Abstract
Background
Functional mitral regurgitation is one of the severe complications of non-ischemic dilated cardiomyopathy (DCM). Non-contrast native T1 mapping has emerged as a non-invasive method to evaluate myocardial fibrosis. We sought to evaluate the potential relationship between papillary muscle T1 time and mitral regurgitation in DCM patients.
Methods
Forty DCM patients (55 ± 13 years) and 20 healthy adult control subjects (54 ± 13 years) were studied. Native T1 mapping was performed using a slice interleaved T1 mapping sequence (STONE) which enables acquisition of 5 slices in the short-axis plane within a 90 s free-breathing scan. We measured papillary muscle diameter, length and shortening. DCM patients were allocated into 2 groups based on the presence or absence of functional mitral regurgitation.
Results
Papillary muscle T1 time was significantly elevated in DCM patients with mitral regurgitation (n = 22) in comparison to those without mitral regurgitation (n = 18) (anterior papillary muscle: 1127 ± 36 msec vs 1063 ± 16 msec, p < 0.05; posterior papillary muscle: 1124 ± 30 msec vs 1062 ± 19 msec, p < 0.05), but LV T1 time was similar (1129 ± 38 msec vs 1134 ± 58 msec, p = 0.93). Multivariate linear regression analysis showed that papillary muscle native T1 time (β = 0.10, 95 % CI: 0.05–0.17, p < 0.05) is significantly correlated with mitral regurgitant fraction. Elevated papillary muscle T1 time was associated with larger diameter, longer length and decreased papillary muscle shortening (all p values <0.05).
Conclusions
In DCM, papillary muscle native T1 time is significantly elevated and related to mitral regurgitant fraction.
Similar content being viewed by others
Background
Functional mitral regurgitation, a consequence of left ventricular (LV) remodeling despite normal mitral valve structure, is one of the common and severe complications in non-ischemic dilated cardiomyopathy patients (DCM) [1–4]. It has been reported that the annular enlargement and mitral leaflet tethering by the displacement of papillary muscles due to LV dilatation are the main mechanisms of functional mitral regurgitation [5]. To date, little is known regarding the relationship between papillary muscle function and mitral regurgitant fraction in DCM patients.
Native (non-contrast) T1 mapping has emerged as a cardiovascular magnetic resonance (CMR) method to assess LV diffuse myocardial fibrosis [6]. Studies have shown that native T1 mapping detects diffuse myocardial abnormalities in hypertrophic cardiomyopathy and DCM [7–9]. The extent of myocardial damage by acute myocardial infarction can also be accurately assessed by native T1 mapping [10]. Diffuse myocardial abnormalities in patients with cardiac amyloidosis [11] and Anderson-Fabry disease [12, 13] can be assessed by native T1 mapping. However, data is lacking regarding native T1 mapping of papillary muscles in these myopathies, including DCM.
Therefore, we sought to examine papillary muscle native T1 mapping in DCM and to investigate the relationship between papillary muscle native T1 time and functional mitral regurgitation in this population.
Methods
Study subjects
Forty DCM patients (55 ± 13 years; 31 male) and 20 healthy adult control subjects (54 ± 13 years; 13 male) free of any cardiovascular diseases were studied. All participants were in sinus rhythm at the time of scan.
CMR acquisition
CMR was performed using a 1.5 T system and a 32-channel cardiac phased array receiver coil (Achieva, Philips Healthcare, Best, The Netherlands). Cine CMR, phase contrast images of the ascending aorta, T1 mapping and 3 dimensional late gadolinium enhancement (LGE) were obtained in all participants [14]. T1 mapping was performed using a free-breathing slice-interleaved T1 (STONE) sequence [15].
Electrocardiogram monitoring leads were positioned with the subject in the supine position. Vertical and horizontal LV long-axis cine images were acquired using a steady-state free precession (SSFP) sequence. LV volumes and mass were calculated from an LV short-axis stack of cine images extending from the apex to the base (repetition time (TR), 3.3 ms; echo time (TE), 1.6 ms; flip angle (FA), 60°; field-of-view (FOV), 320 × 320 mm; acquisition matrix, 128 × 128; slice thickness, 8 mm; gap, 2 mm) [16]. Phase contrast images were acquired perpendicular to the proximal ascending aorta to quantify blood flow by following parameters (TR, 15 ms; TE, 6.5 ms; FA, 30°; velocity encoding, 300 cm/s; FOV, 320 × 320 mm; acquisition matrix, 288 × 288; number of phases per cardiac cycle, 36). STONE native T1 mapping was acquired in the short axis during free-breaching using slice-tracking with a balanced SSFP readout (5 slices, TR/TE = 2.8/1.4 msec, flip angle = 70, FOV = 360 × 351 mm, voxel size = 2.1 × 2.1 mm, slice thickness = 8 mm, TFE factor = 86, SENSE factor = 2).
