Abstract
Background
Phytophthora infestans, causing late blight in potato, remains one of the most devastating pathogens in potato production and late blight resistance is a top priority in potato breeding. The introduction of multiple resistance (R) genes with different spectra from crossable species into potato varieties is required. Cisgenesis is a promising approach that introduces native genes from the crops own gene pool using GM technology, thereby retaining favourable characteristics of established varieties.
Results
We pursued a cisgenesis approach to introduce two broad spectrum potato late blight R genes, Rpi-sto1 and Rpi-vnt1.1 from the crossable species Solanum stoloniferum and Solanum venturii, respectively, into three different potato varieties. First, single R gene-containing transgenic plants were produced for all varieties to be used as references for the resistance levels and spectra to be expected in the respective genetic backgrounds. Next, a construct containing both cisgenic late blight R genes (Rpi-vnt1.1 and Rpi-sto1), but lacking the bacterial kanamycin resistance selection marker (NPTII) was transformed to the three selected potato varieties using Agrobacterium-mediated transformation. Gene transfer events were selected by PCR among regenerated shoots. Through further analyses involving morphological evaluations in the greenhouse, responsiveness to Avr genes and late blight resistance in detached leaf assays, the selection was narrowed down to eight independent events. These cisgenic events were selected because they showed broad spectrum late blight resistance due to the activity of both introduced R genes. The marker-free transformation was compared to kanamycin resistance assisted transformation in terms of T-DNA and vector backbone integration frequency. Also, differences in regeneration time and genotype dependency were evaluated.
Conclusions
We developed a marker-free transformation pipeline to select potato plants functionally expressing a stack of late blight R genes. Marker-free transformation is less genotype dependent and less prone to vector backbone integration as compared to marker-assisted transformation. Thereby, this study provides an important tool for the successful deployment of R genes in agriculture and contributes to the production of potentially durable late blight resistant potatoes.
Similar content being viewed by others
Background
Genetic disease resistance is an effective tool for sustainable management of late blight, caused by Phytophthora infestans, which is economically the most important disease of potato. Breeding at the beginning of the twentieth century concentrated on major dominant late blight resistance (R) genes from the Mexican wild species Solanum demissum and eleven of these R genes were introgressed in potato [1–4]. However, rapid breakdown of resistance in potato varieties containing S. demissum R1, R2, R3, and R10[3, 5] has sparked an increased focus on the introgression of multiple broad spectrum R genes in order to impart durability to commercial varieties. It has turned out in various crops and pathosystems that stacking of multiple R genes is necessary to provide satisfactory resistance in the field [6]. Although the used R genes provide resistance to broad spectra of late blight strains, the predominant agricultural deployment of only one R gene can drive the evolution of new virulent strains. In the absence of chemical controls this might even result in the destruction of an entire harvest [7]. Therefore, the use of combinations of R genes with different spectra must be pursued to increase durability of resistance and thereby providing food security under no or little fungicide application. R gene stacking might be achieved by genetic crossings but the desired variety characteristics will never be fully recovered due to the high level of heterozygosity in potato. Sarpo Mira is an example of a durably late blight resistant potato variety which contains a stack of at least four R genes [8, 9]. Unfortunately, the variety has not acquired a large market share yet because established varieties are preferred by farmers, processors and consumers.
Addition of stacks of cloned R genes [10–17] to existing varieties (resistant or susceptible) through genetic modification (GM) technology is therefore an attractive alternative. Moreover, GM technology circumvents the problem of linkage drag and can speed up the introgression of the R gene [18, 19]. GM technology has, however, met various types of opposition and a major point of criticism concerns the introduction of “foreign” genes into the food chain and environment. However, within the framework provided by cisgenesis only natural genes from the same or crossable species are used [20, 21]. Cisgenes are, therefore, already present in the natural gene pool of the crop plant and cisgenesis only facilitates their introduction into crops. Indeed a majority of a broad panel of European consumers find cisgenic apples safe and not harmfull for the environment [22].
Recently, the transformation of three broad spectrum potato late blight resistance genes (Rpi-sto1, Rpi-vnt1.1 and Rpi-blb3) was described in potato [23]. Rpi-sto1, Rpi-vnt1.1 and Rpi-blb3 are native genes from crossable species and are therefore considered as cisgenes for potato. However, the plants in the study from Zhu et al. [23] are “transgenic” as the selectable marker gene, NPTII, was of bacterial origin. Also beyond the cisgenesis framework it is not desired to introduce antibiotic resistance genes into the environment and in this study, we established a pipeline for Agrobacterium-mediated transformation of potato in the absence of a selectable marker gene (marker-free transformation). After the absence of vector backbone integration was confirmed, these potatoes were designated as “cisgenic” because of the absence of any foreign (non-potato) genes. This is the first scientific report on the production and functional evaluation of cisgenic R gene stacking in different potato varieties.
