Abstract
Background
Autophagy is a major cellular process by which cytoplasmic components such as damaged organelles and misfolded proteins are recycled. Although low levels of autophagy occur in cells under basal conditions, certain cellular stresses including nutrient depletion, DNA damage, and oxidative stress are known to robustly induce autophagy. Krüppel-like factor 4 (KLF4) is a zinc-finger transcription factor activated during oxidative stress to maintain genomic stability. Both autophagy and KLF4 play important roles in response to stress and function in tumor suppression.
Methods
To explore the role of KLF4 on autophagy in mouse embryonic fibroblasts (MEFs), we compared wild-type with Klf4 deficient cells. To determine the levels of autophagy, we starved MEFs for different times with Earle’s balanced salts solution (EBSS). Rapamycin was used to manipulate mTOR activity and autophagy. The percentage of cells with γ-H2AX foci, a marker for DNA damage, and punctate pattern of GFP-LC3 were counted by confocal microscopy. The effects of the drug treatments, Klf4 overexpression, or Klf4 transient silencing on autophagy were analyzed using Western blot. Trypan Blue assay and flow cytometry were used to study cell viability and apoptosis, respectively. qPCR was also used to assay basal and the effects of Klf4 overexpression on Atg7 expression levels.
Results
Here our data suggested that Klf4 −/− MEFs exhibited impaired autophagy, which sensitized them to cell death under nutrient deprivation. Secondly, DNA damage in Klf4-null MEFs increased after treatment with EBSS and was correlated with increased apoptosis. Thirdly, we found that Klf4 −/− MEFs showed hyperactive mTOR activity. Furthermore, we demonstrated that rapamycin reduced the increased level of mTOR in Klf4 −/− MEFs, but did not restore the level of autophagy. Finally, re-expression of Klf4 in Klf4 deficient MEFs resulted in increased levels of LC3II, a marker for autophagy, and Atg7 expression level when compared to GFP-control transfected Klf4 −/− MEFs.
Conclusion
Taken together, our results strongly suggest that KLF4 plays a critical role in the regulation of autophagy and suppression of mTOR activity. In addition, we showed that rapamycin decreased the level of mTOR in Klf4 −/− MEFs, but did not restore autophagy. This suggests that KLF4 regulates autophagy through both mTOR-dependent and independent mechanisms. Furthermore, for the first time, our findings provide novel insights into the mechanism by which KLF4 perhaps prevents DNA damage and apoptosis through activation of autophagy.
Similar content being viewed by others
Introduction
Krüppel-like factor 4 (KLF4) is a zinc-finger transcription factor with diverse regulatory functions in proliferation, differentiation, apoptosis, and development [1,2]. In many human cancers KLF4 is regarded as a tumor suppressor. For instance, the expression of KLF4 is downregulated in bladder, lung, pancreatic, colorectal, gastric, esophageal, and prostate cancers [3–7]. Interestingly, in contrast to its role as a tumor suppressor, in many cancer types KLF4 may act as an oncogene in a context dependent manner, as it is overexpressed in primary breast ductal carcinoma and oral squamous cell carcinoma [8,9].
In vitro, mouse embryonic fibroblasts (MEFs) lacking Klf4 have been shown to exhibit various abnormal cellular processes including increased rate of proliferation, oxidative stress-induced DNA damage and elevated levels of apoptosis [10,11]. Furthermore, KLF4 expression is associated with conditions that initiate cell cycle arrest such as contact inhibition and serum deprivation [12]. KLF4 is thought to play an important role in regulating normal physiological processes by initiating cell cycle checkpoints as induction of KLF4 following DNA damage arrests cells at G1/S and G2/M checkpoints [13]. We have previously shown that a lack of Klf4 in MEFs leads to increased genomic instability such as DNA double stranded breaks, aneuploidy, chromosome aberration, and centrosome amplification [10]. This genomic instability can be corrected by reintroduction of Klf4 to Klf4 −/− MEFs [14]. More recently we have shown that KLF4 regulates the levels of reactive oxygen species (ROS) and prevents accumulation of DNA damage [11]. However, other possible mechanisms through which KLF4 maintains genomic stability await further investigation.
Autophagy is a conserved intracellular process that involves the degradation of cytoplasmic components inside lysosomes [15]. It is induced in response to stress and nutrient starvation to maintain cellular homeostasis by removing misfolded proteins and damaged organelles so that the cell can recycle its components [16]. Both basal level and starvation-induced autophagy maintain cellular homeostasis and perform important housekeeping functions in a variety of physiological processes and pathological conditions including cancer [17]. Previous studies have shown that autophagy suppresses tumorigenesis. For example, monoallelic deletions of beclin1, a gene important for autophagy, lead to many types of cancer including ovarian, breast, and prostate cancer [18]. Furthermore, deletion of genes that result in autophagy deficiency in mice also accelerates tumor progression [19,20]. One mechanism by which autophagy is thought to suppress tumor development is by clearing damaged cellular components and mitigating cellular stress [21]. For instance, the autophagy defective Beclin +/− mouse kidney epithelial cells showed increased DNA damage, centrosome amplification, and chromosomal abnormality, a hallmark of genomic instability [22]. However, the role autophagy plays in cancer development remains controversial. While autophagy plays a role in maintaining normal homeostasis in healthy tissues, studies have also reported that autophagy allows for the survival of cancer cells with defective apoptosis [17].
One crucial step of autophagy is the formation of autophagosomes, which engulf cytoplasmic components and transfer them to the lysosome for degradation. The formation of autophagosome involves the recruitment of lipidated Microtubule-associated protein 1 light chain 3 (LC3, homologue of yeast ATG8). LC3 is first translated as pro-LC3, which is later cleaved at the C-terminal to produce LC3I by ATG4B [23,24]. During starvation when autophagy is induced, cytosolic LC3I is conjugated to phosphatidylethanolamine (PE) to produce LC3II via enzymatic reactions involving an E1 activation enzyme ATG7 [23,25]. PE-conjugated LC3II then binds to the membranes of the elongating autophagosome and might participate in selective intake of target molecules [24,26]. Localization of LC3II to the autophagosome exhibits punctate pattern by microscopy [24]. Thus, conversion to LC3II and its punctate pattern have been used as good indicators for autophagic activity [24].
Autophagy can be regulated by mammalian target of rapamycin (mTOR). The mTOR complex is sensitive to the intracellular abundance of growth factors and nutrients. When nutrients are abundant, energy is high, and cellular stress is low, mTOR is active and ensures that anabolic pathways favor cell growth [27]. During normal physiological conditions, mTOR inhibits autophagy, and stimulates cell growth by phosphorylating p70S6K [28]. However, under nutrient deprivation and cellular stress, mTOR is inhibited and autophagy is induced [16,29]. Previous studies have shown that mTOR hyperactivity is implicated in many cancers. For example, mTOR is overexpressed in colorectal cancers, and several carcinomas are found to contain a single amino acid mutation that leads to mTOR constitutive activation [30,31]. Further understanding of the mTOR pathway, as well as its negative regulators, thus may provide important insights into their role in carcinogenesis.
