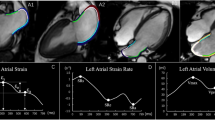
Abstract
Background
The role of the dysfunction of left atrium in the occurrence and development of cardiovascular disease has been gradually recognized. We aim to compare the impact on left atrial (LA) function between patients with hypertrophic cardiomyopathy (HCM) and hypertension (HTN) without LA enlargement using cardiovascular magnetic resonance feature tracking (CMR-FT), and if possible, explore the capability of LA function for providing clinical implication and predicting clinical adverse events in the early stage of cardiovascular disease.
Methods
Consecutive 60 HCM patients and 60 HTN patients with normal LA size among 1413 patients who underwent CMR were retrospectively analyzed as well as 60 controls. Left atrial and ventricular functions were quantified by volumetric and CMR-FT derived strain analysis from long and short left ventricular view cines. The primary endpoint was a composite of all-cause death, stroke, new-onset or worsening heart failure to hospitalization, and paroxysmal or persistent atrial fibrillation.
Results
Compared to the controls, both HTN and HCM participants had impaired LA reservoir function (εs) and conduit function (εe) with the different stage of LA booster pump dysfunction (εa). LA strain was more sensitive than LV longitudinal strain (GLS) for evaluate primary endpoint (εs: 33.9% ± 7.5 vs. 41.2% ± 14.3, p = 0.02; εe: 13.6% ± 6.2 vs. 17.4% ± 10.4, p = 0.03; εa: 20.2% ± 6.0 vs. 23.7% ± 8.8, p = 0.07; GLS: -19.4% ± 6.4 vs. -20.0% ± 6.8, p = 0.70, respectively). After a mean follow-up of 6.8 years, 23 patients reached primary endpoint. Cox regression analyses indicated impaired LA reservoir and booster pump strain were associated with clinical outcomes in patients at the early stage of HTN and HCM (p < 0.05).
Conclusions
CMR-FT-derived strain is a potential and robust tool in demonstrating impaired LA mechanics, quantifying LA dynamics and underlining the impacts on LA-LV coupling in patients with HTN and HCM without LA enlargement. The corresponding LA dysfunction is a promising metric to assess clinical implication and predict prognosis at the early stage, superior to GLS.
Similar content being viewed by others
Background
For the last decades, left atrial (LA) size has been related to increased morbidity and adverse outcomes in hypertension (HTN) and hypertrophic cardiomyopathy (HCM) patients, including atrial fibrillation (AF), heart failure (HF) and death [1, 2]. According to current guidelines, LA size is considered as one of the significant prognostic factors for sudden cardiac death in selected populations [3,4,5]. However, this parameter is not only insensitive, but also often inaccurate for assessing abnormality and predicting outcome, especially in the early stages of the two diseases [4, 6, 7]. In recent years, the role of the dysfunction of left atrium in the occurrence and development of cardiovascular disease has been gradually recognized [7,8,9]. Previous studies have demonstrated impaired LA function prior to LA enlargement assessed by LA deformation and LA volumetric indices and is tightly associated with left ventricular hypertrophy (LVH) and LV diastolic dysfunction [4, 10]. One of the probable mechanism is that it is not a simple adaptive hypertrophy, but a complex remodeling process impacted by the responses of the non-cardiomyocytic and cardiomyocytic components of the heart to dynamic mechanical and neurohumoral stimuli [11].
During hemodynamic stress or exertion, LA serves as the modulation of LV diastolic filling and cardiac performance by reservoir, conduit, and booster pump function [12]. Cardiovascular magnetic resonance (CMR) has emerged as a robust imaging technique to provide a detailed performance of HCM and HTN, including both identification of LV remodeling and impaired function [13, 14]. LA deformation was initially studied by volumetric and strain measurements using echocardiographic speckle tracking (STE) with the advantage of detailed evaluation of LA phasic function [15]. CMR feature tracking (CMR-FT) is a novel offline approach to assess myocardial deformation from steady-state free precession (SSFP) cine CMR by the tracking of tissue voxel motion [16]. In view of the thin anatomical LA walls, CMR-FT is superior to STE considering spatial resolution, view fields and reproducibility [14, 16]. It has been reported that impaired LA function independently predicts new-onset atrial fibrillation and LA function is associated with LV outflow gradient after septal ablation or septal myectomy in patients with HCM using CMR-FT [7, 17]. However, there is limited data comprehensively focusing on the association among LA function, abnormal LA-LV coupling and prognosis in HTN and HCM patients with normal LA size.
In the current study, we aim to compare the impact on LA function between patients with HCM and HTN without LA enlargement, as assessed through simultaneous LA and LV structural and functional analyses using CMR-FT, and explore the capability of LA function for providing clinical implication and predicting clinical adverse events in HTN and HCM patients with normal LA size.
