Abstract
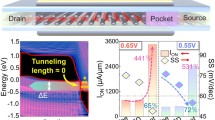
An optimally designed Dual Source Vertical Tunnel Field Effect Transistors is proposed and investigated using technology computer aided design simulation. The vertical tunnel FET have dispersal of source channel drain in the vertical direction which will enhance the scalability of the simulated device. The benefit of the TFET is switching mechanism which is done by quantum tunnelling method through a barrier instead of thermionic emission over the barrier as that of conventional MOSFETs. The key of this paper, we have developed two-dimensional model of single drain with dual source n-type vertical tunnel field effect transistor. Further introduction to an ultra-thin channel among the drain and gate region will makes aggressive improvement in the numerical simulations of minimum threshold voltage (VT) of 0.15 V and average subthreshold slope of 3.47 mV/decade. The variation effect in the channel thickness, source height, drain doping, source doping, temperature and work function has been simulated and examined by 2D silvaco TCAD tool. High ON current and low OFF current is recorded as 1.74 × 10−4 A/µm and 6.92 × 10−13 A/µm respectively with ION/IOFF current ratio in order of 108 to 109.















Similar content being viewed by others
References
D. Kahng, U.S. Patent No. 3,102,230 (1963)
D. Kahng, IEEE Trans. Electron Devices 23, 655 (1976)
G.E. Moore, Proc. IEEE 11, 33 (2006)
S. Borkar, ACM Queue 1, 26 (2003)
S. Veeraraghavan, Jerry G. Fossum, IEEE Trans. Electron Devices 36, 522 (1989)
C. Bulucea, F.-C. Wang, P. Chaparala, U.S. Patent No. 6, 548, 842 (2003)
K. Young, Konrad. IEEE Trans. Electron Devices 36, 399 (1989)
W.Y. Choi, B.-G. Park, J.-D. Lee, T.-J.K. Liu, IEEE Electron Device Lett. 28, 43 (2007)
K. Gopalakrishnan, P.B. Griffin, J.D. Plummer, Digest. International Electron Devices Meeting, IEEE 7509297 (2002)
Y. Khatami, K. Banerjee, IEEE Trans. Electron Devices 56, 2752 (2009)
Z. Jiang, Z. Yiqi, L. Cong, W. Ping, L. Yuqi, J. Semicond. 37, 094003 (2016)
K.-H. Kao, A. Verhulst, W.G. Vandenberghe, B. Soree, G. Groseseneken, K.M. Meyer, IEEE Trans. Electron Devices 59, 292 (2012)
P.-Y. Wang, B.-Y. Tsui, IEEE Trans. Nanotechnol. 15, 74 (2016)
B. Hoefflinger, Int. Roadmap Semicond. 2, 143 (2016)
M. Neisser, S. Wurm, Adv. Opt. Technol. 4, 235 (2015)
K.K. Bhuwalka, J. Schulze, I. Eisele, IEEE Trans. Electron Devices 52, 909 (2005)
K.K. Bhuwalka, S. Sedlmaier, A.K. Ludsteck, C. Tolksdorf, J. Schulze, E. Ignaz, IEEE Trans. Electron Devices 51, 279 (2004)
K. Nigam, P. Kondekar, D. Sharma, Micro Nano Lett. 11, 319 (2016)
N.D. Lang, W. Kohn, Phys. Rev. B 3, 1215 (1971)
W. Girish, R. Balwinder, J. Electron. Mater. 47, 4883 (2018)
S. Singh, B. Raj, J. Electron. Mater. 48, 6253 (2019)
A.C. Ford, C.W. Yeung, S. Chuang, Appl. Phys. Lett. 98, 113105 (2011)
S. Singh, B. Raj, in First International Conference on Secure Cyber Computing and Communication, 192 (2018)
F. Chen, H. Ilatikhameneh, Y. Tan, G. Klimeck, R. Rahman, IEEE Trans. Electron Devices 65, 3065 (2018)
H. Lee, J.-D. Park, C. Shin, IEEE Trans. Electron Devices 63, 1827 (2016)
D.W. Kwon, H.W. Kim, H.K. Jang, E. Park, J. Lee, W. Kim, S. Kim, J.-H. Lee, B.-G. Park, IEEE Trans. Electron Devices 64, 1799 (2017)
Acknowledgements
We thank the VLSI design group of NIT Jalandhar for their interest in this work and useful comments to draft the final form of the paper. The support of DST-SERB Project (ECR/2017/000922) is gratefully acknowledged. We would like to thank NIT Jalandhar for lab facilities and research environment to carry out this work.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Badgujjar, S., Wadhwa, G., Singh, S. et al. Design and Analysis of Dual Source Vertical Tunnel Field Effect Transistor for High Performance. Trans. Electr. Electron. Mater. 21, 74–82 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s42341-019-00154-2
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s42341-019-00154-2