Abstract
Background
Optic nerve injury is an important pathological component in neurodegenerative diseases such as traumatic optic neuropathies and glaucoma. The molecular signaling pathway(s) critical for retinal ganglion cell (RGC) death after axonal insult, however, is/are not fully defined. RGC death after axonal injury is known to occur by BAX-dependent apoptosis. Two transcription factors JUN (the canonical target of JNK) and DDIT3 (CHOP; a key mediator of the endoplasmic reticulum stress response) are known to be important apoptotic signaling molecules after axonal injury, including in RGCs. However, neither Jun nor Ddit3 deficiency provide complete protection to RGCs after injury. Since Jun and Ddit3 are important apoptotic signaling molecules, we sought to determine if their combined deficiency might provide additive protection to RGCs after axonal injury.
Methods
To determine if DDIT3 regulated the expression of JUN after an axonal insult, mice deficient for Ddit3 were examined after optic nerve crush (ONC). In order to critically test the importance of these genes in RGC death after axonal injury, RGC survival was assessed at multiple time-points after ONC (14, 35, 60, and 120 days after injury) in Jun, Ddit3, and combined Jun/Ddit3 deficient mice. Finally, to directly assess the role of JUN and DDIT3 in axonal degeneration, compound actions potentials were recorded from Jun, Ddit3, and Jun/Ddit3 deficient mice after ONC.
Results
Single and combined deficiency of Jun and Ddit3 did not appear to alter gross retinal morphology. Ddit3 deficiency did not alter expression of JUN after axonal injury. Deletion of both Jun and Ddit3 provided significantly greater long-term protection to RGCs as compared to Jun or Ddit3 deficiency alone. Finally, despite the profound protection to RGC somas provided by the deficiency of Jun plus Ddit3, their combined loss did not lessen axonal degeneration.
Conclusions
These results suggest JUN and DDIT3 are independently regulated pro-death signaling molecules in RGCs and together account for the vast majority of apoptotic signaling in RGCs after axonal injury. Thus, JUN and DDIT3 may represent key molecular hubs that integrate upstream signaling events triggered by axonal injury with downstream transcriptional events that ultimately culminate in RGC apoptosis.
Similar content being viewed by others
Background
Axonal injury is an important component in neurodegenerative diseases, including traumatic optic neuropathies and glaucoma [1,2,3,4]. In glaucomatous neurodegeneration, axonal injury at the lamina of the optic nerve head leads to axonal dysfunction and apoptotic RGC death [2, 4,5,6,7,8,9,10,11,12,13,14,15,16,17,18,19,20]. Several pro-death molecular signaling pathways have been implicated in glaucomatous RGC death including mitogen-activated protein kinase (MAPK) and endoplasmic reticulum (ER) signaling [21,22,23,24,25,26,27,28,29,30,31,32,33,34,35,36,37]. The molecular signaling leading from ocular hypertensive insult to apoptotic RGC death, however, is not well defined. Identifying the molecular events leading to RGC apoptosis after a glaucoma-relevant insult is an important step in identifying the molecules responsible for triggering and signaling axonal and somal degeneration in glaucoma.
MAPK pathway components, including c-Jun N-terminal kinases (JNKs) and their canonical target JUN (also known as cJUN), and ER stress signaling, and its downstream effector DNA damage inducible transcript 3, Ddit3 (also known as CCAAT/enhancer binding homologous protein (CHOP)/GADD153), are known to be important pro-apoptotic cascades after glaucoma-relevant injuries [21,22,23,24,25,26,27,28,29,30,31,32,33,34,35,36]. Activation of either JUN or DDIT3 is known to culminate in BAX activation and Bax-dependent apoptosis and BAX is known to be required for RGC death after axonal injury [6, 38, 39]. Importantly, either Jun or Ddit3 deficiency has been shown to protect RGCs after axonal injury. Either Jun or Ddit3 deficiency provided significant, but incomplete protection to RGCs after axonal injury [22, 33]. These data suggest that individually, Jun and Ddit3 are not solely responsible for BAX activation in RGCs after axonal injury. It is possible that JUN and DDIT3 are functioning in the same pathway, and thus protecting RGCs through similar downstream targets. In other systems, ER stress can lead to JNK-JUN activation [40,41,42]. Furthermore, JUN and DDIT3 may be activated in RGCs by the same upstream kinase, dual leucine kinase (DLK) [35, 36, 43]. Alternatively, JUN and DDIT3 may be independently regulated after axonal injury. Therefore, it must be determined if JUN and DDIT3 act through distinct mechanisms in RGCs and provide additive protection to RGCs after axonal injury.
Here, we sought to evaluate if JUN and DDIT3 independently regulate RGC death after axonal injury or if they might function in the same molecular pathway. Previously we showed that DDIT3 upregulation after axonal injury was not prevented by Jun deficiency [23]. We extend these findings and show that similarly, Ddit3 does not control expression of JUN [23]. Thus, JUN and DDIT3 appear to be independently regulated, suggesting that combined deficiency of both JUN and DDIT3 could provide greater protection than either deficiency alone. To determine if protection afforded by JUN and DDIT3 deficiency is additive, animals deficient in both Jun and Ddit3 were generated and evaluated after mechanical optic nerve injury. Combined deficiency of Jun and Ddit3 was more protective of RGCs after axonal injury than either Jun or Ddit3 deficiency alone, and provided profound long-term protection of RGCs after axonal injury. These results suggest that MAPK and ER stress signaling pathways are together the major regulators of RGCs after axonal injury.
Methods
Mice
Mice were housed on a 12-h light dark cycle and fed chow and water ad libitum. Five different alleles were used to generate four different mice strains: 1) mice deficient in Jun (also known as cJun), 2) mice deficient in Ddit3, 3) mice deficient in both Jun and Ddit3, and 4) mice deficient in Dlk. To generate animals conditionally deficient in Jun, a floxed allele of Jun [44] and Six3-cre recombinase (a neural retina cre, Jackson Laboratory, Stock# 019755) were crossed to generate 1) animals carrying the recombined floxed alleles, referred to as Jun −/− or Jun deficient (Jun fl/flSix3cre+), 2) heterozygote animals referred to as Jun +/−(Jun +/flSix3cre+), and 3) animals carrying non-recombined floxed alleles or wildtype alleles with or without the cre recombinase referred to as Jun +/+ or wildtype (WT, Jun +/+Six3cre−, Jun +/+Six3cre+, Jun +/flSix3cre−, or Jun fl/fl Six3cre−). Mice carrying the null allele for Ddit3 were acquired from Jackson Laboratory (Stock# 005530) and intercrossed to generate: 1) animals carrying two copies of the null allele, referred to as Ddit3 −/− or Ddit3 deficient, 2) heterozygote animals carrying one copy of the null allele referred to as Ddit3 −/+, and 3) animals carrying no copies of the null allele, referred to as Ddit3 +/+ or WT in the text. Animals deficient in both Jun and Ddit3 were generated by crossing animals carrying the floxed allele of Jun and Six3-cre with animals carrying the null allele for Ddit3 to generate Ddit3−/−;Jun fl/flSix3cre+ animals referred to as Jun/Ddit3 deficient animals in the text. To generate animals conditionally deficient in Dlk, a floxed allele of Dlk [45] and Six3-cre recombinase (a neural retina cre) were crossed on a C57BL/6 J background to generate 1) animals carrying the recombined floxed alleles, referred to as Dlk −/− or Dlk deficient (Dlk f/flSix3cre+) and 2) animals carrying non-recombined floxed alleles or wildtype alleles with or without the cre recombinase referred to as Dlk +/+ or WT (Dlk +/+Six3cre−, Dlk +/+Six3cre+, Dlk +/flSix3cre−, or Dlk fl/fl Six3cre−). The Jun fl and Dlk fl alleles were all backcrossed at least 3 times to the C57BL/6 J genetic background prior to intercrossing with the Six3cre allele that had been backcrossed at least 10 generations into the C57BL/6 J genetic background. The Ddit3 allele was obtained already backcrossed into C57BL/6 J for 5 generations. All experiments were conducted in adherence with the Association for Research in Vision and Ophthalmology’s statement on the use of animals in ophthalmic and vision research and were approved by the University of Rochester’s University Committee on Animal Resources.
