Abstract
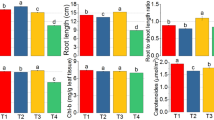
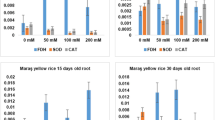
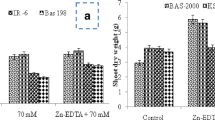
Salinity is a key abiotic stress that limits the plant growth and productivity of crops worldwide. In this study, variations in the growth, physiological and biochemical parameters, and antioxidant defense systems under saline soil conditions among three rice cultivars (Ahlami-Tarom, Salari, and Binam) were investigated. Our results indicated that the all rice cultivars had normal growth and yield under control conditions. All the parameters tested were significantly different in the environments studied (stress vs. control). For all three genotypes, salinity induced a significant decrease in growth characteristics, chlorophyll content and grain yield. By contrast an increase in lipid peroxidation and activity of antioxidant enzymes were observed in all rice cultivars. Among the cultivars studied, Binam genotype with the highest increase in the activity of antioxidant enzymes such as catalase, ascorbate peroxidase, and peroxidase, the lowest increase in malondialdehyde content and smaller drop in chlorophyll content showed better protection against salt stress, which made it possible to maintain a higher yield even under stress conditions. The findings of the present study suggested that the activity of antioxidant enzymes can act as an efficient defense mechanism to deal with salinity stress, and accordingly, the potential tolerance of Binam cultivar with a good antioxidant defense system increases its yield compared to other cultivars under salinity stress conditions.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Aebi H (1984) Catalase in vitro. Methods Enzymol 105:121–126. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0076-6879(84)05016-3
Ali S, Gautam RK, Mahajan R, Krishnamurthy SL, Sharma SK, Singh RK, Ismail AM (2013) Stress indices and selectable traits in SALTOL QTL introgressed rice genotypes for reproductive stage tolerance to sodicity and salinity stresses. Field Crops Res 154:65–73. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.fcr.2013.06.011
Arnon DI (1949) Copper enzymes in isolated chloroplasts. Polyphenol oxidase in Beta vulgaris. Plant Physiol 24:1–15. https://doi.org/10.1104/pp.24.1.1
Ashraf M, Harris P (2013) Photosynthesis under stressful environments: an overview. Photosynthetica 51:163–190. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11099-013-0021-6
Bagheri AA, Khosravinejad F (2016) Study of biochemical parameters and antioxidant enzymes activities on Oryza sativa under salt stress. Quart J Develop Biol 8:1–10
Bagheri L, saadatmand S, Soltani N, Niknam V, (2020) Study of physiological and biochemical responses of rice mutant lines derived from gamma ray irradiation and local varieties under saline field conditions. J Plant Environ Physiol 15(59):30–42
Barus WA, Tarigan DM, Lubis RF (2019) The growth and biochemical characteristics of some upland rice varieties in conditions of salinity stress. Int J Sci Tech Res 8(11):1673–1676
Bouyoucos GJ (1962) Hydrometer method improved for making particle size analysis of soils. Agron J 54:464–465. https://doi.org/10.2134/agronj1962.00021962005400050028x
Bremner JM, Mulvaney CS (1982) Nitrogen-total. In: Page AL, Miller RH, Keeney DR (eds) Methods of soil analysis. Part 2. Chemical and microbiological properties, Agronomy Monographs, ASA, SSSA, Madison, Wisconsin, USA. pp 595‒624
Chunthaburee S, Dongsansuk A, Sanitchon J, Pattanagul W, Theerakulpisut P (2016) Physiological and biochemical parameters for evaluation and clustering of rice cultivars differing in salt tolerance at seedling stage. Saudi J Biol Sci 23(4):467–477. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.sjbs.2015.05.013
Chutipaijit S, Cha-Um S, Sompornpailnd KD (2009) Differential accumulation of proline and flavonoids in indica rice varieties against salinity. Pak J Bot 41:2497–2506
