Abstract
Background
Maternal condition can generate resource-related maternal effects through differential egg provisioning, and can greatly affect offspring performance. In the present study, the speckled wood butterfly Pararge aegeria (L.) was used to investigate whether (after controlling for egg size) maternal age, and increased flight during the oviposition period, resulted in changes in egg provisioning and whether this contributed to variation in offspring performance, i) early in development (egg stage and early post-hatching development), and ii) later in larval development after being exposed to the model viral pathogen system; the baculovirus Autographa californica multinucleocapsid nucleopolyhedrovirus (AcMNPV).
Results
Age-related changes in maternal egg provisioning were observed to influence egg stage development only. Flight-induced changes in maternal egg provisioning had direct consequences for offspring growth and survival across each life stage from egg to adulthood; offspring from forced flight mothers had lower larval masses and longer development times. Offspring with lower larval masses also had reduced survival after exposure to the viral pathogen.
Conclusion
The present study demonstrates that a change in maternal provisioning as a result of increased flight during the oviposition period has the potential to exert non-genetic cross-generational fitness effects in P. aegeria. This could have important consequences for population dynamics, particularly in fragmented anthropogenic landscapes.
Similar content being viewed by others
Background
Maternal condition and/or the environment can generate resource-related maternal effects through differential egg provisioning, and can greatly affect offspring performance (for reviews see [1–4]). In insect species, a decline in resources available for reproduction often results in a decrease in egg size with maternal age [1]. This decrease in egg size has been shown to influence offspring performance, with small eggs having a lower hatching success [5–7], and producing offspring which have; a lower survival during the larval stage [8], slower development [9–12], smaller pupae and/or adults [9, 10, 13] and lower starvation tolerance [[14–16], but see [17]], or desiccation tolerance [18].
The oogenesis-flight syndrome hypothesis [19] predicts that, in flying insect species, physiological constraints caused by an overlap in resources used during flight and during oogenesis results in a resource allocation trade-off, with fewer resources available for egg production [[20, 21], but see [22]]. Increased flight activity during the oviposition period has been shown to have an impact on resource allocation to egg size, with females that were forced to fly laying smaller eggs [7, 23–25]. This suggests the potential for increased flight during oviposition to generate resource-related maternal effects and affect offspring performance.
Resource-related maternal effects may be difficult to measure via egg size alone [12]. Recent studies have shown that variation in offspring performance with maternal age may not necessarily be due to egg size per se, but may be due to changes in the relative proportion of different nutrients allocated to eggs, with egg composition varying independent of egg size [6, 12, 26, 27]. Although increased flight during the oviposition period reduces egg size, currently it is not known whether flight also results in changes in egg composition [[7], but see [25]]. In general, maternal effects usually have their greatest impact during early development [4, 28, 29]. As such, changes in maternal egg provisioning due to, for example, maternal age or increased flight during the oviposition period, may affect embryonic development independently from their effects on egg size per se, influencing early offspring developmental traits such as; embryonic development time, and early post-hatching survival and development rates (reviewed in [30]).
Using the speckled wood butterfly, Pararge aegeria (L.), we have previously shown that mothers alter the size of eggs both, as they age and, in response to increased flight prior to the onset of oviposition [7]. Also, we have demonstrated that larvae hatching from small eggs have lower post-hatching resource availability and need to grow for longer on poor quality host plants to obtain the critical mass required for pupation [7]. In line with predictions from life history theory, there is good evidence (in both vertebrates and invertebrates) to suggest that deployment of the immune system is energetically costly and can result in trade-offs with fitness-related traits such as; development time and pupal weight (for a general review [31]; and for baculoviruses specifically; [32–36]). It is also known that effective resistance to pathogens or parasites is often dependent on resource availability (particularly carbohydrate and protein; [37]), because resource availability affects body condition and also immune system development [38]. Given that P. aegeria larvae hatching from small eggs have lower post-hatching resource availability [7] one may predict that these larvae also have a reduced capacity for effective immune system deployment. As such, we hypothesised that a decline in maternal provisioning of eggs with age and time spent flying, reduces the developing offspring's capacity for effective immune function.
Our aim in this study is to investigate whether, after controlling for egg size, maternal age per se and increased flight during the oviposition period influences offspring performance; i) early in development (egg stage and early post-hatching development), and ii) later in larval development after being exposed to the pathogen system, the baculovirus Autographa californica multinucleocapsid nucleopolyhedrovirus (AcMNPV). AcMNPV is a popular model system to study the effects of a viral infection, and associated immune response, on life history traits in Lepidoptera [35, 36]. In the present study, costs associated with the immune response were estimated in terms of P. aegeria larval survival, development time and pupal mass.
Methods
Study species
Speckled wood butterflies, P. aegeria, are temperate zone butterflies that lay eggs singly on grass plant species from the family Poaceae [39]. Females mate soon after emergence and usually mate only once [40]. At eclosion they have no [41] or only a few (8-24; [42]) mature oocytes, and if mated on the day of emergence they usually start ovipositing 48 hr later on the third day of their life [7, 25]. In female P. aegeria resources for reproduction are, to a significant degree, obtained during the larval stage and there is little opportunity to obtain more nitrogenous resources for reproduction through adult feeding [43] or nuptial gifts [44]. During nectar and honeydew feeding, adults imbibe a dilute aqueous solution of mainly sugar with minute quantities of amino acids and lipids [45, 46]. Therefore, through adult feeding P. aegeria may gain extra carbohydrate (but not lipid and protein) resources to fuel somatic maintenance and flight (cf. [46]).