Optic nerve injury
Mice were anesthetized with 100 mg/kg ketamine and 10 mg/kg xylazine. Optic nerve crush (ONC) was completed as previously described [22, 23, 43, 46]. Briefly, the optic nerve was surgically exposed and crushed immediately behind the eye with a pair of self-closing forceps (Roboz RS-5027) for 5 s. Controls included contralateral eyes that had not been manipulated and eyes in which a sham surgery was performed, where the optic nerve was exposed but not crushed. Animals were harvested at 1, 5, 14, 35, 60, and 120 days following ONC or sham surgery.
Histology and cell counts
Eyes to be processed for retinal morphology were fixed in 2.5% glutaraldehyde, 2% paraformaldehyde (PFA) for 24 h at 4 °C. After dehydration, eyes were embedded in Technovit (Electron Microscopy Services) and sectioned at 2.5 μm. Sections that included the optic nerve were stained with Multiple Stain Solution (Polysciences, Inc). Eyes to be processed for retinal flat mount immunohistochemistry were fixed in 4% PFA for two hours at room temperature. The anterior segment was removed and the posterior segment was processed for retinal flat mount immunohistochemistry as has been previously described [22, 23, 43, 46].
For retinal flat mount immunohistochemistry, retinas were dissected free of the optic cup and were blocked in 10% horse serum in 0.3% TritonX in 1 M PBS (phosphate buffered saline) for 24 h at 4 °C and then incubated in primary antibody for 72 h at 4 °C. Primary antibodies included: rabbit anti-JUN (Abcam, 1:250), rabbit anti-pJUN (Cell Signaling, 1:250) and mouse βIII tubulin (TUJ1; Covance, 1:1000). Whole retinas were washed in PBS and then incubated in secondary antibody, Alexafluor-conjugated secondary antibodies (Invitrogen), for 48 h at 4 °C before being washed in PBS and mounted RGC side up with Fluorogel in TRIS buffer (Electron Microscopy Sciences). Eight 40× fields were obtained for quantification of TUJ1+ and JUN+ cells. Images were taken 220 μm from the edge of the retina and equally spaced around the periphery of the retina (two fields per quadrant) as RGC density is known to vary across different dorso-ventral/medial-lateral retinal quadrants. Quantification was completed using the cell-counter tool in ImageJ.
Western blotting
Mouse retinas were dissected and placed in 100 μl ice cold lysis buffer (1X RIPA buffer (Santa Cruz 24,948) containing 50 μM sodium fluoride, 2 mM PMSF, 2 mM sodium orthovanadate, 1X protease/phosphatase inhibitor cocktail (Cell Signaling 5872S)). Tissue was lysed by sonication (Bransa Digital Sonifier, 10% amplitude for 3 s) prior to spinning down cellular debris in a microcentrifuge (10,000 rotations per minute, 4°C, 5 min). 10 μl of supernatant was combined with 10 μl 2X Laemmli loading buffer (Bio-Rad) and boiled for 10 min. Samples were fractionated by SDS-PAGE on a 12% gel and transferred to a PVDF membrane (transfer buffer: 1X Tris-glycine (Bio-Rad), 20% methanol). Membranes were rinsed with double-distilled H2O and treated with a Qentix Western Blot Signal Enhancer kit (Thermo Scientific 21,050) according to manufacturer’s instructions. Membranes were then blocked at room temperature using 5% milk in TBST buffer for 1 h. Membranes were treated overnight at 4°C with one of the following primary antibodies: rabbit anti-JUN (Cell Signaling 9165S, 1:750) or mouse anti-GAPDH (Calbiochem CB1001, 1:2000). The following day membranes were washed 3X with TBST prior to treatment with secondary antibodies: HRP-conjugated anti-rabbit IgG (Bio-Rad 170–6515, 1:5000) or HRP-conjugated anti-mouse IgG (Bio-Rad 170–6516, 1:5000). Immunoreactive bands were detected using a chemiluminescence kit (Immun-star, Bio-Rad 170–5070) prior to exposure using either film or digital detection equipment (Azure Biosystems c500). Membranes were occasionally stripped following development and treated with another primary antibody (stripping buffer: 0.1 M Tris-Cl pH 6.8, 2% SDS, 0.7% β-mercaptoethanol). Densitometric analysis was conducted using ImageJ software, and pixel densities of experimental bands were normalized to those of GAPDH loading controls.
Electrophysiology
Optic nerve compound action potentials (CAPs) were recorded as described previously [43]. Briefly, animals were euthanized with CO2, and optic nerves were dissected by transecting close to the eye and to the chiasm. Optic nerves were incubated for a minimum of 60 min in artificial cerebrospinal fluid (ACSF) aerated with 95% oxygen/5% CO2 at room temperature. ACSF was prepared with (in mM): 125 NaCl, 1.25 NaH2PO4, 25 glucose, 25 NaHCO3, 2.5 CaCl2, 1.3 MgCl2, and 2.5 KCl. The recording chamber was temperature controlled and perfused with oxygenated ACSF. The nerve was gently drawn into suction pipette electrodes containing ACSF at both the stimulating (retinal) end and the recording (chiasm) end. Stimuli consisted of supramaximal constant current pulses of 50 microseconds duration. CAP amplitudes were normalized by maintaining the ratio of the recording pipet plus nerve resistance to the recording pipet resistance at 1.7 [43]. All traces were taken at 25 °C. Data were digitized and then analyzed off-line.
Statistical analysis
At least four retinas were analyzed for each genotype for all experimental conditions. The experimenters were masked to genotype and experimental cohort for quantification of cell number. The student’s t-test (unpaired) was used to compare differences across two groups. One-way ANOVA followed by the Tukey’s post hoc test for multiple comparisons was used for experiments comparing differences at a single time across more than two groups. Statistical significance was considered for P values <0.05.
