Abstract
Perioperative hemodynamic optimization, or goal-directed therapy (GDT), has been show to significantly decrease complications and risk of death in high-risk patients undergoing noncardiac surgery. An important aim of GDT is to prevent an imbalance between oxygen delivery and oxygen consumption in order to avoid the development of multiple organ dysfunction. The utilization of cardiac output monitoring in the perioperative period has been shown to improve outcomes if integrated into a GDT strategy. GDT guided by dynamic predictors of fluid responsiveness or functional hemodynamics with minimally invasive cardiac output monitoring is suitable for the majority of patients undergoing major surgery with expected significant volume shifts due to bleeding or other significant intravascular volume losses. For patients at higher risk of complications and death, such as those with advanced age and limited cardiorespiratory reserve, the addition of dobutamine or dopexamine to the treatment algorithm, to maximize oxygen delivery, is associated with better outcomes.
Similar content being viewed by others
Introduction
Noncardiac surgery in high-risk patients is associated with a high incidence of postoperative complications and high mortality rates; multiple organ failure is the main cause of death in these patients [1]. Only about 10% of all anesthetic procedures are performed in high-risk surgical patients [2]; however, these patients account for more than 80% of perioperative deaths. Surgical complications are common and often preventable, yet have a huge impact on outcomes of surgical patients. The occurrence of one of a wide range of possible complications reduces median survival by 69% [3].
Total tissue perfusion relies on adequate arterial oxygen saturation, hemoglobin concentration, and cardiac output(CO), the main components of oxygen delivery (DO2).Perioperative derangements in DO2 have been closely correlated to the development of multiple organ failure and death [4]. Meta-analyses of randomized controlled trials have shown that goal-directed therapy (GDT) or peroperative optimization, defined as the use of the DO2, CO, or a surrogate to guide intravenous fluid and inotropic therapy, significantly reduces postoperative complications and risk of death [5–13].
Perioperative physiology of oxygen delivery and consumption
The metabolic rate drives regional blood flow such that individual tissues determine their own blood flow according to their metabolic needs. Hence, CO is determined by peripheral metabolic demand. Major surgical trauma increases oxygen requirements from an average of 110 ml/minute/m2 at rest to an average of 170 ml/minute/m2 in the postoperative period [14]. This increase in oxygen demand is normally met by increases in CO and tissue oxygen extraction. Patients with limited cardiorespiratory reserve who cannot increase CO sufficiently to meet the increased oxygen demand during and after major surgery will develop an imbalance in the DO2/oxygen consumption (VO2) relationship, with an increased oxygen extraction ratio followed by decreases in mixed venous oxygen saturation (SvO2) and central venous oxygen saturation (ScvO2), oxygen debit and lactic acidosis. Lactic acidosis and prolonged lactate clearance are related to increased mortality in surgical ICU patients [1, 15, 16].
Tissue hypoxia is the central pathophysiological process in the development of organ dysfunction [1]. We ultimately wish to improve tissue perfusion, but most trials to date have targeted surrogates. Variables that are commonly used to monitor hemodynamic and oxygenation status, such as blood pressure, heart rate, urine output and arterial blood gases, can be normal in the presence of tissue hypoxia and cannot be used to rule out imbalances between oxygen supply and demand during surgical trauma [4]. SvO2 is a sensitive indicator of the adequacy of whole-body tissue oxygenation but requires placement of a pulmonary artery catheter (PAC). ScvO2 requires insertion of a central venous catheter and can be used as a surrogate for SvO2 because changes and trends in both variables parallel each other [17]. Both measures have been shown to reflect oscillations in the oxygen extraction ratio and an imbalance in the DO2/VO2 relationship in various clinical scenarios.
What are the best hemodynamic targets?
Uncovering and correcting hypovolemia
Correcting hypovolemia is a crucial step. Fluid deficits may occur for various reasons in surgical patients in the absence of obvious fluid losses because of disturbances in capillary permeability and vasodilation. Occult hypoperfusion is associated with increased mortality after major surgery even in hemodynamically stable patients [18].Hypovolemia may be present despite normalization of the heart rate, mean arterial pressure and urine output, resulting in inadequate blood flow for the increased metabolic requirements.
Monitoring of cardiac filling pressures, such as central venous pressure and pulmonary artery occlusion pressure, is unreliable for assessing cardiac preload in mechanically ventilated patients [19]. Assessment of filling pressures or end-diastolic volumes (preload) can better predict the individual response to fluid loading than can static indices (Frank-Starling curve) [19, 20]. The concept of preload dependence/independence describes the effect of fluid infusion on CO. Fluid responders convert fluid loading into a significant increase in CO as long as they have both ventricles operating in the steep portion of the curve. A fluid challenge causing an increase in stroke volume (SV) >10% (steep portion of the curve) defines a patient as a fluid responder and suggests that subsequent fluid challenge is unlikely to result in overfilling. Increases<10% (flat portion of the curve) indicate that further fluid challenge is inappropriate and could decrease ventricular performance, resulting in pulmonary or tissue edema. Nonresponders may benefit with the administration of inotropes by shifting the Frank-Starling curve up-leftwards, thereby improving the response to fluid challenges. Under similar loading conditions, patients working on the flat portion of the curve may be moved to the steep portion of the new curve.
