. 2019;5(10):632–53.
Albadari N, Deng S, Li W. The transcriptional factors HIF-1 and HIF-2 and their novel inhibitors in cancer therapy. Expert Opin Drug Discov. 2019;14(7):667–82.
Tang YA, Chen YF, Bao Y, Mahara S, Yatim S, Oguz G, et al. Hypoxic tumor microenvironment activates GLI2 via HIF-1α and TGF-β2 to promote chemoresistance in colorectal cancer. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2018;115(26):E5990–9.
Dróżdż M, Makuch S, Cieniuch G, Woźniak M, Ziółkowski P. Obligate and facultative anaerobic bacteria in targeted cancer therapy: Current strategies and clinical applications. Life Sci. 2020;261:118296.
Baran N, Konopleva M. Molecular pathways: hypoxia-activated prodrugs in cancer therapy. Clin Cancer Res. 2017;23(10):2382–90.
von Wahlde MK, Hülsewig C, Ruckert C, Götte M, Kiesel L, Bernemann C. The anti-androgen drug dutasteride renders triple negative breast cancer cells more sensitive to chemotherapy via inhibition of HIF-1α-/VEGF-signaling. Gynecol Endocrinol. 2015;31(2):160–4.
Helbig L, Koi L, Brüchner K, Gurtner K, Hess-Stumpp H, Unterschemmann K, et al. Hypoxia-inducible factor pathway inhibition resolves tumor hypoxia and improves local tumor control after single-dose irradiation. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys. 2014;88(1):159–66.
Helbig L, Koi L, Brüchner K, Gurtner K, Hess-Stumpp H, Unterschemmann K, et al. BAY 87–2243, a novel inhibitor of hypoxia-induced gene activation, improves local tumor control after fractionated irradiation in a schedule-dependent manner in head and neck human xenografts. Radiat Oncol. 2014;9:207.
Cretella D, Ravelli A, Fumarola C, La Monica S, Digiacomo G, Cavazzoni A, et al. The anti-tumor efficacy of CDK4/6 inhibition is enhanced by the combination with PI3K/AKT/mTOR inhibitors through impairment of glucose metabolism in TNBC cells. J Exp Clin Cancer Res. 2018;37(1):72.
Zhang T, Zhu X, Wu H, Jiang K, Zhao G, Shaukat A, et al. Targeting the ROS/PI3K/AKT/HIF-1α/HK2 axis of breast cancer cells: Combined administration of Polydatin and 2-Deoxy-d-glucose. J Cell Mol Med. 2019;23(5):3711–23.
Fallah J, Rini BI. HIF Inhibitors: Status of Current Clinical Development. Curr Oncol Rep. 2019;21(1):6.
Soni S, Padwad YS. HIF-1 in cancer therapy: two decade long story of a transcription factor. Acta Oncol. 2017;56(4):503–15.
Semenza GL. HIF-1 mediates metabolic responses to intratumoral hypoxia and oncogenic mutations. J Clin Invest. 2013;123(9):3664–71.
Baumeister J, Chatain N, Hubrich A, Maie T, Costa IG, Denecke B, et al. Hypoxia-inducible factor 1 (HIF-1) is a new therapeutic target in JAK2V617F-positive myeloproliferative neoplasms. Leukemia. 2020;34(4):1062–74.
Noman MZ, Hasmim M, Lequeux A, Xiao M, Duhem C, Chouaib S, et al. Improving cancer immunotherapy by targeting the hypoxic tumor microenvironment: new opportunities and challenges. Cells. 2019;8(9):1083.
Hubbi ME, Semenza GL. Regulation of cell proliferation by hypoxia-inducible factors. Am J Physiol Cell Physiol. 2015;309(12):C775–82.
Zaarour RF, Azakir B, Hajam EY, Nawafleh H, Zeinelabdin NA, Engelsen AST, et al. Role of hypoxia-mediated autophagy in tumor cell death and survival. Cancers. 2021;13(3):533.
Rezaeian AH, Wang YH, Lin HK. DNA damage players are linked to HIF-1α/hypoxia signaling. Cell Cycle. 2017;16(8):725–6.
Noble D. The Nobel Prize for medicine and physiology, 2019. Prog Biophys Mol Biol. 2019;148:1.
Keith B, Johnson RS, Simon MC. HIF1α and HIF2α: sibling rivalry in hypoxic tumour growth and progression. Nat Rev Cancer. 2011;12(1):9–22.
Murugesan T, Rajajeyabalachandran G, Kumar S, Nagaraju S, Jegatheesan SK. Targeting HIF-2α as therapy for advanced cancers. Drug Discov Today. 2018;23(7):1444–51.
Wang L, Xue M, Chung DC. c-Myc is regulated by HIF-2α in chronic hypoxia and influences sensitivity to 5-FU in colon cancer. Oncotarget. 2016;7(48):78910–7.
Rexius-Hall ML, Rehman J, Eddington DT. A microfluidic oxygen gradient demonstrates differential activation of the hypoxia-regulated transcription factors HIF-1α and HIF-2α. Integr Biol (Camb). 2017;9(9):742–50.
Cui XG, Han ZT, He SH, Wu XD, Chen TR, Shao CH, et al. HIF1/2α mediates hypoxia-induced LDHA expression in human pancreatic cancer cells. Oncotarget. 2017;8(15):24840–52.
Bartoszewska S, Kochan K, Piotrowski A, Kamysz W, Ochocka RJ, Collawn JF, et al. The hypoxia-inducible miR-429 regulates hypoxia-inducible factor-1α expression in human endothelial cells through a negative feedback loop. Faseb j. 2015;29(4):1467–79.
