Abstract
Background
SBP-box genes belong to one of the largest families of transcription factors. Though members of this family have been characterized to be important regulators of diverse biological processes, information of SBP-box genes in the third most important oilseed crop Brassica napus is largely undefined.
Results
In the present study, by whole genome bioinformatics analysis and transcriptional profiling, 58 putative members of SBP-box gene family in oilseed rape (Brassica napus L.) were identified and their expression pattern in different tissues as well as possible interaction with miRNAs were analyzed. In addition, B. napus lines with contrasting branch angle were used for investigating the involvement of SBP-box genes in plant architecture regulation. Detailed gene information, including genomic organization, structural feature, conserved domain and phylogenetic relationship of the genes were systematically characterized. By phylogenetic analysis, BnaSBP proteins were classified into eight distinct groups representing the clear orthologous relationships to their family members in Arabidopsis and rice. Expression analysis in twelve tissues including vegetative and reproductive organs showed different expression patterns among the SBP-box genes and a number of the genes exhibit tissue specific expression, indicating their diverse functions involved in the developmental process. Forty-four SBP-box genes were ascertained to contain the putative miR156 binding site, with 30 and 14 of the genes targeted by miR156 at the coding and 3′UTR region, respectively. Relative expression level of miR156 is varied across tissues. Different expression pattern of some BnaSBP genes and the negative correlation of transcription levels between miR156 and its target BnaSBP gene were observed in lines with different branch angle.
Conclusions
Taken together, this study represents the first systematic analysis of the SBP-box gene family in Brassica napus. The data presented here provides base foundation for understanding the crucial roles of BnaSBP genes in plant development and other biological processes.
Similar content being viewed by others
Background
Transcription factors play a critical role in the life-cycle of plants by activating or suppressing the expression of different target genes [1]. The SQUAMOSA promoter-binding protein (SBP) box family represents one of the transcription factor families characterized by a highly conserved SBP domain, 76 amino acids in length [2–4]. Since the first SBP-box gene was identified in Antirrhinum majus, many such genes have been characterized from different plant species, thus identifying a moderately sized gene family. Sixteen SBP-box genes have been identified in model plant Arabidopsis and many genes have also been characterized in worldwide agriculturally important crops such as rice (Oryza sativa) and maize (Zea mays) [5–7]. The SBP-box genes have been shown to influence many aspects of development including leaf and trichome development, vegetative and reproductive phase transition, plant hormone signaling transduction and other physiological processes [8–15].
Among the identified SBP-box genes, many were proven to play essential roles in diverse development processes. Transgenic plants that constitutively express Arabidopsis gene SPL3 exhibited very early flowering and frequent morphology changes [16]. Arabidopsis spl8 mutants show altered pollen sac development and overexpression of SPL8 influences plant fertility by mediating GA dependent signaling pathway [9, 17]. In addition, SPL8 and other SPL genes control gynoecium patterning through interference with auxin homeostasis [18]. AtSBP7 is a central regulator for copper homeostasis in Arabidopsis [19]. AtSPL2, AtSPL10 and AtSPL11 in Arabidopsis have been demonstrated to control morphological changes associated with shoot maturation in the reproductive phase [20]. BraSPL9-2 is the target of microRNA bra-miR156 and controls the heading time of Chinese cabbage [21]. Besides the important roles reported in dicot plants, SBP-box genes in monocot plant, such as rice and maize, were also shown to modulate essential developmental processes. Higher expression of OsSPL14 in the reproductive stage promotes panicle branching and higher grain yield in rice, suggesting the important roles of SPL genes in plant architecture regulation [22, 23]. Maize transcription factors unbranched2 and unbranched3 encoding SBP-box proteins also alter plant architecture and affect yield traits by regulating the rate of lateral primordia initiation [24].
MiRNAs are small non-coding 20–24 nt RNAs that can complementarily bind to their target mRNAs and reduce protein level through translational repression or transcript cleavage and degradation [25, 26]. Many development processes mediated by SBP-box genes are closely linked to miR156. Computational analysis indicated that many SBP-box genes are regulated by miR156 family in Arabidopsis [27]. Some important developmental processes seem to be mediated by both miR156 and their target SBP-box genes since overexpression of miR156 resulted in various phenotypes, including increased number of leaves, delayed flowering and decreased apical dominance [28]. Arabidopsis miR156 complementarily binds to the 3′UTR of SPL3 mRNA and regulates its expression through translation inhibition and transcript cleavage [16, 29]. Overexpression of rice miR156 also resulted in decreased expression of the SPL target genes, suggesting the correlative interaction of SPL and miR156 in monocot plants [6]. Arabidopsis miR156 regulates tolerance to recurring heat stress and SPL genes are posttranscriptional regulated by miR156 after heat stress [30]. Recently, it is reported that miR156/SPLs modulates Arabidopsis lateral root development [31]. In addition to the regulatory roles of miR156, SBP-box genes were also shown to be regulated by miR529 in grasses [32]. Interestingly, miR156 and miR529 are correlated at the nucleotide level sharing a 14–16 nt binding site [33]. However, no miR529 candidates regulating SBP-box genes were found in core eudicots, such as Arabidopsis and poplar [34, 35].
Despite the essential roles of SBP-box genes in Arabidopsis or rice, information of SBP-box genes in oilseed rape (B. napus) is largely undefined. Genome-wide analysis of SBP-box genes has been performed in several species [36–40]. However, analysis of this gene family has not been conducted in Brassica species. Meanwhile, the interaction between the BnaSBP genes and BnaMiR156 was not clearly understood. In the light of recent findings about SBP-box gene function in Arabidopsis, rice and other organisms, analysis of SBP-box genes in B. napus will certainly accelerate the utilization of these genes. Here we report the systematically analysis of SBP-box genes in B. napus for their gene structure, phylogeny, motif composition, miRNA target site, chromosomal localization and expression pattern in various tissues and organs. Moreover, the relative transcript level of BnamiR156 in various tissues was also examined to study the functional relationship of SBP and miR156 genes.