Despite the growing evidence supporting KLF4’s role in preventing tumorigenesis, the exact mechanism by which it exerts such functions remains unclear. In the present study, we sought to investigate whether KLF4 played a role in autophagy regulation and to identify its molecular targets. We propose here that primary MEFs lacking Klf4 exhibited impaired autophagy during starvation, which sensitized the cells to apoptosis. We attributed the cause of autophagy impairment partially to mTOR hyperactivity and showed KLF4 as a negative regulator of mTOR. Results from this work can further elucidate the mechanism by which KLF4 maintains genomic stability and limits carcinogenesis through activation of autophagy.
Results
MEFs lacking Klf4 exhibited impaired autophagy during starvation
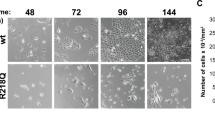
In order to explore their response to starvation conditions, MEFs were treated with Earle’s Balanced Salt Solution (EBSS) for various durations of time. Cell morphology was assessed by microscope in Klf4 +/+and Klf4 −/− MEFs treated with either full-media or EBSS. As shown by the relative number of cells in Figure 1A, Klf4 −/− MEFs were more sensitive to the effects of starvation in time-dependent manner compared with wild-type MEFs. As a control, Klf4 +/+and Klf4 −/− MEFs cultured in full media showed normal increase in confluency after 24 hrs (Additional file 1 Figure S1).
MEFs null for Klf4 exhibit lower levels of autophagy compared to the wild-type during starvation. (A) Morphology of Klf4 +/+ and Klf4 −/− MEFs with time course EBSS treatment. Klf4 +/+ and Klf4 −/− MEFs were treated with EBSS for the durations indicated and photographed with an Olympus IX51 inverted microscope. Cell lysates from Klf4 +/+ (B) and Klf4 −/− (C) MEFs were analyzed using Western blot. Antibodies against LC3B were used to indicate autophagy levels and β-Actin was used as a loading control. (D) Densitometry analysis of LC3B bands shown in (B) and (C). The intensities of LC3BII bands were normalized to that of β-actin using Gel Imager program. Error bars represent standard error. The experiments were repeated 3 times. * indicates p < 0.05, ** indicates p < 0.01.
We next examined the basis of this increased sensitivity to starvation in Klf4 −/− MEFs. Previous reports have shown that autophagy is induced in response to nutrient starvation [16]. Consistent with those reports, Western blot analysis of the autophagy marker, LC3BII, showed that while Klf4 +/+ MEFs significantly exhibited higher levels of autophagy after 8 hrs of treatment with EBSS, starvation failed to induce similar increases of autophagy in Klf4 −/− MEFs (Figures 1B—D). Additionally in the absence of Klf4, Atg7, a gene important for autophagy, exhibited reduced induction compared to that of the wild-type during starvation (data not shown). Our data thus strongly suggested that KLF4 mediates the autophagy process.
Impaired autophagy sensitizes Klf4 −/− MEFs to apoptosis
We next attempted to study the relative effects on cell viability in Klf4 +/+ and Klf4 −/− MEFs caused by impaired autophagy using chloroquine diphosphate (CQ), which inhibited the completion of autophagy by blocking the maturation of the autophagosome and neutralizing cellular pH [32]. Relative cell number and Trypan Blue assay showed a significant increase in the percentage of dead cells in Klf4 −/− MEFs starved with EBSS (Figures 2A—B). Both Klf4 +/+ and Klf4 −/− MEFs starved and co-treated with CQ showed increased percentage of dead cells (Figure 2B). The increased cell death was not likely to be caused by CQ toxicity as CQ treatment alone had little effect on cell viability (Figure 2B). The increased cell death in both Klf4 +/+ and Klf4 −/− MEFs might be caused by apoptosis, necrosis, or autophagy-induced cell death. To determine whether inhibition of autophagy led to increased cell death by sensitizing cells to apoptosis, we performed flow cytometry. Consistent with our previous finding [10], we observed a significantly higher sub-G1 population of cells in Klf4 −/− MEFs compared to the wild-type (Figures 2C—D). During starvation, inhibition of autophagy increased the sub-G1 population from 8.5% to 15.1% in wild-type MEFs as compared to starvation only while the apoptotic population increased from 16.7% to 19.5% in Klf4 −/− MEFs (Figure 2C). Our results thus suggested that inhibition of autophagy increased apoptosis and that Klf4 −/− MEFs may be more sensitive to starvation due to impaired autophagy. However, the slight increase of apoptosis in Klf4 −/− MEFs with CQ and EBSS combined treatment does not fully explain their higher rate of cell death (Figure 2B&D). This suggested that Klf4 −/− MEFs might experience apoptosis-independent cell death.
Impairment of autophagy in Klf4 −/− MEFs leads to increased apoptotic cell death. (A) Morphology of Klf4 +/+ and Klf4 −/− MEFs treated with full media, 10 μM CQ, EBSS, or both CQ and EBSS for 8 hrs. (B) MEFs were collected after respective treatments and subjected to Trypan Blue assay. The percentage of dead cells, as indicated by Trypan Blue staining, was quantified using a hemocytometer under bright field microscopy. Error bars represent standard deviation. The experiments were repeated 3 times. * indicates p < 0.05. (C) Klf4 +/+ and Klf4 −/− MEFs were treated with full media, 10 μM CQ, EBSS, or both CQ and EBSS for 8 hrs before the cells were analyzed using flow cytometry. Representative results from three independent experiments were shown. Sub-G1 population was identified for quantification of cell survival. (D) Sub-G1 population from the three independent experiments represented in (C) was averaged and plotted. Error bars represent standard error. * indicates p < 0.05.
