Abstract
Background
Poly(3-hydroxybutyrate) (PHB), a biodegradable bio-plastic, is one of the most common homopolymer of polyhydroxyalkanoates (PHAs). PHB is synthesized by a variety of microorganisms as intracellular carbon and energy storage compounds in response to environmental stresses. Bio-based production of PHB from renewable feedstock is a promising and sustainable alternative to the petroleum-based chemical synthesis of plastics. In this study, a novel strategy was applied to improve the PHB biosynthesis from different carbon sources.
Results
In this research, we have constructed E. coli strains to produce PHB by engineering the Serine-Deamination (SD) pathway, the Entner-Doudoroff (ED) pathway, and the pyruvate dehydrogenase (PDH) complex. Firstly, co-overexpression of sdaA (encodes L-serine deaminase), L-serine biosynthesis genes and pgk (encodes phosphoglycerate kinase) activated the SD Pathway, and the resulting strain SD02 (pBHR68), harboring the PHB biosynthesis genes from Ralstonia eutropha, produced 4.86 g/L PHB using glucose as the sole carbon source, representing a 2.34-fold increase compared to the reference strain. In addition, activating the ED pathway together with overexpressing the PDH complex further increased the PHB production to 5.54 g/L with content of 81.1% CDW. The intracellular acetyl-CoA concentration and the [NADPH]/[NADP+] ratio were enhanced after the modification of SD pathway, ED pathway and the PDH complex. Meanwhile, these engineering strains also had a significant increase in PHB concentration and content when xylose or glycerol was used as carbon source.
Conclusions
Significant levels of PHB biosynthesis from different kinds of carbon sources can be achieved by engineering the Serine-Deamination pathway, Entner-Doudoroff pathway and pyruvate dehydrogenase complex in E. coli JM109 harboring the PHB biosynthesis genes from Ralstonia eutropha. This work demonstrates a novel strategy for improving PHB production in E. coli. The strategy reported here should be useful for the bio-based production of PHB from renewable resources.
Similar content being viewed by others
Background
Polyhydroxyalkanoates (PHAs) are diverse polyesters synthesized by a variety of microorganisms as intracellular carbon and energy storage compounds in response to environmental stresses [1]. Since PHAs possess thermoplastic or elastomeric properties and are completely biodegradable, PHA bioplastics offer an exciting alternative to petrochemical-derived plastics [2]. Poly(3-hydroxybutyrate) (PHB) is the most wide spread and best-characterized member of PHAs and many different fermentation strategies and recovery methods have been developed for its production as a model polymer [3].
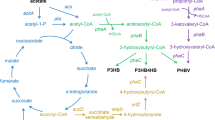
In the majority of native PHB-accumulating species, PHB is synthesized from acetyl-CoA by a sequence of three enzyme reactions catalyzed by β-ketothiolase, acetoacetyl-CoA reductase and PHB synthase, encoded by phaA, phaB and phaC, respectively (Figure 1). Recombinant E. coli harboring the exogenous PHB synthetic pathway was one of the most frequently used hosts for biopolymer production because of its advantages such as having a wide range of utilizable carbon sources, accumulating of large amounts of polymers with a high level of productivity, high cell density fermentation, and lacking PHA degradation system.
Schematic representation of the SD and ED metabolic pathways in PHB accumulation recombinant E.coli . Dashed lines indicate multiple enzymatic steps. The bold lines indicate the enzymes of SD pathway including reactions catalyzed by SerACB and SdaA. The enzymes that had been overexpressed in this work were shown in boldface. G6P, glucose-6-phosphate; FBP, fructose-1,6-bisphosphate; G3P, glycerahyde-3-phosphate; DHAP, dihydroxyacetone phosphate; 6PG, 6-phosphate-gluconate. Enzymes are as follows: Zwf, glucose 6-phosphate-1-dehydrogenase; Edd, phosphogluconate dehydratase; Eda, 2-keto-3-deoxygluconate 6-phosphate aldolase; Pgk, phosphoglycerate kinase; SerA, D-3-phosphoglycerate dehydrogenase; SerB, phosphoserine phosphatase; SerC, 3-phosphoserine aminotransferase; SdaA, L-serine deaminase I; PoxB, pyruvate oxidase; Pta, phosphate acetyltransferase; Ack, acetate kinase; PhaA, β-ketothiolase; PhaB, NADPH-dependent acetoacetyl-CoA reductase; PhaC, PHB synthase.
