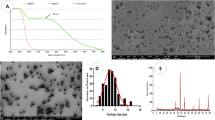
Abstract
Due to the severity of infections caused by P. aeruginosa and the limitations in treatment, it is necessary to find new therapeutic alternatives. Thus, the use of silver nanoparticles (AgNPs) is a viable alternative because of their potential actions in the combat of microorganisms, showing efficacy against Gram-positive and Gram-negative bacteria, including multidrug-resistant microorganisms (MDR). In this sense, the aim of this work was to conduct a literature review related to the antibacterial and antibiofilm activity of AgNPs against antibiotic-sensitive and multidrug-resistant Pseudomonas aeruginosa strains. The AgNPs are promising for future applications, which may match the clinical need for effective antibiotic therapy. The size of AgNPs is a crucial element to determine the therapeutic activity of nanoparticles, since smaller particles present a larger surface area of contact with the microorganism, affecting their vital functioning. AgNPs adhere to the cytoplasmic membrane and cell wall of microorganisms, causing disruption, penetrating the cell, interacting with cellular structures and biomolecules, and inducing the generation of reactive oxygen species and free radicals. Studies describe the antimicrobial activity of AgNPs at minimum inhibitory concentration (MIC) between 1 and 200 μg/mL against susceptible and MDR P. aeruginosa strains. These studies have also shown antibiofilm activity through disruption of biofilm structure, and oxidative stress, inhibiting biofilm growth at concentrations between 1 and 600 μg/mL of AgNPs. This study evidences the advance of AgNPs as an antibacterial and antibiofilm agent against Pseudomonas aeruginosa strains, demonstrating to be an extremely promising approach to the development of new antimicrobial systems.


Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
Not applicable.
References
World health organization (2017) Global antimicrobial resistance surveillance system (GLASS) report: early implementation 2016–2017. Geneva. Available on: https://apps.who.int/iris/bitstream/handle/10665/259744/9789241513449-eng.pdf;jsessionid=DF103DA3FE5FA323F5E291D17C64FF65?sequence=1. Accessed 3 June 2020
Munita JM, Arias CA (2016) Mechanisms of antibiotic resistance. Microbiol Spectr 4. https://doi.org/10.1128/microbiolspec.VMBF-0016-2015
McCracken M, Mataseje LF, Loo V, Walkty A, Adam HJ, Hoban DJ, Zhanel GG, Mulvey MR (2011) Characterization of Acinetobacter baumannii and meropenem-resistant Pseudomonas aeruginosa in Canada: results of the CANWARD 2007–2009 study. Diagn Microbiol Infect Dis 69(3):335–341. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.diagmicrobio.2010.10.030
Yong D, Toleman MA, Bell J, Ritchie B, Pratt R, Ryley H, Walsh TR (2012) Genetic and biochemical characterization of an acquired subgroup B3 metallo-β-lactamase gene, blaAIM-1, and its unique genetic context in Pseudomonas aeruginosa from Australia. Antimicrob Agents Chemother 56(12):6154–6519. https://doi.org/10.1128/AAC.05654-11
Kim MJ, Bae IK, Jeong SH, Kim SH, Song JH, Choi JY, Yoon SS, Thamlikitkul V, Hsueh PR, Yasin RM, Lalitha MK (2013) Dissemination of metallo-β-lactamase-producing Pseudomonas aeruginosa of sequence type 235 in Asian countries. J Antimicrob Chemother 68(12):2820–2824. https://doi.org/10.1093/jac/dkt269
Mudau M, Jacobson R, Minenza N, Kuonza L, Morris V, Engelbrecht H, Nicol MP, Bamford C (2013) Outbreak of multi-drug resistant Pseudomonas aeruginosa bloodstream infection in the haematology unit of a South African Academic Hospital. PLoS One 8(3):e55985. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0055985
