Abstract
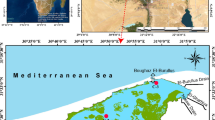
This paper investigated the heavy minerals of coastal sediments, economic prospect and potential placer mining for the extraction of beach sediments. The Cox’s Bazar has been considered as a good source of heavy minerals which has covered approximately 120 km area at the southeastern coast of Bangladesh. The present study includes several deposition points, such as Kutubdia, Dhalghata, Sonadia, Diabetes Point, Sunny Beach Point, Laboni Point, Sughandha, Kolatoli, Doria Nagar, Himchori, Inani, Patuartek, across over the north to south Cox’s Bazar Sea beach. Physical separation technique (density, magnetic, and electric) was used to separate heavy minerals from beach sediments. In total coastal areas, the beaches of Inani, Sugandha, Sonadia, Teknaf, and Laboni points have deposited a higher portion of heavy mineral which is around 46%. The investigation has identified as many as 19 varieties of heavy minerals in collected samples from different areas of the beach. Some of them are Ilmenite, Kyanite, Garnet, Rutile, Zircon, Magnetite, Augite, Hornblende, Enstatite, Epidote, Andalusite, Hypersthene, Diopside, and Cassiterite. However, Ilmenite, Zircon, Garnet, Rutile, Magnetite, and Topaz (Silica) were found in higher quantity overall the areas. A placer mining method for extraction has been recommended based on heavy mineral content, ocean wave direction, sedimentation rate, and equipment cost estimation.







Similar content being viewed by others
References
Abdur Rouf, M. (2012). Investigation of radioactivity level in heavy minerals of Cox's bazar beach sand by neutron activation analysis. Bangladesh University of Engineering and Technology, Retrieved from http://lib.buet.ac.bd:8080/xmlui/handle/123456789/4089. Accessed Oct 2022.
Ahmed, A., Nawaz, R., Drake, F., & Woulds, C. (2018). Modelling land susceptibility to erosion in the coastal area of Bangladesh: A geospatial approach. Geomorphology, 320, 82–97. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.geomorph.2018.08.004
Ahmed, M. T., Quamruzzaman, C., Khan, F. H., & Mehnaz, N. (2019). Coal sludge management approach: A case study on Barapukuria Coal Mine, Dinajpur, Bangladesh. International Journal of Emerging Technology and Advanced Engineering, 9(6), 8–16.
Alam, M., Huq, N., & Rashid, M. (1999). Morphology and sediments of the Cox's Bazar coastal plain, south-east Bangladesh. Journal of coastal Research, 15(4), 902–908.
Ali Elbeblawi, M. M., Abdelhak Elsaghier, H. A., Mohamed Amin, M. T., & Elrawy Abdellah, W. R. (2022). Introduction to mining. In M. M. Ali Elbeblawi, H. A. Abdelhak Elsaghier, M. T. Mohamed Amin, & W. R. Elrawy Abdellah (Eds.), Surface mining technology (pp. 1–23) Springer, Singapore. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-981-16-3568-7_1
Amiruddin. (2018). Distribution of basic sediments (bedload transport) on changes in coastal coastline Donggala, Central Sulawesi Province, Indonesia. Journal of Physics: Conference Series, 983, 012032. https://doi.org/10.1088/1742-6596/983/1/012032
Bailey, S. W., Weege, R. J., Cameron, E. N., & Spedden, H. J. E. G. (1956). The alteration of ilmenite in beach sands. Economic Geology, 51(3), 263–279.
Baloyi, V. D., & Meyer, L. D. (2020). The development of a mining method selection model through a detailed assessment of multi-criteria decision methods. Results in Engineering, 8, 100172. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.rineng.2020.100172
Bari, Z., Rajib, M., & Ameen, S. M. (2011). Heavy mineral assemblages of the beach sands of Kuakata, southern Bangladesh, Jahangirnagar. University Journal of Science, 34, 143–158.
Bose, S. (2006). Environmental accounting and reporting in fossil fuel sector: a study on Bangladesh Oil, Gas and Mineral Corporation (Petrobangla).
BSMEC. (1994). Brochure on Beach Sand Mineral Exploitation Centre (BSMEC), Cox’s Bazar, Bangladesh. Atomic Energy Commission.
Burt, C. N., & Caccetta, L. (2014). Equipment selection for surface mining: A review. Interfaces, 44(2), 143–162.
Chakhmouradian, A. R., & Wall, F. J. E. (2012). Rare earth elements: Minerals, mines, magnets (and more). Elements, 8(5), 333–340.
De Groot, A., Zschuppel, K., & Salomons, W. J. H. (1982). Standardization of methods of analysis for heavy metals in sediments. Hydrobiologia, 91, 689–695.