Results
Jun and Ddit3 deficiency does not alter retinal morphology
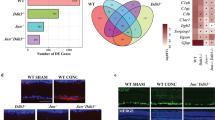
To determine if Jun (also known as cJun) and/or Ddit3 (which encodes the protein CHOP) is necessary for retinal development; adult retinas deficient in Jun, Ddit3, and combined Jun/Ddit3 were evaluated. Jun was conditionally deleted in the retina using Six3-cre, an established cre recombinase which deletes floxed alleles in the early developing neuroepithelium [47]. Animals carrying the null allele for Ddit3 were evaluated independently and also crossed with animals carrying the Jun floxed allele and Six3-cre to generate animals deficient in both Jun and Ddit3. Deficiency in either Jun or Ddit3 or the combined deficiency of Jun and Ddit3 did not alter morphology of the retina (Fig. 1A). Furthermore, no differences were observed across subgroups in the number of TUJ1+ RGCs in adult animals (Fig. 1B; P > 0.05; n = 8 per group). Thus, neither Jun nor Ddit3 deficiency appears to alter the normal development of the retina. To assess the recombination efficiency of Six3-cre, the number of RGCs expressing JUN was evaluated one day after ONC. Consistent with previous studies, JUN accumulation was readily detected in the somas of RGCs of wildtype animals after axonal injury but was not easily detected in sham retinas (Fig. 1C), [22, 23, 48]. In retinas with conditional deletion of Jun, JUN accumulation after ONC was detected in approximately 22% of RGCs after ONC compared to wildtype retinas (Fig. 1D, P<0.001). Western blot analysis was completed to assess the level of JUN in wildtype and Jun deficient animals (Fig. E and F). In unmanipulated eyes, JUN was reduced 85% (p < 0.001) in Jun deficient retinas as compared to wildtype retinas. After ONC, JUN was reduced 92% (p = 0.004) in Jun deficient eyes as compared to wildtype animals. Thus, while recombination was not complete, Jun-mediated changes should be greatly reduced in Jun deficient conditional mutants.
Jun and Ddit3 deficiency does not alter retinal morphology. a Semi-thin retinal cross sections were taken to evaluate the gross structure of the retina in WT, Jun, Ddit3, and Jun/Ddit3 deficient animals. Jun, Ddit3, and combined Jun/Ddit3 deficiency did not appear to alter gross retinal structure. b TUJ1+ cells (a marker of RGCs) were counted in retinal flat mounts in WT, Jun, Ddit3, Jun/Ddit3 deficient animals. No difference was observed across genotypes (P > 0.05 for each comparison; n = 8 per group). c/d JUN accumulation was readily detected in the somas of RGCs of wildtype animals after ONC but was not easily detected in sham retinas. To determine the efficiency of Jun recombination using Six3-cre, the number of JUN+ cells were counted 1 day after controlled optic nerve ONC, a time when JUN is widely expressed prior to RGC death. JUN+ cells are reduced by 77.7% in Jun deficient retinas after ONC (error bars represent standard error of the mean; n = 6 per genotype; P < 0.001; scale bar 50 μm). e/f Western blot analysis was used to determine the level of JUN in wildtype (+/+) and Jun deficient (−/−) animals. JUN was significantly reduced in both Jun deficient unmanipulated retinas (85%, ONC -) and Jun deficient retinas after ONC (92%, ONH +) as compared to wild type animals (* p < 0.01)
Jun and Ddit3 are independently regulated after optic nerve injury
Previously, JUN has been shown to be an important pro-apoptotic signaling pathway after glaucoma-relevant axon injury [21,22,23,24,25,26, 28,29,30, 35, 36]. DDIT3 has also been shown to be expressed after axonal insult [23, 31, 33, 34]. Furthermore, there is evidence to suggest that DDIT3 and JUN may act in the same signaling pathway. Accumulation of the DDIT3-dependent micro-RNA, miR-216b, has been found to directly target JUN [49]. Previously, Jun deficiency was found to not prevent the upregulation of DDIT3 protein after crush [23]. To determine if JUN is regulated by Ddit3, immunohistochemistry was performed on wildtype and Ddit3 deficient retinas. JUN accumulated in RGC somas after optic nerve injury (ONC) in both WT and Ddit3 deficient retinas (Fig. 2A). Quantification of JUN positive RGCs demonstrated no significant difference between JUN positive RGCs in wildtype and Ddit3 deficient retinas. Likewise, quantification of phosphorylated JUN positive RGCs demonstrated no significance difference between wildtype and Ddit3 deficient retinas after ONC (Fig. 2B). Western blot analysis was then completed both in unmanipulated eyes and after ONC to quantify the levels of JUN protein in wildtype and Ddit3 deficient retinas. No significant difference in JUN levels was observed between wildtype and Ddit3 deficient retinas in either condition. Together these results suggest that JUN expression is not dependent on Ddit3 and that Jun and Ddit3 may be independently regulated after optic nerve injury.
Jun and Ddit3 are independently regulated after optic nerve injury. To determine if Ddit3 regulates JUN and pJUN expression, retinal flat mounts (RGC side up) were examined from WT and Ddit3 deficient retinas one day after ONC. a JUN (red) accumulates in RGCs (labeled with TUJ1, a marker of RGCs, green) in WT and Ddit3 deficient retinas one day after ONC, but not in sham retinas (n = 4 per genotype and experimental condition). There was no significance difference (ns) in the number of JUN positive RGCs between wildtype and Ddit3 deficient retinas. b Similarly, pJUN (red) accumulates in RGCs (green) in WT and Ddit3 deficient retinas one day after ONC. There was no significance difference (ns) in the number of pJUN positive RGCs between wildtype and Ddit3 deficient retinas. c Western blot analysis was used to determine the level of JUN in wildtype (+/+) and Ddit3 deficient (−/−) animals. There was no significant difference in JUN levels between Ddit3 deficient and wildtype unmanipulated eyes (ONC -) or between Ddit3 deficient and wildtype eyes after ONC (ONC +). Previously, DDIT3 has been shown to be expressed in Jun deficient retinas after ONC [23]. Scale bar: 50 μm
Combined deficiency of Jun and Ddit3 is more protective after axonal injury than either Jun or Ddit3 deficiency alone
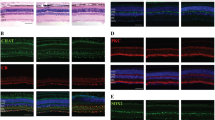
Since our results suggest that Jun and Ddit3 are independently upregulated after optic nerve injury, animals deficient in both Jun and Ddit3 were generated to determine if the protection afforded by the individual deficiencies is additive. RGC survival was assessed 14, 35, 60, and 120 days after ONC with immunohistochemistry in retinal flat mounts using the RGC specific marker, TUJ1. Consistent with previous reports, deficiency of either Jun or Ddit3 significantly increased RGC survival 14 and 35 days after ONC compared to WT animals [Fig. 3, Tables 1, 22, 33]. Jun/Ddit3 deficient animals also had increased survival 14 and 35 days after ONC compared to WT animals (14 days after ONC- WT: 29% survival, Ddit3: 51%, Jun: 93%, Jun/Ddit3: 100%; 35 days after ONC- WT: 22%, Ddit3: 48%, Jun: 75%, Jun/Ddit3: 89%; P < 0.001 for all comparisons against WT animals) Furthermore, combined Jun/Ddit3 deficient animals demonstrated increased survival compared to animals deficient in either Jun or Ddit3 alone at 35 days (p < 0.001). To determine if the protection afforded to RGCs by Jun/Ddit3 deficiency was sustained, as in in Bax deficient mice [7, 50], a cohort of animals was examined 60 and 120 days after ONC. At both of these time points, RGC survival in Jun, Ddit3, and Jun/Ddit3 deficient retinas was increased compared to WT retinas. RGC survival in combined Jun/Ddit3 deficient mice was also significantly increased compared to single deletion of Jun or Ddit3 in animals at both 60 days and 120 days after ONC (60 days after ONC- WT: 14 survival, Ddit3: 33%, Jun: 54%, Jun/Ddit3: 83%; 120 days after ONC- WT: 7%, Ddit3: 25%, Jun: 48%, Jun/Ddit3: 75%; P < 0.001 for all comparisons). The RGC protection conferred by single Jun deficiency and combined Jun and Ddit3 deficiency may be even higher since ~22% of RGCs in Jun and Jun/Ddit3 deficient retinas still express JUN due to incomplete recombination of the Jun floxed allele. Thus, the RGC protection afforded by combined Jun/Ddit3 deficiency is sustained after axonal injury. These results demonstrate that JUN and DDIT3 act as the two principal signaling nodes through which all pro-apoptotic signaling converges resulting in RGC death after axonal injury.