Impaired autophagy in Klf4 −/− MEFs results in increased DNA damage
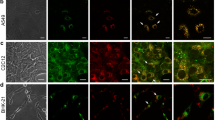
It has been previously established that extensive DNA damage can lead to apoptosis, and autophagy is an important mechanism in maintaining genomic stability [22,33,34]. We thus hypothesized that impaired autophagy in Klf4 −/− MEFs led to the accumulation of DNA damage and sensitized the cells to apoptosis. In order to test our hypothesis, we cultured Klf4 +/+ and Klf4 −/− MEFs in full-media or starved them with EBSS. After 8 hours of EBSS treatment, the cells were immunostained with an antibody against S139-phophorylated H2AX (γ-H2AX), a DNA damage marker. Consistent with our previous findings at the basal level [10,14], Klf4 −/− MEFs exhibited higher levels of γ-H2AX foci compared to the wild-type (Figure 3). When challenged with starvation, Klf4 +/+ MEFs showed a moderate increase in γ-H2AX foci (Figures 3A&B). However, more Klf4 −/− MEFs showed more severe levels of DNA damage (Figures 3A&B). Quantification of γ-H2AX foci showed that most of Klf4 +/+ MEFs treated with EBSS contained 5 foci or fewer per cell and a small fraction had greater than 15 foci per cell. However, the majority of Klf4 −/− MEFs contained more than 15 foci per cell (Figure 3B). Furthermore, Western blot analysis of γ-H2AX also showed similar results. As shown in Figure 3C, the levels of γ-H2AX in EBSS treated Klf4 −/− MEFs is much higher as compared with wild-type cells (Figure 3C). Taken together, these results supported our hypothesis that defective autophagy in Klf4 −/− MEFs led to accumulation of DNA damage.
Impaired autophagy in Klf4 −/− MEFs results in increased DNA damage. Klf4 +/+ and Klf4 −/− MEFs were treated with full-media or EBSS for 8 hrs. (A) Immunostaining against γ-H2AX (green), a DNA damage marker, was performed to assess the levels of DNA damage in Klf4 +/+ and Klf4 −/− MEFs. DAPI (blue) was used to visualize the nuclei. (B) The percentage of Klf4 +/+ and Klf4 −/− MEFs cultured in full-media or EBSS with less than 5, 5—15, or more than 15 γ-H2AX foci was quantified. At least 300 MEFs were counted for each condition. * indicates p < 0.05, ** indicates p < 0.01. (C) Western blot analysis was performed to assay the levels of γ-H2AX. The experiments were repeated 3 times.
MEFs lacking Klf4 exhibit suppressed autophagy level due to mTOR hyperactivity
A previous study of vascular smooth muscle cells has shown that transient knockdown of Klf4 led to increased levels of mTOR downstream targets [35]. Consequently we investigated whether the impaired autophagy in Klf4 −/− MEFs could be due to mTOR hyperactivity. To test our hypothesis, we first transfected Klf4 +/+ and Klf4 −/− MEFs with GFP-LC3B plasmid and treated both MEFs with rapamycin, a known inhibitor of mTOR. The induction of autophagy correlates with the conversion of diffused LC3I in the cytoplasm to LC3II which localized to the autophagosome and results in punctate pattern [24]. Thus the levels of autophagy were visualized under a fluorescence microscope and quantified by the percentage of GFP-LC3B puncta. Consistent with Figures 1B—C, Klf4 −/− MEFs displayed lower basal levels of autophagy compared to Klf4 +/+ MEFs (Figures 4A—B). While rapamycin increased the levels of autophagy in Klf4 +/+ MEFs, no significant increase of LC3 puncta was observed Klf4 −/− MEFs (p = 0.249). Thus rapamycin was unable to restore the reduced levels of autophagy in MEFs lacking Klf4 (Figures 4A—B). The molecular effect of rapamycin treatment was also analyzed by Western blot for assay of mTOR activity. At the basal level, phosphorylated p70S6K increased in Klf4 −/− MEFs compared to the wild-type, suggesting that the mTOR pathway in Klf4 −/− MEFs was hyperactive (Figure 4C). The elevated level of phosphorylated p70S6K was effectively abolished in response to rapamycin in both cell lines (Figure 4C). Interestingly, suppression of the hyperactive mTOR pathway by rapamycin restored the levels of autophagy in wild-type but not in Klf4-null MEFs (Figure 4C).
Rapamycin induced autophagy in Klf4 +/+ but not Klf4 −/− MEFs. (A) Klf4 +/+ and Klf4 −/− MEFs were seeded to 50-70% confluence and transfected with GFP-LC3. Five hours post-transfection, MEFs were treated with 100 nM rapamycin or DMSO for 24 hrs. (B) The percentage of cells in (A) positive for GFP-LC3B puncta was quantified. Error bars represent standard error. The experiments were repeated 3 times. * indicates p < 0.05, ** indicates p < 0.01. No significant difference in the levels of LC3II was observed in Klf4 −/− MEFs treated with either DMSO or rapamycin (p = 0.249). (C) Klf4 +/+ and Klf4 −/− MEFs were treated with rapamycin of indicated dosages or DMSO for 24 hrs. Cell lysates were analyzed by Western blot using antibodies against phospho-p70S6K and LC3B. β-Actin was used as a loading control. The experiments were repeated 3 times.
Knockdown of Klf4 reduces autophagy levels and makes MEFs resistant to the effects of rapamycin
In order to examine whether KLF4 was necessary for autophagy induction, we attempted to transiently silence Klf4 expression using siRNA against Klf4 in wild-type MEFs. Figure 5A confirmed the successful knockdown of Klf4 and the downregulation of its downstream target p21. Supporting our earlier observation in Klf4-null cells, knockdown of Klf4 in wild-type MEFs significantly reduced autophagy level (Figures 5B&C). More importantly, when Klf4 expression was abolished, rapamycin failed to induce autophagy even though it effectively suppressed the mTOR pathway, as indicated by the reduced levels of phospho-p70S6K (Figures 5B—D).
Klf4 knockdown leads to decreased autophagy levels and elevated mTOR activity. (A) Klf4 expression was inhibited by treating Klf4 +/+ MEFs with indicated concentrations of siRNA. Proteins were extracted from the cells 24 hrs after siRNA treatment. The levels of KLF4 and p21, a downstream target of KLF4, were assessed using Western blot. (B) Klf4 +/+ MEFs were treated with control siRNA or Klf4 siRNA complex. Five hours post transfection, transfection media was replaced with full-media that contained 100 nM rapamycin or DMSO as a control. Proteins were extracted 24 hrs after rapamycin treatment and Western blot analysis was performed to assay phospho-p70S6K and LC3 levels. (C) Densitometry analysis of LC3B bands shown in (B). The intensities of LC3BII bands were normalized to that of β-actin using Gel Imager program (Bio-Rad Laboratories, Hercules, CA). Error bars represent standard error. The experiments were repeated 3 times. * indicates p < 0.05, ** indicates p < 0.01. (D) Densitometry analysis of phospho-p70S6K bands shown in (B). The intensities of phospho-p70S6K bands were normalized to that of β-Actin using Gel Imager program. Error bars represent standard error. The experiments were repeated 3 times. * indicates p < 0.05.
