Abstract
Background
Inflorescence architecture and floral development in flowering plants are determined by genetic control of meristem identity, determinacy, and maintenance. The ear inflorescence meristem in maize (Zea mays) initiates short branch meristems called spikelet pair meristems, thus unlike the tassel inflorescence, the ears lack long branches. Maize growth-regulating factor (GRF)-interacting factor1 (GIF1) regulates branching and size of meristems in the tassel inflorescence by binding to Unbranched3. However, the regulatory pathway of gif1 in ear meristems is relatively unknown.
Result
In this study, we found that loss-of-function gif1 mutants had highly branched ears, and these extra branches repeatedly produce more branches and florets with unfused carpels and an indeterminate floral apex. In addition, GIF1 interacted in vivo with nine GRFs, subunits of the SWI/SNF chromatin-remodeling complex, and hormone biosynthesis-related proteins. Furthermore, key meristem-determinacy gene RAMOSA2 (RA2) and CLAVATA signaling-related gene CLV3/ENDOSPERM SURROUNDING REGION (ESR) 4a (CLE4a) were directly bound and regulated by GIF1 in the ear inflorescence.
Conclusions
Our findings suggest that GIF1 working together with GRFs recruits SWI/SNF chromatin-remodeling ATPases to influence DNA accessibility in the regions that contain genes involved in hormone biosynthesis, meristem identity and determinacy, thus driving the fate of axillary meristems and floral organ primordia in the ear-inflorescence of maize.
Similar content being viewed by others
Background
Maize (Zea mays L.), one of the most widely cultivated crop plants in the world, produces two distinct inflorescences, in contrast to other related grasses such as Sorghum bicolor and Oryza sativa, each of which has a panicle of perfect flowers. Whereas the maize male inflorescence (tassel) is a panicle with multiple long branches producing a variable number of spikelets, the female inflorescence (ear) is covered with short branches (i.e. spikelet pair branches) and in each spikelet is two florets, the lower of which aborts. The maize ear, with its dozens to hundreds of kernels, is an important reproductive and agronomic tissue. In normal development of the ear, the inflorescence meristem (IM) first initiates indeterminate spikelet pair meristems (SPMs), which are short branches [1, 2]. Thus, unlike tassels, ears lack long branches. The ear florets initiate a palea, a lemma, two lodicules, three stamens, and three carpels. After initiation, the stamens abort in female flowers, but the carpels develop into a single pistil by fusing congenitally along their edges; two indeterminate abaxial carpels fuse to form the silk, and the third elongates to cover the ovule forming the ovary wall [3, 4]. After double fertilization, ovules enclosed by carpels develop into kernels (caryopses). Therefore, branching and gynoecium development are both critically important for inflorescence architecture and floral fertility, as well as for grain yield.
Previous studies revealed a complex functional hierarchy of genes involved in inflorescence branching in maize. Mutations in three classical RAMOSA (RA) genes produce highly branched male and female inflorescences, in which the SPMs are converted into branch meristems (BMs) [5]. The RA3 encodes a trehalose-6-phosphate phosphatase [6], which removes the phosphate from trehalose 6-phosphate (T6P) to produce free trehalose, suggesting that sugar signaling triggered by polysaccharides may be involved in inflorescence architecture [7,8,9]. Mutation of RA3 leads to reduced expression of the zinc-finger domain protein-encoding gene RA1 [10], suggesting that RA3 may regulate RA1 directly or indirectly. The RA2 encodes a lateral organ boundary (LOB) domain transcription factor (TF) required for initiation of axillary meristems in both inflorescences. In ra2 mutants, expression of RA1 is also down-regulated, suggesting that both RA2 and RA3 positively regulate expression of RA1 [11]. Genes in the CLAVATA-WUSCHEL (CLV-WUS) feedback loop, such as Fasciated ear2 (FEA2) [12], FEA3 [13] and Thick tassel dwarf1 (TD1) [14] also regulate inflorescence branching.
Growth-regulating factor (GRF)-interacting factor1 (GIF1), which is one of the transcriptional coactivators of plant-specific growth-regulating factors (GRFs), has been characterized as a major regulator of plant vegetative and reproductive development [15,16,17,18,19,20]. In Arabidopsis (Arabidopsis thaliana), GIF1/AN3 is required for maintenance of the shoot apical meristem; establishment of the carpel margin meristem; development of flower organs, cotyledons, and leaves; cell proliferation and expansion; and lateral organ growth [17, 21,22,23,24,25]. In rice, OsGIF1 positively regulates plant height, leaf size, stem internodes, grain size, number of grains per panicle, and branches per panicle [26, 27], playing a major role in regulating the size of vegetative and reproductive organs and the number of inflorescence branches.
Recently, we found that maize gif1 mutants have fewer branches in the tassels than wild-type plants but extra branches in the ears [28], showing opposite effects of GIF1 on the branches in the tassel and the ear. Here, we compared the detailed morphological and anatomical differences in the ear inflorescence between the gif1-1 mutant and the wild type. We further identified GIF1-interacting proteins using immunoprecipitation-mass spectrometry (IP-MS) and GIF1 target genes through chromatin immunoprecipitation sequencing (ChIP-seq), integrating these data with transcriptome data. We propose that GIF1 regulates axillary meristems and floral organ primordia in the ear-inflorescence by targeting genes in hormone biosynthesis, genes in meristem identity and determinacy involving RAMOSA and CLV-WUS pathway.
Materials and methods
Plant materials and phenotypic characterization
The maize gif1-1 mutant was from our lab, which was originally found in the BS238 family line. The gif1-1 mutant and GIF1-GFP overexpressing lines were planted at Wuhan (30°N, 114°E), China. The phenotypes of traits including plant height, ear height and leaf length. The sample size for each phenotypic value was more than 30 individuals. All methods, including plant experimental research, were performed in accordance with the relevant institutional, national, and international guidelines and legislation.
GIF1-GFP fusion construct and genetic transformation
The GIF1 coding sequence was amplified with primers GIF1-F and GIF1-R (Supplemental Table 2) and fused to the green fluorescent protein (GFP) coding sequence. The GIF1-GFP fusion construct (Supplemental Fig. 4) was cloned into the pZZ01523 vector (Life Science and technology Center, China National Seed Group CO., LTD, China. http://www.chinaseeds-lstc.com), and the resulting vector was transformed into the maize ZZC01 line by Agrobacterium-mediated transformation [29]. Transgenic genotypes were determined using Trans-F/R primers, with the Trans-F primer designed against the GIF1 sequence and the Trans-R primer designed against the vector sequence. The expression level of gif1 was measured using Q-gif1-F/R primers designed against the 3ʹ-UTR of gif1 (Supplemental Table 3).
Genetic complementation
To analyze biological functions, phenotypes of GIF1-GFP overexpressing lines were evaluated. Additionally, the gif1 allele of the gif1-1 mutant was introduced into ZZC01 genetic background through two cycles of backcrossing using marker-assisted selection. Those + /gif1 heterozygotes were crossed to line OE2. Individuals with gif1gif1 genotype and overexpressing GIF1-GFP (referred to as complemented plants) were selected through genotyping using gene-specific primers (Supplemental Table 3) and evaluated for phenotypic rescue of plant characteristics and inflorescence architecture.