Dynamic predictors of fluid responsiveness are increasingly used. Many studies of GDT have used repeated boluses of artificial colloids to test fluid responsiveness [21–27]. Fluid challenge-induced responses on surrogates of CO, such as the corrected flow time or SV, have been used to guide fluid resuscitation. Bundgaard-Nielsen and colleagues [5], Abbas and Hill [6] and Walsh and colleagues [7] reviewed data from studies in which a GDT strategy was used to maximize flow-derived hemodynamic variables, mostly measured using transesophageal Doppler. These authors reported reductions in postoperative nausea and vomiting, time to first bowel movement, complications and hospital length of stay. Another recent randomized controlled trial in which patients undergoing radical cystectomy were managed with cardiovascular optimization guided by transesophageal Doppler reported similar benefits [28]. In one meta-analysis, a reduction in complications >60% was reported [7].
Functional hemodynamic monitoring is used to evaluate volemia according to indices derived from cardiorespiratory interactions. Positive pressure ventilation is associated with different effects on the left and right sides of the heart. Cyclic changes in intrathoracic pressure can result in concurrent changes in SV and oscillations in arterial pulse pressure [29]. The magnitude of these oscillations is proportional to the degree of preload dependency of the patient. In patients operating on the flat portion of the Frank-Starling curve, pulse pressure variation (PPV)is low and volume loading does not result in a significant increase in SV. In patients operating on the steep portion of the preload-SV relationship, PPV is high and volume loading leads to a significant increase in SV. PPV >13% indicates that the patient is very probably on the steep part of the curve and will be a fluid responder [20].
In a study performed in 33 patients, minimization of PPV to values <10% during surgery by volume loading significantly decreased the median duration of hospital stay (7 days vs. 17 days, P <0.01), postoperative complications, and the median duration of mechanical ventilation [30]. Another study used variability in the pulse oximeter plethysmogram, the pleth variability index [31]. The intraoperative intervention was directed to fluid loading with colloids to minimize the pleth variability index to<13%. Intraoperative crystalloids, the total volume infused, and lactate levels were significantly lower in the pleth variability index group. SV variation or systolic pressure variation as measured by the analysis of the arterial pressure waveform also enables prediction of volume responsiveness in ventilated patients. The greater the variation of these indices, the more CO can be expected to increase in response to volume loading. Fluid optimization guided by minimization of SV variation to<10% during major abdominal surgery was associated with better intraoperative hemodynamic stability, lower serum lactate and fewer postoperative complications [32]. Conversely, compared with conventional treatment, systolic pressure variation-guided intraoperative fluid management in patients undergoing elective major surgery was associated with slightly increased fluid administration, whereas organ perfusion and function were similar [33].
A number of indices based on ventilation-induced variability of the arterial pressure wave are useful during GDT for patients deeply sedated, anesthetized, mechanically ventilated, and with normal cardiac function. Based on current knowledge we can target values of PPV,SV variation or pleth variability index <10 to 13% for these patients, although more studies on the optimal thresholds to predict fluid responsiveness during GDT are warranted as variations may occur even with different devices [34]. For the other patients, monitoring of CO or surrogates and use of dynamic predictors of fluid responsiveness would be more suitable (Table 1).
Targeting tissue perfusion in high-risk surgical patients
Many small single-center studies have demonstrated impressive reductions in morbidity and mortality associated with a treatment strategy aimed at preemptive optimization by increasing the DO2 index to levels >600 ml/minute/m2 [35–38]. These protocols had the following circumstances in common: they were carried out preemptively in high-risk patients, they started before and continued some hours after surgical trauma, and they used inotropes, blood, and vasodilators if necessary, in addition to fluids.
Systematic reviews and meta-analyses [8–13] have explored whether preemptive strategies of hemodynamic monitoring and manipulation in the perioperative period could improve outcomes for moderate-risk and high-risk surgical patients. These systematic reviews showed that interventions aimed at preemptive hemodynamic optimization did reduce mortality.
Hamilton and colleagues identified 29 randomized clinical trials comprising 4,805 moderate-risk or high-risk surgical patients [12]. The use of a preemptive hemodynamic intervention significantly reduced mortality (pooled odds ratio (95% confidence interval) = 0.48 (0.33 to 0.78); P = 0.0002) and surgical complications (odds ratio (95% confidence interval) = 0.43 (0.34 to 0.53); P <0.0001). Complications were reduced in all studies, but subgroup analysis revealed that mortality was reduced solely in those studies using a PAC as opposed to minimally invasive methods of monitoring, in those using fluids and inotropes as opposed to fluids alone, in those using the cardiac index or DO2 as the end point, and in those studies using a supranormal resuscitation target.