Klf4 re-expression in Klf4-null MEFs increases autophagy and decreases mTOR activity
To examine whether KLF4 was sufficient for autophagy induction, we reintroduced Klf4 to Klf4 −/− MEFs. Re-expression of Klf4 in Klf4 −/− MEFs was confirmed via fluorescence microscopy by examining the green fluorescence protein (GFP) signal conjugated to Klf4 and via Western blot by assessing the level of p21 (Figures 6A—B). Reintroduction of Klf4 suppressed the downstream mTOR target, phospho-p70S6K, and induced LC3I to LC3II conversion, whereas mock treatment and GFP expression had a minimal effect on the level of phospho-p70S6K and autophagy (Figures 6C—D). In order to investigate the mechanism by which KLF4 mediates the conversion of LC3I to LC3II, we assayed the expression level of Atg7, which acts as an E1 enzyme to mediate the conversion from LC3I to LC3II [26]. Under normal conditions, no difference in Atg7 expression was observed between Klf4 +/+ and Klf4 −/− MEFs possibly due to minimal induction of autophagy when nutrients were optimal (Figure 6E). However, when KLF4 was reintroduced to Klf4 −/− MEFs, the expression of Atg7 was upregulated, similar to that of the known KLF4 downstream transcription target, Cdkn1a which encodes a cyclin-dependent kinase inhibitor, p21. (Figure 6 F). Our data thus suggested that KLF4 might be involved in the autophagy process by regulating Atg7 expression level.
Overexpression of Klf4 in Klf4-null MEFs restores autophagy levels. Klf4 −/− MEFs were transfected with mock media, GFP, or Klf4-GFP plasmids. (A) GFP signal was visualized under an Olympus IX51 microscope. Proteins were extracted 24 hrs after transfection. The levels of p21 (B) phospho-p70S6K and LC3 (C) were assayed with Western blot analysis. (D) Densitometry analysis of LC3B bands shown in (C). The intensities of LC3BII bands were normalized to that of β-actin using Gel Imager program. Error bars represent standard error. The experiments were repeated 3 times. * indicates p < 0.05. (E) RT-qPCR was performed to assess the expression of Cdkn1a as a positive control and Atg7 at the basal level. The level of Cdkn1a or Atg7 was normalized to β-Actin. The normalized expression level of Cdkn1a and Atg7 was shown as relative fold change of the gene expression level in wild-type. (F) RT-qPCR was performed to assess the expression of Cdkn1a as a positive control and Atg7 in Klf4 −/− MEFs transfected with Klf4. The level of Cdkn1a or Atg7 was normalized to β-Actin. The normalized expression level of Cdkn1a and Atg7 was represented as relative fold change of the gene expression level in GFP alone or Klf4 −/− MEFs transfected with Klf4-GFP. The experiment was done twice each in triplicate.
Discussion
It has been well-established that KLF4 acts as a tumor suppressor in many types of cancers [3–5,7,36]. One way KLF4 exerts its anti-tumorigenic function is by initiating cell cycle checkpoints during DNA damage and mediating p53 transactivation of p21 [13,37]. In addition to its role in inducing cell cycle arrest, we have also shown that KLF4 maintains genomic stability [10,14]. MEFs lacking Klf4 have higher levels of genomic instability including DNA double stranded breaks, centrosome amplification as well as aneuploidy [10]. Restoration of KLF4 to Klf4 −/− MEFs significantly reduces DNA damage and aneuploidy [14]. More recently we have demonstrated that KLF4 reduces genomic instability by regulating antioxidant genes and reducing reactive oxygen species (ROS) [11].
Autophagy is a process by which long-lived proteins and organelles in the cytoplasm are degraded and recycled for cellular use. It can be triggered during nutrient deprivation and stress, but also plays an important role against the progression of some human diseases including cancer, infections, and neurodegenerative diseases [38]. A growing body of evidence shows connections between autophagy and genomic instability [17–22,33]. Autophagy removes misfolded proteins and damaged organelles to prevent cells from inducing the production of ROS [39,40]. As a result, cells deficient for genes required for autophagy exhibit higher genomic instability [33,40]. Furthermore, previous studies have shown that cells with defective autophagy due to hyperactive mTOR activity exhibited increased sensitivity to DNA damage agents [41].
We propose here that MEFs deficient in Klf4 expression exhibit impaired autophagy (Figure 1). Moreover, MEFs lacking Klf4 exhibit higher levels of DNA damage upon starvation as compared to wild-type MEFs (Figure 3). Our results are in accord with previous findings that impaired autophagy predisposes cells to genomic instability during metabolic stress [33,41]. We have previously proposed that KLF4 reduces oxidative DNA damage and reactive oxygen species by regulation of antioxidant genes [11]. In addition to our previously proposed mechanism, genomic instability in Klf4-null MEFs might also be attributed to impaired autophagy. Previous reports indicated that when normal cells are challenged with metabolic stress, autophagy is activated and damaged intracellular components are removed via lysosomes, alleviating stress [42]. Defective autophagy could lead to accumulation of malfunctioning mitochondria, which often causes increased production of ROS [42]. Thus the impairment of autophagy in Klf4 −/− MEFs may result in failure to mitigate metabolic stress and therefore could lead to accumulation of genomic instability. Our current study suggests that in addition to the initiation of cell cycle checkpoints, KLF4 might maintain genomic stability through the induction of autophagy, and that the regulation of autophagy may be a novel mechanism by which KLF4 prevents tumorigenesis.
We have previously reported that MEFs lacking Klf4 experience higher rates of apoptosis compared to wild-type cells [10]. Consistent with our previous finding, we showed here that Klf4 −/− MEFs are more prone to apoptosis under starvation by EBSS (Figure 2). Our data thus strongly argues for a prosurvival role of autophagy under cellular stress. While autophagy helps wild-type cells to recycle nutrients and survive nutrient deprivation, Klf4 −/− MEFs could be more sensitive to starvation because of impaired autophagy and thus they are unable to optimize cellular nutrients. This is in accord with previous findings which report that inhibition of autophagy in MCF cells and Tsc −/− MEFs increases apoptosis [43,44].
Next, we attempted to investigate the molecular mechanism by which KLF4 participates in autophagy induction. mTOR negatively regulates the induction of autophagy by responding to nutrient as well as growth factor deprivation [29]. A study in vascular smooth muscle cells found that overexpression of Klf4 reduced mTOR activity while transient silencing of Klf4 led to increased mTOR activity [35]. Furthermore, knockdown of elF4GI, a downstream target of mTOR, led to increased levels of KLF4 and induced autophagy [45]. We thus hypothesized that reduced autophagy levels in Klf4 −/− MEFs could be due to mTOR hyperactivity. Supporting the findings in vascular smooth muscle cells, we report that MEFs lacking Klf4 showed higher basal levels of mTOR activity (Figure 3C). Transient knockdown of Klf4 led to elevated mTOR activity while restoration of Klf4 into Klf4 −/− MEFs reduced mTOR activity (Figures 4—5). These findings thus suggest that KLF4 negatively regulates mTOR in MEFs (Figure 7).
