Abstract
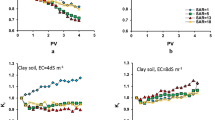
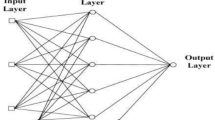
Improved productivity of crops grown in biochar amended soils largely depend on the unsaturated hydraulic conductivity (K (q)) and moisture content of the soil. However, their relationships in biochar amended soil have not been well elucidated in both field and laboratory studies. Moreso, it is important to propose a model, which can accurately predict the K (q), since its determination in field is laborious. The goals of this study were to determine the relationship between moisture content and K (q) in biochar amended soil; (ii) predict K(q) using multiple linear regression (MLR), artificial neural network (ANN) and adaptive neuro-fuzzy inference system (ANFIS), as innovative tools used in soil science; and (iii) evaluate their performances. Field experiments with five levels of biochar applications (0, 3, 6, 10 and 20 t/ha) were used during maize growing seasons. Soil moisture contents in relation to days after planting (DAP) of maize and biochar (B) application rates were recorded and used as model inputs. Results showed that measured K (q) decreased as moisture content increased in biochar amended soil. Also, ANN outperformed ANFIS and MLR in predicting K (q). The coefficients of determination, R2 were 0.98, 0.92 and 0.95 for the ANN, MLR and ANFIS during validation, respectively. Also, the root mean square error (RMSE) values were 1.80, 8.83 and 6.84 mm h−1 for the ANN, MLR and ANFIS during validation, respectively. Artificial neural network is most suitable for modelling water flow in biochar amended soil, and moisture content is important for its determination.







Similar content being viewed by others
References
Abel S, Peters A, Trinks S, Schonsky H, Facklam M, Wessolek G (2013) Impact of biochar and hydrochar addition on water retention and water repellenc of sandy soil. Geoderma 202–203:183–191. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.geoderma.2013.03.003
Abrisqueta JM, Plana V, Ruiz-Canales A, Ruiz-Sanchez MC (2006) Unsaturated hydraulic conductivity of disturbed and undisturbed loam soil. Span J Agric Res 4:91–96. https://doi.org/10.5424/sjar/2006041-179
Ajayi AE, Horn R (2016) Modification of chemical and hydro-physical properties of two texturally differentiated soils due to varying magnitudes of added biochar. Soil Tillage Res 164:34–44. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.still.2016.01.011
Ajayi AE, Horn R (2017) Biochar-induced changes in soil resilience: effects of soil texture and biochar dosage. Pedosphere 27:236–247. https://doi.org/10.1016/S1002-0160(17)60313-8
Akhtar SS, Guitong L, Mathias NA, Fulai L (2014) Biochar enhances yield and quality of tomato under reduced irrigation. Agric Water Manage 138:37–44. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.agwat.2014.02.016
Amer AM, Logsdn SD, Davis D (2009) Prediction of hydraulic conductivity in unsaturated soils. Soil Sci 174:508–515. https://doi.org/10.1097/SS.0b013e3181b76c29
Arshad RR, Sayyad Gh, Mosaddeghi M, Gharabaghi B (2013) Predicting saturated hydraulic conductivity by artificial intelligence and regression models. ISRN Soil Sci. https://doi.org/10.1155/2013/308159
Asai H, Samson BK, Stephan HM, Songyikhangsuthor K, Homma K, Kiyono Y, InoueY ST, Horie T (2009) Biochar amendment techniques for upland rice production in Northern Laos 1. Soil physical properties, leaf SPAD and grain yield. Field Crops Res 111:81–84. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.fcr.2008.10.008
Barnes RT, Gallagher ME, Masiello CA, Liu Z, Dugan B (2014) Biochar-induced changes in soil hydraulic conductivity and dissolved nutrient fluxes constrained by laboratory experiments. PLoS ONE 9:1–9. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0108340
Bonakdari H, Moeeni H, Ebtehaj I et al (2019) New insights into soil temperature time series modelling: linear or nonlinear? Theor Appl Climatol 135:1157–1177. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00704-018-2436-2