Results
Transformation and functional expression of single late blight Rgenes in potato varieties
The resistance spectra of three potato varieties (the American variety Atlantic, the Dutch variety Bintje and the Korean variety Potae9) were tested with five P. infestans isolates with variable virulence spectra and aggressiveness. Atlantic and Bintje were susceptible to all tested isolates while Potae9 was resistant to two isolates (EC1 and 90128; Table 1). These two isolates are a-virulent on plants carrying R2 type of resistance genes. The presence of R2 or a functional homolog in Potae9 was confirmed using AVR2 response experiments (data not shown). In order to make Atlantic and Bintje resistant to late blight and to broaden the resistance spectrum of Potae9, these three varieties were transformed with two constructs (pBINPLUS:Rpi-vnt1.1 and pBINPLUS:Rpi-sto1 harbouring the kanamycin resistance gene NPTII), each containing a single late blight R gene . The transgenic events were collected using selection for kanamycin resistance and, successively, the functional expression of the introduced R genes was tested using agroinfiltration of the cognate a-virulence (Avr) genes. Also the transgenic events were subjected to P. infestans inoculation using a detached leaf assay (DLA; Table 1). As an example, the interactions of a representative set of transgenic events with the selected isolates are shown in Figure 1. As expected, the majority of the transgenic events showed resistance to at least four of the five tested P. infestans isolates. EC1 and pic99189 were described previously to break the Rpi-vnt1.1 and Rpi-sto1 mediated resistances, respectively [13, 24]. Indeed, transgenic Atlantic and Bintje events harbouring the Rpi-vnt1.1 gene were susceptible to isolate EC1. The Potae9 transgenic events containing Rpi-vnt1.1 were resistant to EC1, due to the presence of R2 or a functional homolog in Potae9. The Rpi-sto1-containing events were susceptible to isolate pic99189. It is concluded that both Rpi-vnt1.1 and Rpi-sto1 were able to confer resistance in the selected varieties and these two genes may, therefore, be combined as a cisgenic R gene stack in the selected varieties.
Detached leaf assays of transgenic potatoes obtained by marker-assisted transformation with single R gene constructs. Non transformed Atlantic or Bintje were susceptible to four P. infestans isolates. Rpi-vnt1.1-containing transgenic plants were susceptible to EC1 and Rpi-sto1-containing transgenic plants were susceptible to pic99189.
Selection and validation of cisgenic potato plants with two late blight Rgenes
Cisgenesis excludes antibiotic resistance marker-assisted transformation since the genes encoding the selection markers are derived from non-crossable species. We, therefore, pursued marker-free transformation of the cisgenes Rpi-vnt1.1 and Rpi-sto1 in combination with PCR selection (Table 2). Two hundred stem explants from each of the three selected varieties were prepared and co-cultivated with an A. tumefaciens strain carrying only the cisgenic late blight R genes Rpi-vnt1.1 and Rpi-sto1 between the T-DNA borders of a binary plasmid (Figure 2). Between 31 and -110 days after transformation, over 1515 shoots were collected in five rounds of harvesting (Table 3). During the experiment, the shoot regeneration potential of the callus gradually dropped and at 130 days after transformation no more shoots could be harvested. These 1515 shoots were screened by PCR with Rpi-vnt1 and Rpi-sto1 primers and 27 PCR positive shoots were selected (Table 2). All PCR positive shoots were originating from different explants, indicating that they were independent transformation events. Two Bintje events only contained the Rpi-vnt1 gene and were discarded. The remaining 25 events, containing both Rpi-vnt1 and Rpi-sto1, were further tested using vector backbone gene-specific PCR analysis (Figure 3). We found that six events contained vector backbone sequences (Table 2). The remaining 19 events were vector backbone free and are therefore designated as cisgenic events. The 19 cisgenic events were transferred to the greenhouse for phenotypic characterisation. Three weeks after transfer to the greenhouse, five events displayed abnormal plant morphology that consisted of curly leaves and dwarfed growth (Additional file 1), a phenomenon that is commonly observed after regeneration [25]. The five events with these aberrant phenotypes were disregarded for further studies and the remaining 14 events were tested for their responsiveness to Avrvnt1 and Avrsto1 after agroinfiltration. Five events responded only to Avrvnt1 and not to Avrsto1. Eight events responded to both Avrvnt1 and Avrsto1 infiltration, showing that both Rpi-vnt1 and Rpi-sto1 were functionally expressed (Table 4). The latter eight plants also displayed resistance in DLA to all P. infestans isolates tested. Figure 4 shows an example of the validation of functional expression for both transferred R genes in event H43-7 (Atlantic background) by agroinfiltration and resistance assays in the DLA. Using the single gene-containing transgenic plants as reference it was demonstrated that stacking of R genes with different resistance spectra leads to complementary broad spectrum resistance (Table 1). Interestingly, the two introduced R genes are complementing the resistance spectrum that was already present in Potae9 plants. Using the pursued experimental setup we were able to select two cisgenic events in Atlantic, five cisgenic events in Bintje and one cisgenic event in Potae9 containing and functionally expressing a stack of two late blight R genes.
