Abstract
Background
The genus Saccharothrix is a representative of the family Pseudonocardiaceae, known to include producer strains of a wide variety of potent antibiotics. Saccharothrix espanaensis produces both saccharomicins A and B of the promising new class of heptadecaglycoside antibiotics, active against both bacteria and yeast.
Results
To better assess its capabilities, the complete genome sequence of S. espanaensis was established. With a size of 9,360,653 bp, coding for 8,501 genes, it stands alongside other Pseudonocardiaceae with large genomes. Besides a predicted core genome of 810 genes shared in the family, S. espanaensis has a large number of accessory genes: 2,967 singletons when compared to the family, of which 1,292 have no clear orthologs in the RefSeq database. The genome analysis revealed the presence of 26 biosynthetic gene clusters potentially encoding secondary metabolites. Among them, the cluster coding for the saccharomicins could be identified.
Conclusion
S. espanaensis is the first completely sequenced species of the genus Saccharothrix. The genome discloses the cluster responsible for the biosynthesis of the saccharomicins, the largest oligosaccharide antibiotic currently identified. Moreover, the genome revealed 25 additional putative secondary metabolite gene clusters further suggesting the strain’s potential for natural product synthesis.
Similar content being viewed by others
Background
The discovery of new antibiotics is an essential strategy to effectively combat multidrug-resistant pathogens. Two thirds of all natural products with antibiotic activity are derived from bacteria of the order Actinomycetales[1]. However, their potential to produce new antibiotics is not exhausted [2]. Saccharothrix is a genus of this order which harbors strains producing natural products of industrial interests [3]. Furthermore, Saccharothrix is known for its ability to glycosylate natural products hereby increasing their biological activity [4].
Saccharothrix espanaensis is the producer of the saccharomicins, a new class of heptadecaglycoside antibiotics [5, 6] with activity against MRSA and VRE [7]. In this paper we present the classification and analysis of the genome of this capable antibiotic producer.
Results and discussion
Sequencing and general features of the Saccharothrix espanaensis DSM 44229 chromosome
The genome sequence of S. espanaensis was established using a whole genome shotgun approach applying next generation sequencing techniques. The initial scaffolding was performed by 454 sequencing using a 3 k paired-end library, resulting in 352 contigs in five scaffolds. In order to obtain a single scaffold, a fosmid library of 528 clones was sequenced from the ends and the sequences were mapped onto the scaffolds. This resulted in a single scaffold and delivered templates for primer walking for 283 of the 352 remaining gaps.
After fosmid and PCR-based gap closure, the chromosome was obtained as a single circular contig with a size of 9,360,653 bp. Like all completely sequenced and analyzed genomes of the Pseudonocardiaceae to date [8–13], the genome of S. espanaensis is circular with no extrachromosomal replicons, such as plasmids or chromids, detected. In total, 8,427 protein coding regions (CDS) were predicted (Table 1). The genome size and number of genes fit with the lifestyle of S. espanaensis. In contrast, the genomes of Saccharomonospora viridis and Thermobispora bispora, which both live under elevated temperatures in nutrient rich environments [14, 15], are rather small (around 4.2 Mbp). The genomes of the Pseudonocardiaceae living at moderate temperatures in soil (Actinosynnema mirum, Amycolatopsis mediterranei, Pseudonocardia dioxanivorans, and Saccharopolyspora erythraea) tend to be much larger.
For 4,297 (51.0%) of the annotated CDS, a function could be automatically inferred using a number of sequence similarity based approaches implemented in the GenDB auto-annotator METANOR [16].
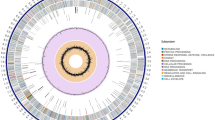
Based on the location of the CDS, no bias for the distribution of the genes on the leading or the lagging strand could be observed (Figure 1, outermost two circles). This coincides with no noticeable G + C skew (Figure 1, innermost circle), in contrast to the other completely sequenced Pseudonocardiaceae. The reason why a G + C skew is observed in some genomes while absent in others is not currently understood. The lack of a gene distribution bias and the lack of a significant G + C skew might indeed be linked. This is suggested as the other sequenced Pseudonocardiaceae display at least some gene distribution bias and G + C skew is thought to be due in part to a mutational bias in synonymous codons resulting in a C avoidance [17, 18]. One may reasonably propose that a strong gene distribution bias might effect a faster growth rate [19]. However, as the growth rates for the completely sequenced Pseudonocardiaceae are not available, this remains pure speculation.
Schematic representation of the S. espanaensis genome. The genome scale is given in kilobases from the start of dnaA. The two outermost circles show all genes on the forward and the reverse strand, respectively, color-coded according to their predicted COG classes. The next five circles represent the genes S. espanaensis color-coded according to their conservation in the genomes of the other completely sequenced Pseudonocardiaceae. Green denotes genes present in the core genome, red those conserved at least in the two compared species and light blue indicates singletons. The comparison with S. espanaensis was done (from the outside in) with A. mirum, A. mediterranei, S. erythraea, S. viridis and T. bispora. The last two circles represent G + C content and G + C skew ((G-C)/(G + C)), both calculated for a 500 bp window with 100 bp stepping.
As a first, rough classification, the amino acid sequence of all predicted CDS were compared against the eggNOG database (evolutionary genealogy of genes: Non-supervised Orthologous Groups [20]; Table 2), and the results were compared to those obtained for the other completely sequenced Pseudonocardiaceae (Additional file 1). This comparison revealed that the genome of S. espanaensis contains a relatively low number of genes involved in energy production and conversion (class C) and at only 3.66%, it is significantly below the average percentage. This is in accordance with the original description of S. espanaensis by Labeda et al.[21], who found that S. espanaensis cannot produce acid from most of the tested carbohydrates. Meanwhile, a disproportionally large number of genes (47.92%) could not be classified, suggesting a great potential to reveal "novel" genes.
