Abstract
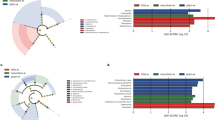
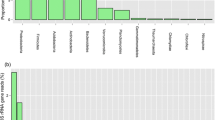
The purpose of this study is to learn about the differences in the composition of the phyllosphere microorganisms relevant to three representative tree species in northwest Liaoning. Use high-throughput amplicon sequencing to investigate the abundances, diversity, and composition of a major microbial community which includes fungi and bacteria on the leaves of three dominant plant species (Populus ×canadensis Moench (PCM), Pinus tabuliformis Carr (PTC), and Pinus sylvestris var. mongolica (PSM)). PCM had the highest levels of total nitrogen (TN), total phosphorus (TP), and soluble sugars and starch, which were higher than PTC and PSM. In addition, the abundance, diversity, and composition of the phyllosphere microbial communities differed greatly among PCM, PTC, and PSM. PTC hold the highest phyllosphere bacterial Chao1 index, Shannon index, Simpson index, Pielou_e index, and Observed_species, as well as phyllosphere fungal Chao 1 index, Observed_species, Pielou_e index, Shannon index, and Simpson index. Proteobacteria, Actinobacteria, Ascomycota, and Basidiomycota were the dominant phyllosphere microbial communities. Leaf characteristics, including TC, TN, TP, soluble sugar starch, and C/N, were the dominant factors affecting phyllosphere microbial communities. Trees of different genotypes have different leaf characteristics. Furthermore, PCM possesses distinct differences on total carbon and soluble sugar and starch content that deciduous and evergreen trees differ significantly. And plant traits are key factors that affect phyllosphere microbial community structure.







Similar content being viewed by others
References
Andrew C, Buntgen U, Egli S, Senn-Irlet B, Grytnes JA, Heilmann-Clausen J, Boddy L, Bassler C, Gange AC, Heegaard E, Hoiland K, Kirk PM, Krisai-Greilhuber I, Kuyper TW, Kauserud H (2019) Open-source data reveal how collections-based fungal diversity is sensitive to global change. Appl plant sci 7:e1227. https://doi.org/10.1002/aps3.1227
Angelini P, Rubini A, Gigante D, Reale L, Pagiotti R, Venanzoni R (2012) The endophytic fungal communities associated with the leaves and roots of the common reed (Phragmites australis) in lake trasimeno (Perugia, italy) in declining and healthy stands. Fungal Ecol 5:683–693. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.funeco.2012.03.001
Bálint M, Tiffin P, Hallström B, O'Hara RB, Olson MS, Fankhauser JD, Piepenbring M, Schmitt I (2013) Host genotype shapes the foliar fungal microbiome of balsam poplar (Populus balsamifera). Plos One 8:e53987. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0053987
Bao L, Cai W, Zhang X, Liu J, Bai Z (2019) Distinct microbial community of phyllosphere associated with five tropical plants on yongxing island, south china sea. Microorganisms 7:525. https://doi.org/10.3390/microorganisms8040570
Beattie GA, Lindow SE (1999) Bacterial colonization of leaves: a spectrum of strategies. Phytopathology 89:353–359. https://doi.org/10.1094/PHYTO.1999.89.5.353
Berg G, Ballin G (1994) Bacterial antagonists to verticillium dahliae kleb. J phytopathol 141:99–110. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1439-0434.1994.tb01449.x
Bulgarelli D, Schlaeppi K, Spaepen S, Ver E, Themaat LV, Schulze-Lefert P (2013) Structure and functions of the bacterial microbiota of plants further. Annu Rev Plant Biol 64:807–838. https://doi.org/10.1146/annurev-arplant-050312-120106
Chen QL, Cai L, Wang HC, Cai LT, Goodwin P, Ma J, Wang F, Li Z (2020) Fungal composition and diversity of the tobacco leaf phyllosphere during curing of leaves. Front microbiol 11:554051. https://doi.org/10.3389/fmicb.2020.554051
Delmotte N, Knief C, Chaffron S, Innerebner G, Roschitzki B, Schlapbach R, von Mering C, Vorholt JA (2009) Community proteogenomics reveals insights into the physiology of phyllosphere bacteria. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 106:16428–16433. https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.0905240106
Fürnkranz M, Wanek W, Richter A, Abell G, Rasche F, Sessitsch A (2008) Nitrogen fixation by phyllosphere bacteria associated with higher plants and their colonizing epiphytes of a tropical lowland rainforest of costa rica. ISME J 2:561–570. https://doi.org/10.1038/ismej.2008.14
Gong TY, Xin XF (2021) Phyllosphere microbiota: community dynamics and its interaction with plant hosts. J Integr Plant Biol 63:297–304. https://doi.org/10.1111/jipb.13060
Gurdeep R, Coaker GL, Leveau JHJ (2013) New insights into the structure and function of phyllosphere microbiota through high-throughput molecular approaches. FEMS Microbiol Lett 348:1–10. https://doi.org/10.1111/1574-6968.12225