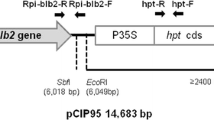
Schematic diagram of the marker-free double gene construct pBINAW2: Rpi-vnt1.1:Rpi-sto1 . In light green and light blue arrows the Rpi-vnt1.1 and Rpi-sto1 genes are shown, respectively. The red arrows indicate the coding regions of Rpi-vnt1.1 or Rpi-sto1. Unique restriction enzyme recognition sites XmaI, SbfI and AscI are shown. RB: right border of T-DNA, LB: left border of T-DNA, TetA, trfA, NPTIII, ColE1, oriV and traJ are vector backbone sequences for plasmid stability and replication in bacterial hosts Agrobacterium tumefaciens and Escherichia coli.
Vector backbone integration in marker-free transformation events. Atlantic (H), Bintje (F) and Potae9 (W), were transformed with construct pBINAW2: Rpi-vnt1.1:Rpi-sto1. PCR analysis was performed using primers specific for tetA, trfA, NPTIII, ColE1, oriV and traJ to detect vector backbone integration. The plasmid pBINAW2:Rpi-vnt1.1:Rpi-sto1 was used as a positive control and the untransformed Atlantic as a negative control. Only the NPTIII primers amplified an a-specific fragment of similar size as shown here for the backbone free events W43-1 and W43-5 in untransformed Potae9. None of the other primers amplified an a-specific band in Potae9 or Bintje (data not shown) M: molecular weight marker.
Functional validation of cisgenic transformants by agroinfiltration and resistance assays. A. Avrvnt1- and Avrsto1-induced hypersensitive responses in cisgenic transformant H43-7 (Rpi-vnt1:Rpi-sto1 in Atlantic background). Avrvnt1 and Avrsto1 were infiltrated in cisgenic plants. A 1:1 mixture of R3a and Avr3a and pK7WG2 were infiltrated as positive and negative controls, respectively. B. Detached leaf assays for cisgenic transformant H43-7. Different isolates are shown in the middle. Cisgenic transformant are shown on the top and the wild type Atlantic on the bottom of the panel.
Comparison of marker-assisted- and marker-free transformation efficiencies
Kanamycin resistance assisted selection is routinely used for plant transformation. It is, therefore, interesting to compare the efficiency of marker-free transformation in the cisgenesis pipeline to marker-assisted transformation. Marker-assisted transformation efficiency was 100% when expressed as the percentage of rooting shoots being PCR positive for the gene of interest (Table 5). In this definition, marker-free transformation efficiency ranged from 1 to 2.4% over the three varieties.
For a better comparison of marker-assisted and marker-free transformation, it was essential to use a different definition for transformation efficiency that also takes shoot regeneration efficiency into account. We define marker-assisted transformation frequency as the percentage of PCR positive events among the number of explants used for transformation. Marker-free transformation frequency is defined as the percentage of shoots that is PCR positive. In variety Atlantic a high marker-assisted transformation frequency (71%) was observed whereas the other two varieties, Bintje and Potae9, had significantly lower marker-assisted transformation frequencies (10-13%) (Tables 5 and 6). In marker-free transformation, variety dependent differences in transformation frequencies were less dramatic (2.4, 1.0 and 1.6% in Atlantic, Bintje and Potae-9, respectively) and statistically insignificant (Table 6). Not only the frequency of transformation, also the timing of transformation was different between marker-free and marker-assisted transformation. In the marker-free transformation experiments, the majority of the PCR-positive shoots was obtained between 1 and 3 months after co-cultivation (Table 3). This was quicker than marker-assisted transformation of the Rpi-vnt1 and Rpi-sto1 genes individually, which took 2-4 months (Table 5). Finally, we compared vector backbone integration frequencies among the different marker-free and marker-assisted transformation experiments. We did not find significant differences in vector backbone integrations frequency when the different varieties or both of the marker-assisted transformation constructs were compared (Table 7). Only when vector backbone integration frequency was compared between the marker-free (24%; Table 2) and marker-assisted transformation experiments (57%; Table 5) we found that marker-free transformation was associated with less vector backbone integration.