Baculovirus production
A stock of AcMNPV was obtained by dosing 3rd instar Trichoplusia ni (Hübner) larvae. Viral inoculum was added to small plugs of artificial diet and larvae were maintained individually and allowed to feed overnight. Once the entire plug of diet was consumed, larvae were incubated in individual pots containing artificial diet until death due to virus. Viral cadavers were collected, macerated and the resulting suspensions filtered through sterile muslin to remove large particulate matter. Viral material was then purified using density gradient centrifugation [47]. The concentration of occlusion bodies in the viral stock was estimated by counting in an improved Neubauer haemocytometer and stored at -20°C until required. Dilution of the stock suspension was done in sterile distilled water to achieve a final concentration of 1 × 106 OB's μl-1 for use in experiments.
Butterfly breeding design
Eggs were collected from a large outbred laboratory population of P. aegeria (kept at 300-400 individuals per generation). This population originated from a woodland population in the south of Belgium (St. Hubert; established from 50 eggs) and, by the time of the experiment, had been reared in the laboratory for 12 generations. Newly hatched larvae (siblings, 4 per plant) were placed on potted host plants of Poa trivialis (L.) with access to ad libitum food and were reared until eclosion in a climate room under a regime (26°C, LD 16:8) that promotes direct development (i.e. no diapause). On the day of eclosion (i.e. day -1, between 9 and 12 h) 36 females from this laboratory stock were weighed (Ohaus Explorer balance; accuracy: ± 0.1 mg) and placed individually in netted cages (0.5 m3) along with a potted P. trivialis plant for oviposition and an artificial flower containing a 10% honey solution [48]. Later the same day (between 13.00 and 16.00 h) a non-sibling virgin male was introduced to the cage and the mating pair was left undisturbed for 24 h.
Maternal treatment (forced flight versus no flight)
On the day after mating (i.e. day 0), females were assigned to one of two treatment groups: control or forced flight. Control females were left undisturbed in their cages until the first egg was laid (i.e. day 1 of oviposition). When the first egg was laid, the male was removed from the cage and the female was left to continue laying for a further 9 days (i.e. 10 days in total). On day 0, experimental females were removed from cages and forced to fly for 5 min at 26°C. These experimental females were placed individually into an empty netted cage (0.5 m3) and stimulated to fly by gently touching their legs with a fine-bristled paintbrush each time they alighted (after [7, 25]). After forced flight, the experimental females were returned to their mating cages until the first egg was laid (i.e. day 1 of oviposition). When the first egg was laid, the male was removed from the cage and the female was left undisturbed in the cage to continue egg laying. On days 4 and 8 of oviposition the flight treatment was repeated so that in total each experimental female was forced to fly 3 times. Each day, the host plants were watered and fresh honey solution was provided. In total, 18 control females and 18 experimental females were set up. All 36 females mated successfully, started egg laying 24 h after mating, and laid viable eggs.
Each day of oviposition, eggs were collected from every cage and counted. These egg counts provided a measure of daily fecundity for each female. A random sample of eggs laid by each female on days 2, 4, 6, 8 and 10 of oviposition were selected, and placed individually into labelled Petri dishes (n = 283 in total; average of 7.7 ± 0.54 eggs per female). Each egg was photographed with a digital camera (Canon A720 IS; Canon, Japan). The resulting images were then analysed using Image J (available at: http://rsb.info.nih.gov/ij/) and the size of each egg was measured as a cross-sectional projection (mm2). This method provides a highly reliable measure of egg size in P. aegeria because there is a strong correlation between egg area and egg mass in this species [49]. These eggs were left undisturbed in Petri dishes until hatching (at 26°C, LD 16:8). Hatching success was recorded for each egg.
Offspring life history: pre-viral inoculation
For each egg, the number of days between being laid and hatching was recorded and used as a measure of embryonic development time. Newly-hatched larvae were placed individually on enclosed potted host plants of P. trivialis and reared under a direct development regime (LD 16:8 h photoperiod at 18°C). Larval development and survival was recorded for each individual up to 21 days. At 21 days of larval development (when the larvae were in their second instar), all larvae were removed from their host plants, weighed (Ohaus Explorer balance; accuracy: ± 0.1 mg) and placed individually into labelled Petri dishes lined with filter paper moistened with sterile water. Larvae were then left for 24 h without food to ensure consumption of inoculated P. trivialis leaves (see below).