There has been a range of studies to evaluate PHB production in E. coli. Enhancing the availability of the precursor acetyl-CoA or/and cofactor NADPH increased the production of PHB. By overexpressing the fructose-bisphosphate aldolase (encoded by fbaA) or/and triosephosphate isomerase (encoded by tpi) [4], the recombinant E. coli accumulated more PHB than the reference strains due to the increase in acetyl-CoA concentration. By inactivating the phosphoglucose isomerase (encoded by pgi) gene, more NADPH was produced from pentose phosphate (PP) pathway, and eventually the PHB production was enhanced [5]. Transketolase (encoded by tktA) or transaldolase (encoded by talA) was used to improve the metabolism in non-oxidative PP pathway to enhance the production of PHB [6,7]. Overexpressing glucose-6-phosphate dehydrogenase (encoded by zwf) and 6-phosphogluconate dehydrogenase (encoded by gnd) in oxidative pentose phosphate pathway increased the PHB production in E. coli by increasing the NADPH availability [8]. In addition, to increase product yields, NADPH levels have been manipulated in the past by overexpressing the NADP+-dependent D-glyceraldehyde-3-phosphate dehydrogenase from Streptococcus mutans [9].
In E. coli, acetyl-CoA was derived mostly from pyruvate which is a key intermediate in catabolic and biosynthetic reactions. Most pyruvate was synthesized through the coupled mechanism of glucose transport by the phosphotransferase transport system or the glycolytic pathways including Embden-Meyerhof-Parnas (EMP), Entner-Doudoroff (ED), and PP pathway [10]. E. coli only produced two mole of NADH per mole of glucose through the EMP pathway, and caused the carbon loss through the PP pathway. Compared with these two pathways, ED pathway enables the strain to produce one molecular NADPH, a direct cofactor for the PHB production, without the carbon loss. Moreover, previous research based on proteome analysis revealed that ED pathway plays an important role during PHB production from glucose [11,12]. In E. coli, pyruvate also can be synthesized from L-serine by L-serine deaminase [13]. L-serine deaminases (encoded by sdaA, sdaB and tdcG) [14] catalyze the conversion of L-serine to pyruvate and ammonia, which may be employed to improve the PHB production in E.coli.
In this research, combined engineering of the Serine-Deamination Pathway (SD pathway, shown in Figure 1) with ED pathway resulted in enhanced PHB production, but accompanying with pyruvate accumulation. Overexpressing PDH complex eliminated the pyruvate accumulation and led to further improvement of the intracellular acetyl-CoA concentration and PHB production. Finally, the metabolically engineered E. coli strain was able to synthesize significant amount of PHB from different carbon sources such as glucose, xylose and glycerol.
Results and discussion
Overexpressing L-serine deaminase for improved PHB production
Under aerobic or anaerobic conditions, acetyl-CoA was derived mostly from the decarboxylation of pyruvate which respectively catalyzed by the PDH complex or pyruvate-formate lyase in E.coli [15,16]. Pyruvate was formed mostly from several glycolysis pathways. Moreover, L-serine derived from D-3-phosphoglycerate can be catalyzed to pyruvate and ammonias by L-serine deaminase. However, L-serine also can be cleaved into glycine and one carbon unit by serine hydroxymethyltransferase (SHMT, encoded by glyA), and be used as a building block for protein synthesis. Considering the competitive pathways existing at L-serine node, we firstly overexpressed the L-serine deaminase to enhance the conversion of L-serine into pyruvate. In E. coli, L-serine is deaminated by three L-serine deaminases, which are encoded by sdaA, sdaB and tdcG, respectively. L-serine deaminases I (SdaA) which is encoded by sdaA gene, is responsible for L-serine degradation in minimal media [14]. Moreover, a previous report has shown that sdaA-overexpressing Corynebacterium glutamicum could grow in the medium using L-serine as the sole carbon source [17]. Thus, in order to activate the SD pathway, sdaA was selected to be overexpressed by replacing the native sdaA promoter with a strong constitutive promoter trc in JM109, resulting in strain SD01 (JM109, P trc -sdaA). To test the effect of overexpressing sdaA on PHB production, SD01 and JM109 were both transformed with the plasmid pBHR68 which consists of the PHB biosynthesis genes from Ralstonia eutropha, creating strains SD01 (pBHR68) and JM109 (pBHR68). The PHB production of SD01 (pBHR68) was 3.58 g/L, 1.72-fold of that of JM109 (pBHR68) (Figure 2), and the PHB content is 73.8% of the cell dry weight (CDW) (Figure 2). These results suggested that overexpression of sdaA obviously “pulled” more L-serine to pyruvate and led to the improvement of PHB production. Thus, SD01 was chosen as the host for subsequent modifications to improve PHB production.
