Abstract
A nonlinear mathematical model of differential equations with piecewise constant arguments is proposed. This model is analyzed by using the theory of both differential and difference equations to show the spread of HIV in a homogeneous population. Because of the solution of this differential equations being established in a certain subinterval, solutions will be analyzed as a system of difference equations. After that, results will be considered for differential equations as well. The population of the model is divided into three subclasses, which are the HIV negative class, the HIV positive class that do not know they are infected and the HIV positive class that know they are infected. As an application of the model we took the spread of HIV in India into consideration.
MSC:39A10, 39A11.
Similar content being viewed by others
1 Introduction
Sexually transmitted diseases such as HIV are overwhelmingly observed in some populations. Countries are dealing with the growing impact of the epidemics on the youngest and most productive population groups; increasing numbers in children and adolescents; worsening situation among the poor and marginalized populations; a continuous aggravation of the existent health problems (such as tuberculosis); and above all, the diversion of resources from other health, welfare, and educational priorities. It is very important to understand how the transmission process of the infectious diseases works in order to avoid ulterior spread of these epidemics [1]. So mathematical models for transmission dynamics in HIV play an important role in better understanding of epidemiological patterns for disease control as they provide short and long term prediction for HIV and AIDS incidence [2].
The first mathematical model used for the explicit study of a sexually transmitted disease was a one sex model that was constructed by Cooke and Yorke in 1973 [1, 3]. A two sex model developed specifically for gonorrhea was formulated by Lajmanovich and Yorke in 1976 [4]. One STD (sexually transmitted disease) that many people are worried about getting is HIV. Mathematical modeling of the HIV epidemic has been studied by various authors recently [5–12]. In 1994, Velasco-Hernandez and Hsieh analyzed the HIV epidemic in a male population [13]. In 2004, Bachar and Dorfmatr considered the mathematical model where the population was divided into three sub populations [14]. Expanding [14], Naresh has studied the effect of contact tracing on reducing the spread of HIV/AIDS in a homogeneous population with constant immigration of susceptibles.
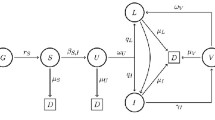
Changes in population involved in a HIV transmission model can take place by discrete steps and continuous processes. In discrete models, difference equations reflect the change over the whole time step, whereas in continuous models, differential equations are developed to explore the changes in one variable with a decreasingly small change in another variable [1]. Because HIV population dynamics involves both continuous and discrete time arguments, for this type of problems, a different point of view came up and Buseenberg and Cooke used piecewise constant arguments to construct the mathematical modeling of biological structures in 1983. By taking into account the work of Naresh [2] we have constructed a new mathematical model. We added new terms and took into consideration both discrete time and continuous time. This model is analyzed by using the theory of both differential and difference equations to show the spread of HIV/AIDS in a homogeneous population. Because of the solution of these differential equations established in a certain subinterval, the solutions will be analyzed as a difference equations system. Furthermore, these results will be considered for differential equations, as well. So our mathematical model that is named a differential equation systems with piecewise constant arguments is as follows:
In the equations above, t is the time and is the exact value of t for . The model monitors three populations; susceptibles , HIV positives that do not know they are infected , HIV positives that know they are infected . The susceptibles are composed of individuals that have not contracted the infection but may get infected through contacts (sexual, blood transfusion etc.) with infectives. is the population growth rate of the susceptible population. The deaths (of natural causes) are given at a rate . is the rate of susceptible population per year. The susceptibles are lost from their class following contacts with the infectives and at a rate and , respectively. are populations that are HIV positive but do not know it, because disease symptoms have not yet appeared in this class. This population is generated by the HIV infection of susceptibles. is the population growth rate of the population . The deaths (of natural causes) are given at a rate . The population of this class decreases and becomes aware after screening at a rate θ. γ is the rate of individuals in class that detect the infection by tracing contacts with class . Following the contacts of class S and , class S becomes aware of the infection and this class is detected further which has the rate of . And also, following the contacts of class S and , class S becomes aware of the infection and is detected further with the rate of . is the population growth rate of the population . The deaths (of natural causes) are given at a rate .
