Abstract
Background
A major concern in malaria vaccine development is genetic polymorphisms typically observed among Plasmodium isolates in different geographical areas across the world. Highly polymorphic regions have been observed in Plasmodium falciparum and Plasmodium vivax antigenic surface proteins such as Circumsporozoite protein (CSP), Duffy-binding protein (DBP), Merozoite surface protein-1 (MSP-1), Apical membrane antigen-1 (AMA-1) and Thrombospondin related anonymous protein (TRAP).
Methods
Genetic variability was assessed in important polymorphic regions of various vaccine candidate antigens in P. vivax among 106 isolates from the Amazon Region of Loreto, Peru. In addition, genetic diversity determined in Peruvian isolates was compared to population studies from various geographical locations worldwide.
Results
The structured diversity found in P. vivax populations did not show a geographic pattern and haplotypes from all gene candidates were distributed worldwide. In addition, evidence of balancing selection was found in polymorphic regions of the trap, dbp and ama-1 genes.
Conclusions
It is important to have a good representation of the haplotypes circulating worldwide when implementing a vaccine, regardless of the geographic region of deployment since selective pressure plays an important role in structuring antigen diversity.
Similar content being viewed by others
Background
Malaria is one of the major global public health problems that affect most tropical regions of the world. Even though Plasmodium falciparum is the most virulent, it is estimated that Plasmodium vivax produces around 80 to 300 million clinical cases per year [1]. Furthermore, there have been several reports of severe P. vivax malaria cases in the last few years [2–4]. In 2008, 560,221 malaria cases were reported in the Americas [5]; 74.2% of them caused by P. vivax and 25.7% by P. falciparum[1]. About 90% of these malaria cases originated in the Amazon basin shared by Bolivia, Brazil, Colombia, Ecuador, French Guiana, Guyana, Venezuela, Suriname and Peru [5], whereas the other 10% was contributed by non-Amazon regions.
Developing a vaccine for P. vivax represents a major challenge especially considering the lack of in vitro cultures. Thus, current efforts focus on orthologs of P. falciparum. Over the past four decades, experiments performed in animals and human subjects have led to the development of several Plasmodium vaccine candidates. Antigenic surface proteins such as the Circumsporozoite protein (CSP), Thrombospondin related anonymous protein (TRAP), Duffy-binding protein (DBP), Merozoite surface protein-1 (MSP-1) and Apical membrane antigen-1 (AMA-1) are currently being evaluated as vaccine candidates in clinical trials [1, 6–8]. The CSP is one of the most extensively studied antigens and it is involved in the motility and invasion of the sporozoite during its entrance in the hepatocyte [9]. Pv CSP has an immunogenic central repeat domain flanked by amino and carboxyl sequences containing highly conserved protein stretches (Regions I and II-plus) [10]. This protein displays two major types of nonapeptide repeats: type I (VK210), which contains repeats of GDRA(A/D)GQPA or related sequences and type II (VK247), which is composed of ANGAGNQPG repeats [11, 12]. A third type of variant, called P. vivax-like has repeat units of APGANQ(E/G)GAA, identical to that described for Plasmodium simiovale[13, 14]. Currently, the P. falciparum RTS, S vaccine, which is based on CSP have showed to protect semi-immune adults [15] and children from P. falciparum natural infection in endemic areas [16–18]; this vaccine is being tested in Phase III clinical trials [8, 19].
Another sporozoite surface protein that stands out as a good vaccine candidate is TRAP, which is a 90 kDa protein with six distinct regions. TRAP is essential for sporozoite gliding and hepatocyte invasion [20, 21]. Genetic analysis of Pv TRAP reveals that most of the polymorphisms occur in Region II (von Willebrand factor A-domain) and III [22]. The potential role of TRAP as a malaria vaccine candidate has been tested in mice and monkeys, inducing high levels of specific antibodies [23]. Furthermore, a synthetic peptide-derived from a conserved region of the TRAP protein located in the N-terminal, proved to be immunogenic and provided partial protection in Aotus monkeys [1, 24].
On the other hand, the asexual P. vivax parasite antigens DBP, MSP-1 and AMA-1 have also received attention for their role in the invasion process and/or their generation of antibody response. DBP interacts with the Duffy blood group antigen of reticulocytes, MSP-1 is expressed abundantly on the merozoite surface and AMA-1 plays a role in apical reorientation of merozoites following initial attachment during invasion [1]. Region II of DBP (DBPII) functions as a ligand domain and consists of 330 aa with 12 cysteines and numerous aromatic residues. Studies have identified the central region of the DBPII domain between cysteines 4 and 8, as the segment containing the conserved contact residues Tyr 94, Asn 95, Lys 96, Arg 103 and Ile 175 required for recognition of DARC (Duffy Antigen/Receptor for Chemokine) on human erythrocytes [25–28].
MSP-1 is part of a complex of proteins that is processed into smaller fragments by serine proteases during invasion of red blood cells [29]. It has been suggested that fragments Pv MSP-114 and Pv MSP-120 could be included in a P. vivax multi-antigen vaccine since they contain high affinity reticulocyte binding (HARB) cluster regions and confer protection in monkeys [30–32]. AMA-1 has also been evaluated for inclusion in a multi- sub-unit vaccine for both P. falciparum and P. vivax[33, 34]. The complete AMA-1 protein contains three domains, from which a higher rate of mutations and level of diversifying selection has been shown in domain I [35, 36]. Indeed, AMA-1 is highly immunogenic, protecting against Plasmodium chabaudi infection in mice [37] and displaying significant antibody and T cell responses in endemic human populations [38–40].
