Abstract
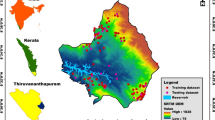
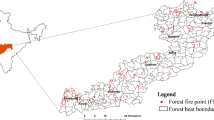
Forest fires are one of the most common natural hazards that occur in the Western Ghats region. There are many protected areas in this part of the Western Ghats; therefore, fire can pose a serious threat to habitats and wildlife. In the past, fires have also affected the Parambikulam Tiger Reserve. The objectives of this study are to demarcate the fire risk zones using GIS techniques and to evaluate the influence of each factor on fire initiation. The following factors are selected for the analysis: land cover types, slope angle, aspect, topographic wetness index, distance from the settlement, distance from the road, distance from the tourist spot, and distance from the anti-poaching camp shed. The analytical hierarchy process method is used to determine the weights, and the ArcGIS and ERDAS Imagine software tools are used to create the fire risk zone map. The area of the prepared map is divided into the following five risk zones: very low, low, moderate, high, and very high. The risk zone map has been validated using fire incidence data for the period from 2002 to 2020 collected from the forest fire portal of the Forest Survey of India. It was found that 71% of fire incidences fall in high-risk and very high–risk zones of the prepared map. The validation using the receiver operating characteristic curve analysis, with an area under ROC curve value of 0.795, confirms the prediction accuracy of the risk zone map. The prepared fire risk zone map will help the planners, officials of the forest, and the disaster management departments to take appropriate mitigation measures in order to prevent future fires and thereby protect the valuable forest resources.












Similar content being viewed by others
Change history
17 May 2021
A Correction to this paper has been published: https://doi.org/10.1007/s41651-021-00083-w
References
Abdi O, Kamkar B, Shirvani Z, da Silva JAT, Buchroithner MF (2018) Spatial-statistical analysis of factors determining forest fires: a case study from Golestan, Northeast Iran. Geom, Nat Hazards Risk 9(1):267–280. https://doi.org/10.1080/19475705.2016.1206629
Ajin RS, Jacob MK, Menon ARR, Vinod PG (2014) Forest fire risk analysis using geo-information technology: a study of Peppara Wildlife Sanctuary, Thiruvananthapuram, Kerala, India. In: Pradeep Kumar AP, Behr FJ, Illiyas FT, Shaji E (eds) Proceedings of the 2nd Disaster Risk Vulnerability Conference 2014 (DRVC-2014). Thiruvananthapuram, India, pp 160–165
Ajin RS, Loghin AM, Jacob MK, Vinod PG, Krishnamurthy RR (2016a) The risk assessment of potential forest fire in Idukki Wildlife Sanctuary using RS and GIS techniques. Int J Adv Earth Sci Eng 5(1):308–318
Ajin RS, Loghin AM, Vinod PG, Jacob MK (2016b) Forest fire risk zone mapping in Chinnar Wildlife Sanctuary, Kerala, India: a study using geospatial tools. J Global Res 3:16–26
Ajin RS, Loghin AM, Vinod PG, Jacob MK (2016c) Forest fire risk zone mapping using RS and GIS techniques: a study in Achankovil forest division, Kerala, India. J Earth Environ Health Sci 2(3):109–115. https://doi.org/10.4103/2423-7752.199288
Ajin RS, Loghin AM, Vinod PG, Jacob MK (2017a) Mapping of forest fire risk zones in Peechi-Vazhani Wildlife Sanctuary, Thrissur, Kerala, India: a study using geospatial techniques. J Wetlands Biodiver 7:7–16
Ajin RS, Loghin AM, Vinod PG, Jacob MK (2017b) The risk analysis of potential forest fires in a wildlife sanctuary in the Western Ghats (Southwest Indian Peninsula) using geospatial techniques. Int J Health Syst Disaster Manag 5(1):18–23. https://doi.org/10.4103/ijhsdm.ijhsdm_26_16