For the second general classification, a BLASTP comparison of all predicted CDS against the RefSeq database [22] was performed and the taxonomic information for the best hits was retrieved. Unsurprisingly, this analysis revealed a close relationship between S. espanaensis and A. mirum (Figure 2), currently the only other completely sequenced member [8] of the recently abolished family of the "Actinosynnemataceae" [23, 24]. In the data some 38.4% of the best hits were against A. mirum. Almost half of the best BLASTP hits (49.7%) were against the suborder of the Pseudonocardianeae, while 80.7% delivered hits against proteins found in members of the order Actinomycetales. In general, the taxonomic distribution derived from this simple approach matches the phylogenetic distance derived from the 16S rDNA (Additional file 2), although it does not take into account the variable genome sizes. 15.2% of the CDS delivered no significant BLASTP hits against the RefSeq database, which is well within the range (10.5% - 19.0%) of the other completely sequenced Pseudonocardiaceae.
Phylogenetic distribution of S. espanaensis proteins based on BlastP hits against the RefSeq database. The amino acid sequences of all predicted CDS in the genome of S. espanaensis were compared against the RefSeq protein database [22] (from August 2011) using BLASTP. The species for each best hit (e-value cutoff 1e-10, hit must cover at least 75% of query and subject) was retrieved and the results were plotted from the least to the most abundantly hit group in the respective taxonomic level. For reasons of clarity, groups with few hits were either lumped together (e.g. under "Other Bacteria") or omitted entirely.
Comparison of the S. espanaensis genome with other completely sequenced Pseudonocardiaceae
For A. mediterranei and S. erythraea [10, 13] it was observed that there exists a striking bias concerning gene conservation and synteny. In both cases, the genes conserved between A. mediterranei respectively S. erythraea and other Actinomycetales were found to be preferentially located close to the oriC and at least some synteny could be detected. With six genomes of the Pseudonocardiaceae available, we performed a similar analysis using EDGAR. Indeed, a strong correlation between conservation and synteny around the oriC could be observed, especially when comparing S. espanaensis with A. mirum or S. erythraea (Figure 3A), but also for the others (Figure 3B: S. viridis and A. mediterranei). This also holds true if one of the other six genomes is used as a basis (data not shown, available via the open EDGAR project). A similar observation was made for the genomes of the species Streptomyces [25, 26] where the conserved core is located in the middle of the circular genome while the accessory genes are found at the variable ends. Interestingly, in another genus of the Actinomycetales with circular genomes, Corynebacterium, this positional bias is not observed [27].
Whole genome comparison of S. espanaensis. To analyze gene synteny, the amino acid sequences of all predicted CDS in the genome of S. espanaensis were compared against those of (A) A. mirum (red) and S. erythraea (green) as well as A. mediterranei (purple) and S. viridis (orange) using the bidirectional BLAST comparison implemented in EDGAR. Aligning all genomes at dnaA, the position of each potential ortholog was then plotted against the position in the S. espanaensis genome. In order to accommodate different genome sizes, the relative position is used for the target genomes.
This raised the question whether this degree of conservation and synteny is more pronounced if several species are taken into account, i.e. for the genes making up the core genome of the family. As a first step to answer this question, the family core genome was calculated, once again using EDGAR. In a first step the core genome was calculated for every possible unique subset of the seven genomes. Following this, an exponential decay function was fitted to the observed core genome counts for every genome quantity as described by Tettelin et al. [28]. Using this function, the development of the core given a presumed sequential addition of more genomes was extrapolated. This led to the predicted core genome of about 810 genes (Figure 4), i.e. the theoretical core of all Pseudonocardiaceae. With the core genome of these seven species comprised of 864 genes the 810 value is almost reached with the seven genomes used. A test including two Streptomyces species (S. coelicolor and S. avermitilis) only reduced the number of genes in the resulting core by about 45 genes to 765 which is already reached with the then nine genomes (data not shown, available via the open EDGAR project). This is quite surprising, as Streptomyces species usually possess linear ends. This implies that Pseudonocardiaceae and Streptomycetaceae, despite having different chromosome topologies, retain their core genes close to the oriC.
Development of the core genome of the Pseudonocardiaceae. Using EDGAR, the development of the core genome of the Pseudonocardiaceae was extrapolated by calculating the mean core genome numbers for all possible permutations of genomes (red crosses/line). By non-linear least squares curve fitting, an exponential decay function (dark blue curve and equation) was fitted to the mean core data. A 95% confidence interval was calculated for the fitted model, and the boundaries are displayed (light blue and purple curves). Using the genomes of A. mirum, A. mediterranei, P. dioxanivorans, S. erythraea, S. espanaensis, S. viridis, and T. bispora, a final core genome of approximately 810 genes is predicted, with the current core of the seven analyzed species consisting of 864 genes.
This implication is backed by further analyzing the correlation between gene conservation and location relative to the oriC: the core genes are found predominantly clustered around the oriC (Figure 1, genes depicted in green in circles 3–7) while genes conserved in only some species and the 2,967 S. espanaensis singletons (Figure 1, genes depicted in red respectively light blue in circles 3–7) are found farther away from the oriC.
The genes of the accessory genome of S. espanaensis are either ancient and/or obtained from closely related species
The distribution of core and accessory genes in the genome raises the question of what mechanism is causing this peculiar pattern. As multiple independent circularization events are exceedingly unlikely, the genome of the common ancestor of the Pseudonocardiaceae was either extremely large and suffered gene loss during speciation or it was rather small and most of the accessory genes were acquired later. This in turn raises the question of whether there is evidence that the accessory genes were acquired recently. To shed light on this timing, we performed a principle component analysis (PCA) of the relative polynucleotide frequencies of all of the genes. Analysis of polynucleotide frequencies were shown to be useful for classification of short DNA fragments obtained from different genomes [29]. In our case, no significant differences on the dinucleotide level could be observed for most of the genes, neither when comparing core and accessory genes (Figure 5A), nor when comparing genes close and distant to the oriC (Figure 5B). We also found that this held true for the tri- and tetranucleotide frequencies (data not shown). Therefore, the accessory genes present in the genome of S. espanaensis had either time to "adapt" to the prevalent polynucleotide bias or were obtained from genomes with a similar polynucleotide composition. While the currently available data does not suffice to decide which scenario is more likely, this question should be revisited when more Pseudonocardiaceae genomes become available.