Investigation of the sequence variation among malaria antigenic regions is necessary for the development of an effective malaria vaccine that includes haplotypes from different regions, considering that Plasmodium is highly diverse and these regions are under strong immunological pressure. In this study, important regions in Pv CSP, Pv TRAP, Pv DBP, Pv MSP-1 and Pv AMA-1 were genotyped using P. vivax Peruvian isolates collected during years 2006-2007. In addition, since natural selection plays a role in structuring diversity of these highly polymorphic antigens, the worldwide distribution of the main variants was determined by comparing the Peruvian samples with sequences previously reported from South America, Asia and Oceania.
Methods
Study area and sample collection
Blood samples from patients were collected during years 2006-2007 from endemic areas in the Peruvian Amazon region of Loreto Department using human use approved protocols (NMRCD.2005.0005). In Peru, P. vivax corresponds to more than 80% of the malaria cases and the majority of them are found in the Amazonic Department of Loreto [41]. Fifty-seven samples were obtained from Padrecocha, in Punchana district, a village situated five km from Iquitos (Loreto's capital) and forty-nine samples were collected from a village located in the San Juan district just south of Iquitos. All samples were confirmed to be positive for P. vivax by microscopic analysis on Giemsa-stained blood smears.
PCR and DNA sequencing
DNA was purified from 200 μL of whole blood using the QIAamp DNA Blood mini kit (QIAGEN, Valencia, CA). PCR amplification was performed in a 50 μL reaction mixture containing 0.2 μM each of forward and reverse primers, 200 μM each dNTP, 0.6 units of DNA polymerase recombinant (Invitrogen, Carlsbad, CA), 3 μL of 10× PCR buffer, 1.5 mM of MgCl2 and 5 μL of DNA extracted from blood. To assess antigenic variability of Pv CSP, the Central Repetitive Region, Region I and Region II were amplified. The PCR conditions were: 5 min at 94°C; 1 min at 94°C, 1 min at 58°C, 2 min at 72°C for 35 cycles; and a final extension of 72°C for 2 min, using the primers VSC-OF (5'ATGTAGATCTGTCCAAGGCCATAAA3') and VSC-OR (5' TAATTGAATAATGCTAGGACTAACAATATG 3') [42]. The amplification of the highly polymorphic regions II and III of Pv TRAP [22] was obtained using the primers Pvsspf: 5' GTCGATTTATACCTCCTAGTTGACGG 3' and Pvsspr: 5' CAGCTTGAACGTCGACCTCCGC 3' with the following conditions: 5 min at 94°C; 1 min at 94°C, 1 min at 50°C, 2 min at 72°C for 35 cycles; and a final extension of 72°C for 2 min. The amplification of the central region of the Pv DBPII domain was done using primers Liz-1 (5' TGGGGAGGAAAAAGATG 3') and Liz-2 (5' AACGGAACAAACGCATAAC 3') [43]. The PCR conditions used were as follows: 4 min at 94°C; 1 min at 94°C, 2 min at 58°C, 2 min at 72°C for 35 cycles; and a final extension of 72°C for 3 min. Pv MSP-1 primers described by Espinosa et al. (HARB1_f: 5' GGCAACAACGATGACGAC 3', HARB1_r: 5' CTTCTCAAGTCGAGCAG 3', HARB2_f: 5' TCACTGTAAAGAAATTGCAG 3' and HARB2_r: 5' ATACATGTGTGCTCGGAG 3') were used for amplifying the two HARB containing regions: Pv MSP-120 and Pv MSP-114 kDa [31] with the following conditions: 5 min at 94°C; 1 min at 94°C, 1 min at 50°C, 1 min at 72°C for 35 cycles; and a final extension of 72°C for 5 min for the first region and 5 min at 94°C; 1 min at 94°C, 1 min at 45°C, 1 min at 72°C for 35 cycles; and a final extension of 72°C for 5 min for the second region. Finally, a nested PCR was used to amplify domain I of Pv AMA-1 as described by Cheng and Saul [44]. PCR products were purified using the QIAquick PCR purifications kit (QIAGEN, Valencia, CA, USA) and sequenced using BigDye® Terminator v3.1 sequencing kit (Applied Biosystems, Foster City, CA, USA), with the primers previously mentioned and an ABI 3100 automated sequencer.
Sequence determination and data analysis
Sequences were analysed using the Sequencher™ software version 4.7 (Gene Codes Corporation, Ann Harbor, MI, USA) and sequence alignments were performed using the MEGA software version 4.1 [45]. Comparison with previously deposited P. vivax sequences in the GenBank was performed using BLAST search. The number of haplotypes (h), haplotype diversity (hd) and nucleotide diversity (Pi) values were obtained using the DnaSP version 5.0 [46]. The effect of natural selection was also evaluated by estimating the difference of non-synonymous and synonymous substitutions (Dn-Ds) using the Nei and Gojobori's method with the Jukes and Cantor correction. The null hypothesis of neutrality was rejected if Dn:Ds ≠ 1. Positive values for Dn-Ds indicated positive selection while negative values indicated negative selection [47]. Standard error was calculated using bootstrap with 1,000 replications and rates of Ds and Dn were compared by the Z-test of selection using Mega version 4.1 [45]. To test whether the haplotypes clustered according to their geographic origin, the model-based clustering algorithm implemented in the Structure 2.1 software was used [48]. This software uses a Bayesian clustering approach to assign isolates to K populations characterized by a set of allele frequencies at each locus. The number of such populations may be either previously known or not. The program was run five times at different K values (from 2 to 10) with a burn-in period of 10,000 iterations followed by 50,000 iterations. The admixture model was used in all analyses, which allows for the presence of individuals with ancestry in two or more of the K populations. However, clustering algorithms incorporate stochastic simulation as part of the inference and, as a consequence, independent analyses of the same data may result in several distinct outcomes, even though the same initial conditions were used. To facilitate the interpretation of population-genetic clustering results, the computer program CLUMPP (Cluster Matching and Permutation Program) was used. CLUMPP strips away the 'label switching' heterogeneity so that the 'genuine multimodality' can be detected and quantified [49]. In addition, distruct 1.1 was used to graphically display the clustering results [50]. The genetic difference between clusters was measured by the fixation index (Fst) calculated from the haplotype frequencies (Hst) and pair-wise DNA sequence diversity (Kst*) using DnaSP version 5.0 [46]. The nearest-neighbour statistic (Snn) was also calculated between geographic populations. Snn is a measure of how often the "nearest neighbours" of sequences are from the same locality in geographic space. This statistic is applicable when genetic data are collected on individuals sampled from two or more localities. Snn is expected to be near one when the populations at the two localities are highly differentiated and near one-half when the populations at the two localities are part of the same pan-mictic population [51].
