Abstract
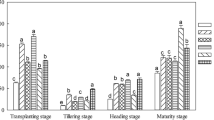
This study evaluated the effect of biochar on the soil nutrients, soil enzyme activity, and rice yield in a heavily saline-sodic paddy soil using a 2-year field experiment conducted in Jilin province in the northeastern part of China. The soil was amended with biochar at 0 biochar (B0), 33.75 t ha−1 (B1), 67.5 t ha−1 (B2), and 101.25 t ha−1 (B3). The field experiment was arranged in a randomized complete block design. Each treatment was replicated three times. The results show that the addition of biochar significantly increased the availability of soil total N, available P, and available K, while it remarkably reduced the content of the soil’s alkali-hydrolysable nitrogen, among which NH4-N and NO3-N were reduced significantly in 2 years. Biochar applications significantly increased the soil organic matter and soil C/N ratio. The soil Na+/K+ ratio was significantly reduced after biochar application in both 2 years. All of the biochar amendment applications improved the soil catalase activity, soil alkaline phosphatase activity, soil urease activity, and soil sucrose activity. The rice biomass, grain yield, and harvest index were significantly increased. Biochar applications can improve the soil nutrient status, decrease Na+/K+ concentration in soil, promote rice growth, and increase the rice yield in heavily saline-sodic paddy soils. It is anticipated that the study results will be useful for formulating novel management ways for improving crop production on saline-sodic soil.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Agbna GHD, Dongli S, Zhipeng L, Elshaikh NA, Timm LC (2017) Effects of deficit irrigation and biochar addition on the growth, yield, and quality of tomato. Sci Hortic 222:90–101. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scienta.2017.05.004
Aikaraki GN (1997) Barley response to salt stress at varied levels of phosphorus. J Plant Nutr 20(11):1635–1643. https://doi.org/10.1080/01904169709365362
Akhtar SS, Andersen MN, Liu FL (2015) Residual effects of biochar on improving growth, physiology and yield of wheat under salt stress. Agric Water Manag 158:61–68. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.agwat.2015.04.010
Amini S, Ghadiri H, Chen CR, Marschner P (2016) Salt-affected soils, reclamation, carbon dynamics, and biochar: a review. J Soils Sediments 16:939–953. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11368-015-1293-1
Bastías EI, González-Moro MB, González-Murua C (2004) Zea mays L. amylacea from the Lluta Valley (Arica-Chile) tolerates salinity stress when high levels of boron are available. Plant Soil 267:73–84. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chemosphere.2015.12.130
Bhaduri D, Saha A, Desai D, Meena HN (2016) Restoration of carbon and microbial activity in salt-induced soil by application of peanut shell biochar during short-term incubation study. Chemosphere 148:86–98. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chemosphere.2015.12.130
Bohara H, Dodla S, Wang JJ, Darapuneni M, Kongchum M, Fromme DD, Harrell D (2018) Impacts of N-stabilizers and biochar on nitrogen losses, nitrogen phytoavailability, and cotton yield in poultry litter-fertilized soils. Agron J 110:1–9. https://doi.org/10.2134/agronj2018.01.0007
Bruun EW, Petersen CT, Hansen E, Holm JK, Hauggaard-Nielsen H (2014) Biochar amendment to coarse sandy subsoil improves root growth and increases water retention. Soil Use Manag 30:109–118. https://doi.org/10.1111/sum.12102
Cabrera ML, Beare MH (1993) Alkaline persulfate oxidation for determining total nitrogen in microbial biomass extracts. Soil Sci Soc Am J 57:1007–1012. https://doi.org/10.2136/sssaj1993.03615995005700040021x
Chaganti VN, Crohn DM (2015) Evaluating the relative contribution of physiochemical and biological factors in ameliorating a saline-sodic soil amended with composts and biochar and leached with reclaimed water. Geoderma 259-260:45–55. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.geoderma.2015.05.005
