Abstract
Background
Cataracts are defects of the lens that cause progressive visual impairment and ultimately blindness in many vertebrate species. Most cataracts are age-related, but up to one third have an underlying genetic cause. Cataracts are common in captive zoo animals, but it is often unclear whether these are congenital or acquired (age-related) lesions.
Results
Here we used a functional candidate gene screening approach to identify mutations associated with cataracts in a captive giant panda (Ailuropoda melanoleuca). We screened 11 genes often associated with human cataracts and identified a novel missense mutation (c.686G > A) in the MIP gene encoding major intrinsic protein. This is expressed in the lens and normally accumulates in the plasma membrane of lens fiber cells, where it plays an important role in fluid transport and cell adhesion. The mutation causes the replacement of serine with asparagine (p.S229N) in the C-terminal tail of the protein, and modeling predicts that the mutation induces conformational changes that may interfere with lens permeability and cell–cell interactions.
Conclusion
The c.686G > A mutation was found in a captive giant panda with a unilateral cataract but not in 18 controls from diverse regions in China, suggesting it is most likely a genuine disease-associated mutation rather than a single-nucleotide polymorphism. The mutation could therefore serve as a new genetic marker to predict the risk of congenital cataracts in captive giant pandas.
Similar content being viewed by others
Background
Cataracts are heterogeneous and multifactorial eye lesions in which the lens becomes opaque due to the accumulation of pigments and protein aggregates induced by progressive oxidative damage [1, 2]. Many cataracts are acquired, age-related lesions but approximately one third of cases have a significant genetic component, and most of these congenital forms are transmitted as autosomal dominant traits with strong penetrance but varying degrees of expressivity [3]. Although the pathogenesis of cataracts often has a genetic component, the etiology is complex because progression is also influenced by nutrition, metabolism and the environment. Cataract formation is therefore the long-term consequence of multiple intrinsic and external factors. For example, epidemiological studies have shown that human cataract development is promoted by ultraviolet radiation, diabetes, hypertension, cardiovascular disease, body trauma, and excess drinking and smoking [4, 5].
Whereas some congenital cataracts are caused by the disruption of eye development, others reflect the presence of mutations in genes required for normal lens function [2]. For example, in humans, underlying mutations have been detected in genes encoding transcription factors that regulate lens activity, such as PITX3 [6] and HSF4 [7], and in genes encoding lens cytoskeletal proteins, such as BFSP2 [8, 9]. Several mutations have been traced to genes encoding crystallin proteins, which normally remain soluble and confer transparency, including α-crystallins [10], β-crystallins [11,12,13], and γ-crystallins [14, 15]. Another major category of cataract-promoting mutations affect genes encoding lens membrane channels or gap junction proteins, such as connexin 46 (GJA3) [16] and connexin 50 (GJA8) [17]. One of the most important membrane channels in the context of cataract formation is the lens major intrinsic protein (MIP), also known as aquaporin 0 (AQP0) [18].
MIP/AQP0 is an integral membrane protein (28 kDa, 263 amino acids) with six transmembrane domains, which assembles into a tetramer containing four independent water channels [19, 20]. It is expressed at high levels in lens fiber cells and constitutes ~ 45% of the total membrane protein [21]. Its main function is the transport of water and small, neutral solutes [22,23,24], but it is also required for the adhesion of lens fiber cells via interactions with crystallins and connexin 50 [25,26,27]. At least 19 mutations in the human MIP gene (Table 1) have been linked to autosomal dominant cataracts with diverse phenotypes, reflecting the multi-domain and multi-functional nature of the protein [28,29,30,31,32,33,34,35,36,37,38,39,40,41,42,43,44,45]. In many cases, these mutations reduce the abundance of MIP and/or prevent normal trafficking to the plasma membrane, thus inhibiting water and solute transport as well as cell–cell interactions [23, 37, 46]. Mutations in the mouse Mip gene have also been linked to genetic cataracts, such as Fraser (CatFr), lens opacity (lop), Hfi, Tohm and Nat [47,48,49,50]. The loss of water permeability in mip-deficient mice [20] can be rescued by the expression of AQP1 [51]. However, this does not restore the ordered packing of the lens fiber cells and still results in the formation of cataracts, confirming that MIP has unique functions in the lens that are not complemented by other aquaporins [51].
Although mutations affecting MIP have been shown to cause cataracts in humans and mice, analogous mutations have not been reported in the giant panda (Ailuropoda melanoleuca). These animals also tend to develop cataracts in captivity because they live much longer than their counterparts in the wild, and they may therefore be exposed to additional risk factors. This phenomenon has been observed in companion animals: for example, cataract development in dogs is often associated with diabetes, obesity, prolonged use of corticosteroid, excessive exposure to sunlight, or previous eye injury/inflammation [52, 53]. It is therefore unclear whether cataracts in captive pandas are age-related acquired or congenital lesions due to the absence of suitable genetic markers [54]. Here we used a functional candidate gene screening approach to test 11 known cataract-associated genes in giant panda specimens with and without cataracts. We identified and characterized a novel missense mutation in the MIP gene of a female panda diagnosed with progressive cortical punctate cataracts. The mutation was not present in 18 healthy controls. The identification of this mutation will help to determine the prevalence of congenital cataracts in pandas, and will provide a new diagnostic tool for cataract risk assessment in the zoo environment.