Results
PvCSP
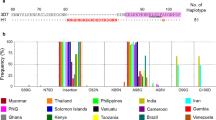
A 1,100 bp PCR product corresponding to Pvcsp was amplified from 106 P. vivax samples from Peru. In addition, 326 complete CSP sequences from Brazil, Colombia, India, Iran and Korea were also included in the amino acid alignment. Sequences from Thailand, China and PNG were used to determine the percentage of strains circulating of each Pv CSP type (Table 1); however, they were not considered in the haplotype analysis since the sequences were not complete. Most of the strains circulating worldwide belonged to the VK210 type and in most population sets analysed (except Colombia and Thailand) a greater percentage of VK210 haplotypes was found. The amino acid alignment of the sequences used in this study showed 97 different VK210 haplotypes and 28 VK247 haplotypes circulating worldwide. Different haplotypes were observed in South American and Asian countries, except for one VK247 Peruvian haplotype, which was also found in Iran [52]. Thirty-seven VK210 and 19 VK247 haplotypes were identified in South America; while in Asia, 51 and 10 haplotypes were observed from each type.
In Peru, 23 different VK210 subtypes and three different VK247 subtypes were found (Figure 1). Pv CSP displayed a different pattern of a nine amino acid oligopeptide repetitions depending on the subtype. The VK210 subtypes contained the repeat region G(D/N)RA(A/D/G/V)G(Q/H)PA either 16, 17, 18 or 19 times, while VK247 subtypes contained the repeated region ANGA(G/D)(D/N)QPG, 17 or 18 times. Region I of Pv CSP showed a polymorphism in position 3 (L/V), whereas the 18 amino acid long linear peptide EWTPCSVTCGVGVRVRRR, located on Region II [53, 54], was highly conserved. Pv CSP analysis of Peruvian isolates also revealed high variability of VK210 and VK247 haplotypes compared to other populations from South America [55, 56]. Region II-plus, which contains dominant B-cell epitopes [57, 1] and block hepatocyte invasion by sporozoites [58], was highly conserved in Peruvian isolates, with the same amino acid sequence as the Sal I strain.
PvTRAP
A total of 104 sequences of regions II and III of Pvtrap were obtained from the Peruvian isolates. In addition, 63 Thailand sequences from GenBank were included in the amino acid alignment. The N-terminal region (209-256aa), which has been proved to be immunogenic and to provide partial protection in Aotus monkeys [24] was highly conserved with only three amino acid substitutions in positions 216 (R/K), 219 (H/Q) and 229 (G/K). In general, more diversity was found in Thailand (h = 34, π = 0.007 ± 0.00029 and Hd = 0.961 ± 0.01) (Table 2) compared to Peru (h = 7, π = 0.00235 ± 0.00012 and Hd = 0.641 ± 0.026) and according to the Dn-Ds test, regions II and III of Pvtrap were under positive selection (Table 3).
PvDBP
A 1,150 bp DNA fragment of Pvdbp was amplified from all 106 Peruvian isolates and 601 P. vivax sequences from Brazil, Colombia, India, Sri Lanka, Thailand, Korea, Iran and Papua New Guinea were also included in the analysis. The alignment of 510 bp from region II of dbp showed 150 different haplotypes, from which 39 were found in South America, 42 in Asia, 56 in Oceania and 13 were found in South America and Asia. In the Peruvian isolates 26 different haplotypes were found with genetic diversity values of π = 0.008 ± 0.00048 and Hd = 0.903 ± 0.014. In general, the average genetic and haplotype diversity in South America and Asia was very similar (Table 2). On the other hand, the analysis of DNA sequence polymorphisms showed a significant difference between synonymous and non-synonymous substitutions, indicating balancing selection in dbp II (Table 3). In addition, several substitutions in the positions underlined were found in DBPII regions corresponding to peptides H1: F HR DITFRKLYLKRKL, H3: DEK AQ QRR KQWWN ES K an 1653: RD YVS ELPTEVQ KLKEK C, previously reported as immunogenic [27, 59].
PvMSP-1
According to the amino acid alignment of PvMSP-120 and PvMSP-114, a total of 28 haplotypes were found worldwide, 11 in South America, 14 in Asia and three in both continents. When comparing genetic diversity between populations, Peru (π = 0.00286 ± 0.00029, Hd = 0.665 ± 0.041) and Brazil (π = 0.00293 ± 0.00061, Hd = 0.75 ± 0.139) showed the highest levels of nucleotide and haplotype diversity, while in Korea, Thailand and Turkey these HARBs were highly conserved. In general, values of genetic diversity for Pvmsp-1 were low when compared with the other genes and no clear signature of selection was found according to the Dn-Ds test (Table 3).