Hahne M, Schumann P, Mursell M, Strehl C, Hoff P, Buttgereit F, et al. Unraveling the role of hypoxia-inducible factor (HIF)-1α and HIF-2α in the adaption process of human microvascular endothelial cells (HMEC-1) to hypoxia: Redundant HIF-dependent regulation of macrophage migration inhibitory factor. Microvasc Res. 2018;116:34–44.
Wang Y, Li Z, Zhang H, Jin H, Sun L, Dong H, et al. HIF-1α and HIF-2α correlate with migration and invasion in gastric cancer. Cancer Biol Ther. 2010;10(4):376–82.
Szendrői A, Szász AM, Kardos M, Tőkés AM, Idan R, Szűcs M, et al. Opposite prognostic roles of HIF1α and HIF2α expressions in bone metastatic clear cell renal cell cancer. Oncotarget. 2016;7(27):42086–98.
Li W, Chen C, Zhao X, Ye H, Zhao Y, Fu Z, et al. HIF-2α regulates non-canonical glutamine metabolism via activation of PI3K/mTORC2 pathway in human pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma. J Cell Mol Med. 2017;21(11):2896–908.
Li J, Xi W, Li X, Sun H, Li Y. Advances in inhibition of protein-protein interactions targeting hypoxia-inducible factor-1 for cancer therapy. Bioorg Med Chem. 2019;27(7):1145–58.
Henley MJ, Koehler AN. Advances in targeting “undruggable” transcription factors with small molecules. Nat Rev Drug Discov. 2021;20(9):669–88.
Ma Z, Xiang X, Li S, Xie P, Gong Q, Goh BC, et al. Targeting hypoxia-inducible factor-1, for cancer treatment: Recent advances in developing small-molecule inhibitors from natural compounds. Semin Cancer Biol. 2022;80:379–90.
Greenberger LM, Horak ID, Filpula D, Sapra P, Westergaard M, Frydenlund HF, et al. A RNA antagonist of hypoxia-inducible factor-1alpha, EZN-2968, inhibits tumor cell growth. Mol Cancer Ther. 2008;7(11):3598–608.
Welsh S, Williams R, Kirkpatrick L, Paine-Murrieta G, Powis G. Antitumor activity and pharmacodynamic properties of PX-478, an inhibitor of hypoxia-inducible factor-1alpha. Mol Cancer Ther. 2004;3(3):233–44.
Mangraviti A, Raghavan T, Volpin F, Skuli N, Gullotti D, Zhou J, et al. HIF-1α- Targeting Acriflavine Provides Long Term Survival and Radiological Tumor Response in Brain Cancer Therapy. Sci Rep. 2017;7(1):14978.
Viziteu E, Grandmougin C, Goldschmidt H, Seckinger A, Hose D, Klein B, et al. Chetomin, targeting HIF-1α/p300 complex, exhibits antitumour activity in multiple myeloma. Br J Cancer. 2016;114(5):519–23.
Kocemba-Pilarczyk KA, Trojan S, Ostrowska B, Lasota M, Dudzik P, Kusior D, et al. Influence of metformin on HIF-1 pathway in multiple myeloma. Pharmacol Rep. 2020;72(5):1407–17.
Fallah J, Rini BI. HIF inhibitors: status of current clinical development. Curr Oncol Rep. 2019;21(1):6.
Warfel NA, El-Deiry WS. HIF-1 signaling in drug resistance to chemotherapy. Curr Med Chem. 2014;21(26):3021–8.
Sun Y, Guan Z, Liang L, Cheng Y, Zhou J, Li J, et al. HIF-1α/MDR1 pathway confers chemoresistance to cisplatin in bladder cancer. Oncol Rep. 2016;35(3):1549–56.
Sun Y, Guan Z, Liang L, Cheng Y, Zhou J, Li J, et al. HIF-1alpha/MDR1 pathway confers chemoresistance to cisplatin in bladder cancer. Oncol Rep. 2016;35(3):1549–56.
Chen J, Ding Z, Peng Y, Pan F, Li J, Zou L, et al. HIF-1alpha inhibition reverses multidrug resistance in colon cancer cells via downregulation of MDR1/P-glycoprotein. PLoS ONE. 2014;9(6):e98882.
Sowa T, Menju T, Chen-Yoshikawa TF, Takahashi K, Nishikawa S, Nakanishi T, et al. Hypoxia-inducible factor 1 promotes chemoresistance of lung cancer by inducing carbonic anhydrase IX expression. Cancer Med. 2017;6(1):288–97.
Dong S, Liang S, Cheng Z, Zhang X, Luo L, Li L, et al. ROS/PI3K/Akt and Wnt/β-catenin signalings activate HIF-1α-induced metabolic reprogramming to impart 5-fluorouracil resistance in colorectal cancer. J Exp Clin Cancer Res. 2022;41(1):15.
Rini BI, Atkins MB. Resistance to targeted therapy in renal-cell carcinoma. Lancet Oncol. 2009;10(10):992–1000.
Chen Z, Li Y, Tan B, Zhao Q, Fan L, Li F, et al. Progress and current status of molecule-targeted therapy and drug resistance in gastric cancer. Drugs Today (Barc). 2020;56(7):469–82.
Oladipupo SS, Hu S, Santeford AC, Yao J, Kovalski JR, Shohet RV, et al. Conditional HIF-1 induction produces multistage neovascularization with stage-specific sensitivity to VEGFR inhibitors and myeloid cell independence. Blood. 2011;117(15):4142–53.
Bottsford-Miller JN, Coleman RL, Sood AK. Resistance and escape from antiangiogenesis therapy: clinical implications and future strategies. J Clin Oncol. 2012;30(32):4026–34.
Lai XM, Liu SY, Tsai YT, Sun GH, Chang SY, Huang SM, et al. HAF mediates the evasive resistance of anti-angiogenesis TKI through disrupting HIF-1alpha and HIF-2alpha balance in renal cell carcinoma. Oncotarget. 2017;8(30):49713–24.