Principle component analysis of the dinucleotide frequencies of the S. espanaensis CDS. A) Using EDGAR, all CDS from S. espanaensis were divided into three groups: "core" (conserved in all six completely sequenced Pseudonocardiaceae; blue "*"), "other" (shared between S. espanaensis and at least one other Pseudonocardiaceae species; green "x") and singletons ("unique" in S. espanaensis; red " + "). For all genes the relative dinucleotide frequencies were calculated, a PCA was performed using the R package and the results for the two main components are plotted. In addition, the median values for all three distributions were calculated and plotted. (B) Using the same calculation as in A, the genes were divided in relation to their position in the genome relative to the origin of replication. Genes close to the oriC (corresponding to the "top half" of the genome) are given as red "x", genes closer to the terminus ("bottom half" of the genome) are depicted as green " + ". Median points are denoted as black "*" and " + ", green and black circles mark the 90% boundaries.
Genes participating in the synthesis of saccharomicins
The most relevant accessory genes from the medical point of view are those for the production of secondary metabolites. For example, S. espanaensis is known to produce the saccharomicins A and B. Due to their activity against multi-resistant pathogens, these two compounds comprise a promising class of new antibiotics [6]. They possess an interesting chemical structure consisting of an exceptional N-(3,4-dihydroxycinnamoyl) taurine aglycon and a heptadecaglycoside side chain (Figure 6A) [6]. Previously, Berner et al. [30] were able to elucidate part of the saccharomicin biosynthetic pathway using a cosmid library. They reconstructed one half of the aglycon by performing co-expression of sam8 and sam5. These genes, encoding a tyrosine ammonia-lyase and a 4-coumarate 3-hydroxylase, respectively, convert l-tyrosine via trans-p-coumaric acid to caffeic acid.
The saccharomicin gene cluster from S. espanaensis. (A) Chemical structures of caffeic acid, taurine, saccharomicin A and B. Fuc, d-fucose; Sac, d-saccharosamine; Rha, l-rhamnose; Eva, l-4-epivancosamine; Dig, l-digitoxose [6]. (B) Organization of the saccharomicin cluster. Proposed functions for individual CDS are summarized in Additional file 1.
Our analysis of the complete genome sequence of S. espanaensis revealed the best candidate for the saccharomicin biosynthetic gene cluster (sam) (Figure 6B and Additional file 3), because this cluster harbors both the genes responsible for the production of the caffeic acid moiety of the aglycon, as well as ten glycosyltransferase genes necessary for the formation of the oligosaccharide side chain. The sam-cluster does not belong to the core genome and is located at the lower part of the circular chromosome, close to termination of replication. It comprises approximately 47,000 base pairs and is predicted to encode 38 genes. The identification of the sam-cluster allows further insights into the assembly of these new antibiotics. The product of sam7 shows similarity to acyl-CoA synthetases. It is therefore tempting to speculate that Sam7 may be involved in the synthesis of caffeoyl-CoA, which might be used to link taurine to form the entire aglycon. This reaction may be catalyzed by Sam36 which shows similarities to penicillin amidases. However, the synthesis of taurine has not been described in bacteria. In mammals, taurine originates from l-cysteine via cysteine sulfinic acid. Even though the dioxygenation of cysteine has been shown in bacteria [31], they are not able to produce taurine due to the lack of a cysteine sulfinic acid decarboxylase (csad). The same is true for S. espanaensis: there are potential cysteine dioxygenase genes (Ses72720, Ses71790) but no csad homologues are detectable in the genome. However, sam29 may encode the required chemistry. The protein Sam29 shows similarities to aspartate-1-decarboxylases which are responsible for the decarboxylation of l-aspartate forming β-alanine. The structures of cysteine sulfinic acid and l-aspartate are identical with the exception of one atom. While aspartate possesses a carbon as part of the carboxyl group, cysteine sulfinic acid contains sulfur in this position. As a result of this similarity we suggest that Sam29 might be able to decarboxylate cysteine sulfinic acid. If this is found to be correct, sam29 would represent the first gene responsible for the production of taurine in bacteria.
In addition to genes accountable for the formation of the aglycon, there are candidates encoding proteins involved in sugar synthesis and attachment. To link the 17 sugars to the aglycon, there are ten glycosyltransferase genes (sam11-sam20) in the cluster. Consequently, some of the glycosyltransferases may work iteratively. Because sequence analyses of those genes gave no further indication, the exact function of each glycosyltransferase will have to be experimentally investigated.
Potential for secondary metabolite production
Aside from the antibiotics saccharomicin A and B, no further secondary metabolites had been known to be produced by S. espanaensis before genome sequencing. The secondary metabolites search tool antiSMASH [32] identified 31 putative clusters, including the sam-cluster. However, several inaccuracies by the search tool had to be manually curated. This resulted in the total number of 26 clusters potentially producing secondary metabolites (Table 3, Figure 7, and Additional file 4). All secondary metabolite clusters are located outside the core genome of S. espanaensis.
