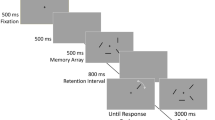
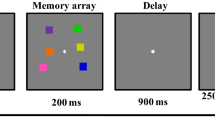
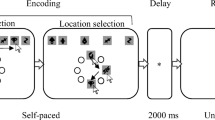
Abstract
Previous studies have indicated that adaptive visual-working-memory (VWM) training could increase VWM capacity. However, it is still unclear whether a training effect is observed in comparison with an active control group, whether the training would apply not only to VWM quantity but also to VWM quality, and whether the training effects would transfer to other VWM tasks. The present study investigated the transfer effect of VWM-quantity training to VWM quality and that of VWM-quality training to VWM quantity in comparison with an active control group. Each training group performed change detection tasks for either VWM quantity or quality for a week, whereas the active control group performed a visual-search task. The results indicated that VWM-quantity training increased VWM quality at post-test over the pre-test and compared to the active control group. VWM-quality training also increased VWM quantity over the pre-test, although the increased VWM quantity at post-test was not significantly higher than in the active control group. Although the transfer effect of VWM-quality training to VWM quantity was weak, the present results support a transfer effect of VWM training to VWM quantity and quality. Adjusted adaptive training of VWM would enhance the allocation of limited resources for VWM quantity and quality.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Alvarez, G. A., & Cavanagh, P. (2004). The capacity of visual short-term memory is set both by visual information load and by number of objects. Psychological Science, 15(2), 106–111. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.0963-7214.2004.01502006.x.
Bays, P. M., & Husain, M. (2008). Dynamic shifts of limited working memory resources in human vision. Science, 321(5890), 851–854. https://doi.org/10.1126/science.1158023.
Bengson, J. J., & Luck, S. J. (2016). Effects of strategy on visual working memory capacity. Psychonomic Bulletin & Review, 23(1), 265–270. https://doi.org/10.3758/s13423-015-0891-7.
Buschkuehl, M., Jaeggi, S. M., Mueller, S. T., Shah, P., & Jonides, J. (2017). Training change detection leads to substantial task-specific improvement. Journal of Cognitive Enhancement, 1(4), 419–433. https://doi.org/10.1007/s41465-017-0055-y.
Chen, D., Yee Eng, H., & Jiang, Y. (2006). Visual working memory for trained and novel polygons. Visual Cognition, 14(1), 37–54. https://doi.org/10.1080/13506280544000282.
Cowan, N. (2001). The magical number 4 in short-term memory: a reconsideration of mental storage capacity. Behavioral and Brain Sciences, 24(1), 87–114. https://doi.org/10.1017/S0140525X01003922.
Curby, K. M., & Gauthier, I. (2010). To the trained eye: perceptual expertise alters visual processing. Topics in Cognitive Science, 2(2), 189–201. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1756-8765.2009.01058.x.
Curby, K. M., Glazek, K., & Gauthier, I. (2009). A visual short-term memory advantage for objects of expertise. Journal of Experimental Psychology: Human Perception and Performance, 35(1), 94–107. https://doi.org/10.1037/0096-1523.35.1.94.
Emrich, S. M., Al-Aidroos, N., Pratt, J., & Ferber, S. (2009). Visual search elicits the electrophysiological marker of visual working memory. PLoS One, 4(11), e8042. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0008042.
Eng, H. Y., Chen, D., & Jiang, Y. (2005). Visual working memory for simple and complex visual stimuli. Psychonomic Bulletin & Review, 12(6), 1127–1133. https://doi.org/10.3758/BF03206454.
Fougnie, D., Cormiea, S. M., Kanabar, A., & Alvarez, G. A. (2016). Strategic trade-offs between quantity and quality in working memory. Journal of Experimental Psychology: Human Perception and Performance, 42(8), 1231–1240. https://doi.org/10.1037/xhp0000211.
Fukuda, K., Vogel, E. K., Mayr, U., & Awh, E. (2010). Quantity, not quality: the relationship between fluid intelligence and working memory capacity. Psychonomic Bulletin & Review, 17(5), 673–679. https://doi.org/10.3758/17.5.673.
Gaspar, J. G., Neider, M. B., Simons, D. J., McCarley, J. S., & Kramer, A. F. (2013). Change detection: training and transfer. PLoS One, 8(6), e67781. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0067781.
Harrison, T. L., Shipstead, Z., Hicks, K. L., Hambrick, D. Z., Redick, T. S., & Engle, R. W. (2013). Working memory training may increase working memory capacity but not fluid intelligence. Psychological Science, 24(12), 2409–2419. https://doi.org/10.1177/0956797613492984.
Jolles, D. D., & Crone, E. A. (2012). Training the developing brain: a neurocognitive perspective. Frontiers in Human Neuroscience, 6, 76. https://doi.org/10.3389/fnhum.2012.00076.
