Abstract
Replication of HIV-1 involves a series of obligatory steps such as reverse transcription of the viral RNA genome into double-stranded DNA, and subsequent integration of the DNA into the human chromatin. Integration is an essential step for HIV-1 replication; yet the natural process of HIV-1 infection generates both integrated and high levels of non-integrated DNA. Although proviral DNA is the template for productive viral replication, the non-integrated DNA has been suggested to be active for limited viral gene synthesis. In this review, the regulation of viral gene expression from proviral DNA will be summarized and issues relating to non-integrated DNA as a template for transcription will be discussed, as will the possible function of pre-integration transcription in HIV-1 replication cycle.
Similar content being viewed by others
Introduction
Intracellular parasites such as viruses depend on cellular machinery to disseminate their genetic information. Different viruses evolve different strategies to utilize the host machinery. The human immunodeficiency virus (HIV), prototype of the lentiviral subfamily of Retroviruses, is one of the ultimate players in exploiting the host mechanism. Its RNA genome is first reverse transcribed into a DNA template, integrated into host chromatin, then transcribed as a cellular gene. Only one viral encoded transcription factor, Tat (Trans-activator of transcription), is directly involved in the process of viral gene transcription. While HIV gene expression heavily depends on cellular machinery, it also has some unique features. This review will cover aspects related to regulations of HIV gene expression, with focus on transcription from non-integrated HIV DNA.
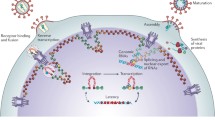
As with most retroviruses, HIV begins its life cycle with the infection of target cells through cell surface receptors. Following viral entry, the viral RNA genome is reverse transcribed into a double-stranded DNA molecule and enters the nucleus as a nucleic acid-protein complex (the preintegration complex), which mediates the integration of viral DNA into the host chromatin. The integrated provirus then serves as a template for the transcription of viral genes [1] (Figure 1). Integration is a decisive step for stable maintenance of the viral genome and an obligatory process for viral replication [2–5]. Nevertheless, some HIV-1 integrase mutants have been shown to replicate unexpectedly in certain T cell lines such as MT-4 and C8166 [6]. These cell lines were transformed with human T-cell leukemia virus (HTLV-1). Possible synergistic effects or complementation between HIV and HTLV may contribute to the replication of integration negative viruses [6]. Rare, non-viral mediated integration of retroviral DNA has also been observed in infection with integration negative viruses. The non-viral integration is characterized by extremely low efficiency, deletions at the viral-cellular DNA junction or oligomerization of viral DNA [7].
HIV-1 life cycle and model of transcription from pre-integrated viral DNA and provirus. Following HIV infection of T cells by specific interaction of viral envelop protein with the CD4 receptor and chemokine co-receptor on T cell surface, the viral RNA genome is reverse transcribed into a full-length double stranded DNA (step 1), and enters the nucleus as a pre-integration complex (step 2). Prior to integration, the non-integrated DNA, in the forms of linear, 1-LTR- or 2-LTR-circles, is active in transcribing all three classes of viral transcripts: the multiply spliced, singly spliced and full-length transcripts (step 3). The multiply spliced, early transcripts such as tat, nef and rev are also translated into products. These early viral factors can enhance T cell activity and promote viral replication process. The non-spliced and singly spliced viral transcripts encoding viral structural proteins are not translated. Following viral integration (step 4), post-integration transcription initiates (step 5). Expression of these transcripts leads to production of progeny virions (step 6).
Retrovial integration is a specific process mediated by viral encoded integrases, which are biochemically both necessary and sufficient for integration. Although integration occurs randomly in vitro in assay conditions, in vivo, it preferentially occurs in the upstream portion of active genes or near DNAse-hypersensitive sites [8]. In addition, not all regions of the genome are equally favored for integration [9]. Recent analyses of 524 HIV DNA integration sites confirmed these early findings and indicate that integration prefers active genes and genes that are activated after HIV infection [10]. Regional hotspots for integration were also found on cellular chromosomes. However, these findings are in contrast to one previous study on an onco-retrovirus, which suggests that active transcription inhibits viral integration [11]. The discrepancy may be due to a difference in integration site selection between HIV and onco-retroviruses. Integration into active genes could be an advantage for viral replication. Presumably the local chromatin environment of transcribing genes would favor proviral transcription.
Transcription from provirus
Regulation of HIV gene expression involves a complex interplay between chromatin-associated proviral DNA, cellular transcription factors and the viral encoded trans-activator of transcription, Tat. The process of viral transcription can be divided into two distinct phases. The first phase occurs early in transcription and is mediated by direct interaction between cellular transcription factors and cis-acting elements located in the HIV promoter region. The second phase immediately follows the first one, and relies on the accumulation of sufficient amounts of Tat from the first phase [12]. Following integration, the HIV promoter is under the control of local chromatin environment, which determines the basal transcriptional activity. Independent of the site of integration, HIV 5' LTR is assembled into three unique nucleosomes: nuc-0, -1 and -2. Nuc-1 is positioned immediately downstream of the transcription start site [13, 14], and is rapidly disrupted upon transcriptional activation of the HIV-1 promoter [15]. Interestingly, the region between nuc-0 and 1 appears to remain nucleosome-free although it is large enough to accommodate an additional nucleosome. Multiple cellular transcription factors constantly bind to this region [16, 17], which can induce significant DNA bending. As a result, these factors may affect nucleosome assembly, either by direct competing with histons or by rendering the nucleosome-free region a disfavored site for nucleosome assembly [14]. This nuclesome-free region is also where the LTR core promoter and enhancer are located. The viral core or basal promoter (nt -78 to -1) contains a TATAA box and three consensus SP1 binding sites. The enhancer (nt -105 to -79) carries a duplication of the 10-bp NF-kB binding sites. Regions upstream from the NF-kB sites also influence viral gene expression and are designated the modulatory region (-454 to -104). This region has been proposed to contain a negative regulatory element (NRE) [18, 19]. Multiple cellular factors such as NF-AT, USF, Ap-1, c-Myb, COUP have been proposed to interact with the modulatory region. For a comprehensive list of cellular transcription factors interacting with the HIV-1 LTR promoter, please refer to a recent review by Pereira et al. [20]. Sequences near the RNA initiation site also contain regulatory elements such as the putative inducer of short transcripts (IST) [21, 22], the initiator and the trans-activation response (TAR) element (nt +1 to +60) which interacts with Tat and plays an important role in Tat mediated trans-activation.