Combined Jun/Ddit3 deficiency is more protective after axonal injury than either Jun or Ddit3 deficiency alone. a Example of TUJ1 staining in control and experimental eyes at 120 days after ONC (scale bar = 50 μm). b Ddit3, Jun, and combined Jun and Ddit3 deficient animals had significantly greater RGC survival than WT animals at all time points assessed (p < 0.001). Furthermore, there were significant differences (P < 0.001) found between the Ddit3, Jun, and combined Jun and Ddit3 groups at all time points evaluated expect for between the Jun, and combined Jun and Ddit3 14 days after ONC. Data are plotted as the percentage survival relative to sham animals (n = 8 per condition per genotype for 14, 35, and 60 days after ONC, except Jun deficient ONC n = 7 at 35 days after ONC and n ≥ 6 per condition per genotype for 120 days after ONC; error bars represent SEM). Raw data in RGCs per mm2 and P values for all comparisons are presented in Table 1
Dlk is not the sole shared upstream regulator of Jun and Ddit3 activity
Dual leucine kinase (DLK) is a mitogen-activated protein kinase kinase kinase (MAP3K) and a critical regulator of RGC death after optic nerve injury [35, 36, 43]. Pharmacologic inhibition of DLK has been shown to be protective in rodent models of ocular hypertension suggesting the importance of this molecule in the pathogenesis of glaucoma [36]. After axonal injury, DLK is a major activator of JNK signaling and regulates both apoptosis and Wallerian degeneration. After optic nerve injury, Dlk deficiency decreases the somal pool of JNK, attenuates somal JUN accumulation, and ultimately increases survival of RGCs as compared to WT animals [35, 36, 43]. Though protective of RGC somas, Dlk deficiency does not prevent activation of axonal JNK [43]. Dlk has also been proposed to regulate Ddit3 expression after axonal injury. Unbiased gene expression profiling after mechanical axonal injury demonstrated that Dlk deficiency significantly reduced the expression of DDIT3 [35]. Together these results raise the possibility that DLK could be upstream of both Jun and Ddit3, thus making Dlk an important common upstream regulator of RGC death after axonal injury. To test this hypothesis, RGC survival was directly compared in WT, Dlk, and Jun/Ddit3 deficient retinas 35 days after ONC. This time point was chosen because there was significant difference in RGC loss between WT, Jun, Ddit3 and Jun/Ddit3 deficiency mice after ONC. TUJ1+ cell counts confirmed that both Dlk and Jun/Ddit3 deficiency provide significant protection to RGCs as compared to WT animals (Fig. 4; P < 0.001 n ≥ 7 per group; WT: 20.4% survival, Dlk: 64.3%, Jun/Ddit3: 88.5%). Furthermore, there was greater protection in Jun/Ddit3 deficient retinas compared to Dlk deficient retinas (p < 0.001) suggesting Dlk may not be the sole upstream regulator of JUN and DDIT3 activation.
Combined Jun/Ddit3 deficiency is more protective after axonal injury than Dlk deficiency. a Example images of TUJ1 staining in control and experimental eyes 35 days after ONC (scale bar = 50 μm). b TUJ1+ cell counts showed that Dlk deficient and combined Jun/Ddit3 deficient animals had significantly greater RGC survival than WT mice 35 days after ONC (% given compared to control eyes of same genotype, WT: 20.4% survival, Dlk: 64.3% Jun/Ddit3: 88.5%; *, P < 0.001, n = 8 per condition per genotype except n = 7 for Dlk deficient animals; error bars represent SEM). Importantly, the protection provided by Jun/Ddit3 deficiency was significantly greater than the protection provided by Dlk deficiency alone (P < 0.001)
Neither Jun, Ddit3, nor combined Jun and Ddit3 deficiency alters axonal degeneration after mechanical optic nerve injury
RGC injury and axonal degeneration are important components of glaucomatous neurodegeneration [2, 8, 9]. After axonal injury, there are differential responses within the RGC somal and axonal compartments [51, 52]. There is spatial compartmentalization of molecular mechanisms that control RGC somal (cell body) and RGC axonal degeneration. Thus, it is necessary to test the role of JUN and DDIT3 in both somal death and axonal degeneration. DDIT3 deficiency promotes optic nerve survival in models of glaucoma, including mechanical optic nerve injury and increased intraocular pressure [33, 34, 37]. Jun deficiency has also been shown to protect axons from degeneration in sensory neuron culture [53]. In the DBA/2 J ocular hypertensive mouse model of glaucoma, Jun deficiency protected RGC somas but not axons from glaucomatous injury [54]. Thus, JUN does not appear to be required for axonal degeneration in adult RGCs after a glaucomatous injury. To test the hypothesis that single and/or combined deficiency of Jun and Ddit3 may protect against axonal degeneration, optic nerve function was tested after mechanical optic nerve injury. Compound action potentials (CAP) were measured in WT, Jun, Ddit3, and Jun/Ddit3 deficient mice five days after ONC, a time when WT animals demonstrate significant reduction in CAP amplitudes [43]. No differences in amplitudes were observed across the four groups, suggesting that deficiency of Jun and Ddit3, either singly or together, does not prevent for axonal degeneration after mechanical optic nerve injury (Fig. 5; P > 0.05 for all comparisons; n = 4 for all groups).
Neither Jun, Ddit3, or combined Jun/Ddit3 deficiency alters axonal degeneration after mechanical optic nerve injury. To assess the role of JUN and DDIT3 in axonal degeneration, compound action potentials (CAPs) were recorded from WT, Jun, Ddit3, and combined Jun/Ddit3 animals 5 days after ONC, a time point when there is significant loss of CAP amplitudes in WT mice [43]. a Representative traces show that sham eyes from all genotypes had normal action potentials, while amplitudes were reduced about 80% in all cases after ONC. b Quantification of CAPs from WT, Jun, Ddit3, and combined Jun/Ddit3 animals showed that there were no differences among the CAP amplitudes of naïve, uninjured eyes of all genotypes (P > 0.05). All genotypes had significantly reduced amplitudes after ONC as compared to naïve animals (P < 0.001 for all comparisons). CAP amplitudes of Jun, Ddit3, and combined Jun/Ddit3 animals were not significantly different after ONC from those of control animals (P > 0.05, n = 4 for each genotype and condition)
Discussion
Axonal injury is a critical component in many neurodegenerative diseases including glaucomatous neurodegeneration [2, 8, 9, 13, 14, 55, 56]. After axonal injury, RGCs undergo apoptosis in a BAX-dependent manner [5,6,7]. The molecular pathway that leads from axonal disruption to BAX activation is only partly defined. In fact, no molecule other than BAX is known to be required for BAX dependent RGC death after axonal injury. The transcription factors JUN and DDIT3 are expressed in RGCs after axonal injury [22,23,24,25,26, 31,32,33,34, 57, 58]. Both JUN and DDIT3 are known to have pro-death functions in neurons [42, 59, 60]. In RGCs, individual deficiency of Jun and Ddit3 provides significant, but incomplete protection of RGCs after axonal injury [22, 23, 33]. Here, we sought to determine if these pathways are independent of each other and if so, whether combined deficiency of JUN and DDIT3 provides complete protection to RGCs after ONC. JUN and DDIT3 appear to control RGC death independently. Single deficiency of Jun or Ddit3 significantly protected RGCs somas at all time points tested. Combined deficiency of Jun and Ddit3 provided robust protection of RGCs after axonal injury, e.g., 89% survival 35 days after ONC. Furthermore, accounting for the incomplete deletion of Jun in RGCs, Jun/Ddit3 deficiency may protect over 95% of RGCs 120 days after ONC. Thus, combined deficiency of Jun and Ddit3 appears to provide nearly complete protection when accounting for incomplete recombination of the Jun allele. Together, JUN and DDIT3 activity accounts for the vast majority of apoptotic signaling in RGCs after axonal injury. Furthermore, because JUN and DDIT3 canonically function as transcription factors, it appears that after axonal injury RGC death requires transcriptional events.