Zhao D, Zhai B, He C, Tan G, Jiang X, Pan S, et al. Upregulation of HIF-2alpha induced by sorafenib contributes to the resistance by activating the TGF-alpha/EGFR pathway in hepatocellular carcinoma cells. Cell Signal. 2014;26(5):1030–9.
Lu Y, Liu Y, Oeck S, Zhang GJ, Schramm A, Glazer PM. Hypoxia Induces Resistance to EGFR Inhibitors in Lung Cancer Cells via Upregulation of FGFR1 and the MAPK Pathway. Cancer Res. 2020;80(21):4655–67.
Shi X, Wang M, Zhang Y, Guo X, Liu M, Zhou Z, et al. Hypoxia activated HGF expression in pancreatic stellate cells confers resistance of pancreatic cancer cells to EGFR inhibition. EBioMedicine. 2022;86:104352.
Kamiyama H, Takano S, Tsuboi K, Matsumura A. Anti-angiogenic effects of SN38 (active metabolite of irinotecan): inhibition of hypoxia-inducible factor 1 alpha (HIF-1alpha)/vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF) expression of glioma and growth of endothelial cells. J Cancer Res Clin Oncol. 2005;131(4):205–13.
Li L, Lin X, Shoemaker AR, Albert DH, Fesik SW, Shen Y. Hypoxia-inducible factor-1 inhibition in combination with temozolomide treatment exhibits robust antitumor efficacy in vivo. Clin Cancer Res. 2006;12(15):4747–54.
Dai S, Huang ML, Hsu CY, Chao KS. Inhibition of hypoxia inducible factor 1alpha causes oxygen-independent cytotoxicity and induces p53 independent apoptosis in glioblastoma cells. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys. 2003;55(4):1027–36.
Cerniglia GJ, Pore N, Tsai JH, Schultz S, Mick R, Choe R, et al. Epidermal growth factor receptor inhibition modulates the microenvironment by vascular normalization to improve chemotherapy and radiotherapy efficacy. PLoS One. 2009;4(8):e6539.
Warshamana-Greene GS, Litz J, Buchdunger E, Garcia-Echeverria C, Hofmann F, Krystal GW. The insulin-like growth factor-I receptor kinase inhibitor, NVP-ADW742, sensitizes small cell lung cancer cell lines to the effects of chemotherapy. Clin Cancer Res. 2005;11(4):1563–71.
Fischer C, Leithner K, Wohlkoenig C, Quehenberger F, Bertsch A, Olschewski A, et al. Panobinostat reduces hypoxia-induced cisplatin resistance of non-small cell lung carcinoma cells via HIF-1alpha destabilization. Mol Cancer. 2015;14:4.
Zhang X, He C, Liu X, Chen Y, Zhao P, Chen C, et al. One-pot synthesis of a microporous organosilica-coated cisplatin nanoplatform for HIF-1-targeted combination cancer therapy. Theranostics. 2020;10(7):2918–29.
Liu Y, Wang X, Li W, Xu Y, Zhuo Y, Li M, et al. Oroxylin A reverses hypoxia-induced cisplatin resistance through inhibiting HIF-1alpha mediated XPC transcription. Oncogene. 2020;39(45):6893–905.
Zhang N, Zhang H, Xia L, Zheng Y, Yu Y, Zhu Y, et al. NSC606985 induces apoptosis, exerts synergistic effects with cisplatin, and inhibits hypoxia-stabilized HIF-1alpha protein in human ovarian cancer cells. Cancer Lett. 2009;278(2):139–44.
Mabuchi S, Altomare DA, Cheung M, Zhang L, Poulikakos PI, Hensley HH, et al. RAD001 inhibits human ovarian cancer cell proliferation, enhances cisplatin-induced apoptosis, and prolongs survival in an ovarian cancer model. Clin Cancer Res. 2007;13(14):4261–70.
Su W, Huang L, Ao Q, Zhang Q, Tian X, Fang Y, et al. Noscapine sensitizes chemoresistant ovarian cancer cells to cisplatin through inhibition of HIF-1alpha. Cancer Lett. 2011;305(1):94–9.
Xu L, Zhang Z, Ding Y, Wang L, Cheng Y, Meng L, et al. Bifunctional liposomes reduce the chemotherapy resistance of doxorubicin induced by reactive oxygen species. Biomater Sci. 2019;7(11):4782–9.
Iovine B, Guardia F, Irace C, Bevilacqua MA. l-carnosine dipeptide overcomes acquired resistance to 5-fluorouracil in HT29 human colon cancer cells via downregulation of HIF1-alpha and induction of apoptosis. Biochimie. 2016;127:196–204.
Jin F, Ji H, Jia C, Brockmeier U, Hermann DM, Metzen E, et al. Synergistic antitumor effects of endostar in combination with oxaliplatin via inhibition of HIF and CXCR4 in the colorectal cell line SW1116. PLoS One. 2012;7(10):e47161.
Prieto-Dominguez N, Mendez-Blanco C, Carbajo-Pescador S, Fondevila F, Garcia-Palomo A, Gonzalez-Gallego J, et al. Melatonin enhances sorafenib actions in human hepatocarcinoma cells by inhibiting mTORC1/p70S6K/HIF-1alpha and hypoxia-mediated mitophagy. Oncotarget. 2017;8(53):91402–14.
Ma L, Li G, Zhu H, Dong X, Zhao D, Jiang X, et al. 2-Methoxyestradiol synergizes with sorafenib to suppress hepatocellular carcinoma by simultaneously dysregulating hypoxia-inducible factor-1 and -2. Cancer Lett. 2014;355(1):96–105.
Xu J, Zheng L, Chen J, Sun Y, Lin H, Jin RA, et al. Increasing AR by HIF-2alpha inhibitor (PT-2385) overcomes the side-effects of sorafenib by suppressing hepatocellular carcinoma invasion via alteration of pSTAT3, pAKT and pERK signals. Cell Death Dis. 2017;8(10):e3095.