In the absence of Tat and cellular stimulation, the nucleosome packed LTR is almost silent. Low levels of transcription are mediated by available cellular transcription factors. Efficient activation of the LTR promoter is largely driven by Tat, and is concomitant with an acetylation-dependent rearrangement of the nucleosome ponsitioned at the viral transcription start site [12, 23–25]. Tat has been suggested to be involved in remodeling nucleosomes to relieve transcriptional blockage imposed by chromatin. It has been shown that Tat associates with p300/CBP and P/CAF histon acetyltransferases (HAT) both in vitro and within the cells [26–28]. Similar association has also been seen in the Tax protein of HTLV-1 [29]. Interestingly, although Tat needs both p300 and P/CAF to activate HIV LTR promoter, only the HAT domain of P/CAF is essential [26]; whereas in HTLV-1, the Tax protein also requires both p300 and P/CAF, but it is the HAT domain of p300 required [29], demonstrating evolutionary similarities and divergences used by the two human retroviruses. Other HATs such as Tip60 [30] and hGCN5 [31] have also been implicated to interact with the HIV Tat protein. It is possible that these HATs become components of the protein complex during activation of viral transcription initiation. Tat may interact with HATs directly or via another cellular factor, and act on the LTR promoter. Additionally, Tat appears to be able to directly interact with some transcription factors such as Sp1 [25] and TBP [32] to promote transcription.
One unique feature of Tat mediated trans-activation is the ability of Tat to interact with RNA rather than with DNA [33]. This interaction occurs specifically between Tat and a specific 59-residue stem-loop structure, TAR, on the RNA leader sequence. Interactions among Tat, TAR and cellular cofactors have been the subject of intense investigation in the past. For a comprehensive review of this subject, please refer to Rana and Jeang [34], Karn [35] and Garber et al. [36]. In general, the current model suggests that Tat causes a dramatic increase in transcriptional levels upon binding to TAR. This effect is due to stimulation of a specific protein kinase called TAK (Tat-associated Kinase), which hyperphosphorylates the carboxyl-terminal domain (CTD) of the large subunit of RNA polymerase II, and leads to promoter clearance and processive elongation. Multiple kinases can phosphorylate RNAP II-CTD and evidence suggests that CDK9 is the TAK Kinase [37–40]. The cyclin component of TAK has also been identified. It is the CDK9 associated cycline T1 [41]. Cyclin T1 does not interact directly with TAR, but forms ternary complex with Tat and TAR. It should be noted that the above model is developed from a cell-free transcription system. Certain in vivo conditions such as a chromatin configured provial template may not be accounted for. As a matter of fact, the nucleosome-free LTR is a highly active promoter even in the absence of Tat in the cell-free system. The Tat responsiveness in the system was achieved not by imposing physiological restrictions but by specific assay conditions. Nevertheless, data from these in vitro systems provided invaluable insight into regulation of HIV gene transcription at the basic molecular level.
Successful transcription leads to the generation of approximately 30 different viral transcripts from the provirus. All these transcripts are derived from a single full-length transcript by alternative splicing, which generates mRNA with common 5' and 3' ends. The spliced viral RNA can be grouped into three classes: the multiply spliced mRNA encoding early regulatory proteins such as Tat, Nef and Rev; the singly spliced mRNA encoding Vpu, Vpr, Vif and Env; the un-spliced, full-length mRNA encoding the Gag-Pol poly protein. HIV gene expression is also regulated at a second level by the nuclear export of intron-containing transcripts. This process is mediated by the viral encoded Rev protein (for a comprehensive review, please see [42]). Both singly-spliced and un-spliced viral RNAs are intron-containing transcripts and carry a secondary structure called Rev Responsive Element (RRE) within the 3' end intron region. Like most pre-spliced transcripts in eukaryotic cells, intro-containing viral transcripts are retained in the nucleus by the interaction of splicing factors until they are spliced to completion or degraded. However, specific interaction between REV and RRE permits nuclear export of incompletely spliced viral transcripts in infected cells [43]. The current model suggests that REV directly binds to RRE and multimerizes upon RRE binding. REV multimerization stablizes the formation of a complex between REV, cellular exportin-1(CRM-1) and the GTPase Ran. This complex targets the mRNA complex to the nuclear pore complex for export. After cytoplasmic translocation, Ran-GTP is converted to Ran-GDP, and dissociated along with exportin-1 from the mRNA complex. REV is also dissociated from mRNA by unknown mechanism and recycled back into the nucleus by cellular importin-β. REV interacts with importin-β in the cytoplasm and dissociates with it in the nucleoplasm due to the action of Ran-GTP. Several other host cofactors have also been implicated to interact with the REV/RRE nuclear export process. These include eIF-5A, Rip/Rab, B23, p32 (for a review, see [44]). However, their distinctive roles in the process of REV/RRE mediated nuclear export still need to be defined.
The shuttling of REV between cytoplasm and nucleus and its interaction with RRE are fundamentally important in the regulation of HIV gene expression. It has been shown that the REV function is nonlinear with respect to the intracellular concentration of REV in transfection-based assays [45]. A threshold amount of REV, albeit still undefined, would be required for multimerization and exerts REV function in infected cells. The requirement for REV multimerization separates HIV gene expression into an early, REV-independent phase for the regulatory gene expression and a late, REV-dependent phase for the structural protein synthesis. An under-threshold level of REV would restrict viral gene expression to the early phase and may render viral infection into a state of latency.
Transcription from un-integrated DNA
Accumulation of non-integrated viral DNA is a feature of HIV infection. It occurs both in vivo in infected T cells, lymphoid and brain tissues, and in cell culture conditions [46–49]. During the asymptomatic phase of HIV infection, levels of non-integrated HIV DNA can reach 99% of total viral DNA [50]. As well, in the brains of patients with AIDS and dementia, non-integrated viral DNA was found to be more than 10 fold higher than intergrated DNA. These findings suggested a common feature shared by both HIV and other retroviruses. As in other retroviral infection, the non-integrated HIV DNA exists as three forms, the 1-LTR circle, the 2-LTR circle and the linear DNA. The circular forms of retroviral DNA were first demonstrated by Varmus and Guntaka as closed circular DNA (form I) in duck cells infected with Avian Sarcoma Virus (ASV) [51, 52], and by Gianni in Moloney Leukemia Virus (MLV) infection [53]. Form I circular DNA was later purified exclusively from the nucleus of the ASV infected quail tumor cells [54], and was shown, within 24 to 48 hours after infection, to constitute as much as 50% of the nuclear viral DNA and 20–25% of viral DNA in whole cells [54]. These early observations have prompted the use of DNA circles as a standard marker for nuclear targeting of HIV preintegration complex [55, 56]. Shank et al. further demonstrated that the form I DNA of Rous Sarcoma Virus actually consists of at least two forms of circular viral DNA: the larger one with the same size as the linear DNA (2-LTR circle) and the smaller one with a 300 bp deletion at the end (1-LTR-circle) [57]. In addition, the smaller circle (1-LTR-circle) is present in great excess over the larger circle (2-LTR circle) in infected cells [57]. These findings were collaborated by a similar study by Yoshimura and Weinberg in Murine Leukemia Virus [58].