Discussion
Cisgenesis, is a new approach for traditional plant breeding that uses genetic modification technology to introduce natural genes from within a plant species or from crossable plant species, into varieties [26]. Therefore, any gene “alien” to the breeder’s gene pool can be avoided in the end product which is causal to many environmental and consumers’ concerns about GM food crops [22]. Not only can widely used susceptible varieties, like Bintje and Atlantic, be converted into resistant varieties, also resistant varieties, like Potae9, can be complemented with additional resistance genes to avoid or delay future resistance breakdown. In order to complement existing varieties with stacks of cisgenic R genes, two choices must be made: 1. The method to introduce the R gene stack and 2. The method to exclude sequences of foreign origin from transformation events. With respect to the introduction method, in this study we chose transformation by marker-free binary vectors and subsequent regeneration in medium without selective antibiotics followed by PCR-based selection of transformation events [27]. Alternatives involving the removal of a selectable marker gene by site specific recombination pose disadvantages because of remnant sequences of foreign origin [28].
The average marker-free transformation frequency was 1.3% and seems to be genotype independent. In a previous marker-free transformation study in potato [27] a T-DNA of 6 kb was transformed with a frequency of 3.5% when A. tumefaciens strain AGL0 was used, and 0.4% when A. tumefaciens strain LB4404 was used. It can not be concluded that AGL1 + virG, which was used in this study, was less efficient in transferring the T-DNA than AGL0 in the study from de Vetten et al. [27]. From unpublished experiments in our laboratory it is known that regeneration time increases with the size of the T-DNA. We, therefore, assume that the lower transformation frequency in our study is rather related to the larger T-DNA size (11 kb) of the Rpi-vnt1:Rpi-sto1 construct. Therefore, for stacking of more than two genes in cisgenic transformation, the effect of an increased insert size (e.g. >11 kb) on transformation frequency remains to be tested. It is known that marker-assisted transformation frequency is highly genotype dependent in potato [29]. Also here we found that transformation frequencies ranged from 10-71% in different varieties (Table 5). This variation was remarkably less (1-2.4%) in marker-free transformation experiments (Table 2). It must be noted that transformation frequencies can vary between different experiments and that we here only performed a limited number of experiments. However, the currently presented experiments show that marker-free transformation is less prone to varietal differences than marker assisted transformation. This could be caused by differences in antibiotic tolerance between the varieties that provides transformed cells different abilities to develop into a shoot.
In terms of vector backbone integration, marker-free transformation apparently produces a lower percentage (24%) of vector backbone integrations compared to marker-assisted transformation (40-50%). Again, the number of experiments is limited and firm conclusions cannot be drawn. The vector backbone and border sequences in pBINPLUS and pBINAW2 are highly similar and we do not expect that these differences affect vector backbone integration. A potential explanation could be that the presence of the NPTII gene directly next to the left border of the T-DNA would stimulate selection of higher levels of backbone integration. As it is known that left border recognition is inaccurate in Solanaceae, [30], especially when agrobacterium strain AGL1 is used [31], positioning of NPTII near the left border would force the integration of the complete T-DNA. So, it might also lead to higher levels of vector backbone integration. In marker-free transformation, six plants out of 14 tested cisgenic plants did not appropriately express Rpi-sto1 as observed using agroinfiltration of the corresponding Avr genes (like H43-1, -10, -12; Table 4). An obvious explanation could be that T-DNA insertion did not proceed all the way to the left border resulting in 3′ truncations of Rpi-sto1. These non-functional cisgenic events and the corresponding DNA samples were discarded in an early phase during the selection and, unfortunately, this hypothesis could not be confirmed. We observed and described some cisgenic plants differing morphologically from wild type varieties in the greenhouse (Table 4, Additional file 1). This is a generally observed phenomenon and in tissue culture-based breeding schemes it should be considered that aberrant plant phenotypes must be selected against [29].
According to the established experimental scheme, it takes less than one year to obtain potato plants with cisgenic R gene stacks from the R gene construct preparation to the functional validation of the resulting cisgenic plants by performing DLAs. As 2-3 shoots per explant can be collected and 30 independent transformed plants are required considering backbone integration and expression, it is recommended that between 1000-1500 explants are to be treated in a marker-free-transformation experiment of potato. The efficiency of PCR analysis can be improved by a factor 10 by pooling ten shoots, so that the labour intensity of the selection of marker-free transformation events is considered reasonable as compared to the marker-assisted transformations. Considering 2-3 years’ field trials, it takes totally 3-4 years to produce late blight resistant cisgenic events in established potato varieties, which can be released for seed tuber multiplication. This time span is remarkably short compared to the conventional breeding scheme. The cisgenic potatoes selected in this study will be further tested for several years to evaluate whether the transferred R genes are stably expressed over many vegetative cycles. Chimeras and epigenetic silencing are issues that could affect stability of resistance. Also agronomic performance needs to be assessed and confirmed in multiple growing seasons.