Methods
Identification and annotation of SBP-box genes in the B. napus genome
Firstly, the HMM profiles of the SBP domains (PF03110) in the Pfam database (http://pfam.xfam.org/) were downloaded and used to search the genome database of B. napus (http://www.genoscope.cns.fr/brassicanapus/) using HHMER search program. All non-redundant sequences were submitted to Interpro (http://www.ebi.ac.uk/interpro) to confirm the presence of the SBP domain. Sequences without complete SBP domain were excluded from the result. We also performed HHMER search against Brassica rapa and Brassica oleracea genome databases to identify SBP proteins. Secondly, Arabidopsis SBP protein sequences were downloaded from TAIR (http://www.arabidopsis.org/) to use as query to perform the BLASTP against B. napus genome. SBP-box gene accession numbers in B. napus genome database were extracted. The nomenclature of putative SBP-box genes in B. napus was in accordance with the homologous gene IDs in Arabidopsis. For one SBP-box gene in Arabidopsis, the orthologous SBP-box genes in oilseed rape were drawn up alphabetically. As the sequence of AtSBP1 and AtSBP12 shows high similarity, only BnaSBP1 genes were named in oilseed rape. SBP-box genes in rice were downloaded from rice genome project (http://rice.plantbiology.msu.edu/).
Gene structure, chromosomal location, duplication and phylogenetic analysis of BnaSBP genes
All the BnaSBP genes were mapped to the B. napus genome chromosomes according to the approximate position information. The exon/intron structure of each BnaSBP genes was displayed in Gene Structure Display Server program (http://gsds.cbi.pku.edu.cn/index.php) by comparing the coding sequence and genomic sequence. MCScanX software (http://chibba.pgml.uga.edu/mcscan2/) was used to analyze the duplication pattern of BnaSBP genes in oilseed rape genome. The local blast + software was used to perform the BLASTP analysis of B. napus with the e-value under 1e-5. The position of SBP-box genes and the blast output were imported into MCScanX software to generate a circle plot under a default criterion. Multiple sequence alignment of SBP-box protein sequence from Oryza sativa, Arabidopsis thaliana and Brasscia napus was performed using ClustalX2.0 with the default parameters [41]. Phylogenetic trees were constructed in MEGA6.0 software using the neighbor-joining (NJ) method and maximum likelihood (ML) method with 1000 bootstrap replications.
Conserved motif identification and miR156 target site prediction
The conserved motifs were identified using the MEME online tool (http://meme-suite.org/) with parameter setup as following: maximum number of motifs, 20; number of repetitions, any; the range of motif width was from 6 to 80. All the identified motifs were searched in InterPro database (http://www.ebi.ac.uk/interpro/) and sequence logos were created using Weblogo online software (http://weblogo.threeplusone.com/). To predict the putative target sites of miR156, full length of BnaSBP genes including exon, intron and UTR sequences were analyzed using psRNATarget tool (http://plantgrn.noble.org/psRNATarget/?function). The conserved target sequences were modified by Genedoc software.
Plant materials and growth condition
Plant samples used for expression pattern analysis and RNA-seq were collected from B. napus var. Zhongshuang 11 at the Oil Crops Research Institute of the Chinese Academy of Agricultural Sciences (OCRI-CAAS). The RNA-seq data were generated from twelve different tissues (root, leaf, bud, silique, stamen, new petal, blooming petal, wilting petal, stem, sepal, ovule and pericarp). The high resolution RNA-seq data of BnaSBP genes were kindly provided by Professor Shengyi Liu from OCRI-CAAS (data not published). The detailed FPKM value (Fragments Per Kilobase of exon model per Million mapped reads) was list in the supplemental data (Additional file 3: Table S2). The FPKM value was log2-transformed and the euclidean distances of all genes were calculated. Clustering tree was constructed and displayed by hierarchical cluster method of “complete linkage clustering” through R package.
To analyze the expression pattern of miR156 and BnaSBP genes, twelve tissue samples were also collected from the same tissue site at the same developmental stage as the sample for RNA-seq. All samples were collected and frozen in liquid nitrogen quickly and stored at the −80 °C. B. napus lines Purler and 6098B, harboring large and small branch angle respectively, were used for expression analysis. Results from different years showed that the branch angle of 6098B was 30−32° larger than that of Purler at the mature stage [42]. Tissue samples at the branch sites were collected at the bolting and early flowering stages for RNA-seq analysis. RNA-seq data were analyzed as described for Zhongshuang 11. Other tissue samples from 6098B and Purler were taken as those from Zhongshuang 11 to perform RT-PCR to verify the RNA-seq result. All plant materials were grown at the field in OCRI-CAAS, Wuhan, China.
RNA extraction and quantitative real-time RT-PCR analysis
Total RNA from diverse tissues at different growth stage was extracted with Trizol Reagent (Invitrogen, America). Before reverse transcription, total RNA was treated with RNase-free DNase I (Promega, America) for 15 min to degrade genomic DNA. Stem-loop RT-PCR was used to examine miR156 expression level in different tissues following the procedure reported previously [43]. miRNA sequences in B. napus were downloaded from miRBase Sequence Database [44]. Primers used for stem-loop RT were designed according to Zhao et al. (2012) [45]. U6 specific primer was added simultaneously as reference for accurate normalization in each reaction. As the mature sequence of miR156 family varies in the 5′ region, five different forward primers were designed for realtime qPCR. qRT-PCR was run in CFX96 Real Time System (Bio-Rad, Hercules, California, USA) using SYBR Green (Tiangen, China) according to the instructions. Briefly, 12.5 μl SYBR mixture, 1 μl universal reverse primer and 1 μl specific primer were added for each reaction. The U6 reaction as a control was conducted using the specific primer. Three replicate reactions were performed for each sample using following program: 10 min at 95 °C, 40 cycles of 5 s at 95 °C, and 30 s at 60 °C. The specificity of the amplification for each primer pair was verified by melting curve analysis. For RT-PCR, two μg of RNA was used for first strand cDNA synthesis with a Transcript First Strand cDNA Synthesis Kit (Tiangen, China) according to manufacturer’s instructions. The reaction was conducted using following program: 5 min at 95 °C, 31–37 cycles of 30 s at 95 °C, 40 s at 54–60 °C and 1 min at 72 °C. Primers used in the qPCR and RT-PCR were listed in Additional file 1: Table S1. The U6 and actin genes were selected as internal reference genes as described previously [45].
Results
Identification of SBP genes in B. napus
All Arabidopsis SBP protein sequences were used as queries for TBLASTN. As a result, fifty-eight putative SBP-box genes were identified initially. All the subsequences were checked by Interpro tool to search the SBP domain. Three proteins without SBP domain or with incomplete SBP domain were excluded. HHMER search was also performed against the B. napus protein database with SBP-domain PF03110 as a query. Ten additional protein sequences were obtained; however, only three of them contain the complete SBP domain checked by Interpro scan. Ultimately, fifty-eight SBP proteins were identified. Six SBP proteins could not be allocated at any B. napus chromosome accurately. All SBP-box genes in B. napus are designated as BnaSBP and named according to the order of closest orthologues in Arabidopsis. The accession number, chromosome distribution, protein molecular weight and length of the BnaSBP genes were listed in Table 1. HHMER search against Brassica rapa and Brassica oleracea genomes resulted in twenty-six and nineteen SBP proteins, respectively. Previous results have shown that sixteen SBP proteins exist in Arabidopsis. By comparison on number of genes in the three closely related species, SBP-box gene family members in B. napus showed an obvious expansion on number of genes.