The precursor to the closed circles is the linear DNA synthesized in the cytoplasm of infected cells [59]. However, it is not clear how the linear DNA is converted into circular form in the nucleus. It is believed that 2-LTR circles are the result of a simple ligation of the linear DNA [60–63] or auto-integration of the linear DNA into itself [60, 62, 64, 65]. The ligation reaction would generate 2-LTR circles with LTR-LTR junction (Simple 2-LTR-circle); whereas auto-integration of linear DNA would generate heterogeneous defective genomes of either single circle with two non-adjacent LTRs or double half-genomic circles each with one LTR [62, 64]. These defective LTR circles were also shown to exist in MLV and HIV infected cells and to carry processed LTR junctions typical of viral mediated integration [60, 62, 65]. These defective circles can also be regenerated, in vitro, from purified linear viral DNA in the extract of viral infected cells [62, 64], but not uninfected cells, suggesting that their formation is catalyzed by the viral integrase. Interestingly, in contrast, both the non-defective 1-LTR and Simple 2-LTR circles can be regenerated from linear DNA from the extract of uninfected cells [62], indicating cellular factors can mediate the formation of these circles independent of viral factors. Indeed, mutant cells lacking proteins of the non-homologous DNA end joining (NHEJ) pathway, such as Ku, ligase IV and XRCC4, did not generate 2-LTR-circles during HIV-1 infection [66]. The generation of 1-LTR-circles has been proposed to arise either from homologous recombination between the LTRs on the linear DNA [57, 61, 62] or from the process of reverse transciption, as demonstrated by the in vitro reverse transcription of permeabilized virion particles [67–69]. The actual process for 1-LTR circle generation in vivo remains to be defined.
Influenced by the Campbell model for integration of lambda bacteriophage [70], it was originally thought that the circular forms were the precursors for integration [60, 71]. Direct evidence from a cell-free in vitro integration system [72] and others [73, 74] conclusively demonstrated that the linear DNA is the precursor for retroviral integration. The cytoplasmic extract from MLV infected cells contains predominantly linear DNA, and mediates efficient integration of the viral DNA into target sequences [72], suggesting that the linear DNA can function directly as a substrate for integration into purified target DNA. In HIV infection, the circles have also been shown to be associated with discrete nuclear complexes, rather than the viral integration complex [75], indicating that they might be isolated from the viral integrase following circulization by cellular factors. Pauza et al. have suggested that these non-integrating circles of HIV-1 are labile in the nucleus and have a half-life of less than 16 hours in proliferating T cells [76]. Based on this notion, the 2-LTR circles have been used as a marker of active viral replication in HIV-1 infected patients [76–79]. However, recent studies on the metabolism of 2-LTR circles indicated that these circles are actually highly stable and to decrease in concentration only as a function of dilution resulting from cell division [80, 81]. It remains to be resolved whether the metabolism of viral DNA circles varies with cell types.
The notion that non-integrated HIV DNA could be active for viral antigen production came from early studies by Stevenson et al. [82, 83]. It was demonstrated that some integration negative viruses were fully competent for HIV-1 core and envelope antigen production, generating wild type levels of extracellular viral p24 antigen in two HTLV transformed T cell lines, MT-4 and Mo-T. Wiskerchen and Muesing [4] also created a panel of 42 HIV-1 integrase mutants and found that a subset of replication-defective mutants, with mutations in the catalytic residues, are capable of mediating transactivation of an indictor gene linked to the viral LTR promoter. These studies suggested that the Tat protein could be expressed from the non-integrated DNA [4, 5]. Preintegration transcription has also been shown to occur in HIV infection of resting CD4 T cells cultured in vitro [83, 84]. As early as one hour post infection, HIV-1 tat transcripts were readily detectable in the absence of integration [83]. Spina et al. have also shown that HIV nef transcript was detectable three days after infection of resting CD4 T cells [85]. We further demonstrated that the nef transcript generated was from non-integrated DNA, and that the Nef protein in resting CD4 T cells plays an important role in enhancing T cell activity and promoting viral infection [84]. In a kinetic study of HIV infection of metabolically active T cells, we concluded that transcription from non-integrated DNA is a normal, early step in HIV replication, and that non-integrated DNA has the full capacity to synthesize all classes of viral transcripts, both the early, multiply spliced and the late, singly spliced and non-spliced transcripts. However, only the early multiply spliced transcripts encoding Nef, Tat and Rev were measurably translated. This restriction on protein expression was due to a lack of Rev function in the absence of integration [86]. Recently, others [87] have further demonstrated that in non-dividing or growth arrested cells, the unintegrated lentiviral vector DNA can persist and sustain reporter gene expression to a level equivalent to wild type vectors, confirming the possibility that this early transcriptional activity from non-integrated viral DNA could be highly significant in certain cells.
Given that non-integrated viral DNA can transcribe in infected cells, it is important to know which forms, the linear DNA or the 1-LTR, 2-LTR circles, are active for transcription. Early attempts to address this question used transfection of different DNA forms into Hela cells [88]. Not suprisingly, all forms of transfected DNA carrying the LTR promoter were found active in transcription. However, the efficiency differs among various DNA forms. It was shown that the circular forms, especially the 2-LTR circles, were an order of magnitude lower than the transfected, proviral DNA carrying flanking cellular sequences. These data suggested that non-integrated DNA can potentially function as templates for viral gene expression. The transfection experiment is reminiscent of early attempts to study viral integration by transfection of purified DNA into cells [89]. It is likely that it may not reflect the actual situation in vivo in infected cells, especially considering possible complexes of non-integrated DNA with viral or cellular factors [55, 75]. Direct evidence suggesting 2-LTR circles as active templates came from studies by Wiskerchen and Muesing [4] and Engelman et al. [5]. It was shown that integrase mutants with mutations in the catalytic domains are capable of mediating expression of a report gene linked to the LTR promoter, suggesting possible expression of the Tat protein from these mutants. In correlation with the ability of Tat-mediated transactivation, cells infected with these mutants contain elevated levels of 2-LTR circles, suggesting that these circles could be templates. We have also investigated transcriptional activity from one of the non-integrating HIV-1 mutants, D116N, and compared it with the wild type virus [86]. We found similar levels of transcriptional activities at early time in both viruses in the absence of integration, although the levels of 2-LTR circles were two orders of magnitude higher in D116N infection. These data indicated that transcription from non-integrated DNA correlates with total viral DNA, rather than only 2-LTR circles. It is likely that even 2-LTR circles can transcribe, they are not the only templates. Other DNA forms such as the linear or 1-LTR circles may also function as templates. The 2-LTR circles are minor fractions of viral DNA early on, prior to integration, constituting about 5% of total viral DNA in SupT1 cells infected with HIV-based vector [90] and 0.03% in CEM cells infected with wild type HIV-1 [86] at 12 hours post infection. Currently it remains to be determined which form or forms of non-integrated DNA function as templates for transcription.
