Abstract
Background
The walnut shell, which is composed of a large number of sclereids originating from the lignified parenchyma of the endocarp, plays an important role in fruit development and during harvesting and storage. The physical and chemical properties of walnut shells are closely related to the lignin content. Laccase is the key enzyme responsible for lignin biosynthesis by the polymerization of monolignols and plays crucial roles in secondary cell wall formation in plants. In this study, we screened and identified laccase family genes from the walnut genome and investigated the expression of laccase during endocarp lignification in walnut.
Results
A total of 37 laccase genes were screened from the walnut genome and distributed on nine chromosomes and classified into 6 subfamilies, among which subfamily IV showed distinct expansion. We observed that endocarp lignification started 44 days after flowering (DAF), and at later periods, the lignin content increased rapidly, with growth peaks at 44–50 DAF and 100–115 DAF. The lignification of the endocarp proceeded from the outside to the inside, as demonstrated by section staining in combination with endocarp staining. Furthermore, the changes in the expression of laccase family genes in the endocarp at different developmental stages were studied, and JrLACs showed different expression trends. The expression of nine genes showed significant increase after 44 DAF, and among these, JrLAC12–1, JrLAC12–2 and JrLAC16 showed a significant change in expression at the lignification stage. A study of the expression of JrLACs in different tissues and at various endocarp developmental stages revealed, that most JrLACs were expressed at low levels in mature tissues and at high levels in young tissues, in particular, JrLAC12–1 showed high expression in the young stems. A significant positive correlation was found between the expression of JrLAC12–1 and the variation in the lignin content in the endocarp.
Conclusion
Laccase genes play an important role in the lignification of the walnut endocarp, and JrLACs play different roles during fruit development. This study shows that JrLAC12–1 may play a key role in the lignification of endocarp.
Similar content being viewed by others
Background
Walnut (Juglans regia L.) is an important oil resource and an economically important forest tree that is widely distributed in many temperate areas of the world, including Asia, the Americas, Europe and Oceania [1]. The walnut fruit consists of a hull, shell (endocarp) and seed (kernel), and the hull and shell together form the pericarp to protect the kernel [2]. The kernel is rich in fatty acids, proteins, and amino acids, among other substances, and is preferred by many people for consumption in various ways, such as in baked goods, salads and jams. For a long time, much attention was given to the quality and nutrition of walnut kernels, and the crucial role of the shell was often ignored. In particular, the shell plays an important role in fruit development [3], during harvest and transport [4, 5], and even during the process of storage [6]. Shell can also be used to make xylose [7], medium [8], activated carbon [9], and extracted pigment [10], which are widely utilized. In particular, a significant correlation exists between the shell structure and quality of walnut kernel [5]. Therefore, the development and structural characteristics of the walnut shell has received increasing attention from scholars [11,12,13,14,15]. The shell is the endocarp of the walnut fruit and consists of sclereids derived from lignification of the parenchyma originating from the primary meristem [13]. Lignification of the parenchyma is the key step in the development of walnut shells. Zhao et al. [16] confirmed that the development of walnut shells is closely related to lignin biosynthesis, and lignin is the major factor affecting the shell structure [13].
The process of walnut shell formation involves lignification of the endocarp parenchyma. Lignification refers to the process of the enzyme-catalyzed oxidation-mediated polymerization of three main hydroxycinnamyl alcohols—p-coumaryl, coniferyl, and sinapyl alcohols (monolignols)—into lignin, which is then deposited in the secondary cell wall in plant vascular tissues and mechanical tissue [17]. Lignin is a phenylpropanoid-derived polymer that functions as a major component of the secondary cell wall and provides hydrophobicity and protection against pathogens [18, 19]. In plants, a series of enzymes involved in phenylalanine metabolism during cell wall formation have been reported, and most key phenylpropanoid biosynthetic enzymes are also critical for lignin biosynthesis [20]. Phenylalanine is catalytically converted in a stepwise manner to p-coumaroyl-CoA by phenylalanine ammonia-lyase (PAL), cinnamate 4-hydroxylase (C4H) and 4-coumarate:CoA ligase (4CL). Subsequently, quinate/shikimate p-hydroxycinnamoyltransferase (HCT), p-coumaroylshikimate 3′-hydroxylase (C3’H), caffeoyl shikimate esterase (CSE), caffeic acid O-methyltransferase (COMT), caffeoyl-CoA O-methyltransferase (CCoAOMT), cinnamoyl-CoA reductase (CCR), ferulate 5-hydroxylase (F5H) and cinnamyl alcohol dehydrogenase (CAD), which work downstream of 4CL, and the catalyzed reactions provide precursors for all of the downstream metabolites [21]. Ultimately, lignin monomers are converted to lignin polymers by reactions catalyzed by peroxidase (POD) or laccase (LAC) [22], and LAC plays an important role in this process [23].
LAC (EC 1.10.3.2) was first identified from the Japanese lacquer tree (Rhus vernicifera) [24] and belongs to a group of three blue multicopper oxidases (LMCOs) belonging to a large gene family found in plants [25], fungi [26] and bacteria [27]. A large number of results have shown that LAC can polymerize lignin monomers to form lignin in various plant tissues [28]. Liang et al. [29] introduced a mutation in AtLAC15 that affected both the extractable lignin and soluble proanthocyanidin content in Arabidopsis seeds. LAC4 and LAC17 contribute to the constitutive lignification of Arabidopsis stems, and LAC17 is involved in the deposition of G-lignin units in fibers [30]. In the whole genome of pear, 41 LACs have been identified, and among these, PbLAC1 is involved in lignin biosynthesis and cell wall development, but the lignin content and cell wall thickness are not significantly changed in PbLAC14-overexpressing transgenic Arabidopsis plants [31]. The promoter of LAC18 could be significantly activated by the PbrMYB169 protein by binding to AC elements, and the overexpression of PbrMYB169 increased both lignin deposition and the cell wall thickness [32]. Furthermore, transgenic Arabidopsis plants overexpressing MsLAC1 exhibit an increased G-lignin content, although recombinant MsLAC1 appears to prefer sinapyl alcohol as a substrate [33].