Chromosome localization and gene duplication analysis
To determine chromosome distribution and gene duplication of SBP genes in B. napus, all the SBP genes except four located on unanchored scaffolds, were mapped to approximate chromosome positions (Fig. 1). These fifty-four SBP genes were unevenly distributed on the Brassica chromosomes. Except for A8 and C8, all chromosomes harbor at least one of the SBP genes. On chromosome A1, A3 and C1, only one SBP gene was found. Four chromosomes contain the maximum number of SBP genes, i.e., A5, A7, C4 and C5 each has five SBP genes. Four clusters each with two SBP genes were identified by the criteria that the distance of adjacent SBP genes is less than 50 kb. Twenty-six and thirty-two SBP genes were found to located at the A genome and C genome respectively. It was interesting to find that the number of SBP genes located at the A genome of B. napus was equal to the number of SBP gene found in the B. rapa genome. However, only 19 SBP genes were identified in B. oleracea genome, which is the progenitor of the C genome in B. napus, indicating that the SBP gene expansion may have occurred in the polyploid C genome.
The tandem and segmental duplication of Brassica SBP genes were also analyzed. Among all the SBP genes, eight members (13.8 %) showed tandem repeats, which include four clusters of tandem repeat genes (Fig. 1). In addition, 49 (84.5 %) of the fifty-eight BnaSBP genes were found to be segmentally duplicated genes. These genes were located at seventeen different chromosomes (Fig. 2).
Structural organization and conserved domain identification
To understand the evolutionary relationship among SBP protein in B. napus, we constructed the unrooted tree based on the alignments of full-length SBP protein sequences using neighbor-joining (NJ) method in MEGA 6.0. The fifty-eight SBP proteins in B. napus were divided into eight distinct groups (from Ito VII). Group I consist of the maximum number (14) of BnaSBPs, while group Vcontains only three BnaSBPs. The entire tandem duplicated BnaSBPs were assigned to one group, in accordance with the results reported in other species, such as tomato, Populus trichocarpa [40, 46]. The genomic sequence of the BnaSBP genes ranged from 510 bp to about 5 kb. To obtain further gene structure information, we compared the coding sequence with the genomic sequence of all BnaSBP genes (Fig. 3a). Different introns (from 0 to 10) were observed among the BnaSBP genes. Except BnaSBP6d, all BnaSBP genes contain at least one intron. The genes possess maximum number of introns were in group IV and VII. The BnaSBP gene clusters that were divided into the same group exhibited similar structure. Several motifs were identified among SBP proteins in B. napus (Fig. 3b). One motif (S) containing the SBP-domain was detected in all BnaSBP proteins except BnaSBP8b which contains a similar SBP-domain that could not be detected due to missing of a few amino acids. The BnaSBP protein in the same group exhibited similar motif composition.
Phylogenetic relationship and gene structure of SBP-box genes in B. napus. a Unrooted phylogenetics tree and structures of SBP-box genes. Unrooted phylogenetic tree was created in MEGA6 software with the neighbor-joining method with 1000 bootstrap iterations according to the 58 coding sequence of SBP-box genes. Exons and introns were represented by boxes and lines, respectively. Size of exons and introns can be estimated using the scale bar at bottom. b Motif prediction of BnaSBP proteins. Twenty motifs were identified by MEME online tool. Each motif is represented by a colored block. S represents the SBP domain. The length and position of the motifs could be estimated according to the scale bar
All the BnaSBP proteins were aligned by the ClustalX 2.0 and the conserved SBP domain was created by the Weblogo online tools. Fifty-eight BnaSBP proteins contained the complete SBP domain with two Zinc motifs and one nuclear localization signal (Fig. 4). The first zinc finger motif was C3H type in all the SBP proteins except BnaSBP5 group. All the SBP proteins contain the second CCHC type zinc motif. As SBP proteins possess the character of transcription factors, all the SBP proteins contain the conserved nuclear localization signal.
Sequence logo of the B. napus SBP-box domain. Multiple sequence alignment was performed by using clustalW2. Sequence logo was obtained from Weblogo online software. The X-axis represents the conserved sequences of the SBP domain. The overall height of letters represents residue conservation. The Y-axis reflects the conservation rate of each amino acid. Two zinc finger and one nuclear localization signal motifs are indicated
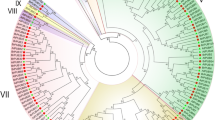
Phylogenetic analysis of SBP genes in B. napus, Arabidopsis and rice
The phylogenetic relationship among BnaSBP genes and other SBP genes with known functions from other species is useful for predicting their roles in oilseed rape development. Sixteen SBP genes from Arabidopsis and nineteen SBP genes from rice, which are model plants for dicot and monocot species respectively, were extracted from the public gene pool. Fifty-eight SBP genes from oilseed rape together with the Arabidopsis and rice genes were used for the construction of an unrooted phylogenetic tree (Fig. 5, Additional file 2: Figure S2). According to phylogenetic analysis, SBP genes from these three plant species can be classified into seven groups (SBP-a to SBP-h). The largest group (SBP-e) contains 21 members which account for 23 % of the total SBPs, whereas group SBP-a forms the smallest group containing only five members. As shown in Fig. 5, genes in group SBP-a were more diverged than those in other groups. BnaSBP genes showed a high similarity to their orthologs from Arabidopsis and were classified into the same group. Among the groups revealed by phylogenetic analysis, group SBP-f only contain SBPs from Arabidopsis and oilseed rape, indicating the diversification of SBP genes between monocot and dicot plants.