Labarca JA, Salles MJ, Seas C, Guzmán-Blanco M (2016) Carbapenem resistance in Pseudomonas aeruginosa and Acinetobacter baumannii in the nosocomial setting in Latin America. Crit Rev Microbio 42(2):276–292. https://doi.org/10.3109/1040841X.2014.940494
Horcajada JP, Montero M, Oliver A, Sorlí L, Luque S, Gómez-Zorrilla S, Benito N, Grau S (2019) Epidemiology and treatment of multidrug-resistant and extensively drug-resistant Pseudomonas aeruginosa infections. Clin Microbiol Rev 32(4) pii: e00031-19. https://doi.org/10.1128/CMR.00031-19
Chen Q, Shah KN, Zhang F, Salazar AJ, Shah PN, Li R, Sacchettini JC, Wooley KL, Cannon CL (2019) Minocycline and silver dual-loaded polyphosphoester-based nanoparticles for treatment of resistant Pseudomonas aeruginosa. Mol Pharm 16(4):1606–1619. https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.molpharmaceut.8b01288
Chen J, Chen Y, Hu P, Zhou T, Xu X, Pei X (2018) Risk assessment of infected children with Pseudomonas aeruginosa pneumonia by combining host and pathogen predictors. Infec Genet Evol 57:82–87. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.meegid.2017.11.015
Liao S, Zhang Y, Pan X, Zhu F, Jiang C, Liu Q, Cheng Z, Dai G, Wu G, Wang L, Chen L (2019) Antibacterial activity and mechanism of silver nanoparticles against multidrug-resistant Pseudomonas aeruginosa. Int J Nanomedicine 14:1469–1487. https://doi.org/10.2147/IJN.S191340
Mann EE, Wozniak DJ (2012) Pseudomonas biofilm matrix composition and niche biology. FEMS Microbiol Rev 36(4):893–916. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1574-6976.2011.00322.x
Dingemans J, Al-Feghali RE, Lau GW, Sauer K (2019) Controlling chronic Pseudomonas aeruginosa infections by strategically interfering with the sensory function of SagS. Mol Microbiol 111(5):1211–1228. https://doi.org/10.1111/mmi.14215
Habash MB, Goodyear MC, Park AJ, Surette MD, Vis EC, Harris RJ, Khursigara CM (2017) Potentiation of tobramycin by silver nanoparticles against Pseudomonas aeruginosa biofilms. Antimicrob Agents Chemother 61(11). pii: e00415-17. https://doi.org/10.1128/AAC.00415-17
Cavalcanti IM, Pontes-Neto JG, Kocerginsky PO, Bezerra-Neto AM, Lima JL, Lira-Nogueira MC, Maciel MA, Neves RP, Pimentel MF, Santos-Magalhães NS (2015) Antimicrobial activity of β-lapachone encapsulated into liposomes against meticillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus and Cryptococcus neoformans clinical strains. J Glob Antimicrob Resist 2:103–108. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jgar.2015.03.007
Lima R, Del Fiol FS, Balcão VM (2019) Prospects for the use of new technologies to combat multidrug-resistant bacteria. Front Pharmacol 10:692. https://doi.org/10.3389/fphar.2019.00692
Quezada CQ, Azevedo CS, Charneau S, Santana JM, Chorilli M, Carneiro MB, Bastos IM (2019) Advances in nanocarriers as drug delivery systems in Chagas disease. Int J Nanomedicine 14:6407–6424. https://doi.org/10.2147/IJN.S206109
Bamburowicz-Klimkowska M, Poplawska M, Grudzinski IP (2019) Nanocomposites as biomolecules delivery agents in nanomedicine. J Nanobiotechnology 17(1):48. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12951-019-0479-x
Le Ouay B, Stellacci F (2015) Antibacterial activity of silver nanoparticles: a surface science insight. Nano Today 10(3):339–354. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.nantod.2015.04.002
Chernousova S, Epple M (2013) Silver as antibacterial agent: ion, nanoparticle, and metal. Angew Chem Int Ed Engl 52(6):1636–1653. https://doi.org/10.1002/anie.201205923