PvAMA-1
The polymorphic region of Pvama-1 (Domain I of protein) was amplified and sequenced from 98 of the 106 Peruvian isolates. A total of 774 Pvama-1 partial sequences were used in the analysis, including samples from Brazil, Venezuela, India, Sri Lanka, China, Korea, Myanmar, Philippines, Thailand, Papua New Guinea and Solomon Islands. A total of 168 haplotypes were identified; 135 were exclusively found in Asia, nine in Oceania and 12 in South America. In addition, seven haplotypes were shared in America and Asia and five in Asia and Oceania. According to the analysis of polymorphisms, the dN-dS test indicated balancing selection in this domain (Table 3) with several haplotypes in low frequency. In addition, values of nucleotide diversity were very similar between geographic regions and populations (Table 2).
Population genetic analysis
When analysing Plasmodium isolates, samples are usually grouped by geographic location; nevertheless, this approach assumes that geographic barriers or distance are the underlying factors that limit gene flow. It also assumes that genetic exchange within each population geographically defined is random. To better estimate the distribution of haplotypes of different P. vivax vaccine candidate antigens, a Bayesian clustering algorithm [48] was used to sub-group samples according to related SNPs haplotypes. The Structure model assumes that loci are independent within populations; however, this assumption is likely to be violated for sequence data, or data from non-recombining regions. It is a matter of debate whether it is valid to group sequences containing potentially linked polymorphisms in a single gene under balancing selection [60]. The main cost of the dependence within regions will be that Structure underestimates the uncertainty in the assignment of particular individuals. However, if there is enough independence across regions than LD within regions, then Structure may actually perform reasonably well [48]. Moreover, our main goal is not to describe the demographic history of the population but to get a graphically representation of the vaccine candidate's haplotype distribution. Genetic differentiation between clusters was calculated using Fst from haplotype-frequencies and pairwise DNA sequence diversity. The haplotype frequency-based statistics are more sensitive for small sample sizes, while the sequence-based statistic is a more sensitive method for detecting population structure in highly polymorphic loci [61, 62].
The results obtained with Pv TRAP, Pv DBP and Pv AMA-1 showed three different clusters. Significant differentiation was observed in haplotype and pair-wise comparisons between all clusters according to the Fst values (Table 4), except for Pvmsp-1, from which a significant number of clusters it was not possible to identify. Although admixed haplotypes were observed in Pvdbp and Pvama-1, the estimate of K = 3 best explained the distribution of haplotypes from all geographic populations; besides, the defined sub-groups were not geographically or even regionally restricted (Figure 2). Snn values between the different geographic populations were also calculated for each of the antigens. We observed that for most of the comparisons in DBP, AMA-1 (Table 5) and TRAP (Snn = 0.86803*), Snn values were near one, which indicates that the localities are highly differentiated. However, close geographic populations such as Sri Lanka and India in South Asia and Peru and Brazil in South America showed almost not genetic differentiation (Snn = 0.58, p < 0.01 and Snn = 0.65, p < 0.01). Thus, relative low Snn values were found between Brazil, India and Sri Lanka, since there are shared haplotypes circulating in South America and South Asia. Moreover, previous work also indicated low genetic differentiation using Fst analysis between dbpII sequences from Brazil and Iran, India or Sri Lanka [63]. On the other hand, at least seven of the pairwise comparisons made using MSP-1 resulted in non-significant values.
Global population structure of the genes encoding P.vivax vaccine antigens based on Bayesian cluster analysis. Each haplotype is represented by an imaginary bar, which is partitioned into K coloured segments that represent the membership fraction of each haplotype in K clusters (K = 3, represented by the three different colours blue, yellow and orange). Samples are grouped in boxes according to their geographic origin.
Discussion
When designing an efficient anti-malarial vaccine, worldwide information of the circulating antigenic variants is necessary for the formulation of a polyvalent vaccine, which would be effective in different regions. Because of the complex parasite life cycle and the co-existence of P. falciparum and P. vivax infections in most endemic areas, it is accepted that a multi-antigen and multi-species vaccine should be developed for most endemic regions [1]. In P. falciparum, the majority of haplotypes upon which current vaccines are based have been found to be present at extremely low frequencies in the global parasite population, except for lsa-1 and msp-1 haplotypes [62]. Since immune selection might be playing a role in structuring the diversity of highly polymorphic antigens, population genetic studies in endemic regions are essential for the next generation of vaccines. In this study, the information obtained from the Peruvian isolates contribute to get a better understanding of the haplotypes circulating in the Amazon basin and to compare these results with other previously reported from different parts of the world.
For the analysis of Peruvian isolates, samples form Padreococha and San Juan were considered as a single geographic population since these areas are relatively closed and they present similar haplotype distribution in all antigens with little or none genetic differentiation between them. In general, data from a two-year period (2006-2007) in Peru revealed high nucleotide and haplotype diversity compared to other geographic populations included in the final analysis. These results suggest that the extent of allelic diversity in this region is determined by complex demographic processes that include heterogeneity of transmission intensities in time and space, as well as the number of recurrent infections that are common in the region, allowing for a high turnover of parasite genotypes [41]. The presence of asymptomatic cases [64] participating in the infection process might also be contributing to the persistence of genetic variation since they are a "reservoir" of untreated patients. In addition, we need to take in consideration possible P. vivax multi clonal infections that might be difficult to observe by direct sequencing. This limitation could potentially affect the overall estimates of genetic diversity and population structure; however, for the goal of this study, the data collected is useful to obtain a broad picture of how these vaccine candidate haplotypes are worldwide distributed. If a fine scale study is considered in which the goal is to understand the population structure of Plasmodium in a specific geographic area then, unlinked microsatellite loci should be used to get a better idea of the parasite's population history.