The role of LAC in plant development has received much attention. Although LACs have been identified and classified in many species, such as Arabidopsis [34], Citrus sinensis [35], soybean [36], Setaria viridis [37], rice [38], sugarcane [39], sweet cherry [40] and cotton (Gossypium arboreum and Gossypium raimondii) [41], an investigation of the LAC gene family in walnut remains to be conducted. In contrast, the formation of naked kernels, dissilient nuts and stained nuts has become a serious problem due to the rapid increase in thin-shell walnut cultivars in China [5]. In this study, we screened and identified the LAC genes in the walnut genome. In addition, changes in JrLAC expression during endocarp lignification were analyzed, and the expression of JrLAC12–1 and JrLAC14–5 was found to change significantly during endocarp lignification. JrLAC12–1 was then used to clarify the role of LACs in endocarp lignification. Therefore, the present study lays the foundation for understanding the function of LACs in endocarp lignification.
Result
Identification and analysis of LAC genes in the walnut genome
A hidden Markov model was constructed using the Arabidopsis LAC family protein sequence information, and the model was used to search walnut protein sequences for the initial screening of 72 walnut LAC family genes. Based on a Pfam structural domain analysis, 37 walnut LAC family genes were finally obtained after eliminating duplicate redundancy, and these genes were associated with 9 chromosomes and encoded 37 protein sequences. The genes were named according to their annotation information, and the position and structural information of these genes are shown in Table 1. The length of the coding sequence (CDS) ranged from 1671 to 1848 bp. The smallest translated protein was 556 aa, and the largest was 615 aa. The predicted molecular weight (MW) of these proteins ranged from 60.86 kD (JrLAC4–4) to 68.40 kD (JrLAC9–1), and the theoretical isoelectric point (pI) ranged from 4.67 to 9.9. JrLAC12–1, which is located on chromosome 7, including 6 exons and 5 introns, had a length of 3981 bp, and the length of the CDS was 1743 bp, encoding 580 amino acids.
Analyses of the evolution, gene structure and motif distribution of JrLAC family members
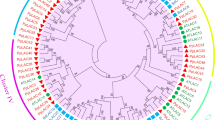
The phylogenetic tree of the walnut LAC protein sequence and the Arabidopsis LAC protein sequence was constructed with the maximum likelihood method using MEGA 7.0 software (Fig. 1). The phylogenetic tree indicates that the LAC gene families of J. regia and Arabidopsis thaliana are similar. According to the classification of Arabidopsis LAC genes, the 37 JrLAC genes were classified into 6 subfamilies: I-VI. Among them, subfamily IV was the largest subfamily, with significant gene duplication and expansion, and contained 15 genes: JrLAC9–1, JrLAC9–2, JrLAC9–3, JrLAC9–4, JrLAC14–1, JrLAC14–2, JrLAC14–3, JrLAC14–4, JrLAC14–5, JrLAC14–6, JrLAC14–7, JrLAC14–8, JrLAC15–1, JrLAC15–2 and JrLAC15–3. A chromosomal localization analysis of the subfamily IV genes showed that all the genes, with the exception of JrLAC9–1 (localized on chromosome 15) were located on chromosome 6 and were extremely close together to, form a gene cluster (Fig. 2). Subfamily I contained seven genes, which were mainly localized on chromosomes 3, 4, 5, and 14. Subfamily II contained eight genes, which were mainly localized on chromosomes 3, 4, 12, 13, and 14. Among these genes, LAC4–1, LAC4–2 and LAC4–4 formed another gene cluster together with LAC17–2 of subfamily I and LAC7–1 and LAC7–2 (the only two genes of subfamily V) on chromosome 3. Subfamily III contained only three JrLAC genes, namely, JrLAC12–1, JrLAC12–2, and JrLAC13, which are localized on chromosomes 7, 12, and 14, respectively. JrLAC1 and JrLAC6 belonged to subfamily VI and were localized on chromosomes 6 and 7, respectively. Interestingly, no JrLAC genes were found on chromosomes 1, 2, 8, 9, 11 and 16.
Phylogenetic analysis of Arabidopsis thaliana and Juglans regia regarding LACs. The areas with different colors represent different subfamilies. The evolutionary history of laccases was created using the maximum likelihood method. The percentage of replicate trees in which the associated taxa clustered together in the bootstrap test (1000 replicates) is shown next to the branches
The within-genome duplication events of the JrLAC genes were analyzed using MCScan [42]. The results indicated that 16 genes located on chromosomes 3 and 6 are involved in tandem duplication events, and formed eleven gene pairs (Fig. 2; Additional file 1). We also performed a collinearity analysis of LACs to explore the evolutionary relationships of JrLACs. The results showed that 15 syntenic JrLAC gene pairs derived from WGD or segmental duplication were distributed on 9 of 16 chromosomes (Fig. 3; Additional file 2).
Distribution of segmental duplication-derived LAC genes in the walnut genome. The red lines represent collinear pairs of the JrLAC genes, whereas the gray lines indicate collinear pairs of all walnut genes. The outer circle indicates the location of the JrLACs on each chromosome. The different colored boxes represent the 16 chromosomes of walnuts
The exon and intron sequences of the 37 genes were analyzed, and the results showed that subfamilies I, II, III and V all contained six exons and five introns and that all the genes except JrLAC7–2 had upstream and downstream untranslated regions (UTRs). All the genes in subfamily IV had 7 exons and 6 introns with the exception of except JrLAC15–2, which had 6 exons and 5 introns; in addition, all the genes had UTRs except JrLAC14–4, which had no upstream or downstream UTR. Subfamily VI had only one copy each of JrLAC1 and JrLAC6, and these genes showed significant differences: JrLAC1 contained 5 exons and 4 introns and no upstream or downstream UTR, and JrLAC6 had 6 exons and 5 introns (Fig. 4A and B).
Predicted exon-intron structures of walnut LACs and conserved motifs of walnut LAC protein. A. The phylogenetic tree was constructed based on the full-length protein sequences of 37 walnut LAC proteins using MEGA V7.0.21 software. B. Location of conserved motifs in walnut JrLAC proteins. Motifs, 1–12, are displayed by differently colored boxes. C. Exon-intron structure of walnut LAC genes. The exons and introns are indicated by yellow boxes and single lines, respectively
An analysis of the amino acid sequences encoded by the genes in this family revealed that all the amino acid sequences contained motifs 1–8 and 11, and motif 10 was missing from three genes in subfamily III and the amino acid sequence encoded by the JrLAC6 gene in subfamily VI. The amino acid sequence encoded by the JrLAC14–4 gene in subfamily IV lacked motifs 10 and 9, and the amino acid sequence encoded by the JrLAC9–4 gene lacked motif 12 (Figs. 4 and 5C).