Influence of gene overexpression in L-serine biosynthetic pathway on PHB production
It is reasonable that efficient conversion of L-serine to pyruvate requires sufficient availability of L-serine. To enhance the biosynthesis of L-serine, we overexpressed the genes of de novo L-serine biosynthetic pathway. L-serine is synthesized from D-3-phosphoglycerate by three reactions catalyzed by D-3-phosphoglycerate dehydrogenase, D-3-phosphoserine aminotransferase and phosphoserine phosphatase, which are encoded by serA, serC and serB, respectively (Figure 1). D-3-phosphoglycerate dehydrogenase is regulated by allosteric end-product inhibition. Moreover, a published report has showed that a truncated D-3-phosphoglycerate dehydrogenase (PGDH) serA Δ197 was no longer inhibited by L-serine in C. glutamicum [18]. As such, we combined serA Δ197 together with serB and serC into an artificial operon driven by the constitutive promoter trc, creating plasmid pTSer. Strain SD01 was transformed with plasmid pTSer for activating the Serine-Deamination (SD) pathway. After 48h cultivation, 3.96 g/L PHB was accumulated by SD01 (pBHR68/pTSer), which was only slightly higher than that of the reference strain SD01 (pBHR68/pTrc101) (Figure 2).
However, the strategy of overexpressing serABC mainly led to improvement of cell growth, rather than specific PHB accumulation (Figure 2). This phenomenon might be due to the difference between the kinetic parameters of the two enzymes, SHMT and SdaA. The Km value for L-serine of SdaA is higher than that of SHMT (2.67 vs 0.3 mM [19,20]). The overexpression of serABC improved the availability of L-serine, which contributed much more to the reaction catalyzed by SHMT than the reaction catalyzed by SdaA. SHMT is the main source of C1 carbon and glycine for cell growth in E.coli, so residual cell dry weight was increased under this condition [21,22].
On the other hand, the kcat value of SdaA is much higher than that of SHMT (436 vs 5 s−1 [19,20]), and the corresponding kcat/Km values are 163.3 and 16.7 mM−1 · s−1, respectively. This means only when the intracellular concentration of L-serine is further improved to some extent, the serine deamination reaction can obviously overwhelm the competing reaction catalyzed by SHMT. Previous researches have shown that pgk (encodes phosphoglycerate kinase) overexpression could divert carbon flux into the D-3-phosphoglycerate pool and further promote the biosynthesis of L-serine [23]. To push more flux into the SD pathway, pgk gene was ligated into pTSer, creating plasmid pTPSer. The PHB production of SD01 (pBHR68/pTPSer) reached 4.92 g/L, increasing by 30.2% compared to that of SD01 (pBHR68/pTrc101) harboring the empty vector (Figure 2). However, when pgk was overexpressed alone, the PHB production of SD01 (pBHR68/pTPgk) showed no significant change, compared with that of SD01 (pBHR68/pTrc101). These results suggested that activating the SD pathway by co-overexpressing the L-serine deaminase, enzymes in L-serine biosynthesis pathway and phosphoglycerate kinase had a significant effect on PHB production.
Considering the instability of plasmid system and the metabolic burden resulted from plasmid replication [24,25], the pgk-serABC operon together with the fragment Trc-162 was integrated into the choromosome of SD01 at serC site, creating strain SD02 (SD01, PTrc-162-SerABC). The transcription levels of genes in SD pathway in strain SD02 were compared with that of the reference strain JM109 through RT-PCR analysis. As shown in Figure 3A, the genes of SD pathway have been successfully overexpressed. SD02 (pBHR68) accumulated 4.86 g/L PHB, which was almost the same as that of SD01 (pBHR68/pTPSer), but had a higher PHB content of 77.2% CDW (Figure 2). Therefore SD02 was selected for further engineering.
Effect of combining gene overexpression in ED pathway with the SD pathway on PHB production
Redirecting the carbon metabolism into the ED pathway in the engineered strain is beneficial to PHB production, since it avoids the carbon loss and balance the NADPH need [12,26]. Moreover, enhancing ED pathway might increase the availability of pyruvate and further enrich the in vivo pool of acetyl-CoA. As such, we tried to test the effect of enhancing the ED pathway on PHB accumulation.