Results
Clinical findings
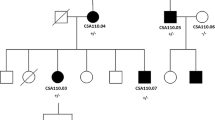
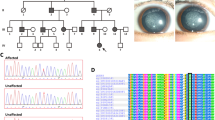
The proband in this study was Jini, a giant panda born in 1993. Routine physical examination were carried out every month for captive pandas, including eye, mouth, nose and physical appearance examination, abdominal palpation, etc. Blood were collected once a month for detection of various physiological and biochemical indicators. Risk factors that affect or cause cataract formation such as injury, diabetes or other factors can be well excluded through examination. Jini’s mild cataract symptoms were first observed in 2013, and in 2017 the lesion was diagnosed as a unilateral senile (age-related) cataract following a professional examination by an ophthalmologist (Fig. 1). However, in the absence of genetic data it was not possible to confirm whether the cataract was acquired or congenital. The ophthalmologist’s diagnosis represented the transition from initial cataract formation to the immature stage of a cortical cataract, and accordingly the pupil area was not occluded and there was only slight visual impairment. In this condition, the cortex absorbs water and swells, the lens volume increases, and the anterior chamber becomes shallow, accompanied by mild secondary glaucoma. Jini’s case records indicated no history of eye trauma or other diseases. We therefore selected Jini for genetic analysis in order to screen for genetic markers that can be used to differentiate between congenital and acquired cataracts. We selected 18 controls without cataracts, including all traceable relatives of Jini and unrelated controls from diverse geographical locations within China (Table 2). This was necessary to distinguish disease-associated mutations from irrelevant single-nucleotide polymorphisms (SNPs).
Mutation detection
Genomic DNA extracted from Jini and the 18 healthy controls was screened for mutations in 11 candidate genes often associated with cataracts in humans (CRYAB, CRYBA1, CRYBB1, CRYGC, HSPB6, HSPB7, HSPB9, GJA3, AQP3, MIP and HSF4). This revealed a novel missense mutation in exon 4 of the MIP gene (c.686G > A) in Jini but in none of the controls. The transition causes the replacement of a serine residue with arginine at position 229 (p.S229N) in the intracellular C-terminal tail of the protein (Fig. 2). We found that Jini is heterozygous for this mutation.
Characterization of the mutation in the MIP gene of Jini. (a) Extended structure of MIP, showing the six transmembrane domains (H1–H6), extracellular loops (A/C/E), intracellular loops (B/D), the intracellular N-terminal portion, and the intracellular C-terminal tail, the latter containing the mutation site (red dot). (b) Sequence trace of the 16-bp region spanning the mutation site, comparing the 18 controls (top) and Jini (bottom), revealing the heterozygous mutation (c.686G > A)
Structural analysis
The amino acid sequences of human, bovine, rat, mouse and panda MIP were aligned, revealing broad conservation throughout the sequence and almost complete conservation in the 10 residues either side of the mutation site, with the only substitutions involving chemically near-identical isoleucine and valine residues (Fig. 3a). The replacement of serine with asparagine within this region therefore swaps a small polar side chain for another that is chemically similar but physically larger, with the potential to form additional hydrogen bonds. ProtScale analysis confirmed that the corresponding mutation in the human MIP protein (p.S229N) would cause a decrease in overall hydrophobicity (Fig. 3b). The potential damaging effect of p.S229N was also predicted by PROVEAN analysis, which generated a score of − 0.805, indicating a neutral mutation.
The p.S229N mutation within the intracellular C-terminal domain of MIP affects protein hydrophobicity. a Multiple alignment of a highly-conserved sequence of 21 amino acids in five orthologs of MIP (panda, mouse, bovine, rat and human) showing that the panda p.S229N substitution affects a serine residue conserved across all species. b ProtScale analysis of the human protein with the equivalent mutation (p.S229N) confirming a decrease in overall hydrophobicity
Structural predictions in SWISS-MODEL showed that the path of the MIP polypeptide backbone is altered by the mutation due to the addition of two hydrogen bonds, increasing the attraction between residue 229 and nearby amino acids (Fig. 4). Following sequence alignment using Clustal X v2.0, the impact of the mutation on protein structure was predicted using Modeller v9.22 with the sheep (Ovis aries) MIP (PDB: 2B6O) as a template, revealing discrete changes on the protein surface (Fig. 5a). As shown in Fig. 5b, Ser229 in wild-type MIP forms a hydrogen bond with Ser231, whereas Asn229 in the mutant forms two weak hydrogen bonds with Ser231 and Glu232. These subtle changes in the surface properties and intramolecular interactions are likely to influence the behavior of the C-terminal tail of panda MIP and thus promote the formation of cataracts.