Cretella D, Fumarola C, Bonelli M, Alfieri R, La Monica S, Digiacomo G, et al. Pre-treatment with the CDK4/6 inhibitor palbociclib improves the efficacy of paclitaxel in TNBC cells. Sci Rep. 2019;9(1):13014.
Jia X, Cheng J, Shen Z, Shao Z, Liu G. Zoledronic acid sensitizes breast cancer cells to fulvestrant via ERK/HIF-1 pathway inhibition in vivo. Mol Med Rep. 2018;17(4):5470–6.
Conley SJ, Baker TL, Burnett JP, Theisen RL, Lazarus D, Peters CG, et al. CRLX101, an investigational camptothecin-containing nanoparticle-drug conjugate, targets cancer stem cells and impedes resistance to antiangiogenic therapy in mouse models of breast cancer. Breast Cancer Res Treat. 2015;150(3):559–67.
Zhao T, Ren H, Jia L, Chen J, Xin W, Yan F, et al. Correction: Inhibition of HIF-1alpha by PX-478 enhances the anti-tumor effect of gemcitabine by inducing immunogenic cell death in pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma. Oncotarget. 2019;10(53):5569–70.
Yeo D, He H, Patel O, Lowy AM, Baldwin GS, Nikfarjam M. FRAX597, a PAK1 inhibitor, synergistically reduces pancreatic cancer growth when combined with gemcitabine. BMC Cancer. 2016;16:24.
Yun SM, Jung KH, Lee H, Son MK, Seo JH, Yan HH, et al. Synergistic anticancer activity of HS-173, a novel PI3K inhibitor in combination with Sorafenib against pancreatic cancer cells. Cancer Lett. 2013;331(2):250–61.
Cheng FY, Chan CH, Wang BJ, Yeh YL, Wang YJ, Chiu HW. The Oxygen-Generating Calcium Peroxide-Modified Magnetic Nanoparticles Attenuate Hypoxia-Induced Chemoresistance in Triple-Negative Breast Cancer. Cancers (Basel). 2021;13(4):606.
Zhang P, Zhang L, Wang J, Zhu L, Li Z, Chen H, et al. An intelligent hypoxia-relieving chitosan-based nanoplatform for enhanced targeted chemo-sonodynamic combination therapy on lung cancer. Carbohydr Polym. 2021;274: 118655.
Vitti ET, Parsons JL. The Radiobiological Effects of Proton Beam Therapy: Impact on DNA Damage and Repair. Cancers (Basel). 2019;11(7):946.
Grimes DR, Partridge M. A mechanistic investigation of the oxygen fixation hypothesis and oxygen enhancement ratio. Biomed Phys Eng Express. 2015;1(4):045209.
Moeller BJ, Cao Y, Li CY, Dewhirst MW. Radiation activates HIF-1 to regulate vascular radiosensitivity in tumors: role of reoxygenation, free radicals, and stress granules. Cancer Cell. 2004;5(5):429–41.
Simon JM. [Hypoxia and angiogenesis]. Bull Cancer. 2007;94 Spec No:S160–5.
Fu Z, Chen D, Cheng H, Wang F. Hypoxia-inducible factor-1α protects cervical carcinoma cells from apoptosis induced by radiation via modulation of vascular endothelial growth factor and p53 under hypoxia. Med Sci Monit. 2015;21:318–25.
Schwartz DL, Bankson J, Bidaut L, He Y, Williams R, Lemos R, et al. HIF-1-dependent stromal adaptation to ischemia mediates in vivo tumor radiation resistance. Mol Cancer Res. 2011;9(3):259–70.
Meng L, Cheng Y, Tong X, Gan S, Ding Y, Zhang Y, et al. Tumor oxygenation and hypoxia inducible factor-1 functional inhibition via a reactive oxygen species responsive Nanoplatform for enhancing radiation therapy and abscopal effects. ACS Nano. 2018;12(8):8308–22.
Okuno T, Kawai K, Hata K, Murono K, Emoto S, Kaneko M, et al. SN-38 Acts as a Radiosensitizer for Colorectal Cancer by Inhibiting the Radiation-induced Up-regulation of HIF-1alpha. Anticancer Res. 2018;38(6):3323–31.
Xie T, Wang JR, Dai CG, Fu XA, Dong J, Huang Q. Vitexin, an inhibitor of hypoxia-inducible factor-1alpha, enhances the radiotherapy sensitization of hyperbaric oxygen on glioma. Clin Transl Oncol. 2020;22(7):1086–93.
Lee JH, Shim JW, Choi YJ, Heo K, Yang K. The combination of sorafenib and radiation preferentially inhibits breast cancer stem cells by suppressing HIF-1alpha expression. Oncol Rep. 2013;29(3):917–24.
Leung E, Cairns RA, Chaudary N, Vellanki RN, Kalliomaki T, Moriyama EH, et al. Metabolic targeting of HIF-dependent glycolysis reduces lactate, increases oxygen consumption and enhances response to high-dose single-fraction radiotherapy in hypoxic solid tumors. BMC Cancer. 2017;17(1):418.
Coliat P, Ramolu L, Jegu J, Gaiddon C, Jung AC, Pencreach E. Constitutive or Induced HIF-2 Addiction is Involved in Resistance to Anti-EGFR Treatment and Radiation Therapy in HNSCC. Cancers (Basel). 2019;11(10):1607.
Pore N, Gupta AK, Cerniglia GJ, Jiang Z, Bernhard EJ, Evans SM, et al. Nelfinavir down-regulates hypoxia-inducible factor 1alpha and VEGF expression and increases tumor oxygenation: implications for radiotherapy. Cancer Res. 2006;66(18):9252–9.