Gurgel and do Nascimento identified 32 studies involving 5,056 high-risk surgical patients in which well-defined protocols were used to maintain tissue perfusion with fluids and/or inotropes [13]. Trials that included perioperative interventions aimed at the hemodynamic optimization of higher-risk surgical patients (studies with mortality rates in the control group >20%) reported significantly reduced mortality rates (pooled odds ratio (95% confidence interval) = 0.32 (0.21 to 0.47); P≤0.00001).Studies using a PAC for hemodynamic monitoring and the cardiac index, DO2 or VO2 as therapeutic goals achieved statistical significance for reductions in mortality. The results of this meta-analysis confirm the findings of an older review by Kern and Shoemaker indicating that patients with higher mortality rates are the most likely to benefit from preoperative or intraoperative GDT [9].
In other preoperative or intraoperative interventional studies, different goals - such as normal values of cardiac index or DO2 - were used, mainly to guide fluid resuscitation [39–43]. These studies did not report better outcomes with this strategy, except for a decrease in the rate of complications in one study [39]. This observation suggests that normal values may not be normal during surgical trauma. One study using DO2-oriented optimization therapy with fluids and dopexamine to achieve levels >600 ml/minute/m2 during the first 8 hours after operation showed a significant decrease in postoperative complications but no differences in mortality rates [44].
Indeed, in patients with a high risk of perioperative death, PAC-guided hemodynamic optimization using dobutamine to obtain DO2 >600 ml/minute/m2 was associated with better outcomes, whereas fluids alone increased the incidence of postoperative complications [45]. The use of two different treatment algorithms of GDT comparing fluids alone with fluids and dobutamine suggests that dobutamine was associated with better recovery of the left ventricular stroke work index during operative trauma and with higher tolerance to fluids. Nevertheless, dobutamine is also able to improve micro-circulation [46]. Jhanji and colleagues reported micro-vascular alterations in patients undergoing major surgeries who developed postoperative complications [47, 48]. By adding SV-guided fluid therapy and low-dose dopexamine to the algorithm of treatment, DO2 increased along with significant improvements in sublingual and cutaneous microcirculatory blood flow [48].
In studies performed in high-risk patients submitted to major surgery, ScvO2 levels of 65% [49] and 73% [50] at ICU admission were found to discriminate best between patients with and without complications. Other authors reported much higher levels of ScvO2 (>80%) intra-operatively and that only preoperative levels of ScvO2<70% were predictive of postoperative complications [51].
Use of SvO2 or ScvO2 as a target variable to improve outcomes in high-risk patients has been tested in a few studies. In vascular surgery patients, optimization of DO2 to achieve SvO2 levels >65% was not associated with better outcomes [52]. However, early management with fluid challenges, dobutamine and blood transfusion directed to maintain the oxygen extraction ratio estimated from ScvO2 values at levels <27%, both during major abdominal surgery and postoperatively, significantly reduced the number of organ failures and duration of hospital stay [53].
Despite the fact that the oxygen extraction ratio, SvO2 or ScvO2 could in theory be a good monitor of the systemic balance between global DO2 and consumption and of the favorable effects on morbidity, pooling of studies using GDT guided by these variables did not demonstrate beneficial effects on mortality [12, 13]. Perioperative oxygen consumption is determined by various factors, particularly the depth of anesthesia and body temperature. Perioperative disturbances in ScvO2 therefore cannot be assumed to relate solely to DO2. Finally, replacing SvO2 monitoring with ScvO2 monitoring in order to avoid the use of a PAC is still controversial, at least in cardiac surgery patients, in severe sepsis during the first 24 hours after ICU admission and in other heterogeneous groups of critically ill patients [54–56].
In view of these conflicting results and the various thresholds reported, we would rather say that SvO2 or ScvO2 should not currently be used as a target in anesthetized high-risk patients. However, postoperatively in the recovery room or ICU, additional therapy titrated to achieve normal levels of ScvO2, serum lactate and venous-to-arterial carbon dioxide difference is necessary to restore adequate systemic oxygenation [57–59].
Does the most current evidence support these targets?
We acknowledge that the small size of the majority of the studies into GDT is a potential source of bias [60]. In addition, many of these studies were carried out several years ago. Indeed, in the last decade invasive hemodynamic monitoring with a PAC has been increasingly replaced by various minimally invasive technologies, and new practices such as enhanced recovery after surgery strategies, restrictive strategies of fluid maintenance, and fast-track surgeries have been adopted. Outcomes have improved as a result, making the benefits of GDT more difficult to demonstrate.
In patients undergoing laparoscopic colectomy, Senagore and colleagues reported a longer time to discharge in the two groups of patients undergoing trans-esophageal Doppler-guided GDT with an enhanced recovery after the surgery protocol compared with control patients [61]. In patients undergoing elective colorectal surgery, Brandstrup and colleagues found no differences when comparing maximization of SV guided by transesophageal Doppler with a restrictive strategy of fluid maintenance aiming at zero fluid balance [62]. Challand and colleagues reported detrimental effects of GDT on hospital length of stay in aerobically fit patients undergoing open or laparoscopic colorectal surgery [63].