The path of the MIP polypeptide backbone predicted using SWISS-MODEL. a Model of wild-type human MIP. b Model of the p.S229N mutant. The arrows indicate the difference in intramolecular interactions between wild-type MIP and the p.S229N mutant, with the latter able to form two new hydrogen bonds (shown as broken green lines)
Predicted changes in the tertiary structure of giant panda MIP caused by the missense mutation p.S229N. a Changes in surface structure visualized using Discovery Studio Visualizer. The yellow circle reveals a subtle but distinct protrusion in the mutant protein caused by the bulkier side chain of asparagine compared to serine. b Interactions between amino acid side chains predicted using THREADER and Modeller. The p.S229N mutant forms two new hydrogen bonds
Discussion
Cataracts can be caused by mutations that affect the activity of several groups of lens proteins, including developmental regulators, transcription factors, lens crystallins, cytoskeletal proteins, gap junction proteins and membrane channels [1, 2]. The best example of the latter is MIP, an aquaporin that not only facilitates the intercellular transport of water and small solutes [22], but also binds lens fiber cells together and ensures their optimal spacing, which is necessary for normal lens refraction behavior [26]. At least 19 mutations in the human MIP gene are associated with congenital cataracts, 11 of which are missense mutations, as well as two nonsense mutations, two frameshifts, two splice-site mutations, and one initiation codon mutation (Table 1). Here we identified the first MIP mutation associated with cataracts in the giant panda. It is a missense mutation in exon 4 (p.S229N) that replaces a highly-conserved serine residue with arginine in the intracellular C-terminal tail of the protein. This mutation was found in Jini (identified as S1 in Table 2) but not in 18 healthy controls representing all Jini’s traceable relatives as well as unrelated pandas from geographically diverse regions of China, supporting our hypothesis that p.S229N is a genuine disease-associated mutation and not an unrelated SNP. Jini’s father (S8) was sampled and did not carry the mutation, but no samples were available from Jini’s mother (who died in 2006) or Jini’s five offspring (two of whom have died, whereas one was exported to a foreign zoo). More distant relatives were also traced, including a female sibling of Jini’s parents who was also diagnosed with cataracts, but no samples were available. We also sampled the father (S11) and grandfather (S4) of Jini’s offspring and found no mutation. In the absence of informative pedigree-related samples, we acquired samples from pandas in Beijing, Baoxing, Ya’an, Wolong and Chengdu to ensure we captured broad genetic diversity.
Like other aquaporins, MIP features six transmembrane domains (H1–H6), three extracellular loops (A, C and E), and two intracellular loops (B and D), as well as intracellular N and C termini (Fig. 2) [18]. The C-terminal segment of the native protein is 44 amino acids in length (residues 220–263) and features an α-helix (residues 230–238) with an overlapping calmodulin-binding domain (residues 223–235) [55, 56] that regulates the permeability of the MIP water channels in response to Ca2+ [57, 58]. The C-terminal segment of MIP interacts not only with calmodulin, but also with the cytoskeletal protein filensin and the gap junction protein connexin 50 [59,60,61]. The novel mutation we identified lies within the calmodulin-binding domain at the N-terminal border of the α-helix, suggesting that the mutation may affect the permeability of MIP either constitutively or in response to Ca2+, or may disrupt its interaction with gap junctions and the cytoskeleton.
Several missense mutations associated with cataracts have been traced to exon 4 of the human MIP gene, but only one of these maps to the calmodulin-binding domain of the C-terminal segment, namely the R233K mutation identified by Lin et al. [31]. R233K is distal to our novel S229N mutation and lies within the α-helix as well as the calmodulin-binding domain, but like our mutation it replaces one residue with a chemically similar one, in this case the positively charged arginine to lysine, resulting in an autosomal dominant polymorphic binocular cataract. The S229N mutation in panda may have a similar effect, although we are unable to determine whether the cataract is polymorphic without other affected individuals (the Chinese family carrying the R233K mutation spanned six generations, with a wealth of clinical data). The presence of the cataract in Jini also suggests that the mutation is pathogenic and transmitted in an autosomal dominant manner, but both of Jini’s parents were apparently healthy and her father did not carry the mutation. We can only speculate that Jini represents a new germline mutation or that her mother was an unaffected carrier due to a lack of penetrance or expressivity, the latter being relatively common for congenital cataracts in human pedigrees [3].
Other mutations are known to truncate the C-terminal segment of MIP, which interferes with its trafficking to the plasma membrane and thus reduces or abolishes its activity [62]. The C-terminal regions spanning residues 223–234 and 235–263 are critical for protein transport from the cytoplasm to the plasma membrane [46, 63] and residue Ser235 is particularly important for MIP translocation to the plasma membrane following PKC-dependent phosphorylation [64]. Therefore, mutant versions of MIP lacking these residues become trapped in the cytoplasm, which restricts the formation of water channels in the plasma membrane and thus reduces lens fiber cell permeability and transparency. A long-terminal repeat inserted at the C-terminus of the mouse MIP protein was shown to disrupt lens fiber cell architecture in the CatFr mutant, indicating that the C-terminal segment is also required for the development of the correct cellular architecture in the crystalline lens [47, 65, 66].