Accumulation of lignin in the endocarp at different developmental stages
Walnut is a pseudodrupes; the husk originates from the hairy involucre that surrounds the pistil [2], and the endocarp is gradually lignified during development to form the hard shell. Lignin is stained pink by methanetriol-hydrochloric acid, and thus, the lignification process of walnut was recorded by using this reagent (Fig. 6). The results showed that the fruit was rapidly enlarging, the endocarp cells were in a period of rapid division from 20 days after flowering (DAF) to 38 DAF, and lignification did not occur. At 32 DAF, the placenta inside the fruit appeared pink, which indicated that the start of lignification occurred in this. At 44 DAF, the fruit was no longer enlarged, and some of the tissue at the junction of the endocarp and the husk was stained pink, particularly at the suture, which indicated that the husk began to lignify at this time. However, the inner endocarp remained white, indicating that its lignification proceeded from the outside to the inside. At 50 DAF, the endosperm was still a liquid, and the endocarp was stained in a circle at the junction with the husk, indicating full lignification of the endocarp. Between 50 and 100 DAF, the husk gradually thickened and became increasingly lignified. From 100 to 115 DAF, similar husk staining was observed, and no significant changes occurred, which indicated that the lignification process was nearly complete.
Walnut endocarp lignification process. The upper side shows a transverse cut of the fruit and the lower side shows a longitudinal cut of the fruit. The lignin in endocarp is stained pink based on Wiesner reaction. The fruit shells were not lignified until 38 days after flowering and began to lignify after 44 days after flowering
Further determination of the endocarp lignin content at different developmental stages showed that the lignin content was low (with a relative level below 4%) until 44 DAF. After 44 DAF, the endocarp lignin content increased rapidly, reaching 26.8% by 115 DAF (Fig. 7), and this founding was similar to the results of the Wiesner reaction. Determination of the changes in the Δ-lignin content showed that the rate of increase in the lignin content changed slowly until 44 DAF; however, faster increases were detected from 44 DAF to 50 DAF and from 100 DAF to 115 DAF. This finding indicates that the rapid accumulation of lignin in the walnut endocarp occurred mainly between 44 and 50 DAF and after 100 DAF.
Expression patterns of JrLAC genes during endocarp lignification
We collected samples at 20 and 45 DAF for tissue observation and staining using the methanetriol-hydrochloric acid method (Fig. 8). The results showed that at 20 DAF, the pericarp cells were polygonal and small in size, which indicated that the tissues were in a period of rapid division and had no deposited lignin (Fig. 8B). At 45 DAF, the pericarp cells were significantly enlarged, and exhibited long cell margins at the junction of the mesocarp and endocarp (Fig. 8C). The Wiesner reaction clearly showed that the endocarp cells near the junction began to lignify and the cell walls appeared to thicken, whereas the endocarp cells away from the exocarp had not yet lignified.
Expression patterns of JrLACs genes. A Heat-map depicting the transcriptional activities of 37 JrLAC genes at 20 DAF and 45 DAF. B Cross-sectional view of the fruit at the junction of the endocarp and husk at 20 DAF; with the white tissue being the endocarp, and the brown tissue is the mesocarp. C Cross-sectional view of the junction of the endocarp and husk at 45 DAF. At this time, the cells were significantly enlarged, the pink tissues in is endocarp, and the cell wall is significantly thickened
The expression level of each JrLAC gene was normalized using the FPKM method (Fig. 8A; Additional file 3). Interestingly, the expression level of JrLAC12–1 during lignification (45 DAF) was higher than that in the nonlignified endocarp (20 DAF). In contrast, the expression of JrLAC14–5 exhibited the opposite changes. In terms of subfamilies, the total expression of subfamily IV and VI genes was significantly decreased at the lignification stage (45 DAF) than at the unlignified stage (20 DAF) (Additional files 3 and 4). In particular, all subfamily IV genes showed a downregulation trend during lignification. The total expression of the subfamily I, II and III genes was significantly higher at the lignification stage than at the unlignified stage. At both stages, the expression of subfamily III and IV genes was significantly higher than that of genes belonging to the other subfamilies. These results suggest that the JrLACs have different functions and that some members are redundant.
Expression analysis of JrLACs at different developmental endocarp stages
The expression of JrLACs during fruit development was further verified by quantitative RT-PCR, and the findings were generally similar to the transcriptome results, but different JrLACs showed different expression at different developmental stages (Fig. 9). Among these genes, the expression of JrLAC4–5, JrLAC6, JrLAC9–1, JrLAC9–2, JrLAC9–3, JrLAC9–4, JrLAC11–2, JrLAC14–1, JrLAC14–6, JrLAC14–7, JrLAC15–3, and JrLAC17–1 decreased during the lignification of endocarp after 44 DAF, and the expression fold change was small. JrLAC2–1, JrLAC2–2, JrLAC2–3, JrLAC4–1, JrLAC4–2, JrLAC4–3, JrLAC4–4, JrLAC7–1, JrLAC7–2, JrLAC12–1, JrLAC12–2, JrLAC13, JrLAC14–3, JrLAC14–4, JrLAC15–2, JrLAC16 and JrLAC17–2 showed a significant increase in gene expression from 38 to 71 DAF followed by decrease, and among these, JrLAC12–1, JrLAC12–2 and JrLAC16 showed the greats changes. The expression of other genes changed slightly and showed irregular changes. A comparison of the expression period and relative expression of JrLACs indicated that different JrLAC genes may play different roles at different periods of shell development. According to the results shown in Figs. 6 and 7, endocarp lignification started at 44 DAF, and the expression of nine genes, JrLAC2–1, JrLAC2–2, JrLAC4–1, JrLAC4–3, JrLAC4–4, JrLAC12–1, JrLAC12–2, JrLAC16 and JrLAC17–2, showed a significant increase after 44 DAF. In particular, the expression of JrLAC12–1, JrLAC12–2 and JrLAC16 exhibited extremely significant expression changes; thus, it can be hypothesized that JrLAC12–1, JrLAC12–2 and JrLAC16 may be involved in the process of shell lignin accumulation. The relative expression of JrLAC12–1 increased starting from 32 DAF, peaked at 38 DAF, and remained at a high level until 50 DAF (Fig. 9). In addition, the expression level of JrLAC12–1 remained high from 85 to 100 DAF, which is also the period when the shell appeared and lignin was deposited in large quantities (Figs. 6 and 7); thus, it is assumed that JrLAC12–1 may play a key role in the process of shell lignin accumulation.