Kane, M. J., Poole, B. J., Tuholski, S. W., & Engle, R. W. (2006). Working memory capacity and the top-down control of visual search: exploring the boundaries of “executive attention”. Journal of Experimental Psychology: Learning, Memory, and Cognition, 32(4), 749–777. https://doi.org/10.1037/0278-7393.32.4.749.
Karbach, J., & Verhaeghen, P. (2014). Making working memory work: a meta-analysis of executive-control and working memory training in older adults. Psychological Science, 25(11), 2027–2037. https://doi.org/10.1177/0956797614548725.
Klingberg, T. (2010). Training and plasticity of working memory. Trends in Cognitive Sciences, 14(7), 317–324. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.tics.2010.05.002.
Kundu, B., Sutterer, D. W., Emrich, S. M., & Postle, B. R. (2013). Strengthened effective connectivity underlies transfer of working memory training to tests of short-term memory and attention. Journal of Neuroscience, 33(20), 8705–8715. https://doi.org/10.1523/JNEUROSCI.5565-12.2013.
Li, C.-H., He, X., Wang, Y.-J., Hu, Z., & Guo, C.-Y. (2017). Visual working memory capacity can be increased by training on distractor filtering efficiency. Frontiers in Psychology, 8, 196. https://doi.org/10.3389/fpsyg.2017.00196.
Luck, S. J., & Vogel, E. K. (1997). The capacity of visual working memory for features and conjunctions. Nature, 390(6657), 279–281. https://doi.org/10.1038/36846.
Luck, S. J., & Vogel, E. K. (2013). Visual working memory capacity: from psychophysics and neurobiology to individual differences. Trends in Cognitive Sciences, 17(8), 391–400. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.tics.2013.06.006.
Luria, R., & Vogel, E. K. (2011). Visual search demands dictate reliance on working memory storage. Journal of Neuroscience, 31(16), 6199–6207. https://doi.org/10.1523/JNEUROSCI.6453-10.2011.
Ma, W. J., Husain, M., & Bays, P. M. (2014). Changing concepts of working memory. Nature Neuroscience, 17, 347–356. https://doi.org/10.1038/nn.3655.
Machizawa, M. G., & Driver, J. (2011). Principal component analysis of behavioural individual differences suggests that particular aspects of visual working memory may relate to specific aspects of attention. Neuropsychologia, 49(6), 1518–1526. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.neuropsychologia.2010.11.032.
Machizawa, M. G., Goh, C. C. W., & Driver, J. (2012). Human visual short-term memory precision can be varied at will when the number of retained items is low. Psychological Science, 23(6), 554–559. https://doi.org/10.1177/0956797611431988.
Moriya, J. (2018). Attentional networks and visuospatial working memory capacity in social anxiety. Cognition and Emotion, 32(1), 158–166. https://doi.org/10.1080/02699931.2016.1263601.
Moriya, J., & Sugiura, Y. (2012). High visual working memory capacity in trait social anxiety. PLoS One, 7(4), e34244. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0034244.
Morrison, A. B., & Chein, J. M. (2011). Does working memory training work? The promise and challenges of enhancing cognition by training working memory. Psychonomic Bulletin & Review, 18(1), 46–60. https://doi.org/10.3758/s13423-010-0034-0.
Murray, A. M., Nobre, A. C., Astle, D. E., & Stokes, M. G. (2012). Lacking control over the trade-off between quality and quantity in visual short-term memory. PLoS One, 7(8), e41223. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0041223.
Olson, I. R., & Jiang, Y. (2004). Visual short-term memory is not improved by training. Memory & Cognition, 32(8), 1326–1332. https://doi.org/10.3758/BF03206323.
Olson, I. R., Jiang, Y., & Moore, K. S. (2005). Associative learning improves visual working memory performance. Journal of Experimental Psychology: Human Perception and Performance, 31(5), 889–900. https://doi.org/10.1037/0096-1523.31.5.889.
Owens, M., Koster, E. H. W., & Derakshan, N. (2013). Improving attention control in dysphoria through cognitive training: transfer effects on working memory capacity and filtering efficiency. Psychophysiology, 50(3), 297–307.
Pashler, H. (1988). Familiarity and visual change detection. Perception & Psychophysics, 44(4), 369–378. https://doi.org/10.3758/BF03210419.
Qi, S., Chen, J., Hitchman, G., Zeng, Q., Ding, C., Li, H., & Hu, W. (2014a). Reduced presentations capacity in visual working memory in trait anxiety. Biological Psychology, 103, 92–99. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biopsycho.2014.08.010.