Phylogenetic analysis of BnaSBP proteins. The protein sequences of SBP-box from Arabidopsis (AtSBP), rice (OsSBP) and B. napus (BnaSBP) were aligned using ClustalW. The phylogenetic tree was constructed using the neighbor-joining algorithm with 1000 replications. Nodes with bootstrap values of >50 % are dotted. Bar indicates 0.05 aa substitution per residue
MiR156 family in B. napus and their target site to BnaSBP genes
Seven putative members of miR156 (BnaMiR156a-g) in oilseed rape were found after querying the miRBase database. Recently, thirty-two putative pre-mature structures of miR156 were predicted in B. napus by high throughput small RNA deep sequencing [47]. Previous results showed that miR156 complementarily bind to SBP genes either at the coding or 3′UTR region and reduced gene activity by translation suppression or cleavage [27, 29]. It was shown that 44 SBP proteins have miR156 binding site, with 30 and 14 at coding and 3′UTR regions, respectively (Fig. 6). According to previous results, 11 out of 17 SBP genes in Arabidopsis are targeted by miR156. The homologous genes in oilseed rape are also predicted to be target of miR156. These results suggest that relationship between miR156 and SBP genes is conserved across species. However, three BnaSBP genes targeted by miR156 differed from other genes. BnaSBP5c possesses the binding site within the coding region, while the other three BnaSBP5 genes are targeted by miR156 in 3′UTR. MiR156 was predicted to bind to 3′UTR sequence of BnaSBP6d and BnaSBP10a, while the relative homologous gene in Arabidopsis were bound by miR156 at the coding region. The distinct regulation pattern of the homologous genes between B. napus and Arabidopsis reveals the divergence of the SBP-box genes in oilseed rape.
Expression profile of BnaSBP
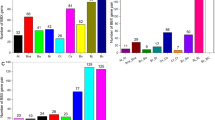
A wide range of SBP genes play important roles in plant development process. In the absence of SBP gene mutants, the expression pattern may provide a clue to elucidate the potential role of the different SBP genes in B. napus. The expression level of BnaSBP genes in twelve tissues were shown by heat map representation (Fig. 7, Additional file 3: Table S2). Transcript of BnaSBP6c was zero in all twelve tissue samples and only very low expression level of BnaSBP4c in leaf was detected. Based on the hierarchical clustering analysis, the BnaSBP genes could be divided into eight categories. The transcription of a large number of BnaSBP genes was enriched in bud, stamen and pericarp. By contrast, most of BnaSBP genes exhibit low expression level in ovule and petal. Eight BnaSBP genes, BnaSBP1a, 1b, 11e, 14a, 14b, 14c, 16a and 16b seemed to be expressed constitutively, from root to pericarp. It should be noted that all these genes, excluding BnaSBP11e, are not predicted to be targeted by the miR156. BnaSBP4c, 4d, 5c, 5d, 10d and 13d sustained low expression level in most tissues. The expression level of BnaSBP3a and 3d was not detected in most tissue samples, but reached clearly higher levels in pericarp. A relative higher expression level of BnaSBP2b and 11d could also be discerned in root tissue. Compared with the SBP genes not bound by miRNA, the BnaSBP genes have the target site represent more divergent expression pattern. We also performed RT-PCR to confirm the expression levels of some BnaSBPs in eight different tissues (Fig. 8). Thirty-nine BnaSBPs were selected to verify the result of RNA-seq data. Results showed that RT-PCR data was generally consistent with RNA-seq data for relative expression of BnaSBPs in most of the tissues. For example, expression level of BnaSBP1a, 1b and 11e could be detected in most tissues (Fig. 8). Though BnaSBPs were expressed at least in one of the tissues, distinction of expression patterns were observed across the gene groups. Some BnaSBPs belongs to a same group exhibited similar expression pattern, such as BnaSBP1a and 1b in group IV, BnaSBP15a and 15b in group III, indicating redundant roles of BnaSBPs in the same group. Therefore, the oilseed rape SBP transcription factors have diverse expression patterns and may be redundant in biological function with each individual in charge of certain physiological processes.
Expression patterns of BnaSBP genes in twelve different tissue samples. Color scale bar at the top of map represents log2 transformed FPKM values, which represents low and high expression, respectively. Tissues used for expression profiling are indicated at the top of each column. The genes are on right of expression bar
Analysis expression level of BnaSBP genes in eight different tissue samples of Zhongshuang 11 by RT-PCR. Tissues used for expression profiling are indicated at the top of each column. Lf, leaf; Bd, bud; Sq, silique; St, Stamen; Pe, petal; Sm, stem; Pr, pericarp; Ps, pistil. The genes are on left of expression bar. Actin, BnaSBP11e and 2b gene was amplified with 28, 31 and 37 cycles respectively. Other BnaSBPs genes were amplified with 35 cycles
To investigate the putative genes involved in branch angle regulation, the expression profile of two B. napus material (6098B and Purler) with different branch angle was conducted (Additional file 4: Figure S1). Sample of branch site from two materials at bolting and early flowering stage was harvested to perform DEGs (Different Expression Genes). The transcription level of all SBP genes was extracted from expression profile (Additional file 5: Table S3). Heat maps representing expression levels in the lines at two developmental stages are shown in Fig. 8. Many BnaSBP genes showed different expression patterns between the two lines at the two development stages. BnaSBP5c, 8a and 7d showed high expression at bolting stage but no or little expression at early flowering stage in the two materials. Ten and thirteen BnaSBP genes were found differentially expressed between the two lines at the two development stages, respectively. Among them, six BnaSBP genes were differentially expressed at the two development stages (Fig. 9). Further studies may focus on the role of these genes on branch angle regulation. RT-PCR was performed to confirm the expression level of BnaSBPs in the same tissues used for RNA-seq. A large number of BnaSBPs in Purler expressed at higher level than those in 6098B (Fig. 10). This RT-PCR result was generally consistent with that from RNA-seq data.
Expression patterns of BnaSBP genes in the branching site of 6098B and Purler at the bolting and early flowering stages. Color scale bar at the top of heat map represents log2 transformed FPKM value, which represent low and high expression, respectively. Tissues used for expression profiling are indicated at the top of each column. The genes are on right of expression bar
Expression level of BnaSBP genes in the branching site of 6098B and Purler at the bolting and early flowering stages by RT-PCR. Tissues used for expression profiling are indicated at the top of each column. B1, branch site in 6098B; B2, branch site in Purler. Bolting and early flowering time represent sampling time. The genes are on left of expression bar. Actin, BnaSBP11e and 2b gene was amplified with 28, 31 and 37 cycles respectively. Other BnaSBPs genes were amplified with 35 cycles
Expression profile of miR156
Several BnaSBP genes carry the complementary sequences to miR156. MiR156 was thus expected to be an important determinant for the expression of these BnaSBP genes. The expression level of miR156 was mostly abundant in bud and silique of Zhongshuang 11 at different developmental stages (Fig. 11a). Relative low levels were found in leaf sample. Meanwhile, the expression level of miR156 in 6098B and Purler was also determined. It was showed that the abundance of miR156 decreased significantly at early flowering time compared to bolting time (Fig. 11b). Besides the stem sample of two materials, the transcription of miR156 was stronger in Purler than in 6098B of the other tissues.