Chakraborty K, Bhaduri D, Meena HN, Kalariya K (2016) External potassium (K+) application improves salinity tolerance by promoting Na+-exclusion, K+-accumulation and osmotic adjustment in contrasting peanut cultivars. Plant Physiol Biochem 103:143–153. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.plaphy.2016.02.039
Chen L, Liu MJ, Ali A, Zhou QC, Zhan SW, Chen YC, Pan XH, Zeng YJ (2020) Effects of biochar on paddy soil fertility under different water management modes. J Soil Sci Plant Nutr 20:1810–1818. https://doi.org/10.1007/s42729-020-00252-8
Chi CM, Zhao CW, Sun XJ, Wang ZC (2012) Reclamation of saline sodic soil properties and improvement of rice (Oriza sativa L.) growth and yield using desulfurized gypsum in the west of Songnen Plain, northeast China. Geoderma 187-188:24–30. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.geoderma.2012.04.005
Demisie W, Liu ZY, Zhang MK (2014) Effect of biochar on carbon fractions and enzyme activity of red soil. Catena 121:214–221. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.catena.2014.05.020
Drake JA, Cavagnar TR, Cunningham SC, Jackson WR, Patti AF (2016) Does biochar improve establishment of tree seedlings in saline sodic soils? Land Degrad Dev 27:52–59. https://doi.org/10.1002/ldr.2374
Egner H, Riehm H, Domingo WR (1960) Untersuchungen über die chemische Bodenanalyse als Grundlage für die Beurteilung de Nährstoffzustandes der Böden II. Chemische Extraktionsmethoden zur Phosphor- und Kaliumbetimmung Annaler 26:199–215
Esfandbod M, Phillips IR, Miller B, Rashti MR, Lan ZM, Srivastava P, Singh B, Chen CR (2017) Aged acidic biochar increases nitrogen retention and decreases ammonia volatilization in alkaline bauxite residue sand. Ecol Eng 98:157–165. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ecoleng.2016.10.077
Fageria NK, Gheyi HR, Moreira A (2011) Nutrient bioavailability in salt affected soils. J Plant Nutr 34:945–962. https://doi.org/10.1080/01904167.2011.555578
Gaskin WJ, Speir A, Harris K, Das KC, Dewey LR, Morris AL, Fisher SD (2010) Effect of peanut hull and pine chip biochar on soil nutrients, corn nutrient status, and yield. Agron J 102:623–633. https://doi.org/10.2134/agronj2009.0083
Ghosh U, Thapa R, Desutter T, Yangbo HE, Chatterjee A (2017) Saline–sodic soils: potential sources of nitrous oxide and carbon dioxide emissions? Pedosphere 27:65–75. https://doi.org/10.1016/S1002-0160(17)60296-0
Guan S (1986) Enzyme in soils and their study methods. China Agriculture Press, Beijing, pp 260–313 (in Chinese)
Hua L, Lu ZQ, Ma HR, Jin SS (2014) Effect of biochar on carbon dioxide release, organic carbon accumulation, and aggregation of soil. Environ Prog Sustain Energy 33:941–946. https://doi.org/10.1002/ep.11867
Huang MG, Zhang ZY, Zhai YM, Lu PR, Zhu CL (2019) Effect of straw biochar on soil properties and wheat production under saline water irrigation. Agronomy 457(9):1–15. https://doi.org/10.3390/agronomy9080457
IUSS Working Group WRB (2014) World Reference Base for soil resources 2014: international soil classification system for naming soils and creating legends for soil maps. World Soil Resources Reports 106; FAO: Roma, Italy
Jin K, Sleutel S, Buchan D, Neve SD, Cai DX, Gabriels D, Jin JY (2009) Changes of soil enzyme activities under different tillage practices in the Chinese Loess Plateau. Soil Tillage Res 104:115–120. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.still.2009.02.004
Jin VL, Potter KN, Johnson MVV, Harmel RD, Arnold JG (2015) Surface-applied biosolids enhance soil organic carbon and nitrogen stocks but have contrasting effects on soil physical quality. Appl Environ Soil Sci 2015:9–11. https://doi.org/10.1155/2015/715916