Campbell GS (1974) A simple method for determining unsaturated conductivity from moisture retention data. Soil Sci 117:311–314. https://doi.org/10.1097/00010694-197406000-00001
Chan KY, Van Zwieten L, Meszaros I, Downie A, Joseph S (2007) Agronomic values of greenwaste biochar as a soil amendment. Aust J Soil Res 45:629–634. https://doi.org/10.1071/SR071090004-9573/07/080629
Devereux RC, Sturrock CJ, Mooney SJ (2012) The effects of biochar on soil physical properties and winter wheat growth. Earth Environ Sci Trans Res Soc Edinb 103:13–18. https://doi.org/10.1017/S1755691012000011
Diana G, Beni C, Marconi S (2008) Organic and mineral fertilization: effects on physical characteristics and Boron Dynamic in an Agricultural soil. Commun Soil Sci Plant Anal 39(1332):1351. https://doi.org/10.1080/00103620802004037
Doussan C, Ruy S (2009) Prediction of unsaturated soil hydraulic conductivity with electric conductivity. Water Resour Res 45:1–12. https://doi.org/10.1029/2008WR007309
Ezlit YD, Ekhmaj AI, Elaalem MM (2014) Artificial neural networks to predict decreasing saturated hydraulic Conductivity in soils irrigated with saline-sodic water. J Nat Resour Dev 04:27–33. https://doi.org/10.5027/jnrd.v4i0.05
Emamgholizadeh SM, Bateni D, Shahsavani T, Ashrafi H, Ghorbani (2015) Estimation of soil cation exchange capacity using genetic expression programming (GEP) and multivariate adaptive regression splines (MARS). J Hydrol 529(2015):1590–1600. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhydrol.2015.08.025
Emami H, Shorafa M, Neyshabouri MR (2012) Evaluation of hydraulic conductivity at inflection point of soil moisture characteristic curve as a matching point for some soil unsaturated hydraulic conductivity models. JWSS - Isfahan Univ Technol 16:169–182. http://jstnar.iut.ac.ir/article-1–2206-en.html
Faloye OT, Ajayi AE, Alatise MO, Ewulo BS, Horn R (2020a) Nutrient uptake, maximum yield production and economic return of maize under deficit irrigation with biochar and inorganic fertiliser amendments. Biochar 1:375–388. https://doi.org/10.1007/s42773-019-00032-3
Faloye OT, Ajayi AE, Alatise MO, Ewulo BS, Horn R (2020b) Maize growth and yield modelling using AquaCrop under deficit irrigation with sole and combined application of biochar and inorganic fertiliser. J Soil Sci Plant Nutr 4:2440–2453. https://doi.org/10.1007/s42729-020-00310-1
Faloye OT, Alatise MO, Ajayi AE, Ewulo BS (2017) Synergistic effects of biochar and inorganic fertiliser on maize yield in an alfsol under drip irrigation. Soil Tillage Res 174:214–220. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.still.2017.07.013
Faloye OT, Alatise MO, Ajayi AE, Ewulo BS (2019) Effects of biochar and inorganic fertiliser applications on growth, yield and water use efficiency of maize under deficit irrigation. Agric Water Manag 217:165–178. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.agwat.2019.02.044
Fasinmirin JT, Olorunfemi IE (2011) Pedotransfer functions for the prediction of soil hydraulic properties in Ekiti state, southwestern Nigeria. J Sustain Technol 6: 64–74. https://www.futa.edu.ng/journal/papers/paper_5_1511262464
Fereshte HF (2014) Evaluation of artificial neural network and regression PTFS in estimating some soil hydraulic parameters. Pro-Environment 7:10–20. https://doi.org/10.15740/HAS/AU/12.TECHSEAR(4)2017/1105-1112
Ghanbarian-Alavijeh B, Liaghat AM, Sohrabi S (2009) Application of artificial neural networks in prediction of saturated hydraulic conductivity using soil physical parameters. J Agric Eng Res 10:97–112. https://doi.org/10.2136/vzj2006.0131
Ghorbani H, Kashi N, Hafezi MS, Emamgholizadeh (2015) Estimation of soil cation exchange capacity using multiple regression, artificial neural networks, and adaptive neuro-fuzzy inference system models in Golestan Province, Iran. Commun Soil Sci Plant Anal 46:763–780. https://doi.org/10.1080/00103624.2015.1006367
Glaser B, Lehmann J, Zech W (2002) Ameliorating physical and chemical properties of highly weathered soils in the tropics with charcoal–a review. Biol Fertil Soils 35:219–230. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00374-002-0466-4