Conclusions
We have set up and pursued an effective cisgenic marker-free transformation strategy for commercial potato varieties. It was found that marker-free transformation frequency was much less genotype dependent than marker-assisted transformation. Also the frequency of vector backbone integration tended to be lower in the marker-free transformations as compared to the marker-assisted transformations. The susceptibility or the narrow late blight resistance spectra of the selected varieties were upgraded to broad spectrum resistance after the successful introduction of two cisgenic late blight R genes. According to the recent conclusion of the European Food Safety Authority GMO Panel, cisgenic plants have a risk level similar to conventionally bred plants [32]. The cisgenic potatoes, generated in this study, will offer a safe, environmentally friendly, alternative to the current agricultural practice which is highly dependent on the use of chemical late blight control agents. For developing countries, where chemical control agents are unaffordable, cisgenic upgrades of local potato varieties might even ensure food security.
Methods
Plant material
The potato varieties Atlantic, Desiree, Bintje, and Potae9 were clonally maintained in vitro using Murashige and Skoog medium [33] supplemented with 3% (w/v) sucrose at 20°C at Wageningen UR Plant Breeding, Wageningen, The Netherlands. The varieties Potae9 from DPR Korea, which is resistant to late blight, was used for testing its reaction to certain late blight isolates and for transformation experiments to broaden its resistance spectrum.
Phytophthora infestansisolates and late blight resistance tests
Five P. infestans isolates (Additional file 2) were used in Detached Leaf Assays (DLAs); The European isolates IPO-C (race 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 10, 11) and 90128 (race 1, 3, 4, 7, 8, 10, 11); the American isolates, EC1 (race 1, 3, 4, 7, 10, 11) and pic99189 (race 1, 2, 5, 7, 10, 11) and the Korean isolate DHD11 (race 1, 2, 3, 4, 6, 7, 10, 11). The DLAs were performed as described previously [34].
Vector construction
The single R gene constructs used in our study have been described before. Genomic DNA fragments from S. venturii, and S. stoloniferum, encompassing the Rpi-vnt1.1 and Rpi-sto1 genes, respectively, are cloned in the pBINPLUS binary vector [13, 16]. The genomic fragments comprise the entire genes including their native promoters and terminators. In order to combine Rpi-sto1 and Rpi-vnt1.1 into one markerfree transformation vector, first the AscI and SbfI fragment from the pBINPLUS:Rpi-sto1 vector, encompassing the Rpi-sto1 gene, was ligated into the corresponding restriction sites of pBINAW2 [35]. pBINAW2 is a modified version of pBINPLUS where the entire T-DNA, including the NPTII gene, and the adjacent TetR gene from the vector backbone was removed and replaced by a minimal T-DNA containing only left and right border and a small multiple cloning site. To the pBINAW2:Rpi-sto1 construct, the Rpi-vnt1.1 gene was added using a SbfI fragment, encompassing the Rpi-vnt1.1 gene from the pBINPLUS:Rpi-blb3:Rpi-vnt1.1:Rpi-sto1 described by Zhu et al. [23]. The clone with the desired Rpi-vnt1.1 insert orientation, in tandem with Rpi-sto1 (pBINAW2:Rpi-vnt1.1:Rpi-sto1, Figure 2; Additional file 3) was selected using restriction analysis. All ligation mixtures was transformed to ElectroMAX E.coli DH10b competent cells (Life technologies). Subsequently, the stability of the R gene constructs in Agrobacterium strain AGL-1 + VirG and functionality of the R genes in N. benthamiana were carried out using PCR and co-agroinfiltration with corresponding Avr genes, respectively. These tests confirmed the stability and activity of the constructs.
Potato transformation
Marker assisted transformation performed as described previously [36]. Marker-free transformations are derived from this protocol but kanamycin was omitted as a selection agent. Briefly, internodes of 2-5 mm in length were cut from thick stems of 4-week-old in vitro-grown plants and were used as explants in transformation experiments. After pre-culture on R3B medium (MS + 3% sucrose + 0.8% agar + 4 mg/ml NAA + 1 mg/ml BAP, pH5.8) supplemented with PACM (MS + 3% sucrose + 0.2% casein hydrolysate + 1 mg/ml 2,4-D + 1 mg/ml kinetin, pH6.5) for two days, explants were inoculated with Agrobacterium strain AGL1 + VirG + binary plasmid resuspended in LB medium to an OD600 of 0.2. After 2 days cocultivation, the explants were transferred to ZCVK medium (MS + 2% sucrose + 0.8% agar + 1 mg/ml zeatin + 200 mg/ml cefotaxim + 200 mg/ml vancomycin, pH5.8) for regeneration of shoots. Explants were transferred to fresh medium every two weeks. Shoots were transferred to CK medium (MS + 2% sucrose + 0.8% agar + 200 mg/ml cefotaxim + 200 mg/ml vancomycin, pH5.8) to induce root formation. To guarantee that regenerated plants were derived from independent transformation events, only shoots from physically separated positions on each explant were collected. Three weeks later, the rooted plantlets were analysed by PCR to determine the presence of the desired R genes. The transformation frequency was calculated as a percentage of the number of R gene-PCR positive shoots over the number of tested shoots.
For marker-assisted transformation, 100 mg/ml Kanamycin was added to ZCVK medium and CK medium for selection of transgenic shoots.