Ajin RS, Loghin AM, Vinod PG, Menon ARR, Jacob MK (2018) Forest fire risk assessment using geospatial techniques: a study in Mannarkkad forest division of Palakkad District, Kerala, India. ECOTERRA - J Environ Res Protect 15(1):1–9
Ambadan JT, Oja M, Gedalof Z, Berg AA (2020) Satellite-observed soil moisture as an indicator of wildfire risk. Remote Sens 12(10). https://doi.org/10.3390/rs12101543
Arca D, Hacısalihoğlu M, Kutoğlu ŞH (2020) Producing forest fire susceptibility map via multi-criteria decision analysis and frequency ratio methods. Nat Hazards 104:73–89. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11069-020-04158-7
Arpaci A, Malowerschnig B, Sass O, Vacik H (2014) Using multi variate data mining techniques for estimating fire susceptibility of Tyrolean forests. Appl Geogr 53:258–270. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apgeog.2014.05.015
Beven KJ, Kirkby MJ (1979) A physically based, variable contributing area model of basin hydrology. Hydrol Sci J 24(1):43–69. https://doi.org/10.1080/02626667909491834
Bui DT, Bui QT, Nguyen QP, Pradhan B, Nampak H, Trinh PT (2017) A hybrid artificial intelligence approach using GIS-based neural-fuzzy inference system and particle swarm optimization for forest fire susceptibility modeling at a tropical area. Agric For Meteorol 233:32–44. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.agrformet.2016.11.002
Busico G, Giuditta E, Kazakis N, Colombani N (2019) A hybrid GIS and AHP approach for modelling actual and future forest fire risk under climate change accounting water resources attenuation role. Sustainability 11. https://doi.org/10.3390/su11247166
Certini G (2005) Effects of fire on properties of forest soils: a review. Oecologia 143:1–10. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00442-004-1788-8
Chen Z (2006) Effects of fire on major forest ecosystem processes: an overview. Ying Yong Sheng Tai Xue Bao (J Appl Ecol) 17(9):1726–1732
Deng O, Su G, Huang Q, Li Y (2013) Forest fire risk mapping based on spatial logistic model of Northeastern China forest zone. In: Bian F, Xie Y, Cui X, Zeng Y (eds) Geo-Informatics in Resource Management and Sustainable Ecosystem (GRMSE 2013), Communications in Computer and Information Science, vol 399. Springer, Berlin, pp 181–192. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-642-41908-9_18
Dong X, Li-min D, Guo-fan S, Lei T, Hui W (2005) Forest fire risk zone mapping from satellite images and GIS for Baihe Forestry Bureau, Jilin, China. J For Res 16:169–174. https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02856809
Dimuccio LA, Ferreira R, Cunha L, de Almeida AC (2011) Regional forest-fire susceptibility analysis in central Portugal using a probabilistic ratings procedure and artificial neural network weights assignment. Int J Wildland Fire 20(6):776–791. https://doi.org/10.1071/WF09083
Eskandari S (2017) A new approach for forest fire risk modeling using fuzzy AHP and GIS in Hyrcanian forests of Iran. Arab J Geosci 10. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12517-017-2976-2
Eskandari S, Miesel JR (2017) Comparison of the fuzzy AHP method, the spatial correlation method, and the Dong model to predict the fire high-risk areas in Hyrcanian forests of Iran. Geom, Nat Hazards Risk 8(2):933–949. https://doi.org/10.1080/19475705.2017.1289249
Estes BL, Knapp EE, Skinner CN, Miller JD, Preisler HK (2017) Factors influencing fire severity under moderate burning conditions in the Klamath Mountains, Northern California, USA. Ecosphere 8(5). https://doi.org/10.1002/ecs2.1794