Microscopy observation
For stereomicroscope observation, immature ears were collected from the gif1-1 mutant and its wild-type siblings, and the complemented plants. The ear inflorescence images were acquired using a Nikon SMZ25 microscope (Nikon, Japan) and merged by NIS (Nikon Imaging Software) elements. Immature ear inflorescences (5 mm) from the gif1-1 mutant and wild type were sampled according to Li et al. [30]. A sequential sampling procedure was performed from the beginning of the ninth leaf stage to observe the time course of inflorescence development. Inflorescence samples were fixed in a glutaraldehyde solution (2.5% v/v glutaraldehyde in 0.08 M phosphoric acid buffer) for 24 h at 4 °C and then dehydrated through a graded series of ethanol from 30 to 90%. Tissue samples were dried using a critical point dryer, sputter coated with gold palladium for 45 s, and observed on a Hitachi S-4700 scanning electron microscope (Hitachi, Japan) at an accelerating voltage of 5 kV [28].
Immunoprecipitation-mass spectrometry (IP-MS)
Developing ears ~ 5 mm in length were collected from line OE2 and ground in a mortar using liquid nitrogen. The frozen powder was mixed with ice-cold extraction buffer (50 mM Tris–HCl, 150 mM NaCl, 1 mM phenylmethanesulfonyl fluoride, and 1% Triton X-100). The mixture was centrifuged at 3,000 g for 15 min. The supernatant was used as total protein for immunoblotting. Total proteins were separated using 30% sodium dodecyl sulfate–polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis (SDS-PAGE). The gel was stained with 0.2% (w/v) silver nitrate. For immunoblotting, proteins were electrotransferred onto polyvinylidene difluoride membranes under 100 V and 60 mA for 1 h. A 1:2,000 dilution of anti-GFP mouse monoclonal antibody (M048-3, MBL, China) was used as the primary antiserum, followed by incubation with a 1:3,000 horseradish peroxidase (HRP)-goat anti-rabbit secondary antibody (ab6721, Abcam).
For co-immunoprecipitation assay, total proteins were placed on ice for 30 min and centrifuged at 10,000 g for 10 min at 4 °C. GFP-Trap®_MA beads (ChromoTek, Planegg-Martinsried, Germany) were washed twice with 500 µL of extraction buffer. Each sample was mixed with 25 µL of clean beads, and the mixture was tumbled end-over-end for 3 h at 4 °C. The beads were magnetically separated, washed twice, and then heated in 100 µL of 2 × SDS sample buffer at 95 °C. Proteins from corresponding non-transgenic line of line OE2 were used as a negative control. Immunocomplexes were analyzed by mass spectrometry. The IP-MS experiment was performed with three biological replicates. Proteins identified in at least two IP-MS experiments were referred to as GIF1-interacting proteins.
Firefly luciferase complementation imaging (LCI) assay
The open reading frames (ORFs) of GIF1 and the four genes encoding GIF1-interacting proteins were separately cloned into both JW771 (NLUC) and JW772 (CLUC) [31] using a ClonExpress II One Step Cloning Kit (Vazyme Biotech, Nanjing, China). The constructs were transformed into Agrobacterium tumefaciens strain GV3101. The transformed Agrobacterium cells were grown to OD(optical density)600 = 0.8, pelleted, and resuspended in infiltration buffer (10 mM methylester sulfonate, 10 mM MgCl2, and 150 mM acetosyringone, pH 5.7) and then infiltrated in different combinations into 3-week-old N. benthamiana leaves using a needleless syringe. After 48 h under 16 h of light and 8 h of dark, leaves were injected with 1 mM luciferin (Promega, Madison, WI, USA). The resulting luciferase signals were observed using a Tanon-5200 image system (Tanon Science, Shanghai,, China). The LCI assay was performed three times independently.
Transcriptome library construction and sequencing
The transcriptome library construction and RNA-seq analysis were done as Zhang et al. [28]. Ten immature ears (~ 5 mm) from the gif1-1 and wild-type sibling were collected and pooled, respectively, with three biological replicates. Fresh immature ears were immediately frozen in liquid nitrogen. Total RNA was extracted from each pool using Trizol (Life Technologies, Invitrogen, USA). After removing DNA with RQ1DNase (Promega, USA), 10 mg of total RNA was used for RNA-seq library preparation. Polyadenylated mRNAs were purified and concentrated with oligo (dT)-conjugated magnetic beads (Life Technologies, USA). Purified mRNAs were fragmented at 95 °C for 1 min, followed by end repair and 5′-adaptor ligation. Reverse transcription was then performed with a specific primer harboring a 3′-adaptor sequence and randomized hexamer. The cDNA was purified and amplified using random hexamers, and PCR products of 200 to 500 bp were collected, purified, quantified, and subjected to paired-end sequencing on an Illumina HiSeq 2000 system (Illumina Inc., San Diego, CA, USA) at the Beijing Genomics Institute (BGI).
For quantifying gene expression level, clean reads were mapped to the maize reference genome (B73 RefGen_v4) using SOAPaligner/SOAP2 [32] with no more than five mismatches allowed in the alignment. Gene expression level was calculated using the FPKM method (fragments per kilobase transcriptome per million mapped). Differentially expressed genes (DEGs) between the gif1-1 mutant and the wild type were identified using p < 10–5 and a two-fold difference. The DEGs are listed in Supplemental Data Set 2. Gene Ontology (GO) analysis (by agriGO, http://systemsbiology.cau.edu.cn/agriGOv2/) was used to identify the enrichment of the DEGs.
Chromatin immunoprecipitation (ChIP)-sequencing and data analysis
The ChIP-Seq was done as Zhang et al. [28]. Approximately 1 g of ear inflorescences (~ 5 mm) was harvested from p35S::GIF1-GFP line OE2 grown in a greenhouse with three biological replicates. Expression of the fused GIF1-GFP was verified by protein gel blotting using anti-GFP antibody (Abcam, AB290) at a dilution of 1:1,000 (v/v) in Tris-buffered saline buffer containing 5% nonfat milk powder. The inflorescences were immediately cross-linked in buffer containing 1% (v/v) formaldehyde for 15 min under vacuum, followed by addition of glycine to a concentration of 0.1 M and infiltration for 5 min. After three washes with distilled water (4 °C), the cross-linked tissues were dried with paper towels and flash-frozen in liquid nitrogen. Frozen tissues were ground thoroughly to a fine powder, which was then transferred to a precooled 50-mL tube with 20 mL of cold complete extraction buffer 1 (0.4 M sucrose, 10 mM Tris–HCl, pH 8.0, 10 mM MgCl, 2.5 mM β-mercaptoethanol, and Plant Protease Inhibitor Cocktail (P9599, Sigma-Aldrich). Homogenized tissues were centrifuged for 20 min at 1,000 g at 4 °C. The pellets were washed five times with 5 mL of complete extraction buffer 2 (0.25 M sucrose, 10 mM Tris–HCl, pH 8.0, 10 mM MgCl2, 1% (v/v) Triton X-100, 5 mM β-mercaptoethanol, and Plant Protease Inhibitor Cocktail) and once with extraction buffer 3 (1.7 M sucrose, 10 mM Tris–HCl, pH 8.0, 2 mM MgCl2, 0.15% (v/v) Triton X-100, 5 mM β-mercaptoethanol, and Plant Protease Inhibitor Cocktail). Washed pellets were resuspended in 300 mL of sonication buffer (50 mM Tris–HCl, pH 8.0, 10 mM EDTA, 1% SDS, and Plant Protease Inhibitor Cocktail), and the suspension was treated with a Bioruptor (Diagenode, Belgium) for 8 to 10 cycles with settings 30 s ON/30 s OFF at 4 °C. The sonicated sample was centrifuged for 10 min at 12,000 g at 4 °C, and the supernatant was collected and used for chromatin isolation. The extracted chromatin was immunoprecipitated with anti-GFP antibody (Invitrogen, A11122) with a Plant ChIP-seq kit (Diagenode, Belgium) according to the manufacturer’s instructions. Following de-cross-linking, isolation, and purification of the immunoprecipitated DNA, libraries were constructed using an Ovation Low Input DR kit (NuGEN Technologies, San Carlos, CA, USA). Two input and two IP libraries were subjected to sequencing on an Illumina HiSeq 2000 sequencer (Illumina Inc., USA).