The ED pathway joins the oxidative pentose phosphate pathway to EMP pathway via two enzyme-catalyzed reactions. The two critical enzymes are phosphogluconate dehydratase and 2-keto-3-deoxygluconate 6-phosphate aldolase, which were encoded by edd and eda, respectively. In E. coli, the ED pathway has been shown to be inactive with glucose as the carbon source [27]. Thus, the upstream regulated region of the edd-eda operon in SD02 was replaced with a constitutive promoter J23119 (http://partsregistry.org/Part:BBa_J23119) for eliminating the repression of the ED pathway and activating the ED pathway, resulting in SD03 (SD02 P J23119 -edd). Unexpectedly, strain SD03 (pBHR68) produced 2.90 g/L PHB which was a significant decrease compared with that of SD02 (pBHR68) (Table 1). Then fragment Trc-162 was inserted at the upstream of zwf gene in SD03 to further enhance the flux of ED pathway, creating strain SD04 (SD03, PTrc-162-zwf). The transcription levels of zwf, edd and eda genes in SD04 were up-regulated by 5.46, 4.57 and 2.16-fold, respectively (Figure 3B). PHB was accumulated to 3.39 g/L in SD04 (pBHR68), a 16.9% increase compared with that of SD03 (pBHR68), but was still lower than that of the parent strain SD02 (pBHR68) (Table 1). In addition, a small amount of pyruvate and acetate had been detected in the media of strains SD03 (pBHR68) and SD04 (pBHR68), but not detected in SD02 (pBHR68) (Table 1). This might be due to the improvement of glucose consumption after co-overexpressing the edd, eda, zwf genes (Table 1), which resulted in pyruvate accumulation in the medium. Moreover, the acetate was produced directly from pyruvate by pyruvate oxidase (encoded by poxB) in the JM109 derivative strains [28]. Thus it was possible that the accumulation of pyruvate and acetate retarded the cell growth and led to lower PHB production, although the intracellular acetyl-CoA concentration and the [NADPH]/[NADP+] ratio was increased (Figure 4, Table 2). So we tried to enhance the conversion of pyruvate to acetyl-CoA to eliminate the pyruvate accumulation and increase the PHB production.
Overexpression of the pyruvate dehydrogenase complex for enhanced PHB production
In E. coli, pyruvate is metabolized by the pyruvate dehydrogenase (PDH) complex and pyruvate oxidase during aerobic growth conditions [15,29]. To enhance the expression of PDH complex, fragment Trc-162 was inserted into the upstream of the PDH operon in SD02 and SD04 as mentioned in the methods section, resulting in strains SD06 (SD02, PTrc-162-aceEF) and SD07 (SD04, PTrc-162-aceEF). The transcript levels of genes encoding the PDH complex were presented in Figure 3C, which indicated that the genes of the PDH complex were successfully overexpressed. The PHB production of SD06 (pBHR68) was 4.63 g/L (69.1% CDW), no significant change compared with the reference strain SD02 (pBHR68) (Table 1), as well as the intracellular concentration of acetyl-CoA (Figure 4).
In contrast, the PHB concentration of the strain SD07 (pBHR68) was 5.54 g/L and PHB content was 81.1% CDW, significantly increased from 2.90 g/L of the parent strain SD04 (pBHR68). As expected, no trace of pyruvate and acetate was detected in the medium of SD07 (pBHR68) (Table 1), and the intracellular acetyl-CoA concentration of SD07 was further increased compared with that of SD04 (Figure 4). These indicated that the diversion of excess pyruvate to acetyl-CoA enhanced the availability of acetyl-CoA for PHB synthesis, and thus rebalanced the flux distribution at the pyruvate node.
PHB fermentation using other unrelated carbon sources
Xylose is a major constituent of lignocellulose biomass, and glycerol is a major byproduct of petrochemical products, both of which have been utilized for the production of various PHAs as cheap carbon sources [30-32]. We also tested the PHB production performance of the recombinant strains by using xylose or glycerol as carbon sources. Compared to wild type strain, SD06 (pBHR68) and SD07 (pBHR68) showed significant increase in PHB production and PHB content (Table 1). However, no significant difference was observed between these two strains when xylose or glycerol was served as the sole carbon source (Table 3). The reason for this phenomenon was that xylose or glycerol turned into D-3-phosphoglyceraldehyde via a series of metabolic reactions and flow into the EMP pathway or SD pathway rather than the ED pathway under aerobic conditions. These results suggested that the strategy reported here should be useful for the bio-based production of PHB from different carbon sources.