Perspectives
Pre-integration transcription is the earliest event following viral entry. In the absence of newly synthesized viral factors such as Tat, initiation of viral transcription likely relies on cellular factors. Direct interaction of cellular transcription factors with the LTR may promote low levels of viral transcription. For example, it has been shown that in the absence of Tat, human cyclin T1 can robustly activate the HIV-1 LTR promoter, and Sp1 is necessary and sufficient for this transcriptional activity [91]. It is possible that cyclin T1 is recruited into the pre-initiation complex through direct interaction with DNA-bound Sp1 [91]. This physical interaction could promote pre-integration transcription without the requirement of Tat (Figure 2).
Model of transcription initiation from non-integrated DNA and proviral DNA. (A) viral early transcription from non-integrated DNA may initiate in the absence of Tat. Interaction between viral LTR-bound SP1 with CyclinT1 could promote the initiation of viral transcription as suggested by Yedavalli et al. [91]. This process appears to be CDK9-independent [91,106]. (B) immediately following viral integration, Tat, generated from pre-integration transcription, can recruit HATs (Histone Acetyltransferases) to remodel nucleosomally assembled LTR, which leads to the assembly of general transcription factors. (C) Tat, can further active viral transcription through its interaction with viral RNA (Tat/TAR/CyclinT1/CDK9 complex), which leads to hyperphosphorylation of RNAP II and processive transcription.
The viral products generated from non-integrated DNA, prior to integration, are Nef, Tat and Rev [84] (Figure 1). There is still no direct evidence to suggest any of these proteins have a direct role in either stabilizing viral DNA or promoting integration, although Nef has been shown to enhance viral DNA synthesis [92] or prevent DNA oligonucleosomal fragmentation in apoptotic cells [93]. Another aspect of Nef is its effect on the state of T cells rather than on the virus itself. Our study has shown that Nef, synthesized prior to integration, can modulate resting T cells and promote viral replication when activation stimulus arrives [84]. Tat has a similar property for promotion of T cell activation [94]. The Tat protein is required not only for the processivity of the RNA elongation process, but also the modulation of cellular chromatin to activate transcription from the integrated provirus. From this point of view, it is tempting to hypothesize that the small amount of Tat initially synthesized prior to integration would function as an "initiator" to relieve possible chromatin restriction on the LTR promoter. Thus, by this way, Tat can turn on viral gene expression immediately following integration without relying on transcription and translation from newly integrated provirus. The Tat protein synthesized could further activate the LTR through its association with TAR RNA and P-TEFb to increase processive transcription (Figure 2). Indeed, it has been shown that there is a marked difference between non-integrated DNA and integrated provirus in requirements for activation of transcription. The Tat-associated histone acetyltransferase activity is preferentially important for transactivation of integrated, but not unintegrated, HIV-1 LTR, supporting a Tat-independent trans-activation for non-integrated DNA and a Tat-dependent trans-activation for provirus [26, 29].
The Rev protein is required for the synthesis of late structural protein from partially or un-spliced transcripts. It has been demonstrated that a threshold amount of Rev is required for the nuclear export of partially or un-spliced viral DNA [45]. Interestingly, in the absence of integration, Rev is present at a low level, and is not functional to support the late, structural protein syntheses [86]. Only early products from multiply spliced transcripts are synthesized prior to integration. It is reasonable to hypothesize that the restriction imposed by the lack of Rev function would be an advantage for the virus. When cellular restriction is imposed on integration, it would be important to synthesize early regulatory proteins such as Nef and Tat to modulate cellular environment for viral integration and replication to occur. Interestingly, simple retroviruses do not encode these accessory proteins, and lack the ability to infect non-mitotic cells. It appears to suggest that pre-integration transcription may be a function most important to complex retroviruses; it would be a process evolved to provide direct control over functions that, in simple retroviruses, are provided by the host cells. This additional control may be important to break barriers imposed by host immune systems. It should be noted that the above hypothesis is based on multiple copies of viral DNA in a single infected cell. It is unknown, however, whether a transcribing DNA is still able to integrate when a single viral DNA molecule is present in infected cells.
The role of non-integrated DNA in the pathogenesis of HIV infection has not been clearly resolved. In addition to our demonstration of modulation of resting T cell activity by non-integrated DNA [84], one recent paper demonstrated a direct role of non-integrating HIV in inducing aberrant methylation in infected cells [95]. In other retroviruses, non-integrated DNA has long been implicated in connection with viral pathogenesis. Keshet and Temin were the first to suggest a correlation between cell killing and accumulation of non-integrated DNA in spleen necrosis virus infection [96]. Similar association was seen in avian leukosis virus induced osteoporosis, feline leukemia virus induced feline AIDS, and equine infectious anemia virus infection of horses [97–99]. In HIV infection, accumulation of non-integrated viral DNA correlates with the extent of syncytia formation [47], but not the occurrence of single-cell killing [100]. Unintegrated circular viral DNA, particularly 2-LTR circles, in the peripheral mononuclear cells of infected patients appears to be associated with high levels of plasma HIV-1 RNA, rapid decline in CD4 count, and clinical progression of AIDS [101]. Circular forms of unintegrated HIV DNA has also been linked with dementia and multinuclear giant cell in the brains of AIDS patients [48, 49]; particularly, the presence of 1-LTR circles was associated with multilnucleated giant cells and clinical diagnosis of dementia and cerebral atrophy [49]. It is not clear, however, whether the mere presence of specific forms of unintegrated DNA triggering cellular process or the products from the DNA caused pathogenic effects.
The ability of non-integrated viral DNA to express viral genes has numerous applications. For example, a non-integrating lentiviral vector would be safer to use for therapy. It dose not disrupt normal cellular genes and induce mutagenesis, as has been demonstrated in previous examples [9, 102]. Recently, it has been demonstrated that the non-integrating lentivirus can be modified into an efficient expression system by incorporation of an functional origin of DNA replication from other viruses [103]. Additionally, the non-integrating HIV mutants, with its restricted gene expression capacity in immu-functional cells such as antigen presentation cells (unpublished data), could be a potential vaccine to stimulate CTL responses [104, 105].
References
Nisole S, Saib A: Early steps of retrovirus replication cycle. Retrovirology. 2004, 1: 9-10.1186/1742-4690-1-9.
Donehower LA, Varmus HE: A mutant murine leukemia virus with a single missense codon in pol is defective in a function affecting integration. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1984, 81: 6461-6465.