ChIP-seq reads were aligned to the maize reference genome (AGPv4) using Hisat2 v.2.0.5 [33]. Only uniquely mapped reads were considered for further processing. PCR duplicates were removed using Picard Mark Duplicates (v.2.9.0; http://picard.sourceforge.net/). Peak calling was performed with MACS (v.1.4.2) [34]. Peaks were identified as significantly enriched (p < 10–5) in each of the ChIP-seq libraries compared with input DNA. The FGS (Functional Gene Set) gene model within 10 kb of the peak summit was considered as a putative target of GIF1. ChIP tracks showing GIF1-GFP fusion protein binding sites were visualized using integrative genomics viewer [35].
ChIP-qPCR
The ChIP-qPCR was done as Zhang et al. [28]. To detect specific DNA targets, ChIP-qPCR was performed to quantify DNA targets immunoprecipitated by anti-GFP antibody relative to input DNA using SYBR Green qPCR Master Mix (Bio-Rad, Hercules, CA, USA) with three biological replicates, each with three technical replicates. The DNA target-specific primers used for the ChIP-PCR assay are listed in Supplemental Table 3. The abundance of a target was normalized to that of nonspecific genomic regions, and fold enrichment of the DNA target relative to the input sample was then calculated. Significant differences were estimated by a Student’s t-test.
Reverse-transcription quantitative PCR (RT-qPCR)
To analyze gene expression, immature ears (~ 5 mm) were collected from the gif1-1 and wild-type plants. Total RNA was extracted from plant tissues using Ambion Pure Link Plant RNA Reagent (Life Technologies, USA) and reverse-transcribed with M-MLV reverse transcriptase (Life Technologies, USA) according to the manufacturer’s instructions. RT-qPCR was performed using a SYBR Green qRT-PCR kit (Bio-Rad, USA) according to the manufacturer’s instructions with three biological replicates; each replicate contained 10 individuals. Fold changes in RNA transcripts were calculated by the 2−ΔCt method with maize Actin gene (Zm00001d010159) as an internal control. All reactions were performed on a CFX96 real-time system (Bio-Rad). All primers used for RT-qPCR are listed in Supplemental Table 3.
Results
The gif1 mutant has highly branched ears with unfused carpels
To uncover the roles of GIF1 in the ear-inflorescence development, we observed the initiation and differentiation of meristems during inflorescence development. We found that wild-type maize ears produced paired spikelets with no long branches (Fig. 1A and C). By contrast, the ears of gif1-1 mutants frequently displayed highly short branched inflorescences (Fig. 1B and D). Spikelet meristems (SMs) on the branched inflorescences produced variable numbers of BMs or SPMs (Fig. 1B and D) and floral meristems (FMs) on the branched inflorescence also convert into BMs (Fig. 1E and F), indicating that GIF1 regulates determinacy of BMs and SMs or FMs identity.
Obvious morphological and anatomical differences between the gif1 mutant and wild-type sibling in the inflorescence architecture and floral organs. A Developing inflorescence architecture of wild type. B Highly branched ear and branch differentiating axillary meristems (zoom) in the gif1. White arrows point to axillary meristems, yellow arrows point to the spikelet meristems on the branch. C Scanning electron microscopy of developing inflorescence architecture in wild type. D Scanning electron microscopy of branch differentiating axillary meristems in the gif1. E and F Scanning electron microscopy of branches converted from gif1 florets (E) and their enlarged images (F). Arrows point to branches converted from florets. G Scanning electron microscopy of the wild-type floret. H Scanning electron microscopy of the gif1-1 mutant. Asterisk points to the naked ovule primordia. WT, wild type. ca, carpel primordium; st, stamen primordium
In wild-type florets, development of the three stamen primordia is arrested and carpel primordia fuse to make a functional silk, and the ovule is well enclosed by the carpel (Fig. 1G). In gif1-1 florets, development of stamen primordia was also arrested; however, carpel primordia frequently failed to be initiated, or were initiated but failed to fuse, or were well developed in only one of the two florets (Fig. 1H). The ovule primordia were enlarged and naked (Fig. 1H), and the floral apex was indeterminate and frequently initiated extra ovule-like protrusions in gif1-1 florets, showing similarities to the ifa1 mutant [36], such as an expanded nucellus. These results indicated that GIF1 regulates fate and determinacy of meristems on the ear inflorescence.
Overexpression of GIF1 rescues the defective phenotypes of the gif1 mutant
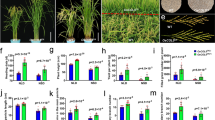
To uncover the function of GIF1 in the ear inflorescence, we created five transgenic lines by introducing the Ubi promoter-driven GIF1-GFP constructs into the maize ZZC01 inbred line. The gif1-1 mutant appeared as a dwarf plant (Fig. 2A), while transgenic lines overexpressing GIF1-GFP (OE) showed normal characteristics with greater plant height and ear height, and longer leaves than the gif1-1 mutant (Fig. 2C, G, H), but displayed non-significant difference from its non-transgenic sibling (NT2) (Fig. 2G). The ears from overexpression line (OE2) generated orderly and fertile florets without long branches (Fig. 2D). As contrast, gif1 ears produced long branches at the base of the ear inflorescence (Fig. 1D and Fig. 2B). To reveal the roles of GIF1 in the ear development, we first introduced gif1 into ZZC01 genetic background through two generations of backcrossing, and then crossed transgenic line OE2 to + /gif1 heterozygotes under ZZC01 genetic background followed by one generation of selfing. Those plants with homozygous gif1/gif1 and overexpressing GIF1-GFP which are referred to as complementation individuals were then selected by genotyping. All of these complementation individuals had normal plant characteristics and inflorescence architectures, both female and male florets were well developed and fertile (Fig. 2E, F). In addition, plant height, ear height and leaf length of complementation individuals were slightly greater than that of wild-type individuals with + /gif1 or + / + genotype although the difference is not statistically significant (Fig. 2H), but were significantly different from in the defective phenotypes of those gif1gif1 individuals (n = 30). The results show that overexpression of GIF1-GFP can rescue the defective phenotypes on the ear inflorescence of the gif1 mutant.