S. espanaensis gene clusters for nonribosomal peptide and polyketide biosynthesis. Genes encoding nonribosomal peptide synthases are depicted in dark blue, type I polyketide synthases in red and type II polyketide synthases in orange. The genes involved in the synthesis of putative precursors are highlighted in light green. The remaining genes of the clusters are presented in pale blue. All genes involved in the biosynthesis of an enediyne core in cluster 6 are framed brown. aao, l-amino-acid oxidase; abc, ABC transporter; acc, acyl-CoA carboxylase; acd, acyl-CoA dehydrogenase; acp, acyl carrier protein; acs, acyl-CoA synthetase; act, acyl-CoA transferase; amo, amine oxidase; amt, aminotransferase; ap, aminopeptidase; ask, adenylylsulfate kinase; asl, AMP-dependent synthetase and ligase; ass, sulfate adenylyltransferase; at, acyl transferase; bh, beta-hydroxylase; cbs, carbamoyltransferase; cd, cysteine desulfurase; cho, cholesterol oxidase; cl, chlorinating protein; clf, chain length factor; ct, carboxyltransferase; cys, cysteine synthase; dbp, DNA-binding protein; dc, decarboxylase; dgb, glyoxalase/bleomycin resistance protein/dioxygenase; dh, dehydratase; dhbas, protein involved in the synthesis of activated 2,3-dihydroxybenzoic acid; dhg, dehydrogenase; e/l, esterase/lipase; eci, enoyl-CoA hydratase/isomerase; eff, efflux protein; gsit, glutamine—scyllo-inositol transaminase; gt, glycosyltransferase; hal, histidine ammonia-lyase; hmacps, protein involved in the synthesis of hydroxymalonyl-ACP; hmbppr, 4-hydroxy-3-methylbut-2-enyl diphosphate reductase; hmg, hydroxymethylglutaryl-CoA synthase; hpah, 4-hydroxyphenylacetate-3-hydroxylase; hyd, hydrolase; int, integrase; kr, ketoreductase; ks II, FabF-like protein; ks III, FabH-like protein; lam, lysine 2,3-aminomutase like protein; llp, lipolytic protein; lys, protein involved in lysine synthesis via alpha-aminoadipate; mfs, transporter of the major facilitator superfamily; mmcd, methylmalonyl-CoA decarboxylase; mo, monooxygenase; mt, methyltransferase; mtr, methionyl-tRNA synthetase; npd, 2-nitropropane dioxygenase; ocd, ornithine cyclodeaminase; oxy, oxidoreductase; p450, cytochrome P450; phas, polyhydroxy alkanoic acid synthase; pkc, polyketide cyclase; ppph, 2-polyprenylphenol 6-hydroxylase; pro, protease; reg, regulatory protein; rsam, radical SAM protein; sarp, streptomyces antibiotic regulatory protein; sip, siderophore-interacting protein; tcd, taurine catabolism dioxygenase; te, thioesterase; tetr, protein similar to the tetracycline repressor; tk, transketolase; tn, transposase.
Seven clusters possibly encoding terpenoid biosynthetic enzymes are distributed throughout the genome. The C5-precursors required for their biosynthesis originate from the methylerythriol phosphate pathway, for which all genes are present. Terpene derived metabolites include carotenoid pigments (crt) serving as UV protector and odorous substances providing actinomycetes with their characteristic smell [33, 34].
In the genome a total of five nonribosomal peptide synthetases (NRPS) encoding clusters could be identified (cluster 1, 2, 3, 7 and 12). Common metabolites produced by NRPS in actinomycetes are for example the antibiotic vancomycin, the cytotoxic agent bleomycin and the iron-scavenging siderophore griseobactin [35–37]. The proteins producing such polypeptides are usually composed of modules consisting of condensation, adenylation and thiolation domains. Remarkably, cluster 1 possesses a set of genes which code for only one nrps domain each. Consequently, this small cluster of about 20 kb may harbor an archetype of nrps. These genes, consisting of a condensation, an adenylation and a thiolation domain, respectively, might be ancestors of our contemporary nrps genes composed of a chain of different domains. The modules of all nrps genes and the specificity of their adenylation domains are listed in Additional file 5.
In addition to the clusters producing nonribosomal peptides, there are three clusters producing type I polyketides (cluster 4, 9 and 11). These natural products are synthesized by decarboxylative condensation of malonyl-CoA derived extender units. Polyketide synthetases (PKS) possess as well a modular assembly and are the well-known producers of the antibiotic erythromycin and the immunosuppressant tacrolimus in other actinomycetes strains [38, 39]. The modules of all polyketide synthetases identified in S. espanaensis are listed in Additional file 6. The PKS containing clusters are the largest in the genome of S. espanaensis and comprise between 50 and 86 kb.
Besides pure NRPS or PKS clusters, we identified six clusters which harbor both types of these secondary metabolite synthesis genes (cluster 5, 6, 8, 10, 13 and 14). Among them, cluster 6 shows high similarity to the maduropeptin cluster from Actinomadura madurae ATCC 39144 [40]. Consequently, cluster 6 is identified as a putative enediyne cluster.
Cluster 13 is not only a NRPS/PKS type I hybrid, but it also contains genes coding for type II PKS. The type II PKS part of the cluster is highly similar to the kinamycin gene cluster from Streptomyces murayamaensis [GenBank:AH012623.1]. All core and tailoring enzymes required for the production of kinamycin are present in cluster 13. Additionally it possesses further genes encoding tailoring enzymes like a P450 dependent monooxygenase (ses54730), an aminotransferase (ses54750) and a methyltransferase (ses54760). The type I PKS and the NRPS part of the cluster may contribute to the modification of the core structure of cluster 13, leading to a kinamycin derivative. Another hybrid, Cluster 14, shows similarities to the azinomycin B biosynthetic gene cluster from Streptomyces sahachiroi [41]. Azinomycin B is an antitumor agent consisting of a PKS-derived naphthoate attached to a nonribosomal peptide. The peptide part of the molecule is composed of unusual building blocks like α-ketoisovaleric acid and an aziridino-[1,2a]-pyrrolidinyl amino acid. Cluster 14 harbors ses56840, whose gene product is similar to AziC1 responsible for the production of α-ketoisovaleric acid from valine. Additionally, all genes are present for the production of the aziridino-[1,2a]-pyrrolidinyl amino acid (aziC2 aziC10; ses56710, ses56680, ses56700, ses56740, ses56730, ses56750, ses56760, and ses56690) except for a homolog to aziC8. Furthermore, the cluster possesses homologues of aziD2 and aziD3 (ses56770 and ses56780) which are responsible for tailoring modifications of the molecule. However, the PKS modules of the azinomycin B cluster differ from the ones found in cluster 14. Therefore we propose that the PKS derived moiety of the compound produced by cluster 14 is not a naphthoate moiety as in azinomycin B. Another interesting fact is that cluster 14 is flanked by transposase and integrase genes. This suggests that the cluster was probably introduced into the genome of S. espanaensis by horizontal gene transfer.
In addition to the secondary metabolite gene clusters belonging to the prevalent groups of NRPS, PKS and terpene synthases, the genome of S. espanaensis also contains rare types of clusters: it harbors a putative aminocyclitol cluster, a melanin cluster and two putative lantibiotic clusters (lan1 and lan2). Lantibiotics are ribosomally produced and posttranslationally modified polypeptides which contain thioether-cross-linked amino acids [42].