Conclusions
Through combined engineering of SD pathway, ED pathway and PDH, a recombinant E. coli strain was obtained which led to significantly enhanced PHB accumulation. The final strain produced 5.52 g/L PHB from glucose with a content of 81.11% CDW. A similar phenomenon was observed when xylose or glycerol was served as carbon sources. In conclusion, enhancing the availability of acetyl-CoA via engineering the SD pathway, ED pathway and the PDH complex offered an effective way for improving the PHB production in E. coli from different carbon sources.
Methods
Bacterial strains, primers, and plasmids construction
Bacterial strains and plasmids used in this study were listed in Table 4. E. coli DH5α was used for plasmid construction. The truncated serA Δ197 from C. glutamicum and serB, serC genes from E. coli with the synthesized ribosome binding sites (RBSs) were amplified by polymerase chain reaction (PCR) using the primers serAF/serAR, serBF/serBR and serCF/serCR, respectively. Primers pTrc101R/pTrc101F were used to amplify the backbone of the plasmid pTrc101. The serABC genes were cloned into pTrc101 by circular polymerase extension cloning (CPEC) [33], resulting in plasmid pTSer. The pgk gene was amplified with the primers pgkF/pgkR from E. coli genome and ligated into the pTSer and pTrc101, creating pTPSer and pTpgk. E.coli strains were transformed with the plasmids for PHB production or activate the SD pathway, for example, JM109 (pBHR68) represent the JM109 haboring the pBHR68 plasmid.
Genome replacement manipulation
The DNA fragment insertion or replacement strains were constructed by using the method reported by Lin et al with appropriate modifications [36]. The strategies of fragment construction were outlined in Figure 5. The final fragments were transformed into the competent cells with expression of the λ red recombination enzymes. The tetracycline resistant mutants were screened and confirmed by colony PCR. To induce I-SceI endonuclease expression and remove the resistance gene tetA from the genome, the positive colony was inoculated into 5 ml of LB medium with 100 μg/mL spectinomycin, 2 mM isopropyl-β-D-thiogalactopyranoside (IPTG), and 0.2% w/v L–arabinose. After overnight cultivation, cultures were diluted to appropriate concentration and plated on LB agar plates. The loss of tetA was confirmed by colony PCR. The technological process in detail was displayed in Figure 5. Primers used were listed in Table 5.
Strategies for chromosomal replacement. A. Genome editing cassettes are constructed by three rounds of PCR and recombinants after the first round of recombineering were selected by tetracycline; B. In the second step, the tetA marker was eliminated by simultaneous induction of I-SceI and Red recombinase expression. C. Fragments for promoter replacement or insertion; D. Fragments for Ptrc-162-pgk-serABC operon insertion. DR for duplicate region; I-sceI for I-SceI endonuclease recognition site.
For swapping the promoter of zwf, PDH complex operon and pgk-serAB fragment insertion, the tetA fragment was amplified from strain Tet-Trc-162, and fused with the up and low homologous flanks (Figure 5C). The low flank of pgk-serABC fragment was amplified from the plasmid pTPSer (Figure 5D). Fragment Trc-162 consisted of the trc promoter core sequence and M1-162[37] in tandem.
Cultivation conditions
During strains and plasmids construction, cultures were grown at 30°C or 37°C, in Luria broth (per liter: 10 g tryptone, 5 g yeast extract, and 10 g NaCl) with or without agar (2%) as indicated. Minimal sodium medium (MS medium) with 1 g/L yeast extract was used as seed culture and shake flask medium which contained (in grams per liter): glucose/xylose/glycerol 20.0, (NH4)2SO4 2.0, MgSO4 · 7H2O 0.4, Na2HPO4 3.83, KH2PO4 1.5, Fe(III)-NH4-citrate 0.05, CaCl2 0.02, and 1 mL/L trace element [38]. When necessary, a final concentration of 10 μg/mL chloromycetin and/or 100 μg/mL ampicillin were added. Colonies were inoculated into 5-ml LB culture medium and grown at 37°C with shaking overnight. Then the culture was inoculated with 1% into 250-ml flask with 50 ml culture medium as seed culture grown at 37°C in MS medium for 12 h at 220 rpm on a rotary shaker. Seed culture was then inoculated into 500-mL flask with 100 ml culture medium (with the initial OD600 of 0.04) and grown at 37°C and 220 rpm on a rotary shaker for 48 h. Three biological replicates were performed to detect the accumulation of PHB. To assess the significant difference of the PHB accumulation, data was subject to Student’s t test analysis with p < 0.05 being significantly different.