Functional tests of resistance (R) genes
Agroinfiltration was performed as previously described [37]. Two leaves per plant from three copies of each of the transformants were infiltrated with the following constructs: two effectors (Avrvnt1 and IpiO = Avrsto1) [13, 24], R3a[38] and Avr3a[39] as the positive control and empty pK7WG2 [40] as the negative control. Agrobacterium tumefaciens strain from glycerol stocks was grown in 3 ml of LB medium supplemented with appropriate antibiotics at 28°C overnight. The next day, the cultures were transferred to 15 ml of YEB medium (5 g beef extract, 5 g bacteriological peptone, 5 g sucrose, 1 g yeast extract, 2 ml 1 M MgSO4 in 1 litre of milli-Q water) supplemented with antibiotics, 10 μl of 200 mM acetosyringone and 1000 μl of 1 M MES. On the third day, the cells were harvested and resuspended in MMA solution (20 g sucrose, 5 g MS salts and 1.95 g MES in 1 litre of distilled water, adjusted to pH5.6) supplemented with 1 ml of 200 mM acetosyringone to a final OD600 of 0.3. Leaves of 4- to 5-weeks old, greenhouse-grown, plants were infiltrated with this suspension. Responses were scored 3 to 4 days after infiltration.
DNA extraction and polymerase chain reaction (PCR)
Total genomic DNA was isolated from young leaves as described by Fulton et al. [41]. The Retsch machine (RETSCH Inc., Hannover, Germany) was used to grind young plant materials frozen in liquid nitrogen. Primers used for analysis of R genes, vector backbone integration are listed in Additional file 4. A pooled sampling method was exploited for PCR analysis of shoots in marker-free transformation. DNA extraction was carried out first by pooling one small leaf from each of ten shoots. If in this first round pools were found which were PCR-positive for both R genes and PCR-negative for backbone integration, a second round of PCR was carried out on genomic DNA of individual shoots within the pools. PCR reactions for Rpi-sto1, Rpi-vnt1.1, NPTIII, trfA, ColE1, oriV and traJ were performed using DreamTaqTM polymerase (Fermentas) in a standard PCR program (94°C for 60 s followed by 30 cycles of 94°C for 30 s, 58°C for 60 s, 72°C for 90 s and a final extension time of 5 min at 72°C).
Statistical analysis
Transformation and vector backbone integrations frequencies are binary data and, therefore, the Pearson Chi-square test was chosen to compare the independent samplings of transformation events in the different transformation experiments. Calculations were performed using the IBM SPSS Statistics 22 software pack. Groupwise comparisons with one degree of freedom were applied.
References
Muller KO, Black W: Potato breeding for resistance to blight and virus diseases during the last hundred years. Z Pflanzenzuchtg. 1951, 31: 305-318.
Malcolmson JF, Black W: New R genes in Solanum demissum Lindl. and their complementary races of Phytophthora infestans (Mont.) de Bary. Euphytica. 1966, 15: 199-203.
Malcolmson JF: Races of Phytophthora infestans occurring in Great Britain. Trans Br Mycol Soc. 1969, 53: 417-423.
Bradshaw JE, Bryan GJ, Lees AK, McLean K, Solomon-Blackburn RM: Mapping the R10 and R11 genes for resistance to late blight (Phytophthora infestans) present in the potato (Solanum tuberosum) R gene differentials of Black. Theor Appl Genet. 2006, 112: 744-751.
Wastie RL: Breeding for resistance. Adv Plant Pathol. 1991, 7: 193-224.
Que Q, Chilton MDM, Fontes CM D, He C, Nuccio M, Zhu T, Wu Y, Chen JS, Shi L: Trait stacking in transgenic crops: the challenges and opportunities. GM Crops. 2010, 1: 220-229.
Strange RN, Scott PR: PLANT DISEASE: a threat to global food security. Annu Rev Phytopathol. 2005, 43: 83-116.
Tomczynska I, Stefanczyk E, Chmielarz M, Karasiewicz B, Kaminski P, Jones JD, Lees AK, Sliwka J: A locus conferring effective late blight resistance in potato cultivar Sarpo Mira maps to chromosome XI. Theor Appl Genet. 2014, 127 (3): 647-657.
Rietman H, Bijsterbosch G, Cano LM, Lee HR, Vossen JH, Jacobsen E, Visser RGF, Kamoun S, Vleeshouwers VGAA: Qualitative and quantitative late blight resistance in the potato cultivar Sarpo Mira is determined by the perception of five distinct RXLR effectors. Mol Plant Microbe Interact. 2012, 25 (7): 910-919.