JUN and DDIT3 activation may function as key molecular hubs that integrate upstream signaling events triggered by glaucomatous axonal injury. Given that the canonical function of JUN and DDIT3 is to regulate transcription, their activation likely leads to the transcription of pro-death genes that ultimately trigger RGC apoptosis. The MAPK and ER stress pathways have both been suggested as pharmacologic targets for glaucomatous injury and there is also some evidence for physiologic overlap [35, 40, 49, 61]. Both systems are known to control pro-death genes in neurons. In RGCs, JUN directly controls the pro-death targets BIM, ATF3, and HRK [23, 46]. In other cell types, DDIT3 has been shown to control pro-death components including DR5 (death receptor-5 or TNFRSF10B), BIM, and GSN [39, 62, 63]. JUN, in RGCs, and DDIT3, in other cell types, have also been shown to inhibit pro-survival targets, such as BCL-2 [23, 64].
Interestingly, JUN and DDIT3 may have overlapping functions. DDIT3 can form protein-protein complexes with JUN and other members of the activator protein-1 (AP-1) transcription factor family [61, 62]. Given these interactions and the fact that activation of both Jun and Ddit3 signaling cascades may culminate in BAX-dependent apoptosis, it is possible that together JUN and DDIT3 may co-regulate downstream effector targets in RGCs after axonal injury. Further work using transcriptomics will be needed to define the downstream effector molecules differentially and mutually controlled by Jun and Ddit3. In addition to glaucoma-relevant injuries, JUN and DDIT3 have been implicated in other neurodegenerative diseases [42, 60]. Thus, investigation into the downstream molecular targets of JUN and DDIT3 may determine molecular events broadly important for neurodegeneration.
Identification of the upstream regulator(s) of Jun and Ddit3 will be an important step towards defining the critical pathway that leads from axonal injury to RGC degeneration. Potential molecules that have been suggested to activate both MAPK and endoplasmic reticulum stress signaling in other systems include mTOR, TLR4, and ETN1 [65,66,67,68,69,70]. Further study, however, should be done to identify molecules that activate both JUN and DDIT3 signaling in RGCs. Identified molecules should then be carefully tested in a model of optic nerve injury or preferably, a model of ocular hypertension to determine 1) if these molecules are expressed at a time point consistent with glaucomatous injury 2) if manipulation of these molecules decreases JUN and DDIT3 expression and 3) if deficiency of these molecules protects RGC somas and their axons. These experiments might also reveal early molecular signaling events that occur in axons after a glaucomatous injury. Dlk is a MAP3K known to activate JNK-JUN signaling in RGCs and has also been proposed to regulate DDIT3 activation in RGCs [35, 43]. Dlk deficiency provided significant protection to RGCs after axonal injury. The level of protection afforded by Dlk deficiency was similar to that provided by Jun deficiency and about 50% more protection then provided by Ddit3 deficiency. Like Jun deficiency, protection provided by Dlk deficiency was not complete. Combined Jun/Ddit3 deficiency provided greater protection to RGCs than Dlk deficiency. Thus, Dlk is likely not the sole or only upstream regulator of JUN and DDIT3 in RGCs after axonal injury. While signaling upstream of JUN and DDIT3 may converge, it is also possible that there is not a sole common upstream molecular regulator of all JUN and DDIT3 signaling. The inciting injury in glaucomatous neurodegeneration itself or early sequelae of this perturbation may activate both Jun and Ddit3 through separate mechanisms. Evidence has implicated several distinct cellular events induced by ocular hypertension-induced axonal injury, including: loss of trophic support, noxious glial signaling, neurovascular unit dysfunction, and disruption of the axonal cytoskeleton [16, 20, 71, 72]. Future work to determine a shared upstream regulator of Jun and Ddit3 activation will be important for further defining the major molecular signaling cascades driving RGC degeneration. Regardless of whether the inciting injury in glaucomatous neurodegeneration is extrinsic or intrinsic to RGCs, sequentially stepping upstream of JUN and DDIT3 activation may define the earliest events in glaucoma.
Determining the events leading to MAPK and ER stress activation may be challenging because the MAPK and ER stress signaling pathways are complex. Both routes have multiple parallel pathways with both divergent and convergent elements [59, 73,74,75]. ER stress is the disruption of normal ER function and activation of the unfolded protein response (UPR) due to the accumulation of unfolded proteins and interruption of normal calcium regulation [76]. The three ER stress response proteins are inositol-requiring transmembrane kinase (IRE1), activating transcription factor-6 (ATF6), and protein kinase RNA-like endoplasmic reticulum kinase (PERK). DDIT3 may be a target of all three protein pathways, but is predominately activated by PERK signaling [77]. Previous work has demonstrated that IRE and ATF6 signaling (the largely pro-survival signals of ER stress) are diminished with persistent ER stress signals, while PERK signaling (largely pro-apoptotic) is maintained [78]. In the same study, overexpression of IRE1, led to enhanced cellular viability after axonal injury. XBP1, a component of the IRE arm, was also activated in RGCs after axonal injury [33, 37], while XBP1 and DDIT3 were differentially expressed [33, 37]. While DDIT3 expression was robust and sustained after axotomy, XBP1 was transiently expressed at modest levels early after injury [33]. Unlike deficiency of Ddit3, deficiency of Xbp1 did not prevent RGC loss after axonal injury suggesting that Ddit3 dependent signaling was the critical part of the ER stress response for RGC death.
Glaucoma is a chronic, age-related disease which may play out over years and potentially decades [3]. Given the extended time period of glaucomatous injury, chronic ER stress may lead to prolonged activation of PERK-DDIT3 signaling which may override the protective components of ER stress signaling. Furthermore, the unfolded protein response, primarily through the IRE1 arm, has also been shown to initiate phosphorylation of c-Jun N-terminal kinase (JNK) that in turn activates JUN [40,41,42]. Therefore, in addition to prolonged pro-apoptotic ER stress signaling, activation of ER stress signaling in glaucoma may lead to sustained pro-apoptotic JNK-JUN signaling.