Jin F, Ran C, Anwari Q, Geng YQ, Guo LY, Li JB, Han D, Zhang XQ, Liu X, Shao XW (2018) Effects of biochar on sodium ion accumulation, yield and quality of rice in saline-sodic soil of the west of Songnen plain, northeast China. Plant Soil Environ 64:612–618. https://doi.org/10.17221/359/2018-PSE
Jin ZW, Chen C, Chen XM, Jiang F, Hopkins I, Zhang XL, Han ZQ, Billy G, Benavides J (2019) Soil acidity, available phosphorus content, and optimal biochar and nitrogen fertilizer application rates: a five-year field trial in upland red soil, China. Field Crop Res 232:77–87. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.fcr.2018.12.013
Karlen DL, Tomer MD, Neppel J, Cambardella A (2008) A preliminary watershed scale soil quality assessment in North Central Iowa, USA. Soil Tillage Res 99:291–299. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.still.2008.03.002
Kim HS, Kim KR, Yang JE, Ok YS, Owens G, Nehls T, Wessolek G, Kim KH (2016) Effect of biochar on reclaimed tidal land soil properties and maize (Zea mays L.) response. Chemosphere 142:153–159. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chemosphere.2015.06.041
Klose S, Tabatabai MA (1999) Urease activity of microbial biomass in soils. Soil Biol Biochem 31:205–211. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0038-0717(98)00090-X
Lakhdar A, Rabhi M, Ghnaya T, Montemurro F, Jedidi N, Abdelly C (2009) Effectiveness of compost use in salt-affected soil. J Hazard Mater 171:29–37. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhazmat.2009.05.132
Lashari MS, Liu Y, Li L, Pan W, Fu J, Pan G, Zheng J, Zheng J, Zhang X, Yu X (2013) Effects of amendment of biochar-manure compost in conjunction with pyroligneous solution on soil quality and wheat yield of a salt-stressed cropland from Central China great plain. Field Crop Res 144:113–118. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.fcr.2012.11.015
Li YY, Huang LH, Zhang H, Wang M, Liang ZW (2017) Assessment of ammonia volatilization losses and nitrogen utilization during the rice growing season in alkaline salt affected soils. Sustainability 132(9):1–15. https://doi.org/10.3390/su9010132
Li YC, Li ZW, Lin WW, Jiang YH, Weng BQ, Lin WX (2018) Effects of biochar and sheep manure on rhizospheric soil microbial community in continuous ratooning tea orchards. J Appl Ecol 29:1273–1282. https://doi.org/10.13287/j.1001-9332.201804.036
Liang BC, Mackenzie AF, Schnitzer M (1997) Management induced change in labile soil organic matter under continuous corn in eastern Canadian soils. Biol Fertil Soils 26:88–94. https://doi.org/10.1007/s003740050348
Liang YC, Si J, Nikolic M, Peng Y, Chen W, Jiang Y (2005) Organic manure stimulates biological activity and barley growth in soil subject to secondary salinization. Soil Biol Biochem 37:1185–1195. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.soilbio.2004.11.017
Liu SN, Meng J, Jiang LL, Yang X, Lan Y, Cheng XY, Chen WF (2017) Rice husk biochar impacts soil phosphorous availability, phosphatase activities and bacterial community characteristics in three different soil types. Appl Soil Ecol 116:12–22. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apsoil.2017.03.020
Masto RE, Kumar S, Rout TK, Sarkar P, George J, Ram LC (2013) Biochar from water hyacinth (Eichornia crassipes) and its impact on soil biological activity. Catena 111:64–71. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.catena.2013.06.025
Munns R, Tester M (2008) Mechanisms of salinity tolerance. Plant Biol 59:651–681. https://doi.org/10.1146/annurev.arplant.59.032607.092911
Nelson PN, Oades JM (1998) Organic matter, sodicity and soil structure. In: Sumner ME, Naidu R (eds) Sodic soils: distribution, properties, management and environmental consequences. Oxford University Press, Oxford, pp 51–75
Qadir M, Schubert S (2002) Degradation processes and nutrient constraints in sodic soils. Land Degrad Dev 13:275–294. https://doi.org/10.1002/ldr.504