Conclusion
The complete genome of S. espanaensis was sequenced and compared to the genomes of the other completely sequenced Pseudonocardiaceae. Thereby, the expected core genome of the family could be predicted to consist of about 810 genes. While the origin of the accessory genome of S. espanaensis remains unclear, some evidence provided suggests that the accessory genes are either part of the genome for quite some time and/or were obtained from bacteria with a similar polynucleotide composition.
Besides providing some insights into the genome evolution of the Pseudonocardiaceae, the genome sequence delivered a good candidate cluster for the production of the saccharomicins. The newly identified sam-cluster consists of 38 genes and comprises approximately 47,000 base pairs. It harbors a presumed operon of ten glycosyltransferase genes centered in the cluster. To our knowledge, there is no other biosynthetic gene cluster identified to date which includes this high number of glycosyltransferase genes. Nevertheless, to produce the heptadecasaccharide side chain of the saccharomicins even more than ten glycosylation steps are proposed, so some glycosyltransferases should work iteratively. We anticipate that the complete genome sequence will facilitate the production and modification of the saccharomicins, by either improving precursor supply or by engineering of genes belonging to the cluster to obtain novel variants.
Methods
Pyrosequencing of Saccharothrix espanaensis DSM 44229T
The type strain of Saccharothrix espanaensis (DSM 44229) was obtained as lyophilized culture from DSMZ (Braunschweig, Germany). Genomic DNA was isolated from 30 ml cultures grown in tryptone soy broth (TSB) [43] at 28°C for 24 hours. Total DNA isolation was performed according to the salting out procedure followed by RNase treatment [43].
10 μg was used to construct both a 3 k PE and a WGS library for the pyrosequencing on a Genome Sequencer FLX (Roche Applied Science). Assembly of the shotgun reads was performed with the GS Assembler software (version 2.0.00.22). A total of 1,536,941 reads (404,849,780 bp) was assembled into 352 contigs in five scaffolds.
Completion of the draft sequence
For gap closure and assembly validation, the genomic contigs were bridged by (i) a fosmid library of 528 clones spanning all but 69 gaps and (ii) 69 PCR products addressing the remaining gaps. For finishing of the genome sequence, the CONSED software package [44] was used.
Sequencing of fosmid ends was carried out by IIT GmbH (Bielefeld, Germany). Gaps between contigs of the whole genome shotgun assembly were closed by sequencing on PCR products and fosmid clones carried out by IIT GmbH on ABI 377 sequencing machines. To obtain a high quality genome sequence, all bases of the consensus sequence were polished to at least phred40 quality by primer walking. Collectively, 854 sequencing reads were added to the shotgun assembly for finishing and polishing of the genomic sequence.
Genome analysis and annotation
In a first step, gene finding was done by using GISMO [45] and an automatic annotation was performed using the genome annotation system GenDB 2.0 [16]. In a second annotation step, all predicted ORFs were manually re-inspected to correct start codon and function assignments. Intergenic regions were checked for ORFs missed by the automatic annotation using the BLAST programs [46].
Genomic comparisons
For comparative analyses, the annotated genome sequences of the following bacteria were imported into EDGAR [47]: Actinosynnema mirum DSM 43827 [GenBank:NC_013093], Amycolatopsis mediterranei U32 [GenBank:NC_014318], Pseudonocardia dioxanivorans CB1190 [GenBank:NC_015312, GenBank:NC_015313, GenBank:NC_015314], Saccharopolyspora erythraea NRRL 2338 [GenBank:NC_009142], Saccharomonospora viridis DSM 43017 [GenBank:NC_013159], and Thermobispora bispora DSM 43833 [GenBank:NC_014165]. The project is available as an open EDGAR project (http://edgar.cebitec.uni-bielefeld.de/cgi-bin/edgar_login.cgi?cookie_test=1&open=1) called EDGAR_BMC_Pseudonocardiaceae.
The gene content comparisons were done via a BLASTP analysis against the bactNOG subset of the eggNOG database [20]. Two genes were considered to be orthologs if the reciprocal BLASTP hit had a sequence identity of at least 40% and a coverage of at least 75%. For the phylogenetic analysis, all predicted CDS were compared against the RefSeq protein database [22] (from August 2011) using BLASTP. The species for each best hit (e-value cutoff 1e-10, hit must cover at least 75% of query and subject) was retrieved and counted.
All other genome comparisons were done using EDGAR, the PCA analyses were done using R (http://cran.r-project.org/).
Analysis of secondary metabolite clusters
For the identification of secondary metabolite clusters the genome of S. espanaensis was scanned for homologues to known secondary metabolite synthases via BLAST search. These manual investigations were supported by antiSMASH [32]. A set of genes was considered to be a cluster, when there was at least one gene encoding a secondary metabolite synthase. Consequently, a locus possessing a gene with only a single domain, for example an A domain, was not considered to be a cluster. The boundaries of the clusters were defined by the last gene upstream and downstream of a secondary metabolite synthase with homology to a gene encoding a regulator, transporter or tailoring enzyme. In cases where this gene was part of a putative operon, the whole operon was included into the cluster. The modular organization of the type I polyketide and nonribosomal peptide megasynthases were determined using web tools [48, 49]. The A domain specificities were investigated using NRPSpredictor2 [50, 51].
Nucleotide sequence accession numbers
The sequences reported here have been deposited in the EMBL database (accession no.: [EMBL:HE804045]). The locus tag prefix "BN6_" assigned by the ENA is replaced by "ses" throughout.
References
Demain AL, Adrio JL: Contributions of microorganisms to industrial biology. Mol Biotechnol. 2008, 38: 41-55. 10.1007/s12033-007-0035-z.
Baltz RH: Renaissance in antibacterial discovery from actinomycetes. Curr Opin Pharmacol. 2008, 8: 557-563. 10.1016/j.coph.2008.04.008.