Hao DC, Song SM, Mu J, Hu WL, Xiao PG (2016) Unearthing microbial diversity of Taxus rhizosphere via MiSeq high-throughput amplicon sequencing and isolate characterization. Sci Rep 6:22006. https://doi.org/10.1038/srep22006
Hooker JE, Piatti P, Cheshire MV, Watson CA (2007) Polysaccharides and monosaccharides in the hyphosphere of the arbuscular mycorrhizal fungi Glomus E3 and Glomus tenue. Soil Biol Biochem 39:680–683. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.soilbio.2006.08.006
Hunter PJ, Hand P, Pink D, Whipps JM, Bending GD (2010) Both leaf properties and microbe-microbe interactions influence within-species variation in bacterial population diversity and structure in the lettuce (Lactuca species) phyllosphere. Appl Environ Microbiol 76:8117–8125. https://doi.org/10.1128/AEM.01321-10
Innerebner G, Knief C, Vorholt JA (2011) Protection of Arabidopsis thaliana against leaf-pathogenic Pseudomonas syringae by Sphingomonas strains in a controlled model system. Appl Environ Microbiol 77:3202–3210. https://doi.org/10.1128/AEM.00133-11
Ji P, Wilson M (2003) Enhancement of population size of a biological control agent and efficacy in control of bacterial speck of tomato through salicylate and ammonium sulfate amendments. Appl Environ Microbiol 69:1290–1294. https://doi.org/10.1128/AEM.69.2.1290-1294.2003
Jia T, Wang R, Fan X, Chai B (2018) A comparative study of fungal community structure, diversity and richness between the soil and the phyllosphere of native grass species in a copper tailings dam in shanxi province, China. Appl Sci 8:1297. https://doi.org/10.3390/app8081297
Kato S, Fukasawa Y, Seiwa K (2017) Canopy tree species and openness affect foliar endophytic fungal communities of understory seedlings. Ecol Res 32:157–162. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11284-016-1426-z
Kembel SW, Mueller RC (2014) Plant traits and taxonomy drive host associations in tropical phyllosphere fungal communities. Botany 92:303–311. https://doi.org/10.1139/cjb-2013-0194
Kembel SW, O'Connor TK, Arnold HK, Hubbell SP, Green JL (2014) Relationships between phyllosphere bacterial communities and plant functional traits in a neotropical forest. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 111:13715–13720. https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.1216057111
Kinkel LL, Wilson M, Lindow SE (2000) Plant species and plant incubation conditions influence variability in epiphytic bacterial population size. Microb Ecol 39:1–11. https://doi.org/10.1007/s002489900182
Knief C, Ramette A, Frances L, Alonso-Blanco C, Vorholt JA (2010) Site and plant species are important determinants of the Methylobacterium community composition in the plant phyllosphere. ISME J 4:719–728. https://doi.org/10.1038/ismej.2010.9
Kovalchuk A, Mukrimin M, Zeng Z, Raffaello T, Liu M, Kasanen R, Sun H, Asiegbu FO (2018) Mycobiome analysis of asymptomatic and symptomatic norway spruce trees naturally infected by the conifer pathogens Heterobasidion spp. Environ Microbiol Rep 10:532–541. https://doi.org/10.1111/1758-2229.12654
Lienhard P, Terrat S, Prevost-Boure NC, Nowak V, Regnier T, Sayphoummie S, Panyasiri K, Tivet F, Mathieu O, Leveque J, Maron PA, Ranjard L (2014) Pyrosequencing evidences the impact of cropping on soil bacterial and fungal diversity in Laos tropical grassland. Agron Sustain Dev 34:525–533. https://doi.org/10.1007/s13593-013-0162-9
Lindow SE, Brandl MT (2003) Microbiology of the phyllosphere [Review]. Appl Environ Microbiol 69:1875–1883. https://doi.org/10.1128/AEM.69.4.1875-1883.2003
Lindow SE, Leveau JHJ (2002) Phyllosphere microbiology. Curr Opin Biotechnol 13:238–243. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0958-1669(02)00313-0
Mercier J, Lindow SE (2000) Role of leaf surface sugars in colonization of plants by bacterial epiphytes. Appl Environ Microbiol 66:369–374. https://doi.org/10.1128/AEM.66.1.369-374.2000
R Development Core Team (2009) R: a language and environment for statistical computing. Vienna: R Foundation for Statistical. Computing 12:21 http://www.R-project.org/
Redford AJ, Bowers RM, Knight R, Yan L, Fierer N (2010) The ecology of the phyllosphere: geographic and phylogenetic variability in the distribution of bacteria on tree leaves. Environ Microbiol 12:2885–2893. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1462-2920.2010.02258.x
Ren G, Zhu C, Alam MS, Tokida T, Sakai H, Nakamura H, Usui Y, Zhu JG, Hasegawa T, Jia ZJ (2015) Response of soil, leaf endosphere and phyllosphere bacterial communities to elevated CO2 and soil temperature in a rice paddy. Plant Soil 392:27–44. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11104-015-2503-8
