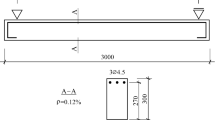
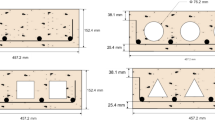
Abstract
Recent earthquakes highlighted the impact of masonry infill walls on structural resilience. Irregular placement of these walls amplifies adverse effects, causing substantial material and human losses. Studies and post-earthquake assessments stress the need to consider infill walls in design and evaluation. This paper investigates the presence of the soft storey in the reinforced concrete structures when the contribution of the infill walls. The results obtained from the investigation of the existence of the soft first storey are discussed using an approximate method that relies on the results of the pushover analysis based on the fiber-section-based macro-modeling was used to model the infill walls. Thanks to the results obtained, infill walls significantly enhance the resistance of weak column—strong beam-designed reinforced concrete frames, with an impressive 250% increase. In contrast, this effect is more moderate at 40% for strong column—weak beam-designed reinforced concrete frames. Notably, uniform distribution of infill walls along the structure’s height, compared to bare structures, has no impact on soft-storey emergence in the same seismic zone, regardless of column-beam strength. In low seismic intensity regions, infill walls dissipate energy, leading to consistent seismic behavior for uniform infill distribution in both strong and weak column configurations. Despite column strength, open ground storey structures remain susceptible to soft first storey emergence, highlighting the indispensable role of infill walls in reinforced concrete structural design.












Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
The data used to support the findings of this study are available from the corresponding author upon request.
References
Adibi, M., Talebkhah, R., & Ghatte, H. F. (2023). Seismic reliability of precast concrete frame with masonry infill wall. Earthquakes and Structures, 24(2), 141–153. https://doi.org/10.12989/eas.2023.24.2.141
Algerian Seismic Rules. (2003). Centre National de Recherche Appliquée en Génie Parasismique. Alger.
Ashraf Habibullah, S. E., & Stephen Pyle, S. E. (1998). Practical three dimensional nonlinear static pushover analysis. Structure magazine, Winter.
Asteris, P. G., Antoniou, S. T., Sophianopoulos, D. S., & Chrysostomou, C. Z. (2011). Mathematical macromodeling of infilled frames: State of the art. Journal of Structural Engineering, 137(12), 1508–1517. https://doi.org/10.1061/(asce)st.1943-541x.0000384
Asteris, P. G., Cavaleri, L., Di Trapani, F., & Sarhosis, V. (2016). A macro-modelling approach for the analysis of infilled frame structures considering the effects of openings and vertical loads. Structure and Infrastructure Engineering, 12(5), 551–566. https://doi.org/10.1080/15732479.2015.1030761
ATC-40. (1996). Seismic evaluation and retrofit of concrete buildings.
Cavaleri, L., & Di Trapani, F. (2014). Cyclic response of masonry infilled RC frames: Experimental results and simplified modeling. Soil Dynamics and Earthquake Engineering, 65, 224–242. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.soildyn.2014.06.016
Di Trapani, F., Cavaleri, L., Bertagnoli, G., Mancini, G., Gino, D., & Malavisi, M. (2017). Definition of a fiber macro-model for nonlinear analysis of infilled frames. Proceedings of the COMPDYN.
Di Trapani, F., Bertagnoli, G., Ferrotto, M. F., & Gino, D. (2018). Empirical equations for the direct definition of stress–strain laws for fiber-section-based macromodeling of infilled frames. Journal of Engineering Mechanics. https://doi.org/10.1061/(asce)em.1943-7889.0001532
Eurocode 8. (2005). Design provisions for earthquake resistance of structures.
Fardis, M. N. (2000). Eurocode 8–Present state, pre-normative and co-normative research needs (including design seismic action). In Proceedings of the Workshop on Mitigation of Seismic Risk Support to Recently Affected European Countries, European Commission-JRC, Belgirate (VB), Italy (pp. 1–10).
FEMA 356. (2000). Prestandard and commentary for the seismic rehabilitation of buildings. Federal Emergency Management Agency.
Guettala, S., Abdesselam, I., Chebili, R., & Guettala, S. (2023). Assessment of the effects of infill walls’ layout in plan and/or elevation on the seismic performance of 3D RC structures. Asian Journal of Civil Engineering. https://doi.org/10.1007/s42107-023-00802-2
Guney, D., & Aydin, E. (2012). The nonlinear effect of infill walls stiffness to prevent soft story collapse of RC structures. The Open Construction & Building Technology Journal, 6(1), 74–80. https://doi.org/10.2174/1874836801206010074
Holmes, M. (1961). Steel frames with brickwork and concrete infilling. Proceedings of the Institution of Civil Engineers, 19(4), 473–478. https://doi.org/10.1680/iicep.1961.11305
Issam, A. (2018). Analyse pushover des structures en béton armé tridimensionnelle à étage souple (Doctoral dissertation).
Kaveh, A., Kalateh-Ahani, M., & Fahimi-Farzam, M. (2013). Constructability optimal design of RC retaining walls using a multi-objective genetic algorithm. Structural Engineering and Mechanics, 47(2), 227–245. https://doi.org/10.12989/sem.2013.47.2.227
Kaveh, A., Izadifard, R. A., & Mottaghi, L. (2020). Optimal design of planar RC frames considering CO2 emissions using ECBO, EVPS and PSO metaheuristic algorithms. Journal of Building Engineering, 28, 101014. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jobe.2019.101014
Kaveh, A., & Zakian, P. (2012). Performance based optimal seismic design of RC shear walls incorporating soil-structure interaction using CSS algorithm. International Journal of Optimization in Civil Engineering, 2(3), 383–405.
