Abstract
In modern societies, with an increase in the older population, age-related neurodegenerative diseases have progressively become greater socioeconomic burdens. To date, despite the tremendous effort devoted to understanding neurodegenerative diseases in recent decades, treatment to delay disease progression is largely ineffective and is in urgent demand. The development of new strategies targeting these pathological features is a timely topic. It is important to note that most degenerative diseases are associated with the accumulation of specific misfolded proteins, which is facilitated by several common features of neurodegenerative diseases (including poor energy homeostasis and mitochondrial dysfunction). Adenosine is a purine nucleoside and neuromodulator in the brain. It is also an essential component of energy production pathways, cellular metabolism, and gene regulation in brain cells. The levels of intracellular and extracellular adenosine are thus tightly controlled by a handful of proteins (including adenosine metabolic enzymes and transporters) to maintain proper adenosine homeostasis. Notably, disruption of adenosine homeostasis in the brain under various pathophysiological conditions has been documented. In the past two decades, adenosine receptors (particularly A1 and A2A adenosine receptors) have been actively investigated as important drug targets in major degenerative diseases. Unfortunately, except for an A2A antagonist (istradefylline) administered as an adjuvant treatment with levodopa for Parkinson’s disease, no effective drug based on adenosine receptors has been developed for neurodegenerative diseases. In this review, we summarize the emerging findings on proteins involved in the control of adenosine homeostasis in the brain and discuss the challenges and future prospects for the development of new therapeutic treatments for neurodegenerative diseases and their associated disorders based on the understanding of adenosine homeostasis.
Similar content being viewed by others
Background
Adenosine is a purine nucleoside. It serves as a neurotransmitter and neuromodulator in the central nervous system (CNS). In addition, adenosine is an essential component of energy production and is utilized in all living cells. Adenosine can be produced during the catabolism of adenosine triphosphate (ATP), which is catalyzed by ectonucleotidases and endonucleotidases [145]. Extracellular and intracellular adenosine levels are modulated through equilibrative nucleoside transporters (ENTs) that bidirectionally transport adenosine across the plasma membrane down a concentration gradient and concentrative nucleoside transporters (CNTs) that transport adenosine into cells in a Na+-dependent manner against the concentration gradient [193]. Extracellular and intracellular adenosine play distinct roles in modulating various physiological functions (e.g., immune responses, blood–brain barrier (BBB) permeability, neuronal activity, and energy balance) in the CNS. Extracellular adenosine regulates intercellular signaling via adenosine receptors (A1R, A2AR, A2BR, and A3R) on the cell surface. In contrast, intracellular adenosine is important in the regulation of energy metabolism and DNA methylation [9, 35, 37, 48, 71, 198]. Disruption of adenosine homeostasis in the brain has been implicated in various pathophysiological dysfunctions, such as sleep disorders, cognitive impairment, and neuroinflammation [63, 198]. In the present review, we summarize the emerging role of dysregulated adenosine homeostasis in brain disorders with a specific focus on neurodegenerative diseases and possible new treatment developments based on these findings.
Most degenerative diseases are associated with abnormal aggregation of a disease-causing protein [203]. Specifically, the major pathogenic hallmarks of Alzheimer's disease (AD) are the accumulation of extracellular amyloid-β (Aβ) plaques and intracellular tau tangles [32]. Brains of patients with Parkinson's disease (PD) commonly contain Lewy bodies with misfolded α-synuclein [28]. Huntington's disease (HD) is caused by the formation of intracellular inclusions of mutant Huntingtin (mHTT), which contains an abnormal expansion of CAG repeats [169]. Amyotrophic lateral sclerosis (ALS) shows progressive loss of motor neurons with the accumulation of ubiquitinated TAR DNA-binding protein-43 (TDP-43) [166]. Although these degenerative diseases present with distinct clinical symptoms and affect different brain areas, poor energy homeostasis and mitochondrial dysfunction have been commonly documented [34, 57, 88, 129, 195, 233]. Furthermore, accumulating evidence also implicates dysregulated purine metabolism and abnormal expression of adenosine metabolism enzymes in these neurodegenerative diseases [8, 25, 90, 99, 114, 127, 217, 230]. Together, these findings suggest a possible association between purine metabolism and mitochondrial function in protein misfolding diseases. Specific details are discussed in the following sections.
Adenosine metabolism enzymes
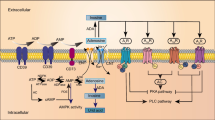
The level of intracellular and extracellular adenosine is tightly regulated by multiple enzymes, including ectonucleotidases, endonucleotidases, adenosine deaminase (ADA), and adenosine kinase (ADK). In the extracellular compartment (e.g., synaptic cleft), two major ectonucleotidases (i.e., NTPDase1/CD39 and eN/CD73) are critical for the breakdown of ATP [261]. As shown in Fig. 1, ATP and adenosine diphosphate (ADP) can be hydrolyzed into adenosine monophosphate (AMP) by CD39. AMP is then converted into adenosine by CD73. Extracellular adenosine can be either degraded into inosine by ADA or transported across the plasma membrane through nucleoside transporters (i.e., ENTs and CNTs). In the intracellular compartment, adenosine metabolism is mediated by nucleotide diphosphokinase (NDPK), adenylate kinase (AK), endonucleotidase (e.g., cytosolic nucleotidase NT5C/cN), ADA, and ADK. Intracellular ATP can be hydrolyzed into ADP and AMP by NDPK and AK, respectively. Intracellular AMP can be further converted into adenosine by cN. Intracellular adenosine can either be degraded into inosine by ADA, transported to the extracellular compartment, or resynthesized into ATP by these metabolic enzymes (for recent reviews, see [27, 91]).
Regulatory components of the adenosinergic signaling pathway. Adenosinergic signaling is regulated by multiple molecules inside and outside of cells. In the extracellular compartment, ATP and ADP can be hydrolyzed into AMP by CD39. AMP is then converted into adenosine by CD73. Extracellular adenosine can either activate AR-mediated cellular signaling through G proteins and associated effectors, degrade into inosine by ADA, or be transported across the plasma membrane through Na+-independent passive nucleoside transporters (i.e., ENTs) or Na+-dependent active nucleoside transporters (i.e., CNTs). In the intracellular compartment, ATP can be hydrolyzed into ADP and AMP by NDPK and AK, respectively. Intracellular AMP can be further converted into adenosine by cN. Intracellular adenosine can either be degraded into inosine by ADA, transported to the extracellular compartment, or resynthesized into ATP by metabolic enzymes. During the adenosine metabolism process, the elevation of the AMP-to-ATP ratio can lead to the activation of AMPK, which further modulates mitochondrial homeostasis (e.g., mitochondrial fission/fusion or mitophagy) by changing the activity of associated enzymes (e.g., MFF or ULK1). Intracellular adenosine is also associated with DNA methylation by negatively regulating transmethylation pathways. In this pathway, SAM is demethylated to SAH by DNMTs, which subsequently enhances the level of DNA methylation. SAH is then hydrolyzed into adenosine and homocysteine by SAHH. Adenosine negatively regulates the activity of SAHH, which alters the SAH level and inhibits SAM-dependent DNMT activity. ADA, adenosine deaminase; ADK, adenosine kinase; AK, adenylate kinase; AMPK, AMP-activated protein kinase; ARs, adenosine receptors; CNTs, concentrative nucleoside transporters; ENTs, equilibrative nucleoside transporters; NDPK, nucleotide diphosphokinase; NT5C/cN, endonucleotidase; SAH, S-adenosyl-homocysteine; DNMTs, DNA methyltransferases; SAHH, S-adenosyl-homocysteine hydrolase; and SAM, S-adenosyl-methionine
The roles of enzymes involved in adenosine metabolism in the CNS have been extensively investigated. CD39 and CD73 are known to control the balance between ATP and adenosine in the extracellular compartment. CD39/CD73-mediated ATP breakdown has been proposed to shift immune cells from a proinflammatory to an anti-inflammatory state [10]. This phenomenon was observed not only in peripheral immune cells but also in glial cells in the CNS. Recent studies have demonstrated that genetic removal of astrocytic CD73 blocks AMP-mediated cytokine release from astrocytes [258]. Badimon et al. [16] recently showed that microglial CD39/CD73-mediated ATP hydrolysis suppresses neuronal activity by activating A1 adenosine receptor (A1R) in a feedback regulatory manner. In addition, genetic removal of CD39 prevents the chronic social defeat stress (CSDS)-induced depression-like behavior of mice [60]. Similarly, ADA and ADK have also been implicated in neurodegenerative diseases. Suppression of ADA resulted in beneficial effects in a MPTP-induced Parkinsonism mouse model [114] but toxic effects on motor neurons in an ALS model established with a cocultured system of induced pluripotent stem cell (iPSC)-derived astrocytes and motor neurons [7]. Accumulating evidence suggests that ADK is an epigenetic modulator in both normal and disordered neurodevelopment [181, 206]. Together, these studies highlight the critical roles of adenosine metabolism in maintaining appropriate brain functions in health and diseases and suggest that adenosine metabolism enzymes may serve as potential drug targets for neurodegenerative diseases.
Adenosine transporters
Nucleoside transporters act mainly on the transportation of adenosine across the plasma membrane and thus modulate adenosine homeostasis. To date, two major types of nucleoside transporters have been identified: (1) equilibrative nucleoside transporters (e.g., ENT1-4) and (2) concentrative nucleoside transporters (e.g., CNT1-3) [193]. ENTs are passive nucleoside transporters that are widely expressed in all tissues (including the brain). The main function of ENTs is facilitation of the bidirectional transportation of nucleosides (including adenosine) across membranes down a concentration gradient (Fig. 1). ENT1 and ENT2 are the most characterized adenosine transporters that are localized on the plasma membrane in the brain. Both ENT3 and ENT4 are pH-sensitive adenosine transporters that function in acidic environments. ENT3 is an intracellular enzyme on lysosomes that controls nucleoside homeostasis [112]. Similar to ENT1 and ENT2, ENT4 is located on the plasma membrane and modulates adenosine transportation across the membrane under acidotic conditions [18]. CNTs, on the other hand, are active nucleoside transporters with distinct expression profiles in various tissues. CNTs transport nucleosides into cells with an inward transmembrane Na+ gradient. The specific role of CNTs has been extensively discussed in recent reviews [91, 193] and therefore is not discussed here. In the current review, we focus on the current progress on understanding the roles of ENT1 and ENT2 in the CNS.
Previous studies have suggested that ENT1 and ENT2 play critical roles in the control of immune responses, mitochondrial activity, and neurological functions. Pharmacological inhibition or genetic deficiency of ENT1 or ENT2 showed beneficial roles in preventing lipopolysaccharide (LPS)-induced neuroinflammation [244], LPS-induced acute pulmonary inflammation [178], Pseudomonas aeruginosa–induced NLR family pyrin domain-containing 3 (NLRP3) inflammasome activation [45], and disease-associated neuroinflammation [46, 144]. In addition, genetic removal of ENT1 reduced essential astrocytic proteins (e.g., glial fibrillary acidic protein, excitatory amino acid transporter 2 (EAAT2), and aquaporin 4) critical for astrocyte functions [110]. In contrast, in endothelial cells, inhibition of ENT1/2 by dipyridamole prevented sustained adenosine exposure-induced mitochondrial dysfunction [135]. This finding is of great interest because Lai et al. had previously reported that human ENT1, but not mouse ENT1, is localized to mitochondria via a PEXN motif and functionally facilitates the transport of nucleoside drugs (e.g., fialuridine) into mitochondria [142, 147]. No further characterization of the role of ENT1 in mitochondrial functions has been recently reported; however, several mitochondrial proteins have been observed in the human ENT1 interactome network [21]. Further investigation is needed to dissect the potential functions and regulatory models of ENTs in different brain cells.
Adenosine receptors
Adenosine signaling is executed by adenosine receptors on the plasma membrane. To date, four types of adenosine receptors (A1R, A2AR, A2BR, and A3R) have been identified and characterized. These receptors are G protein-coupled receptors (GPCRs) that modulate the adenylyl cyclase (AC)-cyclic adenosine monophosphate (cAMP)-protein kinase A (PKA) signaling pathway (Fig. 1). A1R and A3R are Gi/o-coupled receptors that inhibit cAMP signaling, whereas A2AR and A2BR are Gs-coupled receptors that stimulate cAMP signaling. A1R and A2AR are the major adenosine receptor subtypes in the brain and can be found in both neurons and glia. In many pathophysiological conditions tested, A1R and A2AR may have opposite effects in the regulation of cellular functions [145]. For example, synaptic transmission can be either enhanced by A2AR activation or inhibited by A1R activation. The functional roles of A1R and A2AR in many neurodegenerative diseases (including AD, HD, ALS, and PD) have been extensively investigated throughout the past two decades. The current progress has been summarized and discussed in detail in recent reviews [15, 91, 157] and thus is not elaborated here. Previously, A2BR and A3R were believed to exert only minor effects in the brain due to their low levels of expression and relatively low affinities for adenosine. Nonetheless, a few studies recently showed that A2BR participates in synaptic transmission and autoimmune neuroinflammatory reactions in the brain [56, 86, 94]. In addition, A3R may negatively modulate the functional properties of α-amino-3-hydroxy-5-methyl-4-isoxazolepropionic acid (AMPA) receptors in hippocampal neurons [70] and suppress microglial functions (including phagocytic activity and migration) [85]. Activation of A3R by MRS5980 improves traumatic brain injury-induced cognitive impairment [81]. These studies suggest that all four adenosine receptors are involved in the modulation of brain activity. Notably, genetic removal of all four adenosine receptors shortens the life span and causes the loss of adenosine-mediated hypothermia. Given that the overall physiology of these quadruple-knockout mice is similar to that of each of the four single-gene-knockout mice, the functions of these four adenosine receptors appear complementary but not synergistic [246]. To determine how the loss of all four adenosine receptors affects neuroplasticity and neuron-glia interactions, further investigation is required.
Adenosine, AMP-activated protein kinase (AMPK), and energy homeostasis
Ample evidence suggests that adenosine homeostasis is important for cellular metabolism and has been implicated in the status of AMPK activation [46, 171, 192, 207]. AMPK is a key energy sensor and regulator in cells [108]. It is a heterotrimeric complex composed of three distinct subunits: α (catalytic; α1 and α2), β (scaffolding; β1 and β2), and γ (regulatory; γ1, γ2, and γ3) subunits [108]. The binding sites of adenine nucleotides on the γ subunit allow AMPK to sense the intracellular level of AMP, ADP, and ATP [245]. Under low-energy conditions, the AMP level is elevated, and the AMP/ATP ratio is thus increased, which facilitates the phosphorylation of AMPKα subunits at Thr172 and activates AMPK activity [222] (Fig. 1). In addition to sensing the cellular energy status, AMPK modulates multiple metabolic pathways to restore the energy status by inhibiting the anabolic pathway and stimulating the catabolic pathway [108]. AMPK serves as a key regulator of mitochondrial function by phosphorylating mitochondrial fission factor (MFF) and Unc-51-like autophagy-activating kinase 1 (ULK1), which affect mitochondrial dynamics (fission/fusion) and mitophagy, respectively [204, 219] (Fig. 1). This role of AMPK is interesting because mitochondrial dysfunction is a common feature of neurodegenerative diseases [34, 57, 129, 195].
Nonetheless, the role of AMPK in neurodegenerative diseases appears complex. Studies on different experimental models of various disease stages have reported seemingly contradictory conclusions. Assefa and colleagues reviewed recent progress in AD research and concluded that both positive and negative effects of AMPK activation have been found in AD [14]. Similarly, both activation and inhibition of AMPK have been found to be associated with beneficial effects on HD progression [107, 124, 125, 224]. In ALS, although suppression of AMPK has been demonstrated to produce beneficial effects in several experimental ALS models [153, 155, 156], studies have reported that AMPK activation may result in beneficial effects [58, 237]. As an explanation, most of the AMPK activators (e.g., metformin) tested were indirect activators and may have produced contradictory effects through AMPK-independent pathways. Moreover, different AMPK holoenzymes may regulate distinct types of machinery and therefore exert seemingly opposite functions in the brain. For example, recent studies have shown that AMPKα1 and AMPKα2 play detrimental and beneficial roles in memory functions, respectively [250, 262]. It is therefore vital to further evaluate the sensitivity of different AMPK subtypes to various AMPK activators and the exact roles of AMPK holoenzymes composed of different subunits in neurons and glia during the progression of neurodegenerative diseases.