When considering worldwide data, genes encoding non-merozoite antigens in P. falciparum showed variation in diversity [62]. In P. vivax, the same pattern was observed using CSP and TRAP. Although, limited population samples were available for TRAP sequences. On the other hand, the genes encoding merozoite antigens in P. falciparum and P. vivax showed different patterns. P. falciparum genes encoding AMA-1, EBA-175 and MSP-1, MSP-3 and MSP-4 showed similar levels of diversity among countries and regions [62]. In P. vivax, genes dbpII and ama-1 also showed this trend; however, msp-1 exhibited very low but different polymorphism and haplotype diversity values among regions and countries. These results support the hypothesis that maintaining the structural conformation of the HARBs regions (MSP-120 and MSP-114) is important for recognition and binding of reticulocytes [31]. The limited variation of amino acid substitutions in these fragments makes them strong candidates to be tested in immunological studies. Also, TRAP sequences showed low levels of nucleotide and haplotype diversity with a highly conserved region between positions 209 to 256, previously reported to be immunogenic.
Contrary to P. falciparum, a largely structured diversity in all P. vivax populations was not found on the basis of geography. The clusters determined by Structure were found in most countries except in those with small number of samples, suggesting that haplotypes corresponding to those clusters were underrepresented. Moreover, a high level of admixture in all countries was observed, which could be explained by natural and high fluctuations over time, as a result of frequency-dependent selection or the discrepancy due to the sampling used [62], since the worldwide sequences obtained from GenBank came from different time points and locations. On the other hand, the lack of geographic clustering could be explained by balancing selection acting on the genes studied and as a result high worldwide antigen diversity was observed not only in Asia but also in South America.
Conclusion
In conclusion, it would be ideal to have a good representation of the haplotypes circulating worldwide when implementing a vaccine regardless of the geographic region of deployment. Considering that selective pressure plays an important role in structuring the diversity of antigens, it cannot be assumed that a single strain could accurately represent the haplotypes circulating worldwide and as a consequence be effective in all endemic regions. In addition, Plasmodium population definition should be revised since parasite sub-groups are not necessarily geographically restricted and treatment or vaccination in a region cannot be considered as if it was isolated but a dynamic map needs to be acknowledged. Thus, important epidemiological units should be established according to the parasite's gene flow, which would lead to a more effective malaria control strategy.
References
Arevalo-Herrera M, Chitnis C, Herrera S: Current status of Plasmodium vivax vaccine. Hum Vaccin. 2010, 6: 124-132. 10.4161/hv.6.1.9931.
Tjitra E, Anstey NM, Sugiarto P, Warikar N, Kenangalem E, Karyana M, Lampah DA, Price RN: Multidrug-resistant Plasmodium vivax associated with severe and fatal malaria: a prospective study in Papua, Indonesia. PLoS Med. 2008, 5: e128-10.1371/journal.pmed.0050128.
Rogerson SJ, Carter R: Severe vivax malaria: newly recognised or rediscovered. PLoS Med. 2008, 5: e136-10.1371/journal.pmed.0050136.
Price RN, Douglas NM, Anstey NM: New developments in Plasmodium vivax malaria: severe disease and the rise of chloroquine resistance. Curr Opin Infect Dis. 2009, 22: 430-435. 10.1097/QCO.0b013e32832f14c1.
Report on Situation of Malaria in the Americas, PAHO. 2008
Tediosi F, Maire N, Penny M, Studer A, Smith TA: Simulation of the cost-effectiveness of malaria vaccines. Malar J. 2009, 8: 127-10.1186/1475-2875-8-127.
Sharma S, Pathak S: Malaria vaccine: a current perspective. J Vector Borne Dis. 2008, 45: 1-20.
Crompton PD, Pierce SK, Miller LH: Advances and challenges in malaria vaccine development. J Clin Invest. 2010, 120: 4168-4178. 10.1172/JCI44423.
Mota MM, Rodriguez A: Migration through host cells: the first steps of Plasmodium sporozoites in the mammalian host. Cell Microbiol. 2004, 6: 1113-1118. 10.1111/j.1462-5822.2004.00460.x.
Mann VH, Huang T, Cheng Q, Saul A: Sequence variation in the circumsporozoite protein gene of Plasmodium vivax appears to be regionally biased. Mol Biochem Parasitol. 1994, 68: 45-52. 10.1016/0166-6851(94)00148-0.
Rosenberg R, Wirtz RA, Lanar DE, Sattabongkot J, Hall T, Waters AP, Prasittisuk C: Circumsporozoite protein heterogeneity in the human malaria parasite Plasmodium vivax. Science. 1989, 245: 973-976. 10.1126/science.2672336.
Kain KC, Brown AE, Webster HK, Wirtz RA, Keystone JS, Rodriguez MH, Kinahan J, Rowland M, Lanar DE: Circumsporozoite genotyping of global isolates of Plasmodium vivax from dried blood specimens. J Clin Microbiol. 1992, 30: 1863-1866.
Qari SH, Shi YP, Goldman IF, Udhayakumar V, Alpers MP, Collins WE, Lal AA: Identification of Plasmodium vivax-like human malaria parasite. Lancet. 1993, 341: 780-783. 10.1016/0140-6736(93)90559-Y.
Goldman IF, Qari SH, Millet PG, Collins WE, Lal AA: Circumsporozoite protein gene of Plasmodium simiu, a Plasmodium vivax-like monkey malaria parasite. Mol Biochem Parasitol. 1993, 57: 177-180. 10.1016/0166-6851(93)90257-X.
Bojang KA, Milligan PJ, Pinder M, Vigneron L, Alloueche A, Kester KE, Ballou WR, Conway DJ, Reece WH, Gothard P, Yamuah L, Delchambre M, Voss G, Greenwood BM, Hill A, McAdam KP, Tornieporth N, Cohen JD, Doherty T, S Malaria Vaccine Trial Team: Efficacy of RTS, S/AS02 malaria vaccine against Plasmodium falciparum infection in semi-immune adult men in The Gambia: a randomised trial. Lancet. 2001, 358: 1927-1934. 10.1016/S0140-6736(01)06957-4.
