Abstract
Background
Studies uncovering factors beyond socio-economic status (SES) that would explain racial and ethnic disparities in mortality are scarce.
Methods
Using prospective cohort data from the Third National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey (NHANES III), we examined all-cause and cause-specific mortality disparities by race, mediation through key factors and moderation by age (20–49 vs. 50+), sex and poverty status. Cox proportional hazards, discrete-time hazards and competing risk regression models were conducted (N = 16,573 participants, n = 4207 deaths, Median time = 170 months (1–217 months)).
Results
Age, sex and poverty income ratio-adjusted hazard rates were higher among Non-Hispanic Blacks (NHBs) vs. Non-Hispanic Whites (NHW). Within the above-poverty young men stratum where this association was the strongest, the socio-demographic-adjusted HR = 2.59, p < 0.001 was only partially attenuated by SES and other factors (full model HR = 2.08, p = 0.003). Income, education, diet quality, allostatic load and self-rated health, were among key mediators explaining NHB vs. NHW disparity in mortality. The Hispanic paradox was observed consistently among women above poverty (young and old). NHBs had higher CVD-related mortality risk compared to NHW which was explained by factors beyond SES. Those factors did not explain excess risk among NHB for neoplasm-related death (fully adjusted HR = 1.41, 95 % CI: 1.02–2.75, p = 0.044). Moreover, those factors explained the lower risk of neoplasm-related death among MA compared to NHW, while CVD-related mortality risk became lower among MA compared to NHW upon multivariate adjustment.
Conclusions
In sum, racial/ethnic disparities in all-cause and cause-specific mortality (particularly cardiovascular and neoplasms) were partly explained by socio-demographic, SES, health-related and dietary factors, and differentially by age, sex and poverty strata.
Similar content being viewed by others
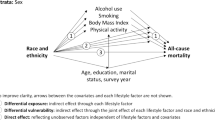
Background
The past several decades have witnessed an overall reduction in mortality rates coupled with a sustained Black-White mortality rate disparity with higher rates observed in Blacks (e.g. 1950: 5310 per 100,000 resident Non-Hispanic Black (NHB) population over 65y vs. 4865 per 100,000 resident Non-Hispanic White (NHW) population over 65y; 2006: Rates were 3669 per 100,000 vs. 2456 per 100,000 in NHB vs. NHW, respectively) [1, 2]. Though narrowing down in recent years, [3] this disparity in mortality remains wide and was explained partly by a long-standing socioeconomic racial stratification [4]. This comes in stark contrast to the Mexican-American (MA) and Hispanic ethnic group disparities with NHWs in mortality rates. In fact, assuming socioeconomic resources are equalized, mortality rate among MAs was consistently lower compared to NHWs a phenomenon known as the Hispanic paradox [3, 5–10]. Thus, in the absence of socio-economic equality, sizeable Black-White disparities in mortality will persist, while MAs would live longer than NHWs under similar socio-economic conditions [3, 9]. While socio-economic status (SES) was shown to moderate as well as mediate racial disparities in adult mortality, [11] only one study to date has systematically uncovered the contribution of behavioral and health-related potential mediators that go beyond SES [12].
We used national data to evaluate race/ethnicity effects on all-cause and cause-specific adult mortality, while stratifying by age group, sex and poverty status for all-cause mortality. We further evaluated the putative mediating effects of SES, lifestyle, social support and health-related factors in the association between race and all-cause mortality risk and examined cause-of-death structure across racial and ethnic groups.
Methods
Study population
The National Center for Health Statistics (NCHS) of the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC) conducted the NHANES III (Phase I: 1988–1991, Phase II: 1991–1994) by applying a complex multistage probability sample design, providing national estimates of health and nutritional status of the civilian non-institutionalized population [13]. Using questionnaire, physical examination and laboratory data from NHANES III, we retained adults age ≥ 20y (n = 18,825), who self-reported their race/ethnicity as NHW, NHB or MA, thus excluding other ethnicities. This yielded a final sample of 18,110 participants, of whom N = 16,573 were retained upon multiple imputations for descriptive statistics and N = 15,889 for survival analyses, with a total of 4,207 deaths (2359 among NHW, 1090 among NHB and 758 among MA). NHANES III is compliant with the ethical rules for human experimentation stated in the Declaration of Helsinki, including approval of an institutional review board and informed written consent. The current study was approved by the Office of Human Subjects Research Protections, National Institutes of Health.
