Abstract
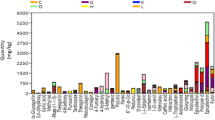
The healing properties of Salvia officinalis L., Lamiaceae, sage are well known. The presence of high levels of polyphenols in S. officinalis leaves is responsible for many of the therapeutic benefits of the herb. This study used ultra-high-performance liquid chromatography coupled with quadrupole-time-of-flight mass spectrometry in conjunction with extensive mass spectral libraries to identify the polyphenols with high sensitivity. The study aimed to evaluate the effectiveness of six different traditional extraction procedures (fresh tissue homogenization, fresh and dry leaf decoction, and their respective fermentation) for efficient recovery of phytochemicals using data-independent acquisition in negative electrospray ionization mode. The concentrations of caffeic acid (477.57 ± 7.26 μg/g) and rosmarinic acid (13,694.13 ± 112.06 μg/g) in fermented dry leaf decoctions were found to be significantly higher than in other extracts. However, the dry leaf decoction yielded significantly higher levels of the flavonoid luteolin-7-O-glucoside (691.60 ± 9.81 μg/g) and the terpenoids carnosol, carnosic acid, and ursolic acid (215.61 ± 4.92 μg/g, 529.61 ± 9.61 μg/g, and 19.90 ± 0.22 μg/g, respectively). Two flavonoid compounds, diosmetin ([M-H]− m/z 299.0554) and pectolinarigenin ([M-H]− m/z 313.0715), were identified for the first time in S. officinalis. Among fifty-four identified polyphenols, gallocatechin, scutellarin, sagerinic acid, salvianolic acids, pectolinarigenin, rosmanol, rosmadial, and 12-methoxy carnosic acid were found in higher intensities. Dry leaf decoction and its fermentation were found to be the most efficient traditional extraction methods for polyphenols in S. officinalis.
Graphical abstract

Similar content being viewed by others
References
Ariffin F, Heong Chew S, Bhupinder K, Karim AA, Huda N (2011) Antioxidant capacity and phenolic composition of fermented Centella asiatica herbal teas. J Sci Food Agric 91:2731–2739. https://doi.org/10.1002/jsfa.4454
Cvetkovikj I, Stefkov G, Acevska J, Stanoeva JP, Karapandzova M, Stefova M, Dimitrovska A, Kulevanova S (2013) Polyphenolic characterization and chromatographic methods for fast assessment of culinary Salvia species from South East Europe. J Chromatogr A 1282:38–45. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chroma.2012.12.068
Ghisoni S, Chiodelli G, Rocchetti G, Kane D, Lucini L (2017) UHPLC-ESI-QTOF-MS screening of lignans and other phenolics in dry seeds for human consumption. J Funct Foods 34:229–236. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jff.2017.04.037
Ghorbani A, Esmaeilizadeh M (2017) Pharmacological properties of Salvia officinalis and its components. J Tradit Complement Med 7:433–440. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jtcme.2016.12.014
Hamidpour M, Hamidpour R, Hamidpour S, Shahlari M (2014) Chemistry, pharmacology and medicinal property of sage (Salvia) to prevent and cure illnesses such as obesity, diabetes, depression, dementia, lupus, autism, heart disease and cancer. J Tradit Complement Med 4:82–88. https://doi.org/10.4103/2225-4110.130373
Heong CS, Bhupinder K, Huda N, Karim AA, Fazilan A (2011) Effect of fermentation on the composition of Centella asiatica teas. Am J Food Technol 6:581–593. https://doi.org/10.3923/ajft.2011.581.593
Hunaefi D, Smetanska I (2013) The effect of tea fermentation on rosmarinic acid and antioxidant properties using selected in vitro sprout culture of Orthosiphon aristatus as a model study. SpringerPlus 2:1–14. https://doi.org/10.1186/2193-1801-2-167
Kamatou P, Viljoen A, Steenkamp P (2009) Antioxidant, anti-inflammatory activities and HPLC analysis of South African Salvia species. Food Chem 119:684–688. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.foodchem.2009.07.010
Kumar S, Singh A, Kumar B (2017) Identification and characterization of phenolics and terpenoids from ethanolic extracts of Phyllanthus species by HPLC-ESI-QTOF-MS/MS. J Pharm Anal 2:214–222. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jpha.2017.01.005
Li H, Yao W, Liu Q, Xu J, Bao B, Shan M, Cao Y, Cheng F, Ding A, Zang L (2017) Application of UHPLC-ESI-Q-TOF-MS to identify multiple constituents in processed products of the herbal medicine Ligustri Lucidi Fructus. Molecules 22:689. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules22050689
Lim H, Son KH, Chang HW, Bae K, Kang SS, Kim HP (2008) Anti-inflammatory activity of pectolinarigenin and pectolinarin isolated from Cirsium chanroenicum. Biol Pharm Bull 31:2063–2067. https://doi.org/10.1248/bpb.31.2063
Lopresti AL (2017) Salvia (Sage): a review of its potential cognitive-enhancing and protective effects. Drugs R D 17:53–64. https://doi.org/10.1007/s40268-016-0157-5