Deeba, F., Kabir, M. Z., Zaman, M. M., Rajib, M., & Rana, S. M. (2009). Difference in grain size distribution among heavy minerals of Cox’s Bazar, Barchara, Patuartek and Teknaf Fore Dune Deposit. In: Proceed. of Int. Confer. on Geosci. for Glob. Dev, pp. 26–31.
Elsner, H. (2013). Heavy minerals of economic importance:(ilmenite and Leucoxene, Rutile, Zircon, Monazite and Xenotime, Kyanite, Sillimanite and Andalusite, Staurolite, Garnet, Chromite, Magnetite, Cassiterite, Columbite-tantalite, Wolframite and Scheelite). BGR.
Farazi, A. H., Mia, A. J., & Mahmud, M. I. (2018). A case study based slope stability analysis at Chittagong City, Bangladesh. Journal of Geoscience, Engineering, Environment, and Technology, 3(3), 164–173.
Fondriest. (2021). Sediment Transport and Deposition. Retrieved from https://www.fondriest.com/environmental-measurements/parameters/hydrology/sediment-transport-deposition/. Accessed Oct 2022.
Garzanti, E., & Andò, S. (2007). Heavy mineral concentration in modern sands: Implications for provenance interpretation. Developments in Sedimentology, 58, 517–545.
Ghosal, S., Agrahari, S., & Sengupta, D. (2022). Provenance studies on the heavy mineral placers along the coastal deposits of Odisha, eastern India. Journal of Palaeogeography, 11(2), 275–285. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jop.2022.03.003
Goonan, T. G. (2012). Materials Flow of Indium in the United States in 2008 and 2009: US Department of the Interior, US Geological Survey.
Gujar, A. R., Ambre, N. V., Mislankar, P. G., & Iyer, S. D. JRg. (2010). Ilmenite, magnetite and chromite beach placers from South Maharashtra, central west coast of India. Resource Geology, 60(1), 71–86.
Haldar, S. K. (2013). Chapter 2—Economic mineral deposits and host rocks. In S. K. Haldar (Ed.), Mineral exploration (pp. 23–39). Elsevier.
Hasan, A. S. M. M., Hossain, I., Rahman, M. A., Zaman, M. N., Biswas, P. K., & Alam, M. S. (2022). Chemistry and mineralogy of Zr- and Ti-rich minerals sourced from Cox’s Bazar beach placer deposits, Bangladesh: Implication of resources processing and evaluation. Ore Geology Reviews, 141, 104687. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.oregeorev.2021.104687
Hossain, H. M. Z., Tarek, M., Armstrong-Altrin, J. S., Monir, M. M. U., Ahmed, M. T., Ahmed, S. I., & Hernandez-Coronado, C. J. (2014). Microtextures of detrital sand grains from the Cox’s Bazar beach, Bangladesh: Implications for provenance and depositional environment. Carpathian Journal of Earth and Environmental Sciences, 9(3), 187–197.
Ingram, R. L. (1971). Sieve Analysis. In R. E. Carver (Ed.), Procedures in Sedimentary Petrology (pp. 49–69). Wiley Interscience, New York.
Islam, M. S., Quamruzzaman, C., Monir, M. M. U., Jahan, S., & Begum, M. (2014). Petrography Of The Basement Complex Of Maddhapara Mining (Production Level) Dinajpur District, Bangladesh. Journal of Engineering. Computers & Applied Sciences (JEC&AS), 3, 1–9.
Jayawardena, U. de S., & Indratilaka, H. M. L. (2015). Use of dune sand as an alternative for river sand for construction industry in Sri Lanka. In: G. Lollino, A. Manconi, F. Guzzetti, M. Culshaw, P. Bobrowsky, & F. Luino (Eds.), Engineering Geology for Society and Territory-Volume 5 (pp. 1277–1280). Springer, Cham. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-319-09048-1_243
Jóźwiakowski, K., Marzec, M., Fiedurek, J., Kamińska, A., Gajewska, M., Wojciechowska, E., Wu, S., Dach, J., Marczuk, A., & Kowlaczyk-Juśko, A. (2017). Application of H2O2 to optimize ammonium removal from domestic wastewater. Separation and Purification Technology, 173, 357–363. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.seppur.2016.08.047
Kabir, M., Deeba, F., Majumder, R., Khalil, M., & Islam, M. (2018). Heavy mineral distribution and geochemical studies of coastal sediments at Sonadia island. Bangladesh. Nuclear Science and Application, 27(1), 2.
Khan, R., Rouf, M. A., Das, S., Tamim, U., Naher, K., Podder, J., & Hossain, S. M. (2017). Spatial and multi-layered assessment of heavy metals in the sand of Cox’s-Bazar beach of Bangladesh. Regional Studies in Marine Science, 16, 171–180.
Mange, M. A., & Maurer, H. (2012). Heavy minerals in colour. Springer Science & Business Media.
McKelvey, V. E. J. A. S. (1972). Mineral resource estimates and public policy: Better methods for estimating the magnitude of potential mineral resources are needed to provide the knowledge that should guide the design of many key public policies. American Scientist, 60(1), 32–40.