Offspring life history: post-viral inoculation
After 24 h without food, half of the larvae from each female were assigned to one of two treatment groups: control or infected. Each larva in the control treatment group was given 5 × 1 cm pieces of P. trivialis leaves inoculated with 1 microlitre of sterile water. Each larva in the infected treatment group was given 5 × 1 cm pieces of P. trivialis leaves inoculated with 1 microlitre of 1 × 106 OB's ml-1 suspension of AcMNPV [after [50]]. Previous bioassays with the model system AcMNPV verified that when inoculated with 1 × 106 OBml-1 at 21 days of larval development, 67% of P. aegeria survived to eclose as an adult (n = 37/55, unpublished data). As such, this concentration of AcMNPV was used to ensure that we could examine the sub-lethal effects of viral infection for the majority of our experimental larvae. All larvae were left for 24 h to consume the P. trivialis leaves. To ensure accurate dosing [35], we starved the larvae before inoculation, and ensured that each larva consumed all 5 of their inoculated P. trivialis leaves within the 24 h period. Thus we ensured that each larva received a comparable dose of virus. After this inoculation period, each larva was returned to its own enclosed potted host plant of P. trivialis. Each individual was monitored daily up to pupation. Larval development time was recorded as the number of days from hatching from the egg to pupation. On the day after pupation (once the pupal case had hardened) each pupa was weighed (Ohaus Explorer balance; accuracy: ± 0.1 mg) and placed into an individual container until eclosion as an adult. Survival to pupation and survival to eclosion as an adult was recorded for each individual.
Statistical analyses
Linear and generalised linear mixed effect (lme or glme) models were fitted where appropriate, by means of restricted maximum likelihood (REML), which produces unbiased estimates of variance and covariance parameters, with female (nested within flight treatment) being declared as a random factor. Likelihood ratio tests were conducted to compare different models (that contained the same set of fixed factors but different random or interaction effects) with each other. The final model only included significant interactions. Residuals were examined for non-linearity in all cases and for non-normality where appropriate. Analyses were performed both in R 2.10.1 (packages nlme and lme4; http://lib.stat.cmu.edu/R/CRAN/) and Statistica 9.1 with R functionality (Statsoft Ltd.). Significances for REML constructed models in R are estimated by means of tdf-values (lme) and z-values (glme). The sign of either the t- or z-values is indicative of the relationship between the effect and the dependent variable (i.e. positive or negative).
Reproductive output
Reproductive output of the 36 females was assessed by means of daily fecundity (egg number for days 1 to 10 of oviposition), and egg size (for a random subsample of eggs from days 2, 4, 6, 8, and 10 of oviposition). These data were analysed by means of a lme model for repeated measures data. Fixed factors were day of oviposition and flight treatment. Female body mass was used as a covariate.
Offspring development
lme models were constructed to investigate how each of the four offspring traits, embryonic development time (in days), larval mass at 21 days of development (mg), total larval development time (in days) and pupal mass (mg) changed over the egg-laying period (i.e. as a function of maternal age), and whether there were differences in these traits between females that had been forced to fly and the controls (i.e. flight treatment was a fixed effect), with viral challenge as an additional treatment factor. In these models, day of oviposition (fixed effect) was thus an indicator of female age. Egg size (mm2), which is known to affect offspring development [7], was used as a covariate, as any relationship between offspring traits and maternal age may simply be due to the fact that females lay differently sized eggs as they age. Larvae that developed to the pupal stage could be sexed, and thus offspring sex was also added as fixed effect to the models for total larval development time and pupal mass.
Survival analyses
Survival (0 = dead, 1 = alive) from; i) egg stage to 21 days of larval development, ii) from 21 days of larval development (when a viral treatment was administered) till pupation, and iii) pupa to adult stage were all analysed using lme models with a logit link function (i.e. logistic regressions with random effects). As the overdispersion parameter, by which p-values and confidence intervals should be adjusted for overdispersion, was never significantly different from 1, overdispersion correction did not alter the model output. For survival from egg stage to 21 days of larval development fixed effects were day of oviposition and flight treatment. Egg size was used as a covariate. For survival from 21 days of larval development till pupation, the fixed effects were viral treatment, day of oviposition and flight treatment. Larval mass at 21 days was used as a covariate. Offspring sex was not included in these models as offspring that did not survive could not be sexed.
Results
Effects of maternal weight, age and flight treatment on egg size and egg number
Egg number
Egg number was affected by flight treatment and day of oviposition, and required a square root transformation for normality. Forced flight females laid significantly fewer eggs than control females over the whole of the 10-day oviposition period (control (± SE) = 140.55 ± 7.42, forced flight (± SE) = 117.11 ± 7.63; ANCOVA F1,32 = 4.80, p = 0.036); most notably in the first 6 days of oviposition (lme model t33 = -2.63, p = 0.013; Figure 1). Female body mass did not significantly explain variation in the number of eggs laid (ANCOVA F1,32 = 0.53, p = 0.47), nor did forced flight and control females differ in body mass (ANOVA F1,33 = 0.007, p = 0.93). The pattern of the number of eggs laid over time was not linear. Females generally reached a peak in egg production by day 3 after which the number of eggs laid declined (Figure 1, significant quadratic term; (day of oviposition)2 t322 = -4.63, p < 0.001). There were no other significant interaction effects.
Egg size
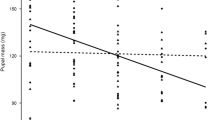
As females aged, increasingly smaller eggs were laid; eggs laid later in the oviposition period are significantly smaller than those laid early. This decline was linear (day of oviposition t143 = -20.63, p < 0.001; Figure 2; non-significant quadratic term not included in final model). There were no differences in egg size between females forced to fly and the controls (flight treatment t33 = 0.62, p = 0.54; Figure 2). There was no effect of female body mass on egg size (female body mass t33 = 0.65, p = 0.52). There were no significant interaction effects.