Wu Y, Zheng Y, Shen Z, Ge W, Xie Y, Li C. Endostar combined with radiotherapy increases radiation sensitivity by decreasing the expression of TGF-beta1, HIF-1alpha and bFGF. Exp Ther Med. 2014;7(4):911–6.
Ikezawa Y, Sakakibara-Konishi J, Mizugaki H, Oizumi S, Nishimura M. Inhibition of Notch and HIF enhances the antitumor effect of radiation in Notch expressing lung cancer. Int J Clin Oncol. 2017;22(1):59–69.
Jafari S, Dabiri S, Mehdizadeh Aghdam E, Fathi E, Saeedi N, Montazersaheb S, et al. Synergistic effect of chrysin and radiotherapy against triple-negative breast cancer (TNBC) cell lines. Clin Transl Oncol. 2023. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12094-023-03141-5.
Noman MZ, Hasmim M, Lequeux A, Xiao M, Duhem C, Chouaib S, et al. Improving Cancer Immunotherapy by Targeting the Hypoxic Tumor Microenvironment: New Opportunities and Challenges. Cells. 2019;8(9):1083.
Daniel SK, Sullivan KM, Labadie KP, Pillarisetty VG. Hypoxia as a barrier to immunotherapy in pancreatic adenocarcinoma. Clin Transl Med. 2019;8(1):10.
Kopecka J, Salaroglio IC, Perez-Ruiz E, Sarmento-Ribeiro AB, Saponara S, De Las RJ, et al. Hypoxia as a driver of resistance to immunotherapy. Drug Resist Updat. 2021;59:100787.
Bao MH, Wong CC. Hypoxia, metabolic reprogramming, and drug resistance in liver cancer. Cells. 2021;10(7):1715.
Wang Z, Guan D, Wang S, Chai LYA, Xu S, Lam KP. Glycolysis and oxidative phosphorylation play critical roles in natural killer cell receptor-mediated natural killer cell functions. Front Immunol. 2020;11:202.
Noman MZ, Hasmim M, Messai Y, Terry S, Kieda C, Janji B, et al. Hypoxia: a key player in antitumor immune response. A Review in the Theme: Cellular Responses to Hypoxia. Am J Physiol Cell Physiol. 2015;309(9):C569–79.
Garziera M, Scarabel L, Toffoli G. Hypoxic Modulation of HLA-G Expression through the Metabolic Sensor HIF-1 in Human Cancer Cells. J Immunol Res. 2017;2017:4587520.
Gao W, Zhang X, Yang W, Dou D, Zhang H, Tang Y, et al. Prim-O-glucosylcimifugin enhances the antitumour effect of PD-1 inhibition by targeting myeloid-derived suppressor cells. J Immunother Cancer. 2019;7(1):231.
Shen Z, Pei Q, Zhang H, Yang C, Cui H, Li B, et al. Hypoxia-inducible factor-1α inhibition augments efficacy of programmed cell death 1 antibody in murine prostatic cancer models. Anticancer Drugs. 2022;33(6):587–94.
Martinez-Saez O, Gajate Borau P, Alonso-Gordoa T, Molina-Cerrillo J, Grande E. Targeting HIF-2 alpha in clear cell renal cell carcinoma: A promising therapeutic strategy. Crit Rev Oncol Hematol. 2017;111:117–23.
Chen W, Hill H, Christie A, Kim MS, Holloman E, Pavia-Jimenez A, et al. Targeting renal cell carcinoma with a HIF-2 antagonist. Nature. 2016;539(7627):112–7.
Ahern E, Harjunpaa H, Barkauskas D, Allen S, Takeda K, Yagita H, et al. Co-administration of RANKL and CTLA4 Antibodies Enhances Lymphocyte-Mediated Antitumor Immunity in Mice. Clin Cancer Res. 2017;23(19):5789–801.
Igari K, Kelly MJ, Yamanouchi D. Digoxin Attenuates Receptor Activation of NF-kappaB Ligand-Induced Osteoclastogenesis in Macrophages. J Vasc Res. 2019;56(2):55–64.
Chiu DK, Tse AP, Xu IM, Di Cui J, Lai RK, Li LL, et al. Hypoxia inducible factor HIF-1 promotes myeloid-derived suppressor cells accumulation through ENTPD2/CD39L1 in hepatocellular carcinoma. Nat Commun. 2017;8(1):517.
Mbofung RM, McKenzie JA, Malu S, Zhang M, Peng W, Liu C, et al. HSP90 inhibition enhances cancer immunotherapy by upregulating interferon response genes. Nat Commun. 2017;8(1):451.
Mielczarek-Lewandowska A, Hartman ML, Czyz M. Inhibitors of HSP90 in melanoma. Apoptosis. 2020;25(1–2):12–28.
Liu YV, Baek JH, Zhang H, Diez R, Cole RN, Semenza GL. RACK1 competes with HSP90 for binding to HIF-1alpha and is required for O(2)-independent and HSP90 inhibitor-induced degradation of HIF-1alpha. Mol Cell. 2007;25(2):207–17.
Saxena R, Wang Y, Mier JW. CXCR4 inhibition modulates the tumor microenvironment and retards the growth of B16-OVA melanoma and Renca tumors. Melanoma Res. 2020;30(1):14–25.
Bao Y, Wang Z, Liu B, Lu X, Xiong Y, Shi J, et al. A feed-forward loop between nuclear translocation of CXCR4 and HIF-1alpha promotes renal cell carcinoma metastasis. Oncogene. 2019;38(6):881–95.
Wu C, Li X, Zhang D, Xu B, Hu W, Zheng X, et al. IL-1beta-Mediated Up-Regulation of WT1D via miR-144-3p and Their Synergistic Effect with NF-kappaB/COX-2/HIF-1alpha Pathway on Cell Proliferation in LUAD. Cell Physiol Biochem. 2018;48(6):2493–502.