Overexpressing GIF1-GFP rescues the defective phenotypes on the ear inflorescence of the gif1 mutant under ZZC01 background. A and B Whole plant (A) and ear inflorescence (B) of the gif1-1 mutant. The gif1-1 mutant produced highly branched inflorescence (B). C and D Whole plant (C) and ear inflorescence (D) of transgenic line OE2 overexpressing GIF1-GFP. E and F Whole plant (E) and ear inflorescence (F) of the complemented line. Gene-specific molecular markers were used to genotype the gif1gif1/OE2 individuals in the progeny families derived from + /gif1 (ZZC01) × GIF1-GFP-OE2 (ZZC01), which are homozygous genotype at the gif1 locus and are expressing the GIF1-GFP. G Plant height, ear height and leaf length of transgenic line OE2 overexpressing GIF1-GFP and corresponding non-transgenic line (NT) under ZZC01 background. H Plant height, ear height and leaf length of complementation individuals with gif1gif1/OE2, wild-type individuals with GIF1/gif1 or GIF1/GIF1 genotype, and gif1gif1 individuals identified from the progeny families derived from + /gif1(ZZC01) × GIF1-GFP-OE2 (ZZC01). The scale bars = 500 μm in (B), (D) and (F), and 10 cm in (A), (C) and (E). Sample size = 30 in (G) and (H). The column shows mean ± standard deviation (s.d.), the statistical significance was estimated using a Student’s t-test. ** P < 0.01. ns: not significant statistically
GIF1 interacting proteins are involved in diverse biological processes
To identify GIF1-interacting proteins, we performed an IP assay using anti-GFP antibody in 5-mm ears from transgenic line OE2 with three biological replicates (Supplemental Fig. 1). We identified 56 GIF1-interacting proteins substantially enriched in at least two biological replicates (Table 1). Some of these proteins might indirectly interact with GIF1, given that GIF1 is a coactivator of GRFs; regardless, they are likely to be components of a GIF1-GRF recruiting complex. Consistent with proteins identified previously in Arabidopsis [37] and maize, nine GRFs, one SWI3D, two SNF12s, two Agenet domain proteins, two helicases, two actin-related proteins (ARP4 and ARP7), and one ATPase were identified as GIF1-interacting proteins in developing ears (Table 1 and Supplemental Table 1). These proteins were identified as subunits of the SWI/SNF complex that regulates chromatin structure by altering nucleosome composition and interactions [38]. And these proteins have been repeatedly identified to interact with GIF1 in different plant species, suggesting a reliable interaction between GIF1 and SWI/SNF subunits.
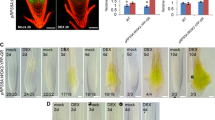
In addition to subunits of the SWI/SNF complex, Importin subunit alpha, a homologous protein of (Importin β4) that regulates Arabidopsis ovule development mediating nuclear import of GRF-interacting factors [21], was found to interact with GIF1 (Table 1). Auxin-binding protein1 (ABP1), one of putative auxin receptors, was also found to interact with GIF1 (Table 1). Notably, a brassinosteroid (BR) biosynthesis-related protein NANA PLANT2 (NA2) [39], an enzyme in jasmonic acid (JA) biosynthesis AOS1 [40, 41], and a key inflorescence factor RAMOSA1 ENHANCER LOCUS2 (REL2) [42] were found to interact in vivo with GIF1 (Table 1). Subsequently, several interaction pairs including NA2-GIF1 and ABP1-GIF1 were verified verify in vitro by firefly luciferase complementation imaging (LCI) assays in Nicotiana benthamiana leaves (Fig. 3A-D). These data suggest that GIF1-interacting complexes are directly and indirectly involved in diverse biological processes, including chromatin remodeling, hormone biosynthesis, and protein transport. GIF1 contains an N-terminal, a C-terminal and a SSXT domain. Furthermore, to understand the domain mediating protein interaction, we created three GIF1 constructs containing N-terminal and C-terminal truncations and performed the yeast-two-hybridization (Y2H) experiments with NA2 and REL2 proteins. We found both N-terminal and SSXT domain are required for mediating interaction with NA2 and REL2 (Fig. 3E). Similarly, a set of NA2 constructs and REL2 constructs were created as illustrated in Fig. 3F. Y2H experiments revealed that GIF1 can interact with the REL2 C-terminal domain (REL2-C), but not the N-terminal domain, the REL2 C-terminal domain lacking the WD40-2 motif can interacts with GIF1 protein as well (Fig. 3F). NA2 has a signal peptide (SP), a transmembrane region (TM), a FAD_lactone_ oxidase domain (FAD_lactone_ox), and C-terminal. Of them, the FAD_lactone_ox domain was required for mediating GIF1-NA2 interaction (Fig. 3F).
GIF1-interacting proteins and dissection of protein–protein interaction domain. A-D GIF1-interaction proteins revealed by firefly luciferase complementation imaging (LCI) assay. Interactions of GIF1 with GRF1 (A), GRF17 (B), ABP1 (C), and NA2 (D), respectively. E Both NA2 and REL2 interact with different domains of the GIF1 protein. F Different domains of the NA2 and REL2 interacts with the GIF1 protein. GRF: Growth-regulating factor; ABP1: Auxin-binding protein1; NA2: NANA PLANT2; REL2: RAMOSA1 ENHANCER LOCUS 2; SP: signal peptide; TM: transmembrane; Glco D: glycolate oxidase GlcD subunit
Hormone and inflorescence development-related genes are regulated by GIF1
To identify genes regulated by GIF1, we performed RNA sequencing (RNA-seq) and found that 2,145 down-regulated and 3,401 up-regulated genes were differentially expressed in 5-mm ears of the gif1 mutant compared to that of wild-type sibling under p < 10–5 and ~ twofold expression difference (Fig. 4A, Supplemental Data Set 1). Those down-regulated genes were primarily enriched in biosynthetic process (22.5%, GO:0,009,058, p = 6.0e-9), biological regulation (20%, GO:0,065,007, p = 5.7e-9), developmental process (4.9%, GO:0,032,502, p = 2.7e-7) and response to stimulus (13%, GO:0,050,896, p = 2.8e-4) these biological processes, and nucleus (20.9%, GO:0,005,634, p = 5.2e-14) this cellular component term (Supplemental Data Set 2). These up-regulated genes were primarily enriched in several biological processes, including 16.0% in the single-organism metabolic process (GO:0,044,710, p = 3.8e-5), 9.7% in the regulation of biosynthetic process (GO:0,009,889, p = 2.9e-5), 9.8% in the regulation of gene expression (GO:0,010,468, p = 2.7e-4), 5.6% in response to chemical (GO:0,042,221, p = 1.4e-5), and 6.6% of up-regulated genes were enriched in the transporter activity (GO:0,005,215, p = 1.8e-5) molecular function (Supplemental Data Set 3).