Methods
Study population
Between August 2012 and March 2016, consecutive 60 HCM patients and 60 hypertensive patients who were evaluated CMR in our hospital were retrospectively enrolled in this study with similar sex distribution (Fig. 1A). HCM was defined as maximal wall thickness ≥ 15 mm in LV myocardial segments, or ≥ 13 mm in subject with family history of HCM, without other diseases accounted for the hypertrophy [3]. Subjects were considered to be hypertensive if they had an office systolic blood pressure > 140 mmHg [5]. The exclusion criteria include the following: (a) Patients with LA enlargement which defined by the presence of LA end-diastolic volume > 95th centile of gender-specific and age-specific CMR reference ranges [18], (b) LV ejection fraction < 50%, (c) history of septal myectomy or alcoholic septal ablation, (d) history of ischemic heart disease or chronic kidney disease, (e) other conventional contraindications to CMR (e.g., previous or present of AF). A total of 60 sex-matched controls were selected and undergone complete CMR examination. None of them had evidence of metabolic or cardiovascular disease throughout the medical history in whom electrocardiograph (ECG), echocardiography, CMR and exercise testing were normal. This study was approved by the committee of our hospital and written informed consents were waived due to retrospective nature.
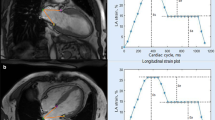
A Flowchart of study inclusion and exclusion. B This figure shows a representative example of CMR performance. HCM, hypertrophic cardiomyopathy; HTN, hypertension; CMR, Cardiac magnetic resonance; ED, end-diastole; ES, end-systole; SAX, short axis slice; LA, left atrium; LV, ventricle; GLS, global longitudinal strain; GLSR, global longitudinal strain rate
CMR scan protocol
CMR images were performed at 1.5 T MR (Magnetom Avanto; Siemens, Erlangen, Germany) with 8-channel cardiac coil and retrospective ECG gating. Balanced SSFP breath-held cine images were obtained in the following planes: a 2-chamber view, a 3-chamber view, a 4-chamber view, and 8 equidistant short-axis planes covering entire LA and LV. Conventional imaging parameters included the following: slice thickness 8 mm, repetition time 2.9 ~ 3.4 ms, echo time 1.1 ~ 1.5 ms, temporal resolution: 30 ~ 55 ms, field of view 320 × 320 mm ~ 380 × 380 mm, matrix size 192 × 162 [14].
CMR analysis
LA volume was measured by commercially available software (Qmass, Medis Suite 3.1, the Netherlands), which was obtained at late LV diastole after LA contraction (LAVmin), at LV diastole before LA contraction (LAVpre-a) and at LV end-systole (LAV max) in 2-, 3- and 4-chamber cine views. LA emptying fraction (LAEF) were respectively calculated as follows: (a) LA total EF = (LAVmax − LAVmin) × 100%/LAVmax, (b) LA passive EF = (LAVmax − LAVpre-a) × 100%/LAVmax, (c) LA active EF = (LAVpre-a − LAVmin) × 100%/LAVpre-a [19].
Left atrial and ventricular strain and strain rate (SR) analysis were performed offline using a commercially available software (QStrain, Medis Suite 3.1, the Netherlands) based on 2-, 3- and 4-chamber cine images (Fig. 1B) [6]. LA endocardial borders were manually drawn without pulmonary veins and the LA appendage when LA was at its maximum and minimum volume. LV longitudinal strain was obtained by standard end-diastolic endo- and epicardial contours with the defining mitral valve plane and LV apex in LV 2-, 3- and 4-chamber cine balanced SSFP single-slice images. Radial and circumferential strain were obtained by standard end-diastolic endo- and epicardial contours to three selected slices at representative basal, mid-ventricular and apical levels in LV short axis cine balanced SSFP stack [20]. Then, the myocardial contours were automatically tracked throughout the entire cardiac cycle. The software feature tracking performance was visually reviewed in order to ensure accurate tracking. In cases of insufficient tracking, the software allows for border readjusted and then propagation algorithm reapplied [19]. Three aspects of LA strain were calculated from outcomes as previously mentioned: total strain (εs, first strain peak, reflective of atrial reservoir function during LV systole), active strain (εa, second strain peak, reflective of LA booster pump function during late LV diastole) and passive strain (εe, difference between εs and εa, reflective of atrial conduit function during early LV diastole), which respectively correspond to LA reservoir function, boost pump function and conduit function [14, 16, 19]. LV global longitudinal strain (GLS), as well as LA global strain, were calculated from the average of the peak stain of the corresponding three slices [16]. Consequently, three LA SR parameters were derived: total SR (SRs, peak positive strain rate), active SR (SRa, late peak negative strain rate) and passive SR (SRe, peak early negative strain rate). And then, three LV global longitudinal peak strain rate values were measured according to its curve, as following: peak GLSR during LV contraction (GLSRs), peak GLSR during early filling (GLSRd1) and peak GLSR during atrial contractility at the end of LV diastole (GLSRd2) [12].
Follow-up
The primary endpoint was a composite of all-cause death, stroke, new-onset or worsening HF to hospitalization, and paroxysmal or persistent AF [21]. Incident HF was identified by (1) a definite diagnosis of decompensated HF; (2) pulmonary congestion proved by clinical or radiological evidence, increased LV filling pressures proved by invasive evidence, or elevated natriuretic peptide levels (NT-proBNP > 1000 ng/L or BNP [B-type natriuretic peptide] > 300 ng/L) [22]. Patients were followed with telephone interviews by two independent trained investigators who used described criteria. Medical records and copies of death certificates were requested to ascertained the incidence of clinical adverse events [22, 23].