Nevertheless, more small clinical trials continue to add to the literature in favor of GDT. Cecconi and colleagues found that GDT with fluids and dobutamine reduced postoperative cardiovascular complications in patients undergoing elective total hip replacement under regional anesthesia [64]. Bisgaard and colleagues showed that the intraoperative optimization of SV, using dobutamine if necessary, in patients undergoing lower-limb arterial surgery significantly decreased postoperative complications [65]. These two studies target DO2 >600 ml/minute/m2. Interestingly, using the same algorithm of treatment in another study performed in patients undergoing aortic surgery, Bisgaard and colleagues found no differences in outcomes [66].
These findings warrant further comment. First, the use of individualized goals instead of a preset arbitrary value >600 ml/minute/m2 is more rational and would avoid potential adverse events related to GDT. However, no marker of adequacy is yet available to be used intraoperatively. The critical DO2 is the point below which dependence between DO2 and VO2 is observed, and this point varies for different organs; regional hypoperfusion may therefore occur despite a normal global oxygen extraction rate. Achievement of the 600 ml/minute/m2 value is possibly not what determines better outcomes. Rather, keeping DO2 above baseline while trying to reach this number and, as a consequence, preventing oxygen debt may be more important. By targeting a supranormal value, the likelihood of having more patients without tissue hypoxia and for longer periods probably increases. Supranormal values of DO2 should perhaps be defined in relation to normal preoperative values and predicted increases in VO2 for different types of surgery and not set at 600 ml/minute/m2 for all, but this suggestion requires further tests in future studies.
Second, despite what many believe to be conflicting bodies of evidence, volume optimization can in fact be complementary to a restrictive fluid approach, particularly with regard to crystalloids [67]. Lobo and colleagues evaluated two regimens of intraoperative fluid maintenance during optimization of DO2 with fluids and dobutamine, and found that a restrictive regimen of crystalloid maintenance at 4 ml/kg/minute during surgery was associated with better outcomes than was a conventional regimen of 12 ml/kg/minute [68]. The total volume used as the maintenance fluid during and after surgery, particularly in prolonged surgeries, might be carefully considered.
Finally, although multicenter prospective randomized controlled trials are lacking, the evidence for the benefits is considered strong. Despite these promising results, this GDT approach has not been widely adopted. Unfortunately, clinical experience, blood pressure, central venous pressure and urine output are still the most widely used indicators of volume expansion and adequacy of resuscitation during surgery [69]. Implementing evidence-based practice such as perioperative hemodynamic optimization in high-risk patients undergoing noncardiac surgery remains a challenge.
Which targets for which patients?
We can separate the candidates for GDT into two groups of patients. The precise correction of hypovolemia will be enough to achieve the goals of therapy in the large majority of surgical patients. For high-risk patients, uncovering and correcting hypovolemia is crucial beforeother therapies likely to increase DO2 - for example, blood transfusions, vasopressors or inotropes - are used.
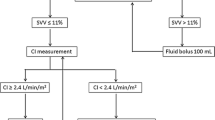
The first group comprises the majority of patients undergoing major surgery, who are at risk of significant volume shifts during surgery because of bleeding or other significant intravascular volume losses. For these patients, the use of dynamic indices to ensure normovolemia and preemptive hemodynamic optimization with minimally invasive CO monitoring or surrogates guided by SV or CO responses to fluid challenge is suitable (Figure 1). Inotropes or vasopressors should be used in this group only in the presence of inadequate CO or blood pressure, a decrease in urine output or signs of hypoperfusion, after fluid responsiveness testing is negative.
The second group of candidate patients includes those with a higher risk of morbidity and mortality. In spite of the multifactorial origin of postoperative complications, compromised physiologic reserves and multiple comorbidities in combination with extensive surgery seem to be a hallmark of high complication and mortality rates [44]. In general, these patients are older, undergoing extensive ablative surgery with limited cardiopulmonary reserve, and/or with other organ dysfunctions/comorbidities (Figure 2) [38, 45, 65]. Shoemaker and colleagues' criteria for identifying a high-risk of perioperative complications will also identify patients to be managed in this group [35]. For these patients we can monitor DO2 continuously, with minimally invasive hemodynamic monitoring or a PAC, initially testing fl uid responsiveness and maximizing SV and then preemptively augmenting DO2 with dobutamine or dopexamine if necessary to achieve the best possible value.
Algorithm for peroperative hemodynamic optimization in high-risk patients undergoing major surgeries. Shoemakers' criteria from [35]. DO2, oxygen delivery; GDT, goal-directed therapy.
Conclusion
A considerable number of randomized and controlled studies in high-risk surgical patients have reported improved outcomes with GDT. As the population ages and more complex surgery is performed, the number of patients requiring major surgery and at a high risk of complications is going to increase. In the intraoperative period, targeting dynamic predictors of fluid responsiveness or functional hemodynamics with minimally invasive CO monitoring is suitable for the majority of patients undergoing major surgery. For patients at a higher risk of complications and death, the maximization of DO2 is associated with better outcomes. In the ICU, additional therapy titrated to increase ScvO2 or the venous-to-arterial carbon dioxide difference and to decrease serum lactate concentrations may be necessary to restore adequate systemic oxygenation.