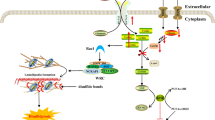
Diagraphic illustration of involvement of Klf4 in autophagy to prevent DNA damage induced apoptosis. This illustration outlines the regulation of autophagy in Klf4 proficient and deficient cells during stress and places our results in the context of known and potential relationships between KLF4, mTOR, autophagy, DNA damage and apoptosis. Based on the present study and as previously shown in [35], in wild-type MEFs, KLF4 is induced under stress and might induce autophagy in mTOR dependent or independent manners. Autophagy then removes damaged cellular components and prevents DNA damage as well as apoptosis (A). On the other hand, in MEFs lacking Klf4, autophagy induction is impaired due to mTOR hyperactivity and other unknown mechanisms. As a result, under starvation stress impaired autophagy promotes DNA damage and leads to increased apoptosis (B). KLF4 might induce autophagy by negatively regulating mTOR. However, KLF4 may also regulate autophagy in an mTOR-independent mechanism, possibly involving regulations of autophagy-related genes such as Atg7.
One interesting observation of our study is that upon addition of rapamycin to wild-type and Klf4-null MEFs the mTOR pathway is highly downregulated. However, pharmacological induction of autophagy with rapamycin increases levels of autophagy only in Klf4 wild-type, but not Klf4-null MEFs (Figures 4C&5B). This impairment of autophagy can be effectively rescued by transient expression of Klf4 in the Klf4-null MEFs. This suggests that mTOR hyperactivity alone is not the only cause of the impaired autophagy in Klf4 −/− MEFs. One possibility is that KLF4 regulates autophagy via mTOR independent mechanisms potentially through autophagy-related genes (Atgs). We thus attempted to examine the expression of Atg7, a gene important for autophagosome expansion, and its knockdown prevented the conversion from LC3I to LC3II [44]. Our data supported this hypothesis, as restoration of KLF4 into Klf4 −/− MEFs led to upregulation of Atg7 expression (Figure 6 F). This suggested that during starvation, KLF4 might mediate the transcription of Atg7 to induce autophagy. However, whether KLF4 regulates Atg7 via direct or indirect interaction awaits further investigation. Additionally our data did not eliminate the possibility that KLF4 might induce autophagy by regulating other autophagy-related genes. Our previous microarray data showed that Klf4 −/− MEFs exhibited enriched expression of autophagy related gene 3 (Atg3) [46]. However, we were not able to validate the microarray data via RT-PCR, as no difference was observed between Klf4 +/+ and Klf4 −/− MEFs at the mRNA level (data not shown). Therefore, future studies remain necessary to understand the possible downstream targets through which KLF4 regulates autophagy.
Conclusion
In summary, the present study suggested that MEFs lacking Klf4 exhibited impaired autophagy, which resulted in their higher sensitivity to nutrient deprivation and increased apoptosis. This impaired autophagy in Klf4 −/− MEFs could be explained partially by mTOR hyperactivity, as KLF4 negatively regulates mTOR. However, other means by which KLF4 regulates autophagy independently of mTOR may exist and future studies should be devoted to shed light on these molecular mechanisms. The high level of DNA damage observed in Klf4 −/− MEFs during starvation could indicate that KLF4 is required to maintain genomic stability during metabolic and oxidative stress. Collectively, these findings provide new insights into the mechanism by which KLF4 maintains genomic stability and protects the cells from apoptosis (Figure 7).
Materials and Methods
Cell Culture, Reagents and Drug Treatments
Mice heterozygous for the Klf4 alleles (Klf4+/−) on a C57BL/6 background were crossbred [47]. MEFs that are wild-type (Klf4 +/+), heterozygous (Klf4 +/−), or null (Klf4 −/−) for Klf4 were derived from day 13.5 embryos. MEFs were subsequently cultured in Dulbecco’s modified Eagle’s medium (DMEM) supplemented with 10% fetal bovine serum and 1% penicillin-streptomycin at 37 °C in atmosphere containing 5% CO2. Cells were passed every 3 days at a density of 106 cells per 10-cm dish following the 3 T3 protocol. All experiments were performed on spontaneously immortalized primary MEFs post-senescence after passage 20 at 50-70% confluence. For starvation experiments MEFs were incubated for the indicated time in EBSS. Rapamycin and chloroquine diphosphate (CQ) were used to inhibit mTOR and autophagy respectively. EBSS (E2888), chloroquine diphosphate and rapamycin were purchased from (Sigma Aldrich St. Louis, MO).
siRNA Transfection
Klf4 +/+ MEFs were grown to 60% confluency in a 6-well plate before siRNA transfection. siRNA against Klf4 was obtained as Silencer® Select siRNA against Klf4 (Life Technologies, Grand Island, NY, USA) and dissolved to a stock solution of 50 μM with water. MEFs were transfected with up to 10 nM siRNA against Klf4 or negative control siRNA provided by the manufacturer using Lipofectamine 3000 (Life Technologies, Grand Island, NY, USA) as the transfection reagent following the manufacturer’s protocol after 24 hrs for collection for analysis.
Plasmid Transfection
To overexpress Klf4, MEFs were transiently transfected with 4 μg DNA plasmids containing Klf4-GFP or GFP as a control in 6-well plate. Lipofectamine 3000 reagent (Life Technologies, Grand Island, NY, USA) was used following manufacturer’s protocol. Cells were photographed and collected for immunoblotting after indicated time. Transfection efficiency was examined under an Olympus IX51 microscope for GFP fluorescence 24 hrs post transfection. To study the role of KLF4 in autophagy, we transiently transfected Klf4 +/+ and Klf4 −/− MEFs with EGFP-LC3 plasmids and cells were treated with either DMSO or rapamycin for 6 hrs. The percentage of cells with punctate pattern of EGFP-LC3B was counted by fluorescence microscopy. The EGFP-LC3 was obtained from Addgene, Incorporated (plasmid 11546) [48] and constructed in the laboratory of K. Kirkegaard, Stanford University. Transfection efficiency was about 40% by visualizing GFP signal under fluorescent microscope. Transfection resulted in an overexpression of KLF4 in both Klf4 +/+ and Klf4 −/− MEFs as indicated by Western blot (Additional file 2 Figure S2). The overexpression of Klf4 was comparable to a previous report [14].