The expression patterns of miR156 in different tissue samples. Relative expression levels of mature miR156 in different tissues were analyzed by qRT-PCR. a The expression level of miR156 in the different tissue samples of Zhongshuang11. The value was normalized to the root at the seedling stage. R, root; St, stem; L, leaf; B, bud; Sl1, silique 15 days after flowering; Sl2, silique 18 days after flowering; Sl3, silique 20 days after flowering; Sl4, silique 23 days after flowering. b The expression level of miR156 in five tissue samples of Puler and 6098B respectively. The value was normalized to 6098B at the bolting stage. L, leaf; B, bud; St, stem; Bs1, branch site at the bolting stage; Bs2, branch site at the early flowering stage. Asterisks indicate a significant difference was detected between Purler and 6098B in the same tissue sample by t-test at *P < 0.01
Discussion
SBP-box genes in Brasscia and their evolution
The SBP-box proteins are characterized by a conserved SBP domain with 76 amino acids and constitute one large family of transcription factors in plants. Plant specific SBP-box transcription factors were only detected in green plants suggesting that it might originate predating the divergence of green algae and the ancestor of land plants [5, 48]. Different numbers of SBP-box genes have been characterized in various land plants [39, 40, 49]. In present study, 58 SBP-box genes in B. napus genome were identified, which is about four times the number of Arabidopsis SBP-box genes. B. napus contains 13 more SBP-box genes than the sum of B. rapa (AA, 2n = 20) and B. oleracea (CC, 2n = 18), which are two immediate progenitor species of B. napus (AACC, 2n = 38) [50]. For one gene family, tandem and segmental duplication events are the main reasons for gene expansion. SBP-box genes are unevenly distributed on 17 of the 19 chromosomes of B. napus, and four clusters each with two BnaSBPs were identified (Fig. 1). Uneven and cluster distribution of SBP-box gene family genes was also found in rice and peach [6]. There are seven and 49 BnaSBP genes which were found to be tandem and segmental duplications respectively. Diversification of BnaSBP genes was observed from many aspects, including phylogenesis, genomic structure, as well as location of miR156 target site. This diversity of SBP-box gene structure is likely to be trigged by gene duplication followed by intron and exon loss.
Functional divergence of SBP-box genes
As the SBP-box genes possess the character of transcription factors, their expression pattern is expected to be correlated with their function on plant development. The expression profile of BnaSBP-box genes showed distinct expression patterns among different tissues. In Arabidopsis, some SPL genes are constitutively expressed, while the transcription level of others is under developmental control [5]. Expression analysis of SBP-box genes in other organisms also presented diverse spatiotemporal expression patterns [39, 40, 49, 51]. SBP transcription factors in B. napus showed diverse expression patterns across tissues, indicating their possible functions in various biological processes. The transcription of a large number of BnaSBP genes was enriched in bud, stamen and pericarp, suggesting most of the SBP-box genes in oilseed rape may be involved in the development of reproductive organs.
SBP-box genes in many species, especially in rice and Arabidopsis, have been demonstrated to play essential roles in diverse developmental processes. The microRNA regulated SBP-box genes SPL9 and SPL15, which are the most close orthologous genes in Arabidopsis, was proven to control shoot maturation [52]. Further support of possible roles for BnaSBP in development comes from the rice genes SPL14 in panicle development and ideal rice plant architecture regulation [22, 23]. We identified four BnaSBP9 genes in oilseed rape genome. Although the BnaSBP9 genes possess similar gene structure, diverse expression patterns were observed. It should be noted that the expression of BnaSBP9d in the compact material Purler is higher than in the loose material 6098B (Figs. 9 and 10). The expression of BnaSBP9d visibly decreased from bolting to early flowering. Further study should be performed to verify whether BnaSBP9d might play a role in regulating branch angle in oilseed rape.
Arabidopsis gene SPL8 affects pollen sac development and also controls gynoecium patterning [18]. Three BnaSBP genes, BnaSBP8a, 8b and 8c showed most similarity to AtSBP8,joining the same group through phylogenetic analysis. BnaSBP8a and BnaSBP8b were highly expressed in the stamen. Further study may focus on the potential role of BnaSBP8 in flower development.
Constitutive expression of AtSPL3 resulted in early flowering [53]. The SPL3 homologous genes in Antirrhinum majus and Silver birch also regulate flower development by binding to the MADS-box genes [16, 54]. Tomato LeSPL-CNR, which is most similar to AtSPL3 gene, is crucial for normal fruit development and ripening [55]. In Arabidopsis, miR156-SPL3 module controls FT expression to regulate ambient temperature-responsive flowering [56]. Among the five genes homologous to AtSPL3 identified in B. napus in our study, BnaSBP3c showed much higher expression level in bud, stamen, silique and pericarp, indicating a possible role in the reproduction phase. Arabidopsis gene AtSPL2, AtSPL10 and AtSPL11 were shown to play important roles in determining leaf shape and embryonic morphogenesis [20, 57]. All the BnaSBP2, 10 and 11 genes were classified into a same group of SBP-e. It would be interesting to explore the exact role of these group SBP-box genes by functional characterization.
Conservation of miR156 target site in SBP-box genes
A larger number of miRNAs targets are transcription factors, such as SBP, MYB, NAC, ARF, GRAS, and AP2 [27]. MiRNAs play important roles in regulating the transcription of target genes. Previous results showed that overexpression of miR164, miR159a, and miR319 affected members of the NAC, MYB, and TCP families of transcription factor genes, respectively [58–60]. In present study, target prediction showed that 44 of the 58 BnaSBP genes were regulated by miR156. The complementary sites of miR156 locate in the coding region of 30 BnaSBP genes, and in the 3′ UTR of the other 14 BnaSBP genes. In Arabidopsis, 10 (AtSBP2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 9, 10, 11, 13, 15) out of 17 SBP genes were predicted or verified to be targeted by miR156. The other six AtSBP genes including (AtSBP1, 7, 8, 12, 14, 16) are not targets of miR156. AtSPL7 has been demonstrated to bind directly to the Cu-response element (CuRE) containing a core sequence of GTAC and regulate Cu homeostasis [3]. The 44 BnaSBP genes predicted to be targeted by miR156 are the homologous genes in Arabidopsis, which also formed 10 gene clusters. Therefore, the miR156 target site in SBP-box genes is conserved across plant species.