Adenosine, DNA methylation, and gene regulation
DNA methylation, a type of epigenetic modification, controls gene expression by preventing the binding of transcription factors to the promoter region of the corresponding gene [122, 238]. The dysregulation of DNA methylation has been implicated in neurodegenerative diseases [158]. For instance, the hypomethylation of APP promoter enhances Aβ level and AD pathology [242]. In addition, the hypomethylation of TNF-α promoter elevates its expression, which subsequently increases the vulnerability of dopaminergic neurons in PD [41, 196]. Interestingly, altered methylation of the 5’UTR region of ADORA2A reduces A2AR expression, which impairs adenosinergic signaling in the striatum of HD [226]. Methylation of the glutamate transporter (EAAT2) promoter contributes to the astroglial dysfunction in ALS [251]. These observations are of great interest because adenosine is also involved in the transmethylation pathway (Fig. 1), in which S-adenosylmethionine (SAM) is demethylated to S-adenosylhomocysteine (SAH) by DNA methyltransferases (DNMTs), subsequently enhancing the level of DNA methylation [50]. SAH is then hydrolyzed into adenosine and homocysteine by S-adenosylhomocysteine hydrolase (SAHH) [190]. Notably, this SAHH reaction is tightly and reversibly controlled by the concentrations of intracellular adenosine and homocysteine [190, 235, 241]. Specifically, adenosine negatively regulates the activity of SAHH, which further alters the SAH level. In addition, SAH can inhibit SAM-dependent DNMT activity, which forms a negative feedback regulation loop [120]. Thus, when the level of SAH is increased, DNA methylation is reduced [43]. Given that DNA methylation controls gene expression, adenosine homeostasis may contribute to the DNA methylation-mediated gene expression profile. Importantly, homocysteine has also been implicated in various diseases (including neurodegenerative diseases), which has been extensively reviewed elsewhere [104, 177, 210]. These studies collectively have shown that the cellular adenosine concentration can be regulated through the transmethylation pathway, while the adenosine concentration conversely may also influence the level of DNA methylation and gene expression profile. Proteins (such as ENTs and ADK) that control the cellular adenosine level are thus thought to play important roles in transmethylation pathway regulation and gene expression.
Previous genetic and pharmacological approaches have clearly demonstrated that adenosine modulates DNA methylation in a receptor-independent manner. For instance, genetic removal of ADK in the mouse forebrain leads to the elevation of intracellular adenosine and a lower level of DNA methylation. Specifically, chronic inhibition of ADK by an ADK inhibitor (5-iodotubercidin administered by intraperitoneal injection) results in the global reduction in DNA methylation in the hippocampus [241]. In addition, downregulation of ADK expression under hypoxic conditions leads to increased intracellular adenosine levels, enhanced DNA hypomethylation of the VEGFR2 promotor, and elevated proliferation of endothelial cells [247]. Interestingly, adenosine receptor genes can also be epigenetically modulated through adenosine-triggered DNA hypomethylation. Three CpG islands in the 5’ untranslated region (5’ UTR) of human ADORA2A have been identified and were shown to modulate the expression of A2AR through DNA methylation [30, 31]. Together, these findings show crucial cross talk among factors influencing adenosine metabolism, the transmethylation pathway, and DNA methylation-dependent gene expression.
Adenosine as a mediator of cross talk between neurons and glial cells
Glial malfunction, which causes abnormal interaction between neurons and glia, has been shown to contribute significantly to neurodegenerative diseases [213]. Adenosine is known to mediate the cross talk between neurons and glia (Fig. 2). Upon neuronal activation, neurotransmitters (e.g., glutamate and ATP) are released from the presynaptic terminal to activate receptors in the synapse [191]. The released ATP can attract microglia through the activation of purinergic receptor P2Y, G-protein coupled,12 (P2RY12), which also mediates the establishment of somatic microglia-neuron junctions [59, 106]. Because ectonucleotidases (e.g., CD39 and CD73) are enriched on the membrane of microglia, the ATP released from neurons can be quickly hydrolyzed into AMP and adenosine. The resultant adenosine then activates neuronal A1R to suppress the further release of neurotransmitters [16]. Neuronal activity can also regulate the metabolism of astrocytes. Astrocytic genes associated with glucose metabolism and lactate export are upregulated via the activation of the A2BR-cAMP-PKA-cAMP-response element-binding protein (CREB) axis, which controls the interaction between neurons and astrocytes [6, 105]. As described in the previous section, adenosine that is abundant in the extracellular compartment can be transported into both astrocytes and neurons via ENTs or hydrolyzed into inosine by ADA to maintain adenosine homeostasis. As glutamate excitotoxicity and neuroinflammation are common features of neurodegenerative diseases [118, 150, 234], these neuron-microglia interactions are critical because excessive activation of neurons can disrupt neuronal functions, shorten their survival and cause severe inflammation by significantly elevating ATP release and altering adenosinergic signaling [72, 184]. In AD, the level of P2RY12 in microglia near amyloid plaques and tau tangle-containing plaques is low [164, 231], suggesting a loss of negative feedback regulation between microglia and neurons. In addition, previous studies have revealed cell-specific expression and dysregulation of genes involved in purinergic signaling and metabolism, which may greatly alter the cross talk between neurons and glia in degenerative diseases [8, 145, 197, 208, 211].
Regulatory roles of adenosine in neurons and glial cells. a Neuronal activity is modulated by the cross talk between neurons and glial cells (i.e., microglia and astrocytes). b Adenosine is an important modulator in the brain. In neurons, upon activation, glutamate and ATP are released from the presynaptic terminal to activate receptors in the synapse, which modulates neuronal activity, calmodulin-mediated regulation of ENT affinity to transport adenosine, and adenosinergic pathways (as shown in Fig. 1). In microglia, released ATP can attract microglia by activating P2RY12. ATP can be quickly hydrolyzed into AMP and adenosine by ectonucleotidases (e.g., CD39 and CD73), which are enriched on the membrane of microglia and expressed on neurons and astrocytes. The resultant adenosine then activates neuronal ARs (e.g., A1R and A2AR) to suppress or facilitate the further release of neurotransmitters from the presynaptic terminal. In astrocytes, adenosine can also regulate the metabolism of astrocytes and the astrocytic transcriptome via the activation of AR (i.e., A2BR). ADK, adenosine kinase; AK, adenylate kinase; AMPK, AMP-activated protein kinase; ARs, adenosine receptors; CaM, calmodulin; ENTs, equilibrative nucleoside transporters; GluRs, glutamate receptors; and P2RY12, purinergic receptor P2Y, G-protein coupled, 12
Adenosine homeostasis in neurodegenerative diseases
Alzheimer’s disease (AD)
AD is characterized by progressive memory loss and cognitive decline and has become the major neurodegenerative disease in aging populations of modern societies. The two key pathogenic hallmarks of AD are the accumulation of extracellular plaques composed of β-amyloid (Aβ) and intracellular neurofibrillary tangles containing hyperphosphorylated tau proteins [32]. Both pathologies are associated with synaptic loss and neuroinflammation, which cause cerebral dystrophy and cognitive impairments during AD progression [49, 146, 209].
Abnormal adenosine homeostasis has been reported earlier in the brains of AD patients [8, 44]. Altered expression of adenosine receptors (including A1R and A2AR) has been found in the frontal cortex of AD patients and AD mice (APP/PS1) [5, 144, 225]. The dysregulated adenosinergic system has long been considered a possible target for the development of new treatments for AD [46, 143, 144, 174, 186, 187]. In particular, suppression of A2AR or A1R provides beneficial effects on different molecular aspects related to the cognitive functions of AD mice [67, 79, 143, 187]. Nonetheless, the beneficial effects of small molecules targeting adenosine receptors seem moderate and may be effective only in specific treatment windows [187]. Because recent progress on this topic has been extensively reviewed [15, 74], no further elaboration on the function and regulation of adenosine receptors in AD is presented here.
Here, we focus on several proteins involved in adenosine metabolism that may serve as novel drug targets for AD; namely, ENT1, which is the most well-characterized adenosine transporter in the brain. Two recent studies reported that chronic treatment with an orally active, BBB-permeable small ENT1 inhibitor (J4) attenuated impaired cognitive function, inferior neuroplasticity, and elevated neuroinflammation in two AD mouse models (APP/PS1 and THY-Tau22) [46, 144]. Other enzymes involved in adenosine metabolism (ADA, ADK, CD39 and CD73) are also abnormally affected in AD, similar to other neurodegenerative diseases (Table 1). In the brains of patients with early stage AD, ADA activity is relatively low in the frontal cortex and high in the temporal cortex, suggesting brain area-specific regulation of adenosine homeostasis in AD [8]. In the hippocampus of an experimental model of tauopathy (THY-Tau22), the levels of ADA, CD39 and CD73 were all higher than those of WT mice (Table 1). Partial blockade of ENT1 by J4 effectively normalized these levels and thus stabilized the aberrant adenosine metabolism in tauopathy [46]. Another interesting finding showed that astrocytes surrounding amyloid deposits and tangle-containing neurons contain abundant ADK [25], suggesting that ADK inhibitors may have therapeutic effects. On the other hand, the elevated CD73 level in AD is known to contribute to the impairment of synaptic plasticity and low cognitive function induced by β-amyloid plaques. Since the detrimental effect of β-amyloid plaques is greatly reduced in the absence of this ecto-5′-nucleotidase, CD73 is also a novel drug target for AD [93].
The abnormal adenosine metabolism observed in the brain with AD implies that neuronal energy status may be similarly dysregulated. Moreover, mitochondrial impairment is a pathological feature of AD, which is thought to further impair energy homeostasis in the brain. AMPK is a molecular sensor of cellular energy status, and abnormal AMPK activation has been reported in AD brains [46, 80, 162, 228]. An early study suggested that the suppression of overactivated AMPK using a selective AMPK inhibitor (compound C) leads to the improvement of AD-associated symptoms [162]. Targeting abnormally regulated AMPK signaling as a therapeutic strategy for AD has therefore attracted considerable attention. Notably, both AMPK subtypes (α1 and α2) can be found in the brain, and they not only perform very different functions but also undergo distinct regulation in AD. Compared with that in the brains of normal subjects, the level of AMPKα1 was significantly increased in the hippocampi of AD patients and Tg19959 mice, while the level of AMPKα2 was reduced. Genetic ablation of AMPKα1 produces beneficial effects on cognitive functions in two AD mouse models (Tg19959 and APP/PS1, [262]) (Table 2). In contrast, selective removal of AMPKα2 in the hippocampus reduces dendritic spine density and neuronal plasticity, probably because of the disturbance in protein translation [250]. The subtype-specific function of AMPKs may contribute to the seemingly controversial findings. For example, treatment with metformin (a known AMPK activator) ameliorates synaptic deficiency and improves the memory function of AD mice (APP/PS1) [236]. However, many AMPK activators that have been tested in experimental models of AD also have AMPK-independent functions. Further investigations are necessary to delineate the detailed regulation and function of AMPK subtypes in AD brains to make therapeutic intervention possible.
Parkinson's disease
Parkinson’s disease (PD) is a common chronic neurodegenerative disease that affects approximately 1% of the elderly population. It is characterized by progressive loss of dopaminergic neurons in the substantia nigra, which directly leads to dopamine deficiency in the striatum and subsequent impairment of motor function. The current therapies rationally aim to normalize dopaminergic levels through specific treatments, such as the administration of a dopamine precursor (levodopa or L-dopa) and dopamine receptor agonists. Catechol-O-methyltransferase inhibitors, which prevent peripheral breakdown of levodopa, are clinically beneficial as adjuvants to levodopa therapy. In addition, inhibitors of monoamine oxidase type B, which suppress the degradation of endogenous dopamine, are also beneficial as a monotherapy or an adjuvant treatment with levodopa for early stage PD [140]. However, although many therapies for PD symptoms are available, these drugs are effective only at the early stage of the disease and are unable to slow or cure the disease. Moreover, long-term dopamine replacement therapy worsens unwanted side effects, particularly involuntary abnormal movements, such as those associated with dyskinesias and dystonia. New therapeutic targets for PD are therefore urgently needed.
The interaction between adenosine and dopamine signaling pathways has been extensively investigated and reviewed previously [183, 218]. Much attention has been focused on the roles of A2AR in the modulation of dopaminergic signaling because this adenosine receptor is highly enriched in the basal ganglia (including the striatum) and forms heteromeric complexes with dopamine receptor 2 (D2R). Nonselective adenosine receptor antagonists, caffeine and theophylline, were found to alleviate classical symptoms in animal models of PD. In addition to D2R, A2AR also interacts with A1R, metabotropic glutamate receptor-5, cannabinoid receptor type-1, and serotonin receptor 1A, modulating striatal neuron activity and motor performance [11, 24, 218]. Accordingly, it has been shown that specific A2AR antagonists attenuate motor impairment in a wide variety of PD models by reducing dopamine depletion, loss of dopaminergic neurons, production of reactive oxygen species, and aggregation of α-synuclein [218]. Among these A2AR antagonists, istradefylline (KW6002) has been approved as an adjunct treatment with levodopa/carbidopa in PD patients. More importantly, the treatment may not exacerbate the dyskinetic response [98]. The outcomes and safety profiles of many other A2AR antagonists have not met expectations [182, 218].
The success of istradefylline encourages the development of novel approaches targeting adenosine homeostasis as a nondopaminergic strategy for PD treatment. Aberrant gene expression involved in purine metabolism, such as ADA and CD73 expression, has been reported in PD-affected brain regions [90, 221] (Table 1), suggesting a primary manifestation or compensatory effects of altered purine metabolism in PD. Consistently, metabolites in purine metabolism pathways were found to be altered in the MPTP-based mouse model of PD [114]. These observations support the idea that the impairment of adenosine homeostasis is a rational target for PD pathogenesis. A hypothesis suggesting that inhibition of ADA with deoxycoformycin significantly ameliorates motor disability, dopamine depletion, and the death of dopaminergic neurons in PD mice has been supported. In addition, cotreatment with an ADA inhibitor and istradefylline showed additive antiparkinsonian activities [114]. Moreover, this combination treatment reduced microglial activation and overproduction of proinflammatory cytokine tumor necrosis factor-α in the substantia nigra and striatum, respectively [114] (Table 2). In contrast, removing extracellular adenosine with ADA was shown to prevent 6-hydroxydopamine (6-OHDA)-induced toxicity in a dopamine-differentiated SH-SY5Y cell model [38] (Table 2). The roles of ADA in the pathogenesis and intervention of PD remain to be clarified.
Extracellular adenosine can be produced through the CD73-mediated pathway. Genetic deletion of CD73 reduced the level of adenosine in the striatum but not in the cortex or hippocampus, showing a region-specific role of CD73 in adenosine formation [175]. With regard to PD, genetic deletion of CD73 modulated microglial-mediated responses, including reducing the release of proinflammatory cytokines in LPS-challenged microglia and increasing microglial process extension and mobility in an acute MPTP mouse model [175]. The role of CD73 in PD pathogenesis was also evaluated in a subacute MPTP model, with the results showing that, in addition to the modulation of neuroinflammatory responses, CD73 knockout partially prevented MPTP-induced dopaminergic neuron loss and motor impairment [175] (Table 2). The underlying mechanism has been shown to be associated with A2AR overactivation and unbalanced dopamine signaling in the nigrostriatal pathway [38, 175]. These findings support not only the supposition that A2AR activation plays a detrimental role in PD but also the idea that the development of CD73 inhibitors and the combined therapy of CD73 inhibitors with A2AR antagonists are worthy of further investigation.
AMPK activation has been shown to be neuroprotective in several disease models, including PD models. The downstream signaling pathways of AMPK have been implicated in the regulation of energy homeostasis, mitochondrial functions, macroautophagy, oxidative stress, and inflammatory responses. All of these pathways are relevant to the pathophysiology of PD. Accordingly, AMPK activation has been demonstrated to alleviate two major pathological hallmarks of PD, the degeneration of nigrostriatal dopaminergic neurons and the accumulation of α-synuclein in Lewy bodies in different PD model systems, including cell culture, fly, and rodent models (Table 2). Several excellent review articles have been devoted to these findings [64, 89, 103]. Among the AMPK activators, resveratrol and metformin have been tested the most extensively in PD models. However, the detrimental effects of activating AMPK have also been reported [64]. For example, AMPK overactivation may contribute to neuronal atrophy and progressive degeneration of dopaminergic neurons in a 6-OHDA-induced PD model [133]. Therefore, for the treatment of PD, the extent and duration of AMPK modulation should be carefully evaluated. On the other hand, identifying a more specific target in AMPK-related signaling pathways may be more favorable.
Huntington’s disease (HD)
HD is a dominant genetic neurodegenerative disease caused by an expansion of the CAG repeat in exon 1 of the Huntingtin gene. This expanded CAG repeat encodes a polyglutamine (polyQ) stretch in the Huntingtin protein (mHTT) and causes the accumulation of mHTT in neurons, which causes neuronal toxicity and death. The clinical presentations of HD include the progression of chorea, motor dysfunction, psychiatric abnormalities, and cognitive impairment, with the striatum and cerebral cortex the most affected brain areas [169]. Because HD is a monogenic disease, in the past two decades, excellent genetic mouse models have been established to support various mechanistic studies of HD pathogenesis. Nonetheless, at this time, drugs are available only for symptom relief, not for disease modification [39, 154].
