Abstract
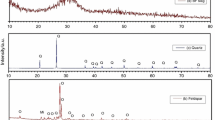
In the present investigation, three quartz-free porcelain compositions were prepared where quartz was fully substituted by fly ash (VPF 1) and feldspar was partly substituted by blast furnace slag (VPF 2) and basic oxygen furnace slag (VPF 3). A quartz-containing porcelain (VPQ) was also considered to compare the results with quartz-free porcelain bodies. Phase transformation and mass loss of the prepared batches were measured up to 1150 °C by simultaneous thermogravimetric and differential thermal analysis (TG-DTA). Endothermic peaks in the range of 519.27–539.01 °C were mainly due to dehydroxylation of kaolin. Exothermic peaks in the range of 814.01–1060.55 °C were attributed to mullite crystallization. No major difference was found in TG-DTA data of quartz-containing sample. Fabricated green samples were heated in the temperature range of 1100–1280 °C based on the softening point (PCE values) of the experimental bodies. Physico-mechanical properties, phase, and microstructure of the heated samples were evaluated by standard techniques. Early vitrification was observed in the case of VPF 1 and VPF 3. Quartz-containing body (VPQ) was vitrified at 1280 °C. X-ray diffraction (XRD), field emission scanning electron microscopic (FESEM), and energy dispersive X-ray analysis (EDAX) studies confirmed the presence of quartz (SiO2) and mullite (3Al2O3·2SiO2) in VPF 1 while quartz, mullite, and anorthite (CaO·Al2O3·2SiO2) were observed in VPF 2 and VPF 3. Alumina-enriched slag used in this study was contributed towards anorthite crystal formation. In quartz-containing body, major phases were found to be quartz and mullite.








Similar content being viewed by others
References
Schuller, K.H.: The development of microstructure in silicate ceramics. I Whiteware. J. Educ. Modules Mater Sci Eng. 4(3), 529–565 (1982)
Carty, W.M., Senapati, U.: Porcelain-raw materials, processing, phase evolution and mechanical behavior. J. Am. Ceram. Soc. 81, 3–20 (1998)
Iqbal, Y., Lee, W.E.: Microstructural evolution in triaxial porcelain. J. Am. Ceram. Soc. 83(12), 3121–3127 (2000)
Ece, O.I., Nagakawa, Z.: Bending strength of porcelains. Ceram. Int. 28, 131–140 (2002)
Ludin, S.T.: Microstructure of porcelain. Nat. Bur. Stan. U. S. A. Misc. Publ. 257, 93–106 (1964)
Wiedmann, T.: Beitrag zur Erfassung des Festigkeitsträgers im Porzellan. Sprechs. 92, 2–5 (1959)
Palatzky, A., Tummler, W.: Einige Untersuchungen zur Steigerung der mechanischen Festigkeit von Porzellanmassen. Silikattechnik. 9, 68–73 (1958)
Weyl, D.: Uber den Einfluss innerer Spannungen auf das Gefuge und die Mechaniche Fstigkeit des Porzellans. Ber Dtsch Keram Ges. 36, 319–324 (1959)
Dana, K., Das, S.K.: Evolution of microstructure in fly ash containing porcelain body on heating at different temperature. Bull. Mater. Sci. 27(2), 183–188 (2004)
Dana, K., Das, S., Das, S.K.: Effect of substitution of fly ash for quartz in triaxial kaolin–quartz–feldspar system. J. Eur. Ceram. Soc. 24, 3169–3175 (2004)
Kumar, S., Singh, K.K.: Effects of fly ash additions on the sintering and physico-mechanical properties of ceramic tiles. J Met Mater Process. 16, 351–358 (2004)
Dana, K., Das, S.K.: Partial substitution of feldspar by BF slag in triaxial porcelain: phase and microstructural evolution. J. Eur. Ceram. Soc. 24, 3833–3839 (2004)
Dana, K., Dey, J., Das, S.K.: Synergistic effect of fly ash and blast furnace slag on the mechanical strength of traditional porcelain tiles. J. Eur. Ceram. Soc. 31, 147–152 (2005)
Dana, K., Das, S.K.: High strength ceramic floor tiles containing Indian metallurgical slag. J. Mater. Sci. Lett. 22, 387–389 (2003)
Das, S.K., Pal, M., Ghosh, J., Pathi, K.V., Mondal, S.: The effect of basic oxygen furnace slag and fly ash additions in triaxial porcelain composition: phase and microstructural evolution. Trans. Indian Inst. Metals. 3, 213–220 (2013)
Siddiqui, A.R., Pal, M., Bhattacharya, D., Das, S.K.: Iron and steel slag an alternative source of raw materials for porcelain ceramics. Global NEST J. 16(4), 587–596 (2014)
Pal, M.: Utilization of inorganic solid wastes generated by iron and steel industries in ceramic composition. PhD Thesis, Jadavpur University, Kolkata (2016)
Pal, M., Das, S., Gupta, S., Das, S.K.: Thermal analysis and vitrification behaviour of slag containing porcelain stoneware body. J. Therm. Anal. Calorim. 124(3), 1169–1177 (2016)
Martin-Marquez, J., Rincón, J.M., Romero, M.: Effect of firing temperature on sintering of porcelain stoneware tiles. Ceram. Int. 34, 1867–1873 (2008)
Romero, M., Martin-Marquez, J., Rincon, J.M.: Kinetic of mullite formation from a porcelain stoneware body for tiles production. J. Eur. Ceram. Soc. 26(9), 1647–1652 (2006)
Bousak, H., Chemanj, H., Serier, A.: Characterization of porcelain tableware formulation containing bentonite clay. Int J Phys Sci. 10(1), 38–45 (2015)
Omani, H., Hamidouche, M., Madjoubi, M.A., Louci, K., Bouaouadja, N.: Etude de la Transformation de trois nuances de kaolin en fonction de la temperature. Silic. Ind. 65(11–12), 119–124 (2000)
Goswami, A.P., Poddar, R.K., Khattry, D.K., Lodha, A.C.: In: Banerjee, G., Das, S.K. (eds.) Refractories and furnaces—new options and new values, p. 145. Allied Publishers, New Delhi;: ISBN81-7764-109-3 (2000)
Acknowledgements
The authors are thankful to the CSIR-CGCRI and Jadavpur University for providing the necessary facilities.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Pal, M., Das, S.K. Phase and microstructural evolution in quartz-free porcelain tile compositions. J Aust Ceram Soc 54, 109–117 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s41779-017-0132-9
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s41779-017-0132-9