Over-expression of miR156 in Arabidopsis significantly represses the SPL transcription and thus reduces apical dominance, leading to dwarfism and increases in total leaf number and plant biomass [28]. The transcripts of the target SBP genes were also suppressed in other miR156 over-expression plants [29, 56]. In present study, the transcript level of miR156 was abundant in bud and silique (Fig. 11). By contrast, most putative target SBP genes with predicted miR156 target sites showed lower expression level in these tissues (Figs. 9 and 10). Among the floral organs, most BnaSBP genes showed a low expression level in petal and ovule, though transcript was relatively high in pericarp, which is a main component of silique. These results suggested that the transcript of miR156 is negatively correlated with the expression of most BnaSBP genes. The level of miR156 was declined with a concomitant rise in SPL levels during the aging time in Arabidopsis [61]. SPL9 and SPL10 mediated the transition from high levels of miR156 to high levels of miR172 through direct activation of miR172 expression, thereby promoting the juvenile to adult phase transition [57, 62]. Our results showed that the lower expression level of miR156 in 6098B with bigger branch angle than in Purler with smaller branch angle (Fig. 11) is negatively correlated with the expression difference of many SBP-box genes, eg. BnaSBP2a, 2d, 3d, 3e, 5d, 8b, 9a, 9b, 10b, 11a, 11c, 13d and 15c (Figs. 9 and 10), indicating that the SBP/miR156 module is likely involved in regulating plant architecture in B. napus.
Conclusion
By genome wide analysis of SBP-box genes in oilseed rape (B. napus L), 58 SBP-box genes were identified in the B. napus genome. The BnaSBP proteins were classified into eight different groups and showed clear orthologous relationships of SBP members from rice and Arabidopsis. Our results showed that many SBP-box genes, which were predicted to be targeted by miR156, have tissue specific expression pattern and the expression pattern diverged after gene duplication. The expression level of miR156s was abundant in the root, flowers and silique samples. The different expression pattern between the miR156 and SBP-box genes in diverse tissues suggests that SBP/miR156 module may play an important role in the development processes. Eleven SBP-box gene groups, similar to those in Arabidopsis, were predicted to be targeted by miR156, implying the conservation of SBP/miR156 module regulation pattern. The involvement of some BnaSBP genes as well as the SBP/miR156 module in plant architecture regulation was also implicated from the results. Taken together, our data presented here provide valuable information for further study on the function of SBP-box in B. napus.
Abbreviations
CuRE, Cu-response element; Mw, The molecular weight; SBP, squamosa promoter binding protein
References
Gong W, Shen YP, Ma LG, Pan Y, Du YL, Wang DH, Yang JY, Hu LD, Liu XF, Dong CX, Ma L, Chen YH, Yang XY, Gao Y, Zhu D, Tan X, Mu JY, Zhang DB, Liu YL, Dinesh-Kumar SP, Li Y, Wang XP, Gu HY, Qu LJ, Bai SN, Lu YT, Li JY, Zhao JD, Zuo J, Huang H, Deng XW, Zhu YX. Genome-wide ORFeome cloning and analysis of Arabidopsis transcription factor genes. Plant Physiol. 2004;135:773–82.
Klein J, Saedler H, Huijser P. A new family of DNA binding proteins includes putative transcriptional regulators of the Antirrhinum majus floral meristem identity gene SQUAMOSA. Mol Gen Genet. 1996;250:7–16.
Yamasaki K, Kigawa T, Inoue M, Tateno M, Yamasaki T, Yabuki T, Aoki M, Seki E, Matsuda T, Nunokawa E. A novel zinc binding motif revealed by solution structures of DNA-binding domains of Arabidopsis SBP-family transcription factors. J Mol Biol. 2004;337:49–63.
Birkenbihl RP, Jach G, Saedler H, Huijser P. Functional dissection of the plant-specific SBP-domain: overlap of the DNA-binding and nuclear localization domains. J Mol Biol. 2005;352:585–96.
Cardon G, Hohmann S, Klein J, Nettesheim K, Saedler H, Huijser P. Molecular characterisation of the Arabidopsis SBP-box genes. Gene. 1999;237:91–104.
Xie K, Wu C, Xiong L. Genomic organization, differential expression, and interaction of SQUAMOSA promoter-binding like transcription factors and microRNA156 in rice. Plant Physiol. 2006;142:280–93.
Hultquist JF, Dorweiler JE. Feminized tassels of maize mop1 and ts1 mutants exhibit altered levels of miR156 and specific SBP-box genes. Planta. 2008;229:99–113.
Moreno MA, Harper LC, Krueger RW, Dellaporta SL, Freeling M. liguleless1 encodes a nuclear-localized protein required for induction of ligules and auricles during maize leaf organogenesis. Genes Dev. 1997;11:616–28.
Zhang Y, Schwarz S, Saedler H, Huijser P. SPL8, a local regulator in a subset of gibberellin-mediated developmental processes in Arabidopsis. Plant Mol Biol. 2007;63:429–39.
Wang JW, Schwab R, Czech B, Mica E, Weigel D. Dual effects of miR156-targeted SPL genes and CYP78A5/KLUH on plastochron length and organ size in Arabidopsis thaliana. Plant Cell. 2008;20:1231–43.
Nodine MD, Bartel DP. MicroRNAs prevent precocious gene expression and enable pattern formation during plant embryogenesis. Genes Dev. 2010;24:2678–92.
Martín-Trillo M, Cubas P. TCP genes: a family snapshot ten years later. Trends Plant Sci. 2010;15:31–9.
Xing S, Salinas M, Hohmann S, Berndtgen R, Huijser P. miR156-targeted and nontargeted SBP-box transcription factors act in concert to secure male fertility in Arabidopsis. Plant Cell. 2010;22:3935–50.
Yu N, Cai W, Wang S, Shan C, Wang L, Chen X. Temporal control of trichome distribution by microRNA156-targeted SPL genes in Arabidopsis thaliana. Plant Cell. 2010;22:2322–35.
Huijser P, Schmid M. The control of developmental phase transitions in plants. Development. 2011;138:4117–29.
Gandikota M, Birkenbihl RP, Höhmann S, Cardon GH, Saedler H, Huijser P. The miRNA156/157 recognition element in the 3′UTR of the Arabidopsis SBP box gene SPL3 prevents early flowering by translational inhibition in seedlings. Plant J. 2007;49:683–93.