Deficiency in Jun, Ddit3, or combined Jun/Ddit3 did not prevent loss of axonal function as measured by compound action potential after mechanical axonal injury. It is possible that deficiency in these molecules could lessen morphological degeneration, which was not measured here. Dlk deficiency, an upstream regulator of JUN in RGCs, and Ddit3 deficiency both provided some protection to RGC somas and axons in an acute intraocular pressure elevation mouse model of glaucoma [34, 36] Recently, we showed deficiency in Jun does not prevent axonal degeneration in a chronic ocular hypertensive mouse model of glaucoma, though it does provide some protection to RGC somas [54]. It is possible, however, that deficiency in both Jun and Ddit3 will protect RGCs in a chronic, ocular hypertensive model of glaucoma. Interestingly, if combined deficiency of Jun and Ddit3 protects both RGC axons and somas in a glaucoma model it will point to new transcriptional pathways underlying RGC degeneration in glaucoma. This protection would suggest that the transcription events that occur during IOP elevation are critical for axonal degeneration. Such events may not be identified after an acute mechanical axonal injury because of axonal severing. Therefore, it will be important to test the role of Jun and Ddit3 in a chronic, age-related model of ocular hypertension, the DBA/2 J mouse, to determine if Jun and Ddit3 are critical for glaucomatous ocular hypertensive injury.
Conclusions
Jun and Ddit3 are independently controlled transcription factors that together provide robust, near complete protection of RGCs after axonal injury. Jun and Ddit3 are ideally positioned to integrate cell-signaling cascades after axonal injury with transcriptional regulation of RGC death. Jun and Ddit3 signaling have been shown to be involved in other injuries to RGCs including ischemic injury, diabetic retinopathy, and traumatic optic neuropathy (and traumatic brain injury) [23, 27, 33, 58, 79,80,81,82]. Given the robust protection shown here after RGC injury, it will be interesting to determine if dual activation of Jun and Ddit may define a canonical signaling pathway (culminating in BAX activation) for RGC death. Furthermore, it will be important to test the effectiveness of inhibiting both JNK-JUN and DDIT3-dependent ER stress signaling in other injury paradigms that result in RGC death. As axonal injury is a critical event in many different diseases, it is possible that JUN and DDIT3 may control neural degeneration after axonal injury in other neuron types. Thus, the finding that together JUN and DDIT3 control RGC death after axonal injury may be broadly applicable to understanding the molecular signaling pathways that control neurodegeneration.
Abbreviations
- ACSF:
-
artificial cerebrospinal fluid
- AP-1:
-
activator protein 1
- ATF6:
-
activating transcription factor 6
- CAP:
-
compound action potential
- CHOP:
-
CCAAT/enhancer binding homologous protein
- DDIT3:
-
DNA damage inducible transcript 3
- DLK:
-
dual leucine kinase
- DR5:
-
death receptor 5
- ER:
-
endoplasmic reticulum
- IRE1:
-
inositol-requiring transmembrane kinase 1
- JNK:
-
c-Jun N-terminal kinase
- MAP3K:
-
mitogen-activated protein kinase kinase kinase
- MAPK:
-
mitogen-activated protein kinase
- ONC:
-
optic nerve crush
- PERK:
-
protein kinase RNA-like endoplasmic reticulum kinase
- PFA:
-
paraformaldehyde
- RGC:
-
retinal ganglion cell
- TUJ1:
-
βIII tubulin
- UPR:
-
unfolded protein response
- WT:
-
wildtype
References
Quigley HA, Addicks EM, Green WR, Maumenee AE. Optic nerve damage in human glaucoma. II. The site of injury and susceptibility to damage. Arch Ophthalmol. 1981;99:635–49.
Howell GR, Libby RT, Jakobs TC, Smith RS, Phalan FC, Barter JW, Barbay JM, Marchant JK, Mahesh N, Porciatti V, et al. Axons of retinal ganglion cells are insulted in the optic nerve early in DBA/2J glaucoma. J Cell Biol. 2007;179:1523–37.
Weinreb RN, Aung T, Medeiros FA. The pathophysiology and treatment of glaucoma: a review. JAMA. 2014;311:1901–11.
Jakobs TC, Libby RT, Ben Y, John SW, Masland RH. Retinal ganglion cell degeneration is topological but not cell type specific in DBA/2J mice. J Cell Biol. 2005;171:313–25.
Li Y, Schlamp CL, Poulsen KP, Nickells RW. Bax-dependent and independent pathways of retinal ganglion cell death induced by different damaging stimuli. Exp Eye Res. 2000;71:209–13.
Libby RT, Li Y, Savinova OV, Barter J, Smith RS, Nickells RW, John SW. Susceptibility to neurodegeneration in a glaucoma is modified by Bax gene dosage. PLoS Genet. 2005;1:17–26.
Semaan SJ, Li Y, Nickells RW. A single nucleotide polymorphism in the Bax gene promoter affects transcription and influences retinal ganglion cell death. ASN Neuro. 2010;2:e00032.
Anderson DR, Hendrickson A. Effect of intraocular pressure on rapid axoplasmic transport in monkey optic nerve. Investig Ophthalmol. 1974;13:771–83.
Quigley HA, Hohman RM, Addicks EM, Massof RW, Green WR. Morphologic changes in the lamina cribrosa correlated with neural loss in open-angle glaucoma. Am J Ophthalmol. 1983;95:673–91.
Maes ME, Schlamp CL, Nickells RW. BAX to basics: How the BCL2 gene family controls the death of retinal ganglion cells. Prog Retin Eye Res. 2017;
Sun D, Lye-Barthel M, Masland RH, Jakobs TC. The morphology and spatial arrangement of astrocytes in the optic nerve head of the mouse. J Comp Neurol. 2009;516:1–19.
Minckler DS, Bunt AH, Johanson GW. Orthograde and retrograde axoplasmic transport during acute ocular hypertension in the monkey. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci. 1977;16:426–41.
Quigley HA, Anderson DR. Distribution of axonal transport blockade by acute intraocular pressure elevation in the primate optic nerve head. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci. 1977;16:640–4.
Quigley HA, Addicks EM. Chronic experimental glaucoma in primates. II. Effect of extended intraocular pressure elevation on optic nerve head and axonal transport. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci. 1980;19:137–52.
Quigley HA, Addicks EM. Regional differences in the structure of the lamina cribrosa and their relation to glaucomatous optic nerve damage. Arch Ophthalmol. 1981;99:137–43.
Howell GR, Soto I, Libby RT, John SW. Intrinsic axonal degeneration pathways are critical for glaucomatous damage. Exp Neurol. 2013;246:54–61.
Radius RL, Anderson DR. Rapid axonal transport in primate optic nerve. Distribution of pressure-induced interruption. Arch Ophthalmol. 1981;99:650–4.
Calkins DJ: Age-related changes in the visual pathways: blame it on the axon. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci 2013, 54:ORSF37–41.
Calkins DJ. Critical pathogenic events underlying progression of neurodegeneration in glaucoma. Prog Retin Eye Res. 2012;31:702–19.
Nickells RW, Howell GR, Soto I, John SW. Under pressure: cellular and molecular responses during glaucoma, a common neurodegeneration with axonopathy. Annu Rev Neurosci. 2012;35:153–79.
Tezel G, Chauhan BC, LeBlanc RP, Wax MB. Immunohistochemical assessment of the glial mitogen-activated protein kinase activation in glaucoma. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci. 2003;44:3025–33.
Fernandes KA, Harder JM, Fornarola LB, Freeman RS, Clark AF, Pang IH, John SW, Libby RT. JNK2 and JNK3 are major regulators of axonal injury-induced retinal ganglion cell death. Neurobiol Dis. 2012;46:393–401.
Fernandes KA, Harder JM, Kim J, Libby RT. JUN regulates early transcriptional responses to axonal injury in retinal ganglion cells. Exp Eye Res. 2013;112:106–17.