Reproducibility
Intra- and inter-observer variability for the LV and LA strain parameters were analyzed in a group of 30 randomly selected subjects (10 HCM subjects, 10HTN subjects and 10 controls) by two investigators who were blinded to each other’s results. The intraclass correlation coefficients (ICC) were assessed to evaluate intra- and inter-observer reproducibility. Agreement was considered excellent when ICC > 0.75, good when ICC = 0.60 ~ 0.74, fair when ICC = 0.40 ~ 0.59, and poor when ICC < 0.4 [24].
Statistical analysis
Normally distributed continuous variables were verified using Kolmogorov–Smirnov test. Continuous variables were presented as the means ± standard deviations as appropriate. Categorical variables were expressed as numbers and percentages. Comparisons of continuous variables among three groups were performed using one-way analysis of variance (ANOVA), followed by the Tukey or Games-Howell post hoc pairwise comparison test, respectively. Categorical variables were compared using Fisher’s exact test or χ2 tests. Accordingly, Pearson correlation was performed to investigate the correlation between LA and LV parameters. The correlation was considered weak if r < 0.3, fair if r was between 0.3–0.5, moderate if r was between 0.5–0.7, and strong if r > 0.7 [25].
We calculated sample size based on representative metric, LA εa, using PASS (version 15), a combined standard deviation of 5% for εa measurements, and a ratio of 1:1:1 for the HCM, HTN and healthy volunteer groups [10]. Based on a one-way analysis of variance study, the result showed that sample sizes of 52, 52, and 52 are obtained from the 3 groups whose means are to be compared. The total sample of 156 subjects achieves 90% power to detect differences among the means versus the alternative of equal means using an F test with a 0.01 significance level. Therefore, we enrolled 60 participants in each group with sufficiently statistical power. For survival analyses, Univariable Cox regression models were computed to evaluate the unadjusted hazard of primary endpoint. Hazard ratios (HRs) with corresponding 95% confidence intervals were generated. Receiver operating characteristic (ROC) analyses were performed to estimate the area under the curves (AUC) and the optimal cutoff values of potential risk factors. Subsequently, the differences in event-free survival according to impaired LA strain, LV hypertrophy were compared by log-rank tests and were evaluated by Kaplan–Meier survival analysis. Parameters were stratified by the median once established cut-off values were lacking. Statistical analysis was performed by using IBM SPSS (version 22.0, Chicago). Statistical significance was defined as p < 0.05, which all values are 2 tailed.
Results
Baseline characteristics
A total of 574 HCM patients and 89 HTN patients were enrolled for screening and 520 patients with LA enlargement were excluded eventually. Another 19 patients were excluded due to the poor quality of CMR images for performing myocardial CMR-FT. Hence, 60 HCM patients and 60 HTN patients were ultimately included for analysis in this study with simple size- and sex-matched controls (Fig. 1A). There was no significant difference in gender or body surface area among the three groups. The complete baseline characteristics were presented in Table 1.
Patients with HTN was elder than that in the groups of HCM and controls. The history of smoking and drinking (both p < 0.01) were also higher in HTN group. There were less patients taking beta-blockers and diuretics, and more patients taking angiotensin-converting enzyme inhibitor or angiotensin receptor blocker in patients with HTN than in patients with HCM. Of the 60 HTN patients, 18 (30%) admitted with a family history of HTN while 7 (11.7%) of HCM patients involved with a family history of HCM (p < 0.01).
Left ventricular structural and functional abnormality
As shown in Table 2, patients with HCM had lower LV end-diastolic diameter (controls, 49.3 mm ± 3.6; HTN patients, 48.9 mm ± 5.2; HCM patients, 45.1 mm ± 4.7, p < 0.01); greater LV mass index (controls, 42.5 g/m2 ± 12.1; HTN patients, 55.7 g/m2 ± 13.0; HCM patients, 78.3 g/m2 ± 39.6, p < 0.01) and LV maximum wall thickness (MWT) (controls, 9.8 mm ± 1.9; HTN patients, 12.1 mm ± 2.7; HCM patients, 23.0 mm ± 6.8, p < 0.01) than patients with HTN and the controls (Fig. 2). The LV mass index was also higher in HTN patients compared with the controls and no significant difference was noted in LV end-diastolic diameter and wall thickness between the HTN and control group. Impaired left ventricular GLS in patients with HCM and higher GLSRd2 in patients with HTN were observed compared to the control (all p < 0.01) (Table 2).
One-way ANOVA with post hoc pairwise comparison test was performed for comparisons of LV hypertrophy and LA strain among three groups. *Indicating p < 0.05 when compared with controls; †Indicating p < 0.05 when compared with HCM group; MWT, maximal wall thickness; LV, left ventricular; EDD, end-diastolic diameter; εs, total strain; εe, passive strain; εa, active strain; LA, left atrial; HCM, hypertrophic cardiomyopathy
Left atrial dysfunction
LA volumes and dynamics as assessed by volumetric changes and deformation indexes were compared among the three groups in Table 3. The LA pre-contractile volumes and minimum LA volumes were the largest in HTN, followed by patients in HCM and controls (HTN vs. controls, LAVpre-a:44.4 ml ± 15.0 vs 34.0 ml ± 14.2, p < 0.01; LAVmin: 23.4 ml ± 10.4 vs 17.5 ml ± 8.3, p = 0.01, respectively, Table 3). Left atrial reservoir and conduit functional parameters, including relative LAEF, strain and strain rate, showed significantly reduced in HTN and HCM cases as compared with those in controls (Figs. 2, 3). LA contractile function was preserved in HCM patients with normal LA size. LA active strain was significantly impaired in patients with HTN compared to the other groups (controls, 24.3% ± 8.9; HTN patients, 20.6% ± 6.1; HCM patients, 25.5% ± 9.7, p < 0.01) (Fig. 2). Although LA active EF also reflected decreased tendency in HTN patients, there was no statistical difference compared with the control.