Part of the C-terminus is cleaved from MIP post-translationally such that mature lens fiber cells accumulate a truncated derivative (residues 1–246) rather than the full-length 263-residue protein. In transgenic knockout mice lacking a functional MIP gene, knocking in the C-terminal truncated sequence (making it the only version of MIP available throughout development) did not prevent the lens becoming opaque, and water permeability was reduced, but cell–cell adhesion was stronger than in the wild-type cells [67]. These results confirmed that full-length MIP is required for normal permeability although the truncated version does function as a water channel, and can be explained by the requirement of the complete C-terminal segment to traffic MIP to the plasma membrane. The truncation clearly plays an important role in cell–cell adhesion, which is enhanced when only the truncated MIP is available. The presence of our novel S229N mutation in this region of the panda MIP sequence indicates that the predicted structural alterations are likely to affect the structure and transparency of the lens by interfering with both permeability and cell–cell interactions. Our data provide more evidence of the pathogenic mechanisms of cataract formation in panda and extend the spectrum of known MIP gene mutations.
Clinically, the diagnostic criteria of age-related cataract are still controversial, and there is still no complete and accurate definition. In this study, the cataract occurrence of giant panda is associated with age, which belongs to the cumulative effect of pathogenic genes. Such pathogenic genes do not directly lead to the onset of early cataract as congenital cataract genes do. However, pathogenic genes accumulate harmful proteins or hinder the maintenance of lens function with the increase of age, eventually leading to cataract formation. This pathogenic gene like MIP gene mutation in this study might also be inherited to the offspring, and show senile cataract.
Conclusions
We screened 11 genes often associated with human cataracts and identified a novel missense mutation (c.686G > A) in the MIP gene in a female panda diagnosed with progressive cortical punctate cataracts by using a functional candidate gene screening approach. This mutation was found in a captive giant panda with a unilateral cataract but not in 18 controls from diverse regions in China, suggesting it is most likely a genuine disease-associated mutation rather than a single-nucleotide polymorphism. The mutation could therefore serve as a new genetic marker to provide a new diagnostic tool for cataract risk assessment in captive giant pandas.
Methods
Proband and controls
Jini is a female giant panda who was born in 1993 in Beijing Zoo (China). Her mother was born in wild in 1981 and her father was born in Beijing Zoo in 1986. Both parents were healthy. Jini underwent examination at 28 years of age and was first diagnosed with senile cataract, but now also shows signs of corneal atrophy. She has poor vision and slow movement but no history of related systemic abnormalities. In addition to Jini (S1), we selected 18 healthy captive giant panda samples as controls, including Jini’s father (S8) and the father (S11) and grandfather (S4) of Jini’s offspring. The other samples (unrelated to Jini) were collected from pandas in Beijing, Baoxing, Ya’an, Wolong and Chengdu (Table 2).
Mutation detection
We selected 11 candidate genes that are often associated with cataracts in humans (CRYAB, CRYBA1, CRYBB1, CRYGC, HSPB6, HSPB7, HSPB9, GJA3, AQP3, MIP and HSF4) and used them as functional candidates for mutation analysis in Jini and the controls. Peripheral venous blood samples (2 ml) were collected and stored at − 80 °C. Genomic DNA was extracted with phenol/chloroform (Sigma-Aldrich/Merck Millipore, Shanghai, China) immediately before analysis. Blood samples were collected in accordance with the Wildlife Protection Law of the People’s Republic of China (President of the People’s Republic of China No. 16), and the experimental approach was approved by the Beijing Zoo Academic and Ethics Committee.
PCR was carried out using the exon-spanning primers listed in Table S1. Each 25-μl reaction comprised 1.5 mM MgCl2, 0.2 mM dNTPs, 0.5 μM of the appropriate forward and reverse primers, 2.5 U Taq DNA polymerase (TianGen, Beijing, China) and 20 ng genomic DNA in 1x PCR buffer (TianGen, Beijing, China). The samples were denatured at 95 °C for 5 min, followed by 34 cycles of 95 °C for 30 s, 57–63 °C (depending on the primer pair) for 30 s, and 72 °C for 30 s, and a final extension step at 72 °C for 10 min. The products were sequenced using an ABI 3730 Automated Sequencer (PE Biosystems, Foster City, CA, USA), analyzed using Chromas v2.33 and compared to the reference sequence in the NCBI database [68]. The sequence of the mutated giant panda MIP gene has been deposited in the NCBI GenBank database under accession number MT447398.
Bioinformatics analysis
MIP amino acid sequences from five different species (human, bovine, rat, mouse and panda) were aligned and analyzed using CLC Free Workbench v4.5.1 (CLC Bio, Aarhus, Denmark). Protein hydrophilicity was determined using ProtScale [69]. The effects of the predicted amino acid substitution on the structure of MIP, and interactions between amino acid side chains, were predicted using SWISS-MODEL [70, 71], THREADER v3.5 [72, 73], Modeller v9.22 [74] and were visualized using Discovery Studio Visualizer. The damaging effects of the mutation were predicted using PROVEAN v1.1.3 (http://provean.jcvi.org/index.php).
Availability of data and materials
Table S1 reports PCR primers designed for screening the candidate gene mutants.