Mortality outcome
The NCHS conducted a mortality linkage for NHANES III with the National Death Index (NDI), allowing investigation of baseline characteristics (1988–1994) in relation to mortality rates at follow-up through December 31, 2006. This public-use linked mortality file included eligibility status, assigned vital status, mortality source, person-months of follow-up from interview date and from Mobile Examination Center (MEC)/home exam date, and the underlying or multiple causes of death [14]. We defined an event as death from any cause, starting from the MEC examination date and ending on or before December 31, 2006; or death from the following underlying causes: “Major cardiovascular disease” (International Classification of Diseases, 10th version, (ICD-10) codes: I00-I78), “Neoplasms” (ICD-10 codes: C00-C97, D50-D64), “Diabetes” as an underlying/contributing cause (ICD-10 codes: E10-E14), “Other causes” (all other ICD-10 codes) [14]. “Other causes” were sub-divided into: “infections and respiratory (A..-B.. and J.. codes), “gastrointestinal (GI), Kidney and urological” (K.. and N.. codes), “Neurological disease” (G.. codes), unintentional/intentional injuries (V..-Y..) and “others” (all other codes). This detailed subdivision of causes (8 groups) was used only in part of the analysis whereby the cause of death structure (proportionate mortality) was compared between the three major race/ethnicity groups. In the main analysis of survival data, only deaths from major cardiovascular disease and neoplasms were examined.
Main predictors
In the selected sample, race/ethnicity was coded as NHW, NHB and MA. Two dummy variables were created to contrast NHB and MA with NHW.
Exogenous variables
In the final models, exogenous variables were the variables that were allowed to predict both potential mediators and the final outcome. Those included continuous age (y), sex, marital status (1 = Never married, 2 = Married, 3 = Divorced, 4 = Widowed, 5 = Other), household size and urban-rural residence (1 = Urban, 2 = Rural).
Potential mediators
Socio-economic status
Socio-economic status was measured alternatively by continuous poverty income ratio, education (years) and health insurance status (1 = yes, 0 = no).
Lifestyle and social support factors
Several factors were included in our models as mediators that could be directly affected by socio-economic status. Those include the latent constructs of “substance abuse”, “nutritional factors”, “physical activity”, “smoking” and “social support”. Substance abuse was operationalized as “alcohol consumption (g/d)” and drug use (1 = Ever, 0 = never); “nutritional factors” as 1995-Healthy Eating Index (1995-HEI) ranging from 0-100, [15] and the mean adequacy ratio score (MAR), [16–18] (Additional file 1); “Physical activity” as 3 related items: Item 1: “Compare activity for past month to past yr (0 = less, 1 = same, 2 = more), item 2: “Active compared with men/women your age” (0 = less, 1 = same, 2 = more), item 3: “Active now compared with self, 10 year ago” (0 = less, 1 = same, 2 = more); “Smoking” with two items: Item 1: “number of cigarettes smoked per day” (0 among non-smokers); item 2: “years smoked cigarettes” (0 among non-smokers); social support with 5 items namely, (1) “In a typical week, how many times do you talk on the telephone with family, friends, or neighbors?”, (2) “How often do you get together with friends or relatives; I mean things like going out together or visiting in each other's homes? (per year)”, (3) “About how often do you visit with any of your other neighbors, either in their homes or in your own? (per year)”, (4) “How often do you attend church or religious services? (per year)”, (5)“Altogether, how often do you attend meetings of the clubs or organizations (per year)”.
Health-related factors
The construct of “Health” was operationalized with self-rated health, co-morbidity index and the allostatic load (AL) score. Participants self-rated their health as: “Excellent” (referent), “Very good”, “Good”, “Fair” or “Poor”, while the co-morbidity index consisted of total sum score of 14 possible self-reported conditions, namely “arthritis“, “congestive heart failure“, “stroke“, “asthma“, “chronic bronchitis“, “emphysema“, “hay fever“, “cataracts“, “goiter“, “thyroid disease“, “lupus“, “gout“, “skin cancer”, “other cancer”. The allostatic load total score (0-9) is composed of 9 items which are described in details in Additional file 1 [19].
Statistical analysis
Using Stata 14.0 (StataCorp, College Station, TX), [20] analyses accounted for survey design complexity [14], by incorporating sampling weights, primary sampling units and strata. Multivariate imputed data [21, 22] was used to estimate means and proportions across race/ethnic groups, as well as various measures of associations including odds ratios and linear regression coefficients, after adjusting for sampling design complexity with survey (svy) commands. Comparison across race/ethnicity groups were made using svy:reg and svy:mlogit commands with race/ethnicity dummy variables as the only predictors. Standard errors were estimated using Taylor series linearization [14]. Comparison between race groups (NHB vs. NHW and MA vs. NHW) in terms of cause-of-death structure was done among all deaths in the selected sample, comparing proportions of each cause by use of a logistic regression model that took into account design complexity and multiple imputations.