Herath H, Camps-Arbestain M, Hedley M (2013) Effect of biochar on soil physical properties in two contrasting soils: an Alfisol and an Andisol. Geoderma 209:188–197. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.geoderma.2013.06.016
Hosseini M, Bahrami H, Khormali F et al (2021) Artificial intelligence statistical analysis of soil respiration improves predictions compared to regression methods. J Soil Sci Plant Nutr 21:2242–2251. https://doi.org/10.1007/s42729-021-00517-w
Hu W, She D, Shao M, Chun KP, Si B (2014) Effects of initial soil water content and saturated hydraulic conductivity variability on small watershed runoff simulation using LISEM. Hydrol Sci J 60:1137–1153. https://doi.org/10.1080/02626667.2014.903332
Jahani A, Maryam S (2021) Human activities impacts prediction in vegetation diversity of Lar National Park in Iran using artificial neural network model. Integr Environ Assess Manag 17:42–52. https://doi.org/10.1002/ieam.4349
Jang JSR (1993) ANFIS: adaptive-network-based fuzzy inference system. IEEE Trans Syst Man Cybern 23:665–685. https://doi.org/10.1109/21.256541
Jeffery S, Verheijen FGA, Van Der Velde M, Bastos AC (2011) A quantitative review of the effects of biochar application to soils on crop productivity using meta-analysis. Agric Ecosyst Environ 144:175–187. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.agee.2011.08.015
Kashi H, Emamgholizadeh SH, Ghorbani (2014) Estimation of soil infiltration and cation exchange capacity based on multiple regression, ANN (RBF, MLP), and ANFIS Models. Commun Soil Sci Plant Anal 45:1195–1213. https://doi.org/10.1080/00103624.2013.874029
Khalid AA, Tuffour HO, Bonsu M, Parker BQ (2014) The effects of poultry manure and NPK fertilizer on physical properties of a sandy soil in Ghana. Int J Agric Sci 1: 1–5. https://doi.org/10.12983/ijsras-2014-p0016-0022
Kinney TJ, Masiello CA, Dugan B, Hockaday WC, Dean MR, Zygourakis K, Barnes RT (2012) Hydrologic properties of biochars produced at different temperatures. Biomass Bioenergy 41:34–43. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biombioe.2012.01.033
Klipa V, Sacha J, Snehota M, Dohnal M, Zumr D, Tacheci P (2014) Automated multi-point mini-disk infiltrometer measurements of unsaturated hydraulic conductivity. GU General Assembly, held 27 April-2 May, 2014 in Vienna, Austria, id.7230
Laghari M, Hu Z, Fazal M, Hu M (2015) Effects of biochar application rate on sandy desert soil properties and sorghum growth. 2015. CATENA 135:313–320. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.catena.2015.08.013
Lakzian A, Aval M M B, Gorbanzadeh N (2010) Comparison of pattern recognition, artificial neural network and pedotransfer functions for estimation of soil water parameters. Not Sci Biol 2:114–120. https://doi.org/10.15835/nsb.2.3.4737
Lehmann J, Czimczik C, Laird C, Sohi S (2009) Stability of biochar in soil. In: Lehmann J, Josep S (eds) Biochar for environmental management: science and technology. Earthscan, London, p 1–12. https://doi.org/10.1007/s13593-016-0372-z
Major J, Rondon M, Molina D, Riha SJ, Johannes L (2010) Maize yield and nutrition after 4 years of doing biochar application to a Colombian savanna Oxisol. Plant Soil 333:117–128. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11104-010-0327-0
Malaya C, Sreedeep S (2013) Correlation between grain size distribution curve and unsaturated hydraulic conductivity curve of soils. Proceedings of Indian Geotechnical Conference December 22–24, Roorkee
Merdun H, Cinar O, Meral R, Apan M (2006) Comparison of artificial neural network and regression pedotransfer functions for prediction of soil water retention and saturated hydraulic conductivity. Soil Tillage Res 90:108–116. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.still.2005.08.011
Minasny B, Hopmans JW, Harter T, Eching SO, Tuli A, Denton MA (2004) Neural networks prediction of soil hydraulic functions for alluvial soils using multistep outflow data. Soil Sci Soc Am J 68:417–429. https://doi.org/10.2136/sssaj2004.4170