Maternal effects during early development (pre-viral inoculation)
Embryonic development time
Both maternal age (i.e. day of oviposition) and egg size significantly explained variation in embryonic development (an increase with maternal age t239 = 2.55, p = 0.011, Figure 3; a decrease with egg size t239 = -2.82, p = 0.0052, Figure 4). Both effects were required in the model as the effect of maternal age on embryonic development time was not only as a result of egg size decreasing over the oviposition period (see earlier). Maternal flight treatment did not affect embryonic development time (t239 = 1.28, p = 0.28). There were no significant interactions.
Relationship between embryonic development time (in days) and day on which the egg was laid. Size of the points is proportional to the frequency of the data points. Smallest point is 1 egg (e.g. egg laid on day 2 and taking 10 days to hatch) and largest corresponds with 40 eggs (e.g. 40 eggs laid on day 2 took 7 days to hatch). Full random slope and intercept lme model fitted was: embryonic development time = egg size + day of oviposition + flight treatment.
Larval mass at 21 days of development
Larvae hatching from large eggs were heavier after 21 days of development than larvae that hatched from small eggs (t193 = 4.52, p << 0.001). There were no size differences between the eggs laid by control and forced flight females (see earlier), but larvae from control mothers were heavier after 21 days of development than larvae from forced flight mothers (control (± SE) = 48.4 ± 2.2 mg, forced flight (± SE) = 39.2 ± 2.1 mg; flight treatment). There was a significant day of oviposition by flight treatment interaction (t193 = 2.64 p = 0.0082; Figure 5). As mothers age, offspring larval mass declines, and this maternal age-specific decline in offspring mass was more pronounced in control compared to forced flight mothers (Figure 5).
Relationship between larval mass at 21 days of development (mg) and the day on which the egg was laid. Larvae had mothers that either had been forced to fly or were controls as indicated. For each of these two groups the linear relationship between development time and day of oviposition is indicated as modelled in the random slope lme model (see text). Full random slope lme model fitted was: √(larval mass at 21 days of development) = egg size + day of oviposition + flight treatment + flight treatment*day of oviposition.
Survival from the egg stage to 21 days of larval development
Larger eggs had a higher chance of survival (effect coefficient = 4.93, z = 2.83, p = 0.0046).
Effects of sub-lethal viral infection
Survival till pupal stage
On average, the size of larvae allocated to either treatment group (i.e. control vs. viral infection) did not differ (F1,229 = 1.56, p = 0.21). Larval mass at day 21 (effect coefficient = 0.022, z = 2.068, p = 0.039), and the viral treatment (effect coefficient = -1.67, z = -3.49, p = 0.00049) had a significant impact on larval survival from day 21 till pupation. Larger larvae had a higher probability of survival, and so did the controls (survival probability, controls (± SE) = 0.94 ± 0.021, infected (± SE) = 0.78 ± 0.042). There were no significant interaction effects.
Survival till the adult stage
Additional mortality occurred in the pupal stage, and the only factor that adequately explained this mortality was viral treatment (effect coefficient = -1.45, z = -3.86, p = 0.00011). Control pupae had a higher chance of surviving than the viral treatment pupae (survival probability, controls (± SE) = 0.91 ± 0.025, infected (± SE) = 0.69 ± 0.046).
Larval development time
Larval development time was significantly influenced by egg size (t144 = -2.61, p = 0.010) and an interaction between day of oviposition and flight treatment (t144 = -2.69, p = 0.0080; Figure 6). Offspring hatching from large eggs developed faster, and overall those from mothers that had been forced to fly took longer to develop (larval development time in days: control (± SE) = 36.39 ± 0.41, forced flight (± SE) = 37.45 ± 0.42). The significant interaction between day of oviposition and flight treatment is primarily the result of very fast developers from eggs laid by control females early in the oviposition period (Figure 6). Viral treatment had no effect on larval development time (t144 = 0.099, p = 0.92). Female offspring developed more slowly than male offspring (t144 = -6.49, p << 0.0001; females (± SE) = 38.72 ± 0.44 days; males (± SE) = 35.17 ± 0.40 days).
Total larval development time (days) of the larvae that successfully pupated for each of the sampled oviposition days. Larvae had mothers that either had been forced to fly or were controls as indicated. For each of these two groups the linear relationship between development time and day of oviposition is indicated as modelled in the random slope lme model (see text). Full fitted random slope lme model: √(larval development time) = egg size + day of oviposition + flight treatment + flight treatment*day of oviposition + viral treatment + sex.
Pupal mass
There was no effect of egg size (t145 = 1.26, p = 0.21), day of oviposition (t145 = 0.11, p = 0.91), flight treatment (t145 = -0.65, p = 0.52) or viral treatment (t145 = 0.79, p = 0.43). There was a significant difference between the sexes (t145 = -11.77, p < 0.0001); females were heavier than males (females (± SE) = 121.34 ± 1.03 mg; males (± SE) = 104.67 ± 0.96 mg).
Discussion
Maternal condition can generate resource-related maternal effects through changes in egg provisioning which can greatly influence offspring growth and survival (for reviews see; [1–4]). In the present study, we observed age-related effects on embryonic development time; with eggs laid by old mothers have longer embryonic development times. Maternal flight treatment influenced maternal reproductive output and this study is the first to demonstrate that increased flight during the oviposition period can reduce both maternal fecundity and the quality or composition of eggs. Changes in maternal egg provisioning due to flight treatment had a direct influence on larval mass and development time. Offspring with lower larval masses had reduced survival after exposure to the viral pathogen.