Defining time-to-event from any age ≥ 20y since baseline visit (i.e. delayed entry) until death or censoring, we conducted Cox proportional hazards models for all-cause mortality stratifying by age group, sex and poverty status as well as competing risk regression models for cause-specific mortality. The time of follow-up is expressed in months. A series of nested models accounting for sampling weights were carried out and using the imputed data, in which socio-demographic, SES, lifestyle, social support and health-related factors were entered consecutively. The mediating effect of each of those factors was tested more thoroughly in a separate analysis using discrete-time survival analysis within a structural equations modeling (SEM) framework that accounted for sampling weights, though using the original un-imputed data. This was suggested as the optimal method to examine causal mediation within the context of survival analysis [12]. In this generalized SEM model, the final outcome was the hazard rate of death from all-causes and the data structure is person-period rather than participant-level data. The mortality outcome Y (0 = alive, 1 = dead of any cause or specific cause) was modeled using discrete-time survival with a logit link, by adding 18 dummy variables for year of follow-up as the main predictors for risk of death in the person-period modified data. Race/ethnicity was the primary exposure with two contrasts (NH black vs. NH whites; MA vs. NH white). A series of generalized SEM models were conducted, in which alternative mediators “M” were included, one at a time. Those mediators could be grouped under SES, substance abuse, diet, PA, smoking, social support and health. The generalized SEM models included covariates (age, sex, marital status, household size and urban/rural area of residence) that were exogenous to the system along with the race contrast variable. Direct and indirect effects of race were estimated from which the mediation proportion, a non-linear combination of the two, was also estimated using the delta method. Of particular interest were MP > 10 %, indicating an appreciable proportion of a total effect mediated by “M” [23]. Type I error was set at 0.05 in all other analyses.
Result
Study sample characteristics by race/ethnicity group
Weighted proportions of NHW, NHB and MA were ~83 %, 12 % and 5 %, respectively. Compared to NHW, NHB and MA participants were younger on average (42y and 38y vs. 46y). NHB had lower proportion male than NHW with the reverse being true for MA. Mean PIR was lower among NHB and MA vs. NHW (2.02 and 1.77 vs. 3.28, p < 0.001); with a similar pattern observed for poverty status and education(y). NHB and MA had a higher likelihood of urban residence and a larger mean household size compared to NHW, with marked racial/ethnic difference in marital status. Lack of health insurance was more common in MA (21.1 %) and NHB (9.3 %) vs. NHW (6.1 %), with both NHBs and MA being less likely to rate their health as “Excellent”. Conversely, both mean daily use and years of cigarette used were higher in NHWs, who were nonetheless more physically active than NHBs and MA, based on an item comparing activity to age peers. Drug ever use was highest among NHB (40.2 %), followed by NHW (37.0 %) and the lowest prevalence was among MA (29.4 %). While alcohol consumption did not differ between race groups, both 1995-HEI and MAR indicated poorer overall dietary quality among NHB compared to NHW. With only one exception (clubs and organizations), NHB had more social support from family, friends, neighbors and church, compared to NHW; with the reverse being true for MA. Self-reported co-morbidity was highest among NHW and lowest in MA. In contrast, total AL score based on objective measures of metabolic and inflammatory disturbance markers was higher among NHB than NHW, with no disparity detected between MA and NHW. Examining individual components of the AL, NHB had specifically a poorer profile in terms of albumin, CRP, glycated hemoglobin, resting heart rate and blood pressure levels compared to NHW (Table 1).
Cause of death structure by race/ethnicity
Out of 4207 deaths, around 60.2 % were caused by either cardiovascular disease or a neoplasm, with another 9 % having diabetes as the main contributing factor. Infectious diseases accounted for 13.1 % of deaths, while neurological, digestive/kidney and injuries accounted for 2–3 % of deaths each. The remaining causes, labelled as “Other” accounted for ~9.6 % of deaths, overall. Comparing NHW to NHB, NHB were more likely to have died from digestive/kidney disease than NHW and less likely to have died from neurological disease. When comparing MA to NHW, diabetes, digestive/kidney disease, injuries and “Other” were more common causes of deaths among MA. The reverse was true for CVD and neurological disease (Fig. 1).
Race/ethnicity and all-cause adult mortality: moderation by sex, age group and poverty status
Smoothed all-cause hazard curves by race/ethnicity (adjusted for age, sex and poverty income ratio) were consistently higher among NHBs compared to NHWs and lowest in MA, with an average HR = 1.44, 95 % CI: 1.31–1.58, p < 0.001, based on 5 imputations. No difference was noted between MA and NHW in that model (Fig. 2).
Using Cox PH models (Tables 2, 3, 4 and 5), higher all-cause mortality among NHBs vs. NHWs was specific to younger men above poverty (Model 0, Table 2: Crude Loge(HR) = +0.87, 95 % CI: 0.50;1.24, p < 0.001), an association that remained significant after adjustment for age, marital status, urban-rural area of residence and household size (Model 1, Table 2). In Model 2 of Table 3, adjusting further for SES factors (i.e. PIR, education and insurance status), the race/ethnicity associations with all-cause mortality among younger men above poverty was attenuated to Loge(HR) = +0.71, 95 % CI:+0.30;1.13, p = 0.001, with the fully adjusted model having a similar effect of race on all-cause mortality in that group (Table 5, model 8).