LA-LV coupling in all subjects. Pearson analysis was performed to investigate the correlations between left atrial strain with left ventricular strain during the whole cardiac cycle in all subjects. εs, total strain; εe, passive strain; GLS, global longitudinal strain; HTN, hypertension; HCM, hypertrophic cardiomyopathy; LA, left atrial; LV, left ventricular
LA-LV coupling
There was a negative correlation between age and εs, εe, without εa in all participants. LA reservoir (εs) and conduit strain (εe) were both significantly associated with LV mass index (r = − 0.27, p < 0.001 and r = − 0.29, p < 0.001), maximal wall thickness (r = − 0.28, p < 0.001 and r = − 0.37, p < 0.001), GLS (r = − 0.27, p < 0.001 and r = − 0.31, p < 0.001), and GLSRd1 (r = 0.24, p < 0.01 and r = 0.28, p < 0.001) (Fig. 3). Further subgroup analysis indicated that LA reservoir and conduit strain were significantly associated with LV GLS in HTN group (all p < 0.01), and LA conduit strain was related to GLSRd2 in HCM group (p < 0.001, Table 4). Importantly, LA and LV time-strain curve has an extremely strong association in the entire cardiac cycle (r = − 0.95, p < 0.001) (Fig. 3).
Outcomes
The mean follow-up duration was 6.8 years ± 2.1. There were 4 patients lost to follow-up. A total of 23 patients (19%) reached primary endpoints including 2 sudden cardiac deaths, 19 new-onset or worsening of HF to hospitalizations and 2 paroxysmal or persistent AF.
LA strain was more sensitive than LV deformation for evaluate clinical adverse events (εs: 33.9% ± 7.5 vs. 41.2% ± 14.3, p = 0.02; εe: 13.6% ± 6.2 vs. 17.4% ± 10.4, p = 0.03; εa: 20.2% ± 6.0 vs. 23.7% ± 8.8, p = 0.07; GLS: − 19.4% ± 6.4 vs. − 20.0% ± 6.8, p = 0.70, respectively) (Fig. 3). Increased risks factors for primary endpoints were impaired LA reservoir strain, greater LV mass index and LV maximal wall thickness in all HCM and HTN patients (εs: HR: 0.960, 95% CI: 0.927–0.995, p = 0.025; Massi: HR: 1.024, 95% CI: 1.015–1.034, p < 0.001; MWT: HR: 1.111, 95% CI: 1.059–1.165, p < 0.001) (Table 5). In addition, patients with HCM experienced significantly higher rate of primary endpoint (log rank p = 0.014). Too few adverse events in the HTN group ceased to further assess clinical outcomes. Further univariate Cox analysis indicated LA contractile strain was solely associated with primary endpoints in the HCM group (HR: 0.924, 95% CI: 0.871–0.979, p = 0.007). ROC analysis indicated that LVMWT, Massi, εs and εa did not show diagnostic value for differentiation of HTN and HCM (Fig. 4A), but were capable to predict outcomes in all patients and in HCM group (Fig. 4B, C). Kaplan–Meier survival analysis revealed worse primary endpoint-free survival in patients with εa < 22.5% (p = 0.04), LVMWT ≥ 16.1 mm (p = 0.01) in all patients with HTN and HCM. For patients with HCM, LV Massi (≥ 111.2 g/m2, p < 0.001) and MWT (≥ 19.5 mm, p < 0.01) were also both related to the outcomes (Fig. 5).
Receiver-operating characteristic curves for LV hypertrophy and LA strain were performed to estimate the area under the curves of these to differentiate HCM from HTN (A) and predict outcomes in HTN and HCM groups (B) and in HCM group (C). εs, total strain; εe, passive strain; εa, active strain; MWT, maximal wall thickness; LV, left ventricular; LA, left atrial; HTN, hypertension; HCM, hypertrophic cardiomyopathy
A Kaplan–Meier survival curves for primary endpoint development using LA εa, and LVMWT in HTN and HCM patients. B Kaplan–Meier survival curves for primary endpoint development using left ventricular Massi and MWT in HCM patients. Composite event-free survival was significantly lower with εa < 22.5% (p = 0.04), LV MWT ≥ 16.1 mm (p = 0.01) in HTN and HCM patients, and with LV Massi ≥ 111.2 g/m2 (p < 0.001), MWT ≥ 19.5 mm (p < 0.01) in HCM patients. LA, left atrial; εa, active strain; LV, left ventricular; MWT, maximal wall thickness; HTN, hypertension; HCM, hypertrophic cardiomyopathy
Reproducibility
ICC of LA volumetric and deformation parameters for intra-observer variability ranged between 0.821 (0.631–0.978) (SRe) and 0.984 (0.743–0.998) (LV GLS), and for inter-observer variability ranged between 0.898 (0.709–0.964) (SRa) and 0.985 (0.969–0.993) (εe) (Table 6).