Western blot analysis
Cell protein extraction and Western blot analyses were performed using standard procedures. Briefly, protein samples were prepared by lysing cells with 100 mM Tris–HCl, pH 6.8, 2% SDS, 100 mM dithiothreitol, 0.01% bromphenol blue, and 10% glycerol and heating to 98 °C for 5 min to denature the proteins. The proteins were loaded into Mini-PROTEAN® TGX™ Precast Gels (Bio-Rad Laboratories, Hercules, CA) in Tri/Glycine/SDS buffer (Bio-Rad Laboratories, Hercules, CA). After electrophoresis, the SDS-polyacrylamide gel was transferred to a nitrocellulose membrane in Tris/glycine transfer buffer (Bio-Rad Laboratories, Hercules, CA) with 10% methanol. The membranes were immunoblotted with the following primary antibodies against: LC3, KLF4, β-Actin (Abcam, Cambridge, MA, USA), p21 (BD Pharmingen, Franklin Lakes, NJ, USA), and phospho-p70S6K and γ-H2AX (Cell Signaling, Danvers, MA, USA). The blots were then incubated with the appropriate horseradish peroxidase-conjugated secondary antibodies for 1 h at room temperature. Anti-rabbit secondary antibody and anti-mouse secondary antibody were purchased from Cell Signaling (Danvers, MA, USA) and Abcam (Cambridge, MA, USA), respectively. The antibody-antigen complex was visualized by an Immun-Star™ HRP Chemiluminescence Kit and ChemiDoc™ XRS+ System (Bio-Rad Laboratories, Hercules, CA). The intensities of the bands were quantified using volume tools in Gel Imager program by normalizing the band intensity of protein of interest to that of β-Actin.
Trypan Blue Assay
MEFs with indicated treatments were trypsinized and resuspended in PBS. Resuspended MEFs were mixed with 0.4% Trypan Blue solution (Sigma Aldrich St. Louis, MO) and let stain for 5 min at room temperature. The number of stained MEFs was then quantified with a hemocytometer under bright field under a microscope.
Flow Cytometry
Flow cytometry to quantify apoptotic cell population was performed as previously described [10]. Briefly, Klf4 +/+ and Klf4 −/− MEFs were plated in 6-well plates at 105 cells/well. The next day cells were treated with full media, 10 μM CQ, EBSS or both 10 μM CQ and EBSS. After 8 hours treatment, cells were rinsed in PBS, trypsinized, and pelleted. Cells were fixed in 70% ethanol in PBS and incubated −20 °C overnight. The fixed cells were pelleted and resuspended in PBS that contain 50 mg/ml propidium iodide, 50 mg/ml RNase A, 0.1% Triton X-100 and 0.1 mM ethylene diaminetetraacetic acid at room temperature for 30 min before analysis. Cell-cycle profile analysis was performed on analyzed with a BD Accuri™ D Biosciences C6 Flow Cytometer (San Jose, CA, USA). Cellular debris was gated out of the analysis using forward and side scatter (Additional file 3 Figure S3). Apoptotic cells were identified by their sub-G1 DNA content.
Immunostaining
Immunostaining was carried out as previously described with modification [14]. MEFs grown on chamber slides were washed briefly with PBS. They were then fixed with 3.7% methanol-free formaldehyde for 30 min at room temperature. MEFs were washed three times with PBS and incubated with blocking solution (3% bovine serum albumin (BSA), 0.2% Triton X-100 in PBS) for 1 h at room temperature. Rabbit anti-γ-H2AX primary antibody (Cell Signaling) diluted in blocking solution was incubated at room temperature for an hour. Primary antibody was detected with Alexa Fluor 488- conjugated goat anti-rabbit IgG antibody (Santa Cruz) for 1 h at room temperature. Cells were then washed once and counterstained with DAPI (Life Technologies) for 5 min at room temperature in the dark. Finally cells were washed three times, mounted in Prolong Antifade kit (Molecular Probes), and visualized with a Zeiss 710 confocal laser scanning microscope (Carl Zeiss, Thornwood, NY). The validity of the immunostaining signal was confirmed by the negative control, which was not incubated in primary antibody, and the positive control, which was treated with etoposide to induce DNA damage (Additional file 4 Figure S4).
Quantitative real-time PCR analysis
Total RNA from cultured Klf4 +/+ and Klf4 −/− MEFs was isolated using RNeasy1 Mini Kit (Qiagen, Valencia, CA) according to the manufacturer’s protocol. RNA was subjected to gDNA elimination columns (Qiagen, Valencia, CA) in order to remove any contaminating genomic DNA. cDNA was prepared from 500 ng of RNA and amplified with Omniscript RT Kit (Qiagen) and polyT primer (Integrated DNA Technologies, Coralville, IA). Synthesized cDNA was subjected for RT-qPCR analysis using SYBR® Green PCR Master Mix for 40 cycles (Life Technologies) following manufacturer’s protocol. The expression of Cdkn1a or Atg7 was normalized to the expression level of β-Actin. Relative fold change in gene expression level was calculated by comparing the normalized gene expression in Klf4 −/− MEFs to that in Klf4 +/+ MEFs, or comparing the Klf4-transfected MEFs to GFP-transfected MEFs. The gene expression levels of Klf4 +/+ or GFP-transfected MEFs were set to 1. Data shown represents two independent experiments, each performed in triplicates. PCR reactions were performed using the following primers purchased from Integrated DNA Technologies (Coralville, IA). Atg7 F: 5’ TCT GGG AAG CCA TAA AGT CAG G 3’; Atg7 R: 5’ GCG AAG GTC AGG AGA A 3’; Cdkn1a F: 5’ ATC ACC AGG ATT GGA CAT GG 3’; Cdkn1a R: 5’ CGG TGT CAG AGT CTA GGG GA 3’; β-Actin F: 5’ ATG GAG GGG AAT ACA GCC C 3’; β-Actin R: 5’ TTC TTT GCA GCT CCT TCG TT 3’.
Statistics
All experiments were done independently at least three times unless otherwise indicated. Student’s t-test was used to analyze statistical significance. P-values lower than 0.05 were considered significant.
Abbreviations
- BSA:
-
Bovine serum albumin
- CQ:
-
Chloroquine Diphosphate
- DAPI:
-
4’,6-Diamidino-2-phenylindol
- DMEM:
-
Dulbecco’s modified Eagle’s Medium
- DMSO:
-
Dimethyl sulfoxide
- EBSS:
-
Earle’s Balanced Salt Solution
- FBS:
-
Fetal bovine serum
- GFP:
-
Green fluorescent protein
- KLF4:
-
Krüppel-like factor 4
- LC3:
-
Light chain 3
- MEFs:
-
Mouse embryonic fibroblasts
- mTOR:
-
Mammalian target of rapamycin
- PBS:
-
Phosphate buffered saline
- ROS:
-
Reactive oxygen species
- ATG:
-
Autophagy-related genes.
- Cdkn1a:
-
Cyclin-dependent kinase inhibitor 1A
References
Shields JM, Christy RJ, Yang VW. Identification and characterization of a gene encoding a gut-enriched Kruppel-like factor expressed during growth arrest. J Biol Chem. 1996;271:20009–17.