In P. aegeria, a decline in reproductive output with maternal age has been previously reported and is hypothesised to result from a decline in maternal resources over time [7, 51, 52]. In line with these previous studies, we observed that daily fecundity (after an initial peak on day 3 of oviposition) and egg size both decline over time with maternal age. Contrary to previous studies on other insect species, we found that offspring from older mothers did not differ in; survival during the egg and larval stages [5–8], larval development time [9–12] or pupal mass [9, 10]. We did find, however, that maternal age significantly influenced embryonic development time; with eggs laid by older mothers having longer embryonic development times. This suggests that age-related changes in maternal condition generate resource-related maternal effects that influence P. aegeria embryonic development [1, 30].
Many previous studies, across a wide range of taxa, have observed that egg size can influence offspring fitness [1–4]. In the present study, we found that egg size significantly influenced P. aegeria offspring development and survival. Offspring from large eggs had significantly shorter embryonic development times, increased larval masses after 21 days of development, shorter larval development times, and higher egg to adult survival. Although larvae from small eggs had longer larval development times, offspring from large and small eggs did not differ in pupal mass. This suggests that offspring from small eggs compensate for a smaller size early in development by growing and feeding for longer (and see [7]).
Forced flight treatment significantly affected female reproductive output. Relative to control females, females forced to fly laid significantly fewer eggs per day, particularly during the first six days of the oviposition period. There was, however, no effect of flight treatment on egg size. This is an interesting finding because a previous study demonstrated that increased flight prior to the onset of oviposition reduces egg size (but not fecundity) in P. aegeria [7]. In the present study, however, a much more intensive flight treatment was used and females were stimulated to fly several times across the oviposition period (rather than once prior to the onset of oviposition as in the previous study). A resource allocation trade-off between fecundity and dispersal has been previously demonstrated in range expanding populations of P. aegeria [20]. It is possible, therefore, that the intensive flight treatment used during this experiment also resulted in a decreased resource investment to egg production rather than to egg size. Further experiments are required, however, to determine whether these differences observed across studies are due to differences in flight duration (or intensity) per se, or due to other context-dependent factors including (amongst others), population-specific differences in response to flight, or across-study differences in the temperature used during the flight treatment and the oviposition period.
Larvae from eggs laid by females forced to fly had significantly smaller masses (at 21 days of development) and longer larval development times. Given that there were no differences in egg size across flight treatment groups, these results strongly indicate egg provisioning differences between flight treatment groups that are over and above those related to egg size per se. As far as we are aware, this is the first study to show that flight during the oviposition period can affect reproductive output both in terms of reducing fecundity and in reducing the quality or composition of resources in eggs. This result also indicates the potential for flight-induced changes in maternal egg provisioning to continue exerting effects later in offspring development. There was, however, no effect of maternal flight treatment on pupal mass. This suggests that offspring from forced flight mothers compensate for a smaller size early in development by growing and feeding for longer.
Viral infection negatively affected survival to both pupation and the adult stage. Effective resistance to pathogens is often dependent on resource availability [37], because resource availability improves body condition and also immune system deployment [38]. It is well recorded that lepidopteran larvae can demonstrate developmental resistance to baculovirus infection and this is often attributed to increasing body weights during larval development [53]. In the present study, offspring with a small larval body mass (at 21 days of development and hence at the time of viral inoculation) had a lower survival to pupation, suggesting that these offspring had reduced resistance to AcMNPV. Further experiments are required, however, to distinguish whether this effect on body masses arises through developmental resistance or through resource allocation to the immune system. Although flight-induced changes in maternal egg provisioning did result in larvae with small masses (at 21 days of development and hence at the time of viral inoculation) we found no significant main effect of flight linking the impact of maternal flight on larval mass. An absence of a direct effect of flight per se may not mean, however, that this maternal effect has no importance from an ecological perspective because the net effect is still a reduction in offspring fitness. As such, given the higher susceptibility of smaller larvae to viral infection it would be anticipated that there would be an indirect effect of maternal flight on offspring survival.
Viral infection had no detectable sub-lethal effects on larval development time and pupal mass. There are inconsistencies in studies of the sub-lethal effects of baculoviruses on lepidopteran larval development rate with some demonstrating little or no effect when early instars are treated (e.g.[54, 55]) whilst others demonstrate significant effects [32–36]. Contrary to our expectations, relative to control larvae, infected larvae did not grow for longer to gain sufficient resources for both immune system deployment and to obtain the critical mass required for pupation. This result probably reflects a reduction in variation in offspring phenotypes due to differential survival at each stage of development; larvae from small/poorly provisioned eggs fail to hatch, small larvae die during early larval development, more small larvae then die due to viral infection, leaving only the most robust, faster growing larvae to complete their development. Overall, this leads to the conclusion that although a decrease in maternal egg provisioning does reduce larval mass, which in turn decreases offspring survival probability, this reduction in mass does not necessarily confer an additional sub-lethal cost to larvae when they are exposed to a viral infection.