Discussion
In the current work, we explored LA function by CMR-FT in patients with HTN or HCM with normal LA size. The results provide several important insights: (1) Even without apparent LA enlargement, LA reservoir and conduit function were impaired in both HTN and HCM patients regardless of the different stage of LA booster pump dysfunction, which may suggest the different pathophysiological mechanisms of LA dysfunction in these two diseases. (2) LA strain is a promising biomarker to assess the hemodynamics dysfunction and impaired LA-LV coupling among different diseases. (3) At the early stage of cardiovascular disease, LA strain was a more sensitive and representative metric for evaluating myocardial impairments and more capable risk factor for prognosis, superior to LV strain.
Left atrial functional impairments have been previously reported in HTN and HCM using myocardial deformation imaging based on echocardiography and-more recently-using CMR-FT [26, 27]. Our data showed that LA reservoir and conduit function were impaired in HTN and HCM consistent with prior investigations concerning patients with LA enlargement [19, 26]. These abnormalities were significantly correlated with LVH and impaired LV GLS. The potential mechanisms contained increased LV wall stiffness, elevated LV filling pressure and impaired LA-LV coupling [6, 28]. We also noticed that HTN patients had lower LA active strain compared to HCM patients and the controls. In contrast to the HTN group, a trend of increased LA contractile function was present in patients with HCM, but this difference was not statistically significant. Preserved LA active function represents a compensatory mechanism to maintain stroke volume and LV filling with mild diastolic dysfunction and its deterioration reflects resultant reduction of LA compliance with LV fibrosis in a stage of “decompensation” [29, 30]. Therefore, LA dysfunctions at an earlier stage are predominantly provoked by the diastolic function abnormalities and may in turn provoke to LV fibrosis and systolic dysfunction [29]. Similarly, in this research, LA functions correlated more strictly with the severity of LV diastolic function (LV mass index, LV peak GLS during atrial contractility) in HCM. While in HTN, it correlates with the chronicity of disease (LV maximal wall thickness, LV deformation parameters reflecting systolic function). Although subjects performed preserved absolute values of LV mass index compared to the relative reference value about LVH in our study [31], we also found HCM patients had greater LV mass index and LV maximal wall thickness, reflecting LV diastolic function, compared to HTN patients. And HCM patients suffered from more serious longitudinal strain impairment, reflecting LV systolic function or fibrosis. In contrast, Dr. Lio and his colleagues described that HCM patients had more serious LA contractile dysfunction and larger LA volume than HTN patients without significant difference in LV mass index [10]. Therefore, it is important to evaluate pathophysiological mechanisms and LA-LV coupling in patients with HTN or HCM. Previous studies demonstrated that LA dysfunction could be initiated by pressure-related LV diastolic dysfunction imposed by chronic hypertension before the clinically apparent LVH in HTN [26, 32]. While HCM is the most common inheritable heart disorder [33], characterized by myocyte hypertrophy, disarray, and fibrosis [34, 35]. The pathological mechanism of HCM reported by studies in animal models has found significant and upregulation of genes involved in extracellular matrix synthesis [36]. These genetic pathways were activated to make increase in extracellular matrix, and then to give rise to LVH or myocardial fibrosis developed [37]. In this context, it is interesting to speculate that LA function derived from CMR-FT may be a promising ongoing biomarker to assess the hemodynamics dysfunction and impaired LA-LV coupling among diseases with pathologic LVH in the early stage.
Although, previous studies roughly demonstrated impaired LA function without LA enlargement, assessed by global longitudinal LA strain and LA volumetric indices, few studies have been completely focused on the association between LA function and prognostic implications in the scenario of various etiology [4, 8, 9, 26]. In our cohort, although no differences were noted in LA volumetric parameters, impaired LA reservoir and contractile strain are significantly worse in patients admitted in primary endpoints, within the normal range of parameters representing LV hypertension. This finding extends finding of prior prospective research with 257 post-MI patients who suffered different grades of diastolic dysfunction [38]. It supported the concept that LA strain, derived of both echo- and CMR, has diagnostic utility for stratifying presence and severity of diastolic dysfunction. In addition, we found patients with abnormal LA contractile strain (< 22.5%) experienced significantly higher rate of adverse clinical events. Investigation in HF subjects proposed that LA declined contractility, coinciding with adverse changes in reduced intrinsic contractility, remodeling, apoptosis, collagen matrix turnover and myosin isoform expression, may contribute to greater burden of AF in HF patients with preserved LVEF [39]. It has been suggested that LA strain could potentially identify ambulatory patients with cardiovascular events at a higher risk of overt HF performances [40]. Interestingly, there was no significantly prognostic value in LV strain in this study. In recently, there are large of studies regarding the prognostic efficacy of LA strain and LV GLS with contradictory results. Some researchers reported that LA reservoir strain and conduit strain were independent predictors of major adverse cardiac events following ST-segment elevation myocardial infarction after adjustment for established clinical and CMR markers of cardiovascular risk including GLS [41, 42]. Negishi et al. demonstrated that LA booster pump strain was an independent and incremental predicted marker of arrhythmias over GLS in 124 patients with non-ischemic dilated cardiomyopathy [43]. In contrast, in a multicenter prospective study that included 1110 patients with myocardial infarction referred for invasive coronary angiography, they found that LA reservoir strain did not add further information in regard to adverse outcome, when readily obtained GLS and maximum LA volume were known [44]. Our results suggest that underlying mechanism of LA-LV coupling is promisingly urgent issue and larger studies are necessary to explore the prognostic role of myocardial phasic function during the different stages of cardiovascular diseases. Although, further studies are needed to support our findings and validate the availability of this tool, the application of cine CMR-FT for assessment and risk stratification in these populations undergoing clinical routine examination, particularly in the early stage, may become a short-term reality [45].