The sequencing data are publicly available at NCBI GenBank (accession number MT447398). All data necessary for confirming the conclusions of the article are present within the article, figures, and tables.
Abbreviations
- MIP:
-
Major intrinsic protein
- PITX3:
-
Paired-like homeodomain 3
- HSF4:
-
Heat shock transcription factor-4
- BFSP2:
-
Beaded filament structural protein-2
- GJA3:
-
Connexin 46
- GJA8:
-
Connexin 50
- AQP0:
-
Aquaporin-0
- AQP1:
-
Aquaporin-1Quaporin-1
- AQP3:
-
Aquaporin-3Quaporin-3
- SNPs:
-
Single-nucleotide polymorphisms
- CRYAB:
-
Crystallin Alpha B
- CRYBA1:
-
Crystallin Beta A1
- CRYBB1:
-
Crystallin Beta B1
- CRYGC:
-
Crystallin Gamma C
- HSPB6:
-
Heat shock protein family B (Small) member 6
- HSPB7:
-
Heat shock protein family B (Small) member 7
- HSPB9:
-
Heat shock protein family B (Small) member 9
- PKC-dependent phosphorylation:
-
Protein kinase C dependent phosphorylation
References
Spector A. Oxidative stress-induced cataract: mechanism of action. FASEB J. 1995;9:1173–82.
Hejtmancik JF. The genetics of cataract: our vision becomes clearer. Am J Hum Genet. 1998;62:520–5.
Francis PJ, Berry V, Bhattacharya SS, Moore AT. Genetics of childhood cataract. J Med Genet. 2000a;37:481–8.
Roberts JE. Ultraviolet radiation as a risk factor for cataract and macular degeneration. Eye Contact Lens. 2011;37:246–9.
Little MP, Cahoon EK, Kitahara CM, Simon SL, Hamada N, Linet MS. Occupational radiation exposure and excess additive risk of cataract incidence in a cohort of US radiologic technologists. Occup Environ Med. 2020;77:1–8.
Semina EV, Ferrell RE, Mintz-Hittner HA, Bitoun P, Alward WL, Reiter RS, Funkhauser C, Daack-Hirsch S, Murray JC. A novel homeobox gene PITX3 is mutated in families with autosomal-dominant cataracts and ASMD. Nat Genet. 1998;19:167–70.
Bu L, Jin Y, Shi Y, Chu R, Ban A, Eiberg H, Andres L, Jiang H, Zheng G, Qian M, Cui B, Xia Y, Liu J, Hu L, Zhao G, Hayden MR, Kong X. Mutant DNA-binding domain of HSF4 is associated with autosomal dominant lamellar and Marner cataract. Nat Genet. 2002;31:276–8.
Conley YP, Erturk D, Keverline A, Mah TS, Keravala A, Barnes LR, Bruchis A, Hess JF, FitzGerald PG, Weeks DE, Ferrell RE, Gorin MB. A juvenile-onset, progressive cataract locus on chromosome 3q21-q22 is associated with a missense mutation in the beaded filament structural protein-2. Am J Hum Genet. 2000;66:1426–31.
Jakobs PM, Hess JF, FitzGerald PG, Kramer P, Weleber RG, Litt M. Autosomal-dominant congenital cataract associated with a deletion mutation in the human beaded filament protein gene BFSP2. Am J Hum Genet. 2000;66:1432–6.
Vanita V, Singh JR, Hejtmancik JF, Nuernberg P, Hennies HC, Singh D, Sperling K. A novel fan-shaped cataractmicrocornea syndrome caused by a mutation of CRYAA in an Indian family. Mol Vis. 2006;12:518–22.
Litt M, Carrero-Valenzuela R, LaMorticella DM, Schultz DW, Mitchell TN, Kramer P, Maumenee IH. Autosomal dominant cerulean cataract is associated with a chain termination mutation in the human beta-crystallin gene CRYBB2. Hum Mol Genet. 1997;6:665–8.
Lu S, Zhao C, Jiao H, Kere J, Tang X, Zhao F, Zhang X, Zhao K, Larsson C. Two Chinese families with pulverulent congenital cataracts and deltaG91 CRYBA1 mutations. Mol Vis. 2007;13:1154–60.
Meyer E, Rahman F, Owens J, Pasha S, Morgan NV, Trembath RC, Stone EM, Moore AT, Maher ER. Initiation codon mutation in betaB1-crystallin (CRYBB1) associated with autosomal recessive nuclear pulverulent cataract. Mol Vis. 2009;15:1014–9.
Zhang LY, Yam GH, Fan DS, Tam PO, Lam DS, Pang CP. A novel deletion variant of gamma D-crystallin responsible for congenital nuclear cataract. Mol Vis. 2007;13:2096–104.
Yao K, Jin C, Zhu N, Wang W, Wu R, Jiang J, Shentu X. A nonsense mutation in CRYGC associated with autosomal dominant congenital nuclear cataract in a Chinese family. Mol Vis. 2008;14:1272–6.
Burdon KP, Wirth MG, Mackey DA, Russell-Eggitt IM, Craig JE, Elder JE, Dickinson JL, Sale MM. A novel mutation in the Connexin 46 gene causes autosomal dominant congenital cataract with incomplete penetrance. J Med Genet. 2004;41:e106.