List J, Haase AT: Integration of visna virus DNA occurs and may be necessary for productive infection. Virology. 1997, 237: 189-197. 10.1006/viro.1997.8785.
Wiskerchen M, Muesing MA: Human immunodeficiency virus type 1 integrase: effects of mutations on viral ability to integrate, direct viral gene expression from unintegrated viral DNA templates, and sustain viral propagation in primary cells. J Virol. 1995, 69: 376-386.
Engelman A, Englund G, Orenstein JM, Martin MA, Craigie R: Multiple effects of mutations in human immunodeficiency virus type 1 integrase on viral replication. J Virol. 1995, 69: 2729-2736.
Nakajima N, Lu R, Engelman A: Human immunodeficiency virus type 1 replication in the absence of integrase-mediated dna recombination: definition of permissive and nonpermissive T-cell lines. J Virol. 2001, 75: 7944-7955. 10.1128/JVI.75.17.7944-7955.2001.
Gaur M, Leavitt AD: Mutations in the human immunodeficiency virus type 1 integrase D,D(35)E motif do not eliminate provirus formation. J Virol. 1998, 72: 4678-4685.
Rohdewohld H, Weiher H, Reik W, Jaenisch R, Breindl M: Retrovirus integration and chromatin structure: Moloney murine leukemia proviral integration sites map near DNase I-hypersensitive sites. J Virol. 1987, 61: 336-343.
King W, Patel MD, Lobel LI, Goff SP, Nguyen-Huu MC: Insertion mutagenesis of embryonal carcinoma cells by retroviruses. Science. 1985, 228: 554-558.
Schroder A, Shinn P, Chen H, Berry C, Ecker J, Bushman F: HIV-1 Integration in the Human Genome Favors Active Genes and Local Hotspots. Cell. 2002, 110: 521-10.1016/S0092-8674(02)00864-4.
Weidhaas JB, Angelichio EL, Fenner S, Coffin JM: Relationship between retroviral DNA integration and gene expression. J Virol. 2000, 74: 8382-8389. 10.1128/JVI.74.18.8382-8389.2000.
Jordan A, Bisgrove D, Verdin E: HIV reproducibly establishes a latent infection after acute infection of T cells in vitro. EMBO J. 2003, 22: 1868-1877. 10.1093/emboj/cdg188.
Verdin E: DNase I-hypersensitive sites are associated with both long terminal repeats and with the intragenic enhancer of integrated human immunodeficiency virus type 1. J Virol. 1991, 65: 6790-6799.
Steger DJ, Workman JL: Stable co-occupancy of transcription factors and histones at the HIV-1 enhancer. Embo J. 1997, 16: 2463-2472. 10.1093/emboj/16.9.2463.
Verdin E, Paras P., Jr., Van Lint C: Chromatin disruption in the promoter of human immunodeficiency virus type 1 during transcriptional activation. Embo J. 1993, 12: 3249-3259.
Demarchi F, D'Agaro P, Falaschi A, Giacca M: In vivo footprinting analysis of constitutive and inducible protein-DNA interactions at the long terminal repeat of human immunodeficiency virus type 1. J Virol. 1993, 67: 7450-7460.
el Kharroubi A, Verdin E: Protein-DNA interactions within DNase I-hypersensitive sites located downstream of the HIV-1 promoter. J Biol Chem. 1994, 269: 19916-19924.
Rosen CA, Sodroski JG, Haseltine WA: The location of cis-acting regulatory sequences in the human T cell lymphotropic virus type III (HTLV-III/LAV) long terminal repeat. Cell. 1985, 41: 813-823.
Siekevitz M, Josephs SF, Dukovich M, Peffer N, Wong-Staal F, Greene WC: Activation of the HIV-1 LTR by T cell mitogens and the trans-activator protein of HTLV-I. Science. 1987, 238: 1575-1578.
Pereira LA, Bentley K, Peeters A, Churchill MJ, Deacon NJ: A compilation of cellular transcription factor interactions with the HIV-1 LTR promoter. Nucleic Acids Res. 2000, 28: 663-668. 10.1093/nar/28.3.663.
Sheldon M, Ratnasabapathy R, Hernandez N: Characterization of the inducer of short transcripts, a human immunodeficiency virus type 1 transcriptional element that activates the synthesis of short RNAs. Mol Cell Biol. 1993, 13: 1251-1263.
Ratnasabapathy R, Sheldon M, Johal L, Hernandez N: The HIV-1 long terminal repeat contains an unusual element that induces the synthesis of short RNAs from various mRNA and snRNA promoters. Genes Dev. 1990, 4: 2061-2074.
Berkhout B, Gatignol A, Rabson AB, Jeang KT: TAR-independent activation of the HIV-1 LTR: evidence that tat requires specific regions of the promoter. Cell. 1990, 62: 757-767. 10.1016/0092-8674(90)90120-4.
Jordan A, Defechereux P, Verdin E: The site of HIV-1 integration in the human genome determines basal transcriptional activity and response to Tat transactivation. Embo J. 2001, 20: 1726-1738. 10.1093/emboj/20.7.1726.
Jeang KT, Chun R, Lin NH, Gatignol A, Glabe CG, Fan H: In vitro and in vivo binding of human immunodeficiency virus type 1 Tat protein and Sp1 transcription factor. J Virol. 1993, 67: 6224-6233.
Benkirane M, Chun RF, Xiao H, Ogryzko VV, Howard BH, Nakatani Y, Jeang KT: Activation of integrated provirus requires histone acetyltransferase. p300 and P/CAF are coactivators for HIV-1 Tat. J Biol Chem. 1998, 273: 24898-24905. 10.1074/jbc.273.38.24898.
Marzio G, Tyagi M, Gutierrez MI, Giacca M: HIV-1 tat transactivator recruits p300 and CREB-binding protein histone acetyltransferases to the viral promoter. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1998, 95: 13519-13524. 10.1073/pnas.95.23.13519.
Hottiger MO, Nabel GJ: Interaction of human immunodeficiency virus type 1 Tat with the transcriptional coactivators p300 and CREB binding protein. J Virol. 1998, 72: 8252-8256.
Okada M, Jeang KT: Differential requirements for activation of integrated and transiently transfected human T-cell leukemia virus type 1 long terminal repeat. J Virol. 2002, 76: 12564-12573. 10.1128/JVI.76.24.12564-12573.2002.
Kamine J, Elangovan B, Subramanian T, Coleman D, Chinnadurai G: Identification of a cellular protein that specifically interacts with the essential cysteine region of the HIV-1 Tat transactivator. Virology. 1996, 216: 357-366. 10.1006/viro.1996.0071.