Garrett-Sinha LA, Eberspaecher H, Seldin MF, de Crombrugghe B. A Gene for a Novel Zinc-finger Protein Expressed in Differentiated Epithelial Cells and Transiently in Certain Mesenchymal Cells. J Biol Chem. 1996;271:31384–90.
Ohnishi S, Ohnami S, Laub F, Aoki K, Suzuki K, Kanai Y, et al. Downregulation and growth inhibitory effect of epithelial-type Krüppel-like transcription factor KLF4, but not KLF5, in bladder cancer. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2003;308:251–6.
Hu W, Hofstetter WL, Li H, Zhou Y, He Y, Pataer A, et al. Putative tumor-suppressive function of Kruppel-like factor 4 in primary lung carcinoma. Clin Cancer Res. 2009;15:5688–95.
Zammarchi F, Morelli M, Menicagli M, Di Cristofano C, Zavaglia K, Paolucci A, et al. KLF4 is a novel candidate tumor suppressor gene in pancreatic ductal carcinoma. Am J Pathol. 2011;178:361–72.
Wei D, Kanai M, Huang S, Xie K. Emerging role of KLF4 in human gastrointestinal cancer. Carcinogenesis. 2006;27:23–31.
Zhao W, Hisamuddin IM, Nandan MO, Babbin BA, Lamb NE, Yang VW. Identification of Krüppel-like factor 4 as a potential tumor suppressor gene in colorectal cancer. Oncogene. 2004;23:395–402.
Foster KW, Frost AR, Mckie-bell P, Lin C, Engler JA, Grizzle WE, et al. Increase of GKLF Messenger RNA and Increase of GKLF messenger RNA and protein expression during progression of breast cancer. Cancer Res. 2000;60:6488–95.
Foster KW, Liu Z, Nail CD, Li X, Fitzgerald TJ, Bailey SK, et al. Induction of KLF4 in basal keratinocytes blocks the proliferation-differentiation switch and initiates squamous epithelial dysplasia. Oncogene. 2005;24:1491–500.
Hagos EG, Ghaleb AM, Dalton WB, Bialkowska AB, Yang V. Mouse embyronic fibroblasts null for Kruppel-like factor 4 gene are genetically unstable. Oncogene. 2009;28:1197–205.
Liu C, La Rosa S, Hagos EG. Oxidative DNA damage causes premature senescence in mouse embryonic fibroblasts deficient for Krüppel-like factor 4. Mol Carcinog. 2014, April 30 doi: 10.1002/mc.22161.
Evans PM, Liu C. Roles of Krüppel-like factor 4 in normal homeostasis, cancer and stem cells. Acta Biochim Biophys Sin (Shanghai). 2008;40:554–64.
Yoon HS, Chen XYV. Kruppel-like factor 4 mediates p53-dependent G1/S cell cycle arrest in response ot DNA damage. J Biol Chem. 2003;278:2101–5.
El-Karim EA, Hagos EG, Ghaleb AM, Yu B, Yang VW. Krüppel-like factor 4 regulates genetic stability in mouse embryonic fibroblasts. Mol Cancer. 2013;12:89.
Yang Z, Klionsky DJ. Eaten alive: a history of macroautophagy. Nat Cell Biol. 2010;12:814–22.
Rabinowitz JD, White E. Autophagy and metabolism. Science. 2010;330:1344–8.
Mathew R, White E. Role of autophagy in cancer. Nat Rev Cancer. 2010;7:961–7.
Qu X, Yu J, Bhagat G. Promotion of tumorigenesis by heterozygous disruption of the beclin 1 autophagy gene. J Clin Invest. 2003;112:1809–20.
Yue Z, Jin S, Yang C, Levine AJ, Heintz N. Beclin 1, an autophagy gene essential for early embryonic development, is a haploinsufficient tumor suppressor. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2003;100:15077–82.
Mariño G, Salvador-Montoliu N, Fueyo A, Knecht E, Mizushima N, López-Otín C. Tissue-specific autophagy alterations and increased tumorigenesis in mice deficient in Atg4C/autophagin-3. J Biol Chem. 2007;282:18573–83.
Mathew R, White E. Autophagy in tumorigenesis and energy metabolism: friend by day, foe by night. Curr Opin Genet Dev. 2011;21:113–9.
Mathew R, Kongara S. Autophagy suppresses tumor progression by limiting chromosomal instability. Genes Dev. 2007;21:1367–81.
Kabeya Y, Mizushima N, Yamamoto A, Oshitani-Okamoto S, Ohsumi Y, Yoshimori T. LC3, GABARAP and GATE16 localize to autophagosomal membrane depending on form-II formation. J Cell Sci. 2004;117:2805–12.
Kabeya Y, Mizushima N, Ueno T, Yamamoto A, Kirisako T, Noda T, Kominami E, Ohsumi Y, Yoshimori. LC3, a mammalian homologue of yeast Apg8p, is localized in autophagosome membranes after processing. EMBO J. 2000;19:5720–5728.
Geng J, Klionsky DJ. The Atg8 and Atg12 ubiquitin-like conjugation systems in macroautophagy. “Protein modifications: beyond the usual suspects” review series. EMBO Rep. 2008;9:859–64.
Glick D, Barth S, Macleod KF. Autophagy: cellular and molecular mechanisms. J Pathol. 2010;221:3–12.
Hay N, Sonenberg N. Upstream and downstream of mTOR. Genes Dev. 2004;18:1926–45.
Mehrpour M, Esclatine A, Beau I, Codogno P. Overview of macroautophagy regulation in mammalian cells. Cell Res. 2010;20:748–62.
Jung CH, Ro S-H, Cao J, Otto NM, Kim D-H. mTOR regulation of autophagy. FEBS Lett. 2010;584:1287–95.
Sato T, Nakashima A, Guo L, Coffman K, Tamanoi F. Single amino-acid changes that confer constitutive activation of mTOR are discovered in human cancer. Oncogene. 2010;29:2746–52.
Gulhati P, Cai Q, Li J, Liu J, Rychahou PG, Qiu S, et al. Targeted inhibition of mammalian target of rapamycin signaling inhibits tumorigenesis of colorectal cancer. Clin Cancer Res. 2009;15:7207–16.
Mizushima N, Yoshimori T, Levine B. Methods in mammalian autophagy research. Cell. 2010;140:313–26.
Karantza-Wadsworth V, Patel S, Kravchuk O, Chen G, Mathew R, Jin S, et al. Autophagy mitigates metabolic stress and genome damage in mammary tumorigenesis. Genes Dev. 2007;21:1621–35.
Roos WP, Kaina B. DNA damage-induced cell death by apoptosis. Trends Mol Med. 2006;12:440–50.