Unte US, Sorensen A, Pesaresi P, Gandikota M, Leister D, Saedler H, Huijser P. SPL8, an SBP-box gene that affects pollen sac development in Arabidopsis. Plant Cell. 2003;15:1009–19.
Xing S, Salinas M, Garcia-Molina A, Höhmann S, Berndtgen R, Huijser P. SPL8 and miR156-targeted SPL genes redundantly regulate Arabidopsis gynoecium differential patterning. Plant J. 2013;75:566–77.
Yamasaki H, Hayashi M, Fukazawa M, Kobayashi Y, Shikanai T. SQUAMOSA promoter binding protein–like7 is a central regulator for copper homeostasis in Arabidopsis. Plant Cell. 2009;21:347–61.
Shikata M, Koyama T, Mitsuda N, Ohme-Takagi M. Arabidopsis SBP-box genes SPL10, SPL11 and SPL2 control morphological change in association with shoot maturation in the reproductive phase. Plant Cell Physiol. 2009;50:2133–45.
Wang T, Pan H, Wang J, Yang W, Cheng T, Zhang Q. Identification and profiling of novel and conserved microRNAs during the flower opening process in Prunus mume via deep sequencing. Mol Genet Genomics. 2014;289:169–83.
Jiao Y, Wang Y, Xue D, Wang J, Yan M, Liu G, Dong G, Zeng D, Lu Z, Zhu X, Qian Q, Li J. Regulation of OsSPL14 by OsmiR156 defines ideal plant architecture in rice. Nat Genet. 2010;42:541–4.
Miura K, Ikeda M, Matsubara A, Song X, Ito M, Asano K, Matsuoka M, Kitano H, Ashikari M. OsSPL14 promotes panicle branching and higher grain productivity in rice. Nat Genet. 2010;42:545–9.
Chuck GS, Brown PJ, Meeley R, Hake S. Maize SBP-box transcription factors unbranched2 and unbranched3 affect yield traits by regulating the rate of lateral primordia initiation. Proc Natl Acad Sci. 2014;111:18775–80.
Voinnet O. Origin, biogenesis, and activity of plant microRNAs. Cell. 2009;136:669–87.
Rogers K, Chen X. Biogenesis, turnover, and mode of action of plant microRNAs. Plant Cell. 2013;25:2383–99.
Rhoades MW, Reinhart BJ, Lim LP, Burge CB, Bartel B, Bartel DP. Prediction of plant microRNA targets. Cell. 2002;110:513–20.
Schwab R, Palatnik JF, Riester M, Schommer C, Schmid M, Weigel D. Specific effects of microRNAs on the plant transcriptome. Dev Cell. 2005;8:517–27.
Wu G, Poethig RS. Temporal regulation of shoot development in Arabidopsis thaliana by miR156 and its target SPL3. Development. 2006;133:3539–47.
Stief A, Altmann S, Hoffmann K, Pant BD, Scheible WR, Baurle I. Arabidopsis miR156 regulates tolerance to recurring environmental stress through SPL transcription factors. Plant Cell. 2014;26:1792–807.
Yu N, Niu QW, Ng KH, Chua NH. The role of miR156/SPLs modules in Arabidopsis lateral root development. Plant J. 2015;83:673–85.
Jeong DH, Park S, Zhai J, Gurazada SG, De Paoli E, Meyers BC, Green PJ. Massive analysis of rice small RNAs: mechanistic implications of regulated microRNAs and variants for differential target RNA cleavage. Plant Cell. 2011;23:4185–207.
Cuperus JT, Fahlgren N, Carrington JC. Evolution and functional diversification of MIRNA genes. Plant Cell. 2011;23:431–42.
Zhang SD, Ling LZ, Yi TS. Evolution and divergence of SBP-box genes in land plants. BMC Genomics. 2015;16:787.
Morea EG, da Silva EM, E Silva GF, Valente GT, Barrera Rojas CH, Vincentz M, Nogueira FT. Functional and evolutionary analyses of the miR156 and miR529 families in land plants. BMC Plant Biol. 2016;16:40.
Riese M, Höhmann S, Saedler H, Münster T, Huijser P. Comparative analysis of the SBP-box gene families in P. patens and seed plants. Gene. 2007;401:28–37.
Yang Z, Wang X, Gu S, Hu Z, Xu H, Xu C. Comparative study of SBP-box gene family in Arabidopsis and rice. Gene. 2008;407:1–11.
Hou H, Li J, Gao M, Singer SD, Wang H, Mao L, Fei Z, Wang X. Genomic organization, phylogenetic comparison and differential expression of the SBP-box family genes in grape. PLoS One. 2013;8:e59358.
Li J, Hou H, Li X, Xiang J, Yin X, Gao H, Zheng Y, Bassett CL, Wang X. Genome-wide identification and analysis of the SBP-box family genes in apple (Malus domestica Borkh.). Plant Physiol Bioch. 2013;70:100–14.
Li C, Lu S. Molecular characterization of the SPL gene family in Populus trichocarpa. BMC Plant Biol. 2014;14:131.
Larkin MA, Blackshields G, Brown NP, Chenna R, McGettigan PA, McWilliam H, Valentin F, Wallace IM, Wilm A, Lopez R, Thompson JD, Gibson TJ, Higgins DG. Clustal W and Clustal X version 2.0. Bioinformatics. 2007;23:2947–8.
Liu J, Wang W, Mei D, Wang H, Fu L, Liu D, Li Y, Hu Q. Characterizing variation of branch angle and genome-wide association mapping in rapeseed (Brassica napus L.). Front Plant Sci. 2016;7:21.
Shen J, Xie K, Xiong L. Global expression profiling of rice microRNAs by one-tube stem-loop reverse transcription quantitative PCR revealed important roles of microRNAs in abiotic stress responses. Mol Genet Genomics. 2010;284:477–88.
Kozomara A, Griffiths-Jones S. miRBase: annotating high confidence microRNAs using deep sequencing data. Nucleic Acids Res. 2014;42:68–73.
Zhao YT, Wang M, Fu SX, Yang WC, Qi CK, Wang XJ. Small RNA profiling in two Brassica napus cultivars identifies microRNAs with oil production- and development-correlated expression and new small RNA classes. Plant Physiol. 2012;158:813–23.
Salinas M, Xing S, Höhmann S, Berndtgen R, Huijser P. Genomic organization, phylogenetic comparison and differential expression of the SBP-box family of transcription factors in tomato. Planta. 2012;235:1171–84.