Zitouni A, Boudjella H, Mathieu F, Sabaou N, Lebrihi A: Mutactimycin PR, a new anthracycline antibiotic from Saccharothrix sp. SA 103. I. Taxonomy, fermentation, isolation and biological activities. J Antibiot (Tokyo). 2004, 57: 367-272. 10.7164/antibiotics.57.367.
Ohuchi T, Ikeda-Araki A, Watanabe-Sakamoto A, Kojiri K, Nagashima M, Okanishi M, Suda H: Cloning and expression of a gene encoding N-glycosyltransferase (ngt) from Saccarothrix aerocolonigenes ATCC39243. J Antibiot (Tokyo). 2000, 53: 393-403. 10.7164/antibiotics.53.393.
Labeda DP, Kroppenstedt RM: Phylogenetic analysis of Saccharothrix and related taxa: proposal for Actinosynnemataceae fam. nov. Int J Syst Bacteriol. 2000, 50: 331-336.
Kong F, Zhao N, Siegel MM, Janota K, Ashcroft JS, Koehn FE, Borders DB, Carter GT: Saccharomicins, Novel Heptadecaglycoside Antibiotics Effective against Multidrug-Resistant Bacteria. J Am Chem Soc. 1998, 120: 13301-13311. 10.1021/ja981641l.
Singh MP, Petersen PJ, Weiss WJ, Kong F, Greenstein M: Saccharomicins, novel heptadecaglycoside antibiotics produced by Saccharothrix espanaensis: antibacterial and mechanistic activities. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 2000, 44: 2154-2159. 10.1128/AAC.44.8.2154-2159.2000.
Land M, Lapidus A, Mayilraj S, Chen F, Copeland A, Del Rio TG, Nolan M, Lucas S, Tice H, Cheng JF, et al, et al: Complete genome sequence of Actinosynnema mirum type strain (101). Stand Genomic Sci. 2009, 1: 46-53. 10.4056/sigs.21137.
Liolios K, Sikorski J, Jando M, Lapidus A, Copeland A, Glavina T, Del R, Nolan M, Lucas S, Tice H, et al: Complete genome sequence of Thermobispora bispora type strain (R51). Stand Genomic Sci. 2010, 2: 318-326. 10.4056/sigs.962171.
Oliynyk M, Samborskyy M, Lester JB, Mironenko T, Scott N, Dickens S, Haydock SF, Leadlay PF: Complete genome sequence of the erythromycin-producing bacterium Saccharopolyspora erythraea NRRL23338. Nat Biotechnol. 2007, 25: 447-453. 10.1038/nbt1297.
Pati A, Sikorski J, Nolan M, Lapidus A, Copeland A, Glavina Del Rio T, Lucas S, Chen F, Tice H, Pitluck S, et al, et al: Complete genome sequence of Saccharomonospora viridis type strain (P101). Stand Genomic Sci. 2009, 1: 141-149. 10.4056/sigs.20263.
Sales CM, Mahendra S, Grostern A, Parales RE, Goodwin LA, Woyke T, Nolan M, Lapidus A, Chertkov O, Ovchinnikova G, et al: Genome sequence of the 1,4-dioxane-degrading Pseudonocardia dioxanivorans strain CB1190. J Bacteriol. 2011, 193: 4549-4550. 10.1128/JB.00415-11.
Zhao W, Zhong Y, Yuan H, Wang J, Zheng H, Wang Y, Cen X, Xu F, Bai J, Han X, et al, et al: Complete genome sequence of the rifamycin SV-producing Amycolatopsis mediterranei U32 revealed its genetic characteristics in phylogeny and metabolism. Cell Res. 2010, 20: 1096-1108. 10.1038/cr.2010.87.
Henssen A: Beiträge zur Morphologie und Systematik der thermophilen Actinomyceten. Arch Mikrobiol. 1957, 26: 373-414. 10.1007/BF00407588.
Küster E, Locci R: Studies on peat and peat microorganism. I. Taxonomic studies on thermophilic Actinomycetes isolated from peat. Arch Mikrobiol. 1963, 45: 188-197. 10.1007/BF00408439.
Meyer F, Goesmann A, McHardy AC, Bartels D, Bekel T, Clausen J, Kalinowski J, Linke B, Rupp O, Giegerich R, Pühler A: GenDB–an open source genome annotation system for prokaryote genomes. Nucleic Acids Res. 2003, 31: 2187-2195. 10.1093/nar/gkg312.
Ermolaeva MD: Synonymous codon usage in bacteria. Curr Issues Mol Biol. 2001, 3: 91-97.
Marin A, Xia X: GC skew in protein-coding genes between the leading and lagging strands in bacterial genomes: new substitution models incorporating strand bias. J Theor Biol. 2008, 253: 508-513. 10.1016/j.jtbi.2008.04.004.
Mao X, Zhang H, Yin Y, Xu Y: The percentage of bacterial genes on leading versus lagging strands is influenced by multiple balancing forces. Nucleic Acids Res. 2012
Powell S, Szklarczyk D, Trachana K, Roth A, Kuhn M, Muller J, Arnold R, Rattei T, Letunic I, Doerks T, et al: eggNOG v3.0: orthologous groups covering 1133 organisms at 41 different taxonomic ranges. Nucleic Acids Res. 2012, 40: D284-D289. 10.1093/nar/gkr1060.
Labeda DP, Lechevalier MP, et al, et al: Amendment of the Genus Saccharothrix Labeda. Descriptions of Saccharothrix espanaensis sp. nov., Saccharothrix cryophilis sp. nov., and Saccharothrix mutabilis comb. nov. Int J Syst Bacteriol. 1989, 39: 420-423. 10.1099/00207713-39-4-420.
Pruitt KD, Tatusova T, Klimke W, Maglott DR: NCBI Reference Sequences: current status, policy and new initiatives. Nucleic Acids Res. 2009, 37: D32-D36. 10.1093/nar/gkn721.
Labeda DP, Goodfellow M, Chun J, Zhi XY, Li WJ: Reassessment of the systematics of the suborder Pseudonocardineae: transfer of the genera within the family Actinosynnemataceae Labeda and Kroppenstedt 2000 emend. Zhi et al. 2009 into an emended family Pseudonocardiaceae Embley et al. 1989 emend. Zhi et al. 2009. Int J Syst Evol Micr. 2011, 61: 1259-1264. 10.1099/ijs.0.024984-0.