There are some limitations in the present study. Firstly, in consideration of the major aim, limited cases in HCM with normal LA size who came to see the doctors, the sample size in our study was relatively small. the correlations of LA-LV measurements are weak-to-fair. Despite age-related correlation and survival analyses, difference in age between groups may confound the conclusions. More and larger scale studies are needed to confirm these findings. Secondly, due to the relatively early disease stage with a few cardiovascular events in this cohort, we acknowledge that only univariable Cox regression analyses were performed at a single time point. Thus, the power of prognostic analysis is limited, and we cannot confirm whether LA strain is an independent risk factor for primary endpoint. Thirdly, differences of strain measurements caused by various CMR-FT vendors cannot be excluded. So standardized postprocessing methods would be desirable to facilitate comparative analysis of LA deformation and may reduce inter-vendor variability.
Conclusions
CMR-FT-derived strain is a promising and robust tool in demonstrating impaired LA mechanics, quantifying LA dynamics and underlining the importance of LA-LV coupling in patients with HTN and HCM, whose left atrium is even in the normal size. The corresponding LA dysfunctions were strictly associated with clinical implication and provided prognostic utility at the early stage of HTN and HCM superior to GLS. Further multicenter, large scale and prospective studies are need to confirm and verify our findings.
Availability of data and materials
The datasets used and/or analyzed during the current study are available from the corresponding author on reasonable request.
Abbreviations
- LA:
-
Left atrial
- HTN:
-
Hypertension
- HCM:
-
Hypertrophic cardiomyopathy
- AF:
-
Atrial fibrillation
- HF:
-
Heart failure
- LVH:
-
Left ventricular hypertrophy
- CMR:
-
Cardiovascular magnetic resonance
- STE:
-
Echocardiographic speckle tracking
- CMR-FT:
-
CMR feature tracking
- SSFP:
-
Steady-state free precession
- LAEF:
-
Left atrial emptying fraction
- SR:
-
Strain rate
- εs:
-
Total strain
- εa:
-
Active strain
- εe:
-
Passive strain
- GLS:
-
Global longitudinal strain
- ICC:
-
Intraclass correlation coefficient
- ANOVA:
-
One-way analysis of variance
- HRs:
-
Hazard ratios
- ROC:
-
Receiver operating characteristic
- AUC:
-
Area under the curves
- MWT:
-
Maximal wall thickness
References
Lang RM, Badano LP, Mor-Avi V, et al. Recommendations for cardiac chamber quantification by echocardiography in adults: an update from the American Society of Echocardiography and the European Association of Cardiovascular Imaging. Eur Heart J Cardiovasc Imaging. 2015;16:233–70.
Guttmann OP, Rahman MS, O’Mahony C, et al. Atrial fibrillation and thromboembolism in patients with hypertrophic cardiomyopathy: systematic review. Heart (British Cardiac Society). 2014;100:465–72.
Elliott PM, Anastasakis A, Borger MA, et al. 2014 ESC Guidelines on diagnosis and management of hypertrophic cardiomyopathy: the Task Force for the Diagnosis and Management of Hypertrophic Cardiomyopathy of the European Society of Cardiology (ESC). Eur Heart J. 2014;35:2733–79.
Demir M, Aktaş İ, Yıldırım A. Left atrial mechanical function and stiffness in patients with nondipper hypertension: a speckle tracking study. Clin Exp Hypertens. 2017;39:319–24.
Williams B, Mancia G, Spiering W, et al. 2018 ESC/ESH Guidelines for the management of arterial hypertension. Eur Heart J. 2018;39:3021–104.
Yang Y, Yin G, Jiang Y, et al. Quantification of left atrial function in patients with non-obstructive hypertrophic cardiomyopathy by cardiovascular magnetic resonance feature tracking imaging: a feasibility and reproducibility study. J Cardiovasc Magn Reson. 2020;22:1.
Debonnaire P, Joyce E, Hiemstra Y, et al. Left atrial size and function in hypertrophic cardiomyopathy patients and risk of new-onset atrial fibrillation. Circ Arrhythm Electrophysiol. 2017;10:e004052.
Sarvari SI, Haugaa KH, Stokke TM, et al. Strain echocardiographic assessment of left atrial function predicts recurrence of atrial fibrillation. Eur Heart J Cardiovasc Imaging. 2016;17:660–7.