Fifteen minutes after the injection of 0.2 mmol/kg gadobenate dimeglumine, LGE images were acquired using a 3 dimensional sequence [14] with following parameters (TR, 5.3 ms; TE, 2.1 ms; FA, 70°; FOV, 320 × 320 × 125 mm3; acquisition matrix, 224 × 224 × 23; spatial resolution,1.4 × 1.4 × 1.5 mm; reconstruction resolution, 0.6 × 0.6 × 0.8 mm).
Image analysis
Data were analyzed using a commercial workstation (Extend MR WorkSpace, version 2.3.6.3, Philips Healthcare). To determine LV mass, epi- and endocardial LV borders were manually traced on the short axis images. LV mass was calculated as the sum of the myocardial volume multiplied by the specific gravity (1.05 g/mL) of myocardial tissue [17]. Left atrial (LA) volume was calculated using biplane area length method [18]. Papillary muscle morphology (diameter, length and shortening), anterior and posterior mitral leaflet length, mitral annulus diameter (both in 2 chamber and 4 chamber views) and tenting height were measured by cine CMR (Fig. 1). Papillary muscle shortening was calculated as follows.
Aortic blood flow was determined using the semi-automated algorithms [19]. Phase offset correction was performed as described previously [20]. Mitral regurgitation volume was calculated as the difference between the LV stroke volume and ascending aorta forward flow [21]. Mitral regurgitant fraction was calculated as follows.
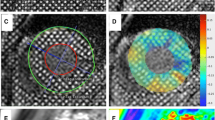
For calculating papillary muscle native T1 time, both anterior and posterior papillary muscles were manually traced on custom software (MediaCare, Boston, MA, USA) (Fig. 2). For calculating LV native T1 time, the three short axis LV slices were then divided into 6 segments for base and mid slices, 4 segments for apical slice using the anterior right ventricular-LV insertion point as reference. The 16 segment model was used to assess native T1 time in each segments. The native T1 time from all the segments was averaged to calculate each subjects LV T1 time. Motion correction was performed using the adaptive registration of varying contrast-weighted images for improved tissue characterization (ARCTIC) approach [22]. To evaluate inter-observer variability, measurements of papillary muscle native T1 time from 10 DCM patients and 10 healthy adult controls were independently taken by two observers. One of the two observers measured papillary muscle native T1 time twice to assess intra-observer variability. The time delay between two read for intra-observer variability was 1 month. Visual assessment was performed to evaluate for LV and papillary muscle scar on LGE.
Statistical analysis
Data were analyzed using SPSS software (version 17.0, SPSS, Inc., Chicago, IL, USA) and MedCalc for Windows (version 14.8.1, MedCalc Software, Ostend, Belgium). Continuous values are presented as mean ± standard deviation (SD). Categorical values are expressed as number (%). DCM patients were divided into 2 groups based on the presence or absence of mitral regurgitation. To assess the difference between 3 groups (DCM patients with mitral regurgitation, n = 22; DCM patients without mitral regurgitation, n = 18; control subjects, n = 20), one-way analysis of variance (ANOVA) with Tukey’s correction was used for continuous variables. Chi-square test was used to assess the difference for categorical variables. Bland and Altman plot [23], coefficient of variation (CV) were used to evaluate intra- and inter-observer variability for measuring papillary muscle native T1 time. Repeatability coefficients were calculated as 1.96 times the SD of the differences on the Bland-Altman plots. Spearman’s correlation coefficient was calculated to evaluate relationship between papillary muscle T1 time and papillary muscle morphology (diameter, length and shortening). Multivariate linear regression analysis was performed to identify the determinants of mitral regurgitation severity in DCM patients. Variables with p-value <0.05 in the univariable analysis were included in the multivariable linear regression analysis (stepwise method). P value <0.05 was considered as statistically significant.
Results
Patients’ characteristics
Table 1 summarizes the clinical characteristics of study subjects. There was no significant difference in gender, age, body mass index, systolic and diastolic blood pressure, heart rate between 3 groups. Information of medical therapy was also shown in Table 1.