Alonso PL, Sacarlal J, Aponte JJ, Leach A, Macete E, Milman J, Mandomando I, Spiessens B, Guinovart C, Espasa M, Bassat Q, Aide P, Ofori-Anyinam O, Navia MM, Corachan S, Ceuppens M, Dubois MC, Demoitié MA, Dubovsky F, Menéndez C, Tornieporth N, Ballou WR, Thompson R, Cohen J: Efficacy of the RTS, S/AS02A vaccine against Plasmodium falciparum infection and disease in young African children: randomised controlled trial. Lancet. 2004, 364: 1411-1420. 10.1016/S0140-6736(04)17223-1.
Moorthy VS, Reed Z, Smith PG: Clinical trials to estimate the efficacy of preventive interventions against malaria in paediatric populations: a methodological review. Malar J. 2009, 8: 23-10.1186/1475-2875-8-23.
Abdulla S, Oberholzer R, Juma O, Kubhoja S, Machera F, Membi C, Omari S, Urassa A, Mshinda H, Jumanne A, Salim N, Shomari M, Aebi T, Schellenberg DM, Carter T, Villafana T, Demoitié MA, Dubois MC, Leach A, Lievens M, Vekemans J, Cohen J, Ballou WR, Tanner M: Safety and immunogenicity of RTS, S/AS02D malaria vaccine in infants. N Engl J Med. 2008, 359: 2533-2544. 10.1056/NEJMoa0807773.
Cohen J, Nussenzweig V, Nussenzweig R, Vekemans J, Leach A: From the circumsporozoite protein to the RTS, S/AS candidate vaccine. Hum Vaccin. 2010, 6: 90-96. 10.4161/hv.6.1.9677.
Sultan AA, Thathy V, Frevert U, Robson KJ, Crisanti A, Nussenzweig V, Nussenzweig RS, Menard R: TRAP is necessary for gliding motility and infectivity of plasmodium sporozoites. Cell. 1997, 90: 511-522. 10.1016/S0092-8674(00)80511-5.
Morahan BJ, Sallmann GB, Huestis R, Dubljevic V, Waller KL: Plasmodium falciparum: genetic and immunogenic characterisation of the rhoptry neck protein PfRON4. Exp Parasitol. 2009, 122: 280-288. 10.1016/j.exppara.2009.04.013.
Putaporntip C, Jongwutiwes S, Tia T, Ferreira MU, Kanbara H, Tanabe K: Diversity in the thrombospondin-related adhesive protein gene (TRAP) of Plasmodium vivax. Gene. 2001, 268: 97-104. 10.1016/S0378-1119(01)00425-5.
Rogers WO, Gowda K, Hoffman SL: Construction and immunogenicity of DNA vaccine plasmids encoding four Plasmodium vivax candidate vaccine antigens. Vaccine. 1999, 17: 3136-3144. 10.1016/S0264-410X(99)00146-2.
Castellanos A, Arevalo-Herrera M, Restrepo N, Gulloso L, Corradin G, Herrera S: Plasmodium vivax thrombospondin related adhesion protein: immunogenicity and protective efficacy in rodents and Aotus monkeys. Mem Inst Oswaldo Cruz. 2007, 102: 411-416. 10.1590/S0074-02762007005000047.
Xainli J, Adams JH, King CL: The erythrocyte binding motif of Plasmodium vivax duffy binding protein is highly polymorphic and functionally conserved in isolates from Papua New Guinea. Mol Biochem Parasitol. 2000, 111: 253-260. 10.1016/S0166-6851(00)00315-7.
Ocampo M, Vera R, Rodriguez LE, Curtidor H, Urquiza M, Suarez J, Garcia J, Puentes A, Lopez R, Trujillo M, Torres E, Patarroyo ME: Plasmodium vivax Duffy binding protein peptides specifically bind to reticulocytes. Peptides. 2002, 23: 13-22. 10.1016/S0196-9781(01)00574-5.
Chootong P, Ntumngia FB, VanBuskirk KM, Xainli J, Cole-Tobian JL, Campbell CO, Fraser TS, King CL, Adams JH: Mapping epitopes of the Plasmodium vivax Duffy binding protein with naturally acquired inhibitory antibodies. Infect Immun. 2010, 78: 1089-1095. 10.1128/IAI.01036-09.
Singh SK, Hora R, Belrhali H, Chitnis CE, Sharma A: Structural basis for Duffy recognition by the malaria parasite Duffy-binding-like domain. Malar J. 2006, 493: 741-744.
Koussis K, Withers-Martinez C, Yeoh S, Child M, Hackett F, Knuepfer E, Juliano L, Woehlbier U, Bujard H, Blackman MJ: A multifunctional serine protease primes the malaria parasite for red blood cell invasion. EMBO J. 2009, 28: 725-735. 10.1038/emboj.2009.22.
Caro-Aguilar I, Rodriguez A, Calvo-Calle JM, Guzman F, De la Vega P, Patarroyo ME, Galinski MR, Moreno A: Plasmodium vivax promiscuous T-helper epitopes defined and evaluated as linear peptide chimera immunogens. Infect Immun. 2002, 70: 3479-3492. 10.1128/IAI.70.7.3479-3492.2002.
Espinosa AM, Sierra AY, Barrero CA, Cepeda LA, Cantor EM, Lombo TB, Guzman F, Avila SJ, Patarroyo MA: Expression, polymorphism analysis, reticulocyte binding and serological reactivity of two Plasmodium vivax MSP-1 protein recombinant fragments. Vaccine. 2003, 21: 1033-1043. 10.1016/S0264-410X(02)00660-6.