Finlay SE, Moffat A, Gazzard R, Baker D, Murray V (2012) Health impacts of wildfires. PLOS Curr Disast. https://doi.org/10.1371/4f959951cce2c
Flach PA (2011) ROC Analysis. In: Sammut C, Webb GI (eds) Encyclopedia of machine learning. Springer, Boston. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-0-387-30164-8_733
Franzen MD (2011) Receiver-operating characteristics. In: Kreutzer JS, DeLuca J, Caplan B (eds) Encyclopedia of clinical neuropsychology. Springer, New York, NY. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-0-387-79948-3_1240
Gheshlaghi HA (2019) Using GIS to develop a model for forest fire risk mapping. J Indian Soc Remote Sens 47(7):1173–1185. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12524-019-00981-z
Gheshlaghi HA, Feizizadeh B, Blaschke T (2020) GIS-based forest fire risk mapping using the analytical network process and fuzzy logic. J Environ Plan Manag 63(3):481–499. https://doi.org/10.1080/09640568.2019.1594726
Güngöroğlu C (2017) Determination of forest fire risk with fuzzy analytic hierarchy process and its mapping with the application of GIS: the case of Turkey/Çakırlar. Human Ecologic Risk Assess: Int J 23(2):388–406. https://doi.org/10.1080/10807039.2016.1255136
Hanley JA, McNeil BJ (1982) The meaning and use of the area under a receiver operating characteristic (ROC) curve. Radiology 143(1):29–36. https://doi.org/10.1148/radiology.143.1.7063747
Hong H, Tsangaratos P, Ilia I, Liu J, Zhu AX, Xu C (2018) Applying genetic algorithms to set the optimal combination of forest fire related variables and model forest fire susceptibility based on data mining models. The case of Dayu County, China. Sci Total Environ 630:1044–1056. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2018.02.278
Hosmer DW, Lemeshow S (2000) Applied logistic regression, 2nd edn. John Wiley & Sons, Inc., United States of America, p 392
Jaiswal RK, Mukherjee S, Raju KD, Saxena R (2002) Forest fire risk zone mapping from satellite imagery and GIS. Int J Appl Earth Obs Geoinf 4(1):1–10. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0303-2434(02)00006-5
Jobin KM, Nameer PO (2012) Diversity of rhacophorids (Amphibia: Anura) in Parambikulam Tiger Reserve, Western Ghats, Kerala, India. J Threat Taxa 4(13):3205–3214. https://doi.org/10.11609/JoTT.o3081.3205-14
Kaur H, Sood SK (2019) Adaptive neuro fuzzy inference system (ANFIS) based wildfire risk assessment. J Exper Theoret Artif Intellig 31(4):599–619. https://doi.org/10.1080/0952813X.2019.1591523
Kayet N, Chakrabarty A, Pathak K, Sahoo S, Dutta T, Hatai BK (2020) Comparative analysis of multi-criteria probabilistic FR and AHP models for forest fire risk (FFR) mapping in Melghat Tiger Reserve (MTR) forest. J For Res 31:565–579. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11676-018-0826-z
Kil SH, Lee DK, Kim JH, Li MH, Newman G (2016) Utilizing the analytic hierarchy process to establish weighted values for evaluating the stability of slope revegetation based on hydroseeding applications in South Korea. Sustainability 8(1). https://doi.org/10.3390/su8010058
Krueger ES, Ochsner TE, Engle DM, Carlson JD, Twidwell D, Fuhlendorf SD (2015) Soil moisture affects growing-season wildfire size in the Southern Great Plains. Soil Sci Soc Am J 79(6):1567–1576. https://doi.org/10.2136/sssaj2015.01.0041
Leuenberger M, Parente J, Tonini M, Pereira MG, Kanevski M (2018) Wildfire susceptibility mapping: deterministic vs. stochastic approaches. Environ Model Softw 101:194–203. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.envsoft.2017.12.019