Expression analysis of JrLACs from different subfamilies in different walnut tissues
The specific expression of JrLACs from different subfamilies in different tissues of walnut was further analyzed, and eight genes in six subfamilies showed significantly different expression patterns in each tissue (Fig. 10). JrLAC2–2 in subfamily I is expressed at relatively high levels in young stems and leaves but exhibits low or no expression in mature stems, catkins and kernels; JrLAC4–4 in subfamily II is highly expressed in catkins, young fruits, and buds and is found at low or no expression in pistils and kernels; JrLAC12–1 and JrLAC12–2 in subfamily III showed similar trends, i.e., high expression in young stems, catkins, pistils and buds and low expression in mature stems and mature leaves, in particular, young woody stems are the site of rapid lignification of plant, and JrLAC12–1 exhibits higher expression in this tissue; in subfamily IV, JrLAC14–2 is highly expressed in catkins and buds, and JrLAC14–5 is highly expressed in young leaves and young fruits and exhibits lower expression in mature stems and mature leaves; JrLAC7–1 in subfamily V is expressed only in pistils, catkins and young fruits; JrLAC6 in subfamily VI is highly expressed in buds and shows low expression in pistils and kernels. Most JrLACs were found to be expressed at low levels in mature tissues and at high levels in young tissues. The expression of genes was higher in young tissues, where lignin is biosynthesized and deposited in large quantities (Additional file 8), whereas their expression was lower in mature organs because these the organs had completed development and no longer needed to accumulate lignin. Because the expression of the JrLAC genes differed among tissues, it can be assumed that these genes have different functions in the lignification process.
Correlation between the lignin content and JrLAC expression
To further verify the relationship between lignin synthesis and LAC genes, we conducted a correlation analysis between the lignin content of the endocarp and the expression of the 37 genes at different developmental stages (Table 2), and the results showed a significant positive correlation between JrLAC12–1 and Δ-lignin content, whereas no correlation was found between the other genes and Δ-lignin content. Although the expression of genes such as JrLAC4–2, JrLAC6, JrLAC7–1, JrLAC7–2, JrLAC9–2 and JrLAC14–2 was significantly positively or negatively correlated with the lignin content, expression trend of these genes is similar or opposite to the cumulative amount of lignin because the lignin is irreversible during the cumulative process. This result further suggests that JrLAC12–1 is involved in the deposition of lignin in the endocarp.
Discussion
According to their oxidation characteristics, LACs are divided into two groups: low-redox-potential and high-redox-potential enzymes [43]; therefore, LACs can catalyze both anabolic and catabolic reactions. In fungi, LACs are involved in catabolism and can degrade lignin and humus [44], whereas in higher plants or insects, LAC catalyzes anabolic reactions involved in various morphogenesis processes, such as lignin synthesis [45], cuticle formation [46], and flavonoid synthesis [47]. Therefore, this finding indicates that the LAC gene family may differ significantly among species of different taxa. In fungi, the LAC gene family is divided into five clusters, and LACs within different clusters can be induced by different substrates [48]. In higher plants, the LAC genes within different species vary, and the LAC gene family of each plant is usually divided into six subfamilies based on protein sequence characteristics, such as those of soybean [36], S. viridis [37], and sweet cherry [40]. However, in C. sinensis and Brassica napus, the LAC gene family is divided into seven and five subfamilies, respectively [35, 49]. Differences in the degree of expansion of LAC genes have been found within different species, such as in subfamilies III and II in B. napus [49], subfamily V in S. viridis [37], soybean [36] and pear [31], and subfamily I in C. sinensis [35]. In sweet cherry [40], which is also a type of drupe, the LAC gene family is significantly expanded in subfamilies II and IV, similar to the result obtained for walnut in the present study. Previous studies have also shown that some of the walnut LAC genes in subfamily II or IV are distributed as chromosomal gene clusters, and 11 pairs of genes in subfamilies II, IV and V show tandem duplication events. The tandem duplication of these LAC genes in the walnut genome may be the main reason for the expansion of subfamilies II and IV. In addition, 15 pairs of genes with collinearity belonged to subfamilies I, II, III and IV, and it is speculated that these collinear pairs of genes might have similar functions.
Xiao et al. found that most of the genes that are highly expressed in lignified tissues, such as roots and stems of B. napus, belong to LAC subfamilies I, II and III [49]. In the C4 model grass S. viridis, SvLAC52, SvLAC15 and SvLAC9 (AtLAC2 or LAC17 homologs) in subfamily I and SvLAC50 (homolog of AtLAC16) in subfamily II are also highly expressed in the transitional and maturation zones, where lignin biosynthesis-related genes are active [37]. In soybean, the genes GMLAC2 and GmLAC9 (AtLAC4 homologs) in subfamily II and GmLAC8 (AtLAC12 homolog) in subfamily III are highly expressed in stems, whereas the 11 genes showing constitutive expression in multiple tissues all belong to subfamily V [36]. In pear, PbLAC1 (AtLAC2 homolog), LAC38 and LAC29 (AtLAC17 homologs) in subfamily I and PbLAC5, PbLAC36, and PbLAC6 (AtLAC4 homologs) in subfamily II are highly expressed at the stage showing peak lignin content in the pulp, whereas PbLAC10, PbLAC11 and PbLAC39 (AtLAC15 homologs) in subfamily IV and PbLAC20 (AtLAC14 homolog) in subfamily IV exhibit the exact opposite results. The LAC genes associated with lignin synthesis in previous studies belong mostly to subfamilies I, II and IV. AtLAC4 in subfamily II in Arabidopsis may be involved in the synthesis of lignin and secondary walls. AtLAC4 is strongly expressed in vascular tissues and specifically in leaf hydathodes, and AtLAC4 overexpressing plants show a dwarf phenotype and have shorter leaf petioles, both of which are effects caused by increase in the lignin content and secondary wall thickness [50]. The expression of JrLAC4–1, JrLAC4–2, JrLAC4–3, JrLAC4–4 and JrLAC16 in subfamily II in walnut, particularly the latter, increased significantly from 44 to 71 DAF. It can be speculated that LAC genes in subfamily II also assume important functions during endocarp lignification in walnut. In addition, the expression patterns of the six subfamilies differed between the unlignified and lignified stages of the endocarp, as demonstrated by an increase in the total expression of subfamilies I, II, III and a decrease in the total expression in subfamilies IV and VI. Based on previous studies and the results of this study, six subfamilies have different functions in endocarp lignification, and the division of labor between these subfamilies is different in walnut.