The functions of two adenosine receptors (A1R and A2AR) have been evaluated as drug targets in HD [23, 47, 145]. The expression of A1R is reduced, while its ability to suppress presynaptic glutaminergic transmission is enhanced in HD mice. In addition, treatment with an A1R agonist (N6-cyclopentyladenosine) reversed mHTT-evoked neuronal toxicity. Compared with that of healthy subjects, the expression level of A1R was also found to be lower in HD patients in the symptomatic stage [167], suggesting that A1R may be a drug target [84]. A2AR is highly enriched in the striatum, the brain area most affected by HD, and therefore has attracted considerable attention in the past decade. Most likely because of mHTT-mediated toxicity induced during HD progression, a gradual loss of A2AR has been reported in patients and in mouse models of HD [99, 145]. Chronic treatment of HD mice (R6/2) with several agonists (CGS21680, T1-11) of A2AR markedly delayed disease progression and reduced the accumulation of the disease-causing protein (mHTT) [47, 54, 113]. Genetic removal of A2AR in HD mice (N171-82Q) also greatly worsened the motor performance and survival of the HD mice [176]. During disease progression, the expression of A2AR is known to gradually decrease in striatal medium spiny neurons (MSNs) and may contribute to the degeneration of MSNs in HD. The loss of A2AR in the late disease stage suggests that the therapeutic window for A2AR agonists might exist in the early symptomatic stage [145].
Abnormal adenosine metabolism has also been observed in several mouse models (R6/2, zQ175) and humans with HD. In the striatum, the expression levels of two ENTs are elevated, while brain adenosine tone is diminished (Table 1) [99, 127]. Suppression of ENT1 by genetic or pharmacological approaches both improved motor functions and prolonged the survival of HD mice (Table 2) [127]. Interestingly, the expression of mHTT enhances the activity of ADA while suppresses those of CD39 and CD73 in a cell model (HEK293) [217]. Moreover, the amount of ADK transcript was found to be upregulated in HD mice (R6/2) [127] (Table 1). These findings collectively indicate that adenosine homeostasis is dysregulated at multiple levels and that proteins controlling adenosine homeostasis (e.g., ENT1) may serve as good drug candidates to delay HD progression.
As mentioned above, adenosine homeostasis is closely associated with cellular energy status. Moreover, the expression of mHTT has long been known to damage mitochondria [212], which may further impair the energy supply to neurons in HD. Consistently, the expression of mHTT in a cell model causes a reduction in ATP [217]. In the brains of HD mice (R6/2) in the late disease stage and HD patients, abnormal overactivation and translocation of AMPK-α1 in MSNs exert detrimental effects [124, 125] (Table 1). Activation of AMPK-α1, therefore, is likely to worsen neuronal survival in HD. Nonetheless, treatment of HD mice (Hdh150Q knock-in, R6/2, and zQ175) with metformin, a first-line antidiabetic drug that can activate both AMPK-dependent and AMPK-independent pathways, produced beneficial effects [12, 107, 163, 205]. As discussed above, it is important to evaluate whether the beneficial effect of metformin is AMPK-dependent. In addition, the contribution of AMPK isoforms to the effect of metformin (or other AMPK activators) and HD pathogenesis at different disease stages requires further investigation.
Amyotrophic lateral sclerosis (ALS)
ALS is a rare motor neuron disease caused by the degeneration of upper and lower motor neurons, resulting in progressive paralysis, muscle wasting, and early death [240]. Most ALS cases are sporadic (sALS, ~ 90%), and approximately 10% of ALS patients (fALS) have mutations in a group of more than 50 genes associated with ALS (including C9orf72, SOD1, TARDBP, FUS, and HuR) [130, 173]. Most likely due to the complex etiology of ALS, only a handful of drugs (e.g., edaradone, riluzole, and dextromethorphan) with limited therapeutic effects are currently available. Although promising approaches targeting various machineries (e.g., neuroinflammation, neuronal hyperexcitability, energy homeostasis, and mitochondrial dysfunction) have been actively pursued, no treatment that can halt or reverse the progression of ALS is currently available [131].
Abnormal adenosine homeostasis has long been observed in ALS. Specifically, the level of adenosine in the cerebrospinal fluid of ALS patients is higher than that of normal subjects [255]. Consistently, the expression levels of ADA in the neurons and astrocytes differentiated from the iPSCs of ALS patients were much lower than those obtained from normal subjects. Previous studies have also revealed the upregulation of ADK activity and the suppression of CD39 in the spinal cord of ALS patients and a mouse model of ALS (SOD1(G93A)) [25, 33, 230]. Collectively, these studies document abnormalities in adenosine homeostasis, which may weaken the ability of motor neurons in the spinal cord of ALS patients to respond to energy stress.
Not only is the adenosine level in the cerebrospinal fluid of ALS patients higher, but the expression of A2AR in the spinal cord of ALS patients also appears to be elevated [185, 227]. In a mouse model of ALS (SOD1(G93A)), A2AR appeared to be dynamically regulated in the spinal cord [185, 200]. Nonetheless, treatments targeting adenosine receptors produce seemingly inconsistent effects. For example, treatment of SOD1(G93A) mice with a nonselective adenosine receptor antagonist (caffeine) worsened their survival without affecting bodyweight or motor function [200]. Surprisingly, although the administration of an A2AR-selective antagonist (KW6002) and partial genetic ablation of A2AR both delayed diminished grip strength and attenuated the shortened lifespan of SOD1(G93A) mice, complete removal of A2AR showed no effect [185]. In contrast, treatment of SOD1(G93A) mice with a specific A2AR agonist (CGS2168) greatly delayed the onset of impaired rotarod performance and protected against the loss of motor neurons without affecting overall survival [254]. The treatment window of A2AR activation may have been narrow in this particular ALS mouse model. Interestingly, in another ALS mouse model (Tg-TDP-43), chronic treatment with another A2AR agonist (JMF1907) significantly improved motor functions by suppressing the overactivation of AMPK-α1 in the spinal cord [155]. In the future, the role of A2AR in ALS certainly needs further investigation, particularly with respect to disease stage, the choice of preclinical model, and route of administration.
Another emerging interest in ALS is the role of AMPK. Several studies have reported that AMPK is activated in motor neurons in the spinal cord of human ALS patients and several experimental models of ALS and that it plays a detrimental role in the survival of motor neurons [153, 155]. Importantly, the abnormal activation of AMPKα1 mediates the mislocalization of TDP-43 from the nuclei to the cytoplasmic region, an early event in ALS pathogenesis (Table 1) [155]. This overactivation of AMPK and mislocalization of several RNA-binding proteins (including TDP-43 and HuR) can be suppressed by inducing A2AR activation with one of several BBB-permeable agonists (JMF1907 and T1-11) via the cAMP/PKA-dependent pathway [141, 155, 156]. In addition, activation of AMPK in the spinal cord of SOD1-(G93A) mice was markedly enhanced by diet restriction, worsening symptom onset (as assessed by grip strength), motor neuron loss, and survival. A high-fat diet not only reduced the overactivation of AMPK but also produced marked beneficial effects, probably through an HSP90-dependent pathway [257]. These findings obtained in preclinical studies are consistent with those of a recent clinical study showing that a high-calorie fatty diet produced a marked survival benefit in ALS patients with fast progression [160]. Collectively, the data show that suppression of AMPK by various means may be a possible therapeutic strategy for ALS. Notably, treatments of ALS mice with several known AMPK activators (e.g., resveratrol, latrepirdine, and metformin) were shown to delay disease progression and enhance the survival of motor neurons [58, 256, 263]. As discussed above, most agents tested in preclinical studies activated not only AMPK but also other AMPK-independent pathway(s). It will be of great interest to determine whether the beneficial effects of these agents are mediated solely by AMPK and to characterize the sensitivity of AMPK subtypes to these agents.
Neurodegenerative disease-associated epilepsy
Epilepsy is a common brain disorder, which can be triggered by multiple pathological factors. Despite being a neuroelectrical disorder, epilepsy shares several pathological features (such as neurodegeneration, astrogliosis, and BBB abnormalities) with multiple neurodegenerative diseases [82], and is frequently observed in patients with neurodegenerative diseases [82, 194]. These observations suggest that neurodegenerative pathways can be the potential stimuli of epileptic seizures. In addition, early recognition and closer management are needed to minimize the morbidity and mortality resulting from seizures in patients with neurodegenerative diseases. Numerous drugs have been approved for the management of epilepsy based on the strategy of decreasing the electrical activity of the neuronal connection. The mechanisms of anti-epileptic drugs include the blockade of sodium channels/calcium channels/glutamate receptors, enhancement of γ-aminobutyric acid (GABA) receptor activity, and inhibition of GABA degradation/reuptake. However, approximately 30% of patients with seizures are respond poorly to the currently available anti-epileptic drugs.
Adenosine is an inhibitory neuromodulator and has been proposed as an endogenous anticonvulsant molecule [73, 78]. An increase in extracellular adenosine and sustained enhancement in adenosine metabolites (including hypoxanthine, xanthine, and inosine) were observed in the brains of epileptic animal models, suggesting a compensatory protective mechanism in response to seizures [1, 111]. On the other hand, since A1R activation mediates presynaptic inhibition and stabilization of excitatory membrane potential, it has been logically speculated that dysregulation of A1R signaling may contribute to epileptogenesis. Pathological evidence has shown that A1R is downregulated in human temporal lobe epilepsy [92]. In the hippocampus of a kindled rat model, the density and neuromodulation effect of A1R were decreased [201]. Another study showed that A1R was unchanged at the protein level but was desensitized in status epileptic rats [101]. Despite downregulation and/or dysfunction, A1R activation has been widely shown to effectively suppress seizures in brain slices of patients with epilepsy [134] and epileptic animal models [83, 95, 101, 137]. These findings suggest that A1R activation may be a promising strategy for epilepsy management. Compared with A1R, less attention has been directed to the role of A2AR in epilepsy. Consistent with the neuronal facilitatory effect of A2AR signaling, the suppression of A2AR by genetic or pharmacological approaches has been reported to protect against seizures [75, 76]. The roles of A2BR and A3R in the pathogenesis of epilepsy are less evident.
Since A1R is a powerful treatment target for seizures, adenosine augmentation is considered an effective therapeutic strategy for epilepsy. Adenosine tone can be regulated by ENT1-mediated uptake machinery on the plasma membrane. The expression level of ENT1 is significantly increased in patients with epilepsy and in epileptic animal models [248, 259] (Table 1). Direct injection of a specific ENT1 inhibitor, nitrobenzylthioinosine, into the hippocampus ameliorated the severity of seizures and prolonged the onset latency of pilocarpine-induced seizures in rats [248]. Recently, systemic administration of BBB-permeable ENT1 inhibitors (JMF1907 and J4) produced beneficial effects in various seizure models that represent generalized tonic–clonic seizures, generalized myoclonic seizures, and focal seizure conditions [111] (Table 2). The anti-epileptic effects were associated with the suppression of excitatory neuronal activities by reducing the action potential-dependent release of neurotransmitters [111]. There was no direct evidence showing that specific adenosine receptors are involved in the protective effects of ENT1 inhibition in epilepsy.
Interestingly, a marijuana derivative (cannabidiol) has been shown experimentally and clinically to have anti-seizure properties for decades [36, 68, 69]. Given that cannabidiol is an ENT1 inhibitor [40], its anticonvulsant effects were proposed to be, at least in part, mediated by the increase in adenosine tone and the subsequent activation of A1R. Cannabidiol has been approved in the US and European Union for the treatment of seizures associated with Lennox-Gastaut syndrome, Dravet syndrome, or tuberous sclerosis complex [109, 216], supporting the idea of ENT1 inhibition for epileptic treatment, even for drug-resistant types. Nevertheless, in addition to the inhibition of ENT1, the molecular target(s) and effects of cannabidiol appear to be complex, including the activation of voltage-gated sodium channels, serotonin receptors, an orphan receptor (G protein-coupled receptor 55), nicotinic acetylcholine receptors, and anandamide transporters [97, 116].
In addition to ENT1, the role of ADK (a key adenosine-metabolizing enzyme) in the pathogenesis of epilepsy has been extensively explored in recent years. ADK is predominantly expressed in astrocytes and is believed to dictate intracellular adenosine levels. Astrogliosis is a pathological hallmark of epilepsy. In the human temporal lobe with epilepsy and in the hippocampus and cortex of rodent models with epilepsy, ADK was found to be overexpressed in reactive astrocytes [13, 165] (Table 1). The increased level of ADK was associated with overproduction of the proinflammatory cytokine interleukin-1β in epileptic conditions [13]. The critical role of ADK in epileptogenesis was confirmed by the findings that pharmacological and genetic inhibition of ADK suppressed seizure-like activities in epileptic models [96, 152] (Table 2). Interestingly, although A1R is involved in the protective effects of ADK inhibition under certain neuropathological conditions [161], it has been increasingly recognized that the anti-seizure effects of ADK inhibition are mainly mediated by the modulation of epigenetic machinery (e.g., DNA methylation) but not the adenosine receptor-dependent pathway. In the epileptic brain, the pathological increase in ADK levels was proposed to cause intracellular adenosine deficiency, sequentially driving the donation of a methyl group from SAM to DNA (Fig. 1). This modification shifts the brain into an aberrant hypermethylated state, in which the expression of many genes underlying neuronal excitation and epileptogenesis are dysregulated [136]. In agreement with this concept, in one study, adenosine treatment normalized DNA hypermethylation and prevented the progression of epilepsy development, regardless of whether a nonselective adenosine receptor antagonist (caffeine) was coadministered [241]. These data indicate that modulation of epigenetic modification by adenosine augmentation therapy has great potential for the treatment of epilepsy.
Both genetic and acquired epilepsies have been linked to the excessive activation of the mammalian target of rapamycin (mTOR) signaling pathway. Because mTOR signaling can be inhibited by AMPK activation-mediated phosphorylation of mTOR regulatory proteins, the role of AMPK in the development and intervention of epilepsy has attracted attention. In the brain tissues of humans with chronic seizures and animals with acute and chronic seizures, the protein expression of AMPK is reduced [252] (Table 1). In addition, AMPK-null mice were reported to have increased seizure susceptibility through unregulated mTOR signaling [179]. Consistently, pharmacological activation of AMPK by metformin, one of the most extensively prescribed antidiabetic drugs, attenuated seizure activity in a pilocarpine-induced epileptic model, with inhibited mTOR phosphorylation [172]. The anticonvulsant effects of metformin are also consistent with the suppression of overexpressed brain-derived neurotropic factor, a contributor to epileptogenesis [22, 172]. Moreover, chronic treatment with metformin decreased mortality and shortened the duration of generalized tonic–clonic seizures in an acute seizure model and reduced the duration of epileptic activity in a chronic seizure model [252]. These findings are summarized in Table 2. Notably, the AMPK-mTOR signaling pathway mediates a wide variety of cellular events. The detailed mechanism modulated by the AMPK-mTOR axis in epilepsy remains unclear and requires further investigation.
Neurodegenerative disease-associated sleep disorder
Sleep disturbances are commonly associated with neurodegenerative diseases and are known to greatly affect the quality of life of patients [119]. For example, sleep disorders, such as nighttime insomnia, daytime hypersomnia, and rapid eye movement (REM) sleep disorders, are often seen in patients with AD [159, 188] or PD [77, 253]. Many effective sedative-hypnotic drug products, including benzodiazepine and Z-drugs (e.g., zolpidem, zaleplon, zopiclone) are used to induce and/or maintain sleep in people with sleep disorders. Previous studies documented that the extracellular level of adenosine increases in the cortex and basal forebrain during wakefulness and decreases during sleep. The dynamic regulation of adenosine in the sleep–wake cycle suggests that adenosine is a homeostatic regulator of sleep [199]. Both A1R and A2AR have been implicated in sleep induction. Activation of A2AR is known to increase sleep, while the arousal effect of caffeine (a nonselective antagonist) is dependent on the blockade of A2AR [20, 115]. Consistent with these findings, oral administration of a BBB-permeable A2AR agonist (T1-11) increases nonrapid eye movement (NREM) sleep [123]. Since adenosine homeostasis is regulated by ENTs, the expression and functions of ENTs (especially ENT1) in the regulation of sleep have also been extensively investigated. For instance, sleep deprivation markedly reduces the amount of ENT1 protein (but not ENT1 transcript) in a specific brain region (the basal forebrain), suggesting that ENT1 is tightly regulated in sleep and that adenosine transport across the plasma membrane can be altered by sleep disruption [4]. In agreement with this concept, genetic removal of ENT1 impairs normal sleep–wake regulation [132]. Notably, sleep deprivation not only affects the level of ENT1 but also reduces the activity of ADK and 5’-endonucleotidases in the basal forebrain. Sleep disruption can thus alter cellular adenosine metabolism at multiple steps [3]. In contrast, the overexpression of ADK (the cytoplasmic isoform) markedly affects sleep physiology in mice and reduces NREM sleep enhanced by sleep deprivation [189]. It was therefore not surprising to find that the loss of CD73, a 5’-ectonuclotidase, increases the duration of NREM sleep and impairs the response of animals to sleep deprivation [260]. Collectively, these findings support the idea that adenosine homeostasis plays a central role in sleep regulation and that proteins involved in controlling adenosine metabolism are feasible drug targets for the development of new treatments for sleep disorders associated with neurodegenerative diseases.
