Abstract
Introduction
Accelerator mass spectrometry (AMS) has been used for the analysis of a lot nuclides in many scientific fields and is one of the most optimal methods to determine very low concentrations of long-lived nuclides. The XCAMS system is an extension of the Compact \(^{14}\mathrm{C}\) Accelerator Mass Spectrometer for \(^{10}\hbox {Be}\) and \(^{26}\hbox {Al}\). A description of the first Chinese XCAMS system and initial performance of three nuclides of \(^{14}\hbox {C}\), \(^{10}\hbox {Be}\), and \(^{26}\hbox {Al}\), respectively, will be reported.
Experimental procedures
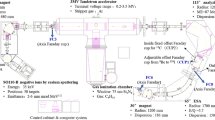
Solid sample material (graphite, \(\mathrm{Al}_{2}\mathrm{O}_{3}\), and \(\mathrm{BeO}\)) is loaded into cathode holders for AMS analysis. The negatively charged ions (\(\mathrm{C}^{-}, \mathrm{Al}^{-}, \mathrm{and }\, \mathrm{BeO}^{-}\)) are extracted and accelerated to the terminal, broken-up, and some orbital electrons stripped off to form positively charged atomic ions, and accelerated further. In the post-acceleration region, the magnetic and electrostatic devices act on momentum and energy analysis, respectively. A multi-anode detector is used for the identification and detection of relevant isotopes and isobars.
System performance
The test criteria of three rare isotopes each were set for beam current intensity, measurement precision, and machine background. The corresponding material and cathode holder were, respectively, used for \(^{14}\hbox {C}\), \(^{10}\hbox {Be}\), and \(^{26}\hbox {Al}\) test. Several batches of real sample have already been analyzed by the new AMS system based on the acceptance test results. In addition, several secondary standards were measured to check the stability of the system.
Conclusion
The new XCAMS facility has been installed successfully, and the latest performance also showed that the machine is reliable enough, in general. Both the hardware components and software system were in good condition for accurate and precise data analysis in the near future.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
J.E. Chen, Z.Y. Guo, K.X. Liu, Rev. Accel. Sci. Technol. 4, 117 (2011)
P. Bierman, P.J. Turner, Quat. Res. 44, 378 (1995)
D. Fink, Nucl. Instrum. Methods Phys. Res. Sect. B 268, 1334 (2010)
A. Zondervan, T.M. Hauser, J. Kaiser, R.L. Kitchen, J.C. Turnbull, J.G. West, Nucl. Instrum. Methods Phys. Res. Sect. B 361, 25 (2015)
P. Kumar, S. Chopra, J.K. Pattanaik, S. Ojha, S. Gargari, R. Joshi, D. Kanjilal, Nucl. Instrum. Methods Phys. Res. Sect. B 361, 115 (2015)
K. Nishiizumi, M. Imamura, M.W. Caffee, J.R. Southon, R.C. Finkel, J. McAninch, Nucl. Instrum. Methods Phys. Res. Sect. B 258, 403 (2007)
S. Gulliksen, M. Scott, Radiocarbon 37, 820 (1995)
E.M. Scott, G.T. Cook, P. Naysmith, Radiocarbon 52, 859 (2010)
K. Nishiizumi, Nucl. Instrum. Methods Phys. Res. Sect. B 223–224, 388 (2004)
Acknowledgements
This work was mainly supported by the National Natural Science Foundations of China (NSFC), under Grant Nos. 11775157 and 11575296.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Dong, K., Lang, Y., Hu, N. et al. The new AMS facility at Tianjin University. Radiat Detect Technol Methods 2, 30 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s41605-018-0064-0
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s41605-018-0064-0