Song J, Bradeen JM, Naess SK, Raasch JA, Wielgus SW, Haberlach GT, Liu J, Kuang H, Austin-Phillips S, Buell CR, Helgeson JP, Jiang J: Gene RB cloned from Solanum bulbocastanum confers broad spectrum resistance to potato late blight. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2003, 100: 9128-9133.
van der Vossen EAG, Sikkema A, te Lintel HB, Gros J, Stevens P, Muskens M, Wouters D, Pereira A, Stiekema WJ, Allefs S: An ancient R gene from the wild potato species Solanum bulbocastanum confers broad-spectrum resistance to Phytophthora infestans in cultivated potato and tomato. Plant J. 2003, 36: 867-882.
van der Vossen EAG, Gros JE, Sikkema A, Muskens M, Wouters D, Wolters P, Pereira A, Allefs S: The Rpi-blb2 gene from Solanum bulbocastanum is an Mi-1 gene homolog conferring broad-spectrum late blight resistance in potato. Plant J. 2005, 44: 208-222.
Vleeshouwers VGAA, Rietman H, Krenek P, Champouret N, Young C, Oh SK, Wang M, Bouwmeester K, Vosman B, Visser RGF, Jacobsen E, Govers F, Kamoun S, van der Vossen EAG: Effector genomics accelerates discovery and functional profiling of potato disease resistance and Phytophthora infestans avirulence genes. PLoS ONE. 2008, 3: e2875-
Lokossou AA, Park TH, Van Arkel G, Arens M, Ruyter-Spira C, Morales J, Whisson SC, Birch PRJ, Visser RGF, Jacobsen E, van der Vossen EAG: Exploiting knowledge of R/Avr genes to rapidly clone a new LZ-NBS-LRR family of late blight resistance genes from potato linkage group IV. Mol Plant Microbe Interact. 2009, 22: 630-641.
Vossen JH, Nijenhuis M, Arens de Reuver MJB, Van der Vossen EAG, Jacobsen E, Visser RGF: Cloning and exploitation of a functional R gene from Solanum chacoense. Patent application, published by: IPO: PCT/NL2010/050612
Pel MA, Foster SJ, Park TH, Rietman H, Van Arkel G, Jones JDG, Eck HJ V, Jacobsen E, Visser RGF, Vossen EAG Van D: Mapping and cloning of late blight resistance genes from Solanum venturii using an interspecific candidate gene approach. Mol Plant Microbe Interact. 2009, 22: 601-615.
Foster SJ, Park TH, Pel MA, Brigneti G, Sliwka J, Jagger L, van der Vossen EAG, Jones JDG: Rpi-vnt1.1, a Tm-2 homolog from Solanum venturii, confers resistance to potato late blight. Mol Plant Microbe Interact. 2009, 22: 589-600.
Mullins E, Milbourne D, Petti C, Doyle-Prestwich BM, Meade C: Potato in the age of biotechnology. Trends Plant Sci. 2006, 11 (5): 254-260.
Barrell PJ, Meiyalaghan S, Jacobs JM, Conner AJ: Applications of biotechnology and genomics in potato improvement. Plant Biotechnol J. 2013, 11 (8): 907-920.
Jacobsen E, Schouten HJ: Cisgenesis strongly improves introgression breeding and induced translocation breeding of plants. Trends Biotechnol. 2007, 25: 219-223.
Jacobsen E: Cisgenesis: a modern way of domesticating traits of the breeders’ gene pool. CAB Reviews. 2013, 8: 56-
Eurobarometer: Europeans and Biotechnology in 2010; Winds of change?. http://ec.europa.eu/research/science-society/document_library/pdf_06/europeans-biotechnology-in-2010_en.pdf accessed March 13, 2014
Zhu SX, Li Y, Vossen JH, Visser RGF, Jacobsen E: Functional stacking of three resistance genes against Phytophthora infestans in potato. Transgenic Res. 2012, 21: 89-99.
Pel MA: Mapping, isolation and characterization of genes responsible for late blight resistance in potato. PhD thesis. 2010, Wageningen University
Wheeler VA, Evans NE, Foulger D, Webb KJ, Karp A, Franklin J, Bright SWJ: Shoot formation from explant cultures of fourteen potato cultivars and studies of the cytology and morphology of regenerated plants. Ann Bot. 1985, 55 (3): 309-320.
Jacobsen E, Schouten HJ: Cisgenesis, a new tool for traditional plant breeding, should be exempted from the regulation on genetically modified organisms in a step by step approach. Potato Res. 2008, 51: 75-88.
de Vetten NCM, Wolters AMA, Raemakers K, van der Meer I, ter Stege R, Heeres E, Heeres P, Visser RGF: A transformation method for obtaining marker-free plants of a cross-pollinating and vegetatively propagated crop. Nat Biotechnol. 2003, 21: 439-442.
Joshi SG: Towards durable resistance to apple scab using cisgenes. PhD thesis. 2010, Wageningen University
Heeres P, Schippers-Rozenboom M, Jacobsen E, Visser RGF: Transformation of a large number of potato varieties: genotype-dependent variation in efficiency and somaclonal variability. Euphytica. 2002, 124: 13-22.