2 Local and global asymptotic stability analysis
In this section, the local and global behavior of the nonlinear system (1.1) under specific conditions is investigated. To show the consistence of the population classes with the model constructed in Section 2, the data of [2] is used. Examples show the spread of the population over the time.
2.1 Equilibrium point of the model (1.1)
For every equation in system (1.1) is a Bernoulli differential equation as follows:
Solving (2.1) for and letting t go to where , we obtain a system of difference equations as follows:
where
It is obvious that (2.3) must hold:
System (2.2) is a system of difference equations. Hence, to explain the global behavior of system (2.1) we must consider the solution of (2.1), that is, the difference equations system (2.2). Firstly, we need to obtain the equilibrium points of this system (2.2), which are also the critical points of system (2.1). We have
From (2.4) we can write
Simplifying this, we get
Substituting in (2.6) the expression
we obtain
To find the positive equilibrium point of (2.2), we have some assumptions in view of the demographic data in [2].
-
(i)
,
-
(ii)
,
-
(iii)
,
-
(iv)
,
-
(v)
,
-
(vi)
,
-
(vii)
,
-
(viii)
.
Thus, the equilibrium points of system (2.2) are . Here
and
The Jacobian matrix for the equilibrium points is (2.13). This gives the linearizing equations of system (2.2),
where
The characteristic equation is
2.2 Local and global stability of the positive equilibrium
In this part, the local and global stability of system (2.2) will be analyzed. For the proof of Theorem 2.1, Theorem 2.2, and Theorem 2.3, it is assumed that conditions (i)-(viii) hold.
Theorem 2.1 Let the positive equilibrium point of system (2.2) and assume that
Furthermore, suppose that
If
where
then the positive equilibrium point of system (2.2) is locally asymptotically stable.
Proof To prove Theorem 2.1, we have used the Schur-Cohn criteria (see [15]) to obtain conditions for the local asymptotic stability of the positive equilibrium points of system (2.2). We have
Considering (i) and (ii) together, we get
By simplifying (2.17), we obtain
Computations for (2.18) lead to the inequality
where we will have
Since , we will also have
Furthermore, the inequality
holds for
where . By considering both (2.9) and (2.25), we get
Taking in view (2.12) and (2.26), we obtain
since . Additionally, from (2.21), we will have
and
Taking in view (2.27) and (2.28), we get
From (2.29), we get
where and
Finally, from (2.21) we consider
where we obtain
where
Considering the condition (iii), we investigate
where
(2.34) can be written as
In this case, we must only show the condition for the inequality
where . For
we must show
So we must only investigate the conditions for the inequality
and
By adding (2.39) and (2.40) side by side we get
which holds for
Furthermore, if the following conditions hold, then the inequality (2.39) is available.
If
then we obtain
where .
If
we have
Considering (2.42), (2.44), and (2.46), we obtain
and we get
For the inequality
let us use (2.47) and (2.48). Also, we can write
and
Using (2.50) and (2.51) in the following, we obtain
This completes the proof. □
Theorem 2.2 Let , be a positive solution of system (2.2). The following statements are true.
-
(i)
If
(2.52)
then the solution of system (2.2) increases monotonically.
-
(ii)
If
(2.53)
then
Proof The proof will be left to the readers. □
Theorem 2.3 Let system (2.2) be written as follows:
where the first order partial derivatives of the functions f, g, and h with regard to , , are continuous in and . If
and
then (2.55) has no 2-cycle in I, where , .
Proof Let the initial values be as follows:
In this case, we must have
to find that has no 2-cycle in I. In view of Theorem 2.2, the following results can be obtained.