Labeda DP, Kroppenstedt RM: Phylogenetic analysis of Saccharothrix and related taxa: proposal for Actinosynnemataceae fam. nov. Int J Syst Evol Micr. 2000, 50: 331-336. 10.1099/00207713-50-1-331.
Bentley SD, Chater KF, Cerdeno-Tarraga AM, Challis GL, Thomson NR, James KD, Harris DE, Quail MA, Kieser H, Harper D, et al: Complete genome sequence of the model actinomycete Streptomyces coelicolor A3(2). Nature. 2002, 417: 141-147. 10.1038/417141a.
Ikeda H, Ishikawa J, Hanamoto A, Shinose M, Kikuchi H, Shiba T, Sakaki Y, Hattori M, Omura S: Complete genome sequence and comparative analysis of the industrial microorganism Streptomyces avermitilis. Nat Biotechnol. 2003, 21: 526-531. 10.1038/nbt820.
Kalinowski J, Bathe B, Bartels D, Bischoff N, Bott M, Burkovski A, Dusch N, Eggeling L, Eikmanns BJ, Gaigalat L, et al, et al: The complete Corynebacterium glutamicum ATCC 13032 genome sequence and its impact on the production of L-aspartate-derived amino acids and vitamins. J Biotechnol. 2003, 104: 5-25. 10.1016/S0168-1656(03)00154-8.
Tettelin H, Masignani V, Cieslewicz MJ, Donati C, Medini D, Ward NL, Angiuoli SV, Crabtree J, Jones AL, Durkin AS, et al: Genome analysis of multiple pathogenic isolates of Streptococcus agalactiae: implications for the microbial "pan-genome". Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 2005, 102: 13950-13955. 10.1073/pnas.0506758102.
Karlin S: Global dinucleotide signatures and analysis of genomic heterogeneity. Curr Opin Microbiol. 1998, 1: 598-610. 10.1016/S1369-5274(98)80095-7.
Berner M, Krug D, Bihlmaier C, Vente A, Muller R, Bechthold A: Genes and enzymes involved in caffeic acid biosynthesis in the actinomycete Saccharothrix espanaensis. J Bacteriol. 2006, 188: 2666-2673. 10.1128/JB.188.7.2666-2673.2006.
Dominy JE, Simmons CR, Karplus PA, Gehring AM, Stipanuk MH: Identification and characterization of bacterial cysteine dioxygenases: a new route of cysteine degradation for eubacteria. J Bacteriol. 2006, 188: 5561-5569. 10.1128/JB.00291-06.
Medema MH, Blin K, Cimermancic P, de Jager V, Zakrzewski P, Fischbach MA, Weber T, Takano E, Breitling R: antiSMASH: rapid identification, annotation and analysis of secondary metabolite biosynthesis gene clusters in bacterial and fungal genome sequences. Nucleic Acids Res. 2011, 39: W339-W346. 10.1093/nar/gkr466.
Lee HS, Ohnishi Y, Horinouchi S: A sigmaB-like factor responsible for carotenoid biosynthesis in Streptomyces griseus. J Mol Microbiol Biotechnol. 2001, 3: 95-101.
Komatsu M, Tsuda M, Omura S, Oikawa H, Ikeda H: Identification and functional analysis of genes controlling biosynthesis of 2-methylisoborneol. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 2008, 105: 7422-7427. 10.1073/pnas.0802312105.
van Wageningen AM, Kirkpatrick PN, Williams DH, Harris BR, Kershaw JK, Lennard NJ, Jones M, Jones SJ, Solenberg PJ: Sequencing and analysis of genes involved in the biosynthesis of a vancomycin group antibiotic. Chem Biol. 1998, 5: 155-162. 10.1016/S1074-5521(98)90060-6.
Du L, Chen M, Sanchez C, Shen B: An oxidation domain in the BlmIII non-ribosomal peptide synthetase probably catalyzing thiazole formation in the biosynthesis of the anti-tumor drug bleomycin in Streptomyces verticillus ATCC15003. FEMS Microbiol Lett. 2000, 189: 171-175. 10.1111/j.1574-6968.2000.tb09225.x.
Patzer SI, Braun V: Gene cluster involved in the biosynthesis of griseobactin, a catechol-peptide siderophore of Streptomyces sp. ATCC 700974. J Bacteriol. 2010, 192: 426-435. 10.1128/JB.01250-09.
Donadio S, Katz L: Organization of the enzymatic domains in the multifunctional polyketide synthase involved in erythromycin formation in Saccharopolyspora erythraea. Gene. 1992, 111: 51-60. 10.1016/0378-1119(92)90602-L.
Motamedi H, Cai SJ, Shafiee A, Elliston KO: Structural organization of a multifunctional polyketide synthase involved in the biosynthesis of the macrolide immunosuppressant FK506. Eur J Biochem. 1997, 244: 74-80. 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1997.00074.x.
Van Lanen SG, Oh TJ, Liu W, Wendt-Pienkowski E, Shen B: Characterization of the maduropeptin biosynthetic gene cluster from Actinomadura madurae ATCC 39144 supporting a unifying paradigm for enediyne biosynthesis. J Am Chem Soc. 2007, 129: 13082-13094. 10.1021/ja073275o.
Zhao Q, He Q, Ding W, Tang M, Kang Q, Yu Y, Deng W, Zhang Q, Fang J, Tang G, Liu W: Characterization of the azinomycin B biosynthetic gene cluster revealing a different iterative type I polyketide synthase for naphthoate biosynthesis. Chem Biol. 2008, 15: 693-705. 10.1016/j.chembiol.2008.05.021.
Chatterjee C, Paul M, Xie L, van der Donk WA: Biosynthesis and mode of action of lantibiotics. Chem Rev. 2005, 105: 633-684. 10.1021/cr030105v.
