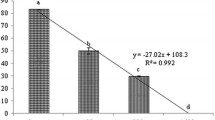
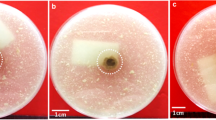
Abstract
In the present study, one Streptomyces species was isolated from a soil sample that was collected in Khafr El Shikh Governorate. Actinomycetes are prolific producers of antibiotics and important suppliers to the pharmaceutical industry. They can produce a wide range of secondary metabolites. The isolate was purified and characterized by morphological, physiological, biochemical methods and using Scanning electron microscope (SEM). The isolate was found to be Streptomyces catenula like microorganism and was therefore called Streptomyces catenula MY 12. The Streptomyces metabolite was extracted using ethyl acetate solvent. The purified extract was used to study the effect against 3rd instar larvae of the greater wax moth, Galleria mellonella. The study showed deleterious effects on growth and development of G. mellonella larvae. The results demonstrated that the mortality increased with increase in concentration. The extract prolonged the larval—pupal periods and reduced both pupation and percentage of adult emergence. The LC50 and LC90 values were calculated. The consumed food by unirradiated and irradiated 3rd instar larvae of G. mellonella in each concentration was studied. The larvae consumed much media in control treatment and fewer amounts in the higher concentration of the extract. The SEM revealed that different malformation or abnormalities were observed in larval cuticle and associated sensilla in the form of tear and ridged tergum cuticle. Also, broken and fallen or scarcity of trichodea sensilla. Undistinguished segments tear sternum and destroy plural membrane. The spiracles were completely closed, and prolegs crochets disappeared.





Similar content being viewed by others
Availability of data and material
Not applicable.
References
Abbott WS (1925) A method of computing the effectiveness of insecticides. J Econ Entomol 18:265–267
Arasu MV, Al-Dhabi NA, Saritha V, Duraipandiyan V, Muthukumar C, Kim SJ (2013) Antifeedant, larvicidal and growth inhibitory bioactivities of novel polyketide metabolite isolated from Streptomyces sp. AP-123 against Helicoverpa armigera and Spodoptera litura. BMC Microbiol 13:105. https://doi.org/10.1186/1471-2180-13-105
Becher PG, Keller S, Jung G, Sussmuth RD, Juttner F (2007) Insecticidal activity of 12-epi-hapalindole. J Isonitrile Phytochemistry 68:2493–2497
Benita Mercy Rajan and Krishnan Kannabiran (2014) Extraction and Identification of Antibacterial Secondary Metabolites from Marine Streptomyces sp VITBRK2. Int J Mol Cell Med 3(3):130–137
Chapman RF (1998) Postembryonic development. In: Chapman RF (ed) The Insects: Structure and Function, 4th edn. Cambridge University, Cambridge, pp 363–378
Cowen LE, Singh SD, Kohler JR, Collins C, Zaas AK, Schell WA et al (2009) Harnessing Hsp90 function as a powerful, broadly effective therapeutic strategy for fungal infectious disease. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 106:2818–2823
Daniel CS, Linda LK (2014) Global biogeography of Streptomyces antibiotic inhibition, resistance, and resource use. FEMS Microbiol Ecolo 88(2):386–397
Dutka A, McNulty A, Williamson SM (2015) A new threat to bees? Entomopathogenic nematodes used in biological pest control cause rapid mortality in Bombus terestis. Peer J 3:e1413. https://doi.org/10.7717/peerj.1413
Elliah P, Ramana T, Bapi Raju KVVS, Sujatha P, Uma Sankar AM (2004) Investigation on marine actinomycetes from Bay of Bengal near Karnataka coast of Andra Pradesh. Asian J Microbiol Biotechnol Environ Sci 6:53–56
Foley K, Fazio AG, Jensen B, Hughes WOH (2014) The distribution of Aspergillus sp. Opportunistic parasites in hives and their pathogenicity to honey bees. Vet Microbiol 169:203–210. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.vetmic.2013.11.029
Gambino P, Plerluisl GJ, Polnar J (1992) Field test of the nematode Steinernema feltiae (Nematoda: Steinernematidae) against yellow jacket colonies (Hym. Vespidae). Entomophaga 37:107–114. https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02372979
Hazaa MAM, Sayed RM, Abdalla RS (2017) Toxicological and ultrastructure studies in control greater wax moth, Galleria mellonella (L.), Using gamma radiation and/or emamectin benzoate. Egypt J Biol Pest Control 27(2):195–203
Jiang WK, Liu YL, Xia EH, Gao LZ (2013) Prevalent role of gene features in determining evolutionary fates of whole-genome duplication duplicated genes in flowering plants. Plant Physiol 161:1844–1861. https://doi.org/10.1104/pp.112.200147
Kaur T, Vasudev A, Sohal SK, Manhas RK (2014) Insecticidal and growth inhibitory potential of Streptomyces hydrogenans DH16 on major pest of India, Spodoptera litura (Fab.) (Lepidoptera: Noctuidae). BMC Microbiol 14:227. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12866-014-0227-1
Krupke C, Hunt G, Eltzer B, Andino G (2012) Glven K (2012) Multiple routes of pesticide exposure for honey bees living near agricultural fields. PLoS ONE 7(1):e29268. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0029268
Mahmoud AAW (2015) Study on the effect of certain bacterial metabolites as antibacterial and antitumor agents. D, Faculty of Science, El Azhar university, Cairo, Egypt, Ph
Mylonakis E (2008) Galleria mellonella and the study of fungal pathogenesis: making the case for another genetically tractable model host. Mycopathologia 165:1–3
Raja A, Prabakarana P (2011) Actinomycetes and drug-An overview. Am J Drug Discov Develop 1(2):75–84. https://doi.org/10.3923/ajdd.2011.75.84
Rishikesh GDR, Haque MA, Islam MAU, Rahman MM, Banu MR (2013) In-vitro insecticidal activity of crude extracts of Streptomyces sp against larvae of Sitophilus oryzae. Drug Discov Ther 1(8):60–63
Sadek MM (2003) Antifeedant and toxic activity of Adhatoda vasica leaf extract against Spodoptera littoralis (Lep. Noctuidae). J Appl Entomol 127(1):396–404. https://doi.org/10.1046/j.1439-0418.2003.00775.x
Bergey’s Manual of Systematic Bacteriology (1989) Vol. 4 Edited by S.T. Williams, M.E. Sharp and J.G. Holt. Williams & Wilkins, Baltimore: USA.
Wiesner A (1993) Die Induktion der Immunabwehreines Insekts (Galleria mellonella, Lepidoptera). Durch Synthetische Materialien und Arteigene Haemolym-phfaktoren, Berlin
Xiong L, Li J, Kong F (2004) Streptomyces sp 173, an insecticidal micro-organism from marine. Lett Appl Microbiol 38(1):32–37. https://doi.org/10.1046/j.1472-765X.2003.01437.x
Xiong L, Jian-zhong L, Hui-li W (2005) Streptomyces avermitilis from marine. J Env Sci 17(1):123–125
Funding
No funds, grants or other support was received.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
All authors have contributed equally to the work.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
All authors declared that there is no conflict of interest.
Code availability
Not applicable.
Ethical approval
Not applicable.
Consent for publication
Not applicable.
Consent to participate
Not applicable.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Soliman, M.A.W., Hamza, A.F., Zahran, N.F. et al. Microbiological study and insecticidal potential of purified extract from Streptomyces sp. on the larvae of Galleria mellonella. J Plant Dis Prot 128, 1565–1574 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s41348-021-00508-0
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s41348-021-00508-0