A lower all-cause mortality rate in MA compared with NHW observed in several age group/sex/poverty strata was retained in the full model only among women above poverty (young and old), (Table 5, Model 8). In the crude model (Model 0, Table 2), a lower risk of all-cause mortality was found among MA compared to NHW, specifically among men below poverty (both age groups) as well as older women(both poverty status groups). Adjustment for age and socio-demographic factors attenuated the effect appreciably in all these strata. Further adjustment for SES factors, however, pronounced the disparity among women above poverty (both young and old), an effect that was attenuated upon adjustment for dietary factors (Model 4, Table 3) as well as in subsequent models. This effect was then markedly pronounced in the final model, particularly among younger women above poverty (Model 7, Table 4: -0.76, p = 0.07 → Model 8, Table 5: -1.17, p = 0.009). On the other hand, a higher mortality risk among MA compared with NHW was unveiled upon adjustment for age and other socio-demographic factors, specifically among younger men above poverty (Loge(HR): Model 0, Table 2: +0.22, p = 0.37 → Model 1, Table 2: +0.49, p < 0.001). This effect, however, was completely explained away by SES factors (Model 2, Table 3: +0.06, p = 0.84).
Race/ethnicity and all-cause mortality: individual mediators in the total adult population
Additional file 1: Tables S1 and S2 show a series of generalized SEM models with the outcome being discrete-time hazard of all-cause death, with the main exposure being race/ethnicity, and individual mediators (M) being entered alternatively to explain the total effect of race on hazard rate. Among key findings, PIR, education, dietary quality indices, AL and self-rated health, were all key mediators in the pathway linking race to mortality when comparing NHB to NHW (MP > 10 %). When contrasting hazard rates between MA and NHW, the total effect was not indicative of any racial disparities. Social support factors, drug and alcohol use, as well as insurance status did not act as mediators.
Race/ethnicity and cause-specific mortality
Table 6 presents findings from competing risk regression models. Age, sex and PIR-adjusted cardiovascular mortality risk was higher in NHBs when compared with NHWs (Loge(HR) = +0.22, 95 % CI: +0.07;+0.37, p = 0.005), an association that was markedly attenuated in the full model Loge(HR) = +0.09, 95 % CI:-0.10;+0.28, p = 0.33). In contrast, MA had a lower cardiovascular mortality risk compared with NHWs, particularly in the fully adjusted model.
Moreover, NHBs had a greater neoplasm-related mortality risk compared to NHWs in both the age, sex and PIR-adjusted and the full model. A lower risk of neoplasm-related death among MAs when compared with NHWs was completely explained away in the full model by factors beyond age, sex and PIR.
Discussion
Using nationally representative data on US adults, we examined all-cause and cause-specific mortality disparities by race/ethnicity, mediation through key factors and moderation by age (20–49 vs. 50+), sex and poverty status. Among key findings, age, sex and poverty income ratio-adjusted hazard rates were higher among NHBs vs. NHWs. Within the above-poverty young men stratum where this association was the strongest, the socio-demographic-adjusted HR = 2.59, p < 0.001 was only partially attenuated by SES and other factors (full model HR = 2.08, p = 0.003). Income, education, diet quality, allostatic load and self-rated health, were among key mediators explaining NHB vs. NHW disparity in mortality. The Hispanic paradox was observed consistently among women above poverty (young and old). NHBs had higher CVD-related mortality risk compared to NHW which was explained by factors beyond SES. Those factors did not explain excess risk among NHBs for neoplasm-related death (fully adjusted HR = 1.41, 95 % CI: 1.02–2.75, p = 0.044). Moreover, those factors explained the lower risk of neoplasm-related death among MAs compared to NHW, while CVD-related mortality risk became lower among MAs compared to NHWs upon multivariate adjustment.
Race disparities in all-cause and cause-specific mortality rates, including death from cardiovascular disease and cancer, among U.S. adults have been previously reported, whereby Blacks or African Americans experienced consistently higher mortality rates compared to Whites [1, 24–26]. Several mediating and moderating factors have been examined in an attempt to explain these race disparities, including the moderating effects of gender, [27] age [4, 28, 29] – described as “Black-White mortality crossover” – and obesity, [30] the mediating [24, 29, 31–33] or moderating effects [4, 11, 25, 34, 35] of social factors, including poverty, culture and social injustice, [24] socioeconomic position, [25] socioeconomic status, [32, 35] social class, [36] education, [4] income, [4, 33, 34, 36] perceived stress, [31] health behaviors [31, 32] and health insurance [32]. Previous studies that examined these mediating and moderating effects were based on surveillance or large cohort data, including vital statistics, [1, 26] the National Health Interview Study, [28, 31, 36] the National Cancer Institute’s Surveillance, Epidemiology, and End Results program, [37] the Southern Community Cohort Study, [30, 35] the Health and Retirement Study, [32] the Multiple Risk Factor Intervention Trial, [33] the Americans’ Changing Lives Study [29].
A consistent finding from previous studies is that socioeconomic factors can moderate the effect of race on risk of death [4, 11, 25]. In addition, socio-economic status and other factors can act in mediating racial disparities in all-cause mortality [31, 32]. In a recent study, Krueger and colleagues used 1990 National Health Interview data involving 38,891 US adults and found distinct mediating effects of socioeconomic status, smoking status, physical activity, perceived stress, sleep duration and alcohol consumption on the relationship between race and all-cause mortality [31]. Similarly, analysis of the 1992–1998 Health and Retirement Study found distinct mediating effects of socioeconomic status, health behaviors and health insurance as mediators of the race disparities in all-cause mortality rates [32].