Cameli M, Lisi M, Focardi M, et al. Left atrial deformation analysis by speckle tracking echocardiography for prediction of cardiovascular outcomes. Am J Cardiol. 2012;110:264–9.
Iio C, Inoue K, Nishimura K, et al. Characteristics of left atrial deformation parameters and their prognostic impact in patients with pathological left ventricular hypertrophy: analysis by speckle tracking echocardiography. Echocardiography. 2015;32:1821–30.
de Simone G, Pasanisi F, Contaldo F. Link of nonhemodynamic factors to hemodynamic determinants of left ventricular hypertrophy. Hypertension. 2001;38:13–8.
Margulescu AD, Rees E, Coulson RM, et al. Do left atrial strain and strain rate reflect intrinsic atrial function, or are they determined by left ventricular function? Kardiol Pol. 2015;73:539–48.
Maron MS. Clinical utility of cardiovascular magnetic resonance in hypertrophic cardiomyopathy. J Cardiovasc Magn Reson. 2012;14:13.
Zareian M, Ciuffo L, Habibi M, et al. Left atrial structure and functional quantitation using cardiovascular magnetic resonance and multimodality tissue tracking: validation and reproducibility assessment. J Cardiovasc Magn Reson. 2015;17:52–52.
Domsik P, Kalapos A, Chadaide S, et al. Three-dimensional speckle tracking echocardiography allows detailed evaluation of left atrial function in hypertrophic cardiomyopathy–insights from the MAGYAR-Path Study. Echocardiography (Mount Kisco, NY). 2014;31:1245–52.
Leng S, Tan R-S, Zhao X, et al. Validation of a rapid semi-automated method to assess left atrial longitudinal phasic strains on cine cardiovascular magnetic resonance imaging. J Cardiovasc Magn Reson. 2018;20:71–71.
Williams LK, Chan RH, Carasso S, et al. Effect of left ventricular outflow tract obstruction on left atrial mechanics in hypertrophic cardiomyopathy. Biomed Res Int. 2015;2015:481245–481245.
Truong VT, Palmer C, Wolking S, et al. Normal left atrial strain and strain rate using cardiac magnetic resonance feature tracking in healthy volunteers. Eur Heart J Cardiovasc Imaging. 2019;jez157.
Kowallick JT, Kutty S, Edelmann F, et al. Quantification of left atrial strain and strain rate using Cardiovascular Magnetic Resonance myocardial feature tracking: a feasibility study. J Cardiovasc Magn Reson. 2014;16:60–60.
Gastl M, Gotschy A, Polacin M, et al. Determinants of myocardial function characterized by CMR-derived strain parameters in left ventricular non-compaction cardiomyopathy. Sci Rep. 2019;9:15882.
Vasquez N, Ostrander BT, Lu D-Y, et al. Low left atrial strain is associated with adverse outcomes in hypertrophic cardiomyopathy patients. J Am Soc Echocardiogr. 2019;32:593-603.e1.
Chirinos JA, Sardana M, Ansari B, et al. Left atrial phasic function by cardiac magnetic resonance feature tracking is a strong predictor of incident cardiovascular events. Circ Cardiovasc Imaging. 2018;11:e007512–e007512.
Kawel-Boehm N, Kronmal R, Eng J, et al. Left ventricular mass at MRI and long-term risk of cardiovascular events: the multi-ethnic study of atherosclerosis (MESA). Radiology. 2019;293:107–14.
Kowallick JT, Morton G, Lamata P, et al. Quantification of atrial dynamics using cardiovascular magnetic resonance: inter-study reproducibility. J Cardiovasc Magn Reson. 2015;17:36–36.
Akoglu H. User’s guide to correlation coefficients. Turk J Emerg Med. 2018;18:91–3.
Li L, Chen X, Yin G, et al. Early detection of left atrial dysfunction assessed by CMR feature tracking in hypertensive patients. Eur Radiol. 2020;30:702–11.
Hinojar R, Zamorano JL, Fernández-Méndez MA, et al. Prognostic value of left atrial function by cardiovascular magnetic resonance feature tracking in hypertrophic cardiomyopathy. Int J Cardiovasc Imaging. 2019;35:1055–65.
Miyoshi H, Oishi Y, Mizuguchi Y, et al. Early predictors of alterations in left atrial structure and function related to left ventricular dysfunction in asymptomatic patients with hypertension. J Am Soc Hypertens. 2013;7:206–15.
Thomas L, Marwick TH, Popescu BA, et al. Left atrial structure and function, and left ventricular diastolic dysfunction: JACC state-of-the-art review. J Am Coll Cardiol. 2019;73:1961–77.
Kowallick JT, Silva Vieira M, Kutty S, et al. Left atrial performance in the course of hypertrophic cardiomyopathy: relation to left ventricular hypertrophy and fibrosis. Invest Radiol. 2017;52:177–85.
Olivotto I, Maron MS, Autore C, et al. Assessment and significance of left ventricular mass by cardiovascular magnetic resonance in hypertrophic cardiomyopathy. J Am Coll Cardiol. 2008;52:559–66.
Yang L, Qiu Q, Fang SH. Evaluation of left atrial function in hypertensive patients with and without left ventricular hypertrophy using velocity vector imaging. Int J Cardiovasc Imaging. 2014;30:1465–71.