Lu Y, Foo LY (1999) Rosmarinic acid derivatives from Salvia officinalis. Phytochemistry 51:91–94. https://doi.org/10.1016/s0031-9422(98)00730-4
Lu Y, Foo LY (2002) Polyphenolics of Salvia - a review. Phytochemistry 59:117–140. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0031-9422(01)00415-0
Madala NE, Piater L, Dubery I, Steenkamp P (2016) Distribution patterns of flavonoids from three Momordica species by ultra-high performance liquid chromatography quadrupole time of flight mass spectrometry: a metabolomics profiling approach. Rev Bras Farmacogn 26:507–513. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bjp.2016.03.009
Martins N, Barros L, Santos-Buelga C, Henriques M, Silva S, Ferreira ICFR (2015) Evaluation of bioactive properties and phenolic compounds in different extracts prepared from Salvia officinalis L. Food Chem 170:378–385. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.foodchem.2014.08.096
Mercolini L, Protti M, Saracino MA, Mandrone M, Antognoni F (2016) Analytical profiling of bioactive phenolic compounds in argan (Argania spinosa) leaves by combined microextraction by packed sorbent (MEPS) and LC–DAD-MS/MS. Phytochem Anal 27:41–49. https://doi.org/10.1002/pca.2585
Mishra AK, Gupta A, Gupta V, Sand R, Bansal P (2010) Asava and arishta: an Ayurvedic medicine – an overview. Int J Pharm Biol Arch 1:24–30
Mulay S, Khale A (2011) Asavarishtas through improved fermentation technology. Int J Pharm Sci Res 2:1421–1425. https://doi.org/10.13040/IJPSR.0975-8232.2(6).1421-25
Neagu E, Paun G, Radu GL (2014) Chemical composition and antioxidant activity of Salvia officinalis concentrated by ultrafiltration. Rom Biotechnol Lett 19:9203–9211
Pandey A, Tripathi S (2014) Concept of standardization, extraction and pre phytochemical screening strategies for herbal drug. J Pharmacogn Phytochem 115:115–119
Panse VG, Sukhatme PV (1985) Statistical methods for agricultural workers. ICAR, New Delhi
Patel K, Gadewar M, Tahilyani V, Patel DK (2013) A review on pharmacological and analytical aspects of diosmetin: a concise report. Chin J Integr Med 19:792–800. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11655-013-1595-3
Qiang Z, Ye Z, Hauck C, Murphy PA, McCoy JA, Widrlechner MP, Reddy M, Hendrich S (2011) Permeability of rosmarinic acid in Prunella vulgaris and ursolic acid in Salvia officinalis extracts across Caco-2 cell monolayers. J Ethnopharmacol 137:1107–1112. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jep.2011.07.037
Sabu A, Haridas M (2015) Fermentation in ancient Ayurveda: its present implications. Front Life Sci 8:324–331. https://doi.org/10.1080/21553769.2015.1041165
Sayyad SF, Randive DS, Jagtap SM, Chaudhari SR, Panda BP (2012) Preparation and evaluation of fermented Ayurvedic formulation: Arjunarishta. J Appl Pharm Sci 5:122–124. https://doi.org/10.7324/JAPS.2012.2521
Sharma Y, Fagan J, Schaefer J (2019) Ethnobotany, phytochemistry, cultivation and medicinal properties of garden sage (Salvia officinalis L.). J Pharmacogn Phytochem 8:3139–3148
Tandon S, Rane S (2008) Decoction and hot continuous extraction techniques. In: Handa SS, Khanuja SPS, Longo G (eds) Extraction technologies for medicinal and aromatic plants. ICS- UNIDO, Trieste, pp 93–106
Valiathan MS (2007) The legacy of Susruta. Orient Longman Pvt Ltd, Hyderabad
Wang J, Xu J, Gong X, Yang M, Zhang C, Li M (1998) Antioxidative phenolic compounds from sage (Salvia officinalis). J Agric Food Chem 46:4869–4873. https://doi.org/10.1021/jf980614b
Zimmermann BF, Walch SG, Tinzoh LN, Stühlinger W, Lachenmeier DW (2011) Rapid UHPLC determination of polyphenols in aqueous infusions of Salvia officinalis L. (sage tea). J Chromatogr B 879:2459–2464. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jchromb.2011.06.038
Acknowledgments
Special thanks are given to Health Research Institute, Fairfield, IA, for providing the facility to analyze the samples.
Funding
The research received funding from Soil Technologies Corporation (Fairfield, IA 52556, USA).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
YS and KV: extraction, analysis, and interpretation; JF and JS: critical review
Corresponding author
Electronic Supplementary Material
ESM 1
(PDF 1544 kb).
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Sharma, Y., Velamuri, R., Fagan, J. et al. UHPLC-ESI-QTOF-Mass Spectrometric Assessment of the Polyphenolic Content of Salvia officinalis to Evaluate the Efficiency of Traditional Herbal Extraction Procedures. Rev. Bras. Farmacogn. 30, 701–708 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s43450-020-00106-5
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s43450-020-00106-5