Potentials and challenges in the future development of adenosine-related therapies
Despite the tremendous efforts that have been devoted to studies of neurodegenerative diseases in the past two decades, effective treatments for many neurological and neurodegenerative diseases remain unmet medical needs. Since neurodegenerative diseases are characterized by specific protein pathologies (e.g., amyloid plaques and neurofibrillary tangles for AD, Lewy bodies for PD, and mHTT inclusions for HD), these proteins are considered as the primary driver of the corresponding disease. Unfortunately, despite promising preclinical success, most treatment attempts by directly targeting these neurotoxic proteins have failed to obtain satisfactory results in clinical studies. The potential difficulties causing such a gap between preclinical observations and clinical applications include inappropriate drug targets, animal models, intervention timing, and patient populations. Taking AD as an example, most advanced disease-modifying drugs under clinical development focus on β-amyloid or tau protein and therefore their treatment responses were usually demonstrated in animal models overexpressing these two targets, respectively. This is because no single animal model can fully recapitulate all the pathological phenotypes of human AD [17]. Before moving into clinical studies, careful evaluation of a therapeutic agent in additional animal models based on different mechanisms thus would be very helpful to reduce the risk of translational failure. Another concern is whether the treatment intervention is early enough to slow or halt neurodegeneration and behavioral declines. Most patients attending clinics usually have developed obvious clinical symptoms with significant protein pathology, neuronal loss, and even brain atrophy. It appears to be critical to initiate the treatment as early as possible. Most importantly, the complex mechanisms of human neurodegenerative diseases need to be extensively investigated in order to design effective therapeutic treatments. Notably, although neurodegenerative diseases are attributable to different neurotoxic proteins, most of them cause common early events, including dysregulations in energy metabolism, mitochondrial function, and neuroinflammation [100, 180]. At the early disease stage in which there may be no detectable clinical and functional abnormality, these pathogenic mechanisms, either alone or in combination, contribute to dysfunction of neurons and glial cells, thereby leading to harmful protein aggregation/accumulation and later neurotoxicity [55, 151]. The implications of adenosine homeostasis in the regulation of bioenergetic and inflammatory pathways as detailed in the previous section provide a strong rationale for exploring the benefit of adenosine-related therapies.
As detailed in this review, ample evidence suggests that adenosine-related mechanisms under various pathophysiological conditions may open up new avenues for the development of novel therapeutic approaches. In recent decades, targeting adenosine receptors has been extensively pursued, and the effort continues to evolve. Accumulating evidence suggests that activation of A1R and A2AR can be neuroprotective and neurodegenerative, respectively [74]. Thus, A1R agonists and A2AR antagonists have been developed as pharmacological agents. The challenges to developing adenosine receptor drugs have been discussed elsewhere [23, 74] and are not elaborated here. In brief, many orthosteric adenosine receptor agonists can cause adverse effects on cardiovascular systems. Although A2AR antagonists seem to be well tolerated, the effectiveness of A2AR ligands may depend on the treatment dosage, timing, and symptoms. For example, in a model of brain autoimmune disease, A2AR activation was shown to be beneficial at an early stage but detrimental at a later stage [117]. In addition, activation of A2AR improved motor function, whereas blockade of A2AR was beneficial for cognitive function in mouse models of HD [23].
In addition to agents targeting adenosine receptors, the development of pharmacological agents that modulate adenosine-metabolizing enzymes or transporters has attracted increasingly interest. Accumulating evidence has shown that these novel strategies (for example, ADK inhibitors and ENT inhibitors) have produced initial promising results in preclinical studies [23, 25, 46, 144]. Further optimization of these newly developed agents and the characterization of the underlying mechanisms warrant further investigation. Another interesting strategy for treating neurodegenerative diseases is the development of anti-inflammatory agents based on the control of adenosine homeostasis. This tactic is of great interest because adenosine, by acting through receptors, is recognized as an endogenous potent anti-inflammatory agent. Nonetheless, its role in the regulation of neuroinflammatory responses is relatively less clear. How neuroinflammation is modulated in the brain by adenosine-related mechanisms is discussed below.
Challenges in the development of ADK inhibitors
Adenosine augmentation therapy has been shown to be beneficial for several brain disorders, particularly epilepsy. Proof-of-concept studies of several ADK inhibitors have been carried out successfully in animal models of epilepsy [139, 170]. Nonetheless, further development of these inhibitors is hindered by adverse reactions (including cardiovascular events and hepatic steatosis) observed during chronic application [26, 96, 239]. It has been proposed that these limitations can be overcome by two strategies. First, using ADK inhibitors in a short-term regimen would help to reduce systemic toxicities. A novel treatment methodology has been successfully developed in which the transient use of a small-molecule ADK inhibitor during the critical stage of epileptogenesis provides disease-modifying effects against epilepsy in animals [206]. Second, the development of selective inhibitors for the nuclear isoform of ADK would reduce the treatment dose of traditional nonselective ADK inhibitors. There are two isoforms of ADK, namely, ADK-long (ADK-L) and ADK-short (ADK-S), in mammalian cells. ADK-L and ADK-S were shown to be localized in the nucleus and cytoplasm, respectively [62], suggesting a specific function for the long isoform in gene regulation. Consistently, ADK-L is significantly more effective than ADK-S in the regulation of DNA methylation [241]. These observations, combined with the finding that ADK-L is predominantly expressed in the brain [61], suggest that targeting ADK-L might lead to the development of a more efficient way of modulating epigenetics in epileptogenesis. Further studies are needed to test whether novel approaches based on ADK inhibition can satisfy the requirements for efficacy and safety.
Challenges in the development of ENT inhibitors
ENTs play essential roles in the control of adenosine homeostasis. The function of ENT1 in the transport of adenosine, regulating cellular functions in the brain, has been extensively studied [214]. As described above, several BBB-permeable ENT1 inhibitors have recently been developed as potential drug candidates for the treatment of multiple neurodegenerative diseases, including AD, HD, ALS, and epilepsy [46, 111, 127, 141, 144]. Although the safety of systemic inhibition of ENT1 using these novel compounds has not yet been revealed, it is unlikely to be a major concern because several potent, but BBB impermeable, ENT1 inhibitors (such as ticagrelor and dipyridamole) have been widely used in the clinic [29, 42]. For future development, the safety profiles of these ENT1 inhibitors in the CNS need to be carefully evaluated before they are entered into clinical trials.
The roles of another ENT member, ENT2, in healthy and diseased brains have been recently investigated. They are very important for the control of adenosine augmentation because the transcript level of ENT2 is significantly higher than that of ENT1 in the brain. In addition, using a genetic deletion approach, ENT2 was shown to be the key determinant for modulating adenosine levels in the brain, particularly in the hippocampus [244]. Because ENT2 exhibits lower affinity and higher capacity than ENT1, it has been postulated that ENT2 is the dominant transporter when the adenosine level is dramatically elevated under certain pathological conditions. In line with this hypothesis, the extracellular adenosine level was found to be significantly elevated in ENT2-knockout mice, especially under LPS-challenge conditions, thereby protecting against LPS-induced neuroinflammation, BBB damage, and memory impairment [243, 244]. Given that neuroinflammation is critical for the pathogenesis of almost all neurodegenerative diseases, ENT2 inhibition may be a potential therapeutic strategy for these disorders in the brain. Unfortunately, to the best of our knowledge, no ENT2-specific inhibitor has been developed thus far. At this time, only a few compounds (e.g., soluflazine, R70960) that have a relatively higher affinity for ENT2 than for ENT1 have been reported [102, 229]. To target brain disorders associated with neuroinflammation, the development of novel ENT2-specific inhibitors that are BBB permeable is highly desirable. Given that no obvious defect in global ENT2-knockout mice was observed [243, 244], systemic inhibition of ENT2 may be a feasible pharmacological approach.
Modulation of neuroinflammation by adenosine-related mechanisms
Neuroinflammation is a common feature of neurological and neurodegenerative diseases. Adenosine has been recognized as an anti-inflammatory molecule because the augmentation of endogenous adenosine diminishes inflammation in peripheral systems [2, 121, 178]. In the CNS, direct adenosine treatment and the activation of several adenosine receptors (e.g., A2AR, A2BR, and A3R) attenuated the LPS-induced upregulation of proinflammatory cytokines and increased the production of anti-inflammatory cytokines in microglia [138, 148, 223]. In addition, adenosine augmentation, induced by either the inhibition of ENTs or ADK or the activation of A1R or A2AR, alleviated neuroinflammation in some pathological animal models of AD and PD and neuroinflammation induced by intracerebral hemorrhage, multiple sclerosis, or LPS [46, 114, 168, 220, 244]. However, opposite results showed that A2AR signaling is involved in the facilitation of neuroinflammation and is associated with neuronal injuries [38, 175, 202]. These seemingly controversial data indicate that adenosine is undoubtedly an immunomodulator in the brain, but the outcome of adenosine receptor-mediated signaling may be dependent on the disease type, disease stage, and brain area involved. For example, it was reported that A2AR activation exhibited anti-inflammatory effects and prevented pathological symptoms only when the treatment was introduced at an early stage of autoimmune neuroinflammation in the brain. In contrast, A2AR activation in the late stage was detrimental [117]. An additional issue is the affected area(s). The differential distribution and interplay of adenosine receptors among themselves and/or with other types of receptors may lead to region-specific regulation of neuroinflammatory responses. Moreover, under certain pathological conditions, compromised BBB and aberrant interaction between the central and peripheral immune systems may contribute to neuroinflammation [66, 128]. Therefore, the combined impact of adenosine modulation on central and peripheral immune responses may be considered. Furthermore, other coexisting factors may modulate the role of adenosine receptors on immune responses. For example, the local level of glutamate, which may be dramatically increased during brain injury, switches the effect of A2AR activation from a proinflammatory to an anti-inflammatory status [65]. Intriguingly, increased adenosine tone and A1R activation in ENT2-knockout mice under neuroinflammatory conditions normalized excessive extracellular glutamate by increasing the level of a major glutamate reuptake transporter, EAAT2 [243]. In this circumstance, activation of both A1R and A2AR may have led to anti-inflammatory effects [244]. It remains unknown whether ENT2 inhibition produces any effect on chronic inflammation in the context of neurodegenerative diseases. Further investigations are required to advance our current understanding regarding how adenosine modulates neuroinflammation caused by different insults, and the findings may offer new insights into the development of novel therapeutic treatments for neurodegenerative diseases.
Conclusions
Ample evidence suggests that the tight control of adenosine levels, a measure of adenosine homeostasis, is critical for the maintenance of cellular functions, particularly energy production and gene regulation [46, 122, 171, 192, 207, 238]. This regulatory importance may explain why coordinated regulation of adenosine metabolic enzymes under various pathophysiological conditions has been reported and may support the contention that adenosine homeostasis undergoes dynamic regulation induced by environmental cues. Moreover, adenosine homeostasis not only plays a critical role in the regulation of neuronal functions/plasticity but also greatly contributes to the interaction between neurons and glia [6, 59, 105, 106]. Assessing the interaction between brain cells in vivo is a challenging task. The recent development of single-cell transcriptome profiling technology is expected to greatly facilitate the delineation of adenosine homeostasis regulation among different types of brain cells (e.g., neurons vs. glia), especially in neuroinflammation. Notably, isotype-specific antibodies and pharmacological tools (i.e., activators, allosteric modulators, and inhibitors) are definitely required for in-depth investigations and future clinical applications. Some of these tools are currently unavailable due to the lack of comprehensive knowledge regarding the structure and function of the proteins that govern adenosine metabolism. Specifically, antibodies and isotype-specific inhibitors of the four members of the ENT family are not commonly available at this time, thus hindering the understanding of the functional roles of these ENTs in neurodegenerative diseases. As an increasing number of high-resolution protein structures have been resolved by cryo-electron microscopy, the protein structures of ENTs may also be thus obtained to facilitate the development of specific antibodies and/or inhibitors for ENTs. These new tools together with the intriguing findings on dysregulated adenosine homeostasis in neurodegenerative diseases are the bases for further investigation, which may pave the wave for the development of novel therapeutic treatments in the future.
Availability of data and materials
Not applicable.
Abbreviations
- 5’UTR:
-
5’ Untranslated region
- 6-OHDA:
-
6-Hydroxydopamine
- Aβ:
-
β-Amyloid
- AC:
-
Adenylyl cyclase
- AD:
-
Alzheimer's disease
- ADA:
-
Adenosine deaminase
- ADK:
-
Adenosine kinase
- ADP:
-
Adenosine diphosphate
- AK:
-
Adenylate kinase
- ALS:
-
Amyotrophic lateral sclerosis
- AMP:
-
Adenosine monophosphate
- AMPA:
-
α-Amino-3-hydroxy-5-methyl-4-isoxazolepropionic acid
- AMPK:
-
AMP-activated protein kinase
- ATP:
-
Adenosine triphosphate
- BBB:
-
Blood–brain barrier
- CNS:
-
Central nervous system
- CNT:
-
Concentrative nucleoside transporters
- CREB:
-
CAMP-response element binding protein
- CSDS:
-
Chronic social defeat stress
- D2R:
-
Dopamine receptor 2
- DNA:
-
Deoxyribonucleic acid
- DNMTs:
-
DNA methyltransferases
- EAAT2:
-
Excitatory amino acid transporter 2
- ENT:
-
Equilibrative nucleoside transporters
- GABA:
-
γ-Aminobutyric acid
- GPCR:
-
G protein-coupled receptor
- HD:
-
Huntington’s disease
- iPSC:
-
Induced pluripotent stem cell
- LPS:
-
Lipopolysaccharide
- mHTT:
-
Mutant Huntingtin
- MFF:
-
Mitochondrial fission factor
- MPTP:
-
1-Methyl-4-phenyl-1,2,3,6-tetrahydropyridine
- MSN:
-
Medium spiny neuron
- mTOR:
-
Mammalian target of rapamycin
- NDPK:
-
Nucleotide diphosphokinase
- NLRP3:
-
NLR family pyrin domain containing 3
- NREM:
-
Non-rapid eye movement
- P2Y12:
-
Purinergic receptor P2Y, G-protein coupled,12
- PEXN motif:
-
Amino acid residues Pro71, Glu72, and Asn74
- PD:
-
Parkinson's disease
- PKA:
-
Protein kinase A
- PolyQ:
-
Polyglutamine
- REM:
-
Rapid eye movement
- SAH:
-
S-adenosylhomocysteine
- SAHH:
-
S-adenosylhomocysteine hydrolase
- SAM:
-
S-adenosylmethionine
- TDP-43:
-
TAR DNA binding protein 43
- ULK1:
-
Unc-51 Like Autophagy Activating Kinase 1
References
Aden U, O’Connor WT, Berman RF. Changes in purine levels and adenosine receptors in kindled seizures in the rat. NeuroReport. 2004;15(10):1585–9.
Aherne CM, Collins CB, Rapp CR, Olli KE, Perrenoud L, Jedlicka P, Bowser JL, Mills TW, Karmouty-Quintana H, Blackburn MR, Eltzschig HK. Coordination of ENT2-dependent adenosine transport and signaling dampens mucosal inflammation. JCI Insight. 2018. https://doi.org/10.1172/jci.insight.121521.
Alanko L, Heiskanen S, Stenberg D, Porkka-Heiskanen T. Adenosine kinase and 5’-nucleotidase activity after prolonged wakefulness in the cortex and the basal forebrain of rat. Neurochem Int. 2003;42(6):449–54.
Alanko L, Stenberg D, Porkka-Heiskanen T. Nitrobenzylthioinosine (NBMPR) binding and nucleoside transporter ENT1 mRNA expression after prolonged wakefulness and recovery sleep in the cortex and basal forebrain of rat. J Sleep Res. 2003;12(4):299–304.
Albasanz JL, Perez S, Barrachina M, Ferrer I, Martin M. Up-regulation of adenosine receptors in the frontal cortex in Alzheimer’s disease. Brain Pathol. 2008;18(2):211–9.
Allaman I, Lengacher S, Magistretti PJ, Pellerin L. A2B receptor activation promotes glycogen synthesis in astrocytes through modulation of gene expression. Am J Physiol Cell Physiol. 2003;284(3):C696-704.
Allen SP, Hall B, Castelli LM, Francis L, Woof R, Siskos AP, Kouloura E, Gray E, Thompson AG, Talbot K, Higginbottom A, Myszczynska M, Allen CF, Stopford MJ, Hemingway J, Bauer CS, Webster CP, De Vos KJ, Turner MR, Keun HC, Hautbergue GM, Ferraiuolo L, Shaw PJ. Astrocyte adenosine deaminase loss increases motor neuron toxicity in amyotrophic lateral sclerosis. Brain. 2019;142(3):586–605.
Alonso-Andrés P, Albasanz JL, Ferrer I, Martín M. Purine-related metabolites and their converting enzymes are altered in frontal, parietal and temporal cortex at early stages of Alzheimer’s disease pathology. Brain Pathol. 2018;28(6):933–46.
Antonioli L, Csoka B, Fornai M, Colucci R, Kokai E, Blandizzi C, Hasko G. Adenosine and inflammation: what’s new on the horizon? Drug Discov Today. 2014;19(8):1051–68.