The final step in lignin biosynthesis is the polymerization of lignin monomers by dehydrogenation in response to enzymes such as POD, LAC and polyphenol oxidase (PPO) [51]. Previous studies have concluded that PODs use hydrogen peroxide (H2O2) to oxidize their substrates [52]. In contrast to PODs, LACs consume O2 instead of H2O2 to oxidize monolignols. LACs of a variety of species are expressed in lignifying cells [53]. The lignification of cells from different parts of the plant may proceed in different manners, depending on whether the lignin is local or widespread. Casparian strip formation requires PODs but not LACs [54]. The walnut shell consists of sclereids formed by the thickening and lignification of the secondary walls of the parenchyma in the endocarp [13]. Our previous study found that shell formation is accompanied by increases in the lignin, cellulose and phenolic content, no mark change in PPO activity and POD activity, and that POD activity is negatively correlated with lignin accumulation [12]. In this study, the expression pattern of LAC genes during lignification was further analyzed. Subfamily III genes, such as JrLAC12–1 and JrLAC12–2 were highly expressed during the lignification stage; in particular, the expression of JrLAC12–1 showed a significant positive correlation with the change in the lignin content. Consistent with the results obtained for walnut shell sclereids, sclereids in pear pulp also show high LAC expression during the developmentally critical stage of formation [31], and the silencing of three LAC genes reduces the lignin content and sclereid number in pear fruit [55]. Therefore, LACs may play a key role in the lignification of walnut shells.
Previous studies found that in poplar, PtoLAC14 is mainly expressed in lignified tissues in the vascular bundles, such as the stem xylem, and that the overexpression of PtoLAC14 resulted in smaller cells with secondary wall thickening and an increased lignin content [56]. In Arabidopsis, AtLAC4 in interfascicular fibers and seed coat columella, AtLAC15 in seed coat cell walls, AtLAC14 in vascular tissues, such as roots, stems, leaves, petals and leaves but not in siliques (the fruit of Arabidopsis), are uniquely expressed [34]. In contrast, AtLAC12 is expressed in all tissues of Arabidopsis, particularly in the replum and abscission zone of the siliques. In this study, high expression of JrLAC14–1, JrLAC14–3, JrLAC14–4, JrLAC14–6 and JrLAC14–7 were observed in young fruits, which was presumed to be mainly related to vascular tissue formation at the early stages of young fruit development period. JrLAC12–1, JrLAC12–2 and JrLAC6 are highly expressed in young stems and buds, and the changes in the expression of JrLAC12–1 during shell development were consistent with the changes in lignin deposition, which suggested that JrLAC12–1 is involved in tissue formation and is a key factor in the lignification of sclereids in the shell. Therefore, the regulatory mechanism of JrLAC12–1 in walnut pericarp development needs to be further investigated.
Conclusion
Thirty-seven LAC genes were identified in the walnut genome, are distributed on nine chromosomes and can be divided into six subfamilies. During walnut endocarp development, different JrLACs show significantly different expression trends, and JrLAC12–1, JrLAC12–2 and JrLAC16 may be involved in endocarp lignification. Changes in walnut JrLAC12–1 gene expression were found to be positively correlated with Δ-lignin in the shell, which suggests that JrLAC12–1 plays a key role during lignin accumulation in endocarp lignification.
Methods
Plant and materials
The material used in this study was collected in 2016–2017 from the Experimental Field of Hebei Agricultural University (EFHAU) (EFHAU; 38°48′N, 115°24′E), China. No special permission was necessary to collect such samples. The walnut cultivar ‘Zanmei’ in the full fruit-bearing period was selected as the test material. The plants were pruned when necessary and received standard fertilization. Fresh fruit of ‘Zanmei’ were collected every 5 days starting at the early stage of fruit growth and every 14 days after the shell appeared from 20 DAF until 115 DAF. Thirty samples of walnut fruit at each stage were randomly collected from all four cardinal directions on the ‘Zanmei’ trees. After the fresh fruit cut, part of the pericarp was frozen with liquid nitrogen and frozen to −80 °C for transcriptome sequencing, gene expression analysis and lignin content determination, and the other part was cut into ≈5 mm3 cubes and fixed in 2.5% (v/v) glutaraldehyde and 3% (v/v) polyformaldehyde in phosphate-buffered saline [PBS; 4 mM sodium phosphate (pH 7.2), 200 mM sodium chloride (NaCl)] [13]. Tissues (root, young stem, mature stem, young leaf, mature leaf, pistil, catkin, young fruit, kernel and bud tissues) were collected separately from field-grown trees at EFHAU, frozen with liquid nitrogen and frozen to −80 °C for organ-specific expression analyses.
Identification of the LAC gene family and bioinformatic analysis
The sequences of Arabidopsis LAC proteins were downloaded from the UniProt protein database (http://www.uniprot.org). The hidden Markov model was constructed using HMMER 3.1b software and the Arabidopsis LAC family protein sequences (Additional file 7) in the UniProt database, and the protein sequences of walnut were downloaded from GenBank (accession GCA_001411555.2). The conserved domains of the proteins were analyzed with the Pfam protein family database (http://pfam.org/) [57] of the European Institute of Bioinformatics using the Gene Structure Display Server (GSDS, http://gsds.cbi.pku.edu.cn/) [58] and MEME (http://meme-suite.org/) for the walnut LAC family. The phylogenetic tree of the JrLAC and AtLAC gene families was constructed with the maximum likelihood method using MEGA 7.0 software with a bootstrap value of 1000.
The physical locations of the JrLAC genes were obtained from the genome annotation information (gff3) of J. regia, and the JrLAC genes were mapped to the walnut chromosomes.
The duplication events of the JrLAC genes were calculated using MCScanX software [42] and then, visualized using TBtools software [59]. The CDSs and protein sequences of collinear gene pairs were compared, and the ratio of nonsynonymous substitution to synonymous substitution (Ka/Ks) was calculated using TBtools software [59]. The figure was processed using Adobe Illustrator software.
Analysis and validation of RNA-Seq data
The endocarp of walnut collected at 20 DAF (unlignified stage) and 45 DAF (lignification stage) was selected for transcriptome sequencing, and three replicates were used in the analysis. The sequence data were deposited in GSA (https://bigd.big.ac.cn/gsa/browse/CRA005050) [60]. Using RNA-Seq, we explored the gene expression patterns of the JrLAC gene family in the endocarp at the unlignified and lignification stages.