Minasny B, McBratney AB (2002) The neuro-m method for fitting neural network parametric pedotransfer functions. Soil Sci Soc Am J 66:352–361. https://doi.org/10.2136/sssaj2002.1407a
Moosavi AA, Sepaskhah A (2012) Artificial neural networks for predicting unsaturated soil hydraulic characteristics at different applied tensions. Arch Agron Soil Sci 58:125–153. https://doi.org/10.1080/03650340.2010.512289
Mosavi A, Samadianfard S, Darbandi S, Nabipour N, Qasem SN, Salwana E, Band SS (2021) predicting soil electrical conductivity using multi-layer perceptron integrated with grey wolf optimizer. J Geotech Eng. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.gexplo.2020.106639
Mosaffaei Z, Jahani A, Chahouki MAZ et al (2020) Soil texture and plant degradation predictive model (STPDPM) in national parks using artificial neural network (ANN). Model Earth Syst Environ 6:715–729. https://doi.org/10.1007/s40808-020-00723-y
Motie JB, Aghkhani MH, Rohani A, Lakzian A (2021) A soft-computing approach to estimate soil electrical conductivity. Biosyst Eng 205:105–120. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biosystemseng.2021.02.015
Mubarak AR, Omaima ER, Amal AA, Nemat EH (2009) Short term studies on use of organic amendments for amelioration of a sandy soil. Afr J Agric Res 4:621–627. https://doi.org/10.5897/AJAR.9000631
Mukherjee A, Lal R (2013) Biochar impacts on soil physical properties and greenhouse gas emissions. J Agron 3:313–339. https://doi.org/10.3390/agronomy3020313
Neyshabouri MR, Rafiee Alavi SR, Rezaei H, Nazemi AH (2010) Estimating unsaturated hydraulic conductivity from air permeability. In ‘19th World Congress of Soil Science Soil Solutions for a Changing World’. 1–6 August 2010, Brisbane, Qld. (IUSS)
Nosrati KF, Movahedi NS, Hezarjaribi AR, Roshani A, Dehghani AA (2012) Using artificial neural networks to estimate saturated hydraulic conductivity from easily available soil properties. Electron J Soil Manag Sustain Prod 2: 95–110. https://www.sid.ir/en/journal/ViewPaper.aspx?id=266846
Novak JM, Busscher WJ, Watts DW, Amonette JE, Ippolito JA, Lima IM, Gaskin J, Das KC, Steine C, Ahmedna M, Rehrah D, Schomberg H (2012) Biochars impact on soil moisture-storage in an Ultisol and two Aridisols. Soil Sci 177:310–320. https://doi.org/10.1097/SS.0b013e31824e5593
Novak JM, Busscher WJ, Laird DL, Ahmedna M, Watts DW, Niandou MA (2009) Impact of biochar amendment on fertility of a southeastern coastal plain soil. Soil Sci 174:105–112. https://doi.org/10.1097/SS.0b013e3181981d9a
Oladele SO, Adeyemo AJ, Awodun MA (2019) Influence of rice husk biochar an inorganic fertiliser on soil nutrients availability on rain-fed rice yield on two contrasting soils. Geoderma 336:1–11. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.geoderma.2018.08.025
Pachepsky YA, Timlin DJ, Varallyay G (1996) Artificial neural networks to estimate soil water retention from easily measurable data. Soil Sci Soc Am J 60:727–773. https://doi.org/10.2136/sssaj1996.03615995006000030007x
Safariha M, Jahani A, Jahani R, Latif R (2021) Prediction of hypericin content in Hypericum perforatum L. in diferent ecological habitat using artificial neural networks. Plant Methods 1–17. https://doi.org/10.1186/s13007-021-00710-z (pages 1 - 17)
Saffariha M, Jahani A, Potter D (2020) Seed germination prediction of Salvia limbata under ecological stresses in protected areas: an artificial intelligence modeling approach. BMC Ecol 20:48. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12898-020-00316-4
Samadianfard S, Ghorbani MA, Mohammadi B (2018) Forecasting soil temperature at multiple-depth with a hybrid artificial neural network model coupled-hybrid firefly optimizer algorithm. Inf Process Agric 5:465–476. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.inpa.2018.06.005
Schuh WM, Bauder JW (1986) Effect of soil properties on hydraulic conductivity moisture relationships. Soil Sci Soc Am J 50:848–855. https://doi.org/10.2136/SSSAJ1986.03615995005000040004X