Abbreviations
- CO:
-
cardiac output
- DO2:
-
oxygen delivery
- GDT:
-
goal-directed therapy
- PAC:
-
pulmonary artery catheter
- PPV:
-
pulse pressure variation
- ScvO2:
-
central venous oxygen saturation
- SV:
-
stroke volume
- SvO2:
-
mixed venous oxygen saturation
- VO2:
-
oxygen consumption.
References
Lobo SM, Rezende E, Knibel MF, Silva NB, Páramo JA, Nácul FE, Mendes CL, Assunção M, Costa RC, Grimm CC, Pinto SF, Mello PM, Maia MO, Duarte PA, Gutierrez F, Silva JM Jr, Lopes MR, Cordeiro JA, Mellot C: Early determinants of death due to multiple organ failure after non cardiac surgery in high-risk patients. Anesth Analg 2011, 112: 877-883. 10.1213/ANE.0b013e3181e2bf8e
Pearse RM, Harrison DA, James P, Pearse RM, Harrison DA, James P, Watson D, Hinds C, Rhodes A, Grounds M, Bennett D: Identification and characterisation of the high-risk surgical population in the United Kingdom. Crit Care 2006, 10: R8. 10.1186/cc3934
Khuri SF, Henderson WG, DePalma RG, Mosca C, Healey NA, Kumbhani DJ, Participants in the VA National Surgical Quality Improvement Program: Determinants of long-term survival after major surgery and the adverse effect of postoperative complications. Ann Surg 2005, 242: 326-341.
Shoemaker WC, Montgomery ES, Kaplan E, Elwyn DW: Physiologic patterns in surviving and nonsurviving shock patients. Use of sequential cardiorespiratory variables in defining criteria for therapeutic goals and early warning of death. Arch Surg 1993, 106: 630-636.
Bundgaard-Nielsen M, Holte K, Secher NH, Kehlet H: Monitoring of perioperative fluid administration by individualized goal-directed therapy. Acta Anaesthesiol Scand 2007, 51: 331-340. 10.1111/j.1399-6576.2006.01221.x
Abbas SM, Hill AG: Systematic review of the literature for the use of oesophageal Doppler monitor for fluid replacement in major abdominal surgery. Anaesthesia 2008, 63: 44-45.
Walsh SR, Tang T, Bass S, Gaunt ME: Doppler-guided intra-operative fluid management during major abdominal surgery: systematic review and meta-analysis. Int J Clin Pract 2008, 62: 466-470.
Heyland DK, Cook DJ, King D, Kernerman P, Brun-Buisson C: Maximizing oxygen delivery in critically ill patients: a methodologic appraisal of the evidence. Crit Care Med 1996, 24: 517-524. 10.1097/00003246-199603000-00025
Kern JW, Shoemaker WC: Meta-analysis of hemodynamic optimization in high-risk patients. Crit Care Med 2002, 30: 1686-1692. 10.1097/00003246-200208000-00002
Boyd O: Optimisation of oxygenation and tissue perfusion in surgical patients. Intensive Crit Care Nurs 2003, 19: 171-181. 10.1016/S0964-3397(03)00026-0
Poeze M, Greve JW, Ramsay G: Meta-analysis of hemodynamic optimization: relationship to methodological quality. Crit Care 2005, 9: R771-R779. 10.1186/cc3902
Hamilton MA, Cecconi M, Rhodes A: A systematic review and meta-analysis on the use of preemptive hemodynamic intervention to improve postoperative outcomes in moderate and high-risk surgical patients. Anesth Analg 2011, 112: 1392-1402. 10.1213/ANE.0b013e3181eeaae5
Gurgel ST, do Nascimento P Jr: Maintaining tissue perfusion in high-risk surgical patients: a systematic review of randomized clinical trials. Anesth Analg 2011, 112: 1384-1391. 10.1213/ANE.0b013e3182055384
Older P, Hall A, Hader R: Cardiopulmonary exercise testing as a screening test for perioperative management of major surgery in the elderly. Chest 1999, 116: 355-362. 10.1378/chest.116.2.355
Husain FA, Martin MJ, Mullenix PS, Steele SR, Elliott DC: Serum lactate and base deficit as predictors of mortality and morbidity. Am J Surg 2003, 185: 485-491. 10.1016/S0002-9610(03)00044-8
McNelis J, Marini CP, Jurkiewicz A, Szomstein S, Simms HH, Ritter G, Nathan IM: Prolonged lactate clearance is associated with increased mortality in the surgical intensive care unit. Am J Surg 2001, 182: 481-485. 10.1016/S0002-9610(01)00755-3
Reinhart K, Kuhn HJ, Hartog C, Bredle DL: Continuous central venous and pulmonary artery oxygen saturation monitoring in the critically ill. Intensive Care Med 2004, 30: 1572-1578.