Differentially expressed genes in ears of the gif1 mutant and wild type. A Number and percentage of up-regulated and down-regulated genes. B Representative terms of differentially expressed genes enriched in ears of the gif1 mutant and wild type. Each box represents the median and interquartile range. Whiskers extend to maximum and minimum values. Numbers show the number of differentially expressed genes in terms. C Differentially expressed WUS-related homeobox (wox) genes and CLV3/ENDOSPERM SURROUNDING REGION (ESR)-related (cle) genes in ears of the gif1 and the wild type. The 999 and -999 represent genes expressed specifically in the gif1 and wild-type ear, respectively. D and E Relative expression levels of known inflorescence and floret-related genes. Inflorescence and floret-related genes with up-regulated expression (D) and down-regulated expression (E) in gif1 ears. Relative expression level is detected using RNA-seq and reverse transcription quantitative PCR (RT-qPCR), respectively. RT-qPCR is performed with three biological replicates, each with three technical replicates. Fold changes in RNA transcripts are calculated by the 2−ΔCt method with maize Actin gene (Zm00001d010159) as an internal control. All bars represent means ± s.d.; s.d.: standard deviation. FC: fold change = FPKM of a given gene detected in the gif1/FPKM of the gene detected in the wild-type sibling. FPKM: fragments per kilobase of transcript per million fragments mapped
Because of the interaction between GIF1 and NA2, we detected expression of hormone-related genes, and found that genes in BR metabolism and signaling (GO:0,016,131 and GO:0,009,742), including nana plant1 (Zm00001d042843, NA1), brassinosteroid-deficient dwarf1 (Zm00001d033180, BRD1), and BR-signaling kinases (Zm00001d030021 and Zm00001d047053), were drastically down-regulated, while response to auxin (GO:0,009,733) and response to jasmonic acid (GO:0,009,753) including JA-related genes silkless1 (Zm00001d002970, SK1), tasselseed1 (Zm00001d003533, TS1) were up-regulated, suggesting disturbed homeostasis of hormones in the gif1-1 ear (Fig. 4B, Supplemental Data Sets 2 and 3). Furthermore, down-regulated genes were significantly enriched in those terms for development of floret, inflorescence and meristem (Fig. 4B). In particular, genes in the CLV-WUS feedback loop were differentially expressed in ears of the gif1-1 and wild-type plants: two clv3/endosperm surrounding region-related genes (CLE4a and CLE23) were down-regulated, while four WUS-related homeobox genes (WOX2b, WOX4, WOX5b, and WOX13b) were up-regulated in gif1-1 ears (Fig. 4C, Supplemental Data Set 3). Importantly, a subset of well-characterized genes for inflorescence architecture including RA1 [6, 10], RA3 [11] Unbranched2 (UB2), UB3, Tassel sheath1 (TSH1) and TSH4 [43, 44], and genes for floral development including Silky1 (SI1) and Silkless 1 (SK1) [45, 46] were down-regulated in gif1-1 ears (Supplemental Data Set 4). Expression levels of 20 representative DEGs, which are candidates to be associated with defective phenotypes in the gif1-1 mutant, was verified by reverse transcription-quantitative PCR (RT-qPCR) (Fig. 4D, E).
To determine the occupancy of GIF1, we performed ChIP-seq to detect GIF1-bound DNA regions in immature ears (~ 5 mm) of transgenic line OE2 overexpressing GIF1-GFP using anti-GFP antibody. A total of 10,460 high-confidence peaks were identified by comparing significantly GIF1-enriched peaks with the input control (p < 10–5), of which, 1,308 peaks were shared in at least two replicates, respectively (Supplemental Fig. 2). GIF1 bound in various genomic contexts, with a high proportion (45.0%) of binding within intergenic regions which agree with the interaction between GIF1 and SWI/SNF subunits, and 12.9% and 11.9% binding within 1.0 kb downstream of the terminal site and within exons, respectively (Supplemental Fig. 2). Within 10 kb of high-confidence peaks, we identified 540 genes as putative targets of GIF1 in at least two replicates (Supplemental Fig. 2). Furthermore, 79 DEGs including 47 down-regulated (59.5%) and 32 up-regulated (40.5%) genes in gif1 ears were bound by GIF1 (Fig. 5A, Supplemental Table 2), suggesting that these genes are direct targets of GIF1, which acts as a repressor and an activator of gene expression in developing ears. The function of GIF1 in repression of gene expression can be partially explained by its interactors (Table 1), such as subunits of SWI/SNF chromatin remodeling complex, and RAMOSA1 ENHANCER LOCUS2 (REL2) which is a transcriptional co-repressor functioning in vegetative and reproductive architecture [42]. Notably, these targets of GIF1 were significantly enriched in 5 GO terms including cell periphery (GO: 0,071,944) and response to hormone (GO: 0,009,725) (Fig. 5B). In addition, several meristem identify, determinacy and maintenance-related genes were also bound by GIF1 (Supplemental Table 2). For example, GIF1 bound to the promoter and 3′-untranslated region (UTR) of CLE4a, the promoter region of TPS2, gene body of AGO108. As expression of CLE4a and AGO108 was significantly down-regulated in gif1 ears (Fig. 5C-E,I-K), the data suggest that CLE4a and AGO108 are two positively regulated targets of GIF1. The expression of TPS2 was significantly up-regulated in gif1 ears (Fig. 5F-H), indicating that TPS2 is a negatively regulated target of GIF1. Moreover, PIN8, RA2, OFP21 (Supplemental Fig. 3) and several TF-encoding genes (Supplemental Table 2) were also strong candidates for key targets of GIF1.
Putative targets of GIF1 detected by chromatin immunoprecipitation sequencing (ChIP-seq). A Genes both detected by ChIP-seq and showing differential expression detected by RNA-seq. DEG: differentially expressed gene. B Gene Ontology (GO) enrichment of 79 GIF1 targets. Gene num. = gene number. C, F, I Peak distribution of three representative targets including CLE4a C, TPS2 F and AGO108 (I). D, G, J Fold enrichment of three representative targets detected by ChIP-qPCR. Gene specific primers were used to quantify DNA targets including CLE4a (D), TPS2 (G) and AGO108 (J) immunoprecipitated by anti-GFP antibody relative to input DNA, respectively. The columns are the mean value of fold enrichment detected in three separate experiments, each with three technical replicates. Error bars show the standard deviation. The statistical significance was estimated using a Student’s t-test. ** P < 0.01. E, H, K Relative expression levels of CLE4a (E), TPS2 (H) and AGO108 (K) in ears of the gif1 and the wild type detected by RNA-seq and qPCR. qPCR is performed with three biological replicates, each with three technical replicates. Error bars show the standard deviation. CLE4a: CLAVATA3 (CLV3)/ENDOSPERM SURROUNDING REGION (ESR) 4a. TPS2: Trehalose-6-phosphate synthase 2. AGO108: Argonaute108
Discussion
To explore the role of GIF1 regulation in ear meristems, we created GIF1-overexpressing lines to complement gif1 and identified GIF1-interacting proteins and GIF1 target genes. We found that a set of GRFs and some subunits of the SWI/SNF complex interact with GIF1 in vivo, the finding is consistent with those results from early investigations on GIF1-interacting protein in vegetative and reproductive development of Arabidopsis [16, 18], rice [26, 27], and maize [35]. SWI/SNF are high molecular weight complexes that could change interactions between histone octamers and the DNA [38]. GIF1 working together with GRFs recruits SWI/SNF chromatin-remodeling ATPases to influence DNA accessibility and might expose the cis-element of target genes to GRFs. GRFs could stimulate or inhibit the transcription of target genes (Fig. 6). In addition to GRFs and SWI/SNF factors, we found that GIF1 interacts with proteins that involve in cell division, molecular signaling, etc. Thus, we suggest that GIF1 is involved in a wide spectrum of biological processes by selectively interacting with diverse proteins during ear development.