Kaveh, A., & Zakian, P. (2014). Optimal seismic designs of RC shear wall-frame structures. KSCE Journal of Civil Engineering, 18(7), 2181–2190. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12205-014-0640-x
Khelaifia, A., Chebili, R., & Zine, A. (2023). Impact of the position and quantity of shear walls in buildings on the seismic performance. Asian Journal of Civil Engineering. https://doi.org/10.1007/s42107-023-00824-w
Klingner, R. E., & Bertero, V. V. (1978). Earthquake resistance of infilled frames. Journal of the Structural Division, 104(6), 973–989. https://doi.org/10.1061/jsdeag.0004947
Krawinkler, H., & Seneviratna, G. D. P. K. (1998). Pros and cons of a pushover analysis of seismic performance evaluation. Engineering Structures, 20(4–6), 452–464. https://doi.org/10.1016/s0141-0296(97)00092-8
Mander, J. B., Priestley, M. J. N., & Park, R. (1988). Theoretical stress-strain model for confined concrete. Journal of Structural Engineering, 114(8), 1804–1826. https://doi.org/10.1061/(asce)0733-9445(1988)114:8(1804)
Negro, P., & Verzeletti, G. (1996). Effect of infills on the global behaviour of R/C frames: Energy considerations from pseudodynamic tests. Earthquake Engineering & Structural Dynamics, 25(8), 753–773. https://doi.org/10.1002/(sici)1096-9845(199608)25:8%3c753::aid-eqe578%3e3.0.co;2-q
Panagiotakos, T. B., & Fardis, M. N. (1996). Seismic response of infilled RC frames structures. In 11th world conference on earthquake engineering, p. 28.
Panthi, B., Dahal, P., Shrestha, P., & Thapa, K. B. (2021). Fundamental period of RC buildings with infill walls in Nepal. Asian Journal of Civil Engineering, 22(5), 983–993. https://doi.org/10.1007/s42107-021-00359-y
Papia, M., Cavaleri, L., & Fossetti, M. (2003). Infilled frames: Developments in the evaluation of the stiffening effect of infills. Structural Engineering and Mechanics, 16(6), 675–693. https://doi.org/10.12989/sem.2003.16.6.675
Park, R., & Paulay, T. (1975). Reinforced Concrete Structures. https://doi.org/10.1002/9780470172834
Polyakov, S. V. (1960). On the interaction between masonry filler walls and enclosing frame when loaded in the plane of the wall. Translations in Earthquake Engineering, 2(3), 36–42.
Powell, G. H., & Chen, P. F. S. (1986). 3D beam-column element with generalized plastic hinges. Journal of Engineering Mechanics, 112(7), 627–641. https://doi.org/10.1061/(asce)0733-9399(1986)112:7(627)
Sattar, S., & Liel, A. B. (2010). Seismic performance of RC frame structures with and without masonry infill walls. In 9th US National and 10th Canadian conference on earthquake engineering.
Scott, M. H., & Fenves, G. L. (2006). Plastic hinge integration methods for force-based beam-column elements. Journal of Structural Engineering, 132(2), 244–252. https://doi.org/10.1061/(asce)0733-9445(2006)132:2(244)
Shing, P. B., & Mehrabi, A. B. (2002). Behaviour and analysis of masonry-infilled frames. Progress in Structural Engineering and Materials, 4(3), 320–331. https://doi.org/10.1002/pse.122
Smith, B. S. (1966). Behavior of square infilled frames. Journal of the Structural Division, 92(1), 381–404. https://doi.org/10.1061/jsdeag.0001387
Smith, B. S., & Carter, C. (1969). A method of analysis for infilled frames. Proceedings of the Institution of Civil Engineers, 44(1), 31–48. https://doi.org/10.1680/iicep.1969.7290
Taucer, F., Spacone, E., & Filippou, F. C. (1991). A fiber beam-column element for seismic response analysis of RC structures (Vol. 91). Earthquake Engineering Research Center, College of Engineering, University of California.
Tena-Colunga, A. (2010). Review of the soft first story irregularity condition of buildings for seismic design. The Open Civil Engineering Journal, 4(1), 1–15. https://doi.org/10.2174/18741495010040100001
Van, T. C., Lau, T. L., & Mohamed Nazri, F. (2022). Macro-modeling approach incorporating fiber plastic hinge for RC frames with masonry infill. Engineering Structures, 251, 113421. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.engstruct.2021.113421
Zakian, P., & Kaveh, A. (2020). Topology optimization of shear wall structures under seismic loading. Earthquake Engineering and Engineering Vibration, 19(1), 105–116. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11803-020-0550-5
Funding
This research received no specific grant from funding agencies in any sector.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
All authors contributed equally to this research but Issam Abdesselam wrote this paper.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors have no competing interests to declare relevant to this article’s content.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Abdesselam, I., Guettala, S. & Zine, A. Fiber-based modeling for investigating the existence of a soft storey for masonry infilled reinforced concrete structures. Asian J Civ Eng 25, 1949–1965 (2024). https://doi.org/10.1007/s42107-023-00887-9
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s42107-023-00887-9