Kieser T, Bibb MJ, Buttner MJ, Charter KF, Hopwood D: Practical Streptomyces Genetics. 2000, John Innes Foundation, Norwich, United Kingdom
Gordon D, Abajian C, Green P: Consed: a graphical tool for sequence finishing. Genome Res. 1998, 8: 195-202.
Krause L, McHardy AC, Nattkemper TW, Puhler A, Stoye J, Meyer F: GISMO–gene identification using a support vector machine for ORF classification. Nucleic Acids Res. 2007, 35: 540-549.
Altschul SF, Gish W, Miller W, Myers EW, Lipman DJ: Basic local alignment search tool. J Mol Biol. 1990, 215: 403-410.
Blom J, Albaum SP, Doppmeier D, Puhler A, Vorholter FJ, Zakrzewski M, Goesmann A: EDGAR: a software framework for the comparative analysis of prokaryotic genomes. BMC Bioinformatics. 2009, 10: 154-10.1186/1471-2105-10-154.
Bachmann BO, Ravel J: Chapter 8. Methods for in silico prediction of microbial polyketide and nonribosomal peptide biosynthetic pathways from DNA sequence data. Methods Enzymol. 2009, 458: 181-217.
Anand S, Prasad MV, Yadav G, Kumar N, Shehara J, Ansari MZ, Mohanty D: SBSPKS: structure based sequence analysis of polyketide synthases. Nucleic Acids Res. 2010, 38: W487-W496. 10.1093/nar/gkq340.
Rottig M, Medema MH, Blin K, Weber T, Rausch C, Kohlbacher O: NRPSpredictor2–a web server for predicting NRPS adenylation domain specificity. Nucleic Acids Res. 2011, 39: W362-W367. 10.1093/nar/gkr323.
Rausch C, Weber T, Kohlbacher O, Wohlleben W, Huson DH: Specificity prediction of adenylation domains in nonribosomal peptide synthetases (NRPS) using transductive support vector machines (TSVMs). Nucleic Acids Res. 2005, 33: 5799-5808. 10.1093/nar/gki885.
Cole JR, Wang Q, Cardenas E, Fish J, Chai B, Farris RJ, Kulam-Syed-Mohideen AS, McGarrell DM, Marsh T, Garrity GM, Tiedje JM: The Ribosomal Database Project: improved alignments and new tools for rRNA analysis. Nucleic Acids Res. 2009, 37: D141-D145. 10.1093/nar/gkn879.
Stachelhaus T, Mootz HD, Marahiel MA: The specificity-conferring code of adenylation domains in nonribosomal peptide synthetases. Chem Biol. 1999, 6: 493-505. 10.1016/S1074-5521(99)80082-9.
Acknowledgements
CR and RS acknowledge funding by a research grant awarded by the MIWFT within the BIO.NRW initiative (grant 280371902).The project was funded by a grant from the Federal Ministry of Education and Research (BMBF, grant 0313805A).
We gratefully acknowledge John Quimby at MIT for his very helpful improvements in choice of language.
We acknowledge support of the publication fee by Deutsche Forschungsgemeinschaft and the Open Access Publication Funds of Bielefeld University.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Competing interests
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Authors’ contributions
TS, annotated the saccharomicin gene cluster, coordinated and worked on the annotation of silent biosynthetic gene clusters and performed the comparison with the clusters of completely sequenced Pseudonocardiaceae. AAD worked on the initial stages of the genome finishing, performing primer design and gap closure. JB performed the EDGAR and PCA analyses. AG participated in the manual gene annotation. JK and AP were involved in coordination of the genome sequencing project. ML, worked on the identification and annotation of secondary metabolite clusters. RS created the sequencing libraries and performed the high-throughput sequencing steps. AB, assisted with the analysis of biosynthetic gene clusters. CR coordinated the initial phases of the genome sequencing and assembly, performed the final stages of genome finishing and polishing, and worked on the genome comparison. All authors read and approved of the final manuscript.
Electronic supplementary material
12864_2012_4235_MOESM1_ESM.xls
Additional file 1 : Comparative analysis based on the general eggNOG functional categories. The gene content comparisons were done via a BLASTP analysis against the bactNOG subset of the eggNOG database. Two genes were considered to be orthologs if the reciprocal BLASTP hit had a sequence identity of at least 40% and a coverage of at least 75%. Average and standard deviation were calculated for the relative numbers over all species excluding S. espanaensis and the cells were colored based on the significance level. (XLS 35 KB)
12864_2012_4235_MOESM2_ESM.png
Additional file 2 : Phylogenetic tree of the type and completely sequenced strains of the Pseudonocardiaceae family based on 16S rDNA sequences. The 16S rDNA sequences of the relevant type strains were retrieved from RDP [52], with Streptomyces avermitilis added as an outgroup, and the 16S rDNA sequence of A. mediterranei U32 was taken from RefSeq. After alignment with the RDP pipeline, a phylogenetic tree was constructed using the Tree Builder of RDP. Completely sequenced strains are highlighted in bold type and color. (PNG 98 KB)
12864_2012_4235_MOESM3_ESM.doc
Additional file 3 : Deduced functions of the ORFs located in the saccharomicin biosynthetic gene cluster from S. espanaensis. (DOC 92 KB)
12864_2012_4235_MOESM5_ESM.doc
Additional file 5 : Deduced function of genes encoding nonribosomal peptide synthases in S. espanaensis. Adenylation (A) domain numbering according to Stachelhaus et al.[53]. Substrates for A domains were determined using NRPSpredictor2 [50]. Their specificities are indicated when there is a nearest neighbor consistent in at least 8 residues and the prediction lies in the applicability domain of the model. (DOC 128 KB)
Authors’ original submitted files for images
Below are the links to the authors’ original submitted files for images.
Rights and permissions
Open Access This article is published under license to BioMed Central Ltd. This is an Open Access article is distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License ( https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/2.0 ), which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original work is properly cited.
About this article
Cite this article
Strobel, T., Al-Dilaimi, A., Blom, J. et al. Complete genome sequence of Saccharothrix espanaensis DSM 44229T and comparison to the other completely sequenced Pseudonocardiaceae. BMC Genomics 13, 465 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1186/1471-2164-13-465
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1186/1471-2164-13-465