Monir, M. M. U. (2014). Estimation of vertical distance and Reduce Level using modern mine survey equipments (Total Station) at sub level in Madhapara Granite mine, Bangladesh. International Journal of Advances in Applied Sciences, 3(2), 75–81.
Monir, M. M. U., & Hossain, H. Z. (2012). Coal mine accidents in Bangladesh: Its causes and remedial measures. International Journal of Economic and Environmental Geology, 3, 33–40.
Munizaga-Rosas, J. C., & Percca, E. L. (2022). Advanced analytics for mine materials handling. In A. Soofastaei (Ed.), Advanced analytics in mining engineering (pp. 557–612). Springer International Publishing.
Otto, J., Andrews, C. B., Cawood, F., Doggett, M., Guj, P., Stermole, F., Stermole, J., & Tilton, J. (2006). Mining royalties: A global study of their impact on investors, government, and civil society. The World Bank.
Rahman, A., Tardio, J., Bhargava, S. K., Zaman, M. N., Hasan, A. S. M. M., Torpy, A., & Pownceby, M. I. (2020a). Comparison of the chemistry and mineralogy of ilmenite concentrates sourced from fluvial (Brahmaputra River) and beach placer (Cox’s Bazar) deposits, Bangladesh. Ore Geology Reviews, 117, 103271. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.oregeorev.2019.103271
Rahman, M. J. J., Bari, Z., Chodhury, K. R., & Suzuki, S. (2008). Heavy mineral composition of the Neogene sandstones and beach sands across the Inani-Dakhin Nhila area, Southeast Bangladesh: Implications for provenance. Journal of the Sedimentological Society of Japan, 67(1), 3–17.
Rahman, M. J. J., Pownceby, M., & Rana, M. S. (2020b). Occurrence and distribution of valuable heavy minerals in sand deposits of the Jamuna River. Bangladesh. Ore Geology Reviews, 116, 103273.
Rajib, M., & Oguchi, C. T. (2020). Radioactive and rare earth containing materials in beach minerals of Bangladesh: A SEM study. In: Proc. of International Conference on Earth & Environmental Sciences and Technology, ICGR-O32. pp. 134–140.
Ramani, R. V. (2012). Surface mining technology: Progress and prospects. Procedia Engineering, 46, 9–21.
Singh, Y. (2020). Beach sand deposits. In Y Singh (Ed.), Rare earth element resources: Indian context (pp. 31–60). Springer, Cham.
Stebbins, S. A. (1987). Cost estimation handbook for small placer mines (Vol. 9170). US Department of the Interior Bureau of Mines.
Walker, R. (2006). Automated accounting system that values, controls, records and bills the uses of equipment/vehicles for society. In: Google Patents.
Xia, Q.-X., Zheng, Y.-F., & Hu, Z. (2010). Trace elements in zircon and coexisting minerals from low-T/UHP metagranite in the Dabie orogen: Implications for action of supercritical fluid during continental subduction-zone metamorphism. Lithos, 114(3–4), 385–412.
Zaman, M. M., Rajib, M., Kabir, M. Z., Deeba, F., Rana, S. M., Hossain, S. M., Latif, S. A., & Rasul, M. G. (2016). Presence of uranium and thorium in zircon assemblages separated from beach sands of Cox’s Bazar, Bangladesh. Journal of Science Technology and Environment Informatics, 3(01), 161–169. https://doi.org/10.18801/jstei.030116.18
Zaman, M., Schubert, M., & Antao, S. (2012). Elevated radionuclide concentrations in heavy mineral-rich beach sands in the Cox’s Bazar region, Bangladesh and related possible radiological effects. Isotopes in Environmental and Health Studies, 48(4), 512–525.
Acknowledgements
We would like to express our heartfelt appreciation to the Beach Sand Minerals Exploitation Centre, Bangladesh Atomic Energy Commission, Kalatoli, Cox's Bazar-4700, Bangladesh, and the Energy Conversion Laboratory, Department of Petroleum and Mining Engineering, Jashore University of Science and Technology, Jashore-7408, Bangladesh, for providing us with laboratory assistance in analyzing beach sand samples.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
Conceptualization and Methodology: MTA, MUM and MR; Formal analysis, data collection, and investigation: MTA, MUM, MR, SMS and YH; Writing—original draft preparation: MTA, MUM, MR; Writing—review and editing: CQ, AAA, MFHK, NH, FH, FAA, SMS; Supervision: MUM and MTA; All authors read and approved the final manuscript.
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Competing interests
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Communicated by M. V. Alves Martins
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Ahmed, M.T., Monir, M.U., Rajib, M. et al. Heavy minerals identification and extraction along coastal sediments using placer mining technique. J. Sediment. Environ. 8, 81–95 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s43217-022-00120-8
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s43217-022-00120-8