Chen G, Roy I, Yang C, Prasad PN (2016) Nanochemistry and nanomedicine for nanoparticle-based diagnostics and therapy. Chem Rev 116(5):2826–2885. https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.chemrev.5b00148
Iravani S, Korbekandi H, Mirmohammadi SV, Zolfaghari B (2014) Synthesis of silver nanoparticles: chemical, physical and biological methods. Res Pharm Sci 9(6):385–406
Güzel R, Erdal G (2018) Synthesis of silver nanoparticles. In: Maaz K (ed) Silver nanoparticles—fabrication. Characterization and Applications. Intechopen, London, pp 03–20
Abbasi E, Milani M, Fekri Aval S, Kouhi M, Akbarzadeh A, Tayefi Nasrabadi H, Nikasa P, Joo SW, Hanifehpour Y, Nejati-Koshki K, Samiei M (2014) Silver nanoparticles: synthesis methods, bio-applications and properties. Crit Rev Microbiol 42(2):173–180. https://doi.org/10.3109/1040841X.2014.912200
Beyene HD, Werkneh AA, Bezabh HK, Ambaye TG (2017) Synthesis paradigm and applications of silver nanoparticles (AgNPs), a review. Sustain Mater Technol 13:18–23. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.susmat.2017.08.001
Zhang XF, Liu ZG, Shen W, Gurunathan S (2016) Silver nanoparticles: synthesis, characterization, properties, applications, and therapeutic approaches. Int J Mol Sci 17(9):1534. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms17091534
Perito B, Giorgetti E, Marsili P, Muniz-Miranda M (2016) Antibacterial activity of silver nanoparticles obtained by pulsed laser ablation in pure water and in chloride solution. Beilstein J Nanotechnol 7:465–473. https://doi.org/10.3762/bjnano.7.40
Tsuji T, Iryo K, Watanabe N, Tsuji M (2002) Preparation of silver nanoparticles by laser ablation in solution: influence of laser wavelength on particle size. Appl Surf Sci 202(1–2):80–85. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0169-4332(02)00936-4
Lee SH, Jun BH (2019) Silver nanoparticles: synthesis and application for nanomedicine. Int J Mol Sci 20(4):865. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms20040865
Mathur P, Jha S, Ramteke S, Jain NK (2018) Pharmaceutical aspects of silver nanoparticles. Artif Cell Nanomed 46(1):115–126. https://doi.org/10.1080/21691401.2017.1414825
Scotti L, Angelini G, Gasbarri C, Bucciarelli T (2017) Uncoated negatively charged silver nanoparticles: speeding up the electrochemical synthesis. Mater Res Express 4(10):105001. https://doi.org/10.1088/2053-1591/aa8c39
Almadiy AA, Nenaah GE (2018) Ecofriendly synthesis of silver nanoparticles using potato steroidal alkaloids and their activity against phytopathogenic fungi. Braz Arch Biol 61(1):1–14. https://doi.org/10.1590/1678-4324-2018180013
Ge L, Li Q, Wang M, Ouyang J, Li X, Xing MM (2014) Nanosilver particles in medical applications: synthesis, performance, and toxicity. Int J Nanomedicine 9(1):2399. https://doi.org/10.2147/IJN.S55015
Ojo OA, Oyinloye BE, Ojo AB, Afolabi OB, Peters OA, Olaiya O, Fadaka A, Jonathan J, Osunlana O (2017) Green synthesis of silver nanoparticles (AgNPs) using Talinum triangulare (Jacq.) Willd. Leaf extract and monitoring their antimicrobial activity. J Bionanosci 11(4):292–296. https://doi.org/10.1166/jbns.2017.1452
Jyoti K, Baunthiyal M, Singh A (2016) Characterization of silver nanoparticles synthesized using Urtica dioica Linn. leaves and their synergistic effects with antibiotics. J Radiat Res Appl Sc 9(3):217–227. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jrras.2015.10.002
Ahmed S, Ahmad M, Swami BL, Ikram S (2016) A review on plants extract mediated synthesis of silver nanoparticles for antimicrobial applications: a green expertise. J Adv Res 7(1):17–28. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jare.2015.02.007