Meregalli A, Oliveira RP, Friedman G: Occult hypoperfusion is associated with increased mortality in hemodynamically stable, high-risk, surgical patients. Crit Care 2004, 8: R60-R65. 10.1186/cc2423
Vincent JL, Weil MH: Fluid challenge revisited. Crit Care Med 2006, 34: 1333-1337. 10.1097/01.CCM.0000214677.76535.A5
Marik PE, Cavallazzi R, Vazu T, Hirani A: Dynamic changes in arterial waveform derived variables and fluid responsiveness in mechanically ventilated patients: a systematic review of the literature. Crit Care Med 2009, 37: 2642-2647. 10.1097/CCM.0b013e3181a590da
Mythen MG, Webb AR: Perioperative plasma volume expansion reduces the incidence of gut mucosal hypoperfusion during cardiac surgery. Arch Surg 1995, 130: 423-429. 10.1001/archsurg.1995.01430040085019
Sinclair S, James S, Singer M: Intraoperative intravascular volume optimization and length of stay after repair of proximal femoral fracture: randomized control trial. BMJ 1997, 315: 909-912. 10.1136/bmj.315.7113.909
Gan TJ, Soppitt A, Maroof M, el-Moalem H, Robertson KM, Moretti E, Dwane P, Glass PS: Goal-directed intraoperative fluid administration reduces length of hospital stay after major surgery. Anesthesiology 2002, 97: 820-826. 10.1097/00000542-200210000-00012
Conway DH, Mayall R, Abdul-Latif MS, Gilligan S, Tackaberry C: Randomised controlled trial investigating the influence of intravenous fluid titration using oesophageal Doppler monitoring during bowel surgery. Anaesthesia 2002, 57: 845-849. 10.1046/j.1365-2044.2002.02708.x
Venn R, Steele A, Richardson P, Poloniecki J, Grounds M, Newman : Randomized controlled trial to investigate influence of the fluid challenge on duration of hospital stay and perioperative morbidity in patients with hip fractures. Br J Anaesth 2002, 88: 65-71. 10.1093/bja/88.1.65
Wakeling HG, McFall MR, Jenkins CS, Woods WG, Miles WF, Barclay GR, Fleming SC: Intraoperative oesophageal Doppler guided fluid management shortens postoperative hospital stay after major bowel surgery. Br J Anaesth 2005, 95: 634-642. 10.1093/bja/aei223
Noblett SE, Snowden CP, Shenton BK, Horgan AF: Randomized clinical trial assessing the effect of Doppler-optimized fluid management on outcome after elective colorectal resection. Br J Surg 2006, 93: 1069-1076. 10.1002/bjs.5454
Pillai P, Gaughan M, Snowden C, Nesbitt I, Durkan G, Johnson M, Cosgrove J, Thorpe A: A double-blind randomized controlled clinical trial to assess the effect of Doppler optimized intraoperative fluid management on outcome following radical cystectomy. J Urol 2011, 186: 2201-2206. 10.1016/j.juro.2011.07.093
Michard F, Teboul JL: Using heart-lung interactions to assess fluid responsiveness during mechanical ventilation. Crit Care 2000, 4: 282-289. 10.1186/cc710
Lopes MR, Oliveira MA, Pereira VOS, Lemos IPB, Auler JOC Jr, Michard F: Goal-directed fluid management based on pulse pressure variation monitoring during high-risk surgery: a pilot randomized controlled trial. Crit Care 2007, 11: R100. 10.1186/cc6117
Forget P, Lois F, de Kock M: Goal-directed fluid management based on the pulse oximeter-derived pleth variability index reduces lactate levels and improves fluid management. Anesth Analg 2010, 111: 910-914.