GIF1 regulates the fate of ear axillary meristems and floral organ primordia in ear inflorescence of maize. We found that GIF1 could regulate identity and determinacy of reproductive axillary meristems by hormone biosynthesis process (Fig. 6). We found that BR biosynthesis enzyme NA2 interacts with GIF1, and 10 genes related with BR metabolism and signaling pathway including BRD1 and NA1 were significantly down-regulated in the gif1 mutant. BR is found to affect plant height, branching, and sexual organ (stamen and pistil) development in maize [39, 47, 48]. The severely reduced plant height and ear with anthers in na2 mutants was similar to dwarf plant and highly frequent branches in gif1 mutants. We also found that JA-related genes SK1, TS1 and TS2 were up-regulated in gif1 ears. Both TS1 and TS2 are required for JA-mediated elimination of pistils in the staminate [49, 50]. Conversely, SK1 could protect pistils in the ear florets from JA-mediated elimination [46]. The up-regulated JA-related genes might participate in the identity of SMs and FMs in the gif1 mutant. Therefore, we propose that BR-related and JA-related pathway for floral organ development and meristem identity are regulated by GIF1 (Fig. 6).
GIF1 also regulates BM determinacy by targeting RAMOSA and CLV-WUS pathway. The gif1 mutant produced ear with long branches similar to that of ramosa mutants. The well characterized RAMOSA genes, RA1, RA2, RA3 and REL2 are involved in AM formation and BM determinacy [6, 10, 11, 51]. We found that GIF1 is directly interacted with REL2, an enhancer of RA1. The GIF1-REL2 complex might regulate the BM determinacy by RA1. GIF1 is a positive regulator of RA2 but a negative regulator of TPS2. TPS2 encodes a trehalose-6-phosphate (T6P) synthase. RA3 controls long branches in the ear and the tassel by catalyzing dephosphorylation of T6P [6]. Thus, we infer that GIF1 regulates AM determinacy with RAMOSA pathway genes. The CLAVATA genes encode CLV ligands and CLV receptors. CLV3, a small peptide ligand secreted from cells of the central zone, is perceived by CLV1 and CLV2 to repress WUS transcription to regulate the meristem size [52]. Two maize CLV3 orthologs secreted peptides, ZmCLE7 and ZmFCP1, interact with CLV2 ortholog FEA2 to transmit signals and regulate inflorescence meristem size [53]. We found that GIF1 binds to the promoter of CLE4a and down-regulated the expression of CLE4a in the gif1 mutant, suggesting that GIF1 is a positive regulator of CLE4a and the IM activity of gif1 ears might result from transcriptional repression of CLE4a.
Conclusions
The transcription coactivator Growth-regulating factor (GRF)-interacting factor 1 (GIF1) interacts with given GRFs dependent upon the developmental context, and also recruit additional protein factors, for example SWI/SNF chromatin remodeling complexes, Ramosa1 Enhancer Locus 2 (REL2), to establish a multi-factor transcription complex. The transcription complex specifically bind to its target genes to repress Brassinolide (BR) biosynthesis and metabolism genes (BRD1 and NA1); meristem maintenance gene CLE4a and axillary meristem determinacy gene TPS, but activate Jasmonic acid (JA) biosynthesis genes (SK1, TS1 and TS2). Consequently, the fine transcription control of these target genes determines the identity and determinacy of reproductive axillary meristems in the ear inflorescence (Fig. 6).
Availability of data and materials
Sequence data from this article can be found in the NCBI SRA dataset under the following accession numbers: PRJNA790036.
Abbreviations
- BM:
-
Branch meristem
- BR:
-
Brassinolide
- ChIP:
-
Chromatin immunoprecipitation
- DEG:
-
Differentially expressed gene
- FEA:
-
Fasciated ear
- FM:
-
Floral meristem
- GFP:
-
Green fluorescent protein
- GIF:
-
Growth-regulating factor-interacting factor
- GO:
-
Gene ontology
- GRF:
-
Growth-regulating factor
- HRP:
-
Horseradish peroxidase
- IM:
-
Inflorescence meristem
- IP-MS:
-
Immunoprecipitation-mass spectrometry
- JA:
-
Jasmonic acid
- LCI:
-
Firefly luciferase complementation imaging
- LOB:
-
Lateral organ boundary
- NT:
-
Non-transgenic sibling
- OE:
-
Overexpression line
- ORF:
-
Open reading frame
- SDS-PAGE:
-
Sodium dodecyl sulfate–polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis
- SM:
-
Spikelet meristem
- SPM:
-
Spikelet pair meristem
- T6P:
-
Trehalose 6-phosphate
- TF:
-
Transcription factor
- UTR:
-
3′-Untranslated region
- Y2H:
-
Yeast-two-hybridization
References
Cheng PC, Greyson RI, Walden DB. Organ initiation and the development of unisexual flowers in the tassel and ear of Zea mays. Amer J Bot. 1983;70:450–62.
Vollbrecht E, Schmidt RJ. Development of the inflorescences. Handbook of maize: Its biology. New York: Springer; 2009. 13–40.
Irish EE, Szymkowiak EJ, Garrels K. The wandering carpel mutation of Zea mays (Gramineae) causes misorientation and loss of zygomorphy in flowers and two-seeded kernels. Am J Bot. 2003;90:551–60.
McSteen P, Laudencia-Chingcuanco D, Colasanti J. A floret by any other name: control of meristem identity in maize. Trends Plant Sci. 2000;5:61–6.
Kellogg EA. Floral displays: Genetic control of grass inflorescences. Curr Opin Plant Biol. 2007;10:26–31.
Satoh-Nagasawa N, Nagasawa N, Malcomber S, Sakai H, Jackson DA. trehalose metabolic enzyme controls inflorescence architecture in maize. Nature. 2006;441:227–30.
Paul MJ, Primavesi LF, Jhurreea D, Zhang Y. Trehalose metabolism and signaling. Annu Rev Plant Biol. 2008;59:417–41.
Paul MJ, Gonzalez-Uriarte A, Griffiths CA, Hassani-Pak K. The Role of trehalose 6-phosphate in crop yield and resilience. Plant Physiol. 2018;177(1):12–23.
Griffiths CA, Sagar R, Geng Y, Primavesi LF, Patel MK, Passarelli MK, Gilmore IS, Steven RT, Bunch J, Paul MJ, Davis BG. Chemical intervention in plant sugar signalling increases yield and resilience. Nature. 2016;540:574–8.
Vollbrecht E, Springer PS, Goh L, Buckler ES 4th, Martienssen R. Architecture of floral branch systems in maize and related grasses. Nature. 2005;436(7054):1119–26.
Bortiri E, Chuck G, Vollbrecht E, Rocheford T, Martienssen R, Hake S. ramosa2 encodes a LATERAL ORGAN BOUNDARY domain protein that determines the fate of stem cells in branch meristems of maize. Plant Cell. 2006;18:574–85.
Bommert P, Nagasawa NS, Jackson D. Quantitative variation in maize kernel row number is controlled by the FASCIATED EAR2 locus. Nat Genet. 2013;45(3):334–7.