Manna I, Bandyopadhyay M (2019) Chapter 16 - Physicochemical perturbation of plants on exposure to metal oxide nanoparticle. In: Tripathi DK, Ahmad P, Sharma S, Chauhan DK, Dubey NK (eds) Nanomaterials in plants, algae and microorganisms: concepts and controversies, vol 2. Academic Press, pp 323–352. https://doi.org/10.1016/B978-0-12-811488-9.00016-0
Martin D, Tomida M, Meacham B (2016) Environmental impact of fire. Fire Sci Rev 5. https://doi.org/10.1186/s40038-016-0014-1
Melo F (2013) Area under the ROC curve. In: Dubitzky W, Wolkenhauer O, Cho KH, Yokota H (eds) Encyclopedia of systems biology. Springer, New York. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-1-4419-9863-7_209
Mohammadi F, Bavaghar MP, Shabanian N (2014) Forest fire risk zone modeling using logistic regression and GIS: an Iranian case study. Small-scale Forestry 13:117–125. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11842-013-9244-4
Nadporozhskaya MA, Chertov OG, Bykhovets SS, Shaw CH, Maksimova EY, Abakumov EV (2018) Recurring surface fires cause soil degradation of forest land: a simulation experiment with the EFIMOD model. Land Degrad Dev 29(7):2222–2232. https://doi.org/10.1002/ldr.3021
Nameer PO, Molur S, Walker S (2001) Mammals of Western Ghats: a simplistic overview. Zoos' Print J 16(11):629–639
Nuthammachot N, Stratoulias D (2019) A GIS- and AHP-based approach to map fire risk: a case study of Kuan Kreng peat swamp forest, Thailand. Geocarto Int 36:212–225. https://doi.org/10.1080/10106049.2019.1611946
Novo A, Fariñas-Álvarez N, Martínez-Sánchez J, González-Jorge H, Fernández-Alonso JM, Lorenzo H (2020) Mapping forest fire risk - a case study in Galicia (Spain). Remote Sens 12(22). https://doi.org/10.3390/rs12223705
Pan J, Wang W, Li J (2016) Building probabilistic models of fire occurrence and fire risk zoning using logistic regression in Shanxi Province, China. Nat Hazards 81:1879–1899. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11069-016-2160-0
Pastro LA, Dickman CR, Letnic M (2011) Burning for biodiversity or burning biodiversity? Prescribed burn vs. wildfire impacts on plants, lizards, and mammals. Ecol Appl 21(8):3238–3253. https://doi.org/10.1890/10-2351.1
Pourtaghi ZS, Pourghasemi HR, Aretano R, Semeraro T (2016) Investigation of general indicators influencing on forest fire and its susceptibility modeling using different data mining techniques. Ecol Indic 64:72–84. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ecolind.2015.12.030
Pradhan B, Suliman MDHB, Awang MAB (2007) Forest fire susceptibility and risk mapping using remote sensing and geographical information systems (GIS). Disaster Prev Manag 16(3):344–352. https://doi.org/10.1108/09653560710758297
Ricotta C, Bajocco S, Guglietta D, Conedera M (2018) Assessing the influence of roads on fire ignition: does land cover matter? Fire 1(2). https://doi.org/10.3390/fire1020024
Saaty TL (1980) The analytic hierarchy process: planning, priority setting, resource allocation (decision making series). McGraw Hill, New York
Sannigrahi S, Pilla F, Basu B, Basu AS, Sarkar K, Chakraborti S, Joshi PK, Zhang Q, Wang Y, Bhatt S, Bhatt A, Jha S, Keesstra S, Roy PS (2020) Examining the effects of forest fire on terrestrial carbon emission and ecosystem production in India using remote sensing approaches. Sci Total Environ 725:138331. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2020.138331
Santín C, Doerr SH (2016) Fire effects on soils: the human dimension. Philosophical transactions of the Royal Society of London. Ser B, Biol Sci 371(1696). https://doi.org/10.1098/rstb.2015.0171
Satir O, Berberoglu S, Donmez C (2016) Mapping regional forest fire probability using artificial neural network model in a Mediterranean forest ecosystem. Geom, Nat Hazards Risk 7(5):1645–1658. https://doi.org/10.1080/19475705.2015.1084541