Conclusion
This study clearly demonstrates that in P. aegeria, changes in maternal condition due to age, or increased flight during the oviposition period, can generate resource-related maternal effects with consequences for offspring performance across the whole of development from egg to adulthood. In some species, activation of the immune system can influence adult dispersal, particularly if immune system activation indicates a high infection risk in the present habitat [56]. Pararge aegeria has attracted attention in studies of distribution and dispersal in response to climate change (e.g. [57]), and in studies of evolutionary trade-offs at both expanding range margins (e.g. [58, 59]) and in relation to habitat fragmentation (e.g. [60]). Although duration of our forced flight is longer than estimates from previous studies of average female P. aegeria flight periods in the field (12-90 s; for a detailed discussion of flight in female P. aegeria see [24]), it remains difficult to determine exactly how relevant our flight treatment is for drawing conclusions about the cost of flight in nature. What is clear from our results, however, is that even a small increase in flight during the oviposition period induces variation in resource allocation to reproduction which generates cross-generational maternal effects that have the potential to influence population dynamics [61]. We suggest, therefore, that more consideration needs to be given to the role that flight-induced maternal effects may play in these ecological processes [61].
References
Mousseau TA, Dingle H: Maternal effects in insect life histories. Ann Rev Entomol. 1991, 36: 511-534. 10.1146/annurev.en.36.010191.002455.
Bernardo J: Maternal effects in animal ecology. Am Zool. 1996, 36: 83-105.
Mousseau T, Fox CW: Maternal effects as adaptations. 1998, Oxford University Press
Uller T: Developmental plasticity and the evolution of parental effects. Trends Ecol Evol. 2008, 23: 432-438. 10.1016/j.tree.2008.04.005.
Simmons LW: The contribution of multiple mating and spermatophore consumption to the lifetime reproductive success of female field crickets (Gryllus bimaculatus). Ecol Entomol. 1988, 13: 57-69. 10.1111/j.1365-2311.1988.tb00333.x.
Geister TL, Lorenz MW, Meyering-Vos M, Hoffmann KH, Fischer K: Effects of temperature on reproductive output, egg provisioning, juvenile hormone and vitellogenin titres in the butterfly Bicyclus anynana. J Insect Physiol. 2008, 54: 1253-1260. 10.1016/j.jinsphys.2008.06.002.
Gibbs M, Breuker CJ, Van Dyck H: Flight during oviposition reduces maternal egg provisioning and influences offspring development in Pararge aegeria (L.). Physiol Entomol. 2010, 35: 29-39. 10.1111/j.1365-3032.2009.00706.x.
Wallin H, Chiverton PA, Ekbom BS, Borg A: Diet, fecundity and egg size in some polyphagous predatory carabid beetles. Entomol Exp Appl. 1992, 65: 129-140. 10.1007/BF00221363.
Steinwascher K: Egg size variation in Aedes aegypti - Relationship to body size and other variables. Am Midland Nat. 1984, 112: 76-84. 10.2307/2425459.
Rossiter MC: Maternal effects generate variation in life-history - Consequences of egg weight plasticity in the gypsy moth. Func Ecol. 1991, 5: 386-393. 10.2307/2389810.
Fox CW, Dingle H: Dietary mediation of maternal age effects on offspring performance in a seed beetle (Coleoptera, Bruchidae). Func Ecol. 1994, 8: 600-606. 10.2307/2389921.
Benton TG, St Clair JJH, Plaistow SJ: Maternal effects mediated by maternal age: from life histories to population dynamics. J Anim Ecol. 2008, 77: 1038-1046. 10.1111/j.1365-2656.2008.01434.x.
Honek A: Regulation of body size in a Heteropteran bug, Pyrrhocoris apterus. Entomol Exp Appl. 1987, 44: 257-262. 10.1007/BF00369187.
Solbreck C, Olsson R, Anderson DB, Forare J: Size, life-history and responses to food shortage in two geographical strains of a seed bug Lygaeus equestris. Oikos. 1989, 55: 387-396. 10.2307/3565599.
Tauber CA, Tauber MJ, Tauber MJ: Egg size and taxon - Their influence on survival and development of Chrysopid hatchlings after food and water deprivation. Can J Zool. 1991, 69: 2644-2650. 10.1139/z91-372.
Torres-Vila LM, Rodriguez-Molina MC: Egg size variation and its relationship with larval performance in the Lepidoptera: the case of the European grapevine moth Lobesia botrana. Oikos. 2002, 99: 272-283. 10.1034/j.1600-0706.2002.990207.x.
Lamb RJ, Smith SM: Comparison of egg size and related life-history characteristics for two predaceous tree-hole mosquitos (Toxorhynchites) (Diptera, Culicidae). Can J Zool. 1980, 58: 2065-2070. 10.1139/z80-283.
Sota T, Mogi M: Interspecific variation in desiccation survival-time of Aedes (Stegomyia) mosquito eggs is correlated with habitat and egg size. Oecologia. 1992, 90: 353-358. 10.1007/BF00317691.
Johnson CG: Physiological factors in insect migration by flight. Nature. 1963, 198: 423-427. 10.1038/198423a0.
Hughes CL, Hill JK, Dytham C: Evolutionary trade-offs between reproduction and dispersal in populations at expanding range boundaries. Proc R Soc Lond B. 2003, 270: S147-S150. 10.1098/rsbl.2003.0049.
Jervis MA, Boggs CL, Ferns PN: Egg maturation strategy and its associated trade-offs: a synthesis focusing on Lepidoptera. Ecol Entomol. 2005, 30: 359-375. 10.1111/j.0307-6946.2005.00712.x.