Levkovitch-Verbin H, Quigley HA, Martin KR, Harizman N, Valenta DF, Pease ME, Melamed S. The transcription factor c-jun is activated in retinal ganglion cells in experimental rat glaucoma. Exp Eye Res. 2005;80:663–70.
Isenmann S, Bahr M. Expression of c-Jun protein in degenerating retinal ganglion cells after optic nerve lesion in the rat. Exp Neurol. 1997;147:28–36.
Munemasa Y, Ohtani-Kaneko R, Kitaoka Y, Kumai T, Kitaoka Y, Hayashi Y, Watanabe M, Takeda H, Hirata K, Ueno S. Pro-apoptotic role of c-Jun in NMDA-induced neurotoxicity in the rat retina. J Neurosci Res. 2006;83:907–18.
Roth S, Shaikh AR, Hennelly MM, Li Q, Bindokas V, Graham CE. Mitogen-activated protein kinases and retinal ischemia. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci. 2003;44:5383–95.
Gesslein B, Hakansson G, Carpio R, Gustafsson L, Perez MT, Malmsjo M. Mitogen-activated protein kinases in the porcine retinal arteries and neuroretina following retinal ischemia-reperfusion. Mol Vis. 2010;16:392–407.
Kwong JM, Caprioli J. Expression of phosphorylated c-Jun N-terminal protein kinase (JNK) in experimental glaucoma in rats. Exp Eye Res. 2006;82:576–82.
Lukas TJ, Wang AL, Yuan M, Neufeld AH. Early cellular signaling responses to axonal injury. Cell Commun Signal. 2009;7:5.
Doh SH, Kim JH, Lee KM, Park HY, Park CK. Retinal ganglion cell death induced by endoplasmic reticulum stress in a chronic glaucoma model. Brain Res. 2010;1308:158–66.
Ghosh AS, Wang B, Pozniak CD, Chen M, Watts RJ, Lewcock JW. DLK induces developmental neuronal degeneration via selective regulation of proapoptotic JNK activity. J Cell Biol. 2011;194:751–64.
Hu Y, Park KK, Yang L, Wei X, Yang Q, Cho KS, Thielen P, Lee AH, Cartoni R, Glimcher LH, et al. Differential effects of unfolded protein response pathways on axon injury-induced death of retinal ganglion cells. Neuron. 2012;73:445–52.
Yang L, Li S, Miao L, Huang H, Liang F, Teng X, Xu L, Wang Q, Xiao W, Ridder WH 3rd, et al. Rescue of Glaucomatous Neurodegeneration by Differentially Modulating Neuronal Endoplasmic Reticulum Stress Molecules. J Neurosci. 2016;36:5891–903.
Watkins TA, Wang B, Huntwork-Rodriguez S, Yang J, Jiang Z, Eastham-Anderson J, Modrusan Z, Kaminker JS, Tessier-Lavigne M, Lewcock JW. DLK initiates a transcriptional program that couples apoptotic and regenerative responses to axonal injury. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2013;110:4039–44.
Welsbie DS, Yang Z, Ge Y, Mitchell KL, Zhou X, Martin SE, Berlinicke CA, Hackler L Jr, Fuller J, Fu J, et al. Functional genomic screening identifies dual leucine zipper kinase as a key mediator of retinal ganglion cell death. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2013;110:4045–50.
Hu Y. Axon injury induced endoplasmic reticulum stress and neurodegeneration. Neural Regen Res. 2016;11:1557–9.
Papadakis ES, Finegan KG, Wang X, Robinson AC, Guo C, Kayahara M, Tournier C. The regulation of Bax by c-Jun N-terminal protein kinase (JNK) is a prerequisite to the mitochondrial-induced apoptotic pathway. FEBS Lett. 2006;580:1320–6.
Puthalakath H, O'Reilly LA, Gunn P, Lee L, Kelly PN, Huntington ND, Hughes PD, Michalak EM, McKimm-Breschkin J, Motoyama N, et al. ER stress triggers apoptosis by activating BH3-only protein Bim. Cell. 2007;129:1337–49.
Urano F, Wang X, Bertolotti A, Zhang Y, Chung P, Harding HP, Ron D. Coupling of stress in the ER to activation of JNK protein kinases by transmembrane protein kinase IRE1. Science. 2000;287:664–6.
Sano R, Reed JC. ER stress-induced cell death mechanisms. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1833;2013:3460–70.
Lindholm D, Wootz H, Korhonen L. ER stress and neurodegenerative diseases. Cell Death Differ. 2006;13:385–92.
Fernandes KA, Harder JM, John SW, Shrager P, Libby RT. DLK-dependent signaling is important for somal but not axonal degeneration of retinal ganglion cells following axonal injury. Neurobiol Dis. 2014;69:108–16.
Behrens A, Sibilia M, David JP, Mohle-Steinlein U, Tronche F, Schutz G, Wagner EF. Impaired postnatal hepatocyte proliferation and liver regeneration in mice lacking c-jun in the liver. EMBO J. 2002;21:1782–90.
Miller BR, Press C, Daniels RW, Sasaki Y, Milbrandt J, DiAntonio A. A dual leucine kinase-dependent axon self-destruction program promotes Wallerian degeneration. Nat Neurosci. 2009;12:387–9.
Harder JM, Fernandes KA, Libby RT. The Bcl-2 family member BIM has multiple glaucoma-relevant functions in DBA/2J mice. Sci Rep. 2012;2:530.
Furuta Y, Lagutin O, Hogan BL, Oliver GC. Retina- and ventral forebrain-specific Cre recombinase activity in transgenic mice. Genesis. 2000;26:130–2.
Koistinaho J, Hicks KJ, Sagar SM. Long-term induction of c-jun mRNA and Jun protein in rabbit retinal ganglion cells following axotomy or colchicine treatment. J Neurosci Res. 1993;34:250–5.
Xu Z, Bu Y, Chitnis N, Koumenis C, Fuchs SY, Diehl JA. miR-216b regulation of c-Jun mediates GADD153/CHOP-dependent apoptosis. Nat Commun. 2016;7:11422.
Harder JM, Libby RT. BBC3 (PUMA) regulates developmental apoptosis but not axonal injury induced death in the retina. Mol Neurodegener. 2011;6:50.
Whitmore AV, Libby RT, John SW. Glaucoma: thinking in new ways-a role for autonomous axonal self-destruction and other compartmentalised processes. Prog Retin Eye Res. 2005;24:639–62.
Raff MC, Whitmore AV, Finn JT. Axonal self-destruction and neurodegeneration. Science. 2002;296:868–71.
Simon DJ, Pitts J, Hertz NT, Yang J, Yamagishi Y, Olsen O, Tesic Mark M, Molina H, Tessier-Lavigne M. Axon Degeneration Gated by Retrograde Activation of Somatic Pro-apoptotic Signaling. Cell. 2016;164:1031–45.
Syc-Mazurek SB, Fernandes KA, Libby RT. JUN is important for ocular hypertension-induced retinal ganglion cell degeneration. Cell Death Dis. 2017;8:e2945.
Schlamp CL, Li Y, Dietz JA, Janssen KT, Nickells RW. Progressive ganglion cell loss and optic nerve degeneration in DBA/2J mice is variable and asymmetric. BMC Neurosci. 2006;7:66.
Anderson DR, Hendrickson AE. Failure of increased intracranial pressure to affect rapid axonal transport at the optic nerve head. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci. 1977;16:423–6.