Gene expression analysis by quantitative RT-PCR
RNA isolation from different tissues and the endocarp at different developmental stages was performed using an isolation kit (product number: DP441; Tiangen, Beijing, China). The isolated RNA was solubilized in diethyl phosphorocyanidate (DEPC)-treated RNase-free water and treated with DNase. Pure RNA was used for cDNA synthesis with a commercial kit (product number: RR047A; Tiangen, Beijing, China) according to the manufacturer’s guidelines. The resulting cDNA was diluted 9-fold and stored at −20 °C for subsequent RT-PCR and qRT-PCR assays.
Specific primers for JrLAC genes expression quantification were designed using Primer Premier 5.0 software. qRT-PCR experiments were performed using an FX96 Touch™ Real-Time PCR Detection System (Bio-Rad) in conjunction with TransStart Top Green qPCR SuperMix (product number: AQ131; TransGen Biotech, Beijing China). Primers (Additional file 8) were used to analyze the JrLACs transcripts. JrACT2 (NCBI reference: XM_018972062.1) was used as the reference gene to calculate the relative fold differences based on the comparative cycle threshold (2-ΔΔct) [61]. The PCR mixture (20 μL) consisted of 10 μL of 2 × TransStart Top Green qPCR SuperMix, 1 μL of each primer (10 μmol/L), 1 μL of diluted cDNA and 7 μL of ddH2O. The following conditions were used for RT-PCR: 95 °C for 15 min; 40 cycles of 95 °C for 10 s, 60 °C for 30 s, and 72 °C for 45 s; and a final extension at 72 °C for 10 min. Three experiments (biological replicates) were performed for each sample.
Preparation of specimen for light microscopy
After extensive washing in PBS, the samples of fixed endocarp were processed as follows: sequentially dehydrated at ambient temperature in 70, 85, 95, and 100% ethanol (1 h for each step); vitrified with a gradient from 100% ethanol to 100% xylene; and infiltrated with and embedded in paraffin [13]. Eight-micron sections were prepared using a microtome (KEDEE KD-225) mounted on adhesive microscopic slides, stained with 2% phloroglucinol in 95% ethanol solution for 5 min and mounted in 6 M HCl. Subsequently, the sections were examined with an Olympus (Tokyo, Japan) microscope (BH-2).
Lignin deposition and determination
The fruit was longitudinally and transversely cut into halves for the Wiesner test (Lin et al., 2002). Each part was treated with 2% phloroglucinol in a 95% ethanol solution for 5 min and mounted in 6 M HCl to examine the presence of the cinnamaldehyde groups of the lignin [12].
The endocarps of walnut fruit were chopped into small pieces, frozen in liquid N2, and ground to a fine powder with a grinder. This lyophilized powder was used for lignin content determination, which was carried out as described by Zhao et al [12]. The change in the lignin content (Δ-lignin content) was calculated by subtracting the lignin content in the previous period from the lignin content in the current period.
Statistical analysis
The experiments were established in accordance with a completely randomized design. The data are shown as the means ± standard errors (SEs) of 3 or 6 independent biological replicates. The data were analyzed with SPSS version 20.0 (IBM Corp., Armonk, NY, USA) and Excel 2016 software (Microsoft Corp., Redmond, WA, USA).
Availability of data and materials
The RNA-Seq datasets are available in the National Genomics Data Center, China National Center for Bioinformation (https://bigd.big.ac.cn/gsa/browse/CRA005050; accession number: CRA005050). The CDS and genome sequences of LACs in walnut were retrieved from the whole walnut genome database (accession GCA_001411555.2) in NCBI. All data and materials are presented in the main paper and additional file.
Abbreviations
- LAC:
-
Laccase
- PPO:
-
Polyphenol oxidase
- POD:
-
Peroxidase
References
Zhang Z, Pei D. Walnut. Beijing: China Agricultural Press; 2018. p. 4–5.
Ramos DE. Walnut production mannual. University of California Division of Agriculture and Natural Resources. Oakland: Publication 3373; 1998. p. 139–43.
Zhao S, Liu K, Wen J, Wang H, Zhang Z, Hua L. Effect of GA3 and 6-BA on the Development of Walnut Shell. Acta Hortic Sin. 2019;46(11):2119–28.
Khir R, Pan Z, Atungulu GG, Thompson JF, Shao D. Size and moisture distribution characteristics of walnuts and their components. Food Bioprocess Technol. 2013;6(3):771–82.
Zhao Y, Zhao S, Wang H, Zhang Z, Gao Y. The relations between shell structures and kernel qualities of Juglans regia. Sci Silvae Sin. 2007;43(12):81–5.
Wang W, Li P, Guixi W, Yujie W, Huali H. Study of fatty acid oxidation of walnut kernel with or without shell at ambient-temperature [J]. Acad Periodical Farm Prod Process. 2008;8:8–10.
Yu X, Zhou C, Zhang Y, Lin L, Wang Y, Bing L. Process and kinetics of acid hydrolysis from Carya cathayensis Sarg. shell to xylose [J]. Trans Chin Soc Agri Mach. 2011;42(6):138–42.
Yu H, Feng Z, Guo Q, Shang X, Zhang L, Tan Q. Cultivation of Pleurotus eryngii using walnut processing wastes. Acta Edulis Fungi. 2011;18(2):33–5.
Martinez ML, Torres MM, Guzman CA, Maestri D. Preparation and characteristics of activated carbon from olive stones and walnut shells. Ind Crop Prod. 2006;23(1):23–8.
Sun Y, Li S, Zeng F, Qi J, Qin W, Tan C, et al. Functional components, antioxidant activity and hypoglycemic ability following simulated gastro-intestinal digestion of pigments from walnut brown shell and green husk. Antioxidants. 2019;8(12):573.
Yu S, Rui Z, Guo Z, Song Y, Fu J, Wu P, et al. Dynamic changes of auxin and analysis of differentially expressed genes in walnut endocarp during hardening. Acta Hortic Sin. 2021;48(3):487–504.
Zhao S, Wen J, Wang H, Zhang Z, Li X. Changes in lignin content and activity of related enzymes in the endocarp during the walnut shell development period. Hortic Plant J. 2016;2(3):141–6.
Zhao S, Niu J, Yun L, Liu K, Wang S, Wen J, et al. The relationship among the structural, cellular, and physical properties of walnut shells. Hortic Sci. 2019;54(2):275–81.