-
(1)
has no cycle in I, since for we obtain
(2.61)
where
-
(2)
Similarly, has no cycle in I, since for , we get
(2.63)
where
-
(3)
Finally, has no cycle in I, since (2.62) and (2.64) hold, and we have
(2.65)
This completes the proof. □
Some additional assumptions of (2.55) are needed to verify global asymptotic stability for the positive equilibrium point .
Let f, g, h be continuous functions and
-
i.
,
-
ii.
,
-
iii.
.
Corollary 2.1 Let us have a positive equilibrium point of system (2.2). If Theorems 2.1-2.3 hold, then the positive equilibrium point of system (2.2) is globally asymptotically stable.
Example
We considered the health system in India in view of the information of [2]. The unit of parameters is in units of per year:
Considering the condition , we obtain , . Initial values are selected as , , in Figure 1.
The health system in India has been considered in view of the information of [2]. Figures 1-8 show the variation of classes for different values of the parameters. In Figures 1-8, blue graph denotes susceptible class (), red graph denotes HIV positives that do not know they are infected (), green graph denotes HIV positives that know they are infected. The value taken in Figure 1 is . In Figure 2, we have only changed the variable . And also in Figure 3, we have changed , . In this case, one can say that is an important parameter for the spread of the populations over the time t. Considering Figure 1, it is seen that after 75 years an important increase of the class and decrease of the S class will happen for the selected values in system (2.2). When Figures 1 and 2 are compared, one can see that in the same years the class increases more in Figure 2 and that the S class decreases more in Figure 2. In Figure 3, for and after 25 years an important increase of class and decrease of class S will happen. In that case it is said that as the value of (per capita contact rate for susceptibles with unaware infectives ()) increases, the class decreases in earlier years.
In Figures 4-6 the variation of populations for different values of θ and k is shown. It is seen that as infected persons, i.e. the unaware HIV infectives become aware about their infection, detect by a rate θ, we may trace out the other infectives which have had the sexual contacts in the past by contact tracing by a rate γ, which results in the decrease of the number of unaware infectives. It is seen that as the rate of θ and k become zero (see Figure 6) i.e. the infectives who do not know that they are infected will continue maintaining sexual relationships in the community which will ultimately increase the infective populations.
In Figure 1 due to immigration, the susceptible population increases continuously, therefore, infection becomes more endemic and always persists in the population (see also Figure 7). In Figure 8 the distribution of population with time is shown in different classes without immigration. It is seen that in the absence of immigration into the community, the susceptible population decreases continuously as the population is closed, which results in an increase in the infective population first and then it decreases as all infectives will develop AIDS will die out by disease-induced deaths. Thus the total population will be eradicating after some time.
Thus, on changing the behavior and increasing the awareness about the HIV infection in the population the infection can be slowed down and may be kept under control.
Discussion
In this paper, a mathematical model with piecewise constant arguments is proposed to investigate the impact of the parameters (e.g. contact tracing, screening) on the spread of HIV in a population with variable size structure. The model is analyzed using Schur-Cohn criteria on difference equations and numerical simulation. The equilibrium point is found to be locally asymptotically stable and globally asymptotically stable under certain conditions. It is observed that if the aware HIV infectives, detected by screening and contact tracing, do not take part in spreading the disease, HIV infection reduces significantly. It is also found that the disease becomes more endemic due to immigration and the endemicity of the disease decreases when the infectives become aware of their infection after screening and contact tracing and do not take part in sexual interaction, whereas it increases in the absence of contact tracing. In the absence of screening and contact tracing, the infected people continue to spread the disease without taking any precaution due to unawareness of their infection.
Finally from the analysis, it may be speculated that the most effective way to reduce the infection rate and prevalence level is to educate the people about the HIV and make them aware of the consequences of practicing non-safe sex or any other kind of risky behavior. If the population presents a positive attitude toward preventive procedures, the disease may tend to vanish, even for relatively small random screening rates.