We find that NHBs had a higher rate of CVD mortality compared to NHWs, which is in accord with previous investigations [25, 33]. Our findings also suggest that by factors beyond SES mediated this association. Other variables may be important in explaining the higher CVD mortality in NHBs. Jones-Webb et al. found that neighborhood socioeconomic status moderated associations between race and CVD mortality among older men; older NHBs living in impoverished neighborhoods had a higher rate of CVD mortality, compared to older NHWs living in similar conditions [25]. Unsurprisingly, increased prevalence of CVD risk factors in NHBs may explain the higher prevalence of CVD mortality in this group [33].
Neoplasm-related death rates among NHB have remained high or have increased over time in certain instances [38]. Racial/Ethnic differences in neoplasm-related mortality can result from a combination of factors including smoking, nutrition, access to preventive, diagnostic, therapeutic, screening services and aggressiveness of treatment [38]. Modifying those factors could potentially prevent over half of cancer deaths and eliminate most racial/ethnic disparities [38]. Specifically, racial differences in breast cancer survival prevailed even after controlling for disease stage and known tumor characteristics, reflecting the potential mediating effects of social determinants beyond the biological, genetic and environmental factors, including the barriers of poverty (e.g. lack of a primary care physician, geographical access to care, competing survival priorities, burden of comorbidities, health insurance status, lack of information and knowledge, risk-promoting lifestyles and provider/system-level factors), culture (spirituality, perceived susceptibility to breast cancer, cultural beliefs and attitudes, and medical mistrust) and social injustice (racial prejudice and injustice) [24]. Menashe et al. indicated that the rate of decline in breast cancer mortality was slower among NH black women compared to White women, while age-specific incidence rate in black women was lower among blacks. Thus, the widening disparity in breast cancer mortality could not be explained by a higher incidence rate between 1990 and 2004 [37]. Thorpe et. al. showed that there was about 70 % excess risk of cancer mortality among Blacks compared to Whites, with socio-economic status, health insurance, psychosocial factors, behavioral factors and self-rated health accounting for 30 %, 18 %, 1 %, 17 % and 8 % of this excess risk [12]. Our study indicated that there was a 41 % excess risk of neoplasm-related death among NHBs compared to NHWs, which were not explained by SES, lifestyle or health-related factors.
In terms of diabetes-related mortality, studies have suggested that NHB have more than double the risk compared to NHW [12]. Using national death files and census data, for the 50 most populous US cities, that age-adjusted rate ratios of mortality from diabetes were higher in NHB compared to NHW in 39 of 41 cities, ranging from 1.57 (95 % CI: 1.33–1.86) in Baltimore to 3.78 (95 % CI: 2.84–5.02) in Washington, DC. Poverty alone explained 58.5 % of the NHB/NHW disparity in diabetes-related mortality and segregation explained 72.6 % of the disparity. However, those mediating effects of poverty and segregation varied widely across US cities [39]. Between 1994 and 2001, the annual rate of newly diagnosed elderly individuals with diabetes increased by 36.9 %, overall with Hispanics having the greatest increase at 55 % [40]. Our study indicated that MA had indeed a greater share of deaths attributed to diabetes compared to NHWs.
The Hispanic paradox, a consistently observed phenomenon, [9] occurs when mortality rates, specifically cardiovascular [6] and smoking-related mortality [5] among US Hispanics is similar or lower to NHWs’ rates, despite lower SES among Hispanics. Hunt et al. reported the age and sex-adjusted HR for all-cause mortality of US-born MAs vs. NHWs as 1.66 (95 % CI 1.15–2.40), while Mexico-born MAs vs. NHWs as 1.14 (95 % CI 0.63–2.06), [41] suggesting that “acculturation” in young MA may be a multifactorial covariate that is inadequately represented in large study sets such as NHANES III, which is sampling for a “paradoxically healthy” new immigrant population, rather than a truly representative sample of young Mexicans as a whole [42]. Generally, mortality rate differences between MA and NHW are greater among older age groups. Suggested mechanisms behind this paradox include less acculturation to the US resulting in better health, healthy migrant bias, and death records’ misreporting of ethnicity or missing records upon return to country of origin (“salmon bias”) [43]. Previous studies show that diet was healthier and smoking level was lower among Hispanics compared to non-Hispanics, which may partly explain their lower mortality rates [7, 8]. These findings are not universal, with studies in San Antonio [44, 45] and Corpus Christi [46] refuting the apparent paradox. Our findings support the Hispanic paradox mainly for cardiovascular mortality, which concurs with a recent meta-analysis [6]. It has been suggested that increased fruit and legume consumption among this group may have a protective effect [6]. Country of birth may be an important consideration; data from the San Antonio Heart Study show that diabetic MAs born in the US have higher rates of CVD mortality, compared to NHWs, while risk for CVD mortality was similar between diabetic US-born MAs and NHWs [41]. The findings also support the perplexing disassociation of several common risk factors with cardiovascular disease mortality in US Hispanic populations. MAs in our study had both lower income and a lower mean education years, when compared with NHWs. They also had a higher waist-hip-ratio and glycated hemoglobin levels, as well as lower access to health insurance. In contrast, MA were less likely to smoke and had a comparable diet quality to NHW. Smoking behavior differentials have accounted for >50 % life expectancy variability between Hispanics and non-Hispanics at age 50y [7]. Acculturation may influence our findings as only 51 % of MA in our sample were US-born.
