Abstract
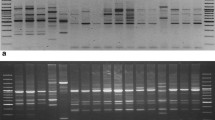
The efficacy of universal rice primer (URP) and inter simple sequence repeat (ISSR) markers was assessed in genetic diversity analysis among ten diverse isolates of Curvularia lunata. The parameters like percentage polymorphism (PP), polymorphism information content (PIC), expected heterozygosity (He), resolution power (RP), Shannon’s information index (I), effective multiplex ratio (EMR), marker index (MI) and cophenetic matrix were used in the study. The PIC, PP, He, RP and I values were nearly identical for both marker systems while, EMR, MI and cophenetic correlation coefficient were found to be higher in ISSR than URP marker system. Based on these parameters, ISSR markers were proved to be more efficient than URP markers in diversity analysis of C. lunata. Combined markers based dendrogram, grouped all the isolates of C. lunata into six clusters. Indigenous isolates except one form one cluster while most of the exotic isolates form separate clusters based on their geographical regions. The combine analysis of URP and SRAP markers showed high cophenetic correlation coefficient (r = 0.942), which indicated that combined markers analysis is giving better results for genetic diversity study.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Aghemiri A, Mehrabi R, Talebi R (2015) Isolation, characterization and genetic diversity analysis of Bipolaris sorokiniana (Sacc.) Shoen., the causal agent of spot blotch of wheat using molecular markers. Crop. Biotechnol 5(11):15–27
Akhtar J, Kandan A, Singh B, Dev U, Chand D, Kumar J, Agarwal PC (2014) A simple modified technique for obtaining pure cultures of seed-borne fungi. Indian J Plant Prot 42:156–159
Akhtar J, Singh B, Kandan A, Kumar P, Dubey SC (2017) Status of Colletotrichum species infecting chilli germplasm processed for pathogen-free conservation in national gene bank, India. Bangladesh J Bot 46(2):631–637
Alam MZ, Hamim I, Ali MA, Ashrafuzzaman M (2014) Effect of seed treatment on seedling health of chili. J Environ Sci Nat Resour 7(1):177–181
Kamaluddeen SS, Simon S, Lal AA (2013) A new blight disease of rice caused by Curvularia lunata from Uttar Pradesh. Int J Agric Sci Res 3(5):13–16
Kandan A, Akhtar J, Singh B, Dixit D, Chand D, Roy A, Rajkumar S, Agarwal PC (2014) Molecular diversity of Bipolaris oryzae infecting Oryza sativa in India. Phytoparasitica 43(1):5–14
Kandan A, Akhtar J, Singh B, Pal D, Chand D, Rajkumar S, Agarwal PC (2016) Genetic diversity analysis of fungal pathogen Bipolaris sorghicola infecting Sorghum bicolor in India. J Environ Biol 37(6):1323–1330
Kang HW, Park DS, Park YJ, You CH, Lee BM, Eun MY, Go SJ (2002) Fingerprinting of diverse genomes using PCR with universal rice primers generated from repetitive sequence of Korean weedy rice. Mol Cells 13:281–287
Khare MN, Tiwari SP, Sharma YK (2014) Disease problems in the cultivation of I. Cumin (Cuminum cyminum L.) II. Caraway (Carum carvi L.) and their management leading to the production of high quality pathogen free seed. Int J Seed Spices 4(1):1–8
Lamare A, Rao SR (2015) Efficacy of RAPD, ISSR and DAMD markers in assessment of genetic variability and population structure of wild Musa acuminata colla. Physiol Mol Biol Plants 21(3):349–358
Lapointe FJ, Legendre P (1995) Comparison tests for dendrograms: a comparative evaluation. J Classif 12:265–282
Liu X, X-h Zhu, Qiu P, Chen W (2012) A correlation-matrix-based hierarchical clustering method for functional connectivity analysis. J Neurosci Methods 211(1):94–102
Mahmodi F, Kadir JB, Puteh A, Pourdad SS, Nasehi A, Soleimani N (2014) Genetic diversity and differentiation of Colletotrichum spp. isolates associated with leguminosae using multigene loci, RAPD and ISSR. Plant Pathol J 30(1):10–24
Mantel N (1967) The detection of disease clustering and a generalized regression approach. Cancer Res 27:209–220
Mathur SB, Kongsdal O (2003) Common laboratory seed health testing method for detecting fungi. International Seed Testing Association, Bassersdorf
Nei M (1973) Analysis of gene diversity in subdivided populations. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 70:3321–3323
Peakall R, Smouse PE (2006) GENEALEX 6: genetic analysis in Excel. Population genetic software for teaching and research. Mol Ecol Notes 6:288–295
Powell W, Morgante M, Andre C, Hanafey M, Vogel J, Tingey S, Rafalski A (1996) The comparison of RFLP, AFLP and SSR (microsatellite) markers for germplasm analysis. Mol Breed 2:225–238
Prevost A, Wilkinson MJ (1999) A new system of comparing PCR primers applied to ISSR fingerprinting of potato cultivars. Theor Appl Genet 98:107–112
Rao PN, Salam MA (1954) Curvularia species from discoloured grains from Hyderabad. J Indian Bot Soc 33:268–271
Rohlf FJ (1998) NTSYS-pc: Numerical taxonomy and multivariate analysis system. Version 2.02i. Biostatistics Inc. Setauket, NY, USA: Exeter Biological Software
Sneath PHA, Sokal RR (1973) Numerical taxonomy: the principles and practice of numerical classification. WH Freeman and Company, San Francisco
Wang X-D, Gao Z-G, Yao Y, Liu X, Su J, Li W-Y (2014) Genetic diversity of Curvularia lunata by UP-PCR and ISSR analysis. Acta Agric Bor-Sin 29(3):227–233
Yago JI, Roh J-H, Bae S, Yoon Y-N, Kim H-J, Nam M (2011) The effect of seed-borne mycoflora from sorghum and foxtail millet seeds on germination and disease transmission. Mycobiology 39(3):206–218
Acknowledgements
Authors gratefully acknowledge the Director, ICAR-NBPGR for support and encouragement and Indian Council of Agricultural Research (ICAR), New Delhi for financial support.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Kumar, P., Akhtar, J., Kandan, A. et al. Efficacy of URP and ISSR markers to determine diversity of indigenous and exotic isolates of Curvularia lunata. Indian Phytopathology 71, 235–242 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s42360-018-0038-7
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s42360-018-0038-7