Analytical techniques
The growth of cell was monitored by measuring the OD600 with an ultraviolet spectrophotometer (Beijing Puxi Universal Co Ltd). Glucose in the fermentation broth was determined utilizing a SBA sensor machine (Institute of Microbiology, Shangdong, China). Bacteria were harvested by centrifugation at 8,000 × g for 10 min and then washed with distilled water. Cell dry weight (CDW) was measured after lyophilization and vacuum drying. PHB content was analyzed by gas chromatography (Persee, China) with an Agilent J&W Capillary GC column after methanolysis of lyophilized cells in chloroform. To determine the concentration of pyruvate, acetate, glycerol and xylose, culture samples were centrifuged at 12,000 × g for 5 min and the aqueous supernatant used for HPLC analysis on an Agilent 1100 Series HPLC system equipped with an Aminex HPX-87H anion exchange column (Bio-Rad Laboratories, Richmond, CA, USA) and refractive index detector. A mobile phase of 5 mM H2SO4 at a 0.4 mL/min flow rate was used.
For the determination of intracellular acetyl-CoA, 40 mL mid-exponential phase cell culture was taken into precooled centrifuge tubes and centrifuged at 8000 g and 4°C for 10 min. The cell pellets were washed with 40 mL 100 mM Tris-HCl buffer (pH 8.0). Acetyl-CoA was analyzed by HPLC as previous reported [39,40]. For determination of intracellular NADP+ and NADPH, 10 mL mid-exponential phase cell culture was taken into precooled centrifuge tubes and centrifuged at 8000 g and 4°C for 10 min. The intracellular NADP+ and NADPH were analyzed by HPLC as previous reported [41].
Quantitative real-time reverse transcription (RT)-PCR analysis
The recombinant strains harboring pBHR68 plasmid were cultured with the same fermentation media and culture condition with 1% (w/v) glucose. Cells were harvested when OD600 reached 1. Total mRNA were extracted using the RNAprep pure Cell/Bacteria Kit (Tiangen, Beijing, China) as described by the manufacturer. The cDNA was amplified using FastQuant RT Kit (Tiangen, Beijing, China) with the total mRNA as the templates. Samples were then analyzed using a Light Cycler® 480 II (Roche, Basel, Switzerland) with RealMasterMix (SYBR Green I) (Tiangen, Beijing, China). Quantity real-time PCR (qPCR) amplification primers were designed and were listed in Table 5. The rrsA gene was selected as internal standard for normalization and three biological replicates were performed. The obtained data were analyzed by using the 2-ΔΔCt method described previously [42].
References
Gao X, Chen JC, Wu Q, Chen GQ: Polyhydroxyalkanoates as a source of chemicals, polymers, and biofuels. Curr Opin Biotechnol 2011, 22:768–774.
Choi JI, Lee SY: High-level production of poly(3-hydroxybutyrate-co-3-hydroxyvalerate) by fed-batch culture of recombinant Escherichia coli. Appl Environ Microbiol 1999, 65:4363–4368.
Choi J, Lee SY: Efficient and economical recovery of poly(3-hydroxybutyrate) from recombinant Escherichia coli by simple digestion with chemicals. Biotechnol Bioeng 1999, 62:546–553.
Lee SH, Kang KH, Kim EY, Chae TU, Oh YH, Hong SH, Song BK, Jegals J, Park SJ, Lee SY: Metabolic engineering of Escherichia coli for enhanced biosynthesis of poly(3-hydroxybutyrate) based on proteome analysis. Biotechnol Lett 2013, 35:1631–1637.
Kabir MM, Shimizu K: Gene expression patterns for metabolic pathway in pgi knockout Escherichia coli with and without phb genes based on RT-PCR. J Biotechnol 2003, 105:11–31.
Jung YM, Lee JN, Shin HD, Lee YH: Role of tkt A gene in pentose phosphate pathway on odd-ball biosynthesis of poly-beta-hydroxybutyrate in transformant Escherichia coli harboring phbCAB operon. J Biosci Bioeng 2004, 98:224–227.
Song BG, Kim TK, Jung YM, Lee YH: Modulation of talA gene in pentose phosphate pathway for overproduction of poly-beta-hydroxybutyrate in transformant Escherichia coli harboring phbCAB operon. J Biosci Bioeng 2006, 102:237–240.
Lim SJ, Jung YM, Shin HD, Lee YH: Amplification of the NADPH-related genes zwf and gnd for the oddball biosynthesis of PHB in an E. coli transformant harboring a cloned phbCAB operon. J Biosci Bioeng 2002, 93:543–549.