Arora A, Minogue PJ, Liu X, Addison PK, Russel-Eggitt I, Webster AR, Hunt DM, Ebihara L, Beyer EC, Berthoud VM, Moore AT. A novel connexin50 mutation associated with congenital nuclear pulverulent cataracts. J Med Genet. 2008;45:155–6.
Chepelinsky AB. Structural function of MIP/aquaporin 0 in the eye lens; genetic defects lead to congenital inherited cataracts. Handb Exp Pharmacol. 2009;190:265–97.
Chepelinsky AB. The ocular lens fiber membrane specific protein MIP/aquaporin 0. J Exp Zool A Comp Exp Biol. 2003;300:41–6.
Shiels A, Bassnett S, Varadaraj K, Mathias R, Al-Ghoul K, Kuszak J, Donoviel D, Lilleberg S, Friedrich G, Zambrowicz B. Optical dysfunction of the crystalline lens in aquaporin-0-deficient mice. Physiol Genomics. 2001;7:179–86.
Bassnett S, Wilmarth PA, David LL. The membrane proteome of the mouse lens fiber cell. Mol Vis. 2009;15:2448–63.
Borgnia M, Nielsen S, Engel A, Agre P. Cellular and molecular biology of the aquaporin water channels. Annu Rev Biochem. 1999;68:425–58.
Francis P, Chung JJ, Yasui M, Berry V, Moore A, Wyatt MK, Wistow G, Bhattacharya SS, Agre P. Functional impairment of lens aquaporin in two families with dominantly inherited cataracts. Hum Mol Genet. 2000b;9:2329–34.
Mathias RT, Kistler J, Donaldson P. The lens circulation. J Membr Biol. 2007;216:1–16.
Liu BF, Liang JJ. Confocal fluorescence microscopy study of interaction between lens MIP26/AQP0 and crystallins in living cells. J Cell Biochem. 2008;104:51–8.
Kumari SS, Varadaraj K. Intact AQP0 performs cell-to-cell adhesion. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2009;390:1034–9.
Liu J, Xu J, Gu S, Nicholson BJ, Jiang JX. Aquaporin 0 enhances gap junction coupling via its cell adhesion function and interaction with connexin 50. J Cell Sci. 2011;124:198–206.
Berry V, Francis P, Kaushal S, Moore A, Bhattacharya S. Missense mutations in MIP underlie autosomal dominant ‘polymorphic’ and lamellar cataracts linked to 12q. Nat Genet. 2000;25:15–7.
Geyer DD, Spence MA, Johannes M, Flodman P, Clancy KP, Berry R, Sparkes RS, Jonsen MD, Isenberg SJ, Bateman JB. Novel single-base deletional mutation in major intrinsic protein (MIP) in autosomal dominant cataract. Am J Ophthalmol. 2006;141:761–3.
Gu F, Zhai H, Li D, Zhao L, Li C, Huang S, Ma X. A novel mutation in major intrinsic protein of the lens gene (MIP) underlies autosomal dominant cataract in a Chinese family. Mol Vis. 2007;13:1651–6.
Lin H, Hejtmancik JF, Qi Y. A substitution of arginine to lysine at the COOH-terminus of MIP caused a different binocular phenotype in a congenital cataract family. Mol Vis. 2007;13:1822–7.
Jiang J, Jin C, Wang W, Tang X, Shentu X, Wu R, Wang Y, Xia K, Yao K. Identification of a novel splice-site mutation in MIP in a Chinese congenital cataract family. Mol Vis. 2009;15:38–44.
Wang W, Jiang J, Zhu Y, Li J, Jin C, Shentu X, Yao K. A novel mutation in the major intrinsic protein (MIP) associated with autosomal dominant congenital cataracts in a Chinese family. Mol Vis. 2010;16:534–9.
Wang KJ, Li SS, Yun B, Ma WX, Jiang TG, Zhu SQ. A novel mutation in MIP associated with congenital nuclear cataract in a Chinese family. Mol Vis. 2011;17:70–7.
Xiao X, Li W, Wang P, Li L, Li S, Jia X, Sun W, Guo X, Zhang Q. Cerulean cataract mapped to 12q13 and associated with a novel initiation codon mutation in MIP. Mol Vis. 2011;17:2049–55.
Yang G, Zhang G, Wu Q, Zhao J. A novel mutation in the MIP gene is associated with autosomal dominant congenital nuclear cataract in a Chinese family. Mol Vis. 2011;17:1320–3.
Senthil Kumar G, Kyle JW, Minogue PJ, Dinesh Kumar K, Vasantha K, Berthoud VM, Beyer EC, Santhiya ST. An MIP/AQP0 mutation with impaired trafficking and function underlies an autosomal dominant congenital lamellar cataract. Exp Eye Res. 2013;110:136–41.
Zeng L, Liu W, Feng W, Wang X, Dang H, Gao L, Yao J, Zhang X. A novel donor splice-site mutation of major intrinsic protein gene associated with congenital cataract in a Chinese family. Mol Vis. 2013;19:2244–9.