Elsheery NI, Cao KF (2008) Gas exchange, chlorophyll fluorescence, and osmotic adjustment in two mango cultivars under drought stress. Acta Physiol Planta 30:769–777. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11738-008-0179-x
FAO (2010) Food and agriculture organization of the united nations desertification
Forough M, Navbpour S, Ebrahimie E, Ebadi AA, Kiani D (2018) Evaluation of salinity response through the antioxidant defense system and osmolyte accumulation in a mutant rice. J Plant Mol Breed 6(2):27–37
Ghadirnezhad Shiade SR, Esmaeili M, Pirdashti H, Nematzadeh GA (2020) Physiological and biochemical evaluation of sixth generation of rice (Oryza sativa L.) mutant lines under salinity stress. J Plant Proc Func 9(35):58–72
Ghosh B, Ali MdN, Saikat G (2016) Response of rice under salinity stress: a review update. Rice Res 4:167. https://doi.org/10.4172/2375-4338.1000167
Heath R, Packer L (1968) Photoperoxidation in isolated chloroplasts. I. Kinetics and stoichiometry of fatty acid peroxidation. Arch Biochem Biophys 125:189–198. https://doi.org/10.1016/0003-9861(68)90654-1
Hosseini SJ, Tahmasebi Z, Pirdashti H (2012) Screening of rice (Oryza sativa L.) genotypes for NaCl tolerance at early seedling stage. Int J Agron Plant Produc 3(8):274–283
Jankangram W, Thammasirirak S, Jones MG, Hartwell J, Theerakulpisut P (2011) Proteomic and transcriptomic analysis reveals evidence for the basis of salt sensitivity in Thai jasmine rice (Oryza sativa L. cv. KDML 105). African J Biotech 10(72):16157–16166. https://doi.org/10.5897/AJB11.1559
Kibria MG, Hossain M, Murata Y, Hoque MdA (2017) Antioxidant defense mechanisms of salinity tolerance in rice genotypes. Rice Sci 24(3):155–162. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.rsci.2017.05.001
Kong W, Sun T, Zhang C, Deng X, Li Y (2021) Comparative transcriptome analysis reveals the mechanisms underlying differences in salt tolerance between indica and japonica rice at seedling stage. Front Plant Sci 12:725436
Kordrostami M, Rabiei B, Hassani Kumleh H (2017) Biochemical, physiological and molecular evaluation of rice cultivars differing in salt tolerance at the seedling stage. Physiol Mol Biol Plants 23(3):529–544. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12298-017-0440-0
Kumar S, Li G, Yang J, Huang X, Ji Q, Liu Z, Ke W, Hou H (2021) Effect of salt stress on growth, physiological parameters, and ionic concentration of water dropwort (Oenanthe javanica) cultivars. Front Plant Sci 12:660409. https://doi.org/10.3389/fpls.2021.660409
Li YF, Zheng Y, Vemireddy LR, Panda SK, Jose S, Ranjan A, Panda P, Govindan G, Cui j, Wei K, Yaish MW, Naidoo GC, Sunkar R, (2018) Comparative transcriptome and translatome analysis in contrasting rice genotypes reveals differential mRNA translation in salt-tolerant Pokkali under salt stress. BMC Genom 19:935. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12864-018-5279-4
Manjappa Uday G, Hittalmani S (2014) Association analysis of drought and yield related traits in F2 population of Moroberekan/IR64 rice cross under aerobic condition. Int J Agric Sci Res 4(2):79–88
Meloni DA, Oliva MA, Martinez CA, Cambraia J (2003) Photosynthesis and activity of superoxide dismutase, peroxidase and glutathione reductase in cotton under salt stress. Environ Exp Bot 49:69–76. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0098-8472(02)00058-8
Moraditelavat M, Alamisaeed K, Karmollachaab A, Hasanvand H (2018) Response antioxidant enzymes, lipid peroxidation and cell death of rice cultivars to salinity stress. J Plant Proc Func 6(19):293–302
Nakano Y, Asada K (1981) Hydrogen peroxide is scavenged by ascorbate peroxidase in spinach chloroplasts. Plant Cell Physiol 22(5):867–880. https://doi.org/10.1093/oxfordjournals.pcp.a076232
Olsen SR, Cole CV, Watanabe FS, Dean LA (1954) Estimation of available phosphorus in soils by extraction with sodium bicarbonate. Circ. 939. USDA, Washington, DC. 19 p.