Centeno-Leija S, Huerta-Beristain G, Giles-Gomez M, Bolivar F, Gosset G, Martinez A: Improving poly-3-hydroxybutyrate production in Escherichia coli by combining the increase in the NADPH pool and acetyl-CoA availability. Antonie Van Leeuwenhoek 2014, 105:687–696.
Postma PW, Lengeler JW, Jacobson GR: Phosphoenolpyruvate:carbohydrate phosphotransferase systems of bacteria. Microbiol Rev 1993, 57:543–594.
Han MJ, Yoon SS, Lee SY: Proteome analysis of metabolically engineered Escherichia coli producing Poly(3-hydroxybutyrate). J Bacteriol 2001, 183:301–308.
Hong SH, Park SJ, Moon SY, Park JP, Lee SY: In silico prediction and validation of the importance of the Entner-Doudoroff pathway in poly(3-hydroxybutyrate) production by metabolically engineered Escherichia coli. Biotechnol Bioeng 2003, 83:854–863.
Su HS, Lang BF, Newman EB: L-serine degradation in Escherichia coli K-12: cloning and sequencing of the sdaA gene. J Bacteriol 1989, 171:5095–5102.
Zhang X, Newman E: Deficiency in L-serine deaminase results in abnormal growth and cell division of Escherichia coli K-12. Mol Microbiol 2008, 69:870–881.
Quail MA, Haydon DJ, Guest JR: The pdhR-aceEF-lpd operon of Escherichia coli expresses the pyruvate dehydrogenase complex. Mol Microbiol 1994, 12:95–104.
Knappe J, Blaschkowski HP, Grobner P, Schmitt T: Pyruvate formate-lyase of Escherichia coli : the acetyl-enzyme intermediate. Eur J Biochem 1974, 50:253–263.
Netzer R, Peters-Wendisch P, Eggeling L, Sahm H: Cometabolism of a nongrowth substrate: L-serine utilization by Corynebacterium glutamicum. Appl Environ Microbiol 2004, 70:7148–7155.
Peters-Wendisch P, Netzer R, Eggeling L, Sahm H: 3-Phosphoglycerate dehydrogenase from Corynebacterium glutamicum : the C-terminal domain is not essential for activity but is required for inhibition by L-serine. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 2002, 60:437–441.
Cicchillo RM, Baker MA, Schnitzer EJ, Newman EB, Krebs C, Booker SJ: Escherichia coli L-serine deaminase requires a [4Fe-4S] cluster in catalysis. J Biol Chem 2004, 279:32418–32425.
Fu TF, Boja ES, Safo MK, Schirch V: Role of proline residues in the folding of serine hydroxymethyltransferase. J Biol Chem 2003, 278:31088–31094.
Miller BA, Newman EB: Control of serine transhydroxymethylase synthesis in Escherichia coli K12. Can J Microbiol 1974, 20:41–47.
Newman EB, Magasanik B: The Relation of Serine–Glycine Metabolism to the Formation of Single-Carbon Units. Biochim Biophys Acta 1963, 78:437–448.
Lai S, Zhang Y, Liu S, Liang Y, Shang X, Chai X, Wen T: Metabolic engineering and flux analysis of Corynebacterium glutamicum for L-serine production. Sci China Life Sci 2012, 55:283–290.
Friehs K: Plasmid copy number and plasmid stability. Adv Biochem Eng Biotechnol 2004, 86:47–82.
Jones KL, Kim SW, Keasling JD: Low-copy plasmids can perform as well as or better than high-copy plasmids for metabolic engineering of bacteria. Metab Eng 2000, 2:328–338.
Yamane T: Yield of poly-D(-)-3-hydroxybutyrate from various carbon sources: a theoretical study. Biotechnol Bioeng 1993, 41:165–170.
Fraenkel DG, Levisohn SR: Glucose and gluconate metabolism in an Escherichia coli mutant lacking phosphoglucose isomerase. J Bacteriol 1967, 93:1571–1578.
Phue JN, Shiloach J: Transcription levels of key metabolic genes are the cause for different glucose utilization pathways in E. coli B (BL21) and E. coli K (JM109). J Biotechnol 2004, 109:21–30.
Abdel-Hamid AM, Attwood MM, Guest JR: Pyruvate oxidase contributes to the aerobic growth efficiency of Escherichia coli . Microbiology 2001, 147:1483–1498.