Col E, Caron C, Seigneurin-Berny D, Gracia J, Favier A, Khochbin S: The histone acetyltransferase, hGCN5, interacts with and acetylates the HIV transactivator, Tat. J Biol Chem. 2001, 276: 28179-28184. 10.1074/jbc.M101385200.
Kashanchi F, Shibata R, Ross EK, Brady JN, Martin MA: Second-site long terminal repeat (LTR) revertants of replication- defective human immunodeficiency virus: effects of revertant TATA box motifs on virus infectivity, LTR-directed expression, in vitro RNA synthesis, and binding of basal transcription factors TFIID and TFIIA. J Virol. 1994, 68: 3298-3307.
Berkhout B, Silverman RH, Jeang KT: Tat trans-activates the human immunodeficiency virus through a nascent RNA target. Cell. 1989, 59: 273-282. 10.1016/0092-8674(89)90289-4.
Rana TM, Jeang KT: Biochemical and functional interactions between HIV-1 Tat protein and TAR RNA. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1999, 365: 175-185. 10.1006/abbi.1999.1206.
Karn J: Tackling Tat. J Mol Biol. 1999, 293: 235-254. 10.1006/jmbi.1999.3060.
Garber ME, Jones KA: HIV-1 Tat: coping with negative elongation factors. Curr Opin Immunol. 1999, 11: 460-465. 10.1016/S0952-7915(99)80077-6.
Herrmann CH, Rice AP: Specific interaction of the human immunodeficiency virus Tat proteins with a cellular protein kinase. Virology. 1993, 197: 601-608. 10.1006/viro.1993.1634.
Herrmann CH, Rice AP: Lentivirus Tat proteins specifically associate with a cellular protein kinase, TAK, that hyperphosphorylates the carboxyl-terminal domain of the large subunit of RNA polymerase II: candidate for a Tat cofactor. J Virol. 1995, 69: 1612-1620.
Zhu Y, Pe'ery T, Peng J, Ramanathan Y, Marshall N, Marshall T, Amendt B, Mathews MB, Price DH: Transcription elongation factor P-TEFb is required for HIV-1 tat transactivation in vitro. Genes Dev. 1997, 11: 2622-2632.
Mancebo HS, Lee G, Flygare J, Tomassini J, Luu P, Zhu Y, Peng J, Blau C, Hazuda D, Price D, Flores O: P-TEFb kinase is required for HIV Tat transcriptional activation in vivo and in vitro. Gene Dev. 1997, 11: 2633-2644.
Wei P, Garber ME, Fang SM, Fischer WH, Jones KA: A novel CDK9-associated C-type cyclin interacts directly with HIV-1 Tat and mediates its high-affinity, loop-specific binding to TAR RNA. Cell. 1998, 92: 451-462. 10.1016/S0092-8674(00)80939-3.
Pollard VW, Malim MH: The HIV-1 Rev protein. Annu Rev Microbiol. 1998, 52: 491-532. 10.1146/annurev.micro.52.1.491.
Malim MH, Hauber J, Le SY, Maizel JV, Cullen BR: The HIV-1 rev trans-activator acts through a structured target sequence to activate nuclear export of unspliced viral mRNA. Nature. 1989, 338: 254-257. 10.1038/338254a0.
Kjems J, Askjaer P: Rev protein and its cellular partners. Adv Pharmacol. 2000, 48: 251-298. 10.1016/S1054-3589(00)48009-9.
Pomerantz RJ, Seshamma T, Trono D: Efficient replication of human immunodeficiency virus type 1 requires a threshold level of Rev: potential implications for latency. J Virol. 1992, 66: 1809-1813.
Shaw GM, Hahn BH, Arya SK, Groopman JE, Gallo RC, Wong-Staal F: Molecular characterization of human T-cell leukemia (lymphotropic) virus type III in the acquired immune deficiency syndrome. Science. 1984, 226: 1165-1171.
Pauza CD, Galindo JE, Richman DD: Reinfection results in accumulation of unintegrated viral DNA in cytopathic and persistent human immunodeficiency virus type 1 infection of CEM cells. J Exp Med. 1990, 172: 1035-1042. 10.1084/jem.172.4.1035.
Pang S, Koyanagi Y, Miles S, Wiley C, Vinters HV, Chen IS: High levels of unintegrated HIV-1 DNA in brain tissue of AIDS dementia patients. Nature. 1990, 343: 85-89. 10.1038/343085a0.
Teo I, Veryard C, Barnes H, An SF, Jones M, Lantos PL, Luthert P, Shaunak S: Circular forms of unintegrated human immunodeficiency virus type 1 DNA and high levels of viral protein expression: association with dementia and multinucleated giant cells in the brains of patients with AIDS. J Virol. 1997, 71: 2928-2933.
Chun TW, Carruth L, Finzi D, Shen X, DiGiuseppe JA, Taylor H, Hermankova M, Chadwick K, Margolick J, Quinn TC, Kuo YH, Brookmeyer R, Zeiger MA, Barditch-Crovo P, Siliciano RF: Quantification of latent tissue reservoirs and total body viral load in HIV-1 infection [see comments]. Nature. 1997, 387: 183-188. 10.1038/387183a0.
Varmus HE, Guntaka RV, Deng CT, Bishop JM: Synthesis, structure and function of avian sarcoma virus-specific DNA in permissive and nonpermissive cells. Cold Spring Harb Symp Quant Biol. 1975, 39: 987-996.
Guntaka RV, Mahy BW, Bishop JM, Varmus HE: Ethidium bromide inhibits appearance of closed circular viral DNA and integration of virus-specific DNA in duck cells infected by avian sarcoma virus. Nature. 1975, 253: 507-511.
Gianni AM, Smotkin D, Weinberg RA: Murine leukemia virus: detection of unintegrated double-stranded DNA forms of the provirus. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1975, 72: 447-451.
Guntaka RV, Richards OC, Shank PR, Kung HJ, Davidson N: Covalently closed circular DNA of avian sarcoma virus: purification from nuclei of infected quail tumor cells and measurement by electron microscopy and gel electrophoresis. J Mol Biol. 1976, 106: 337-357.
Bukrinsky MI, Sharova N, Dempsey MP, Stanwick TL, Bukrinskaya AG, Haggerty S, Stevenson M: Active nuclear import of human immunodeficiency virus type 1 preintegration complexes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1992, 89: 6580-6584.
Bukrinsky MI, Haggerty S, Dempsey MP, Sharova N, Adzhubel A, Spitz L, Lewis P, Goldfarb D, Emerman M, Stevenson M: A nuclear localization signal within HIV-1 matrix protein that governs infection of non-dividing cells [see comments]. Nature. 1993, 365: 666-669. 10.1038/365666a0.