Rahneshan Z, Nasibi F, Moghadam AA (2018) Effects of salinity stress on some growth, physiological, biochemical parameters and nutrients in two pistachio (Pistacia vera L.) rootstocks. J Plant Interact 13:73–82. https://doi.org/10.1080/17429145.2018.1424355
Reddy INBL, Kim BK, Yoon IS, Kim KH, Kwon TR (2017) Salt tolerance in rice: Focus on mechanisms and approaches. Rice Sci 24:123–144. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.rsci.2016.09.004
Rossatto T, do Amaral MN, Benitez LC, Vighi IL, Braga EJB, de Magalhães Júnior AM, Maia MAC, da Silva Pinto L (2017) Gene expression and activity of antioxidant enzymes in rice plants, cv. BRS AG, under saline stress. Physiol Mol Biol Plants 23(4):865–875. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12298-017-0467-2
Saeidzadeh F, Taghizadeh R, Ghorbanof E (2018) Investigation the effect of salinity on agronomic and biochemical traits of different rice cultivars under field conditions. Crop Physiol J 9(36):101–120
Saha P, Chatterjee P, Biswas AK (2010) NaCl pretreatment alleviates salt stress by enhancement of antioxidant defense system and osmolyte accumulation in mungbean (Vigna radiata L. Wilczek). Indian J Exp Biol 48:593–600
Sahin U, Ekinci M, Ors S, Turan M, Yildiz S, Yildirim E (2018) Effects of individual and combined effects of salinity and drought on physiological, nutritional and biochemical properties of cabbage (Brassica oleracea var. capitata). Sci Hortic 240:196–204. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scienta.2018.06.016
Singh MP, Singh DK, Rai M (2007) Assessment of growth, physiological and biochemical parameters and activities of antioxidative enzymes in salinity tolerant and sensitive basmati rice varieties. J Agron Crop Sci 193:398–412. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1439-037X.2007.00267.x
Soares C, Carvalho MEA, Azevedo RA, Fidalgo F (2019) Plants facing oxidative challenges—A little help from the antioxidant networks. Environ Exp Bot 161:4–25. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.envexpbot.2018.12.009
Stepien P, Klobus G (2005) Antioxidant defense in the leaves of C3 and C4 plants under salinity stress. Physiol Planta 125:31–40. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1399-3054.2005.00534.x
Taibi K, Taibi F, Abderrahim LA, Ennajah A, Belkhodja M, Mulet JM (2016) Effect of salt stress on growth, chlorophyll content, lipid peroxidation and antioxidant defence systems in Phaseolus vulgaris L. South African J Bot 105:306–312. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.sajb.2016.03.011
Toth SJ, Prince AL (1949) Estimation of cation exchange capacity and exchangeable Ca, K and Na contents of soils by flame photometer techniques. Soil Sci 67:439–446. https://doi.org/10.1097/00010694-194906000-00003
Velikova V, Yordanov I, Edreva A (2000) Oxidative stress and some antioxidant systems in acid rain-treated bean plants. Plant Sci 151:59–66. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0168-9452(99)00197-1
Yaghubi M, Nematzadeh GA, Pirdashti H, Modarresi M, Motaghian A (2014) The effects of salinity on antioxidant enzymes activity in the leaves of two contrast rice (Oryza sativa L) cultivars. Int J Biosci 4(11):116–125
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Communicated by J. Zimny.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Talubaghi, M.J., Daliri, M.S., Mazloum, P. et al. Effect of salt stress on growth, physiological and biochemical parameters and activities of antioxidative enzymes of rice cultivars. CEREAL RESEARCH COMMUNICATIONS 51, 403–411 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s42976-022-00314-w
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s42976-022-00314-w