Antonioli L, Pacher P, Vizi ES, Haskó G. CD39 and CD73 in immunity and inflammation. Trends Mol Med. 2013;19(6):355–67.
Armentero MT, Pinna A, Ferre S, Lanciego JL, Muller CE, Franco R. Past, present and future of A(2A) adenosine receptor antagonists in the therapy of Parkinson’s disease. Pharmacol Ther. 2011;132(3):280–99.
Arnoux I, Willam M, Griesche N, Krummeich J, Watari H, Offermann N, Weber S, Narayan DP, Chen C, Monteiro O, Buettner S, Meyer K, Bano D, Radyushkin K, Langston R, Lambert JJ, Wanker E, Methner A, Krauss S, Schweiger S, Stroh A. Metformin reverses early cortical network dysfunction and behavior changes in Huntington’s disease. Elife. 2018. https://doi.org/10.7554/eLife.38744.
Aronica E, Zurolo E, Iyer A, de Groot M, Anink J, Carbonell C, van Vliet EA, Baayen JC, Boison D, Gorter JA. Upregulation of adenosine kinase in astrocytes in experimental and human temporal lobe epilepsy. Epilepsia. 2011;52(9):1645–55.
Assefa BT, Tafere GG, Wondafrash DZ, Gidey MT. The bewildering effect of AMPK activators in Alzheimer’s disease: review of the current evidence. Biomed Res Int. 2020;2020:9895121.
Atif M, Alsrhani A, Naz F, Imran M, Imran M, Ullah MI, Alameen AAM, Gondal TA, Raza Q. Targeting adenosine receptors in neurological diseases. Cell Reprogram. 2021;23(2):57–72.
Badimon A, Strasburger HJ, Ayata P, Chen X, Nair A, Ikegami A, Hwang P, Chan AT, Graves SM, Uweru JO, Ledderose C, Kutlu MG, Wheeler MA, Kahan A, Ishikawa M, Wang YC, Loh YE, Jiang JX, Surmeier DJ, Robson SC, Junger WG, Sebra R, Calipari ES, Kenny PJ, Eyo UB, Colonna M, Quintana FJ, Wake H, Gradinaru V, Schaefer A. Negative feedback control of neuronal activity by microglia. Nature. 2020;586(7829):417–23.
Balducci C, Forloni G. APP transgenic mice: their use and limitations. Neuromol Med. 2011;13(2):117–37.
Barnes K, Dobrzynski H, Foppolo S, Beal PR, Ismat F, Scullion ER, Sun L, Tellez J, Ritzel MW, Claycomb WC, Cass CE, Young JD, Billeter-Clark R, Boyett MR, Baldwin SA. Distribution and functional characterization of equilibrative nucleoside transporter-4, a novel cardiac adenosine transporter activated at acidic pH. Circ Res. 2006;99(5):510–9.
Baron R, Babcock AA, Nemirovsky A, Finsen B, Monsonego A. Accelerated microglial pathology is associated with Abeta plaques in mouse models of Alzheimer’s disease. Aging Cell. 2014;13(4):584–95.
Basheer R, Strecker RE, Thakkar MM, McCarley RW. Adenosine and sleep-wake regulation. Prog Neurobiol. 2004;73(6):379–96.
Bicket A, Mehrabi P, Naydenova Z, Wong V, Donaldson L, Stagljar I, Coe IR. Novel regulation of equlibrative nucleoside transporter 1 (ENT1) by receptor-stimulated Ca2+-dependent calmodulin binding. Am J Physiol Cell Physiol. 2016;310(10):C808-820.
Binder DK, Croll SD, Gall CM, Scharfman HE. BDNF and epilepsy: too much of a good thing? Trends Neurosci. 2001;24(1):47–53.
Blum D, Chern Y, Domenici MR, Buée L, Lin CY, Rea W, Ferré S, Popoli P. The role of adenosine tone and adenosine receptors in Huntington’s disease. J Caffeine Adenosine Res. 2018;8(2):43–58.
Bogenpohl JW, Ritter SL, Hall RA, Smith Y. Adenosine A2A receptor in the monkey basal ganglia: ultrastructural localization and colocalization with the metabotropic glutamate receptor 5 in the striatum. J Comp Neurol. 2012;520(3):570–89.
Boison D, Aronica E. Comorbidities in neurology: is adenosine the common link? Neuropharmacology. 2015;97:18–34.
Boison D, Scheurer L, Zumsteg V, Rulicke T, Litynski P, Fowler B, Brandner S, Mohler H. Neonatal hepatic steatosis by disruption of the adenosine kinase gene. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2002;99(10):6985–90.
Boison D, Yegutkin GG. Adenosine metabolism: emerging concepts for cancer therapy. Cancer Cell. 2019;36(6):582–96.
Braak H, Del Tredici K, Rüb U, de Vos RA, Jansen Steur EN, Braak E. Staging of brain pathology related to sporadic Parkinson’s disease. Neurobiol Aging. 2003;24(2):197–211.
Brott DA, Andersson HAS, Stewart J, Ewart L, Christoph G, Harleman J, Armstrong D, Kinter LB. A peripherally restricted P2Y(12) receptor antagonist altered rat tumor incidences with no human relevance: mode of action consistent with dopamine agonism. Toxicol Rep. 2014;1:1202–12.
Buira SP, Albasanz JL, Dentesano G, Moreno J, Martin M, Ferrer I, Barrachina M. DNA methylation regulates adenosine A(2A) receptor cell surface expression levels. J Neurochem. 2010;112(5):1273–85.
Buira SP, Dentesano G, Albasanz JL, Moreno J, Martín M, Ferrer I, Barrachina M. DNA methylation and Yin Yang-1 repress adenosine A2A receptor levels in human brain. J Neurochem. 2010;115(1):283–95.
Busche MA, Hyman BT. Synergy between amyloid-beta and tau in Alzheimer’s disease. Nat Neurosci. 2020;23(10):1183–93.
Butovsky O, Jedrychowski MP, Cialic R, Krasemann S, Murugaiyan G, Fanek Z, Greco DJ, Wu PM, Doykan CE, Kiner O, Lawson RJ, Frosch MP, Pochet N, Fatimy RE, Krichevsky AM, Gygi SP, Lassmann H, Berry J, Cudkowicz ME, Weiner HL. Targeting miR-155 restores abnormal microglia and attenuates disease in SOD1 mice. Ann Neurol. 2015;77(1):75–99.
Calió ML, Henriques E, Siena A, Bertoncini CRA, Gil-Mohapel J, Rosenstock TR. Mitochondrial dysfunction, neurogenesis, and epigenetics: putative implications for amyotrophic lateral sclerosis neurodegeneration and treatment. Front Neurosci. 2020;14:679.
Camici M, Garcia-Gil M, Tozzi MG. The inside story of adenosine. Int J Mol Sci. 2018;19(3):784.
Carlini EA, Cunha JM. Hypnotic and antiepileptic effects of cannabidiol. J Clin Pharmacol. 1981;21(S1):417S-427S.
Carman AJ, Mills JH, Krenz A, Kim DG, Bynoe MS. Adenosine receptor signaling modulates permeability of the blood-brain barrier. J Neurosci. 2011;31(37):13272–80.
Carmo M, Goncalves FQ, Canas PM, Oses JP, Fernandes FD, Duarte FV, Palmeira CM, Tome AR, Agostinho P, Andrade GM, Cunha RA. Enhanced ATP release and CD73-mediated adenosine formation sustain adenosine A2A receptor over-activation in a rat model of Parkinson’s disease. Br J Pharmacol. 2019;176(18):3666–80.
Caron NS, Dorsey ER, Hayden MR. Therapeutic approaches to Huntington disease: from the bench to the clinic. Nat Rev Drug Discov. 2018;17(10):729–50.
Carrier EJ, Auchampach JA, Hillard CJ. Inhibition of an equilibrative nucleoside transporter by cannabidiol: a mechanism of cannabinoid immunosuppression. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2006;103(20):7895–900.
Carvey PM, Chen EY, Lipton JW, Tong CW, Chang QA, Ling ZD. Intra-parenchymal injection of tumor necrosis factor-alpha and interleukin 1-beta produces dopamine neuron loss in the rat. J Neural Transm (Vienna). 2005;112(5):601–12.
Cattaneo M, Schulz R, Nylander S. Adenosine-mediated effects of ticagrelor: evidence and potential clinical relevance. J Am Coll Cardiol. 2014;63(23):2503–9.
Caudill MA, Wang JC, Melnyk S, Pogribny IP, Jernigan S, Collins MD, Santos-Guzman J, Swendseid ME, Cogger EA, James SJ. Intracellular S-adenosylhomocysteine concentrations predict global DNA hypomethylation in tissues of methyl-deficient cystathionine beta-synthase heterozygous mice. J Nutr. 2001;131(11):2811–8.
Cellai L, Carvalho K, Faivre E, Deleau A, Vieau D, Buee L, Blum D, Meriaux C, Gomez-Murcia V. The adenosinergic signaling: a complex but promising therapeutic target for Alzheimer’s disease. Front Neurosci. 2018;12:520.
Chambers ED, White A, Vang A, Wang Z, Ayala A, Weng T, Blackburn M, Choudhary G, Rounds S, Lu Q. Blockade of equilibrative nucleoside transporter 1/2 protects against Pseudomonas aeruginosa-induced acute lung injury and NLRP3 inflammasome activation. Faseb J. 2020;34(1):1516–31.
Chang CP, Chang YG, Chuang PY, Nguyen TNA, Wu KC, Chou FY, Cheng SJ, Chen HM, Jin LW, Carvalho K, Huin V, Buée L, Liao YF, Lin CJ, Blum D, Chern Y. Equilibrative nucleoside transporter 1 inhibition rescues energy dysfunction and pathology in a model of tauopathy. Acta Neuropathol Commun. 2021;9(1):112.
Chen JF, Eltzschig HK, Fredholm BB. Adenosine receptors as drug targets–what are the challenges? Nat Rev Drug Discov. 2013;12(4):265–86.
Chen JF, Lee CF, Chern Y. Adenosine receptor neurobiology: overview. Int Rev Neurobiol. 2014;119:1–49.
Chetelat G, Villemagne VL, Bourgeat P, Pike KE, Jones G, Ames D, Ellis KA, Szoeke C, Martins RN, O’Keefe GJ, Salvado O, Masters CL, Rowe CC, Australian Imaging B, Lifestyle Research G. Relationship between atrophy and beta-amyloid deposition in Alzheimer disease. Ann Neurol. 2010;67(3):317–24.
Chiang PK, Gordon RK, Tal J, Zeng GC, Doctor BP, Pardhasaradhi K, McCann PP. S-Adenosylmethionine and methylation. FASEB J. 1996;10(4):471–80.
Chiba S, Kashiwagi M, Kobayashi N, Saito M, Matsumoto H. Serum adenosine deaminase and its isozyme activities in patients with Parkinson’s disease. Rinsho Shinkeigaku. 1993;33(1):86–8.
Chiba S, Matsumoto H, Saitoh M, Kasahara M, Matsuya M, Kashiwagi M. A correlation study between serum adenosine deaminase activities and peripheral lymphocyte subsets in Parkinson’s disease. J Neurol Sci. 1995;132(2):170–3.
Chikahisa S, Fujiki N, Kitaoka K, Shimizu N, Sei H. Central AMPK contributes to sleep homeostasis in mice. Neuropharmacology. 2009;57(4):369–74.
Chou SY, Lee YC, Chen HM, Chiang MC, Lai HL, Chang HH, Wu YC, Sun CN, Chien CL, Lin YS, Wang SC, Tung YY, Chang C, Chern Y. CGS21680 attenuates symptoms of Huntington’s disease in a transgenic mouse model. J Neurochem. 2005;93(2):310–20.
Chung CG, Lee H, Lee SB. Mechanisms of protein toxicity in neurodegenerative diseases. Cell Mol Life Sci. 2018;75(17):3159–80.
Coppi E, Dettori I, Cherchi F, Bulli I, Venturini M, Lana D, Giovannini MG, Pedata F, Pugliese AM. A2B adenosine receptors: when outsiders may become an attractive target to treat brain ischemia or demyelination. Int J Mol Sci. 2020;21(24):9697.
Costa V, Scorrano L. Shaping the role of mitochondria in the pathogenesis of Huntington’s disease. Embo J. 2012;31(8):1853–64.
Coughlan KS, Mitchem MR, Hogg MC, Prehn JH. “Preconditioning” with latrepirdine, an adenosine 5’-monophosphate-activated protein kinase activator, delays amyotrophic lateral sclerosis progression in SOD1(G93A) mice. Neurobiol Aging. 2015;36(2):1140–50.
Cserep C, Posfai B, Lenart N, Fekete R, Laszlo ZI, Lele Z, Orsolits B, Molnar G, Heindl S, Schwarcz AD, Ujvari K, Kornyei Z, Toth K, Szabadits E, Sperlagh B, Baranyi M, Csiba L, Hortobagyi T, Magloczky Z, Martinecz B, Szabo G, Erdelyi F, Szipocs R, Tamkun MM, Gesierich B, Duering M, Katona I, Liesz A, Tamas G, Denes A. Microglia monitor and protect neuronal function through specialized somatic purinergic junctions. Science. 2020;367(6477):528–37.
Cui QQ, Hu ZL, Hu YL, Chen X, Wang J, Mao L, Lu XJ, Ni M, Chen JG, Wang F. Hippocampal CD39/ENTPD1 promotes mouse depression-like behavior through hydrolyzing extracellular ATP. EMBO Rep. 2020;21(4):e47857.
Cui XA, Agarwal T, Singh B, Gupta RS. Molecular characterization of Chinese hamster cells mutants affected in adenosine kinase and showing novel genetic and biochemical characteristics. BMC Biochem. 2011;12:22.
Cui XA, Singh B, Park J, Gupta RS. Subcellular localization of adenosine kinase in mammalian cells: the long isoform of AdK is localized in the nucleus. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2009;388(1):46–50.
Cunha RA. How does adenosine control neuronal dysfunction and neurodegeneration? J Neurochem. 2016;139(6):1019–55.
Curry DW, Stutz B, Andrews ZB, Elsworth JD. Targeting AMPK signaling as a neuroprotective strategy in Parkinson’s disease. J Parkinsons Dis. 2018;8(2):161–81.
Dai SS, Zhou YG, Li W, An JH, Li P, Yang N, Chen XY, Xiong RP, Liu P, Zhao Y, Shen HY, Zhu PF, Chen JF. Local glutamate level dictates adenosine A2A receptor regulation of neuroinflammation and traumatic brain injury. J Neurosci. 2010;30(16):5802–10.
de Vries HE, Kooij G, Frenkel D, Georgopoulos S, Monsonego A, Janigro D. Inflammatory events at blood-brain barrier in neuroinflammatory and neurodegenerative disorders: implications for clinical disease. Epilepsia. 2012;53(Suppl 6):45–52.
Dennissen FJ, Anglada-Huguet M, Sydow A, Mandelkow E, Mandelkow EM. Adenosine A1 receptor antagonist rolofylline alleviates axonopathy caused by human Tau DeltaK280. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2016;113(41):11597–602.
Devinsky O, Cilio MR, Cross H, Fernandez-Ruiz J, French J, Hill C, Katz R, Di Marzo V, Jutras-Aswad D, Notcutt WG, Martinez-Orgado J, Robson PJ, Rohrback BG, Thiele E, Whalley B, Friedman D. Cannabidiol: pharmacology and potential therapeutic role in epilepsy and other neuropsychiatric disorders. Epilepsia. 2014;55(6):791–802.
Devinsky O, Marsh E, Friedman D, Thiele E, Laux L, Sullivan J, Miller I, Flamini R, Wilfong A, Filloux F, Wong M, Tilton N, Bruno P, Bluvstein J, Hedlund J, Kamens R, Maclean J, Nangia S, Singhal NS, Wilson CA, Patel A, Cilio MR. Cannabidiol in patients with treatment-resistant epilepsy: an open-label interventional trial. Lancet Neurol. 2016;15(3):270–8.
Di Angelantonio S, Bertollini C, Piccinin S, Rosito M, Trettel F, Pagani F, Limatola C, Ragozzino D. Basal adenosine modulates the functional properties of AMPA receptors in mouse hippocampal neurons through the activation of A1R A2AR and A3R. Front Cell Neurosci. 2015;9:409.
Dias RB, Rombo DM, Ribeiro JA, Henley JM, Sebastiao AM. Adenosine: setting the stage for plasticity. Trends Neurosci. 2013;36(4):248–57.
Dosch M, Gerber J, Jebbawi F, Beldi G. Mechanisms of ATP release by inflammatory cells. Int J Mol Sci. 2018;19(4):1222.
Dunwiddie TV, Worth T. Sedative and anticonvulsant effects of adenosine analogs in mouse and rat. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 1982;220(1):70–6.
Effendi WI, Nagano T, Kobayashi K, Nishimura Y. Focusing on adenosine receptors as a potential targeted therapy in human diseases. Cells. 2020;9(3):785.
El Yacoubi M, Ledent C, Parmentier M, Costentin J, Vaugeois JM. Adenosine A2A receptor deficient mice are partially resistant to limbic seizures. Naunyn Schmiedebergs Arch Pharmacol. 2009;380(3):223–32.