Ding X, Zhou N, Lin H, Chen J, Zhao C, Zhou G, Hejtmancik JF, Qi Y. A novel MIP gene mutation analysis in a Chinese family affected with congenital progressive punctate cataract. PLoS One. 2014;9:e102733.
Yu Y, Yu Y, Chen P, Li J, Zhu Y, Zhai Y, Yao K. A novel MIP gene mutation associated with autosomal dominant congenital cataracts in a Chinese family. BMC Med Genet. 2014;15:6–12.
Shentu X, Miao Q, Tang X, Yin H, Zhao Y. Identification and functional analysis of a novel MIP gene mutation associated with congenital cataract in a Chinese family. PLoS One. 2015;10:e0126679.
Song Z, Wang L, Liu Y, Xiao W. A novel nonsense mutation in the MIP gene linked to congenital posterior polar cataracts in a Chinese family. PLoS One. 2015;10:e0119296.
Qin L, Guo L, Wang H, Li T, Lou G, Guo Q, Hou Q, Liu H, Liao S, Liu Z. A novel MIP mutation in familial congenital nuclear cataracts. Eur J Med Genet. 2016;59:488–91.
Jiang B, Chen Y, Xu B, Hong N, Liu R, Qi M, Shen L. Identification of a novel missense mutation of MIP in a Chinese family with congenital cataracts by target region capture sequencing. Sci Rep. 2017;7:40129.
Long X, Huang Y, Tan H, Li Z, Zhang R, Linpeng S, Lv W, Cao Y, Li H, Liang D, Wu L. Identification of a novel MIP frameshift mutation associated with congenital cataract in a Chinese family by whole-exome sequencing and functional analysis. Eye (Lond). 2018;32:1359–64.
Varadaraj K, Kumari SS, Patil R, Wax MB, Mathias RT. Functional characterization of a human aquaporin 0 mutation that leads to a congenital dominant lens cataract. Exp Eye Res. 2008;87:9–21.
Shiels A, Mackay D, Bassnett S, Al-Ghoul K, Kuszak J. Disruption of lens fiber cell architecture in mice expressing a chimeric AQP0-LTR protein. FASEB J. 2000;14:2207–12.
Sidjanin DJ, Parker-Wilson DM, Neuhäuser-Klaus A, Pretsch W, Favor J, Deen PM, Ohtaka-Maruyama C, Lu Y, Bragin A, Skach WR, Chepelinsky AB, Grimes PA, Stambolian DE. A 76-bp deletion in the Mip gene causes autosomal dominant cataract in Hfi mice. Genomics. 2001;74:313–9.
Okamura T, Miyoshi I, Takahashi K, Mototani Y, Ishigaki S, Kon Y, Kasai N. Bilateral congenital cataracts result from a gain-of-function mutation in the gene for aquaporin-0 in mice. Genomics. 2003;81:361–8.
Takahashi G, Hasegawa S, Fukutomi Y, Harada C, Furugori M, Seki Y, Kikkawa Y, Wada K. A novel missense mutation of Mip causes semi-dominant cataracts in the Nat mouse. Exp Animals. 2017;66:271–82.
Kumari SS, Eswaramoorthy S, Mathias RT, Varadaraj K. Unique and analogous functions of aquaporin 0 for fiber cell architecture and ocular lens transparency. Biochim Biophys Acta. 2011;1812:1089–97.
Salgado D, Reusch C, Spiess B. Diabetic cataracts: different incidence between dogs and cats. Schweizer Archiv fur Tierheilkunde. 2000;142:349–53.
Kador PF, Webb TR, Bras D, Ketring K, Wyman M. Topical KINOSTAT™ ameliorates the clinical development and progression of cataracts in dogs with diabetes mellitus. Vet Ophthalmol Actions. 2010;13:363–8.
You Y, Bai C, Liu X, Xia M, Jia T, Li X, Zhang C, Chen Y, Zhao S, Wang L, Wang W, Yin Y, Xiu Y, Niu L, Zhou J, Ma T, Du Y, Liu Y. Genome-wide analysis of methylation in giant pandas with cataract by methylation-dependent restriction-site associated DNA sequencing (MethylRAD). PLoS One. 2019;14:e0222292.
Louis CF, Hogan P, Visco L, Strasburg G. Identity of the calmodulin-binding proteins in bovine lens plasma membranes. Exp Eye Res. 1990;50:495–503.
Girsch SJ, Peracchia C. Calmodulin interacts with a C-terminus peptide from the lens membrane protein MIP26. Curr Eye Res. 1991;10:839–49.
Nemeth-Cahalan KL, Hall JE. pH and calcium regulate the water permeability of aquaporin 0. J Biol Chem. 2000;275:6777–82.
Nemeth-Cahalan KL, Kalman K, Hall JE. Molecular basis of pH and Ca2+ regulation of aquaporin water permeability. J Gen Physiol. 2004;123:573–80.
Yu XS, Yin X, Lafer EM, Jiang JX. Developmental regulation of the direct interaction between the intracellular loop of connexin 45.6 and the C-terminus of major intrinsic protein (aquaporin-0). J Biol Chem. 2005;280:22081–90.