Qi RM, Li J, Lin ZA, Li ZJ, Li YT, Yang XD, Zhang JJ, Zhao BQ (2016) Temperature effects on soil organic carbon, soil labile organic carbon fractions, and soil enzyme activities under long-term fertilization regimes. Appl Soil Ecol 102:36–45. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apsoil.2016.02.004
Ran C, Gulaqa A, Zhu J, Wang WW, Zhang SQ, Geng YQ, Guo LY, Jin F, Shao XW (2019) Benefits of biochar for improving ion contents, cell membrane permeability, leaf water status and yield of rice under saline-sodic paddy field condition. J Plant Growth Regul 39:370–377. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00344-019-09988-9
Rengasamy P (2010) Soil processes affecting crop production in salt-affected soils. Funct Plant Biol 37:613–620. https://doi.org/10.1071/FP09249
Saifullah, Dahlawi S, Naeem A, Rengel Z, Naidu R (2018) Biochar application for the remediation of salt-affected soils: challenges and opportunities. Sci Total Environ:320–335. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2017.12.257
Shi SH, Tian L, Nasir F, Bahadur A, Batool A, Luo SS, Yang F, Wang ZC, Tian CJ (2019) Response of microbial communities and enzyme activities to amendments in saline-alkaline soils. Appl Soil Ecol 135:16–24. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apsoil.2018.11.003
Song YY, Song CC, Yang GS, Miao YQ, Wang JY, Guo YD (2012) Changes in labile organic carbon fractions and soil enzyme activities after marshland reclamation and restoration in the Sanjiang Plain in Northeast China. Environ Manag 50:418–426. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00267-012-9890-x
Song YY, Song CC, Shi FX, Wang MQ, Ren JS, Wang XW, Jiang L (2019) Linking plant community composition with the soil C pool, N availability and enzyme activity in boreal peatlands of Northeast China. Appl Soil Ecol 140:144–154. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apsoil.2019.04.019
Tabatabai MA, Bremner JA (1969) Use of p-nitrophenyl phosphate for assay of soil phosphatase activity. Soil Biol Biochem 1:301–307. https://doi.org/10.1016/0038-0717(69)90012-1
Xiao Q, Zhu LX, Zhang HP, Li XY, Shen YF, Li SQ (2016) Soil amendment with biochar increases maize yields in a semi-arid region by improving soil quality and root growth. Crop Pasture Sci 67:495–507. https://doi.org/10.1071/CP15351
Xu M, Xia HX, Wu J, Yang G, Zhang XH, Peng H, Yu XY, Li L, Xiao H, Qi H (2017) Shifts in the relative abundance of bacteria after wine-lees-derived biochar intervention in multi metal-contaminated paddy soil. Sci Total Environ 599-600:1297–1307. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2017.05.086
Yang X, Liu JJ, McGrouther K, Huang HG, Lu KP, Guo X, He LZ, Lin XM, Che L, Ye ZQ, Wang HL (2016) Effect of biochar on the extractability of heavy metals (Cd, Cu, Pb, and Zn) and enzyme activity in soil. Environ Sci Pollut Res 23:974–984. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-015-4233-0
Ye LL, Campsarbestai M, Shen QH, Lehmann J, Singh B, Sabir M (2020) Biochar effects on crop yields with and without fertilizer: a meta-analysis of field studies using separate controls. Soil Use Manag 36(1):2–18. https://doi.org/10.1111/sum.12546
Funding
This study was funded by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (No.32071951) and Jilin Province Education Department Planning Project (No.JJKH20200340KJ).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of Interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Publisher’s note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Yao, T., Zhang, W., Gulaqa, A. et al. Effects of Peanut Shell Biochar on Soil Nutrients, Soil Enzyme Activity, and Rice Yield in Heavily Saline-Sodic Paddy Field. J Soil Sci Plant Nutr 21, 655–664 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s42729-020-00390-z
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s42729-020-00390-z