Nikel PI, Giordano AM, de Almeida A, Godoy MS, Pettinari MJ: Elimination of D-lactate synthesis increases poly(3-hydroxybutyrate) and ethanol synthesis from glycerol and affects cofactor distribution in recombinant Escherichia coli . Appl Environ Microbiol 2010, 76:7400–7406.
Nduko JM, Matsumoto K, Ooi T, Taguchi S: Effectiveness of xylose utilization for high yield production of lactate-enriched P(lactate-co-3-hydroxybutyrate) using a lactate-overproducing strain of Escherichia coli and an evolved lactate-polymerizing enzyme. Metab Eng 2013, 15:159–166.
Le Meur S, Zinn M, Egli T, Thony-Meyer L, Ren Q: Poly(4-hydroxybutyrate) (P4HB) production in recombinant Escherichia coli : P4HB synthesis is uncoupled with cell growth. Microb Cell Fact 2013, 12:123.
Quan J, Tian J: Circular polymerase extension cloning for high-throughput cloning of complex and combinatorial DNA libraries. Nat Protoc 2011, 6:242–251.
Spiekermann P, Rehm BH, Kalscheuer R, Baumeister D, Steinbuchel A: A sensitive, viable-colony staining method using Nile red for direct screening of bacteria that accumulate polyhydroxyalkanoic acids and other lipid storage compounds. Arch Microbiol 1999, 171:73–80.
Kuhlman TE, Cox EC: Site-specific chromosomal integration of large synthetic constructs. Nucleic Acids Res 2010, 38:e92.
Lin Z, Xu Z, Li Y, Wang Z, Chen T, Zhao X: Metabolic engineering of Escherichia coli for the production of riboflavin. Microbial Cell Factories 2014, 13:104.
Zhao J, Li Q, Sun T, Zhu X, Xu H, Tang J, Zhang X, Ma Y: Engineering central metabolic modules of Escherichia coli for improving beta-carotene production. Metab Eng 2013, 17:42–50.
Li ZJ, Cai L, Wu Q, Chen GQ: Overexpression of NAD kinase in recombinant Escherichia coli harboring the phbCAB operon improves poly(3-hydroxybutyrate) production. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 2009, 83:939–947.
Zhu N, Xia H, Wang Z, Zhao X, Chen T: Engineering of acetate recycling and citrate synthase to improve aerobic succinate production in Corynebacterium glutamicum . PLoS One 2013, 8:e60659.
Boynton ZL, Bennett GN, Rudolph FB: Intracellular concentrations of coenzyme A and its derivatives from Clostridium acetobutylicum ATCC 824 and their roles in enzyme regulation. Appl Environ Microbiol 1994, 60:39–44.
Fu J, Wang Z, Chen T, Liu W, Shi T, Wang G, Tang YJ, Zhao X: NADH plays the vital role for chiral pure D-(-)-2,3-butanediol production in Bacillus subtilis under limited oxygen conditions. Biotechnol Bioeng 2014, 111(10):2126–2131.
Livak KJ, Schmittgen TD: Analysis of relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and the 2(-Delta Delta C(T)) Method. Methods 2001, 25:402–408.
Acknowledgments
We thank Prof. Guo-Qiang Chen (Tsinghua University) for kindly providing the plasmid pBHR68. We thank Dr. Thomas E. Kuhlman for kindly providing requested plasmids. This work was supported by National 973 Project [2012CB725203, 2011CBA00804]; National Natural Science Foundation of China [NSFC-21176182, NSFC-21206112, NSFC-21390201]; and National High-tech R&D Program of China [2012AA02A702, 2012AA022103].
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Competing interests
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Authors’ contributions
YZ, ZQL and TC designed the experiments; YZ, ZQL, QJL, YFL and ZWW performed the experiments; YZ, ZQL, TC and HWM wrote the manuscript; TC and XMZ supervised the work; and all authors contributed to the discussion of the research. All authors read and approved the final manuscript.
Yan Zhang and Zhenquan Lin contributed equally to this work.
Rights and permissions
This article is published under an open access license. Please check the 'Copyright Information' section either on this page or in the PDF for details of this license and what re-use is permitted. If your intended use exceeds what is permitted by the license or if you are unable to locate the licence and re-use information, please contact the Rights and Permissions team.
About this article
Cite this article
Zhang, Y., Lin, Z., Liu, Q. et al. Engineering of Serine-Deamination pathway, Entner-Doudoroff pathway and pyruvate dehydrogenase complex to improve poly(3-hydroxybutyrate) production in Escherichia coli . Microb Cell Fact 13, 172 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1186/s12934-014-0172-6
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1186/s12934-014-0172-6