Rajeshkumar S, Bharath LV (2017) Mechanism of plant-mediated synthesis of silver nanoparticles—a review on biomolecules involved, characterisation and antibacterial activity. Chem Biol Interact 273:219–227. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cbi.2017.06.019
Kumar M, Curtis A, Hoskins C (2018) Application of nanoparticle technologies in the combat against antimicrobial resistance. Pharmaceutics 10(1):11. https://doi.org/10.3390/pharmaceutics10010011
Prabhu S, Poulose EK (2012) Silver nanoparticles: mechanism of antimicrobial action, synthesis, medical applications, and toxicity effects. Int Nano Lett 2(1):32
Dhand V, Soumya L, Bharadwaj S, Chakra S, Bhatt D, Sreedhar B (2016) Green synthesis of silver nanoparticles using Coffea arabica seed extract and its antibacterial activity. Mater Sci Eng C 58:36–43. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.msec.2015.08.018
Dakal TC, Kumar A, Majumdar RS, Yadav V (2016) Mechanistic basis of antimicrobial actions of silver nanoparticles. Front Microbiol 7:1831. https://doi.org/10.3389/fmicb.2016.01831
Kędziora A, Speruda M, Krzyżewska E, Rybka J, Łukowiak A, Bugla-Płoskońska G (2018) Similarities and differences between silver ions and silver in nanoforms as antibacterial agents. Int J Mol Sci 19(2):444. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms19020444
Cassir N, Rolain JM, Brouqui P (2014) A new strategy to fight antimicrobial resistance: the revival of old antibiotics. Front Microbiol 5:551. https://doi.org/10.3389/fmicb.2014.00551
Dehnavi AS, Raisi A, Aroujalian A (2013) Control size and stability of colloidal silver nanoparticles with antibacterial activity prepared by a green synthesis method. Synth React Inorg M 43(5):543–551. https://doi.org/10.1080/15533174.2012.741182
Zhang M, Zhang K, De Gusseme B, Verstraete W, Field R (2014) The antibacterial and anti-biofouling performance of biogenic silver nanoparticles by Lactobacillus fermentum. Biofouling 30(3):347–357. https://doi.org/10.1080/08927014.2013.873419
Sadeghi B, Gholamhoseinpoor F (2015) A study on the stability and green synthesis of silver nanoparticles using Ziziphora tenuior (Zt) extract at room temperature. Spectrochim Acta A Mol Biomol Spectrosc 134:310–315. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.saa.2014.06.046
Franci G, Falanga A, Galdiero S, Palomba L, Rai M, Morelli G, Galdiero M (2015) Silver nanoparticles as potential antibacterial agents. Molecules 20(5):8856–8874. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules20058856
Vazquez-Muñoz R, Borrego B, Juárez-Moreno K, García-García M, Morales JD, Bogdanchikova N, Huerta-Saquero A (2017). Toxicity of silver nanoparticles in biological systems: does the complexity of biological systems matter? Toxicology letters 276:(1)11-20. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.toxlet.2017.05.007
Vazquez-Muñoz R, Avalos-Borja M, Castro-Longoria E (2014). Ultrastructural analysis of Candida albicans when exposed to silver nanoparticles. PLoS One 9(10) 1–10. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0108876
Chung IM, Park I, Seung-Hyun K, Thiruvengadam M, Rajakumar G (2016) Plant-mediated synthesis of silver nanoparticles: their characteristic properties and therapeutic applications. Nanoscale Res Lett 11(1):2–14. https://doi.org/10.1186/s11671-016-1257-4
Kora AJ, Arunachalam J (2011) Assessment of antibacterial activity of silver nanoparticles on Pseudomonas aeruginosa and its mechanism of action. World J Microbiol Biotechnol 27(5):1209–1216. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11274-010-0569-2