Cine MRI and LGE findings
Table 2 summarizes CMR findings. LV end-diastolic volume index, LV end-systolic volume index, LV mass index were significantly higher (all p < 0.05) in DCM patients in comparison to controls. Stroke volume index and LV ejection fraction were significantly decreased (p < 0.05) in DCM patients compared to control subjects. LA volume was significantly higher in DCM patients with MR compared to those without MR (p = 0.04). LGE of LV myocardium was observed in 8 of 40 (20 %) DCM patients, while no DCM patients had LGE of the papillary muscles. Healthy control subjects did not show any LGE in the LV or the papillary muscles. Table 3 shows comparison of papillary muscle parameters. Papillary muscle was significantly thicker, longer in DCM patients in comparison to healthy controls. Regarding mitral annulus diameter, papillary muscle shortening and tenting height, significant difference was also observed between DCM patients with mitral regurgitation and those without mitral regurgitation. Table 4 summarizes the intra- and inter-observer variability for measurement of papillary muscle size. Intra class correlation coefficients for papillary muscle size measurement were >0.80 both for intra- and inter-observer variability.
Comparison of papillary muscle T1 time between cardiomyopathy and healthy control subjects
Figure 3 illustrates individual papillary muscle and LV T1 time for 3 groups. Mean anterior papillary muscle T1 time was 1127 ± 36 msec for DCM with mitral regurgitation (p < 0.05 vs DCM without mitral regurgitation; p < 0.05 vs healthy controls), 1063 ± 16 msec for DCM without mitral regurgitation (p = 0.29 vs healthy controls) and 1051 ± 20 msec for healthy controls. Mean posterior papillary muscle T1 time was 1124 ± 30 msec for DCM with mitral regurgitation (p < 0.05 vs DCM without mitral regurgitation; p < 0.05 vs healthy controls), 1062 ± 19 msec for DCM without mitral regurgitation (p = 0.51 vs healthy controls) and 1053 ± 25 msec for healthy controls. LV native T1 time was significantly elevated in DCM patients in comparison to healthy controls (p < 0.05, Fig. 3), but similar between DCM patients with mitral regurgitation and those without mitral regurgitation (1129 ± 38 msec vs 1134 ± 58 msec, p = 0.93). Figure 4 demonstrates regional LV native T1 time in each segments. There was no substantial variability across 16 segments both in DCM patients and controls. In addition, there was no significant correlation between papillary muscle T1 time and mid-level LV T1 time (r = 0.31, p = 0.05 by Spearman’s correlation coefficient). There was no significant difference in T1 time between base, mid and apical slices (base, 1125 ± 52 msec; mid, 1130 ± 47 msec; apex, 1138 ± 54 msec, p = 0.53 by one-way ANOVA). Figure 5 shows the relationship between papillary muscle T1 time and papillary muscle morphology. Elevated papillary muscle T1 time was associated with increased papillary muscle diameter, increased papillary muscle length and decreased papillary muscle shortening.
Comparison of papillary muscle native T1 time and left ventricular T1 time. Papillary muscle T1 time was significantly elevated in DCM patients with mitral regurgitation in comparison to DCM patients without mitral regurgitation and healthy controls. DCM dilated cardiomyopathy, MR mitral regurgitation
Relationship between papillary muscle T1 time and mitral regurgitant fraction
Figure 6 shows the relationship between papillary muscle T1 time and mitral regurgitant fraction in DCM patients. Mitral regurgitant fraction was significantly correlated with both anterior and posterior papillary muscle T1 time (p < 0.05) but not with LV myocardial T1 time (p = 0.67). Table 5 summarizes the results of multivariate linear regression analysis for determinants of mitral regurgitant fraction in all DCM patients (n = 40). In the multivariate analysis, average of anterior and posterior papillary muscle native T1 time was employed for analysis. Multivariate linear regression analysis identified papillary muscle native T1 time (β = 0.10, 95 % CI: 0.03–0.17, p < 0.05) as an independent determinant of mitral regurgitant fraction. Table 6 shows the results of multivariate linear regression analysis for determinants of mitral regurgitant fraction in DCM patients with MR (n = 22). Multivariable linear regression analysis identified posterior papillary muscle maximum diameter (β = 1.32, 95 % CI: 0.50–2.16, p < 0.05) and papillary muscle native T1 time (β = 0.11, 95 % CI: 0.03–0.20, p < 0.05) as independent determinants of mitral regurgitant fraction.