Lindsey Rose KM, Gourdie RG, Prescott AR, Quinlan RA, Crouch RK, Schey KL. The C-terminus of lens aquaporin 0 interacts with the cytoskeletal proteins filensin and CP49. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci. 2006;47:1562–70.
Rose KM, Wang Z, Magrath GN, Hazard ES, Hildebrandt JD, Schey KL. Aquaporin 0-calmodulin interaction and the effect of aquaporin 0 phosphorylation. Biochemistry. 2008;47:339–47.
Ball LE, Little M, Nowak MW, Garland DL, Crouch RK, Schey KL. Water permeability of C-terminally truncated aquaporin 0 (AQP0 1–243) observed in the aging human lens. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci. 2003;44:4820–8.
Sindhu KS, Varadaraj K. Intact and N- or C-terminal end truncated AQP0 function as open water channels and cell-to-cell adhesion proteins: end truncation could be a prelude for adjusting the refractive index of the lens to prevent spherical aberration. Biochim Biophys Acta. 2014;1840:2862–77.
Golestaneh N, Fan J, Zelenka P, Chepelinsky AB. PKC putative phosphorylation site Ser235 is required for MIP/AQP0 translocation to the plasma membrane. Mol Vis. 2008;14:1006–14.
Shiels A, Bassnett S. Mutations in the founder of the MIP gene family underlie cataract development in the mouse. Nat Genet. 1996;12:212–5.
Kalman K, Nemeth-Cahalan KL, Froger A, Hall JE. AQP0- LTR of the cat Fr mouse alters water permeability and calcium regulation of wild type AQP0. Biochim Biophys Acta. 2006;1758:1094–9.
Sindhu KS, Varadaraj K. A predominant form of C-terminally end-cleaved AQP0 functions as an open water channel and an adhesion protein in AQP0DC/DC mouse lens. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2019;511:626–30.
Li R, Fan W, Tian G, Zhu H, He L, Cai J, Huang Q, Cai Q, Li B, Bai Y, et al. The sequence and de novo assembly of the giant panda genome. Nature. 2010;63:311–7.
Gasteiger E, Hoogland C, Gattiker A, Duvaud S, Wilkins MR, Appel RD, Bairoch A. Protein identification and analysis tools on the ExPASy server. In: Walker JM, editor. The proteomics protocols handbook. Totowa: Academic: Humana Press; 2005. p. 571–607.
Schwede T, Kopp J, Guex N, Peitsch MC. SWISS-MODEL: an automated protein homology-modeling server. Nucleic Acids Res. 2003;31:3381–5.
Bienert S, Waterhouse A, de Beer TA, Tauriello G, Studer G, Bordoli L, Schwede T. The SWISS-MODEL repository-new features and functionality. Nucleic Acids Res. 2017;45:D313–9.
Jones DT, Taylor WR, Thornton JM. A new approach to protein fold recognition. Nature. 1992;358:86–9.
Jones DT, Miller RT, Thornton JM. Successful protein fold recognition by optimal sequence threading validated by rigorous blind testing. Proteins. 1995;23:387–97.
Sali A, Blundell TL. Comparative protein modelling by satisfaction of spatial restraints. J Mol Biol. 1993;234:779–815.
Acknowledgements
The authors acknowledge the support of the Strait (Fuzhou) Giant Panda Research and Exchange Centers.
Funding
This study was supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (NSFC 31872257).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
CB: writing draft article, data collection and analysis. YY: conceptualization, funding acquisition, writing draft article, data collection and analysis. Resources: XFL, MHX, WW, TJ, TCP, YL, CLZ, XGL, YQY, LQW, JZ, LLN. All authors have read and approved the manuscript.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Ethics approval and consent to participate
Blood samples were collected in accordance with the Wildlife Protection Law of the People’s Republic of China (President of the People’s Republic of China No. 16), and the experimental approach was approved by the Beijing Zoo Academic and Ethics Committee.
Consent for publication
Not applicable.
Competing interests
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary Information
Rights and permissions
Open Access This article is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License, which permits use, sharing, adaptation, distribution and reproduction in any medium or format, as long as you give appropriate credit to the original author(s) and the source, provide a link to the Creative Commons licence, and indicate if changes were made. The images or other third party material in this article are included in the article's Creative Commons licence, unless indicated otherwise in a credit line to the material. If material is not included in the article's Creative Commons licence and your intended use is not permitted by statutory regulation or exceeds the permitted use, you will need to obtain permission directly from the copyright holder. To view a copy of this licence, visit http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/. The Creative Commons Public Domain Dedication waiver (http://creativecommons.org/publicdomain/zero/1.0/) applies to the data made available in this article, unless otherwise stated in a credit line to the data.
About this article
Cite this article
Bai, C., You, Y., Liu, X. et al. A novel missense mutation in the gene encoding major intrinsic protein (MIP) in a Giant panda with unilateral cataract formation. BMC Genomics 22, 100 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1186/s12864-021-07386-8
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1186/s12864-021-07386-8