Je BI, Gruel J, Lee YK, Bommert P, Arevalo ED, Eveland AL, Wu Q, Goldshmidt A, Meeley R, Bartlett M, Komatsu M, Sakai H, Jönsson H, Jackson D. Signaling from maize organ primordia via FASCIATED EAR3 regulates stem cell proliferation and yield traits. Nat Genet. 2016;48(7):785–91.
Bommert P, Lunde C, Nardmann J, Vollbrecht E, Running M, Jackson D, Hake S, Werr W. Thick tassel dwarf1 encodes a putative maize ortholog of the Arabidopsis CLAVATA1 leucine-rich repeat receptor-like kinase. Development. 2005;132(6):1235–45.
Kim JH, Kende H. A transcriptional coactivator, AtGIF1, is involved in regulating leaf growth and morphology in Arabidopsis. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 2004;101(36):13374–9.
Kim JH, Tsukaya H. Regulation of plant growth and development by the growth-regulating factor and grf-interacting factor duo. J Exp Bot. 2015;66(20):6093–107.
Horiguchi G, Kim GT, Tsukaya H. The transcription factor AtGRF5 and the transcription coactivator AN3 regulate cell proliferation in leaf primordia of Arabidopsis thaliana. Plant J. 2005;43(1):68–78.
Omidbakhshfard MA, Proost S, Fujikura U, Mueller-Roeber B. Growth-Regulating Factors (GRFs): a small transcription factor family with important functions in plant biology. Mol Plant. 2015;8(7):998–1010.
Omidbakhshfard MA, Fujikura U, Olas JJ, Xue GP, Balazadeh S, Mueller-Roeber B. Growth-regulating factor 9 negatively regulates arabidopsis leaf growth by controlling org3 and restricting cell proliferation in leaf primordia. PLoS Genet. 2018;14(7):e1007484.
Liu Z, Li N, Zhang Y, Li Y. Transcriptional repression of GIF1 by the KIX-PPD-MYC repressor complex controls seed size in Arabidopsis. Nat Commun. 2020;11(1):1–16.
Liu HH, Xiong F, Duan CY, Wu YN, Zhang Y, Li S. Importin β4 mediates nuclear import of grf-interacting factors to control ovule development in Arabidopsis. Plant Physiol. 2019;179(3):1080–92.
Lee SJ, Lee BH, Jung JH, Park SK, Song JT, Kim JH. Growth-regulating factor and GRF-interacting factor specify meristematic cells of gynoecia and anthers. Plant Physiol. 2018;176(1):717–29.
Lee BH, Ko JH, Lee S, Lee Y, Pak JH, Kim JH. The Arabidopsis GRF-interacting factor gene family performs an overlapping function in determining organ size as well as multiple developmental properties. Plant Physiol. 2009;151(2):655–68.
Lee BH, Wynn AN, Franks RG, Hwang YS, Lim J, Kim JH. The Arabidopsis thaliana GRF-interacting factor gene family plays an essential role in control of male and female reproductive development. Dev Biol. 2014;386(1):12–24.
Kanei M, Horiguchi G, Tsukaya H. Stable establishment of cotyledon identity during embryogenesis in Arabidopsis by angustifolia3 and Hanaba taranu. Development. 2012;139(13):2436–46.
Li S, Gao F, Xie K, Zeng X, Cao Y, Zeng J, He Z, Ren Y, Li W, Deng Q, Wang S, Zheng A, Zhu J, Liu H, Wang L, Li P. The osmir396c-osgrf4-osgif1 regulatory module determines grain size and yield in rice. Plant Biotechnol J. 2016;14:2134–46.
He Z, Zeng J, Ren Y, Chen D, Li W, Gao F, Cao Y, Luo T, Yuan G, Wu X, Liang Y, Deng Q, Wang S, Zheng A, Zhu J, Liu H, Wang L, Li P, Li S. OsGIF1 positively regulates the sizes of stems, leaves, and grains in rice. Front Plant Sci. 2017;8:1730.
Zhang D, Sun W, Singh R, Zheng Y, Cao Z, Li M, Lunde C, Hake S, Zhang Z. GRF-interacting factor1 regulates shoot architecture and meristem determinacy in maize. Plant Cell. 2018;30(2):360–74.
Lowe K, Wu E, Wang N, Hoerster G, Hastings C, Cho MJ, Scelonge C, Lenderts B, Chamberlin M, Cushatt J, Wang L, Ryan L, Khan T, Chow-Yiu J, Hua W, Yu M, Banh J, Bao Z, Brink K, Igo E, Rudrappa B, Shamseer PM, Bruce W, Newman L, Shen B, Zheng P, Bidney D, Falco C, Register J, Zhao ZY, Xu D, Jones T, Gordon-Kamm W. Morphogenic regulators baby boom and wuschel improve monocot transformation. Plant Cell. 2016;28(9):1998–2015.
Li W, Ruf S, Bock R. Constancy of organellar genome copy numbers during leaf development and senescence in higher plants. Mol Genet Genom. 2006;275(2):185–92.
Chen H, Zou Y, Shang Y, Lin H, Wang Y, Cai R, Zhou JM. Firefly luciferase complementation imaging assay for protein-protein interactions in plants. Plant physiol. 2008;146(2):368–76.
Li R, Li Y, Kristiansen K, Wang J. SOAP: short oligonucleotide alignment program. Bioinformatics. 2008;24(5):713–4.
Kim D, Langmead B, Salzberg SL. HISAT: a fast spliced aligner with low memory requirements. Nat methods. 2015;12(4):357.
Zhang Y, Liu T, Meyer CA, Eeckhoute J, Johnson DS, Bernstein BE, Liu XS. Model-based analysis of ChIP-Seq (MACS). Genome biol. 2008;9(9):R137.
Thorvaldsdóttir H, Robinson JT, Mesirov JP. Integrative Genomics Viewer (IGV): high-performance genomics data visualization and exploration. Brief Bioinform. 2013;14(2):178–92.
Laudencia-Chingcuanco D, Hake S. The indeterminate floral apex1 gene regulates meristem determinacy and identity in the maize inflorescence. Development. 2002;129(11):2629–38.
Vercruyssen L, Verkest A, Gonzalez N, Heyndrickx KS, Eeckhout D, Han SK, Jégu T, Archacki R, Van Leene J, Andriankaja M, De Bodt S, Abeel T, Coppens F, Dhondt S, De Milde L, Vermeersch M, Maleux K, Gevaert K, Jerzmanowski A, Benhamed M, Wagner D, Vandepoele K, De Jaeger G, Inzé D. ANGUSTIFOLIA3 binds to SWI/SNF chromatin remodeling complexes to regulate transcription during Arabidopsis leaf development. Plant Cell. 2014;26(1):210–29.
Clapier CR, Cairns BR. The biology of chromatin remodeling complexes. Annu Rev Biochem. 2009;78:273–304.
Best NB, Hartwig T, Budka J, Fujioka S, Johal G, Schulz B, Dilkes BP. Nana plant2 encodes a maize ortholog of the Arabidopsis brassinosteroid biosynthesis gene DWARF1, identifying developmental interactions between Brassinosteroids and Gibberellins. Plant Physiol. 2016;171(4):2633–47.
Song WC, Brash AR. Purification of an allene oxide synthase and identification of the enzyme as a cytochrome P450. Sci. 1991;252:781–4.