Variability of papillary muscle T1 measurement
Repeatability coefficients of anterior papillary muscle T1 time were 2.0 % for intra-observer variability, 4.1 % for inter-observer variability. Repeatability coefficients of posterior papillary muscle native T1 time were 1.3 % for intra-observer variability, 5.0 % for inter-observer variability. Variability of papillary muscle native T1 time measurement was high (CV of intra-observer variability: 0.9 % for anterior papillary muscle and 0.7 % for posterior papillary muscle; CV of inter-observer variability: 1.6 % for anterior papillary muscle and 1.8 % for posterior papillary muscle).
Discussion
To the best of our knowledge, this study is the first investigation to examine the feasibility and variability of papillary muscle native T1 time measurement, and to investigate the relationship between papillary muscle T1 time and severity of functional mitral regurgitation in DCM patients. We found a significant difference of papillary muscle native T1 time between DCM patients with mitral regurgitation and those without mitral regurgitation, a correlation between papillary muscle native T1 time and mitral regurgitant fraction in DCM patients and low variability of papillary muscle T1 time measurement.
Papillary muscle T1 time and papillary muscle morphology in DCM patients
Previous echocardiographic studies have shown that the papillary muscle dysfunction is observed in several cardiovascular diseases. Papillary muscle shortening has been assessed using transthoracic echocardiography and used as a functional parameter [24, 25]. In myocardial infarction patients, papillary muscle function was substantially reduced compared to healthy controls (papillary muscle shortening: 15 ± 14 % vs 30 ± 8 %) [25]. Reduced papillary muscle shortening has also been reported in cardiomyopathy patients including hypertrophic cardiomyopathy or DCM [24, 26]. In the current study, we measured papillary muscle diameter, length and shortening using cine CMR and showed that papillary muscle shortening was significantly reduced in DCM patients in comparison to healthy controls. This absolute value and difference findings were consistent with previous echocardiographic studies. In addition, we found a significant difference in papillary muscle shortening between DCM patients with mitral regurgitation in comparison to those without mitral regurgitation, suggesting that papillary muscle dysfunction may be contributing to mitral regurgitation.
The maximum papillary muscle diameter was approximately 7 mm in healthy controls and 10 mm in DCM patients. Elevated papillary muscle native T1 time was associated with larger diameter, longer length, decreased shortening in DCM patients. This finding suggested that papillary muscle T1 time might reflect papillary muscle pathological changes in DCM patients (i.e. papillary muscle fibrosis). Furthermore, papillary muscle native T1 time was increased in DCM patients with mitral regurgitation compared to those without mitral regurgitation, but LV native T1 time was similar between 2 groups. These results suggest that the papillary muscle native T1 time may be a more sensitive for the mechanical stress induced by functional mitral regurgitation. A previous study by Okayama et al. showed that LGE evidence of bilateral papillary muscle infarction correlated with LV remodeling and functional mitral regurgitation [27]. Although the assessment of papillary muscle abnormality is feasible by LGE, an important advantage of non-contrast native T1 mapping is the ability to evaluate papillary muscle abnormality in patients with renal dysfunction who are at high risk of systemic nephrogenic fibrosis [28]. In addition, we did not observe any papillary muscle LGE in this study, suggesting that the papillary muscle pathological change is diffuse rather than focal in DCM patients.
Clinical implication
We found significant difference in papillary muscle native T1 time between DCM patients with mitral regurgitation and those without mitral regurgitation. However, no significant difference was found in LV native T1 time. In addition, papillary muscle T1 time was independently correlated with severity of functional mitral regurgitation after adjustment of conventional determinants, including tenting height, mitral annulus diameter. Previous transthoracic echocardiographic studies showed that tenting height is a strong indicator of effective orifice area in patents with LV dysfunction and functional mitral regurgitation [29]. Further study is necessary to elucidate if papillary muscle native T1 time has prognostic value in DCM patients.