El Yacoubi M, Ledent C, Parmentier M, Costentin J, Vaugeois JM. Evidence for the involvement of the adenosine A(2A) receptor in the lowered susceptibility to pentylenetetrazol-induced seizures produced in mice by long-term treatment with caffeine. Neuropharmacology. 2008;55(1):35–40.
Elfil M, Bahbah EI, Attia MM, Eldokmak M, Koo BB. Impact of obstructive sleep apnea on cognitive and motor functions in Parkinson’s disease. Mov Disord. 2021;36(3):570–80.
Etherington LA, Frenguelli BG. Endogenous adenosine modulates epileptiform activity in rat hippocampus in a receptor subtype-dependent manner. Eur J Neurosci. 2004;19(9):2539–50.
Faivre E, Coelho JE, Zornbach K, Malik E, Baqi Y, Schneider M, Cellai L, Carvalho K, Sebda S, Figeac M, Eddarkaoui S, Caillierez R, Chern Y, Heneka M, Sergeant N, Muller CE, Halle A, Buee L, Lopes LV, Blum D. Beneficial effect of a selective adenosine A2A receptor antagonist in the APPswe/PS1dE9 mouse model of Alzheimer’s disease. Front Mol Neurosci. 2018;11:235.
Fang EF, Hou Y, Palikaras K, Adriaanse BA, Kerr JS, Yang B, Lautrup S, Hasan-Olive MM, Caponio D, Dan X, Rocktaschel P, Croteau DL, Akbari M, Greig NH, Fladby T, Nilsen H, Cader MZ, Mattson MP, Tavernarakis N, Bohr VA. Mitophagy inhibits amyloid-beta and tau pathology and reverses cognitive deficits in models of Alzheimer’s disease. Nat Neurosci. 2019;22(3):401–12.
Farr SA, Cuzzocrea S, Esposito E, Campolo M, Niehoff ML, Doyle TM, Salvemini D. Adenosine A3 receptor as a novel therapeutic target to reduce secondary events and improve neurocognitive functions following traumatic brain injury. J Neuroinflamm. 2020;17(1):339.
Farrell JS, Wolff MD, Teskey GC. Neurodegeneration and pathology in epilepsy: clinical and basic perspectives. Adv Neurobiol. 2017;15:317–34.
Fedele DE, Li T, Lan JQ, Fredholm BB, Boison D. Adenosine A1 receptors are crucial in keeping an epileptic focus localized. Exp Neurol. 2006;200(1):184–90.
Ferrante A, Martire A, Pepponi R, Varani K, Vincenzi F, Ferraro L, Beggiato S, Tebano MT, Popoli P. Expression, pharmacology and functional activity of adenosine A1 receptors in genetic models of Huntington’s disease. Neurobiol Dis. 2014;71:193–204.
Ferreira-Silva J, Aires ID, Boia R, Ambrosio AF, Santiago AR. Activation of adenosine A3 receptor inhibits microglia reactivity elicited by elevated pressure. Int J Mol Sci. 2020;21(19):7218.
Fusco I, Cherchi F, Catarzi D, Colotta V, Varano F, Pedata F, Pugliese AM, Coppi E. Functional characterization of a novel adenosine A2B receptor agonist on short-term plasticity and synaptic inhibition during oxygen and glucose deprivation in the rat CA1 hippocampus. Brain Res Bull. 2019;151:174–80.
Gandelman M, Peluffo H, Beckman JS, Cassina P, Barbeito L. Extracellular ATP and the P2X7 receptor in astrocyte-mediated motor neuron death: implications for amyotrophic lateral sclerosis. J Neuroinflamm. 2010;7:33.
Ganjam GK, Bolte K, Matschke LA, Neitemeier S, Dolga AM, Höllerhage M, Höglinger GU, Adamczyk A, Decher N, Oertel WH, Culmsee C. Mitochondrial damage by α-synuclein causes cell death in human dopaminergic neurons. Cell Death Dis. 2019;10(11):865.
Gao HM, Liu B, Zhang W, Hong JS. Novel anti-inflammatory therapy for Parkinson’s disease. Trends Pharmacol Sci. 2003;24(8):395–401.
Garcia-Esparcia P, Hernandez-Ortega K, Ansoleaga B, Carmona M, Ferrer I. Purine metabolism gene deregulation in Parkinson’s disease. Neuropathol Appl Neurobiol. 2015;41(7):926–40.
Garcia-Gil M, Camici M, Allegrini S, Pesi R, Tozzi MG. Metabolic aspects of adenosine functions in the brain. Front Pharmacol. 2021;12:672182.
Glass M, Faull RL, Bullock JY, Jansen K, Mee EW, Walker EB, Synek BJ, Dragunow M. Loss of A1 adenosine receptors in human temporal lobe epilepsy. Brain Res. 1996;710(1–2):56–68.
Goncalves FQ, Lopes JP, Silva HB, Lemos C, Silva AC, Goncalves N, Tome AR, Ferreira SG, Canas PM, Rial D, Agostinho P, Cunha RA. Synaptic and memory dysfunction in a beta-amyloid model of early Alzheimer’s disease depends on increased formation of ATP-derived extracellular adenosine. Neurobiol Dis. 2019;132:104570.
Gonçalves FQ, Pires J, Pliassova A, Beleza R, Lemos C, Marques JM, Rodrigues RJ, Canas PM, Köfalvi A, Cunha RA, Rial D. Adenosine A2b receptors control A1 receptor-mediated inhibition of synaptic transmission in the mouse hippocampus. Eur J Neurosci. 2015;41(7):878–88.
Gouder N, Fritschy JM, Boison D. Seizure suppression by adenosine A1 receptor activation in a mouse model of pharmacoresistant epilepsy. Epilepsia. 2003;44(7):877–85.
Gouder N, Scheurer L, Fritschy JM, Boison D. Overexpression of adenosine kinase in epileptic hippocampus contributes to epileptogenesis. J Neurosci. 2004;24(3):692–701.
Gray RA, Whalley BJ. The proposed mechanisms of action of CBD in epilepsy. Epileptic Disord. 2020;22(S1):10–5.
Grondin R, Bedard PJ, Tahar HA, Gregoire L, Mori A, Kase H. Antiparkinsonian effect of a new selective adenosine A2A receptor antagonist in MPTP-treated monkeys. Neurology. 1999;52(8):1673–7.
Guitart X, Bonaventura J, Rea W, Orru M, Cellai L, Dettori I, Pedata F, Brugarolas M, Cortes A, Casado V, Chang CP, Narayanan M, Chern Y, Ferre S. Equilibrative nucleoside transporter ENT1 as a biomarker of Huntington disease. Neurobiol Dis. 2016;96:47–53.
Guzman-Martinez L, Maccioni RB, Andrade V, Navarrete LP, Pastor MG, Ramos-Escobar N. Neuroinflammation as a common feature of neurodegenerative disorders. Front Pharmacol. 2019;10:1008.
Hamil NE, Cock HR, Walker MC. Acute down-regulation of adenosine A(1) receptor activity in status epilepticus. Epilepsia. 2012;53(1):177–88.
Hammond JR. Interaction of a series of draflazine analogues with equilibrative nucleoside transporters: species differences and transporter subtype selectivity. Naunyn Schmiedebergs Arch Pharmacol. 2000;361(4):373–82.
Hang L, Thundyil J, Lim KL. Mitochondrial dysfunction and Parkinson disease: a Parkin-AMPK alliance in neuroprotection. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 2015;1350:37–47.
Hasan T, Arora R, Bansal AK, Bhattacharya R, Sharma GS, Singh LR. Disturbed homocysteine metabolism is associated with cancer. Exp Mol Med. 2019;51(2):1–13.
Hasel P, Dando O, Jiwaji Z, Baxter P, Todd AC, Heron S, Márkus NM, McQueen J, Hampton DW, Torvell M, Tiwari SS, McKay S, Eraso-Pichot A, Zorzano A, Masgrau R, Galea E, Chandran S, Wyllie DJA, Simpson TI, Hardingham GE. Neurons and neuronal activity control gene expression in astrocytes to regulate their development and metabolism. Nat Commun. 2017;8:15132.
Haynes SE, Hollopeter G, Yang G, Kurpius D, Dailey ME, Gan WB, Julius D. The P2Y12 receptor regulates microglial activation by extracellular nucleotides. Nat Neurosci. 2006;9(12):1512–9.
Hervas D, Fornes-Ferrer V, Gomez-Escribano AP, Sequedo MD, Peiro C, Millan JM, Vazquez-Manrique RP. Metformin intake associates with better cognitive function in patients with Huntington’s disease. PLoS ONE. 2017;12(6):e0179283.
Herzig S, Shaw RJ. AMPK: guardian of metabolism and mitochondrial homeostasis. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol. 2018;19(2):121–35.
Hess EJ, Moody KA, Geffrey AL, Pollack SF, Skirvin LA, Bruno PL, Paolini JL, Thiele EA. Cannabidiol as a new treatment for drug-resistant epilepsy in tuberous sclerosis complex. Epilepsia. 2016;57(10):1617–24.
Hinton DJ, Lee MR, Jang JS, Choi DS. Type 1 equilibrative nucleoside transporter regulates astrocyte-specific glial fibrillary acidic protein expression in the striatum. Brain Behav. 2014;4(6):903–14.
Ho SY, Chen IC, Chang KC, Lin HR, Tsai CW, Lin CJ, Liou HH. Equilibrative nucleoside transporters-1 inhibitors act as anti-epileptic agents by inhibiting glutamatergic transmission. Front Neurosci. 2020;14:610898.
Hsu CL, Lin W, Seshasayee D, Chen YH, Ding X, Lin Z, Suto E, Huang Z, Lee WP, Park H, Xu M, Sun M, Rangell L, Lutman JL, Ulufatu S, Stefanich E, Chalouni C, Sagolla M, Diehl L, Fielder P, Dean B, Balazs M, Martin F. Equilibrative nucleoside transporter 3 deficiency perturbs lysosome function and macrophage homeostasis. Science. 2012;335(6064):89–92.
Huang NK, Lin JH, Lin JT, Lin CI, Liu EM, Lin CJ, Chen WP, Shen YC, Chen HM, Chen JB, Lai HL, Yang CW, Chiang MC, Wu YS, Chang C, Chen JF, Fang JM, Lin YL, Chern Y. A new drug design targeting the adenosinergic system for Huntington’s disease. PLoS ONE. 2011;6(6):e20934.
Huang W, Xu Y, Zhang Y, Zhang P, Zhang Q, Zhang Z, Xu F. Metabolomics-driven identification of adenosine deaminase as therapeutic target in a mouse model of Parkinson’s disease. J Neurochem. 2019;150(3):282–95.
Huang ZL, Qu WM, Eguchi N, Chen JF, Schwarzschild MA, Fredholm BB, Urade Y, Hayaishi O. Adenosine A2A, but not A1, receptors mediate the arousal effect of caffeine. Nat Neurosci. 2005;8(7):858–9.
Ibeas CB, Chen T, Nunn AV, Bazelot M, Dallas M, Whalley BJ. Molecular targets of cannabidiol in neurological disorders. Neurotherapeutics. 2015;12(4):699–730.
Ingwersen J, Wingerath B, Graf J, Lepka K, Hofrichter M, Schroter F, Wedekind F, Bauer A, Schrader J, Hartung HP, Prozorovski T, Aktas O. Dual roles of the adenosine A2a receptor in autoimmune neuroinflammation. J Neuroinflamm. 2016;13:48.
Iovino L, Tremblay ME, Civiero L. Glutamate-induced excitotoxicity in Parkinson’s disease: the role of glial cells. J Pharmacol Sci. 2020;144(3):151–64.
Iranzo A. Sleep in neurodegenerative diseases. Sleep Med Clin. 2016;11(1):1–18.
James SJ, Melnyk S, Pogribna M, Pogribny IP, Caudill MA. Elevation in S-adenosylhomocysteine and DNA hypomethylation: potential epigenetic mechanism for homocysteine-related pathology. J Nutr. 2002;132(8 Suppl):2361S-2366S.
Jarvis MF. Therapeutic potential of adenosine kinase inhibition-Revisited. Pharmacol Res Perspect. 2019;7(4):e00506.
Jones PL, Veenstra GJ, Wade PA, Vermaak D, Kass SU, Landsberger N, Strouboulis J, Wolffe AP. Methylated DNA and MeCP2 recruit histone deacetylase to repress transcription. Nat Genet. 1998;19(2):187–91.
Jou SB, Tsai CJ, Fang CY, Yi PL, Chang FC. Effects of N(6) -(4-hydroxybenzyl) adenine riboside in stress-induced insomnia in rodents. J Sleep Res. 2021;30(1):e13156.
Ju TC, Chen HM, Chen YC, Chang CP, Chang C, Chern Y. AMPK-alpha1 functions downstream of oxidative stress to mediate neuronal atrophy in Huntington’s disease. Biochim Biophys Acta. 2014;1842(9):1668–80.
Ju TC, Chen HM, Lin JT, Chang CP, Chang WC, Kang JJ, Sun CP, Tao MH, Tu PH, Chang C, Dickson DW, Chern Y. Nuclear translocation of AMPK-alpha1 potentiates striatal neurodegeneration in Huntington’s disease. J Cell Biol. 2011;194(2):209–27.
Kang SS, Zhang Z, Liu X, Manfredsson FP, He L, Iuvone PM, Cao X, Sun YE, Jin L, Ye K. Alpha-Synuclein binds and sequesters PIKE-L into Lewy bodies, triggering dopaminergic cell death via AMPK hyperactivation. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2017;114(5):1183–8.
Kao YH, Lin MS, Chen CM, Wu YR, Chen HM, Lai HL, Chern Y, Lin CJ. Targeting ENT1 and adenosine tone for the treatment of Huntington’s disease. Hum Mol Genet. 2017;26(3):467–78.
Kempuraj D, Thangavel R, Selvakumar GP, Zaheer S, Ahmed ME, Raikwar SP, Zahoor H, Saeed D, Natteru PA, Iyer S, Zaheer A. Brain and peripheral atypical inflammatory mediators potentiate neuroinflammation and neurodegeneration. Front Cell Neurosci. 2017;11:216.
Kerr JS, Adriaanse BA, Greig NH, Mattson MP, Cader MZ, Bohr VA, Fang EF. Mitophagy and Alzheimer’s disease: cellular and molecular mechanisms. Trends Neurosci. 2017;40(3):151–66.
Kiernan MC, Vucic S, Cheah BC, Turner MR, Eisen A, Hardiman O, Burrell JR, Zoing MC. Amyotrophic lateral sclerosis. Lancet. 2011;377(9769):942–55.
Kiernan MC, Vucic S, Talbot K, McDermott CJ, Hardiman O, Shefner JM, Al-Chalabi A, Huynh W, Cudkowicz M, Talman P, Van den Berg LH, Dharmadasa T, Wicks P, Reilly C, Turner MR. Improving clinical trial outcomes in amyotrophic lateral sclerosis. Nat Rev Neurol. 2021;17(2):104–18.
Kim T, Ramesh V, Dworak M, Choi DS, McCarley RW, Kalinchuk AV, Basheer R. Disrupted sleep-wake regulation in type 1 equilibrative nucleoside transporter knockout mice. Neuroscience. 2015;303:211–9.
Kim TW, Cho HM, Choi SY, Suguira Y, Hayasaka T, Setou M, Koh HC, Hwang EM, Park JY, Kang SJ, Kim HS, Kim H, Sun W. (ADP-ribose) polymerase 1 and AMP-activated protein kinase mediate progressive dopaminergic neuronal degeneration in a mouse model of Parkinson’s disease. Cell Death Dis. 2013;4(11):e19.
Klaft ZJ, Hollnagel JO, Salar S, Caliskan G, Schulz SB, Schneider UC, Horn P, Koch A, Holtkamp M, Gabriel S, Gerevich Z, Heinemann U. Adenosine A1 receptor-mediated suppression of carbamazepine-resistant seizure-like events in human neocortical slices. Epilepsia. 2016;57(5):746–56.
Ko J, Rounds S, Lu Q. Sustained adenosine exposure causes endothelial mitochondrial dysfunction via equilibrative nucleoside transporters. Pulm Circ. 2020;10(2):2045894020924994.
Kobow K, Blumcke I. The methylation hypothesis: do epigenetic chromatin modifications play a role in epileptogenesis? Epilepsia. 2011;52(Suppl 4):15–9.
Kochanek PM, Vagni VA, Janesko KL, Washington CB, Crumrine PK, Garman RH, Jenkins LW, Clark RS, Homanics GE, Dixon CE, Schnermann J, Jackson EK. Adenosine A1 receptor knockout mice develop lethal status epilepticus after experimental traumatic brain injury. J Cereb Blood Flow Metab. 2006;26(4):565–75.
Koscso B, Csoka B, Selmeczy Z, Himer L, Pacher P, Virag L, Hasko G. Adenosine augments IL-10 production by microglial cells through an A2B adenosine receptor-mediated process. J Immunol. 2012;188(1):445–53.