Zhao S, Zhao Y, Wang H, Gao Y, Zhang Z, Feng D. Factors affecting nutshell structure of walnut. Sci Silvae Sin. 2011;47(4):70–5.
Sideli GM, Marrano A, Montanari S, Leslie CA, Allen BJ, Cheng H, et al. Quantitative phenotyping of shell suture strength in walnut (Juglans regia L.) enhances precision for detection of QTL and genome-wide association mapping. PLoS One. 2020;15(4):e0231144.
Xiao L, Xu Y, Zhao X, Luo J. The developmental anatomy on the pericarp of Juglans regia. Acta Bot Boreali-Occidentalia Sin. 1998;18(4):577–80.
Guo Y, Xu H, Zhao Y, Wu H, Lin J. Plant lignification and its regulation. Sci Sin Vitae. 2020;50(2):111–22.
Geng P, Zhang S, Liu J, Zhao C, Wu J, Cao Y, et al. MYB20, MYB42, MYB43 and MYB85 regulate phenylalanine and lignin biosynthesis during secondary cell wall formation. Plant Physiol. 2019;182(3):1272–83.
Neiva DM, Rencoret J, Marques G, Gutiérrez A, Gominho J, Pereira H, et al. Lignin from tree barks: chemical structure and valorization. ChemSusChem. 2020;13:4537–47.
Vanholme R, Morreel K, Ralph J, Boerjan W. Lignin engineering. Curr Opin Plant Biol. 2008;11(3):278–85.
Xie M, Zhang J, Tschaplinski TJ, Tuskan GA, Chen JG, Muchero W. Regulation of lignin biosynthesis and its role in growth-defense tradeoffs. Front Plant Sci. 2018;9:1427.
Takahama U. Oxidation of hydroxycinnamic acid and hydroxycinnamyl alcohol derivatives by laccase and peroxidase. Interactions among p-hydroxyphenyl, guaiacyl and syringyl groups during the oxidation reactions. Physiol Plantarum. 1995;93(1):61–8.
Berthet S, Thevenin J, Baratiny D, Demont-Caulet N, Debeaujon I, Bidzinski P, et al. Role of plant laccases in lignin polymerization. Adv Bot Res. 2012;61:145–72.
Yoshida H. LXIII.—Chemistry of lacquer (Urushi). Part I. Communication from the chemical society of Tokio. J Chem Soc Trans. 1883;43:472–86.
Dean JF, Eriksson K-EL. Laccase and the deposition of lignin in vascular plants. Holzforschung. 1994;48:21–33.
Nihei R, Usami M, Taguchi T, Amachi S. Role of fungal laccase in iodide oxidation in soils. J Environ Radioact. 2018;189:127–34.
Komori H, Higuchi Y. Structural insights into the O2 reduction mechanism of multicopper oxidase. J Biochem. 2015;158(4):293–8.
O'Malley DM, Whetten R, Bao W, Chen CL, Sederoff RR. The role of of laccase in lignification. Plant J. 1993;4(5):751–7.
Liang M, Davis E, Gardner D, Cai X, Wu Y. Involvement of AtLAC15 in lignin synthesis in seeds and in root elongation of Arabidopsis. Planta. 2006;224(5):1185–96.
Berthet S, Demont-Caulet N, Pollet B, Bidzinski P, Cezard L, Le Bris P, et al. Disruption of LACCASE4 and 17 results in tissue-specific alterations to lignification of Arabidopsis thaliana stems. Plant Cell. 2011;23(3):1124–37.
Cheng X, Li G, Ma C, Abdullah M, Zhang J, Zhao H, et al. Comprehensive genome-wide analysis of the pear (Pyrus bretschneideri) laccase gene (PbLAC) family and functional identification of PbLAC1 involved in lignin biosynthesis. PLoS One. 2019;14(2):e0210892.
Xue C, Yao JL, Xue YS, Su GQ, Wang L, Lin LK, et al. PbrMYB169 positively regulates lignification in fruit stone cells of pear (Pyrus bretschneideri). J Exp Bot. 2019;70(6):1801–14.
He F, Machemer-Noonan K, Golfier P, Unda F, Dechert J, Zhang W, et al. The in vivo impact of MsLAC1, a Miscanthus laccase isoform, on lignification and lignin composition contrasts with its in vitro substrate preference. BMC Plant Biol. 2019;19(1):552.
Turlapati PV, Kim KW, Davin LB, Lewis NG. The laccase multigene family in Arabidopsis thaliana: towards addressing the mystery of their gene function(s). Planta. 2011;233(3):439–70.
Xu X, Zhou Y, Wang B, Ding L, Wang Y, Luo L, et al. Genome-wide identification and characterization of laccase gene family in Citrus sinensis. Gene. 2019;689:114–23.
Wang Q, Li G, Zheng K, Zhu X, Ma J, Wang D, et al. The soybean laccase gene family: evolution and possible roles in plant defense and stem strength selection. Genes. 2019;10:701.
Simões MS, Carvalho GG, Ferreira SS, Hernandes-Lopes J, de Setta N, Cesarino I. Genome-wide characterization of the laccase gene family in Setaria viridis reveals members potentially involved in lignification. Planta. 2020;251:46.
Liu Q, Luo L, Wang X, Shen Z, Zheng L. Comprehensive analysis of rice laccase gene (OsLAC) family and ectopic expression of OsLAC10 enhances tolerance to copper stress in Arabidopsis. Int J Mol Sci. 2017;18:209.
Zhang W, Lin J, Dong F, Ma Q, Wu S, Ma X, et al. Genomic and allelic analyses of laccase genes in sugarcane (Saccharum spontaneum L.). Trop Plant Biol. 2019;12(3):219–29.
Berni R, Piasecki E, Legay S, Hausman JF, Siddiqui KS, Cai G, et al. Identification of the laccase-like multicopper oxidase gene family of sweet cherry (Prunus avium L.) and expression analysis in six ancient Tuscan varieties. Sci Rep. 2019;9:3557.
Balasubramanian VK, Rai KM, Thu SW, Hii MM, Mendu V. Genome-wide identification of multifunctional laccase gene family in cotton (Gossypium spp.); expression and biochemical analysis during fiber development. Sci Rep. 2016;6:34309.
Wang Y, Tang H, Debarry JD, Tan X, Li J, Wang X, et al. MCScanX: a toolkit for detection and evolutionary analysis of gene synteny and collinearity. Nucleic Acids Res. 2012;40(7):e49.