Gopinath V, MubarakAli D, Priyadarshini S, Priyadharsshini NM, Thajuddin N, Velusamy P (2012) Biosynthesis of silver nanoparticles from Tribulus terrestris and its antimicrobial activity: a novel biological approach. Colloids Surf B Biointerfaces 96:69–74. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.colsurfb.2012.03.023
Amirulhusni AN, Palanisamy NK, Mohd-Zain Z, Ping LJ, Durairaj R (2012) Antibacterial effect of silver nanoparticles on multi drug resistant Pseudomonas aeruginosa. Int J Med Sci Public Health 6(7):291–294. https://doi.org/10.5281/zenodo.1329579
Logeswari P, Silambarasan S, Abraham J (2015) Synthesis of silver nanoparticles using plants extract and analysis of their antimicrobial property. Journal of Saudi Chemical Society 19(3):311–317. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jscs.2012.04.007
Park HJ, Park S, Roh J, Kim S, Choi K, Yi J, Kim Y, Yoon J (2013) Biofilm-inactivating activity of silver nanoparticles: a comparison with silver ions. J Ind Eng Chem 19(2):614–619. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jiec.2012.09.013
Jasuja ND, Gupta DK, Reza M, Joshi SC (2014) Green synthesis of AgNPs stabilized with biowaste and their antimicrobial activities. Braz J Microbiol 45(4):1325–1332. https://doi.org/10.1590/s1517-83822014000400024
Palanisamy NK, Ferina N, Amirulhusni AN, Mohd-Zain Z, Hussaini J, Ping LJ, Durairaj R (2014) Antibiofilm properties of chemically synthesized silver nanoparticles found against Pseudomonas aeruginosa. J nanobiotechnology 12:2. https://doi.org/10.1186/1477-3155-12-2
Singh K, Panghal M, Kadyan S, Chaudhary U, Yadav JP (2014) Antibacterial activity of synthesized silver nanoparticles from Tinospora cordifolia against multi drug resistant strains of Pseudomonas aeruginosa isolated from burn patients. J Nanomed Nanotechnol 5:192. https://doi.org/10.4172/2157-7439.1000192
Markowska K, Grudniak AM, Krawczyk K, Wróbel I, Wolska KI (2014) Modulation of antibiotic resistance and induction of a stress response in Pseudomonas aeruginosa by silver nanoparticles. J Med Microbiol 63(6):849-54. https://doi.org/10.1099/jmm.0.068833-0
Singh K, Panghal M, Kadyan S, Chaudhary U, Yadav JP (2014) Green silver nanoparticles of Phyllanthus amarus: as an antibacterial agent against multi drug resistant clinical isolates of Pseudomonas aeruginosa. J Nanobiotechnol 12:40. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12951-014-0040-x
Ansari MA, Khan HM, Khan AA, Cameotra SS, Saquib Q, Musarrat J (2014) Gum arabic capped-silver nanoparticles inhibit biofilm formation by multi-drug resistant strains of Pseudomonas aeruginosa. J Basic Microbiol 54(7):688–699. https://doi.org/10.1002/jobm.201300748
Bose D, Chatterjee S (2015) Antibacterial activity of green synthesized silver nanoparticles using Vasaka (Justicia adhatoda L.) leaf extract. Indian J Microbiol 55(2):163–167. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12088-015-0512-1
Bose D, Chatterjee S (2016) Biogenic synthesis of silver nanoparticles using guava (Psidium guajava) leaf extract and its antibacterial activity against Pseudomonas aeruginosa. Appl Nanosci 6(6):895–901. https://doi.org/10.1007/s13204-015-0496-5
Arokiyaraj S, Vincent S, Saravanan M, Lee Y, Oh YK, Kim KH (2017). Green synthesis of silver nanoparticles using Rheum palmatum root extract and their antibacterial activity against Staphylococcus aureus and Pseudomonas aeruginosa. Artif Cell Nanomed B 45(2):372–379 https://doi.org/10.3109/21691401.2016.1160403
Yuan YG, Peng QL, Gurunathan S (2017) Effects of silver nanoparticles on multiple drug-resistant strains of Staphylococcus aureus and Pseudomonas aeruginosa from mastitis-infected goats: an alternative approach for antimicrobial therapy. Int J Mol Sci 18(3):569. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms18030569