Qi, S., Ding, C., & Li, H. (2014b). Neural correlates of inefficient filtering of emotionally neutral distractors from working memory in trait anxiety. Cognitive, Affective, & Behavioral Neuroscience, 14(1), 253–265. https://doi.org/10.3758/s13415-013-0203-5.
Redick, T. S., Shipstead, Z., Harrison, T. L., Hicks, K. L., Fried, D. E., Hambrick, D. Z., … Engle, R. W. (2013). No evidence of intelligence improvement after working memory training: a randomized, placebo-controlled study. Journal of Experimental Psychology: General, 142(2), 359–379. https://doi.org/10.1037/a0029082.
Roggeman, C., Klingberg, T., Feenstra, H. E. M., Compte, A., & Almeida, R. (2014). Trade-off between capacity and precision in visuospatial working memory. Journal of Cognitive Neuroscience, 26(2), 211–222. https://doi.org/10.1162/jocn_a_00485.
Shin, E., Lee, H., Yoo, S.-A., & Chong, S. C. (2015). Training improves the capacity of visual working memory when it is adaptive, individualized, and targeted. PLoS One, 10(4), e0121702. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0121702.
Simmons, J. P., Nelson, L. D., & Simonsohn, U. (2011). False-positive psychology: undisclosed flexibility in data collection and analysis allows presenting anything as significant. Psychological Science, 22(11), 1359–1366. https://doi.org/10.1177/0956797611417632.
Stout, D. M., & Rokke, P. D. (2010). Components of working memory predict symptoms of distress. Cognition & Emotion, 24(8), 1293–1303. https://doi.org/10.1080/02699930903309334.
Szmalec, A., Verbruggen, F., Vandierendonck, A., & Kemps, E. (2011). Control of interference during working memory updating. Journal of Experimental Psychology: Human Perception and Performance, 37(1), 137–151. https://doi.org/10.1037/a0020365.
Unsworth, N., Fukuda, K., Awh, E., & Vogel, E. K. (2014). Working memory and fluid intelligence: capacity, attention control, and secondary memory retrieval. Cognitive Psychology, 71, 1–26. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cogpsych.2014.01.003.
Unsworth, N., Fukuda, K., Awh, E., & Vogel, E. K. (2015). Working memory delay activity predicts individual differences in cognitive abilities. Journal of Cognitive Neuroscience, 27(5), 853–865. https://doi.org/10.1162/jocn_a_00765.
Vogel, E. K., & Machizawa, M. G. (2004). Neural activity predicts individual differences in visual working memory capacity. Nature, 428(6984), 748–751. https://doi.org/10.1038/nature02447.
Vogel, E. K., Woodman, G. F., & Luck, S. J. (2001). Storage of features, conjunctions and objects in visual working memory. Journal of Experimental Psychology. Human Perception and Performance, 27(1), 92–114. https://doi.org/10.1037/0096-1523.27.1.92.
Vogel, E. K., McCollough, A. W., & Machizawa, M. G. (2005). Neural measures reveal individual differences in controlling access to working memory. Nature, 438(7067), 500–503. https://doi.org/10.1038/nature04171.
von Bastian, C. C., & Oberauer, K. (2014). Effects and mechanisms of working memory training: a review. Psychological Research, 78, 803–820. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00426-013-0524-6.
Woodman, G. F., Vogel, E. K., & Luck, S. J. (2001). Visual search remains efficient when visual working memory is full. Psychological Science, 12(3), 219–224. https://doi.org/10.1111/1467-9280.00339.
Ye, C., Hu, Z., Li, H., Ristaniemi, T., Liu, Q., & Liu, T. (2017). A two-phase model of resource allocation in visual working memory. Journal of Experimental Psychology: Learning, Memory, and Cognition, 43(10), 1557–1566. https://doi.org/10.1037/xlm0000376.
Zhang, W., & Luck, S. J. (2008). Discrete fixed-resolution representations in visual working memory. Nature, 453(7192), 233–235. https://doi.org/10.1038/nature06860.
Zhang, W., & Luck, S. J. (2011). The number and quality of representations in working memory. Psychological Science, 22(11), 1434–1441. https://doi.org/10.1177/0956797611417006.
Zimmer, H. D., Popp, C., Reith, W., & Krick, C. (2012). Gains of item-specific training in visual working memory and their neural correlates. Brain Research, 1466, 44–55. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.brainres.2012.05.019.
Funding
The preparation of this paper was supported by the Japan Society for the Promotion of Science (JSPS): Grant-in-Aid for Young Scientists (B) (15K21518). No further potential competing financial interests exist.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of Interest
I declare that there are no conflicts of interest.
Additional information
Publisher’s note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Moriya, J. Visual-Working-Memory Training Improves Both Quantity and Quality. J Cogn Enhanc 3, 221–232 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s41465-018-00120-5
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s41465-018-00120-5