Lu LC, Chang CJ, Hsu CH. Targeting myeloid-derived suppressor cells in the treatment of hepatocellular carcinoma: current state and future perspectives. J Hepatocell Carcinoma. 2019;6:71–84.
Tang ZN, Zhang F, Tang P, Qi XW, Jiang J. Hypoxia induces RANK and RANKL expression by activating HIF-1alpha in breast cancer cells. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2011;408(3):411–6.
Park HJ, Baek KH, Lee HL, Kwon A, Hwang HR, Qadir AS, et al. Hypoxia inducible factor-1alpha directly induces the expression of receptor activator of nuclear factor-kappaB ligand in periodontal ligament fibroblasts. Mol Cells. 2011;31(6):573–8.
Renema N, Navet B, Heymann MF, Lezot F, Heymann D. RANK-RANKL signalling in cancer. Biosci Rep. 2016;36(4):e00366.
Jackson SE. Hsp90: structure and function. Top Curr Chem. 2013;328:155–240.
Lee H, Saini N, Howard EW, Parris AB, Ma Z, Zhao Q, et al. Ganetespib targets multiple levels of the receptor tyrosine kinase signaling cascade and preferentially inhibits ErbB2-overexpressing breast cancer cells. Sci Rep. 2018;8(1):6829.
Cercek A, Shia J, Gollub M, Chou JF, Capanu M, Raasch P, et al. Ganetespib, a novel Hsp90 inhibitor in patients with KRAS mutated and wild type, refractory metastatic colorectal cancer. Clin Colorectal Cancer. 2014;13(4):207–12.
Guan L, Zou Q, Liu Q, Lin Y, Chen S. HSP90 Inhibitor Ganetespib (STA-9090) Inhibits Tumor Growth in c-Myc-Dependent Esophageal Squamous Cell Carcinoma. Onco Targets Ther. 2020;13:2997–3011.
Sun YZ, Cai N, Liu NN. Celecoxib Down-Regulates the Hypoxia-Induced Expression of HIF-1alpha and VEGF Through the PI3K/AKT Pathway in Retinal Pigment Epithelial Cells. Cell Physiol Biochem. 2017;44(4):1640–50.
Sui W, Zhang Y, Wang Z, Wang Z, Jia Q, Wu L, et al. Antitumor effect of a selective COX-2 inhibitor, celecoxib, may be attributed to angiogenesis inhibition through modulating the PTEN/PI3K/Akt/HIF-1 pathway in an H(2)(2) murine hepatocarcinoma model. Oncol Rep. 2014;31(5):2252–60.
Weber R, Fleming V, Hu X, Nagibin V, Groth C, Altevogt P, et al. Myeloid-derived suppressor cells hinder the anti-cancer activity of immune checkpoint inhibitors. Front Immunol. 2018;9:1310.
Saxena R, Wang Y, Mier JW. CXCR4 inhibition modulates tumor microenvironment and robustly inhibits growth of B16-OVA melanoma. AACR; 2018.
Martínez-Sáez O, Gajate Borau P, Alonso-Gordoa T, Molina-Cerrillo J, Grande E. Targeting HIF-2 α in clear cell renal cell carcinoma: A promising therapeutic strategy. Crit Rev Oncol Hematol. 2017;111:117–23.
Shen C, Beroukhim R, Schumacher SE, Zhou J, Chang M, Signoretti S, et al. Genetic and functional studies implicate HIF1α as a 14q kidney cancer suppressor gene. Cancer Discov. 2011;1(3):222–35.
Mandriota SJ, Turner KJ, Davies DR, Murray PG, Morgan NV, Sowter HM, et al. HIF activation identifies early lesions in VHL kidneys: evidence for site-specific tumor suppressor function in the nephron. Cancer Cell. 2002;1(5):459–68.
Zimmer M, Doucette D, Siddiqui N, Iliopoulos O. Inhibition of hypoxia-inducible factor is sufficient for growth suppression of VHL-/- tumors. Mol Cancer Res. 2004;2(2):89–95.
Ruf M, Moch H, Schraml P. PD-L1 expression is regulated by hypoxia inducible factor in clear cell renal cell carcinoma. Int J Cancer. 2016;139(2):396–403.
Vaupel P, Schmidberger H, Mayer A. The Warburg effect: essential part of metabolic reprogramming and central contributor to cancer progression. Int J Radiat Biol. 2019;95(7):912–9.
Xie J, Wu H, Dai C, Pan Q, Ding Z, Hu D, et al. Beyond Warburg effect–dual metabolic nature of cancer cells. Sci Rep. 2014;4:4927.
Abdel-Wahab AF, Mahmoud W, Al-Harizy RM. Targeting glucose metabolism to suppress cancer progression: prospective of anti-glycolytic cancer therapy. Pharmacol Res. 2019;150:104511.
Maher JC, Wangpaichitr M, Savaraj N, Kurtoglu M, Lampidis TJ. Hypoxia-inducible factor-1 confers resistance to the glycolytic inhibitor 2-deoxy-D-glucose. Mol Cancer Ther. 2007;6(2):732–41.
Hong SE, Jin HO, Kim HA, Seong MK, Kim EK, Ye SK, et al. Targeting HIF-1alpha is a prerequisite for cell sensitivity to dichloroacetate (DCA) and metformin. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2016;469(2):164–70.
Kim JW, Tchernyshyov I, Semenza GL, Dang CV. HIF-1-mediated expression of pyruvate dehydrogenase kinase: a metabolic switch required for cellular adaptation to hypoxia. Cell Metab. 2006;3(3):177–85.
Xiao H, Li S, Zhang D, Liu T, Yu M, Wang F. Separate and concurrent use of 2-deoxy-D-glucose and 3-bromopyruvate in pancreatic cancer cells. Oncol Rep. 2013;29(1):329–34.