Salomoni R, Léo P, Montemor AF, Rinaldi BG, Rodrigues MFA (2017) Antibacterial effect of silver nanoparticles in Pseudomonas aeruginosa. Nanotechnol Sci Appl 10:115–121. https://doi.org/10.2147/NSA.S133415
Senthilkumar P, Rashmitha S, Veera P, Ignatious CV, Saipriya C, Samrot AV (2018) Antibacterial activity of neem extract and its green synthesized silver nanoparticles against Pseudomonas aeruginosa.. J Pure App Microbiol 12(2):969-974. https://doi.org/10.22207/JPAM.12.2.60
Devanesan S, AlSalhi MS, Balaji RV, Ranjitsingh AJ, Ahamed A, Alfuraydi AA, AlQahtani FY, Aleanizy FS, Othman AH (2018) Antimicrobial and cytotoxicity effects of synthesized silver nanoparticles from Punica granatum peel extract. Nanoscale rese l 13(1):315. https://doi.org/10.1186/s11671-018-2731-y
Singh P, Pandit S, Garnæs J, Tunjic S, Mokkapati VR, Sultan A, Thygesen A, Mackevica A, Mateiu RV, Daugaard AE, Baun A (2018) Green synthesis of gold and silver nanoparticles from Cannabis sativa (industrial hemp) and their capacity for biofilm inhibition. Int J Nanomedicine 13:3571–3591. https://doi.org/10.2147/IJN.S157958
Shah S, Gaikwad S, Nagar S, Kulshrestha S, Vaidya V, Nawani N, Pawar S (2019) Biofilm inhibition and anti-quorum sensing activity of phytosynthesized silver nanoparticles against the nosocomial pathogen Pseudomonas aeruginosa. Biofouling 35:34–49. https://doi.org/10.1080/08927014.2018.1563686
Silva RT, Petri MV, Valencia EY, Camargo PH, Torresi SI, Spira B (2020) Visible light plasmon excitation of silver nanoparticles against antibiotic-resistant Pseudomonas aeruginosa. BioRxiv. https://doi.org/10.1101/2020.01.10.902676
Ghosh S, Patil S, Ahire M, Kitture R, Kale S, Pardesi K, Cameotra SS, Bellare J, Dhavale DD, Jabgunde A, Chopade BA (2012) Synthesis of silver nanoparticles using Dioscorea bulbifera tuber extract and evaluation of its synergistic potential in combination with antimicrobial agents. Int J Nanomedicine 7:483. https://doi.org/10.2147/IJN.S24793
Jasim R, Schneider EK, Han M, Azad MAK, Hussein M, Nowell C, Baker MA, Wang J, Li J, Velkov T (2017) A fresh shine on cystic fibrosis inhalation therapy: antimicrobial synergy of polymyxin B in combination with silver nanoparticles. J Biomed Nanotechnol 13(4):447–457. https://doi.org/10.1166/jbn.2017.2355
Al-Obaidi H, Kalgudi R, Zariwala MG (2018) Fabrication of inhaled hybrid silver/ciprofloxacin nanoparticles with synergetic effect against Pseudomonas aeruginosa. Eur J Pharm Biopharm 128:27–35. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ejpb.2018.04.006
Dinos GP, Athanassopoulos CM, Missiri DA, Giannopoulou PC, Vlachogiannis IA, Papadopoulos GE, Papaioannou D, Kalpaxis DL (2016) Chloramphenicol derivatives as antibacterial and anticancer agents: historic problems and current solutions. Antibiotics 5(2):20. https://doi.org/10.3390/antibiotics5020020
Zhang X, Wang J, Wu Q, Li L, Wang Y, Yang H (2019) Determination of kanamycin by high performance liquid chromatography. Molecules 24(10):1902. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules24101902
Bruniera FR, Ferreira FM, Saviolli LR, Bacci MR, Feder D, da Luz Goncalves Pedreira M, Sorgini Peterlini MA, Azzalis LA, Campos Junqueira VB, Fonseca FL (2015) The use of vancomycin with its therapeutic and adverse effects: a review. Eur Rev Med Pharmacol Sci 19(4):694–700
Vazquez-Muñoz R, Meza-Villezcas A, Fournier PGJ, Soria-Castro E, Juarez-Moreno K, Gallego-Hernández AL, Bogdanchikova N, Vazquez-Duhalt R, Huerta-Saquero A (2019) Enhancement of antibiotics antimicrobial activity due to the silver nanoparticles impact on the cell membrane. PLoS One 14:e0224904. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0224904