Study limitations
Our study has several limitations. The sample size was modest and the study population was limited to DCM patients and healthy controls. Our T1 mapping sequence, STONE, has not been histologically validated for papillary muscle T1 mapping. Therefore, we do not know the true cause of the elevated papillary muscle native T1 time in DCM patients. Although T1 mapping images acquired by STONE were motion corrected, relatively low spatial resolution of T1 mapping images and the partial volume effect are not negligible for T1 measurement of papillary muscle. To avoid partial volume effect with blood pool, we’ve carefully placed the ROI on papillary muscle much smaller than actual papillary muscle diameter not to include the pixels from LV blood pool. As shown on Fig. 2, size of ROI on papillary muscle was much smaller than actual size of papillary muscle. The pixel size of ROI drawn on papillary muscle was 16–40 pixels. It would be also interesting to investigate the relationship between papillary muscle extra cellular volume (ECV) and mitral regurgitant fraction. However, calculation of ECV requires registration between native and post-contrast T1 images, which will be challenging for a mobile and small papillary muscle anatomy. Regarding LV ECV, in our cohort, there were 21 DCM patients and 9 controls with ECV data. Significant difference was found between DCM patients and controls in LV ECV averaged over 16 segments (0.30 ± 0.04 vs 0.27 ± 0.02, p = 0.03). However, no significant difference was found between DCM patients with MR and those without MR (0.31 ± 0.05 vs 0.29 ± 0.04, p = 0.63). A larger, more diverse study is required to assess the clinical relevance of papillary muscle native T1 time. Because this study is a cross-sectional study, we can’t say any causal relationship between papillary muscle T1 time and functional mitral regurgitation. Examination of the potential difference of the time course of T1 change in the myocardium and papillary muscle would also be of interest, but is beyond the scope of this study.
Conclusions
Measurement of papillary muscle native T1 time is both feasible and reproducible. This CMR approach successfully detects abnormal papillary muscle native T1 time in DCM patients with functional mitral regurgitation.
Abbreviations
- ANOVA:
-
Analysis of variance
- ARCTIC:
-
Adaptive registration of varying contrast-weighted images for improved tissue characterization
- CI:
-
Confidence interval
- CMR:
-
Cardiovascular magnetic resonance
- CV:
-
Coefficient of variation
- DCM:
-
Dilated cardiomyopathy
- ECV:
-
Extracellular volume
- FA:
-
Flip angle
- FOV:
-
Field of view
- LA:
-
Left atrial
- LGE:
-
Late gadolinium enhancement
- LV:
-
Left ventricular
- MR:
-
Mitral regurgitation
- ROI:
-
Region of interest
- SD:
-
Standard deviation
- SENSE:
-
Sensitivity encoding
- SSFP:
-
Steady-state free precession
- STONE:
-
Slice-interleaved T1
- TE:
-
Echo time
- TFE:
-
Turbo field echo
- TR:
-
Repetition time
References
Romeo F, Pelliccia F, Cianfrocca C, Gallo P, Barilla F, Cristofani R, Reale A. Determinants of end-stage idiopathic dilated cardiomyopathy: a multivariate analysis of 104 patients. Clin Cardiol. 1989;12:387–92.
Blondheim DS, Jacobs LE, Kotler MN, Costacurta GA, Parry WR. Dilated cardiomyopathy with mitral regurgitation: decreased survival despite a low frequency of left ventricular thrombus. Am Heart J. 1991;122:763–71.
Junker A, Thayssen P, Nielsen B, Andersen PE. The hemodynamic and prognostic significance of echo-doppler-proven mitral regurgitation in patients with dilated cardiomyopathy. Cardiology. 1993;83:14–20.
Burch GE, De Pasquale NP, Phillips JH. Clinical manifestations of papillary muscle dysfunction. Arch Intern Med. 1963;112:112–7.
Otsuji Y, Handschumacher MD, Schwammenthal E, Jiang L, Song JK, Guerrero JL, Vlahakes GJ, Levine RA. Insights from three-dimensional echocardiography into the mechanism of functional mitral regurgitation: direct in vivo demonstration of altered leaflet tethering geometry. Circulation. 1997;96:1999–2008.
Moon JC, Messroghli DR, Kellman P, Piechnik SK, Robson MD, Ugander M, Gatehouse PD, Arai AE, Friedrich MG, Neubauer S, Schulz-Menger J, Schelbert EB. Myocardial T1 mapping and extracellular volume quantification: a society for cardiovascular magnetic resonance (SCMR) and CMR working group of the European Society of Cardiology consensus statement. J Cardiovasc Magn Reson. 2013;15:92.