Hanski I, Saastamoinen M, Ovaskainen O: Dispersal-related life-history trade-offs in a butterfly metapopulation. J Anim Ecol. 2006, 75: 91-100. 10.1111/j.1365-2656.2005.01024.x.
Gibbs M, Lace LA, Jones MJ, Moore AJ: Egg size-number trade-off and a decline in oviposition site choice quality: Female Pararge aegeria butterflies pay a cost of having males present at oviposition. J Insect Sci. 2005, 5: 39-available online: insectscience.org/5.39
Gibbs M, Van Dyck H: Butterfly flight activity affects reproductive performance and longevity relative to landscape structure. Oecologia. 2010, 163: 341-350. 10.1007/s00442-010-1613-5.
Gibbs M, Van Dyck H, Karlsson B: Reproductive plasticity, ovarian dynamics and maternal effects in response to temperature and flight in Pararge aegeria. J Insect Physiol. 2010, 56: 1275-1283. 10.1016/j.jinsphys.2010.04.009.
Giron D, Casas J: Mothers reduce egg provisioning with age. Ecol Letters. 2003, 6: 273-277. 10.1046/j.1461-0248.2003.00429.x.
Karl I, Lorenz MW, Fischer K: Energetics of reproduction: consequences of divergent selection on egg size, food limitation, and female age for egg composition and reproductive effort in a butterfly. Biol J Linn Soc. 2007, 91: 403-418. 10.1111/j.1095-8312.2007.00806.x.
Cheverud JM, Leamy LJ, Atchley WR, Rutledge JJ: Quantitative genetics and the evolution of ontogeny.1. Ontogenetic changes in quantitative genetic variance-components in Random bred mice. Genetical Res. 1983, 42: 65-75. 10.1017/S0016672300021492.
Wolf JB, Brodie ED, Cheverud JM, Moore AJ, Wade MJ: Evolutionary consequences of indirect genetic effects. Trends Ecol Evol. 1998, 13: 64-69. 10.1016/S0169-5347(97)01233-0.
Bernardo J: The particular maternal effect of propagule size, especially egg size: Patterns, models, quality of evidence and interpretations. Am Zool. 1996, 36: 216-236.
Zuk M, Stoehr AM: Immune defense and host life history. Am Nat. 2002, 160: S9-S22. 10.1086/342131.
Matthews HJ, Smith I, Edwards JP: Lethal and sublethal effects of a granulovirus on the tomato moth Lacanobia oleracea. J Invert Path. 2002, 80: 73-80. 10.1016/S0022-2011(02)00100-3.
Milks ML, Burnstyn I, Myers JH: Influence of larval age on the lethal and sublethal effects of the nucleopolyhedrovirus of Trichoplusia ni in the cabbage looper. Biol Control. 1998, 12: 119-126. 10.1006/bcon.1998.0616.
Monobrullah M, Shankar U: Sub-lethal effects of SpltMNPV infection on developmental stages of Spodoptera litura (Lepidoptera: Noctuidae). Biocontrol Sci Technol. 2008, 18: 431-437. 10.1080/09583150801994137.
Sait SM, Begon M, Thompson DJ: The effects of a sublethal baculovirus infection on the Indian meal moth Plodia interpunctella. J Anim Ecol. 1994, 63: 541-550. 10.2307/5220.
Sait SM, Begon M, Thompson DJ: The influence of larval age on the response of Plodia interpunctella to a granulovirus virus. J Invert Path. 1994, 63: 107-110. 10.1006/jipa.1994.1020.
Lee KP, Cory JS, Wilson K, Raubenheimer D, Simpson SJ: Flexible diet choice offsets protein costs of pathogen resistance in a caterpillar. Proc R Soc Lond B. 2006, 273: 823-829. 10.1098/rspb.2005.3385.
Lee KP: Ecological factors impacting on the nutritional biology of a generalist and specialist caterpillar: effects of pathogens and plant structural compounds on macro nutrient balancing. 2002, Zoology Department & Wolfson College. Oxford University, Oxford
Shreeve TG: Egg laying by the speckled wood butterfly (Pararge aegeria): the role of female behaviour, plant abundance and temperature. Ecol Entomol. 1986, 11: 229-236. 10.1111/j.1365-2311.1986.tb00298.x.
Wickman PO, Wiklund C: Territorial defense and its seasonal decline in the speckled wood butterfly (Pararge aegeria). Anim Behav. 1983, 31: 1206-1216. 10.1016/S0003-3472(83)80027-X.
Karlsson B: Variation in egg weight, oviposition rate and reproductive reserves with female age in a natural population of the speckled wood butterfly, Pararge aegeria. Ecol Entomol. 1987, 12: 473-476. 10.1111/j.1365-2311.1987.tb01029.x.
Bink FA: Ecologische atlas van de dagvlinders van Noordwest-Europa. 1992, Harlem, The Netherlands, Schultz & Co
Karlsson B: Feeding habits and change of body composition with age in three nymphalid butterfly species. Oikos. 1994, 69: 224-230. 10.2307/3546142.
Svärd L, Wiklund C: Mass and production rates of ejaculates in relation to monandry/polyandry in butterflies. Behav Ecol Sociobiol. 1989, 24: 395-402. 10.1007/BF00293267.
Murphy DD, Launer AE, Ehrlich PR: The role of adult feeding in egg production and population dynamics of the checkerspot butterfly Euphydryas editha. Oecologia. 1983, 56: 257-263. 10.1007/BF00379699.