Brasil MSL, Filgueiras AL, Campos MB, Neves MSL, Eugênio M, Sena LA, Sant’Anna CB, Silva VL, Diniz CG, Sant’Ana AC (2018). Synergism in the antibacterial action of ternary mixtures involving silver nanoparticles, chitosan and antibiotics. Journal of the Brazilian Chemical Society 29(10):2026–2033. https://doi.org/10.21577/0103-5053.20180077
Deng H, McShan D, Zhang Y, Sinha SS, Arslan Z, Ray PC, Yu H (2016) Mechanistic study of the synergistic antibacterial activity of combined silver nanoparticles and common antibiotics. Environmental Science & Technology 50(16):8840–8848. https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.est.6b00998
Grant SS, Hung DT (2013) Persistent bacterial infections, antibiotic tolerance, and the oxidative stress response. Virulence 4:273–283. https://doi.org/10.4161/viru.23987
Pérez-Díaz M, Alvarado-Gomez E, Magaña-Aquino M, Sánchez-Sánchez R, Velasquillo C, Gonzalez C, Martinez-Gutierrez F (2016) Anti-biofilm activity of chitosan gels formulated with silver nanoparticles and their cytotoxic effect on human fibroblasts. Mater Sci Eng C 60:317–323. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.msec.2015.11.036
Seth AK, Geringer MR, Hong SJ, Leung KP, Mustoe TA, Galiano RD (2012) In vivo modeling of biofilm-infected wounds: a review. J Surg Res 178:330–338. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jss.2012.06.048
Neethu S, Midhun SJ, Radhakrishnan EK, Jyothis M (2020) Surface functionalization of central venous catheter with mycofabricated silver nanoparticles and its antibiofilm activity on multidrug resistant Acinetobacter baumannii. Microb Pathog 138:103832. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.micpath.2019.103832
Gondil VS, Chhibber S (2018) Exploring potential of phage therapy for tuberculosis using model organism. Biomed Biotechnol Res J 2:9–15. https://doi.org/10.4103/bbrj.bbrj_93_17
Barapatre A, Aadil KR, Jha H (2016) Synergistic antibacterial and antibiofilm activity of silver nanoparticles biosynthesized by lignin-degrading fungus. Bioresour Bioprocess 3(1):3–8. https://doi.org/10.1186/s40643-016-0083-y
Regí MV, González B, Barba II (2019) Nanomaterials as promising alternative in the infection treatment. Int J Mol Sci 20(15):3806. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms20153806
Sharma D, Misba L, Khan AU (2019) Antibiotics versus biofilm: an emerging battleground in microbial communities. Antimicrob Resist Infect Control 8:76. https://doi.org/10.1186/s13756-019-0533-3
Bala Subramaniyan S, Senthilnathan R, Arunachalam J, Anbazhagan V (2019) Revealing the significance of glycan binding property of butea monosperma seed lectin for enhancing the antibiofilm activity of silver nanoparticles against uropathogenic Escherichia coli. Bioconjug Chem 31(1):139–148. https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.bioconjchem.9b00821
Pompilio A, Germiniani C, Bosco D, Rana R, Aceto A, Bucciarelli T, Scotti L, Bonaventura GD (2018) Electrochemically synthesized silver nanoparticles are active against planktonic and biofilm cells of Pseudomonas aeruginosa and other cystic fibrosis-associated bacterial pathogens. Front Microbiol 9:1349. https://doi.org/10.3389/fmicb.2018.01349
Guo J, Quin S, Wei Y, Liu S, Peng H, Li Q, Luo L, Lv M (2019) Silver nanoparticles exert concentration-dependent influences on biofilm development and architecture. Cell Prolif 52(4):e12616. https://doi.org/10.1111/cpr.12616