Laudert D, Pfannschmidt U, Lottspeich F, Hollander-Czytko H, Weiler EW. Cloning, molecular and functional characterization of Arabidopsis thaliana allene oxide synthase (CYP 74), the first enzyme of the octadecanoid pathway to jasmonates. Plant Mol Biol. 1996;31:323–35.
Liu X, Galli M, Camehl I, Gallavotti A. RAMOSA1 ENHANCER LOCUS2-mediated transcriptional repression regulates vegetative and reproductive architecture. Plant Physiol. 2019;179(1):348–63.
Chuck G, Whipple C, Jackson D, Hake S. The maize SBP-box transcription factor encoded by tasselsheath4 regulates bract development and the establishment of meristem boundaries. Development. 2010;137(8):1243–50.
Chuck GS, Brown PJ, Meeley R, Hake S. Maize SBP-box transcription factors unbranched2 and unbranched3 affect yield traits by regulating the rate of lateral primordia initiation. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 2014;111:18775–80.
Ambrose BA, Lerner DR, Ciceri P, Padilla CM, Yanofsky MF, Schmidt RJ. Molecular and genetic analyses of the silky1 gene reveal conservation in floral organ specification between eudicots and monocots. Mol Cell. 2000;5(3):569–79.
Hayward AP, Moreno MA, Howard TP 3rd, Hague J, Nelson K, Heffelfinger C, Romero S, Kausch AP, Glauser G, Acosta IF, Mottinger JP, Dellaporta SL. Control of sexuality by the sk1-encoded UDP-glycosyltransferase of maize. Sci Adv. 2016;2(10):e1600991.
Hartwig T, Chuck GS, Fujioka S, Klempien A, Weizbauer R, Potluri DPV, Choe S, Johal GS, Schulz B. Brassinosteroid control of sex determination in maize. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 2011;108:19814–9.
Makarevitch I, Thompson A, Muehlbauer GJ, Springer NM. Brd1 gene in maize encodes a brassinosteroid C-6 oxidase. PLoS One. 2012;7:e30798.
Acosta IF, Laparra H, Romero SP, Schmelz E, Hamberg M, Mottinger JP, Moreno MA, Dellaporta SL. Tasselseed1 is a lipoxygenase affecting jasmonic acid signaling in sex determination of maize. Science. 2009;323:262–5.
DeLong A, Calderon-Urrea A, Dellaporta SL. Sex determination gene TASSELSEED2 of maize encodes a short-chain alcohol dehydrogenase required for stage-specific floral organ abortion. Cell. 1993;74(4):757–68.
Gallavotti A, Long JA, Stanfield S, Yang X, Jackson D, Vollbrecht E, Schmidt RJ. The control of axillary meristem fate in the maize ramosa pathway. Development. 2010;137:2849–56.
Wu Q, Regan M, Furukawa H, Jackson D. Role of heterotrimeric Gα proteins in maize development and enhancement of agronomic traits. PLoS Genet. 2018;14(4):e1007374.
Je BI, Xu F, Wu Q, Liu L, Meeley R, Gallagher JP, Corcilius L, Payne RJ, Bartlett ME, Jackson D. The CLAVATA receptor FASCIATED EAR2 responds to distinct CLE peptides by signaling through two downstream effectors. Elife. 2018;7:e35673.
Acknowledgements
We are grateful to Dr. Sarah Hake (Plant Gene Expression Center, USDA-ARS and UC Berkeley) for her critical review and comments.
Funding
This work was supported by the National Key Research and Development Program of China (2016YFD0100400) and the National Natural Science Foundation of China (31671700, 31760388).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
Conceived and designed the experiments: ZZ. Performed the experiments: YZ, YD, WS, ML and DZ. Analyzed the data: ZZ and ML. Revised the manuscript: ML and HD. Wrote the manuscript: ZZ. All authors have read and approved the manuscript.
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Ethics approval and consent to participate
Not applicable in this study.
Consent for publication
Not applicable in this study.
Competing interests
The authors have declared that no competing interests exist.
Additional information
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary Information
Additional file 1:
Supplemental Figure 1. Identification of total proteins and immunoprecipitated proteins by sodium dodecyl sulfate-polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis (SDS-PAGE) and immunoblotting. Supplemental Figure 2. Summary of chromatin immunoprecipitation sequencing (ChIP-seq). Supplemental Figure 3. Targets of GIF1 detected by chromatin immunoprecipitation sequencing (ChIP-seq). Supplemental Figure 4. Schematic diagram of the gif1 over-expression construct. The construct components include the T-DNA right border, RB; and left border, LB; CaMV35S promoter, CaMV35S; terminator of nopaline synthase gene, tnos; enhanced green fluorescent protein gene, eGFP; the phosphinothricin acetyltransferase cassette, bar. Supplemental Table 1. Conservation of identified proteins in Arabidopsis, maize leaf and maize ear. Supplemental. Table 2. Putative GIF1-bound targets identified by ChIP-seq and RNA-seq. Supplemental Table 3. Primer sequences used in this study.
Additional file 2:
Supplemental Data Set 1. A list of differentially expressed genes and their expression levels. Gene expression is calculated using the FPKM (Fragments per kilobase transcriptome per million mapped) method. Fold change: average FPKM of given gene in gif1 mutant / that in wild type. The differentially expression genes (DEGs) are identified using p<10-5 and q <10-4. Rep: biological replicate.
Additional file 3:
Supplemental Data Set 2. Gene ontology enrichment of down-regulated differentially expressed genes. GO_acc: GO accession; term_type includes molecular function (F), cellular component (C), biological process (P); queryitem: item number mapping the GO in the query list; querytotal: total number of query list; bgitem: item number mapping the GO in the background; bgtotal: total number of background; FDR: Yekutieli (FDR under dependency).
Additional file 4:
Supplemental Data Set 3. Gene ontology enrichment of up-regulated differentially expressed genes. GO_acc: GO accession; term_type includes molecular function (F), cellular component (C), biological process (P); queryitem: item number mapping the GO in the query list; querytotal: total number of query list; bgitem: item number mapping the GO in the background; bgtotal: total number of background; FDR: Yekutieli (FDR under dependency).
Additional file 5:
Supplemental Data Set 4. Representative GO terms of differentially expressed genes in the ~5 mm ears of the gif1-1 and the wild type.
Rights and permissions
Open Access This article is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License, which permits use, sharing, adaptation, distribution and reproduction in any medium or format, as long as you give appropriate credit to the original author(s) and the source, provide a link to the Creative Commons licence, and indicate if changes were made. The images or other third party material in this article are included in the article's Creative Commons licence, unless indicated otherwise in a credit line to the material. If material is not included in the article's Creative Commons licence and your intended use is not permitted by statutory regulation or exceeds the permitted use, you will need to obtain permission directly from the copyright holder. To view a copy of this licence, visit http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/. The Creative Commons Public Domain Dedication waiver (http://creativecommons.org/publicdomain/zero/1.0/) applies to the data made available in this article, unless otherwise stated in a credit line to the data.
About this article
Cite this article
Li, M., Zheng, Y., Cui, D. et al. GIF1 controls ear inflorescence architecture and floral development by regulating key genes in hormone biosynthesis and meristem determinacy in maize. BMC Plant Biol 22, 127 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1186/s12870-022-03517-9
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1186/s12870-022-03517-9