Puntmann VO, Voigt T, Chen Z, Mayr M, Karim R, Rhode K, Pastor A, Carr-White G, Razavi R, Schaeffter T, Nagel E. Native T1 mapping in differentiation of normal myocardium from diffuse disease in hypertrophic and dilated cardiomyopathy. JACC Cardiovasc Imaging. 2013;6:475–84.
Dass S, Suttie JJ, Piechnik SK, Ferreira VM, Holloway CJ, Banerjee R, Mahmod M, Cochlin L, Karamitsos TD, Robson MD, Watkins H, Neubauer S. Myocardial tissue characterization using magnetic resonance noncontrast T1 mapping in hypertrophic and dilated cardiomyopathy. Circ Cardiovasc Imaging. 2012;5:726–33.
Malek LA, Werys K, Klopotowski M, Spiewak M, Milosz-Wieczorek B, Mazurkiewicz L, Petryka-Mazurkiewicz J, Marczak M, Witkowski A. Native T1-mapping for non-contrast assessment of myocardial fibrosis in patients with hypertrophic cardiomyopathy - comparison with late enhancement quantification. Magn Reson Imaging. 2015;33:718–24.
Dall’Armellina E, Piechnik SK, Ferreira VM, Si QL, Robson MD, Francis JM, Cuculi F, Kharbanda RK, Banning AP, Choudhury RP, Karamitsos TD, Neubauer S. Cardiovascular magnetic resonance by non contrast T1-mapping allows assessment of severity of injury in acute myocardial infarction. J Cardiovasc Magn Reson. 2012;14:15.
Fontana M, Banypersad SM, Treibel TA, Maestrini V, Sado DM, White SK, Pica S, Castelletti S, Piechnik SK, Robson MD, Gilbertson JA, Rowczenio D, Hutt DF, Lachmann HJ, Wechalekar AD, Whelan CJ, Gillmore JD, Hawkins PN, Moon JC. Native T1 mapping in transthyretin amyloidosis. JACC Cardiovasc Imaging. 2014;7:157–65.
Sado DM, White SK, Piechnik SK, Banypersad SM, Treibel T, Captur G, Fontana M, Maestrini V, Flett AS, Robson MD, Lachmann RH, Murphy E, Mehta A, Hughes D, Neubauer S, Elliott PM, Moon JC. Identification and assessment of anderson-fabry disease by cardiovascular magnetic resonance noncontrast myocardial T1 mapping. Circ Cardiovasc Imaging. 2013;6:392–8.
Thompson RB, Chow K, Khan A, Chan A, Shanks M, Paterson I, Oudit GY. T1 mapping with cardiovascular MRI is highly sensitive for fabry disease independent of hypertrophy and sex. Circ Cardiovasc Imaging. 2013;6:637–45.
Akcakaya M, Rayatzadeh H, Basha TA, Hong SN, Chan RH, Kissinger KV, Hauser TH, Josephson ME, Manning WJ, Nezafat R. Accelerated late gadolinium enhancement cardiac MR imaging with isotropic spatial resolution using compressed sensing: initial experience. Radiology. 2012;264:691–9.
Weingartner S, Roujol S, Akcakaya M, Basha TA, Nezafat R. Free-breathing multislice native myocardial T1 mapping using the slice-interleaved T1 (STONE) sequence. Magn Reson Med. 2015;74:115–24.
Grothues F, Smith GC, Moon JC, Bellenger NG, Collins P, Klein HU, Pennell DJ. Comparison of interstudy reproducibility of cardiovascular magnetic resonance with two-dimensional echocardiography in normal subjects and in patients with heart failure or left ventricular hypertrophy. Am J Cardiol. 2002;90:29–34.
Semelka RC, Tomei E, Wagner S, Mayo J, Kondo C, Suzuki J, Caputo GR, Higgins CB. Normal left ventricular dimensions and function: interstudy reproducibility of measurements with cine MR imaging. Radiology. 1990;174:763–8.
Gulati A, Ismail TF, Jabbour A, Ismail NA, Morarji K, Ali A, Raza S, Khwaja J, Brown TD, Liodakis E, Baksi AJ, Shakur R, Guha K, Roughton M, Wage R, Cook SA, Alpendurada F, Assomull RG, Mohiaddin RH, Cowie MR, Pennell DJ, Prasad SK. Clinical utility and prognostic value of left atrial volume assessment by cardiovascular magnetic resonance in non-ischaemic dilated cardiomyopathy. Eur J Heart Fail. 2013;15:660–70.