Benes J, Chytra I, Altmann P, Hluchy M, Kasal E, Svitak R, Pradl R, Stepan M: Intraoperative fluid optimization using stroke volume variation in high risk surgical patients: results of prospective randomized study. Crit Care 2010, 14: R118. 10.1186/cc9070
Buettner M, Schummer W, Huettemann E, Schenke S, van Hout N, Sakka SG: Influence of systolic-pressure-variation guided intraoperative fluid management on organ function and oxygen transport. Br J Anaesth 2008, 101: 194-199. 10.1093/bja/aen126
Hofer CK, Senn A, Weibel L, Zollinger A: Assessment of stroke volume variation for prediction of fluid responsiveness using the modified FloTrac and PiCCOplus system. Crit Care 2008, 12: R82. 10.1186/cc6933
Shoemaker WC, Appel PL, Kram HB, Waxman K, Lee TS: Prospective trial of supranormal values of survivors as therapeutic goals in high-risk surgical patients. Chest 1988, 94: 1176-1186. 10.1378/chest.94.6.1176
Boyd O, Grounds M, Bennett D: Preoperative increase of oxygen delivery reduces mortality in high-risk surgical patients. JAMA 1993, 270: 2699-2707. 10.1001/jama.1993.03510220055034
Wilson J, Woods I, Fawcett J, Whall R, Dibb W, Morris C, McManus E: Reducing the risk of major surgery: randomized controlled trial of preoptimization of oxygen delivery. BMJ 1999, 318: 1099-1103. 10.1136/bmj.318.7191.1099
Lobo SMA, Salgado PF, Castillo VGT, Borin AA, Poalachini J, Palchetti JC, Brienzi SL, Oliveira GG: Effects of maximizing oxygen delivery on morbidity and mortality in high risk surgical patients. Crit Care Med 2000, 28: 3396-3404. 10.1097/00003246-200010000-00003
Berlauk JF, Abrams JH, Gilmour IJ, O'Connor SR, Knighton DR, Cerra FB: Pre-operative optimization of cardiovascular hemodynamics improves outcome in peripheral vascular surgery. Ann Surg 1991, 214: 289-297. 10.1097/00000658-199109000-00011
Bender JS, Smith-Meek MA, Jones CE: Routine pulmonary artery catheterization does not reduce morbidity and mortality of elective vascular surgery: results of a prospective, randomized trial. Ann Surg 1997, 226: 229-236. 10.1097/00000658-199709000-00002
Valentine RJ, Duke ML, Inman MH, Grayburn PA, Hagino RT, Kakish HB, Clagett GP: Effectiveness of pulmonary artery catheters in aortic surgery: a randomized trial. J Vasc Surg 1998, 27: 203-212. 10.1016/S0741-5214(98)70351-9
Bonazzi M, Gentile F, Biasi GM, Migliavacca S, Esposti D, Cipolla M, Marsicano M, Prampolini F, Ornaghi M, Sternjakob S, Tshomba Y: Impact of perioperative haemodynamic monitoring on cardiac morbidity after major vascular surgery in low risk patients. A randomised pilot trial. Eur J Vasc Endovasc Surg 2002, 23: 445-451. 10.1053/ejvs.2002.1617
Sandham JD, Hull RD, Brant RF, Knox L, Pineo GF, Doig CJ, Laporta DP, Viner S, Passerini L, Devitt H, Kirby A, Jacka M, Canadian Critical Care Clinical Trials Group: A randomized, controlled trial of the use of pulmonary-artery catheters in high-risk surgical patients. N Engl J Med 2003, 348: 5-14. 10.1056/NEJMoa021108
Pearse R, Dawson D, Fawcett J, Rhodes A, Grounds RM, Bennett ED: Early goal-directed therapy after major surgery reduces complications and duration of hospital stay. A randomised, controlled trial [ISRCTN38797445]. Crit Care 2005, 9: R687-R693. 10.1186/cc3887
Lobo SM, Lobo FR, Polachini CA, Patini DS, Yamamoto AE, de Oliveira NE, Serrano P, Sanches HS, Spegiorin MA, Queiroz MM, Christiano AC Jr, Savieiro EF, Alvarez PA, Teixeira SP, Cunrath GS: Prospective, randomized trial comparing fluids and dobutamine optimization of oxygen delivery in high-risk surgical patients [ISRCTN42445141]. Crit Care 2006, 10: R72. 10.1186/cc4913
De Backer D, Creteur J, Dubois MJ, Sakr Y, Koch M, Verdant C, Vincent JL: The effects of dobutamine on microcirculatory alterations in patients with septic shock are independent of its systemic effects. Crit Care Med 2006, 34: 403-408. 10.1097/01.CCM.0000198107.61493.5A
Jhanji S, Lee C, Watson D, Hinds C, Pearse RM: Microvascular flow and tissue oxygenation after major abdominal surgery: association with postoperative complications. Intensive Care Med 2009, 35: 671-677. 10.1007/s00134-008-1325-z
Jhanji S, Vivian-Smith A, Lucena-Amaro S, Watson D, Hinds CJ, Pearse RM: Haemodynamicoptimisation improves tissue microvascular flow and oxygenation after major surgery: a randomised controlled trial. Crit Care 2010, 14: R151. 10.1186/cc9220
Pearse R, Dawson D, Fawcett J Rhodes A, Grounds RM, Bennett ED: Changes in central venous saturation after major surgery, and association with outcome. Crit Care 2005, 9: R694-R699. 10.1186/cc3888
Collaborative Study Group on Perioperative ScvO2 Monitoring: Multicentre study on peri- and postoperative central venous oxygen saturation in high-risk surgical patients. Crit Care 2006, 10: R158.
Silva Junior JM, Oliveira AM, Morais SZ, Araujo LS, Victoria LGF, Marubayashi LY: Influência da saturação venosa central de oxigênio na mortalidade hospitalar de pacientes cirúrgicos. Rev Bras Anestesiol 2010, 60: 597-602.