Jervis MA, Ellers J, Harvey JA: Resource acquisition, allocation, and utilization in parasitoid reproductive strategies. Ann Rev Entomol. 2008, 53: 361-385. 10.1146/annurev.ento.53.103106.093433.
Hunter-Fajita FR, Entwistle PF, Evans HF, Crook NE: Insect viruses and pest management. 1998, Chichester, John Wiley and Sons
Cory JS, Goulson D: Flower constancy and learning in foraging preferences of the green veined butterfly Pieris napi. Ecol Entomol. 1993, 18: 315-320. 10.1111/j.1365-2311.1993.tb01107.x.
Bauerfeind SS, Fischer K: Maternal body size as a morphological constraint on egg size and fecundity in butterflies. Basic Appl Ecol. 2008, 9: 443-451. 10.1016/j.baae.2007.05.005.
Goulson D, Cory JS: Sublethal effects of baculovirus in the cabbage moth, Mamestra brassicae. Biol Control. 1995, 5: 361-367. 10.1006/bcon.1995.1042.
Wiklund C, Persson B: Fecundity, and the relation of egg weight variation to offspring fitness in the speckled wood butterfly Pararge aegeria, or why don't butterfly females lay more eggs?. Oikos. 1983, 40: 53-63. 10.2307/3544198.
Wiklund C, Karlsson B: Egg size variation in satyrid butterflies: adaptive vs. historical, "Bauplan", and mechanistic explanations. Oikos. 1984, 43: 391-400. 10.2307/3544158.
Evans HF: Quantitative assessment of the relationships between dosage and response of the nuclear polyhedrosis virus of Mamestra brassicae. J Invert Path. 1981, 37: 101-109. 10.1016/0022-2011(81)90061-6.
Perelle AH, Harper JD: An evaluation of the impact of sublethal dosages of nuclear polyhedrosis virus in larvae, on pupae, adults, and adult progeny of the fall armyworm, Spodoptera frugiperda. J Invert Path. 1986, 47: 42-47. 10.1016/0022-2011(86)90161-8.
Shapiro M, Robertson JL: Yield and activity of gypsy moth (Lepidoptera: Lymantriidae) nucleopolyhedrosis virus recovered from survivors of viral challenge. J Econ Entomol. 1987, 80: 901-905.
Suhonen J, Honkavaara J, Rantala MJ: Activation of the immune system promotes insect dispersal in the wild. Oecologia. 2010
Hill JK, Thomas CD, Huntley B: Climate and habitat availability determine 20th century changes in a butterfly's range margin. Proc R Soc Lond B. 1999, 266: 1197-1206. 10.1098/rspb.1999.0763.
Hill JK, Dytham C, Hughes CL: Evolutionary changes in expanding butterfly populations. Insect Evolutionary Ecology. Edited by: Fellowes MDE, Holloway GJ, Rolff J. 2005, CABI Publishing
Hughes CL, Dytham C, Hill JK: Modelling and analysing evolution of dispersal in populations at expanding range boundaries. Ecol Entomol. 2007, 32: 437-445. 10.1111/j.1365-2311.2007.00890.x.
Merckx T, Van Dyck H: Landscape structure and phenotypic plasticity in flight morphology in the butterfly Pararge aegeria. Oikos. 2006, 113: 226-232. 10.1111/j.2006.0030-1299.14501.x.
Gibbs M, Van Dyck H: Reproductive plasticity, oviposition site selection and maternal effects in fragmented landscapes. Behav Ecol Sociobiol. 2009, 64: 1-11. 10.1007/s00265-009-0849-8.
Acknowledgements
MG was supported by funding to HVD (FRFC research grant 2.4595.07 of the Fund of Scientific Research FRS-FNRS and FSR06 grant of the Université catholique de Louvain, UCL) and a mobility grant to MG within the framework of this FRFC research project. This is publication no BRC 197 of the Biodiversity Research Centre (UCL). HVD was also funded by ARC grant no 10/15-031 of the Académie Universitaire Louvain. HH and RSH were funded by the Environmental Change Integrating Fund through the NERC (Natural Environment Research Council) Centre for Ecology and Hydrology (CEH). The authors are grateful to Emma Turner for practical assistance. Steven White and Helen Roy provided valuable comments on an earlier version of this manuscript.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Authors' contributions
MG conceived of the study, carried out the experiments and drafted the manuscript. CJB performed the statistical analyses and helped draft the manuscript. HH designed the inoculation method, carried out the baculovirus production and helped draft the manuscript. RSH provided statistical advice and helped draft the manuscript. HVD coordinated and helped draft the manuscript. All authors participated in the design of the study and read and approved the final manuscript.
Authors’ original submitted files for images
Below are the links to the authors’ original submitted files for images.
Rights and permissions
Open Access This article is published under license to BioMed Central Ltd. This is an Open Access article is distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License ( https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/2.0 ), which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original work is properly cited.
About this article
Cite this article
Gibbs, M., Breuker, C.J., Hesketh, H. et al. Maternal effects, flight versus fecundity trade-offs, and offspring immune defence in the Speckled Wood butterfly, Pararge aegeria. BMC Evol Biol 10, 345 (2010). https://doi.org/10.1186/1471-2148-10-345
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1186/1471-2148-10-345