References
López-Cruz, R: Structured SI epidemic models with applications to HIV epidemic. Postgraduate thesis, Arizona State University (2006)
Naresh R, Sharma D, Tripathi A: A nonlinear HIV/AIDS model with contact tracing. Appl. Math. Comput. 2011, 217(23):9575-9591. 10.1016/j.amc.2011.04.033
Cooke KL, Yorke JA: Some equations modelling growth processes and gonorrhea epidemics. Math. Biosci. 1973, 16: 75-101. 10.1016/0025-5564(73)90046-1
Lajmanovich A, Yorke JA: A deterministic model for gonorrhea in a nonhomogeneous population. Math. Biosci. 1976, 28: 221-236. 10.1016/0025-5564(76)90125-5
Dietz K, Heesterbeek JAP: Daniel Bernoulli’s epidemiological model revisited. Math. Biosci. 2002, 180(1-2):1-21. 10.1016/S0025-5564(02)00122-0
Anderson RM, Medley GF, May RM, Johnson AM: A preliminary study of the transmission dynamics of the human immunodeficiency virus HIV, the causative agent of AIDS. IMA J. Math. Appl. Med. Biol. 1986, 3: 229-263. 10.1093/imammb/3.4.229
Adams BM, Banks HT, Davidian M, Kwon HD, Tran HT, Wynne SN, Rosenberg ES: HIV dynamics: modeling, data analysis, and optimal treatment protocols. J. Comput. Appl. Math. 2005, 184(1):10-49. 10.1016/j.cam.2005.02.004
Blythe SP, Anderson RM: Variable infectiousness in HIV transmission models. IMA J. Math. Appl. Med. Biol. 1988, 5: 181-200. 10.1093/imammb/5.3.181
Naresh R, Sharma D, Tripathi A: Modelling the effect of risky sexual behaviour on the spread of HIV/AIDS. Int. J. Appl. Math. Comput. 2009, 1(3):132-147.
Arazoza HD, Lounes R: A non-linear model for a sexually transmitted disease with contact tracing. IMA J. Math. Appl. Med. Biol. 2002, 19: 221-234. 10.1093/imammb/19.3.221
Doyle M, Greenhalgh D: Asymmetry and multiple endemic equilibria in a model for HIV transmission in a heterosexual population. Math. Comput. Model. 1999, 29(3):43-61. 10.1016/S0895-7177(99)00029-1
Nyabadza F, Mukandavire Z, Hove-Musekwa SD: Modelling the HIV/AIDS epidemic trends in South Africa: insights from a simple mathematical model. Nonlinear Anal., Real World Appl. 2011, 12(4):2091-2104. 10.1016/j.nonrwa.2010.12.024
Velasco-Hernandez JX, Hsieh Y-H: Modelling the effect of treatment and behavioral change in HIV transmission dynamics. J. Math. Biol. 1994, 32: 233-249. 10.1007/BF00163880
Bachar M, Dorfmayr A: HIV treatment models with time delay. C. R. Biol. 2004, 327(11):983-994. 10.1016/j.crvi.2004.08.007
Allen LJS: An Introduction to Mathematical Biology. Pearson/Prentice Hall, Upper Saddle River; 2007.
Acknowledgements
Authors are thankful to the reviewers, whose suggestions and constructive comments helped us in finalizing the paper. This research is supported by the Erciyes University Bap organization within the scope of the FBA-12-3993 project.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Competing interests
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Authors’ contributions
In light of the master’s thesis, the authors have had the chance to share this work. All authors have contributed equally. Also they have read and approved the final manuscript.
Authors’ original submitted files for images
Below are the links to the authors’ original submitted files for images.
Rights and permissions
Open Access This article is distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution 2.0 International License (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/2.0), which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original work is properly cited.
About this article
Cite this article
Bozkurt, F., Peker, F. Mathematical modelling of HIV epidemic and stability analysis. Adv Differ Equ 2014, 95 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1186/1687-1847-2014-95
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1186/1687-1847-2014-95