Shamshirband S, Esmaeilbeiki F, Zarehaghi D, Neyshabouri D, Samadianfard S, Ghorbani M A, Amir Mosavi Nabipour N, Chau K (2020) Comparative analysis of hybrid models of firefly optimization algorithm with support vector machines and multilayer perceptron for predicting soil temperature at different depths. Eng Appl Comput Fluid Mech 14: 939-953. https://doi.org/10.1080/19942060.2020.1788644
Sihag P (2018) Prediction of unsaturated hydraulic conductivity using fuzzy logic and artificial neural network Earth Syst Environ Model https://doi.org/10.1007/s40808-018-0434-0
Siltecho S, Hammecker C, Sriboonlue V, Clermont-Dauphin C, Trelo-ges V, Antonino ACD (2015) Angulo-Jaramillo R (2014) Use of field and laboratory methods for estimating unsaturated hydraulic properties under different land-use. Hydrol Earth Syst Sci Discuss 11(6):6099–6137. https://doi.org/10.5194/hess-19-1193-2015
Six J, Conant RT, Paul EA, Paustian K (2002) Stabilization mechanisms of soil organic matter: Implications for C – saturation of soils. Plant Soil 241:155–176. https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1016125726789
Steiner C, Das KC, Melear N, Lakly D (2009) Reduced nitrogen loss during poultry litter composting using biochar. J Environ Qual 39:1236–1242. https://doi.org/10.2134/jeq2009.0337
Tamari S, Wosten JHM, Ruiz-Suarez JC (1996) Testing an artificial neural network for predicting soil hydraulic conductivity. Soil Sci Soc Am J 60:1732–1741. https://doi.org/10.2136/sssaj1996.03615995006000060018x
Ulyett J, Sakrabani R, Kibblewhite M G, Hann M (2014) Impact of biochar addition on water retention, nitrification, and carbon dioxide evolution from two sandy loam soils. Eur J Soil Sci 65. https://doi.org/10.1111/ejss.12081
Uzoma KC, Inoue M, Andry H, Fujimaki H, Zahoor A, Nishihara E (2011) Effect of cow manure biochar on maize productivity under sandy soil condition. Soil Use Manage 27:205–212. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1475-2743.2011.00340.x
Weynants M, Vereecken H, Javaux M (2008) Revisiting Vereecken pedotransfer functions. Introducing a closed – form hydraulic model. Vadose Zone J 8:86–95. https://doi.org/10.2136/vzj2008.0062
Yilmaz I, Marschalko M, Bednarik M, Kaynar O, Fojtova L (2012) Neural computing models for prediction of permeability coefficient of coarse-grained soils. Neural Comput Appl 21:957–968. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00521-011-0535-4
Zhang B, Govindaraju RS (2003) Geomorphology based artificial neural networks (GANNs) for estimation of direct run off over watersheds. J Hydrol 273:18–34. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0022-1694(02)00313-X
Zhang N, Zou H, Zhang L, Puppala AJ, Liu S, Cai G (2020) A unified soil thermal conductivity model based on artificial neural network. Int J Therm Sci 155. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijthermalsci.2020.106414
Zhang R (1997) Determination of soil sorptivity and hydraulic conductivity from the disc infiltrometer. https://doi.org/10.2136/SSSAJ1997.03615995006100040005X
Zheng H, Han L, Shojaaddini A (2021) Predicting saturated hydraulic conductivity by pedo-transfer function and spatial methods in calcareous soils. J Appl Geophys 191. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jappgeo.2021.104367
Acknowledgements
We acknowledge TETFUND Nigeria for financing part of the project and AVH for desktop work.
Funding
This study was partly funded by the Tertiary Education Trust Fund (TETFUND), Nigeria (Grant number 234).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of Interest
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary Information
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Faloye, O.T., Ajayi, A.E., Ajiboye, Y. et al. Unsaturated Hydraulic Conductivity Prediction Using Artificial Intelligence and Multiple Linear Regression Models in Biochar Amended Sandy Clay Loam Soil. J Soil Sci Plant Nutr 22, 1589–1603 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s42729-021-00756-x
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s42729-021-00756-x