Yang L, Wu L, Wang D, Li Y, Dou H, Tso MO, Ma Z. Role of endoplasmic reticulum stress in the loss of retinal ganglion cells in diabetic retinopathy. Neural Regen Res. 2013;8:3148–58.
Nashine S, Liu Y, Kim BJ, Clark AF, Pang IH. Role of C/EBP homologous protein in retinal ganglion cell death after ischemia/reperfusion injury. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci. 2015;56:221–31.
Wang M, Kaufman RJ. Protein misfolding in the endoplasmic reticulum as a conduit to human disease. Nature. 2016;529:326–35.
Kim EK, Choi EJ. Pathological roles of MAPK signaling pathways in human diseases. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1802;2010:396–405.
Ubeda M, Vallejo M, Habener JF. CHOP enhancement of gene transcription by interactions with Jun/Fos AP-1 complex proteins. Mol Cell Biol. 1999;19:7589–99.
Li T, Su L, Lei Y, Liu X, Zhang Y, Liu X. DDIT3 and KAT2A Proteins Regulate TNFRSF10A and TNFRSF10B Expression in Endoplasmic Reticulum Stress-mediated Apoptosis in Hum0an Lung Cancer Cells. J Biol Chem. 2015;290:11108–18.
Wang XZ, Kuroda M, Sok J, Batchvarova N, Kimmel R, Chung P, Zinszner H, Ron D. Identification of novel stress-induced genes downstream of chop. EMBO J. 1998;17:3619–30.
McCullough KD, Martindale JL, Klotz LO, Aw TY, Holbrook NJ. Gadd153 sensitizes cells to endoplasmic reticulum stress by down-regulating Bcl2 and perturbing the cellular redox state. Mol Cell Biol. 2001;21:1249–59.
Shanware NP, Bray K, Eng CH, Wang F, Follettie M, Myers J, Fantin VR, Abraham RT. Glutamine deprivation stimulates mTOR-JNK-dependent chemokine secretion. Nat Commun. 2014;5:4900.
Babcock JT, Nguyen HB, He Y, Hendricks JW, Wek RC, Quilliam LA. Mammalian target of rapamycin complex 1 (mTORC1) enhances bortezomib-induced death in tuberous sclerosis complex (TSC)-null cells by a c-MYC-dependent induction of the unfolded protein response. J Biol Chem. 2013;288:15687–98.
Kuper C, Beck FX, Neuhofer W. Toll-like receptor 4 activates NF-kappaB and MAP kinase pathways to regulate expression of proinflammatory COX-2 in renal medullary collecting duct cells. Am J Physiol Renal Physiol. 2012;302:F38–46.
Gadea A, Schinelli S, Gallo V. Endothelin-1 regulates astrocyte proliferation and reactive gliosis via a JNK/c-Jun signaling pathway. J Neurosci. 2008;28:2394–408.
Jain A. Endothelin-1-induced endoplasmic reticulum stress in disease. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 2013;346:163–72.
Afrazi A, Branca MF, Sodhi CP, Good M, Yamaguchi Y, Egan CE, Lu P, Jia H, Shaffiey S, Lin J, et al. Toll-like receptor 4-mediated endoplasmic reticulum stress in intestinal crypts induces necrotizing enterocolitis. J Biol Chem. 2014;289:9584–99.
Almasieh M, Wilson AM, Morquette B, Cueva Vargas JL, Di Polo A. The molecular basis of retinal ganglion cell death in glaucoma. Prog Retin Eye Res. 2012;31:152–81.
Libby RT, Gould DB, Anderson MG, John SW. Complex genetics of glaucoma susceptibility. Annu Rev Genomics Hum Genet. 2005;6:15–44.
Plotnikov A, Zehorai E, Procaccia S, Seger R. The MAPK cascades: signaling components, nuclear roles and mechanisms of nuclear translocation. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1813;2011:1619–33.
Chang L, Karin M. Mammalian MAP kinase signalling cascades. Nature. 2001;410:37–40.
Cao SS, Kaufman RJ. Unfolded protein response. Curr Biol. 2012;22:R622–6.
Ron D, Walter P. Signal integration in the endoplasmic reticulum unfolded protein response. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol. 2007;8:519–29.
Kim I, Xu W, Reed JC. Cell death and endoplasmic reticulum stress: disease relevance and therapeutic opportunities. Nat Rev Drug Discov. 2008;7:1013–30.
Lin JH, Li H, Yasumura D, Cohen HR, Zhang C, Panning B, Shokat KM, Lavail MM, Walter P. IRE1 signaling affects cell fate during the unfolded protein response. Science. 2007;318:944–9.
Shimazawa M, Inokuchi Y, Ito Y, Murata H, Aihara M, Miura M, Araie M, Hara H. Involvement of ER stress in retinal cell death. Mol Vis. 2007;13:578–87.
Ho FM, Lin WW, Chen BC, Chao CM, Yang CR, Lin LY, Lai CC, Liu SH, Liau CS. High glucose-induced apoptosis in human vascular endothelial cells is mediated through NF-kappaB and c-Jun NH2-terminal kinase pathway and prevented by PI3K/Akt/eNOS pathway. Cell Signal. 2006;18:391–9.
Ortolano F, Colombo A, Zanier ER, Sclip A, Longhi L, Perego C, Stocchetti N, Borsello T, De Simoni MG. c-Jun N-terminal kinase pathway activation in human and experimental cerebral contusion. J Neuropathol Exp Neurol. 2009;68:964–71.
Begum G, Yan HQ, Li L, Singh A, Dixon CE, Sun D. Docosahexaenoic acid reduces ER stress and abnormal protein accumulation and improves neuronal function following traumatic brain injury. J Neurosci. 2014;34:3743–55.
Acknowledgements
The authors would like to thank Drs. Furuta (Six3-cre) and Wagner (Jun fl) for generously providing mice.
Funding
This work was supported by EY018606 (RTL) and Research to Prevent Blindness, an unrestricted grant to the Department of Ophthalmology at the University of Rochester Medical Center. The funding agencies had no role in the design of the study and collection, analysis, and interpretation of data and in writing the manuscript.
Availability of data and materials
The datasets used and/or analyzed during the current study are available from the corresponding author on reasonable request.
Author’s contributions
All authors designed and interpreted the experiments. SBS performed the experiments except for the western blot analysis performed by MW and the compound action potentials that were performed by KAF. SBS and RTL drafted the manuscript. All authors edited the manuscript and read and approved the final manuscript.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Ethics approval and consent to participate
All experiments were conducted in adherence with the Association for Research in Vision and Ophthalmology’s statement on the use of animals in ophthalmic and vision research and were approved by the University of Rochester’s University Committee on Animal Resources.
Consent for publication
Not applicable.
Competing interests
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Open Access This article is distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/), which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided you give appropriate credit to the original author(s) and the source, provide a link to the Creative Commons license, and indicate if changes were made. The Creative Commons Public Domain Dedication waiver (http://creativecommons.org/publicdomain/zero/1.0/) applies to the data made available in this article, unless otherwise stated.
About this article
Cite this article
Syc-Mazurek, S.B., Fernandes, K.A., Wilson, M.P. et al. Together JUN and DDIT3 (CHOP) control retinal ganglion cell death after axonal injury. Mol Neurodegeneration 12, 71 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1186/s13024-017-0214-8
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1186/s13024-017-0214-8