Semsarian C, Ingles J, Maron MS, et al. New perspectives on the prevalence of hypertrophic cardiomyopathy. J Am Coll Cardiol. 2015;65:1249–54.
Maron BJ, Gardin JM, Flack JM, et al. Prevalence of hypertrophic cardiomyopathy in a general population of young adults. Echocardiographic analysis of 4111 subjects in the CARDIA Study. Coronary Artery Risk Development in (Young) Adults. Circulation. 1995;92:785–9.
Keren A, Syrris P, McKenna WJ. Hypertrophic cardiomyopathy: the genetic determinants of clinical disease expression. Nat Clin Pract Cardiovasc Med. 2008;5:158–68.
Kim JB, Porreca GJ, Song L, et al. Polony multiplex analysis of gene expression (PMAGE) in mouse hypertrophic cardiomyopathy. Science. 2007;316:1481–4.
Xu J, Zhuang B, Sirajuddin A, et al. MRI T1 mapping in hypertrophic cardiomyopathy: evaluation in patients without late gadolinium enhancement and hemodynamic obstruction. Radiology. 2020;294:275–86.
Kim J, Yum B, Palumbo MC, et al. Left atrial strain impairment precedes geometric remodeling as a marker of post-myocardial infarction diastolic dysfunction. JACC Cardiovasc Imaging. 2020;13:2099–113.
Melenovsky V, Hwang SJ, Redfield MM, et al. Left atrial remodeling and function in advanced heart failure with preserved or reduced ejection fraction. Circ Heart Fail. 2015;8:295–303.
Sanchis L, Gabrielli L, Andrea R, et al. Left atrial dysfunction relates to symptom onset in patients with heart failure and preserved left ventricular ejection fraction. Eur Heart J Cardiovasc Imaging. 2015;16:62–7.
Leng S, Ge H, He J, et al. Long-term prognostic value of cardiac MRI left atrial strain in ST-segment elevation myocardial infarction. Radiology. 2020;296:299–309.
Schuster A, Backhaus SJ, Stiermaier T, et al. Left atrial function with MRI enables prediction of cardiovascular events after myocardial infarction: insights from the AIDA STEMI and TATORT NSTEMI trials. Radiology. 2019;293:292–302.
Negishi K, Negishi T, Zardkoohi O, et al. Left atrial booster pump function is an independent predictor of subsequent life-threatening ventricular arrhythmias in non-ischaemic cardiomyopathy. Eur Heart J Cardiovasc Imaging. 2016;17:1153–60.
Ersbøll M, Andersen MJ, Valeur N, et al. The prognostic value of left atrial peak reservoir strain in acute myocardial infarction is dependent on left ventricular longitudinal function and left atrial size. Circ Cardiovasc Imaging. 2013;6:26–33.
Schuster A, Hor KN, Kowallick JT, et al. Cardiovascular magnetic resonance myocardial feature tracking: concepts and clinical applications. Circ Cardiovasc Imaging. 2016;9:e004077.
Acknowledgements
Not applicable.
Funding
Minjie Lu was supported by the Construction Research Project of Key Laboratory (Cultivation) of Chinese Academy of Medical Sciences (2019PT310025), Capital Clinically Characteristic Applied Research Fund (Grant No. Z191100006619021), National Foreign Expert Talent Project (G20190001630), Education Reform Project of Peking Union Medical College (10023201900204), National Natural Science Foundation of China (Grant No. 81971588) and Clinical and Translational Fund of Chinese Academy of Medical Sciences (2019XK320063). The funders had no role in study design, data collection and analysis, decision to publish, or preparation of the manuscript.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
DZ designed the study protocol, performed data acquisition and measurements, performed statistical analysis and drafted the manuscript. WJY, YXY and GY performed data acquisition and measurements. SL, BYZ, JH and YNW revised the manuscript; WCW, YJ, XXS, AS and SHZ participated in the scientific discussion during the study. MJL revised the manuscript and participated in the scientific discussion. All authors read and approved the final manuscript.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Ethics approval and consent to participate
This study was approved by the institution Ethics Review Board of Fuwai hospital, Beijing, China. Written informed consents were waived due to retrospective nature.
Consent for publication
Not applicable.
Competing interests
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Open Access This article is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License, which permits use, sharing, adaptation, distribution and reproduction in any medium or format, as long as you give appropriate credit to the original author(s) and the source, provide a link to the Creative Commons licence, and indicate if changes were made. The images or other third party material in this article are included in the article's Creative Commons licence, unless indicated otherwise in a credit line to the material. If material is not included in the article's Creative Commons licence and your intended use is not permitted by statutory regulation or exceeds the permitted use, you will need to obtain permission directly from the copyright holder. To view a copy of this licence, visit http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/. The Creative Commons Public Domain Dedication waiver (http://creativecommons.org/publicdomain/zero/1.0/) applies to the data made available in this article, unless otherwise stated in a credit line to the data.
About this article
Cite this article
Zhou, D., Yang, W., Yang, Y. et al. Left atrial dysfunction may precede left atrial enlargement and abnormal left ventricular longitudinal function: a cardiac MR feature tracking study. BMC Cardiovasc Disord 22, 99 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1186/s12872-022-02532-w
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1186/s12872-022-02532-w