Munk L, Sitarz AK, Kalyani DC, Dalgaard Mikkelsen J, Meyer AS. Can laccases catalyze bond cleavage in lignin? Biotechnol Adv. 2015;33(1):13–24.
Moiseenko KV, Maloshenok LG, Vasina DV, Bruskin SA, Tyazhelova TV, Koroleva OV. Laccase multigene families in Agaricomycetes. J Basic Microbiol. 2016;56(12):1392–7.
Richardson A, McDougall GJ. A laccase-type polyphenol oxidase from lignifying xylem of tobacco. Phytochemistry. 1997;44(2):229–35.
Asano T, Seto Y, Hashimoto K, Kurushima H. Mini-review an insect-specific system for terrestrialization: Laccase-mediated cuticle formation. Insect Biochem Molec. 2019;108:61–70.
Pourcel L, Routaboul J-M, Kerhoas L, Caboche M, Lepiniec L, Debeaujon I. TRANSPARENT TESTA10 encodes a laccase-like enzyme involved in oxidative polymerization of flavonoids in Arabidopsis seed coat. Plant Cell. 2005;17(11):2966–80.
Vasina DV, Mustafaev ON, Moiseenko KV, Sadovskaya NS, Glazunova OA, Tyurin А, et al. The Trametes hirsuta 072 laccase multigene family: Genes identification and transcriptional analysis under copper ions induction. Biochimie. 2015;116:154–64.
Ping X, Wang T, Lin N, Di F, Li Y, Jian H, et al. Genome-wide identification of the LAC Gene family and its expression analysis under stress in Brassica napus. Molecules. 2019;24(10):1985.
Zhang S, Changliang J, Wang X. Arabidopsis laccase gene AtLAC4 regulates plant growth and responses to abiotic stress. Chinese Bull Bot. 2012;47(4):357–65.
Boerjan W, Ralph J, Baucher M. Lignin biosynthesis. Annu Rev Plant Biol. 2003;54(1):519–46.
Donaldson LA. Lignification and lignin topochemistry—an ultrastructural view. Phytochemistry. 2001;57(6):859–73.
Dean JF, LaFayette PR, Rugh C, Tristram AH, Hoopes JT, Eriksson K-EL. Merkle Laccase associated with lignifying vascular tissues. In: Lewis NG, Sarkanen S, editors. Lignin and lignan biosynthesis. Washington, DC: American Chemical Society; 1998. p. 96–108.
Rojas-Murcia N, Hematy K, Lee Y, Emonet A, Ursache R, Fujita S, et al. High-order mutants reveal an essential requirement for peroxidases but not laccases in Casparian strip lignification. P Natl Acad Sci USA. 2020;117:29166–77.
Xue C, Yao JL, Qin MF, Zhang MY, Allan AC, Wang DF, et al. PbrmiR397a regulates lignification during stone cell development in pear fruit. Plant Biotechnol J. 2019;17(1):103–17.
Qin S, Fan C, Li X, Li Y, Hu J, Li C, et al. LACCASE14 is required for the deposition of guaiacyl lignin and affects cell wall digestibility in poplar. Biotechnol Biofuels. 2020;13(1):197.
Finn RD, Coggill P, Eberhardt RY, Eddy SR, Mistry J, Mitchell AL, et al. The Pfam protein families database: towards a more sustainable future. Nucleic Acids Res. 2016;44:D279–85.
Guo A, Zhu Q, Chen X, Luo J. GSDS: a gene structure display server. Yi Chuan. 2007;29(8):1023–6.
Chen C, Chen H, Zhang Y, Thomas HR, Xia R. TBtools: An integrative toolkit developed for interactive analyses of big biological data. Mol Plant. 2020;13:1194–202.
Wu X, Zhang Z, Sun M, An X, Qi Y, Zhao S, et al. Comparative transcriptome profiling provides insights into endocarp lignification of walnut (Juglans regia L.). Sci Hortic. 2021;282:110030.
Livak KJ, Schmittgen TD. Analysis of relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and the 2-ΔΔCT method. Methods. 2001;25(4):402–8.
Acknowledgements
We would also like to thank Dr. Jin Zhao and Dr. Shoumian Li for valuable suggestions on the data analysis and manuscript.
Funding
This work was supported by the Natural Science Foundation of Hebei Province (C2019204270), the Science and Technology Research Project of the Universities of Hebei Province (QN2019159), Research Foundations for Returned Scholars from Overseas of the Human Resources Dept. of Hebei Province (C20190345) and Hebei Key R&D Program Project (21326352D), Hebei Province Ph.D. graduate student innovation project (CXZZBS2021043). Funds were used for the design of the study, sample collection, analysis or interpretation of data and in writing the manuscript.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
SZ and PL designed the research. PL, PL, HW and SZ performed the experiments, analyzed the data and wrote the paper. KL, XA, YL and ZZ participated in the data analysis. All authors read and approved the final the manuscript.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Ethics approval and consent to participate
Walnut is one of widespread fruit trees in China, and it is not an endangered species. The walnut trees were from the Experimental Field of Hebei Agricultural University. No specific permits are required for sample collection on walnut.
Consent for publication
Not applicable.
Competing interests
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary Information
Additional file 1: Table S1.
Tandem genes of the JrLAC gene family.
Additional file 2: Table S2.
Collinearity data of the JrLAC gene family.
Additional file 3: Table S3.
Expression of JrLAC genes at the unlignified and lignified stages.
Additional file 4: Figure S1.
Heatmap of JrLAC subfamily expression.
Additional file 5.
LAC protein sequences of Arabidopsis.
Additional file 6.
LAC protein Sequences of J. regia.
Additional file 7.
Primers.
Additional file 8.
Relative lignin percentage of different tissues.
Additional file 9.
Original photographs.
Rights and permissions
Open Access This article is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License, which permits use, sharing, adaptation, distribution and reproduction in any medium or format, as long as you give appropriate credit to the original author(s) and the source, provide a link to the Creative Commons licence, and indicate if changes were made. The images or other third party material in this article are included in the article's Creative Commons licence, unless indicated otherwise in a credit line to the material. If material is not included in the article's Creative Commons licence and your intended use is not permitted by statutory regulation or exceeds the permitted use, you will need to obtain permission directly from the copyright holder. To view a copy of this licence, visit http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/. The Creative Commons Public Domain Dedication waiver (http://creativecommons.org/publicdomain/zero/1.0/) applies to the data made available in this article, unless otherwise stated in a credit line to the data.