Setiawan I, Mahmud AR, Mansor S, Shariff ARM, Nuruddin AA (2004) GIS-grid-based and multi-criteria analysis for identifying and mapping peat swamp forest fire hazard in Pahang, Malaysia. Disaster Prev Manag 13(5):379–386. https://doi.org/10.1108/09653560410568507
Soman D, Anitha V (2020) Community dependence on the natural resources of Parambikulam Tiger Reserve, Kerala, India. Trees, Forests People 2:100014. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.tfp.2020.100014
Soto MEC (2012) The identification and assessment of areas at risk of forest fire using fuzzy methodology. Appl Geogr 35(1-2):199–207. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apgeog.2012.07.001
Sreehari R, Nameer PO (2016) Small carnivores of Parambikulam Tiger Reserve, Southern Western Ghats, India. J Threat Taxa 8(11):9306–9315. https://doi.org/10.11609/jott.2311.8.11.9306-9315
Tedim F, Garcin M, Vinchon C, Carvalho S, Desramaut N, Rohmer J (2014) Chapter 7 - Comprehensive vulnerability assessment of forest fires and coastal erosion: evidences from case-study analysis in Portugal. In: Birkmann J, Kienberger S, Alexander DE (eds) Assessment of vulnerability to natural hazards. Elsevier, Netherlands, pp 149–177. https://doi.org/10.1016/B978-0-12-410528-7.00007-2
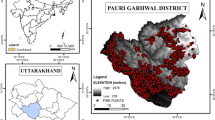
Tiwari A, Shoab M, Dixit A (2020) GIS-based forest fire susceptibility modeling in Pauri Garhwal, India: a comparative assessment of frequency ratio, analytic hierarchy process and fuzzy modeling techniques. Nat Hazards 105:1189–1230. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11069-020-04351-8
Veena HS, Ajin RS, Loghin AM, Sipai R, Adarsh P, Viswam A, Vinod PG, Jacob MK, Jayaprakash M (2017) Wildfire risk zonation in a tropical forest division in Kerala, India: a study using geospatial techniques. Int J Conserv Sci 8(3):475–484
Vinod PG, Ajin RS, Jacob MK (2016) RS and GIS based spatial mapping of forest fire risk zones in Wayanad Wildlife Sanctuary, North Kerala, India. Int J Earth Sci Eng 9(2):498–502
Ye J, Wu M, Deng Z, Xu S, Zhou R, Clarke KC (2017) Modeling the spatial patterns of human wildfire ignition in Yunnan province, China. Appl Geogr 89:150–162. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apgeog.2017.09.012
Yin HW, Kong FH, Li XZ (2004) RS and GIS-based forest fire risk zone mapping in da Hinggan mountains. Chin Geogr Sci 14:251–257. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11769-003-0055-y
Yong B, Ren LL, Hong Y, Gourley JJ, Chen X, Zhang YJ, Yang XL, Zhang ZX, Wang WG (2012) A novel multiple flow direction algorithm for computing the topographic wetness index. Hydrol Res 43(1-2):135–145. https://doi.org/10.2166/nh.2011.115
Gigović L, Pourghasemi HR, Drobnjak S, Bai S (2019) Testing a new ensemble model based on SVM and random forest in forest fire susceptibility assessment and its mapping in Serbia’s Tara National Park. Forests 10(5). https://doi.org/10.3390/f10050408
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Ethics Approval and Consent to Participate
This article does not contain any studies with human participants or animals performed by any of the authors. Informed consent is not applicable.
Conflict of Interest
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Nikhil, S., Danumah, J.H., Saha, S. et al. Application of GIS and AHP Method in Forest Fire Risk Zone Mapping: a Study of the Parambikulam Tiger Reserve, Kerala, India. J geovis spat anal 5, 14 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s41651-021-00082-x
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s41651-021-00082-x