Our study has several strengths. First, to our knowledge, it among few nationally representative studies testing associations between race/ethnicity and all-cause and cause-specific mortality in the adult US population by systematically examining effects within sex, age and poverty status and investigating potential mediators for all-cause and cause-specific mortality. Second, its large sample size allowed testing associations with mortality from homogeneous groups of causes. Competing risk, selection bias, missing data, unequal probability of sampling and design complexity were all addressed in our analyses. Some limitations include residual confounding, measurement error in covariates, particularly self-reported potential mediators (e.g. co-morbid conditions), and misclassification error of underlying and contributing causes of death.
Conclusion
In sum, racial/ethnic disparities in all-cause and cause-specific mortality (particularly cardiovascular and neoplasms) were partly explained by socio-demographic, SES, health-related and dietary factors, and differentially by age, sex and poverty strata. More studies are needed to uncover neighborhood-level and individual-level psychosocial factors mediating the effect of racial disparities on all-cause and cause-specific mortality among US adults.
Abbreviations
- AL:
-
Allostatic load
- CDC:
-
Centers for disease control and prevention
- CI:
-
Confidence interval
- DBP:
-
Diastolic blood pressure
- HDL-C:
-
High-density lipoprotein-cholesterol
- HEI:
-
Healthy eating index
- HR:
-
Hazard ratio
- HR:
-
Hazard ratio
- ICD-10:
-
International classification of diseases
- MA:
-
Mexican-American
- MAR:
-
Mean adequacy ratio
- MEC:
-
Mobile examination center
- MP:
-
Mediation proportion
- NCHS:
-
National center for health statistics
- NDI:
-
National death index
- NHANES:
-
National health and nutrition examination surveys
- NHB:
-
Non-hispanic black
- NHW:
-
Non-hispanic white
- SBP:
-
Systolic blood pressure
- TC:
-
Total cholesterol
- TG:
-
Triglycerides
- US:
-
United States
- USDA:
-
US department of agriculture
References
Levine RS, Foster JE, Fullilove RE, Fullilove MT, Briggs NC, Hull PC, Husaini BA, Hennekens CH. Black-white inequalities in mortality and life expectancy, 1933-1999: implications for healthy people 2010. Public Health Rep. 2001;116(5):474–83.
Thorpe Jr RJ, Wilson-Frederick SM, Bowie JV, Coa K, Clay OJ, LaVeist TA, Whitfield KE. Health behaviors and all-cause mortality in African American men. Am J Mens Health. 2013;7(4 Suppl):8S–18S.
Hummer RA, Chinn JJ. RACE/ETHNICITY AND U.S. ADULT MORTALITY: Progress, Prospects, and New Analyses. Du Bois Rev. 2011;8(1):5–24.
Sautter JM, Thomas PA, Dupre ME, George LK. Socioeconomic status and the Black-White mortality crossover. Am J Public Health. 2012;102(8):1566–71.
Fenelon A, Blue L. Widening life expectancy advantage of Hispanics in the United States: 1990-2010. J Immigr Minor Health. 2015;17(4):1130–7.
Cortes-Bergoderi M, Goel K, Murad MH, Allison T, Somers VK, Erwin PJ, Sochor O, Lopez-Jimenez F. Cardiovascular mortality in Hispanics compared to non-Hispanic whites: a systematic review and meta-analysis of the Hispanic paradox. Eur J Intern Med. 2013;24(8):791–9.
Blue L, Fenelon A. Explaining low mortality among US immigrants relative to native-born Americans: the role of smoking. Int J Epidemiol. 2011;40(3):786–93.
Elder JP, Castro FG, Demoor C, Mayer J, Candelaria JI, Campbell N, Talavera G, Ware LM. Differences in cancer-risk-related behaviors in Latino and anglo adults. Prev Med. 1991;20(6):751–63.
Ruiz JM, Steffen P, Smith TB. Hispanic mortality paradox: a systematic review and meta-analysis of the longitudinal literature. Am J Public Health. 2013;103(3):e52–60.
Markides KS, Eschbach K. Aging, migration, and mortality: current status of research on the Hispanic paradox. J Gerontol Ser B Psychol Sci Soc Sci. 2005;60 Spec No 2:68–75.