Malm SW, Hanke NT, Gill A, Carbajal L, Baker AF. The anti-tumor efficacy of 2-deoxyglucose and D-allose are enhanced with p38 inhibition in pancreatic and ovarian cell lines. J Exp Clin Cancer Res. 2015;34:31.
Zhang T, Zhu X, Wu H, Jiang K, Zhao G, Shaukat A, et al. Targeting the ROS/PI3K/AKT/HIF-1alpha/HK2 axis of breast cancer cells: Combined administration of Polydatin and 2-Deoxy-d-glucose. J Cell Mol Med. 2019;23(5):3711–23.
Jin J, Qiu S, Wang P, Liang X, Huang F, Wu H, et al. Cardamonin inhibits breast cancer growth by repressing HIF-1alpha-dependent metabolic reprogramming. J Exp Clin Cancer Res. 2019;38(1):377.
Li B, Zhu Y, Sun Q, Yu C, Chen L, Tian Y, et al. Reversal of the Warburg effect with DCA in PDGFtreated human PASMC is potentiated by pyruvate dehydrogenase kinase1 inhibition mediated through blocking Akt/GSK3beta signalling. Int J Mol Med. 2018;42(3):1391–400.
Rena G, Hardie DG, Pearson ER. The mechanisms of action of metformin. Diabetologia. 2017;60(9):1577–85.
Zhou X, Chen J, Yi G, Deng M, Liu H, Liang M, et al. Metformin suppresses hypoxia-induced stabilization of HIF-1alpha through reprogramming of oxygen metabolism in hepatocellular carcinoma. Oncotarget. 2016;7(1):873–84.
Qi X, Xu W, Xie J, Wang Y, Han S, Wei Z, et al. Metformin sensitizes the response of oral squamous cell carcinoma to cisplatin treatment through inhibition of NF-kappaB/HIF-1alpha signal axis. Sci Rep. 2016;6:35788.
Ling S, Tian Y, Zhang H, Jia K, Feng T, Sun D, et al. Metformin reverses multidrug resistance in human hepatocellular carcinoma Bel7402/5fluorouracil cells. Mol Med Rep. 2014;10(6):2891–7.
Harada K, Ferdous T, Harada T, Ueyama Y. Metformin in combination with 5-fluorouracil suppresses tumor growth by inhibiting the Warburg effect in human oral squamous cell carcinoma. Int J Oncol. 2016;49(1):276–84.
Li Y, Luo J, Lin MT, Zhi P, Guo WW, Han M, et al. Co-Delivery of Metformin Enhances the Antimultidrug Resistant Tumor Effect of Doxorubicin by Improving Hypoxic Tumor Microenvironment. Mol Pharm. 2019;16(7):2966–79.
Fan Y, Cheng H, Liu Y, Liu S, Lowe S, Li Y, et al. Metformin anticancer: Reverses tumor hypoxia induced by bevacizumab and reduces the expression of cancer stem cell markers CD44/CD117 in human ovarian cancer SKOV3 cells. Front Pharmacol. 2022;13:955984.
Zhao L, Wang J, Zhang Y, Wang L, Yu M, Wang F. Vitamin C decreases VEGF expression levels via hypoxiainducible factor1alpha dependent and independent pathways in lens epithelial cells. Mol Med Rep. 2020;22(1):436–44.
Qi X, Xu W, Xie J, Wang Y, Han S, Wei Z, et al. Erratum: Metformin sensitizes the response of oral squamous cell carcinoma to cisplatin treatment through inhibition of NF-kappaB/HIF-1alpha signal axis. Sci Rep. 2017;7:42934.
Scharping NE, Menk AV, Whetstone RD, Zeng X, Delgoffe GM. Efficacy of PD-1 Blockade Is Potentiated by Metformin-Induced Reduction of Tumor Hypoxia. Cancer Immunol Res. 2017;5(1):9–16.
Cha JH, Yang WH, Xia W, Wei Y, Chan LC, Lim SO, et al. Metformin promotes antitumor immunity via endoplasmic-reticulum-associated degradation of PD-L1. Mol Cell. 2018;71(4):606–20e7.
Zannella VE, Dal Pra A, Muaddi H, McKee TD, Stapleton S, Sykes J, et al. Reprogramming metabolism with metformin improves tumor oxygenation and radiotherapy response. Clin Cancer Res. 2013;19(24):6741–50.
Burroughs SK, Kaluz S, Wang D, Wang K, Van Meir EG, Wang B. Hypoxia inducible factor pathway inhibitors as anticancer therapeutics. Future Med Chem. 2013;5(5):553–72.
Miyazawa M, Yasuda M, Fujita M, Kajiwara H, Hirabayashi K, Takekoshi S, et al. Therapeutic strategy targeting the mTOR-HIF-1alpha-VEGF pathway in ovarian clear cell adenocarcinoma. Pathol Int. 2009;59(1):19–27.
Rapisarda A, Uranchimeg B, Sordet O, Pommier Y, Shoemaker RH, Melillo G. Topoisomerase I-mediated inhibition of hypoxia-inducible factor 1: mechanism and therapeutic implications. Cancer Res. 2004;64(4):1475–82.
Xiang L, Gilkes DM, Chaturvedi P, Luo W, Hu H, Takano N, et al. Ganetespib blocks HIF-1 activity and inhibits tumor growth, vascularization, stem cell maintenance, invasion, and metastasis in orthotopic mouse models of triple-negative breast cancer. J Mol Med (Berl). 2014;92(2):151–64.
Weldon Gilcrease G, Stenehjem DD, Wade ML, Weis J, McGregor K, Whisenant J, et al. Phase I/II study of everolimus combined with mFOLFOX-6 and bevacizumab for first-line treatment of metastatic colorectal cancer. Invest New Drugs. 2019;37(3):482–9.