Sierra AY, Barrero CA, Rodriguez R, Silva Y, Moncada C, Vanegas M, Patarroyo MA: Splenectomised and spleen intact Aotus monkeys' immune response to Plasmodium viva MSP-1 protein fragments and their high activity binding peptides. Vaccine. 2003, 21: 4133-4144. 10.1016/S0264-410X(03)00455-9.
Gentil F, Bargieri DY, Leite JA, Francoso KS, Patricio MB, Espindola NM, Vaz AJ, Palatnik-de-Sousa CB, Rodrigues MM, Costa FT, Soares IS: A recombinant vaccine based on domain II of Plasmodium vivax Apical Membrane Antigen 1 induces high antibody titres in mice. Vaccine. 2010, 28: 6183-6190. 10.1016/j.vaccine.2010.07.017.
Cech PG, Aebi T, Abdallah MS, Mpina M, Machunda EB, Westerfeld N, Stoffel SA, Zurbriggen R, Pluschke G, Tanner M, Daubenberger C, Genton B, Abdulla S: Virosome-formulated Plasmodium falciparum AMA-1 & CSP derived peptides as malaria vaccine: randomized phase 1b trial in semi-immune adults & children. PLoS One. 2011, 6: e22273-10.1371/journal.pone.0022273.
Cortes A, Mellombo M, Mueller I, Benet A, Reeder JC, Anders RF: Geographical structure of diversity and differences between symptomatic and asymptomatic infections for Plasmodium falciparum vaccine candidate AMA1. Infect Immun. 2003, 71: 1416-1426. 10.1128/IAI.71.3.1416-1426.2003.
Garg S, Alam MT, Das MK, Dev V, Kumar A, Dash AP, Sharma YD: Sequence diversity and natural selection at domain I of the apical membrane antigen 1 among Indian Plasmodium falciparum populations. Malar J. 2007, 6: 154-10.1186/1475-2875-6-154.
Crewther PE, Matthew ML, Flegg RH, Anders RF: Protective immune responses to apical membrane antigen 1 of Plasmodium chabaudi involve recognition of strain-specific epitopes. Infect Immun. 1996, 64: 3310-3317.
Thomas AW, Narum D, Waters AP, Trape JF, Rogier C, Goncalves A, Rosario V, Druilhe P, Mitchell GH, Dennis D: Aspects of immunity for the AMA-1 family of molecules in humans and non-human primates malarias. Mem Inst Oswaldo Cruz. 1994, 89 (Suppl 2): 67-70.
Wickramarachchi T, Premaratne PH, Perera KL, Bandara S, Kocken CH, Thomas AW, Handunnetti SM, Udagama-Randeniya PV: Natural human antibody responses to Plasmodium vivax apical membrane antigen 1 under low transmission and unstable malaria conditions in Sri Lanka. Infect Immun. 2006, 74: 798-801. 10.1128/IAI.74.1.798-801.2006.
Bueno LL, Fujiwara RT, Soares IS, Braga EM: Direct effect of Plasmodium vivax recombinant vaccine candidates AMA-1 and MSP-119 on the innate immune response. Vaccine. 2008, 26: 1204-1213. 10.1016/j.vaccine.2007.12.031.
Van den Eede P, Soto-Calle VE, Delgado C, Gamboa D, Grande T, Rodriguez H, Llanos-Cuentas A, Anne J, D'Alessandro U, Erhart A: Plasmodium vivax sub-patent infections after radical treatment are common in Peruvian patients: results of a 1-year prospective cohort study. PLoS One. 2011, 6: e16257-10.1371/journal.pone.0016257.
Imwong M, Pukrittayakamee S, Gruner AC, Renia L, Letourneur F, Looareesuwan S, White NJ, Snounou G: Practical PCR genotyping protocols for Plasmodium vivax using P csp and P msp1. Malar J. 2005, 4: 20-10.1186/1475-2875-4-20.
Ampudia E, Patarroyo MA, Patarroyo ME, Murillo LA: Genetic polymorphism of the Duffy receptor binding domain of Plasmodium vivax in Colombian wild isolates. Mol Biochem Parasitol. 1996, 78: 269-272. 10.1016/S0166-6851(96)02611-4.
Cheng Q, Saul A: Sequence analysis of the apical membrane antigen I (AMA-1) of Plasmodium vivax. Mol Biochem Parasitol. 1994, 65: 183-187. 10.1016/0166-6851(94)90127-9.
Tamura K, Dudley J, Nei M, Kumar S: MEGA4: Molecular evolutionary genetics analysis (mega) software version 4.0. Mol Biol Evol. 2007, 24: 1596-1599. 10.1093/molbev/msm092.
Librado P, Rozas J: DnaSP v5: a software for comprehensive analysis of DNA polymorphism data. Bioinformatics. 2009, 25: 1451-1452. 10.1093/bioinformatics/btp187.
Escalante AA, Cornejo OE, Rojas A, Udhayakumar V, Lal AA: Assessing the effect of natural selection in malaria parasites. Trends Parasitol. 2004, 20: 388-395. 10.1016/j.pt.2004.06.002.
Pritchard JK, Stephens M, Donnelly P: Inference of population structure using multilocus genotype data. Genetics. 2000, 155: 945-959.
Jakobsson M, Rosenberg NA: CLUMPP: a cluster matching and permutation program for dealing with label switching and multimodality in analysis of population structure. Bioinformatics. 2007, 23: 1801-1806. 10.1093/bioinformatics/btm233.