Kowaluk EA, Jarvis MF. Therapeutic potential of adenosine kinase inhibitors. Expert Opin Investig Drugs. 2000;9(3):551–64.
Krishna R, Ali M, Moustafa AA. Effects of combined MAO-B inhibitors and levodopa vs monotherapy in Parkinsons’disease. Front Aging Neurosci. 2014;6:180.
Lai CY, Liu YJ, Lai HL, Chen HM, Kuo HC, Liao YP, Chern Y. The D2 dopamine receptor interferes with the protective effect of the A2A adenosine receptor on TDP-43 mislocalization in experimental models of motor neuron degeneration. Front Neurosci. 2018;12:187.
Lai Y, Tse CM, Unadkat JD. Mitochondrial expression of the human equilibrative nucleoside transporter 1 (hENT1) results in enhanced mitochondrial toxicity of antiviral drugs. J Biol Chem. 2004;279(6):4490–7.
Laurent C, Burnouf S, Ferry B, Batalha VL, Coelho JE, Baqi Y, Malik E, Mariciniak E, Parrot S, Van der Jeugd A, Faivre E, Flaten V, Ledent C, D’Hooge R, Sergeant N, Hamdane M, Humez S, Muller CE, Lopes LV, Buee L, Blum D. A2A adenosine receptor deletion is protective in a mouse model of Tauopathy. Mol Psychiatry. 2016;21(1):97–107.
Lee CC, Chang CP, Lin CJ, Lai HL, Kao YH, Cheng SJ, Chen HM, Liao YP, Faivre E, Buée L, Blum D, Fang JM, Chern Y. Adenosine augmentation evoked by an ENT1 inhibitor improves memory impairment and neuronal plasticity in the APP/PS1 mouse model of Alzheimer’s disease. Mol Neurobiol. 2018;55(12):8936–52.
Lee CF, Chern Y. Adenosine receptors and Huntington’s disease. Int Rev Neurobiol. 2014;119:195–232.
Lee CW, Shih YH, Wu SY, Yang T, Lin C, Kuo YM. Hypoglycemia induces tau hyperphosphorylation. Curr Alzheimer Res. 2013;10(3):298–308.
Lee EW, Lai Y, Zhang H, Unadkat JD. Identification of the mitochondrial targeting signal of the human equilibrative nucleoside transporter 1 (hENT1): implications for interspecies differences in mitochondrial toxicity of fialuridine. J Biol Chem. 2006;281(24):16700–6.
Lee JY, Jhun BS, Oh YT, Lee JH, Choe W, Baik HH, Ha J, Yoon KS, Kim SS, Kang I. Activation of adenosine A3 receptor suppresses lipopolysaccharide-induced TNF-alpha production through inhibition of PI 3-kinase/Akt and NF-kappaB activation in murine BV2 microglial cells. Neurosci Lett. 2006;396(1):1–6.
Lee SB, Kim HT, Yang HO, Jang W. Anodal transcranial direct current stimulation prevents methyl-4-phenyl-1,2,3,6-tetrahydropyridine (MPTP)-induced neurotoxicity by modulating autophagy in an in vivo mouse model of Parkinson’s disease. Sci Rep. 2018;8(1):15165.
Lewerenz J, Maher P. Chronic glutamate toxicity in neurodegenerative diseases-what is the evidence? Front Neurosci. 2015;9:469.
Li Q, Haney MS. The role of glia in protein aggregation. Neurobiol Dis. 2020;143:105015.
Li T, Ren G, Lusardi T, Wilz A, Lan JQ, Iwasato T, Itohara S, Simon RP, Boison D. Adenosine kinase is a target for the prediction and prevention of epileptogenesis in mice. J Clin Invest. 2008;118(2):571–82.
Lim MA, Selak MA, Xiang Z, Krainc D, Neve RL, Kraemer BC, Watts JL, Kalb RG. Reduced activity of AMP-activated protein kinase protects against genetic models of motor neuron disease. J Neurosci. 2012;32(3):1123–41.
Liot G, Valette J, Pepin J, Flament J, Brouillet E. Energy defects in Huntington’s disease: why “in vivo” evidence matters. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2017;483(4):1084–95.
Liu YJ, Ju TC, Chen HM, Jang YS, Lee LM, Lai HL, Tai HC, Fang JM, Lin YL, Tu PH, Chern Y. Activation of AMP-activated protein kinase alpha1 mediates mislocalization of TDP-43 in amyotrophic lateral sclerosis. Hum Mol Genet. 2015;24(3):787–801.
Liu YJ, Lee LM, Lai HL, Chern Y. Aberrant activation of AMP-activated protein kinase contributes to the abnormal distribution of HuR in amyotrophic lateral sclerosis. FEBS Lett. 2015;589(4):432–9.
Lopes CR, Cunha RA, Agostinho P. Astrocytes and adenosine A2A receptors: active players in Alzheimer’s disease. Front Neurosci. 2021;15:666710.
Lu H, Liu X, Deng Y, Qing H. DNA methylation, a hand behind neurodegenerative diseases. Front Aging Neurosci. 2013;5:85.
Lucey BP. It’s complicated: the relationship between sleep and Alzheimer’s disease in humans. Neurobiol Dis. 2020;144:105031.
Ludolph AC, Dorst J, Dreyhaupt J, Weishaupt JH, Kassubek J, Weiland U, Meyer T, Petri S, Hermann A, Emmer A, Grosskreutz J, Grehl T, Zeller D, Boentert M, Schrank B, Prudlo J, Winkler AS, Gorbulev S, Roselli F, Schuster J, Dupuis L, Group L-AS. Effect of high-caloric nutrition on survival in amyotrophic lateral sclerosis. Ann Neurol. 2020;87(2):206–16.
Lynch JJ 3rd, Alexander KM, Jarvis MF, Kowaluk EA. Inhibition of adenosine kinase during oxygen-glucose deprivation in rat cortical neuronal cultures. Neurosci Lett. 1998;252(3):207–10.
Ma T, Chen Y, Vingtdeux V, Zhao H, Viollet B, Marambaud P, Klann E. Inhibition of AMP-activated protein kinase signaling alleviates impairments in hippocampal synaptic plasticity induced by amyloid beta. J Neurosci. 2014;34(36):12230–8.
Ma TC, Buescher JL, Oatis B, Funk JA, Nash AJ, Carrier RL, Hoyt KR. Metformin therapy in a transgenic mouse model of Huntington’s disease. Neurosci Lett. 2007;411(2):98–103.
Maeda J, Minamihisamatsu T, Shimojo M, Zhou X, Ono M, Matsuba Y, Ji B, Ishii H, Ogawa M, Akatsu H, Kaneda D, Hashizume Y, Robinson JL, Lee VM, Saito T, Saido TC, Trojanowski JQ, Zhang MR, Suhara T, Higuchi M, Sahara N. Distinct microglial response against Alzheimer’s amyloid and tau pathologies characterized by P2Y12 receptor. Brain Commun. 2021;3(1):fcab011.
Masino SA, Li T, Theofilas P, Sandau US, Ruskin DN, Fredholm BB, Geiger JD, Aronica E, Boison D. A ketogenic diet suppresses seizures in mice through adenosine A(1) receptors. J Clin Invest. 2011;121(7):2679–83.
Masrori P, Van Damme P. Amyotrophic lateral sclerosis: a clinical review. Eur J Neurol. 2020;27(10):1918–29.
Matusch A, Saft C, Elmenhorst D, Kraus PH, Gold R, Hartung HP, Bauer A. Cross sectional PET study of cerebral adenosine A(1) receptors in premanifest and manifest Huntington’s disease. Eur J Nucl Med Mol Imaging. 2014;41(6):1210–20.
Mayne M, Fotheringham J, Yan HJ, Power C, Del Bigio MR, Peeling J, Geiger JD. Adenosine A2A receptor activation reduces proinflammatory events and decreases cell death following intracerebral hemorrhage. Ann Neurol. 2001;49(6):727–35.
McColgan P, Tabrizi SJ. Huntington’s disease: a clinical review. Eur J Neurol. 2018;25(1):24–34.
McGaraughty S, Cowart M, Jarvis MF, Berman RF. Anticonvulsant and antinociceptive actions of novel adenosine kinase inhibitors. Curr Top Med Chem. 2005;5(1):43–58.
Medina-Pulido L, Molina-Arcas M, Justicia C, Soriano E, Burgaya F, Planas AM, Pastor-Anglada M. Hypoxia and P1 receptor activation regulate the high-affinity concentrative adenosine transporter CNT2 in differentiated neuronal PC12 cells. Biochem J. 2013;454(3):437–45.
Mehrabi S, Sanadgol N, Barati M, Shahbazi A, Vahabzadeh G, Barzroudi M, Seifi M, Gholipourmalekabadi M, Golab F. Evaluation of metformin effects in the chronic phase of spontaneous seizures in pilocarpine model of temporal lobe epilepsy. Metab Brain Dis. 2018;33(1):107–14.
Mejzini R, Flynn LL, Pitout IL, Fletcher S, Wilton SD, Akkari PA. ALS genetics, mechanisms, and therapeutics: where are we now? Front Neurosci. 2019;13:1310.
Mendiola-Precoma J, Padilla K, Rodriguez-Cruz A, Berumen LC, Miledi R, Garcia-Alcocer G. Theobromine-induced changes in A1 purinergic receptor gene expression and distribution in a rat brain Alzheimer’s disease model. J Alzheimers Dis. 2017;55(3):1273–83.
Meng F, Guo Z, Hu Y, Mai W, Zhang Z, Zhang B, Ge Q, Lou H, Guo F, Chen J, Duan S, Gao Z. CD73-derived adenosine controls inflammation and neurodegeneration by modulating dopamine signalling. Brain. 2019;142(3):700–18.
Mievis S, Blum D, Ledent C. A2A receptor knockout worsens survival and motor behaviour in a transgenic mouse model of Huntington’s disease. Neurobiol Dis. 2011;41(2):570–6.
Moretti R, Caruso P. The controversial role of homocysteine in neurology: from labs to clinical practice. Int J Mol Sci. 2019;20(1):231.
Morote-Garcia JC, Köhler D, Roth JM, Mirakaj V, Eldh T, Eltzschig HK, Rosenberger P. Repression of the equilibrative nucleoside transporters dampens inflammatory lung injury. Am J Respir Cell Mol Biol. 2013;49(2):296–305.
Muraleedharan R, Gawali MV, Tiwari D, Sukumaran A, Oatman N, Anderson J, Nardini D, Bhuiyan MAN, Tkac I, Ward AL, Kundu M, Waclaw R, Chow LM, Gross C, Rao R, Schirmeier S, Dasgupta B. AMPK-regulated astrocytic lactate shuttle plays a non-cell-autonomous role in neuronal survival. Cell Rep. 2020;32(9):108092.
Murphy AN, Fiskum G, Beal MF. Mitochondria in neurodegeneration: bioenergetic function in cell life and death. J Cereb Blood Flow Metab. 1999;19(3):231–45.
Murugan M, Fedele D, Millner D, Alharfoush E, Vegunta G, Boison D. Adenosine kinase: an epigenetic modulator in development and disease. Neurochem Int. 2021;147:105054.
Navarro G, Borroto-Escuela DO, Fuxe K, Franco R. Purinergic signaling in Parkinson’s disease. Relevance for treatment. Neuropharmacology. 2016;104:161–8.
Nazario LR, da Silva RS, Bonan CD. Targeting adenosine signaling in Parkinson’s disease: from pharmacological to non-pharmacological approaches. Front Neurosci. 2017;11:658.
Negro S, Bergamin E, Rodella U, Duregotti E, Scorzeto M, Jalink K, Montecucco C, Rigoni M. ATP released by injured neurons activates schwann cells. Front Cell Neurosci. 2016;10:134.
Ng SK, Higashimori H, Tolman M, Yang Y. Suppression of adenosine 2a receptor (A2aR)-mediated adenosine signaling improves disease phenotypes in a mouse model of amyotrophic lateral sclerosis. Exp Neurol. 2015;267:115–22.
Orr AG, Hsiao EC, Wang MM, Ho K, Kim DH, Wang X, Guo W, Kang J, Yu GQ, Adame A, Devidze N, Dubal DB, Masliah E, Conklin BR, Mucke L. Astrocytic adenosine receptor A2A and Gs-coupled signaling regulate memory. Nat Neurosci. 2015;18(3):423–34.
Orr AG, Lo I, Schumacher H, Ho K, Gill M, Guo W, Kim DH, Knox A, Saito T, Saido TC, Simms J, Toddes C, Wang X, Yu GQ, Mucke L. Istradefylline reduces memory deficits in aging mice with amyloid pathology. Neurobiol Dis. 2018;110:29–36.
Pak VM, Onen SH, Bliwise DL, Kutner NG, Russell KL, Onen F. Sleep Disturbances in MCI and AD: neuroinflammation as a possible mediating pathway. Front Aging Neurosci. 2020;12:69.
Palchykova S, Winsky-Sommerer R, Shen HY, Boison D, Gerling A, Tobler I. Manipulation of adenosine kinase affects sleep regulation in mice. J Neurosci. 2010;30(39):13157–65.
Palmer JL, Abeles RH. The mechanism of action of S-adenosylhomocysteinase. J Biol Chem. 1979;254(4):1217–26.
Pankratov Y, Lalo U, Verkhratsky A, North RA. Vesicular release of ATP at central synapses. Pflugers Arch. 2006;452(5):589–97.
Pastor-Anglada M, Errasti-Murugarren E, Aymerich I, Casado FJ. Concentrative nucleoside transporters (CNTs) in epithelia: from absorption to cell signaling. J Physiol Biochem. 2007;63(1):97–110.
Pastor-Anglada M, Perez-Torras S. Emerging roles of nucleoside transporters. Front Pharmacol. 2018;9:606.
Paudel YN, Angelopoulou E, Piperi C, Othman I, Shaikh MF. Revisiting the impact of neurodegenerative proteins in epilepsy: focus on alpha-synuclein, beta-amyloid, and tau. Biology (Basel). 2020;9(6):122.
Pickrell AM, Youle RJ. The roles of PINK1, parkin, and mitochondrial fidelity in Parkinson’s disease. Neuron. 2015;85(2):257–73.
Pieper HC, Evert BO, Kaut O, Riederer PF, Waha A, Wüllner U. Different methylation of the TNF-alpha promoter in cortex and substantia nigra: implications for selective neuronal vulnerability. Neurobiol Dis. 2008;32(3):521–7.
Pietrowski MJ, Gabr AA, Kozlov S, Blum D, Halle A, Carvalho K. Glial purinergic signaling in neurodegeneration. Front Neurol. 2021;12:654850.
Porkka-Heiskanen T, Kalinchuk AV. Adenosine, energy metabolism and sleep homeostasis. Sleep Med Rev. 2011;15(2):123–35.
Porkka-Heiskanen T, Strecker RE, Thakkar M, Bjorkum AA, Greene RW, McCarley RW. Adenosine: a mediator of the sleep-inducing effects of prolonged wakefulness. Science. 1997;276(5316):1265–8.
Potenza RL, Armida M, Ferrante A, Pezzola A, Matteucci A, Puopolo M, Popoli P. Effects of chronic caffeine intake in a mouse model of amyotrophic lateral sclerosis. J Neurosci Res. 2013;91(4):585–92.
Rebola N, Coelho JE, Costenla AR, Lopes LV, Parada A, Oliveira CR, Soares-da-Silva P, de Mendonca A, Cunha RA. Decrease of adenosine A1 receptor density and of adenosine neuromodulation in the hippocampus of kindled rats. Eur J Neurosci. 2003;18(4):820–8.
Rebola N, Simoes AP, Canas PM, Tome AR, Andrade GM, Barry CE, Agostinho PM, Lynch MA, Cunha RA. Adenosine A2A receptors control neuroinflammation and consequent hippocampal neuronal dysfunction. J Neurochem. 2011;117(1):100–11.
Ross CA, Poirier MA. Protein aggregation and neurodegenerative disease. Nat Med. 2004;10(Suppl):S10-17.
Russell RC, Yuan HX, Guan KL. Autophagy regulation by nutrient signaling. Cell Res. 2014;24(1):42–57.
Sanchis A, Garcia-Gimeno MA, Canada-Martinez AJ, Sequedo MD, Millan JM, Sanz P, Vazquez-Manrique RP. Metformin treatment reduces motor and neuropsychiatric phenotypes in the zQ175 mouse model of Huntington disease. Exp Mol Med. 2019;51(6):1–16.
Sandau US, Yahya M, Bigej R, Friedman JL, Saleumvong B, Boison D. Transient use of a systemic adenosine kinase inhibitor attenuates epilepsy development in mice. Epilepsia. 2019;60(4):615–25.
Sayama S, Song A, Brown BC, Couturier J, Cai X, Xu P, Chen C, Zheng Y, Iriyama T, Sibai B, Longo M, Kellems RE, D’Alessandro A, Xia Y. Maternal erythrocyte ENT1-mediated AMPK activation counteracts placental hypoxia and supports fetal growth. JCI Insight. 2020;5(10):e130205.