Shank PR, Hughes SH, Kung HJ, Majors JE, Quintrell N, Guntaka RV, Bishop JM, Varmus HE: Mapping unintegrated avian sarcoma virus DNA: termini of linear DNA bear 300 nucleotides present once or twice in two species of circular DNA. Cell. 1978, 15: 1383-1395. 10.1016/0092-8674(78)90063-6.
Yoshimura FK, Weinberg RA: Restriction endonuclease cleavage of linear and closed circular murine leukemia viral DNAs: discovery of a smaller circular form. Cell. 1979, 16: 323-332. 10.1016/0092-8674(79)90009-6.
Gianni AM, Weinberg RA: Partially single-stranded form of free Moloney viral DNA. Nature. 1975, 255: 646-648.
Shoemaker C, Goff S, Gilboa E, Paskind M, Mitra SW, Baltimore D: Structure of a cloned circular Moloney murine leukemia virus DNA molecule containing an inverted segment: implications for retrovirus integration. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1980, 77: 3932-3936.
Katz RA, Omer CA, Weis JH, Mitsialis SA, Faras AJ, Guntaka RV: Restriction endonuclease and nucleotide sequence analyses of molecularly cloned unintegrated avian tumor virus DNA: structure of large terminal repeats in circle junctions. J Virol. 1982, 42: 346-351.
Farnet CM, Haseltine WA: Circularization of human immunodeficiency virus type 1 DNA in vitro. J Virol. 1991, 65: 6942-6952.
Swanstrom R, DeLorbe WJ, Bishop JM, Varmus HE: Nucleotide sequence of cloned unintegrated avian sarcoma virus DNA: viral DNA contains direct and inverted repeats similar to those in transposable elements. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1981, 78: 124-128.
Lee YM, Coffin JM: Efficient autointegration of avian retrovirus DNA in vitro. J Virol. 1990, 64: 5958-5965.
Shoemaker C, Goff S, Gilboa E, Paskind M, Mitra SW, Baltimore D: Structure of cloned retroviral circular DNAs: implications for virus integration. Cold Spring Harb Symp Quant Biol. 1981, 45: 711-717.
Li L, Olvera JM, Yoder KE, Mitchell RS, Butler SL, Lieber M, Martin SL, Bushman FD: Role of the non-homologous DNA end joining pathway in the early steps of retroviral infection. Embo J. 2001, 20: 3272-3281. 10.1093/emboj/20.12.3272.
Dina D, Benz E. W., Jr.: Structure of murine sarcoma virus DNA replicative intermediates synthesized in vitro. J Virol. 1980, 33: 377-389.
Gilboa E, Goff S, Shields A, Yoshimura F, Mitra S, Baltimore D: In vitro synthesis of a 9 kbp terminally redundant DNA carrying the infectivity of Moloney murine leukemia virus. Cell. 1979, 16: 863-874. 10.1016/0092-8674(79)90101-6.
Junghans RP, Boone LR, Skalka AM: Products of reverse transcription in avian retrovirus analyzed by electron microscopy. J Virol. 1982, 43: 544-554.
Campbell A: Some general questions about movable elements and their implications. Cold Spring Harb Symp Quant Biol. 1981, 45: 1-9.
Panganiban AT, Temin HM: Circles with two tandem LTRs are precursors to integrated retrovirus DNA. Cell. 1984, 36: 673-679. 10.1016/0092-8674(84)90347-7.
Brown PO, Bowerman B, Varmus HE, Bishop JM: Correct integration of retroviral DNA in vitro. Cell. 1987, 49: 347-356. 10.1016/0092-8674(87)90287-X.
Lobel LI, Murphy JE, Goff SP: The palindromic LTR-LTR junction of Moloney murine leukemia virus is not an efficient substrate for proviral integration. J Virol. 1989, 63: 2629-2637.
Ellis J, Bernstein A: Retrovirus vectors containing an internal attachment site: evidence that circles are not intermediates to murine retrovirus integration. J Virol. 1989, 63: 2844-2846.
Bukrinsky M, Sharova N, Stevenson M: Human immunodeficiency virus type 1 2-LTR circles reside in a nucleoprotein complex which is different from the preintegration complex. J Virol. 1993, 67: 6863-6865.
Pauza CD, Trivedi P, McKechnie TS, Richman DD, Graziano FM: 2-LTR circular viral DNA as a marker for human immunodeficiency virus type 1 infection in vivo. Virology. 1994, 205: 470-478. 10.1006/viro.1994.1667.
Sharkey ME, Teo I, Greenough T, Sharova N, Luzuriaga K, Sullivan JL, Bucy RP, Kostrikis LG, Haase A, Veryard C, Davaro RE, Cheeseman SH, Daly JS, Bova C, Ellison R. T., 3rd, Mady B, Lai KK, Moyle G, Nelson M, Gazzard B, Shaunak S, Stevenson M: Persistence of episomal HIV-1 infection intermediates in patients on highly active anti-retroviral therapy. Nat Med. 2000, 6: 76-81. 10.1038/71569.
Zazzi M, Romano L, Catucci M, Venturi G, De Milito A, Almi P, Gonnelli A, Rubino M, Occhini U, Valensin PE: Evaluation of the presence of 2-LTR HIV-1 unintegrated DNA as a simple molecular predictor of disease progression. J Med Virol. 1997, 52: 20-25. 10.1002/(SICI)1096-9071(199705)52:1<20::AID-JMV4>3.0.CO;2-T.
Panther LA, Coombs RW, Aung SA, dela Rosa C, Gretch D, Corey L: Unintegrated HIV-1 circular 2-LTR proviral DNA as a marker of recently infected cells: relative effect of recombinant CD4, zidovudine, and saquinavir in vitro. J Med Virol. 1999, 58: 165-173. 10.1002/(SICI)1096-9071(199906)58:2<165::AID-JMV11>3.0.CO;2-1.
Butler SL, Johnson EP, Bushman FD: Human immunodeficiency virus cDNA metabolism: notable stability of two- long terminal repeat circles. J Virol. 2002, 76: 3739-3747. 10.1128/JVI.76.8.3739-3747.2002.
Pierson TC, Kieffer TL, Ruff CT, Buck C, Gange SJ, Siliciano RF: Intrinsic stability of episomal circles formed during human immunodeficiency virus type 1 replication. J Virol. 2002, 76: 4138-4144. 10.1128/JVI.76.8.4138-4144.2002.
Stevenson M, Haggerty S, Lamonica CA, Meier CM, Welch SK, Wasiak AJ: Integration is not necessary for expression of human immunodeficiency virus type 1 protein products. J Virol. 1990, 64: 2421-2425.
Stevenson M, Stanwick TL, Dempsey MP, Lamonica CA: HIV-1 replication is controlled at the level of T cell activation and proviral integration. Embo J. 1990, 9: 1551-1560.