Uretsky S, Gillam L, Lang R, Chaudhry FA, Argulian E, Supariwala A, Gurram S, Jain K, Subero M, Jang JJ, Cohen R, Wolff SD. Discordance between echocardiography and mri in the assessment of mitral regurgitation severity: a prospective multicenter trial. J Am Coll Cardiol. 2015;65:1078–88.
Chernobelsky A, Shubayev O, Comeau CR, Wolff SD. Baseline correction of phase contrast images improves quantification of blood flow in the great vessels. J Cardiovasc Magn Reson. 2007;9:681–5.
Uretsky S, Supariwala A, Nidadovolu P, Khokhar SS, Comeau C, Shubayev O, Campanile F, Wolff SD. Quantification of left ventricular remodeling in response to isolated aortic or mitral regurgitation. J Cardiovasc Magn Reson. 2010;12:32.
Roujol S, Foppa M, Weingartner S, Manning WJ, Nezafat R. Adaptive registration of varying contrast-weighted images for improved tissue characterization (ARCTIC): application to T1 mapping. Magn Reson Med. 2015;73:1469–82.
Bland JM, Altman DG. Statistical methods for assessing agreement between two methods of clinical measurement. Lancet. 1986;1:307–10.
Madu ECRR, D’Cruz IA. Tee assessment of papillary muscle anatomy and contraction in patients with and without left ventricular hypertrophy. J Am Coll Cardiol. 1996;27:350.
Kisanuki A, Otsuji Y, Kuroiwa R, Murayama T, Matsushita R, Shibata K, Yutsudo T, Nakao S, Nomoto K, Tomari T, et al. Two-dimensional echocardiographic assessment of papillary muscle contractility in patients with prior myocardial infarction. J Am Coll Cardiol. 1993;21:932–8.
Madu EC, Baugh DS, D’Cruz IA, Johns C. Left ventricular papillary muscle morphology and function in left ventricular hypertrophy and left ventricular dysfunction. Med Sci Monit. 2001;7:1212–8.
Okayama S, Uemura S, Soeda T, Onoue K, Somekawa S, Ishigami K, Watanabe M, Nakajima T, Fujimoto S, Saito Y. Clinical significance of papillary muscle late enhancement detected via cardiac magnetic resonance imaging in patients with single old myocardial infarction. Int J Cardiol. 2011;146:73–9.
Thomsen HS. Esur guideline: Gadolinium-based contrast media and nephrogenic systemic fibrosis. Eur Radiol. 2007;17:2692–6.
Sadeghpour A, Abtahi F, Kiavar M, Esmaeilzadeh M, Samiei N, Ojaghi SZ, Bakhshandeh H, Maleki M, Noohi F, Mohebbi A. Echocardiographic evaluation of mitral geometry in functional mitral regurgitation. J Cardiothorac Surg. 2008;3:54.
Acknowledgements
Not applicable.
Funding
Shingo Kato, MD receives scholarship from Banyu Life Science Foundation International. Reza Nezafat, PhD receives grant support from NIH R01EB008743, 1R21HL127650, 1R01HL129185, AHA 15EIA22710040 and Samsung Electronics.
Availability of data and materials
Not applicable.
Authors’ contributions
Author contribution are as following; conception and design (SK, SR, TB, SB, KVK, BG, WJM, RN), analysis and interpretation of data (SK, SA, SN, SR, JJ), drafting (SK, SR), revising (SK, SN, FND, WJM, RN). All authors read and approved the final manuscript.
Authors’ information
Not applicable.
Competing interests
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Consent for publication
All participants in this study gave written informed consent to participate and to publish.
Ethics approval and consent to participate
The study was approved by the Beth Israel Deaconess Medical Center Institutional Ethics Committee, and all subjects gave written informed consent to participate and to publish.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
Open Access This article is distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/), which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided you give appropriate credit to the original author(s) and the source, provide a link to the Creative Commons license, and indicate if changes were made. The Creative Commons Public Domain Dedication waiver (http://creativecommons.org/publicdomain/zero/1.0/) applies to the data made available in this article, unless otherwise stated.
About this article
Cite this article
Kato, S., Nakamori, S., Roujol, S. et al. Relationship between native papillary muscle T1 time and severity of functional mitral regurgitation in patients with non-ischemic dilated cardiomyopathy. J Cardiovasc Magn Reson 18, 79 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1186/s12968-016-0301-y
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1186/s12968-016-0301-y