Sebastião AM, Rei N, Ribeiro JA. Amyotrophic lateral sclerosis (ALS) and adenosine receptors. Front Pharmacol. 2018;9:267.
Sergeant N, Bretteville A, Hamdane M, Caillet-Boudin ML, Grognet P, Bombois S, Blum D, Delacourte A, Pasquier F, Vanmechelen E, Schraen-Maschke S, Buee L. Biochemistry of Tau in Alzheimer’s disease and related neurological disorders. Expert Rev Proteomics. 2008;5(2):207–24.
Smith AD, Refsum H, Bottiglieri T, Fenech M, Hooshmand B, McCaddon A, Miller JW, Rosenberg IH, Obeid R. Homocysteine and dementia: an international consensus statement. J Alzheimers Dis. 2018;62(2):561–70.
Soliman AM, Fathalla AM, Moustafa AA. Adenosine role in brain functions: pathophysiological influence on Parkinson’s disease and other brain disorders. Pharmacol Rep. 2018;70(4):661–7.
Song W, Chen J, Petrilli A, Liot G, Klinglmayr E, Zhou Y, Poquiz P, Tjong J, Pouladi MA, Hayden MR, Masliah E, Ellisman M, Rouiller I, Schwarzenbacher R, Bossy B, Perkins G, Bossy-Wetzel E. Mutant huntingtin binds the mitochondrial fission GTPase dynamin-related protein-1 and increases its enzymatic activity. Nat Med. 2011;17(3):377–82.
Stevenson R, Samokhina E, Rossetti I, Morley JW, Buskila Y. Neuromodulation of glial function during neurodegeneration. Front Cell Neurosci. 2020;14:278.
Stockwell J, Jakova E, Cayabyab FS. Adenosine A1 and A2A receptors in the brain: current research and their role in neurodegeneration. Molecules. 2017;22(4):676.
Su J, Zhang J, Bao R, Xia C, Zhang Y, Zhu Z, Lv Q, Qi Y, Xue J. Mitochondrial dysfunction and apoptosis are attenuated through activation of AMPK/GSK-3beta/PP2A pathway in Parkinsons’ disease. Eur J Pharmacol. 2021; 174202.
Thiele EA, Bebin EM, Bhathal H, Jansen FE, Kotulska K, Lawson JA, O’Callaghan FJ, Wong M, Sahebkar F, Checketts D, Knappertz V, Group GS. Add-on cannabidiol treatment for drug-resistant seizures in tuberous sclerosis complex: a placebo-controlled randomized clinical trial. JAMA Neurol. 2021;78(3):285–92.
Toczek M, Pierzynowska K, Kutryb-Zajac B, Gaffke L, Slominska EM, Wegrzyn G, Smolenski RT. Characterization of adenine nucleotide metabolism in the cellular model of Huntington’s disease. Nucleosides Nucleotides Nucleic Acids. 2018;37(11):630–8.
Toth A, Antal Z, Bereczki D, Sperlagh B. Purinergic signalling in Parkinson’s disease: a multi-target system to combat neurodegeneration. Neurochem Res. 2019;44(10):2413–22.
Toyama EQ, Herzig S, Courchet J, Lewis TL Jr, Losón OC, Hellberg K, Young NP, Chen H, Polleux F, Chan DC, Shaw RJ. Metabolism. AMP-activated protein kinase mediates mitochondrial fission in response to energy stress. Science. 2016;351(6270):275–81.
Tsutsui S, Schnermann J, Noorbakhsh F, Henry S, Yong VW, Winston BW, Warren K, Power C. A1 adenosine receptor upregulation and activation attenuates neuroinflammation and demyelination in a model of multiple sclerosis. J Neurosci. 2004;24(6):1521–9.
Tufi R, Gandhi S, de Castro IP, Lehmann S, Angelova PR, Dinsdale D, Deas E, Plun-Favreau H, Nicotera P, Abramov AY, Willis AE, Mallucci GR, Loh SH, Martins LM. Enhancing nucleotide metabolism protects against mitochondrial dysfunction and neurodegeneration in a PINK1 model of Parkinson’s disease. Nat Cell Biol. 2014;16(2):157–66.
Turnley AM, Stapleton D, Mann RJ, Witters LA, Kemp BE, Bartlett PF. Cellular distribution and developmental expression of AMP-activated protein kinase isoforms in mouse central nervous system. J Neurochem. 1999;72(4):1707–16.
van der Putten C, Zuiderwijk-Sick EA, van Straalen L, de Geus ED, Boven LA, Kondova I, IjzermanAP, Bajramovic J.J. Differential expression of adenosine A3 receptors controls adenosine A2A receptor-mediated inhibition of TLR responses in microglia. J Immunol. 2009; 182(12):7603–7612.
Vazquez-Manrique RP, Farina F, Cambon K, Sequedo DM, Parker AJ, Millan JM, Weiss A, Deglon N, Neri C. AMPK activation protects from neuronal dysfunction and vulnerability across nematode, cellular and mouse models of Huntington’s disease. Hum Mol Genet. 2016;25(6):1043–58.
da Vianna VS, Haberl MG, Zhang P, Bethge P, Lemos C, Goncalves N, Gorlewicz A, Malezieux M, Goncalves FQ, Grosjean N, Blanchet C, Frick A, Nagerl UV, Cunha RA, Mulle C. Early synaptic deficits in the APP/PS1 mouse model of Alzheimer’s disease involve neuronal adenosine A2A receptors. Nat Commun. 2016;7:11915.
Villar-Menéndez I, Blanch M, Tyebji S, Pereira-Veiga T, Albasanz JL, Martín M, Ferrer I, Pérez-Navarro E, Barrachina M. Increased 5-methylcytosine and decreased 5-hydroxymethylcytosine levels are associated with reduced striatal A2AR levels in Huntington’s disease. Neuromol Med. 2013;15(2):295–309.
Vincenzi F, Corciulo C, Targa M, Casetta I, Gentile M, Granieri E, Borea PA, Popoli P, Varani K. A2A adenosine receptors are up-regulated in lymphocytes from amyotrophic lateral sclerosis patients. Amyotroph Lateral Scler Frontotemporal Degener. 2013;14(5–6):406–13.
Vingtdeux V, Davies P, Dickson DW, Marambaud P. AMPK is abnormally activated in tangle- and pre-tangle-bearing neurons in Alzheimer’s disease and other tauopathies. Acta Neuropathol. 2011;121(3):337–49.
Visser F, Sun L, Damaraju V, Tackaberry T, Peng Y, Robins MJ, Baldwin SA, Young JD, Cass CE. Residues 334 and 338 in transmembrane segment 8 of human equilibrative nucleoside transporter 1 are important determinants of inhibitor sensitivity, protein folding, and catalytic turnover. J Biol Chem. 2007;282(19):14148–57.
Volonte C, Apolloni S, Parisi C, Amadio S. Purinergic contribution to amyotrophic lateral sclerosis. Neuropharmacology. 2016;104:180–93.
Walker DG, Tang TM, Mendsaikhan A, Tooyama I, Serrano GE, Sue LI, Beach TG, Lue LF. Patterns of expression of purinergic receptor P2RY12, a putative marker for non-activated microglia, in aged and Alzheimer’s disease brains. Int J Mol Sci. 2020;21(2):678.
Wang L, Shi FX, Li N, Cao Y, Lei Y, Wang JZ, Tian Q, Zhou XW. AMPK ameliorates tau acetylation and memory impairment through Sirt1. Mol Neurobiol. 2020;57(12):5011–25.
Wang P, Deng J, Dong J, Liu J, Bigio EH, Mesulam M, Wang T, Sun L, Wang L, Lee AY, McGee WA, Chen X, Fushimi K, Zhu L, Wu JY. TDP-43 induces mitochondrial damage and activates the mitochondrial unfolded protein response. PLoS Genet. 2019;15(5):e1007947.
Wang R, Reddy PH. Role of glutamate and NMDA receptors in Alzheimer’s disease. J Alzheimers Dis. 2017;57(4):1041–8.
Wang Y, Kavran JM, Chen Z, Karukurichi KR, Leahy DJ, Cole PA. Regulation of S-adenosylhomocysteine hydrolase by lysine acetylation. J Biol Chem. 2014;289(45):31361–72.
Wang Y, Zhao J, Guo FL, Gao X, Xie X, Liu S, Yang X, Yang X, Zhang L, Ye Y, Fan L, Wang J. Metformin ameliorates synaptic defects in a mouse model of AD by inhibiting Cdk5 activity. Front Cell Neurosci. 2020;14:170.
Watanabe S, Komine O, Endo F, Wakasugi K, Yamanaka K. Intracerebroventricular administration of Cystatin C ameliorates disease in SOD1-linked amyotrophic lateral sclerosis mice. J Neurochem. 2018;145(1):80–9.
Watt F, Molloy PL. Cytosine methylation prevents binding to DNA of a HeLa cell transcription factor required for optimal expression of the adenovirus major late promoter. Genes Dev. 1988;2(9):1136–43.
Wiesner JB, Ugarkar BG, Castellino AJ, Barankiewicz J, Dumas DP, Gruber HE, Foster AC, Erion MD. Adenosine kinase inhibitors as a novel approach to anticonvulsant therapy. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 1999;289(3):1669–77.
Wijesekera LC, Leigh PN. Amyotrophic lateral sclerosis. Orphanet J Rare Dis. 2009;4:3.
Williams-Karnesky RL, Sandau US, Lusardi TA, Lytle NK, Farrell JM, Pritchard EM, Kaplan DL, Boison D. Epigenetic changes induced by adenosine augmentation therapy prevent epileptogenesis. J Clin Invest. 2013;123(8):3552–63.
Wu J, Basha MR, Brock B, Cox DP, Cardozo-Pelaez F, McPherson CA, Harry J, Rice DC, Maloney B, Chen D, Lahiri DK, Zawia NH. Alzheimer’s disease (AD)-like pathology in aged monkeys after infantile exposure to environmental metal lead (Pb): evidence for a developmental origin and environmental link for AD. J Neurosci. 2008;28(1):3–9.
Wu KC, Lee CY, Chern Y, Lin CJ. Amelioration of lipopolysaccharide-induced memory impairment in equilibrative nucleoside transporter-2 knockout mice is accompanied by the changes in glutamatergic pathways. Brain Behav Immun, 2021.
Wu KC, Lee CY, Chou FY, Chern Y, Lin CJ. Deletion of equilibrative nucleoside transporter-2 protects against lipopolysaccharide-induced neuroinflammation and blood-brain barrier dysfunction in mice. Brain Behav Immun. 2020;84:59–71.
Xiao B, Heath R, Saiu P, Leiper FC, Leone P, Jing C, Walker PA, Haire L, Eccleston JF, Davis CT, Martin SR, Carling D, Gamblin SJ. Structural basis for AMP binding to mammalian AMP-activated protein kinase. Nature. 2007;449(7161):496–500.
Xiao C, Liu N, Jacobson KA, Gavrilova O, Reitman ML. Physiology and effects of nucleosides in mice lacking all four adenosine receptors. PLoS Biol. 2019;17(3):e3000161.
Xu Y, Wang Y, Yan S, Zhou Y, Yang Q, Pan Y, Zeng X, An X, Liu Z, Wang L, Xu J, Cao Y, Fulton DJ, Weintraub NL, Bagi Z, Hoda MN, Wang X, Li Q, Hong M, Jiang X, Boison D, Weber C, Wu C, Huo Y. Intracellular adenosine regulates epigenetic programming in endothelial cells to promote angiogenesis. EMBO Mol Med. 2017;9(9):1263–78.
Xu Z, Xu P, Chen Y, Liu J, Zhang Y, Lv Y, Luo J, Fang M, Zhang J, Wang J, Wang K, Wang X, Chen G. ENT1 inhibition attenuates epileptic seizure severity via regulation of glutamatergic neurotransmission. Neuromol Med. 2015;17(1):1–11.
Yan Q, Han C, Wang G, Waddington JL, Zheng L, Zhen X. Activation of AMPK/mTORC1-mediated autophagy by metformin reverses Clk1 deficiency-sensitized dopaminergic neuronal death. Mol Pharmacol. 2017;92(6):640–52.
Yang W, Zhou X, Zimmermann HR, Ma T. Brain-specific suppression of AMPKalpha2 isoform impairs cognition and hippocampal LTP by PERK-mediated eIF2alpha phosphorylation. Mol Psychiatry. 2020;26:1880.
Yang Y, Gozen O, Vidensky S, Robinson MB, Rothstein JD. Epigenetic regulation of neuron-dependent induction of astroglial synaptic protein GLT1. Glia. 2010;58(3):277–86.
Yang Y, Zhu B, Zheng F, Li Y, Zhang Y, Hu Y, Wang X. Chronic metformin treatment facilitates seizure termination. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2017;484(2):450–5.
Yang Z, Zhang X, Li C, Chi S, Xie A. Molecular mechanisms underlying reciprocal interactions between sleep disorders and Parkinson’s disease. Front Neurosci. 2020;14:592989.
Yanpallewar SU, Barrick CA, Buckley H, Becker J, Tessarollo L. Deletion of the BDNF truncated receptor TrkB.T1 delays disease onset in a mouse model of amyotrophic lateral sclerosis. PLoS ONE. 2012;7(6):e39946.
Yoshida Y, Une F, Utatsu Y, Nomoto M, Furukawa Y, Maruyama Y, Machigashira N, Matsuzaki T, Osame M. Adenosine and neopterin levels in cerebrospinal fluid of patients with neurological disorders. Intern Med. 1999;38(2):133–9.
Yun YC, Jeong SG, Kim SH, Cho GW. Reduced sirtuin 1/adenosine monophosphate-activated protein kinase in amyotrophic lateral sclerosis patient-derived mesenchymal stem cells can be restored by resveratrol. J Tissue Eng Regen Med. 2019;13(1):110–5.
Zhao Z, Sui Y, Gao W, Cai B, Fan D. Effects of diet on adenosine monophosphate-activated protein kinase activity and disease progression in an amyotrophic lateral sclerosis model. J Int Med Res. 2015;43(1):67–79.
Zhou S, Liu G, Guo J, Kong F, Chen S, Wang Z. Pro-inflammatory effect of downregulated CD73 expression in EAE astrocytes. Front Cell Neurosci. 2019;13:233.
Zhou X, Chen Q, Huang H, Zhang J, Wang J, Chen Y, Peng Y, Zhang H, Zeng J, Feng Z, Xu Z. Inhibition of p38 MAPK regulates epileptic severity by decreasing expression levels of A1R and ENT1. Mol Med Rep. 2020;22(6):5348–57.
Zielinski MR, Taishi P, Clinton JM, Krueger JM. 5’-Ectonucleotidase-knockout mice lack non-REM sleep responses to sleep deprivation. Eur J Neurosci. 2012;35(11):1789–98.
Zimmermann H, Zebisch M, Sträter N. Cellular function and molecular structure of ecto-nucleotidases. Purinergic Signal. 2012;8(3):437–502.
Zimmermann HR, Yang W, Kasica NP, Zhou X, Wang X, Beckelman BC, Lee J, Furdui CM, Keene CD, Ma T. Brain-specific repression of AMPKalpha1 alleviates pathophysiology in Alzheimer’s model mice. J Clin Invest. 2020;130(7):3511–27.
Zu T, Guo S, Bardhi O, Ryskamp DA, Li J, Tusi KS, Engelbrecht A, Klippel K, Chakrabarty P, Nguyen L, Golde TE, Sonenberg N, Ranum LPW. Metformin inhibits RAN translation through PKR pathway and mitigates disease in C9orf72 ALS/FTD mice. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2020;117(31):18591–9.
Acknowledgements
We are grateful to the Medical Art Department of the Institute of Biomedical Sciences, Academia Sinica for the art work and design.
Funding
This research was supported by the Academia Sinica (AS-BRPT-110-11) and Ministry of Science and Technology (MOST 110-2321-B-001-011).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
CPC, KCW and CYL contributed to literature mining and manuscript writing. YC directed the project and edited the manuscript. All authors read and approved the manuscript.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Ethical approval and consent to participate
Not applicable.
Consent for publication
Not applicable.
Competing interests
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Open Access This article is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License, which permits use, sharing, adaptation, distribution and reproduction in any medium or format, as long as you give appropriate credit to the original author(s) and the source, provide a link to the Creative Commons licence, and indicate if changes were made. The images or other third party material in this article are included in the article's Creative Commons licence, unless indicated otherwise in a credit line to the material. If material is not included in the article's Creative Commons licence and your intended use is not permitted by statutory regulation or exceeds the permitted use, you will need to obtain permission directly from the copyright holder. To view a copy of this licence, visit http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/. The Creative Commons Public Domain Dedication waiver (http://creativecommons.org/publicdomain/zero/1.0/) applies to the data made available in this article, unless otherwise stated in a credit line to the data.
About this article
Cite this article
Chang, CP., Wu, KC., Lin, CY. et al. Emerging roles of dysregulated adenosine homeostasis in brain disorders with a specific focus on neurodegenerative diseases. J Biomed Sci 28, 70 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1186/s12929-021-00766-y
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1186/s12929-021-00766-y