Zighelboim I, Wright JD, Gao F, Case AS, Massad LS, Mutch DG, et al. Multicenter phase II trial of topotecan, cisplatin and bevacizumab for recurrent or persistent cervical cancer. Gynecol Oncol. 2013;130(1):64–8.
Pentheroudakis G, Kotoula V, Koliou GA, Karavasilis V, Samantas E, Aravantinos G, et al. AMALTHEA: Prospective, Single-Arm Study of the Hellenic Cooperative Oncology Group (HeCOG) Evaluating Efficacy and Safety of First-Line FOLFIRI + Aflibercept for 6 Months Followed by Aflibercept Maintenance in Patients With Metastatic Colorectal Cancer. Clin Colorectal Cancer. 2018;17(4):e631–7.
Subramaniam DS, Liu SV, Crawford J, Kramer J, Thompson J, Wang H, et al. A Phase Ib/II Study of Ganetespib With Doxorubicin in Advanced Solid Tumors Including Relapsed-Refractory Small Cell Lung Cancer. Front Oncol. 2018;8:64.
Ray-Coquard I, Braicu I, Berger R, Mahner S, Sehouli J, Pujade-Lauraine E, et al. Part I of GANNET53: A European Multicenter Phase I/II Trial of the Hsp90 Inhibitor Ganetespib Combined With Weekly Paclitaxel in Women With High-Grade, Platinum-Resistant Epithelial Ovarian Cancer-A Study of the GANNET53 Consortium. Front Oncol. 2019;9:832.
Garrett CR, Bekaii-Saab TS, Ryan T, Fisher GA, Clive S, Kavan P, et al. Randomized phase 2 study of pegylated SN-38 (EZN-2208) or irinotecan plus cetuximab in patients with advanced colorectal cancer. Cancer. 2013;119(24):4223–30.
Krasner C, Birrer M, Peters C, Jayaraman L, Eliasof S, Tellez A, Downing W, Senderowicz A. Phase II trial of the NDC CRLX101 in combination with bevacizumab in patients with platinumresistant ovarian cancer (PROC). [Abstract]. In: Proceedings of the 107th Annual Meeting of the American Association for Cancer Research; 2016 Apr 16-20. New Orleans, LA. Philadelphia (PA): AACR; Cancer Res. 2016;76(14 Suppl):Abstract nr CT090.
Meehan R, Kummar S, Do K, O’Sullivan Coyne G, Juwara L, Zlott J, et al. A Phase I Study of Ganetespib and Ziv-Aflibercept in Patients with Advanced Carcinomas and Sarcomas. Oncologist. 2018;23(11):1269-e125.
McDermott DF, Choueiri TK, Bauer TM, Arrowsmith E, Roy A, Perini R, et al. 656MO Phase II study of belzutifan (MK-6482), an oral hypoxia-inducible factor 2α (HIF-2α) inhibitor, plus cabozantinib for treatment of advanced clear cell renal cell carcinoma (ccRCC). Ann Oncol. 2021;32:S681.
Rini BI, Appleman LJ, Figlin RA, Plimack ER, Merchan JR, Wang K, et al. Results from a phase I expansion cohort of the first-in-class oral HIF-2α inhibitor PT2385 in combination with nivolumab in patients with previously treated advanced RCC. American Society of Clinical Oncology; 2019.
Wu L, Li K, Chen B, Peng W, Wang J, Jiang M, et al. P48.15 A Case from a Single-Arm, Phase Two, Open Label Study Assessing Sindilimab Plus Metaformin in Chemotherapy Failed PD-L1 Positive Advanced SCLC. J Thorac Oncol. 2021;16(3):S505–6.
Hudson CC, Liu M, Chiang GG, Otterness DM, Loomis DC, Kaper F, et al. Regulation of hypoxia-inducible factor 1alpha expression and function by the mammalian target of rapamycin. Mol Cell Biol. 2002;22(20):7004–14.
Acknowledgements
Not applicable.
Funding
This review has been prepared on the basis of the research carried out in the laboratory of YA Shen, supported by a Taipei Medical University grant (TMU108-AE1-B12), a grant from the Ministry of Science and Technology, Taiwan (MOST 109–2314-B-038–021-MY3), and grants from the National Science and Technology Council, Taiwan (NSTC 111–2622-B-038–008, NSTC 112–2823-8–038-001).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
Conceptualization, YA.S.; writing—original draft preparation,TW.K., GH.B., CM.C, CL.L, MC. T, LY.C., YA.S.; writing—review and editing, TL. W., IM.S., YA.S.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Ethics approval and consent to participate
Not applicable.
Consent for publication
Not applicable.
Competing interests
The authors have declared no potential conflicts of interest concerning the research, authorship, and/or publication of this article.
Additional information
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Open Access This article is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License, which permits use, sharing, adaptation, distribution and reproduction in any medium or format, as long as you give appropriate credit to the original author(s) and the source, provide a link to the Creative Commons licence, and indicate if changes were made. The images or other third party material in this article are included in the article's Creative Commons licence, unless indicated otherwise in a credit line to the material. If material is not included in the article's Creative Commons licence and your intended use is not permitted by statutory regulation or exceeds the permitted use, you will need to obtain permission directly from the copyright holder. To view a copy of this licence, visit http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/. The Creative Commons Public Domain Dedication waiver (http://creativecommons.org/publicdomain/zero/1.0/) applies to the data made available in this article, unless otherwise stated in a credit line to the data.
About this article
Cite this article
Kao, TW., Bai, GH., Wang, TL. et al. Novel cancer treatment paradigm targeting hypoxia-induced factor in conjunction with current therapies to overcome resistance. J Exp Clin Cancer Res 42, 171 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1186/s13046-023-02724-y
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1186/s13046-023-02724-y