Wang Y, Zhao B, Zhang Y, Tang Z, Shen Q, Zhang Y, et al. Krüppel-like factor 4 is induced by rapamycin and mediates the anti-proliferative effect of rapamycin in rat carotid arteries after balloon injury. Br J Pharmacol. 2012;165:2378–88.
Wei D, Gong W, Kanai M. Drastic down-regulation of Krüppel-like factor 4 expression is critical in human gastric cancer development and progression critical in human gastric cancer development and progression. Cancer Res. 2005;65:2746–54.
Zhang W, Geiman D, Shields J. The gut-enriched Krüppel-like factor (Krüppel-like factor 4) mediates the transactivating effect of p53 on the p21 WAF1/Cip1 promoter. J Biol Chem. 2000;275:18391–8.
Levine B, Kroemer G. Autophagy in the pathogenesis of disease. Cell. 2008;132:27–42.
Rosenfeldt MT, Ryan KM. The multiple roles of autophagy in cancer. Carcinogenesis. 2011;32:955–63.
Komatsu M, Waguri S, Ueno T, Iwata J, Murata S, Tanida I, et al. Impairment of starvation-induced and constitutive autophagy in Atg7-deficient mice. J Cell Biol. 2005;169:425–34.
Wang Y, Hu Z, Liu Z, Chen R, Peng H, Guo J, et al. MTOR inhibition attenuates DNA damage and apoptosis through autophagy-mediated suppression of CREB1. Autophagy. 2013;9:2069–86.
Jin S. Autophagy, mitochondrial quality control, and oncogenesis. Autophagy. 2006;2:80–84.
Abedin MJ, Wang D, McDonnell MA, Lehmann U, Kelekar A. Autophagy delays apoptotic death in breast cancer cells following DNA damage. Cell Death Differ. 2007;14:500–10.
Ng S, Wu Y, Chen B, Zhou J, Shen H. Impaired autophagy due to constitutive mTOR activation sensitizes TSC2-null cells to cell death under stress. Autophagy. 2011;3:1173–86.
Ramírez-Valle F, Braunstein S, Zavadil J, Formenti SC, Schneider RJ. eIF4GI links nutrient sensing by mTOR to cell proliferation and inhibition of autophagy. J Cell Biol. 2008;181:293–307.
Hagos EG, Ghaleb AM, Kumar A, Neish AS, Yang VW. Expression profiling and pathway analysis of Krüppel-like factor 4 in mouse embryonic fibroblasts. Am J Cancer Res. 2011;1:85–97.
Katz JP, Perreault N, Goldstein BG, Lee CS, Labosky PA, Yang VW, et al. The zinc-finger transcription factor Klf4 is required for terminal differentiation of goblet cells in the colon. Development. 2002;129:2619–28.
Jackson WT, Giddings TH, Taylor MP, Mulinyawe S, Rabinovitch M, Kopito RR, et al. Subversion of cellular autophagosomal machinery by RNA viruses. PLoS Biol. 2005;3:0861–71.
Acknowledgements
This work was supported in part by Picker Research Fellowship and Major Grant from Colgate University Research Council. We acknowledge the lab of Dr. Vincent W. Yang (Stony Brook Medical School, NY) for providing KLF4-GFP and GFP constructs. The authors would also like to thank Dr. Kenneth Belanger for critically reviewing the manuscript.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Competing interests
None of the authors had any competing financial interests in relation to the work described.
Author’s contributions
CL carried out the all the experimental studies, participated in the design of the study and drafted the manuscript. EPD and CS. participated in siRNA transfections and in western blots. MW carried out EBSS treatment and microscope imaging. MS participated in plasmid transfections, flow cytometry and statistical analysis. EH conceived of the study, participated in its design and coordination, carried out cell transfections, immune-staining, microscope imaging, and Western blots, and drafted the manuscript. All authors read and approved the final manuscript.
Additional files
Additional file 1: Figure S1.
Morphology and relative number of cells in MEFs. Klf4 +/+ and Klf4 −/− MEFs incubated in full-media (FM) were allowed to seed for 24 hours. Cells then were photographed using Olympus IX51 microscope at 2, 4, 8, 12, and 24 hours. Showing is relative numbers of cells under different confluency.
Additional file 2: Figure S2.
Klf4-GFP plasmid overexpression in MEFs. Transfection resulted in an overexpression of KLF4 in MEFs as indicated by western blot (A) wild-type (B) Klf4-null. We compared the levels of KLF4 in Klf4 +/+ and Klf4 −/− MEFs that transfected with either Klf4-GFP or GFP as a control. The expression of KLF4 is highly increased in both Klf4 +/+ and Klf4 −/− MEFs that transfected with Klf4-GFP as compared to GFP-control-transfected Klf4 +/+ and Klf4 −/− MEFs (Lane A1 and Lane B3). Endogenous levels of Klf4 showed at 55 KD where as Klf4 conjugated with GFP showed at 82 KD (A). Materials and Methods Plasmid were constructed as previously described in [14].
Additional file 3: Figure S3.
Flow cytometry analysis of MEFs. Flow cytometry studies were performed in MEFs as described in Materials and Methods. Briefly, Klf4 +/+ and Klf4 −/− MEFs were plated in 6-well plates at 105 cells/well. The next day cells were treated with full media, 10 μM CQ, EBSS or both 10 μM CQ and EBSS. Cellular debris was gated out of the analysis using forward and side scatter to prevent against cellular debris from interfering with the quality of our results. Klf4 +/+ (A - D) and Klf4 −/− (E - H) .
Additional file 4: Figure S4.
Control for immunofluorescence labeling. Immunofluorescence studies were performed in MEFs as described in Materials and Methods. Cells were counterstained with DAPI to visualize the nuclei. MEFs were exposed to etoposide for 5 hours and collected for γH2AX (A) immunostaining and (B) western blot. MEFs treated with etoposide for 5hrs to acquired greater levels of DNA damage as compared with DMSO treated control MEFs as indicated by γH2AX (lanes 1 and 2). An increase in γH2AX immunostaining was also observed as positive control. The validity of the immunostaining signal was confirmed by the negative control, which was not incubated in primary antibody.
Rights and permissions
This article is published under an open access license. Please check the 'Copyright Information' section either on this page or in the PDF for details of this license and what re-use is permitted. If your intended use exceeds what is permitted by the license or if you are unable to locate the licence and re-use information, please contact the Rights and Permissions team.
About this article
Cite this article
Liu, C., DeRoo, E.P., Stecyk, C. et al. Impaired autophagy in mouse embryonic fibroblasts null for Krüppel-like Factor 4 promotes DNA damage and increases apoptosis upon serum starvation. Mol Cancer 14, 101 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1186/s12943-015-0373-6
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1186/s12943-015-0373-6