Arya G, Sharma N, Mankamna R, Nimesh S (2019) Antimicrobial silver nanoparticles: future of nanomaterials. In: Prasad R (ed) Microbial Nanobionics, Basic research and applications, vol 2. Springer, Cham, pp 89–119
Loo CY, Young PM, Cavaliere R, Whitchurch CB, Lee WH, Rohanizadeh R (2014) Silver nanoparticles enhance Pseudomonas aeruginosa PAO1 biofilm detachment. Drug Dev Ind Pharmacy 40(6):719–729. https://doi.org/10.3109/03639045.2013.780182
Radzig MA, Nadtochenko VA, Koksharova OA, Kiwi J, Lipasova VA, Khmel IA (2013) Antibacterial effects of silver nanoparticles on gram-negative bacteria: influence on the growth and biofilms formation, mechanisms of action. Colloids Surf B Biointerfaces 102:300–306. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.colsurfb.2012.07.039
Gurunathan S, Han JW, Kwon DN, Kim JH (2014) Enhanced antibacterial and anti-biofilm activities of silver nanoparticles against gram-negative and gram-positive bacteria. Nanoscale Res Lett 9:373. https://doi.org/10.1186/1556-276X-9-373
Saraswathi VS, Kamarudheen N, BhaskaraRao KV, Santhakumar K (2017) Phytoremediation of dyes using Lagerstroemia speciosa mediated silver nanoparticles and its biofilm activity against clinical strains Pseudomonas aeruginosa. J Photochem Photobiol B 168:107–116. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jphotobiol.2017.02.004
Singh P, Pandit S, Beshay M, Mokkapati VR, Garnaes J, Olsson ME, Sultan A, Mackevica A, Mateiu RV, Lütken H, Daugaard AE (2018) Anti-biofilm effects of gold and silver nanoparticles synthesized by the Rhodiola rosea rhizome extracts. Artif Cells Nanomed Biotechnol 46(sup3):S886-S899. https://doi.org/10.1080/21691401.2018.1518909
Muthuraman MS, Nithya S, Kumar VV, Christena LR, Vadivel V, Subramanian NS, Anthony SP (2019) Green synthesis of silver nanoparticles using Nardostachys jatamansi and evaluation of its anti-biofilm effect against classical colonizers. Microb Pathog 126:1–5. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.micpath.2018.10.024
Habibipour R, Moradi-Haghgou L, Farmany A (2019) Green synthesis of AgNPs@PPE and its Pseudomonas aeruginosa biofilm formation activity compared to pomegranate peel extract. Inter J Nanomed 14:6891. 10.2147%2FIJN.S209912
Tang S, Zheng J (2018) Antibacterial activity of silver nanoparticles: structural effects. Adv Healthc Mater 7(13):1701503. https://doi.org/10.1002/adhm.201701503
Salman M, Rizwana R, Khan H, Munir I, Hamayun M, Rehman A, Amin K, Ahmed G, Khan M, Khan A, Amin FU (2019) Synergistic effect of silver nanoparticles and polymyxin B against biofilm produced by Pseudomonas aeruginosa isolates of pus samples in vitro. Artif Cells Nanomed Biotechnol 47:2465–2472. https://doi.org/10.1080/21691401.2019.1626864
Habash MB, Park AJ, Vis EC, Harris RJ, Khursigara CM (2014) Synergy of silver nanoparticles and aztreonam against Pseudomonas aeruginosa PAO1 biofilms. Antimicrob Agents Chemother 58(10):5818–5830. https://doi.org/10.1128/AAC.03170-14
Code availability
Not applicable.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Ethics approval
Not applicable.
Consent to participate
Not applicable.
Consent for publication
Not applicable.
Additional information
Editorial Responsibility: Luis Henrique Souza Guimaraes
Publisher’s note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
de Lacerda Coriolano, D., de Souza, J.B., Bueno, E.V. et al. Antibacterial and antibiofilm potential of silver nanoparticles against antibiotic-sensitive and multidrug-resistant Pseudomonas aeruginosa strains. Braz J Microbiol 52, 267–278 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s42770-020-00406-x
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s42770-020-00406-x