Jones-Webb R, Yu X, Wall M, Cui Y, Hellerstedt W, Oswald J. Race, socioeconomic status, and premature mortality. Minn Med. 2009;92(2):40–3.
Thorpe Jr RJ, Koster A, Bosma H, Harris TB, Simonsick EM, van Eijk JT, Kempen GI, Newman AB, Satterfield S, Rubin SM, et al. Racial differences in mortality in older adults: factors beyond socioeconomic status. Ann Behav Med. 2012;43(1):29–38.
NCHS: Plan and operation of the third National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey, 1988-94. In: Vital Health Stat, vol. 1. Hyattsville: Centers for Disease Control, National Center for Health Statistics; 1994.
NCHS: Office of Analysis and Epidemiology, Public-use Third National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey Linked Mortality File. Hyattsville: Centers for Disease Control, National Center for Health Statistics; 2010.
McCullough ML, Feskanich D, Rimm EB, Giovannucci EL, Ascherio A, Variyam JN, Spiegelman D, Stampfer MJ, Willett WC. Adherence to the dietary guidelines for Americans and risk of major chronic disease in men. Am J Clin Nutr. 2000;72(5):1223–31.
Beydoun MA, Fanelli-Kuczmarski MT, Allen A, Beydoun HA, Popkin BM, Evans MK, Zonderman AB. Monetary value of diet is associated with dietary quality and nutrient adequacy among urban adults, differentially by sex, race and poverty status. PLoS One. 2015;10(11):e0140905.
Kuczmarski MF, Mason MA, Allegro D, Zonderman AB, Evans MK. Diet quality is inversely associated with C-reactive protein levels in urban, low-income African-American and white adults. J Acad Nutr Diet. 2013;113(12):1620–31.
Raffensperger S, Kuczmarski MF, Hotchkiss L, Cotugna N, Evans MK, Zonderman AB. Effect of race and predictors of socioeconomic status on diet quality in the HANDLS Study sample. J Natl Med Assoc. 2010;102(10):923–30.
Seeman T, Merkin SS, Crimmins E, Koretz B, Charette S, Karlamangla A. Education, income and ethnic differences in cumulative biological risk profiles in a national sample of US adults: NHANES III (1988-1994). Soc Sci Med. 2008;66(1):72–87.
STATA. Statistics/Data Analysis: Release 14.0. Texas: Stata Corporation; 2015.
Lee KJ, Carlin JB. Multiple imputation for missing data: fully conditional specification versus multivariate normal imputation. Am J Epidemiol. 2010;171(5):624–32.
van Buuren S. Multiple imputation of discrete and continuous data by fully conditional specification. Stat Methods Med Res. 2007;16(3):219–42.
Ditlevsen S, Christensen U, Lynch J, Damsgaard MT, Keiding N. The mediation proportion: a structural equation approach for estimating the proportion of exposure effect on outcome explained by an intermediate variable. Epidemiology. 2005;16(1):114–20.
Gerend MA, Pai M. Social determinants of Black-White disparities in breast cancer mortality: a review. Cancer Epidemiol Biomarkers Prev. 2008;17(11):2913–23.
Jones-Webb R, Yu X, O'Brien J, Hannan P, Wall M, Oswald J. Does socioeconomic position moderate the effects of race on cardiovascular disease mortality? Ethn Dis. 2004;14(4):489–96.
Macinko J, Elo IT. Black-white differences in avoidable mortality in the USA, 1980-2005. J Epidemiol Community Health. 2009;63(9):715–21.
Zajacova A, Hummer RA. Gender differences in education effects on all-cause mortality for white and black adults in the United States. Soc Sci Med. 2009;69(4):529–37.
Eberstein IW, Nam CB, Heyman KM. Causes of death and mortality crossovers by race. Biodemography Soc Biol. 2008;54(2):214–28.
Yao L, Robert SA. Examining the racial crossover in mortality between African American and White older adults: a multilevel survival analysis of race, individual socioeconomic status, and neighborhood socioeconomic context. J Aging Res. 2011;2011:132073.
Cohen SS, Signorello LB, Cope EL, McLaughlin JK, Hargreaves MK, Zheng W, Blot WJ. Obesity and all-cause mortality among black adults and white adults. Am J Epidemiol. 2012;176(5):431–42.
Krueger PM, Saint Onge JM, Chang VW. Race/ethnic differences in adult mortality: the role of perceived stress and health behaviors. Soc Sci Med. 2011;73(9):1312–22.
Sudano JJ, Baker DW. Explaining US racial/ethnic disparities in health declines and mortality in late middle age: the roles of socioeconomic status, health behaviors, and health insurance. Soc Sci Med. 2006;62(4):909–22.
Thomas AJ, Eberly LE, Davey Smith G, Neaton JD, Stamler J. Race/ethnicity, income, major risk factors, and cardiovascular disease mortality. Am J Public Health. 2005;95(8):1417–23.
Nuru-Jeter AM, Williams T, LaVeist TA. Distinguishing the race-specific effects of income inequality and mortality in U.S. metropolitan areas. Int J Health Serv. 2014;44(3):435–56.