Ruppel S, Krumbein A, Schreiner M (2008) Composition of the phyllospheric microbial populations on vegetable plants with different glucosinolate and carotenoid compositions. Microb Ecol 56:364–372. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00248-007-9354-7
Sardans J, Peñuelas J (2013) Tree growth changes with climate and forest type are associated with relative allocation of nutrients, especially phosphorus, to leaves and wood. Global Ecol Biogeogr 22:494–507. https://doi.org/10.1111/geb.12015
Sivakumar N, Sathishkumar R, Selvakumar G, Shyamkumar R, Arjunekumar K (2020) Phyllospheric microbiomes: diversity, ecological significance, and biotechnological applications. Plant Microb Sust Agricult 25:113–172. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-030-38453-1_5
Terhonen E, Blumenstein K, Kovalchuk A, Asiegbu FO (2019) Forest tree microbiomes and associated fungal endophytes: functional roles and impact on forest health. For Ecol Manage 10:42. https://doi.org/10.3390/f10010042
Vacher C, Hampe A, Porte AJ, Sauer U, Compant S, Morris CE (2016) The phyllosphere: microbial jungle at the plant-climate interface. Annu Rev Ecol Evol Syst 47:1–24. https://doi.org/10.1146/annurev-ecolsys-121415-032238
Van Aken B, Peres CM, Doty SL, Yoon JM, Schnoor JL (2004) Methylobacterium populi sp. nov., a novel aerobic, pink-pigmented, facultatively methylotrophic, methane-utilizing bacterium isolated from poplar trees (Populus deltoides x nigra DN34). Int J Syst Evol Microbiol 54:1191–1196. https://doi.org/10.1099/ijs.0.02796-0
Van der Putten W, Bardgett RD, Bever JD, Bezemer TM, Casper BB, Fukami T, Kardol P, Klironomos JN, Kulmatiski A, Schweitzer JA, Suding KN, van de Voorde TFJ, Wardle DA (2013) Plant–soil feedbacks: the past, the present and future challenges. J Ecol 101:265–276. https://doi.org/10.1111/1365-2745.12054
Vanden-Broeck A, Cox K, Michiels B, Verschelde P, Villar M (2012) With a little help from my friends: hybrid fertility of exotic Populus x canadensis enhanced by related native Populus nigra. Biol Invasions 14:1683–1696. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10530-012-0180-6
Wang J, Liu ZX (2003) Analysis on plantation resources in west Liaoning province. ARAA 01:129–133. https://doi.org/10.3321/j.issn:1000-7601.2003.01.030
Whipps JM, Hand P, Pink D, Bending GD (2010) Phyllosphere microbiology with special reference to diversity and plant genotype. J Appl Microbiol 105:1744–1755. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1365-2672.2008.03906.x
Yadav RKP, Karamanoli K, Vokou D (2005) Bacterial colonization of the phyllosphere of mediterranean perennial species as influenced by leaf structural and chemical features. Microb Ecol 50:185–196. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00248-004-0171-y
Yang CH, Crowley DE, Borneman J, Keen NT (2001) Microbial phyllosphere populations are more complex than previously realized. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 98:3889–3894. https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.051633898
Yutthammo C, Thongthammachat N, Pinphanichakarn P, Luepromchai E (2010) Diversity and activity of pah-degrading bacteria in the phyllosphere of ornamental plants. Microb Ecol 59:357–368. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00248-009-9631-8
Zheng SX, Shangguan ZP (2007) Spatial patterns of leaf nutrient traits of the plants in the Loess Plateau of China. Trees 21:357–370. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00468-007-0129-z
Zhu JJ, Kang HZ, Hui TH, Xu ML, Wang J (2005) Natural regeneration characteristics of Pinus sylvestris var. mongolica forests on sandy land in Honghuaerji. China. J For Res (Harbin) 16:253–259. https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02858184
Zhu D, Chen QL, Ding J, Wang YF, Zhu YG (2019) Antibiotic resistance genes in the soil ecosystem and planetary health: progress and prospect. Scientia Sinica Vitae 49:1652–1663. https://doi.org/10.1360/SSV-2019-0267
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of Interest
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher’s note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary Information
ESM 1
(JPG 699 KB)
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Zhu, K., Zhu, W., Zhang, W. et al. Characteristics of Phyllosphere Microbial Communities Associated with Three Different Plants in the Semi-arid Areas of Northwest Liaoning. J Soil Sci Plant Nutr 23, 2066–2079 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s42729-023-01162-1
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s42729-023-01162-1