Ziegler DW, Wright JG, Choban PS, Flancbaum L: A prospective randomized trial of preoperative 'optimization' of cardiac function in patients undergoing elective peripheral vascular surgery. Surgery 1997, 122: 584-592. 10.1016/S0039-6060(97)90132-X
Donati A, Loggi S, Preiser JC, Orsetti G, Münch C, Gabbanelli V, Pelaia P, Pietropaoli P: Goal-directed intraoperative therapy reduces morbidity and length of hospital stay in high-risk surgical patients. Chest 2007, 132: 1817-1824. 10.1378/chest.07-0621
Lequeux PY, Bouckaert Y, Sekkat H, Van der Linden P, Stefanidis C, Huynh CH, Bejjani G, Breads P: Continuous mixed venous and central venous oxygen saturation in cardiac surgery with cardiopulmonary bypass. Eur J Anaesthesiol 2010, 27: 295-299. 10.1097/EJA.0b013e3283315ad0
Van Besst PA, van Ingen J, Boerma EC, Holman ND, Groen H, Koopmans M, spronk PE, Kuiper MA: No agreement of mixed venous and central venous saturation in sepsis, independent of sepsis origin. Crit Care 2010, 14: R219. 10.1186/cc9348
Chawla LS, Zia H, Gutierrez G, Katz NM, Shah M: Lack of equivalence between central and mixed venous oxygen saturation. Chest 2004, 126: 1891-1896. 10.1378/chest.126.6.1891
Rady MY, Rivers EP, Nowak RM: Resuscitation of the critically ill in the ED: responses of blood pressure, heart rate, shock index, central venous oxygen saturation, and lactate. Am J Emerg Med 1996, 14: 218-225. 10.1016/S0735-6757(96)90136-9
Futier E, Robin E, Jabaudon M, Guerin R, Petit A, Bazin JE, Constantin JM, Vallet B: Central venous O 2 saturation and venous-to-arterial CO 2 difference as complementary tools for goal-directed therapy during high-risk surgery. Crit Care 2010, 14: R193. 10.1186/cc9310
Jansen TC, van Bommel J, Schoonderbeek FJ, SleeswijkVisser SJ, van der Klooster JM, Lima AP, Willemsen SP, Bakker J, Lactate Study Group: Early lactate-guided therapy in intensive care unit patients: a multicenter, open-label, randomized controlled trial. Am J Respir Crit Care Med 2010, 182: 752-761. 10.1164/rccm.200912-1918OC
MacDonald N, Pearse RM: Peri-operative hemodynamic therapy: only large clinical trials can resolve our uncertainty. Crit Care 2011, 15: 122. 10.1186/cc10011
Senagore AJ, Emery T, Luchtefeld M, Kim D, Dujovny N, Hoedema R: Fluid management for laparoscopic colectomy: a prospective, randomized assessment of goal-directed administration of balanced salt solution or hetastarch coupled with an enhanced recovery program. Dis Colon Rectum 2009, 52: 1935-1940. 10.1007/DCR.0b013e3181b4c35e
Brandstrup B, Svendsen PE, Rasmussen M, Belhage B, Rodt SÅ, Hansen B, Møller DR, Lundbech LB, Andersen N, Berg V, Thomassen N, Andersen ST, Simonsen L: Which goal for fluid therapy during colorectal surgery is followed by the best outcome: near-maximal stroke volume or zero fluid balance? Br J Anaesth 2012, 109: 191-199. 10.1093/bja/aes163
Challand C, Struthers R, Sneyd JR, Erasmus PD, Mellor N, Hosie KB, Minto G: Randomized controlled trial of intraoperative goal-directed fluid therapy in aerobically fit and unfit patients having major colorectal surgery. Br J Anaesth 2012, 108: 53-62. 10.1093/bja/aer273
Cecconi M, Fasano N, Langiano N, Divella M, Costa MG, Rhodes A, Della Rocca G: Goal-directed haemodynamic therapy during elective total hip arthroplasty under regional anaesthesia. Crit Care 2011, 15: R132. 10.1186/cc10246
Bisgaard J, Gilsaa T, Rønholm E, Toft P: Haemodynamic optimisation in lower limb arterial surgery: room for improvement? Acta Anaesthesiol Scand 2012, in press.
Bisgaard J, Gilsaa T, Rønholm E, Toft P: Optimising stroke volume and oxygen delivery in abdominal aortic surgery: a randomised controlled trial. Acta Anaesthesiol Scand 2012, in press.
Miller TE, Roche AM, Gan TJ: Poor adoption of hemodynamic optimization during major surgery: are we practicing substandard care? Anesth Analg 2011, 112: 1274-1276. 10.1213/ANE.0b013e318218cc4f
Lobo SM, Ronchi LS, Oliveira NE, Brandão PG, Froes A, Cunrath GS, Nishiyama KG, Netinho JG, Lobo FR: Restrictive strategy of intraoperative fluid maintenance during optimization of oxygen delivery decreases major complications after high-risk surgery. Crit Care 2011, 15: R226. 10.1186/cc10466
Cannesson M, Pestel G, Ricks C, Hoeft A, Perel A: Hemodynamic monitoring and management in patients undergoing high-risk surgery: a survey among North American and European anesthesiologists. Crit Care 2011, 15: R197. 10.1186/cc10364
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Competing interests
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Authors’ original submitted files for images
Below are the links to the authors’ original submitted files for images.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Lobo, S.M., de Oliveira, N.E. Clinical review: What are the best hemodynamic targets for noncardiac surgical patients?. Crit Care 17, 210 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1186/cc11861
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1186/cc11861