Signorello LB, Cohen SS, Williams DR, Munro HM, Hargreaves MK, Blot WJ. Socioeconomic status, race, and mortality: a prospective cohort study. Am J Public Health. 2014;104(12):e98–e107.
Muntaner C, Hadden WC, Kravets N. Social class, race/ethnicity and all-cause mortality in the US: longitudinal results from the 1986-1994 National Health Interview Survey. Eur J Epidemiol. 2004;19(8):777–84.
Menashe I, Anderson WF, Jatoi I, Rosenberg PS. Underlying causes of the black-white racial disparity in breast cancer mortality: a population-based analysis. J Natl Cancer Inst. 2009;101(14):993–1000.
Centers for Disease C, Prevention. Recent trends in mortality rates for four major cancers, by sex and race/ethnicity--United States, 1990-1998. MMWR Morb Mortal Wkly Rep. 2002;51(3):49–53.
Rosenstock S, Whitman S, West JF, Balkin M. Racial disparities in diabetes mortality in the 50 most populous US cities. J Urban Health. 2014;91(5):873–85.
McBean AM, Li S, Gilbertson DT, Collins AJ. Differences in diabetes prevalence, incidence, and mortality among the elderly of four racial/ethnic groups: whites, blacks, hispanics, and asians. Diabetes Care. 2004;27(10):2317–24.
Hunt KJ, Williams K, Resendez RG, Hazuda HP, Haffner SM, Stern MP. All-cause and cardiovascular mortality among diabetic participants in the San Antonio Heart Study: evidence against the "Hispanic Paradox". Diabetes Care. 2002;25(9):1557–63.
Teruya SA, Bazargan-Hejazi S. The immigrant and Hispanic Paradoxes: a systematic review of their predictions and effects. Hisp J Behav Sci. 2013;35(4):486–509.
Medina-Inojosa J, Jean N, Cortes-Bergoderi M, Lopez-Jimenez F. The Hispanic paradox in cardiovascular disease and total mortality. Prog Cardiovasc Dis. 2014;57(3):286–92.
Hunt KJ, Resendez RG, Williams K, Haffner SM, Stern MP, Hazuda HP. All-cause and cardiovascular mortality among Mexican-American and non-Hispanic White older participants in the San Antonio Heart Study- evidence against the "Hispanic paradox". Am J Epidemiol. 2003;158(11):1048–57.
Espinoza SE, Jung I, Hazuda H. The Hispanic paradox and predictors of mortality in an aging biethnic cohort of Mexican Americans and European Americans: the san antonio longitudinal study of aging. J Am Geriatr Soc. 2013;61(9):1522–9.
Pandey DK, Labarthe DR, Goff DC, Chan W, Nichaman MZ. Community-wide coronary heart disease mortality in Mexican Americans equals or exceeds that in non-Hispanic whites: The Corpus Christi Heart Project. Am J Med. 2001;110(2):81–7.
Acknowledgements
The authors would like to thank Ola S. Rostant and Danielle Shaked for internal review of the manuscript.
Funding
This work was fully supported by the Intramural Research Program of the NIH, National Institute on Aging.
Availability of data and materials
The data used in publicly available at http://www.cdc.gov/nchs/nhanes/
Authors’ contributions
MAB contributed to the study design, manuscript conceptualization, data management, statistical analysis and interpretation, manuscript preparation; HAB contributed to the study design, literature search and review, write-up of parts of the manuscript, revision of the manuscript; NM contributed to literature search and review, write-up of parts of the manuscript, revision of the manuscript; GAD; JAC; SME; ABZ contributed to manuscript conceptualization, write-up and revision of the manuscript. All authors read and approved the final manuscript.
Competing interests
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Consent for publication
Not applicable.
Ethics approval and consent to participate
NHANES III is compliant with the ethical rules for human experimentation stated in the Declaration of Helsinki, including approval of an institutional review board and informed written consent. The current study was approved by the Office of Human Subjects Research Protections, National Institutes of Health.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional file
Additional file 1: Table S1.
Total and direct effects of race on all cause mortality and effects mediated through socio-economic, lifestyle and social support factors, NHANES III. Table S2. Total and direct effects of race on all-cause mortality and effects mediated through health-related factors, NHANES III. (DOCX 54 kb)
Rights and permissions
Open Access This article is distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/), which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided you give appropriate credit to the original author(s) and the source, provide a link to the Creative Commons license, and indicate if changes were made. The Creative Commons Public Domain Dedication waiver (http://creativecommons.org/publicdomain/zero/1.0/) applies to the data made available in this article, unless otherwise stated.
About this article
Cite this article
Beydoun, M.A., Beydoun, H.A., Mode, N. et al. Racial disparities in adult all-cause and cause-specific mortality among us adults: mediating and moderating factors. BMC Public Health 16, 1113 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1186/s12889-016-3744-z
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1186/s12889-016-3744-z