Abacassamo F, Enosse S, Aponte JJ, Gomez-Olive FX, Quinto L, Mabunda S, Barreto A, Magnussen P, Ronn AM, Thompson R, Alonso PL: Efficacy of chloroquine, amodiaquine, sulphadoxine-pyrimethamine and combination therapy with artesunate in Mozambican children with non-complicated malaria. Trop Med Int Health. 2004, 9: 200-208. 10.1046/j.1365-3156.2003.01182.x.
Hudson RR: A new statistic for detecting genetic differentiation. Genetics. 2000, 155: 2011-2014.
Zakeri S, Abouie Mehrizi A, Djadid ND, Snounou G: Circumsporozoite protein gene diversity among temperate and tropical Plasmodium vivax isolates from Iran. Trop Med Int Health. 2006, 11: 729-737. 10.1111/j.1365-3156.2006.01613.x.
Seth RK, Bhat AA, Rao DN, Biswas S: Acquired immune response to defined Plasmodium viva antigens in individuals residing in northern India. Microbes Infect Institut Pasteur. 2010, 12: 199-206. 10.1016/j.micinf.2009.12.006.
Sinnis PCP, Fenyo D, Chait BT, Cerami C, Nussenzweig V: Structural and functional properties of region II-plus of the malaria circumsporozoite protein. J Exp Med. 1994, 180: 297-306. 10.1084/jem.180.1.297.
Gonzalez JM, Hurtado S, Arevalo-Herrera M, Herrera S: Variants of the Plasmodium vivax circumsporozoite protein (VK210 and VK247) in Colombian isolates. Mem Inst Oswaldo Cruz. 2001, 96: 709-712. 10.1590/S0074-02762001000500023.
Santos-Ciminera PD, Alecrim MG, Roberts DR, Quinnan GV: Molecular epidemiology of Plasmodium vivax in the State of Amazonas, Brazil. Acta Trop. 2007, 102: 38-46. 10.1016/j.actatropica.2007.02.013.
Chatterjee S, Wery M, Sharma P, Chauhan VS: A conserved peptide sequence of the Plasmodium falciparum circumsporozoite protein and antipeptide antibodies inhibit Plasmodium berghei sporozoite invasion of Hep-G2 cells and protect immunized mice against P. berghei sporozoite challenge. Infect Immun. 1995, 63: 4375-4381.
Tewari R, Spaccapelo R, Bistoni F, Holder AA, Crisanti A: Function of region I and II adhesive motifs of Plasmodium falciparum circumsporozoite protein in sporozoite motility and infectivity. J Biol Chem. 2002, 277: 47613-47618. 10.1074/jbc.M208453200.
Martinez P, Lopez C, Saravia C, Vanegas M, Patarroyo MA: Evaluation of the antigenicity of universal epitopes from PvDBPII in individuals exposed to Plasmodium vivax malaria. Microbes Infect. 2010, 12: 1188-1197. 10.1016/j.micinf.2010.08.007.
Takala SL, Coulibaly D, Thera MA, Batchelor AH, Cummings MP, Escalante AA, Ouattara A, Traoré K, Niangaly A, Djimdé AA, Doumbo OK, Plowe CV: Extreme polymorphism in a vaccine antigen and risk of clinical malaria: implications for vaccine development. Sci Transl Med. 2009, 1: 2ra5-10.1126/scitranslmed.3000257.
Hudson RR, Boos DD, Kaplan NL: A statistical test for detecting geographic subdivision. Mol Biol Evol. 1992, 9: 138-151.
Barry AE, Schultz L, Buckee CO, Reeder JC: Contrasting population structures of the genes encoding ten leading vaccine-candidate antigens of the human malaria parasite, Plasmodium falciparum. PLoS One. 2009, 4: e8497-10.1371/journal.pone.0008497.
Nobrega de Sousa T, Carvalho LH, Alves de Brito CF: Worldwide genetic variability of the Duffy binding protein: insights into Plasmodium vivax vaccine development. PLoS One. 2011, 6: e22944-10.1371/journal.pone.0022944.
Branch O, Casapia WM, Gamboa DV, Hernandez JN, Alava FF, Roncal N, Alvarez E, Perez EJ, Gotuzzo E: Clustered local transmission and asymptomatic Plasmodium falciparum and Plasmodium vivax malaria infections in a recently emerged, hypoendemic Peruvian Amazon community. Malar J. 2005, 4: 27-10.1186/1475-2875-4-27.
Acknowledgements
Several authors of this manuscript are employees of the US Government. This work was prepared as part of their duties. Title 17 U.S.C. § 105 provides that 'Copyright protection under this title is not available for any work of the United States Government.' Title 17 U.S.C. § 101 defines US Government work as a work prepared by a military service member or employee of the US Government as part of that person's official duties. The views expressed in this article are those of the authors only and do not necessarily reflect the official policy or position of the Department of the Navy, Department of Defense, nor the US Government. This research was supported in part by the grant R01GM80586 from the National Institute of Health to AE.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Competing interests
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Authors' contributions
SC conducted the molecular genetic studies, performed the genetic diversity experiments, analysed the data and wrote the first draft of the manuscript. LT performed part of the genetic diversity experiments. AE, CL, SD contributed to the write up and reviewed the final draft. DB designed the project, supervised and directed the research team and contributed to the writing and editing of the manuscript. All authors read and approved the final manuscript.
Authors’ original submitted files for images
Below are the links to the authors’ original submitted files for images.
Rights and permissions
Open Access This article is published under license to BioMed Central Ltd. This is an Open Access article is distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License ( https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/2.0 ), which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original work is properly cited.
About this article
Cite this article
Chenet, S.M., Tapia, L.L., Escalante, A.A. et al. Genetic diversity and population structure of genes encoding vaccine candidate antigens of Plasmodium vivax. Malar J 11, 68 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1186/1475-2875-11-68
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1186/1475-2875-11-68