Shen E, Zou J, Hubertus Behrens F, Chen L, Ye C, Dai S, Li R, Ni M, Jiang X, Qiu J, Liu Y, Wang W, Zhu QH, Chalhoub B, Bancroft I, Meng J, Cai D, Fan L. Identification, evolution, and expression partitioning of miRNAs in allopolyploid Brassica napus. J Exp Bot. 2015; erv420. [Epub ahead of print]
Guo AY, Zhu QH, Gu X, Ge X, Yang J, Luo J. Genome-wide identification and evolutionary analysis of the plant specific SBP-box transcription factor family. Gene. 2008;418:1–8.
Zhang S, Ling L. Genome-wide identification and evolutionary analysis of the SBP-Box gene family in Castor Bean. PLoS One. 2014;9:e86688.
UN. Genome analysis in Brassica with special reference to the experimental formation of B. napus and peculiar mode of fertilization. Jpn J Bot. 1935;7:389–452.
Xu Z, Sun L, Zhou Y, Yang W, Cheng T, Wang J, Zhang Q. Identification and expression analysis of the SQUAMOSA promoter-binding protein (SBP)-box gene family in Prunus mume. Mol Genet Genomics. 2015;290:1701–15.
Schwarz S, Grande AV, Bujdoso N, Saedler H, Huijser P. The microRNA regulated SBP-box genes SPL9 and SPL15 control shoot maturation in Arabidopsis. Plant Mol Biol. 2008;67:183–95.
Cardon G, Höhmann S, Nettesheim K, Saedler H, Huijser P. Functional analysis of the Arabidopsis thaliana SBP-box gene SPL3: a novel gene involved in the floral transition. Plant J. 1997;12:367–77.
Lännenpää M, Jänönen I, Hölttä Vuori M, Gardemeister M, Porali I, Sopanen T. A new SBP-box gene BpSPL1 in silver birch (Betula pendula). Physiol Plantarum. 2004;120:491–500.
Manning K, Tör M, Poole M, Hong Y, Thompson AJ, King GJ, Giovannoni JJ, Seymour GB. A naturally occurring epigenetic mutation in a gene encoding an SBP-box transcription factor inhibits tomato fruit ripening. Nat Genet. 2006;38:948–52.
Kim JJ, Lee JH, Kim W, Jung HS, Huijser P, Ahn JH. The microRNA156-SQUAMOSA PROMOTER BINDING PROTEIN-LIKE3 module regulates ambient temperature-responsive flowering via FLOWERING LOCUS T in Arabidopsis. Plant Physiol. 2012;159:461–78.
Wu G, Park MY, Conway SR, Wang JW, Weigel D, Poethig RS. The sequential action of miR156 and miR172 regulates developmental timing in Arabidopsis. Cell. 2009;138:750–9.
Achard P, Herr A, Baulcombe DC, Harberd NP. Modulation of floral development by a gibberellin-regulated microRNA. Development. 2004;131:3357–65.
Laufs P, Peaucelle A, Morin H, Traas J. MicroRNA regulation of the CUC genes is required for boundary size control in Arabidopsis meristems. Development. 2004;131:4311–22.
Palatnik JF, Allen E, Wu X, Schommer C, Schwab R, Carrington JC, Weigel D. Control of leaf morphogenesis by microRNAs. Nature. 2003;425:257–63.
Wang JW, Czech B, Weigel D. miR156-regulated SPL transcrip-tion factors define an endogenous flowering pathway in Arabidopsis thaliana. Cell. 2009;138:738–49.
Fornara F, Coupland G. Plant phase transitions make a SPLash. Cell. 2009;138:625–7.
Acknowledgments
We would like to thank Dr. Rachel Wells in John Innes Centre for revision and comments on the manuscript.
Funding
This work was supported by the Science and technology innovation project of Chinese Academy of Agricultural Sciences(Group No. 118),the Earmarked Fund for China Agriculture Research System (CARS-13), the Hubei Agricultural Science and Technology Innovation Center and Hubei National Science Foundation (2015CFA103).
Availability of supporting data
The data sets supporting the results of this article are included within the article and its additional files. Materials described in the article will be freely available upon request to any scientist wishing to use them for non-commercial purposes. Phylogenetic and genomic data could be achieved from Dryad database (http://dx.doi.org/10.5061/dryad.3rk33).
Authors’ contributions
HTC and QH designed research; HTC, WXW performed the bioinformatics analysis, HTC, MYH performed qRT-PCR experiments and miRNA analysis, DSM, JL performed RNA-seq analysis, CBT carried out expression pattern analysis, HW, LF provided plant material and prepared RNA samples, HTC and QH wrote the paper. All authors have read and approved the version of manuscript.
Competing interests
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Consent for publication
Not applicable.
Ethics approval and consent to participate
Not applicable.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional files
Additional file 1: Table S1.
Primers used for quantitative polymerase chain reaction (qPCR) in gene expression analysis. (DOC 36 kb)
Additional file 2: Figure S2.
Phylogenetic analysis of BnaSBP proteins. The conserved SBP domain sequences encoded by Arabidopsis (AtSBP), rice (OsSBP) and B. napus SBP-box proteins were aligned using ClustalW. The phylogenetic tree was constructed using the maximum likelihood method with 1000 replication. Bar indicates 0.1 aa substitution per residue. (PPTX 73 kb)
Additional file 3: Table S2.
Absolute gene expression values in twelve tissue samples. (XLSX 18 kb)
Additional file 4: Figure S1.
Phenotypes of two lines with different branch angle. (A) 6098B and Purler lines grown at the middle flowering stage. Bar = 25 cm. (B) The branch angle of 6098B is larger than that of Purler. The arrows indicate the different branch angle of two lines. Bar = 2 cm. (PPTX 145 kb)
Additional file 5: Table S3.
Absolute gene expression values in two samples. (XLSX 15 kb)
Rights and permissions
Open Access This article is distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/), which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided you give appropriate credit to the original author(s) and the source, provide a link to the Creative Commons license, and indicate if changes were made. The Creative Commons Public Domain Dedication waiver (http://creativecommons.org/publicdomain/zero/1.0/) applies to the data made available in this article, unless otherwise stated.
About this article
Cite this article
Cheng, H., Hao, M., Wang, W. et al. Genomic identification, characterization and differential expression analysis of SBP-box gene family in Brassica napus . BMC Plant Biol 16, 196 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1186/s12870-016-0852-y
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1186/s12870-016-0852-y