Thomas CM, Jones JDG: Molecular analysis of Agrobacterium T-DNA integration in tomato reveals a role for left border sequence homology in most integration events. Mol Genet Genomics. 2007, 278 (4): 411-420.
Petti C, Wendt T, Meade C, Mullins E: Evidence of genotype dependency within Agrobacterium tumefaciens in relation to the integration of vector backbone sequence in transgenic Phytophthora infestans-tolerant potato. J Biosci Bioeng. 2009, 107 (3): 301-306.
EFSA: Scientific opinion addressing the safety assessment of plants developed through cisgenesis and intragenesis. EFSA J. 2012, 10: 2561-
Murashige T, Skoog F: A revised medium for rapid growth and bioassays with tobacco tissue cultures. Physiol Plant. 1962, 15: 473-497.
Vleeshouwers VGAA, Van DW, Keizer LC P, Sijpkes L, Govers F, Colon LT: A laboratory assay for Phytophthora infestans resistance in various Solanum species reflects the field situation. Eur J Plant Pathol. 1999, 105: 241-250.
de Vetten NCM, Visser RGF, Jacobsen E, van der Vossen EAG, Wolters AMA: Use of R-genes as a selection marker in plant transformation and use of cisgenes in plant transformation. patent application, published by: IPO: WO 2008091154 A1
Visser RGF: Regeneration and transformation of potato by Agrobacterium tumefaciens. Plant Tissue Culture Manual. Edited by: Lindsey K. 1991, Dordrecht, Boston, London: Kluwer Academic Publishers, 1-9.
Vleeshouwers VGAA, Rietman H: In planta expression systems. Oomycete Genetics and Genomics. Edited by: Lamour KH, Kamoun S. 2009, Hoboken, New Jersey: John Wiley & Sons, 455-475.
Huang S, van der Vossen EAG, Kuang H, Vleeshouwers VGAA, Zhang N, Borm TJA, van Eck HJ, Baker B, Jacobsen E, Visser RGF: Comparative genomics enabled the isolation of the R3a late blight resistance gene in potato. Plant J. 2005, 42: 251-261.
Armstrong MR, Whisson SC, Pritchard L, Bos JIB, Venter E, Avrova AO, Rehmany AP, Bohme U, Brooks K, Cherevach I, Hamlin N, White B, Fraser A, Lord A, Quail MA, Churcher C, Hall N, Berriman M, Huang S, Kamoun S, Beynon JL, Birch PRJ: An ancestral oomycete locus contains late blight avirulence gene Avr3a, encoding a protein that is recognized in the host cytoplasm. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 2005, 102: 7766-7777.
Karimi M, Inze D, Depicker A: GATEWAY(TM) vectors for Agrobacterium- mediated plant transformation. Trends Plant Sci. 2002, 7: 193-195.
Fulton T, Chunwongse J, Tanksley S: Microprep protocol for extraction of DNA from tomato and other herbaceous plants. Plant Mol Biol Rep. 1995, 13: 207-209.
Acknowledgements
pBINAW2 was kindly provided by Dr Annemarie Wolters, Wageningen UR plant Breeding. KRJ, TYK, CJK, SJK and MJ were financially supported by the European Commission (EuropeAid project DCI-FOOD/2009/218-671), and the Dutch Ministry of Agriculture, Nature and Fisheries (International Cooperation project BO-10-010-112 and BO-10-001-200). JHV was supported by the DuRPh program, financed by the Dutch Ministry of Economic affairs, formerly the Ministery of Agriculture, Nature and Fisheries.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Competing interests
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Authors’ contributions
JKR wrote the manuscript and was involved in the experimental guidance of KCJ, KTY and MJ established the collaboration between the P-Y and the Wageningen institutes. KTY designed and cloned the marker-free transformation construct. MJ designed the integrated pest management strategy as pursued in the “EuropeAid” and “International Cooperation” projects and he, thereby, provided the scientific blueprint for this study. KCJ, MB and KSJ performed the transformations, PCRs, and late blight resistance assays. RV was involved in manuscript writing. EJ and JV provided the experimental design and supervised the manuscript writing. All authors read and approved the final manuscript.
Electronic supplementary material
Authors’ original submitted files for images
Below are the links to the authors’ original submitted files for images.
Rights and permissions
This article is published under an open access license. Please check the 'Copyright Information' section either on this page or in the PDF for details of this license and what re-use is permitted. If your intended use exceeds what is permitted by the license or if you are unable to locate the licence and re-use information, please contact the Rights and Permissions team.
About this article
Cite this article
Jo, KR., Kim, CJ., Kim, SJ. et al. Development of late blight resistant potatoes by cisgene stacking. BMC Biotechnol 14, 50 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1186/1472-6750-14-50
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1186/1472-6750-14-50