Wu Y, Marsh JW: Selective transcription and modulation of resting T cell activity by preintegrated HIV DNA. Science. 2001, 293: 1503-1506. 10.1126/science.1061548.
Spina CA, Guatelli JC, Richman DD: Establishment of a stable, inducible form of human immunodeficiency virus type 1 DNA in quiescent CD4 lymphocytes in vitro. J Virol. 1995, 69: 2977-2988.
Wu Y, Marsh JW: Early transcription from nonintegrated DNA in human immunodeficiency virus infection. J Virol. 2003, 77: 10376-10382. 10.1128/JVI.77.19.10376-10382.2003.
Saenz DT, Loewen N, Peretz M, Whitwam T, Barraza R, Howell KG, Holmes JM, Good M, Poeschla EM: Unintegrated lentivirus DNA persistence and accessibility to expression in nondividing cells: analysis with class I integrase mutants. Journal of Virology. 2004, 78: 2906-2920. 10.1128/JVI.78.6.2906-2920.2004.
Cara A, Cereseto A, Lori F, Reitz M. S., Jr.: HIV-1 protein expression from synthetic circles of DNA mimicking the extrachromosomal forms of viral DNA. J Biol Chem. 1996, 271: 5393-5397. 10.1074/jbc.271.10.5393.
Luciw PA, Oppermann H, Bishop JM, Varmus HE: Integration and expression of several molecular forms of Rous sarcoma virus DNA used for transfection of mouse cells. Mol Cell Biol. 1984, 4: 1260-1269.
Butler SL, Hansen MS, Bushman FD: A quantitative assay for HIV DNA integration in vivo. Nat Med. 2001, 7: 631-634. 10.1038/87979.
Yedavalli VS, Benkirane M, Jeang KT: Tat and trans-activation-responsive (TAR) RNA-independent induction of HIV-1 long terminal repeat by human and murine cyclin T1 requires Sp1. J Biol Chem. 2003, 278: 6404-6410. 10.1074/jbc.M209162200.
Chowers MY, Pandori MW, Spina CA, Richman DD, Guatelli JC: The growth advantage conferred by HIV-1 nef is determined at the level of viral DNA formation and is independent of CD4 downregulation. Virology. 1995, 212: 451-457. 10.1006/viro.1995.1502.
Rasola A. Gramaglia D. Boccaccio C. Conoglio P. M.: Apoptosis enhancement by the HIV-1 Nef protein. J Immu. 2001, 166: 81-88.
Ott M, Emiliani S, Van Lint C, Herbein G, Lovett J, Chirmule N, McCloskey T, Pahwa S, Verdin E: Immune hyperactivation of HIV-1-infected T cells mediated by Tat and the CD28 pathway. Science. 1997, 275: 1481-1485. 10.1126/science.275.5305.1481.
Fang JY, Mikovits JA, Bagni R, Petrow-Sadowski CL, Ruscetti FW: Infection of lymphoid cells by integration-defective human immunodeficiency virus type 1 increases de novo methylation. J Virol. 2001, 75: 9753-9761. 10.1128/JVI.75.20.9753-9761.2001.
Keshet E, Temin HM: Cell killing by spleen necrosis virus is correlated with a transient accumulation of spleen necrosis virus DNA. J Virol. 1979, 31: 376-388.
Weller SK, Joy AE, Temin HM: Correlation between cell killing and massive second-round superinfection by members of some subgroups of avian leukosis virus. J Virol. 1980, 33: 494-506.
Mullins JI, Chen CS, Hoover EA: Disease-specific and tissue-specific production of unintegrated feline leukaemia virus variant DNA in feline AIDS. Nature. 1986, 319: 333-336.
Rice NR, Lequarre AS, Casey JW, Lahn S, Stephens RM, Edwards J: Viral DNA in horses infected with equine infectious anemia virus. J Virol. 1989, 63: 5194-5200.
Bergeron L, Sodroski J: Dissociation of unintegrated viral DNA accumulation from single-cell lysis induced by human immunodeficiency virus type 1. Journal of Virology. 1992, 66: 5777-5787.
Panther LA, Coombs RW, Zeh JE, Collier AC, Corey L: Unintegrated circular HIV-1 DNA in the peripheral mononuclear cells of HIV-1-infected subjects: association with high levels of plasma HIV-1 RNA, rapid decline in CD4 count, and clinical progression to AIDS. J Acquir Immune Defic Syndr Hum Retrovirol. 1998, 17: 303-313.
Li Z, Dullmann J, Schiedlmeier B, Schmidt M, von Kalle C, Meyer J, Forster M, Stocking C, Wahlers A, Frank O, Ostertag W, Kuhlcke K, Eckert HG, Fehse B, Baum C: Murine leukemia induced by retroviral gene marking. Science. 2002, 296: 497-10.1126/science.1068893.
Lu R, Nakajima N, Hofmann W, Benkirane M, Jeang KT, Sodroski J, Engelman A, Teh-Jeang K: Simian virus 40-based replication of catalytically inactive human immunodeficiency virus type 1 integrase mutants in nonpermissive T cells and monocyte-derived macrophages.[erratum appears in J Virol. 2004 Mar;78(5):2654 Note: Teh-Jeang Kuan [corrected to Jeang Kuan-Teh]. J Virol. 2004, 78: 658-668. 10.1128/JVI.78.2.658-668.2004.
Smith SM: HIV vaccine development in the nonhuman primate model of AIDS. J Biomed Sci. 2002, 9: 100-111. 10.1159/000048205.
Lu W, Wu X, Lu Y, Guo W, Andrieu JM: Therapeutic dendritic-cell vaccine for simian AIDS. Nat Med. 2003, 9: 27-32. 10.1038/nm806.
West MJ, Karn J: Stimulation of Tat-associated kinase-independent transcriptional elongation from the human immunodeficiency virus type-1 long terminal repeat by a cellular enhancer. EMBO J. 1999, 18: 1378-1386. 10.1093/emboj/18.5.1378.
Acknowledgements
I thank Jon. W. Marsh for his helpful discussions on numerous issues in this review and Kathryn Crockett for her editorial assistance.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Authors’ original submitted files for images
Below are the links to the authors’ original submitted files for images.
Rights and permissions
This article is published under an open access license. Please check the 'Copyright Information' section either on this page or in the PDF for details of this license and what re-use is permitted. If your intended use exceeds what is permitted by the license or if you are unable to locate the licence and re-use information, please contact the Rights and Permissions team.
About this article
Cite this article
Wu, Y. HIV-1 gene expression: lessons from provirus and non-integrated DNA. Retrovirology 1, 13 (2004). https://doi.org/10.1186/1742-4690-1-13
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1186/1742-4690-1-13