Abstract
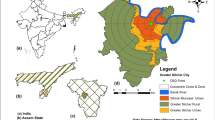
This study aims to explore transformations of urban morphology in an Indian city, Prayagraj because it widely unexplored. This work is examined by Shannon’s entropy, relative entropy, density index, and spatial metrics [percentage of landscape (PLAND), number of patches (NP), and patch density (PD)] to evaluate the state of compactness or, dispersion over the landscape in the study area. The built-up growth has shown increased from 25.385 to 98.942 km2 during 1988–2018. Shannon’s entropy results are indicating enlargement of urban sprawl from 1.48 to 1.77 during 1988–2018. Relative entropy results are found dispersed growth in 1988 (i.e., 0.594) to compact growth in 2018 (i.e., 0.246). Density index has shown drastic growth in core city (0–6 km) during 1988–2018. Spatial metrics results are showed growth of 16.26% in PLAND, 11507 in NP, and 2543.634 in PD during 1988–2018 respectively. While mean PLAND has shown that growth has been declining from city center to Zone-6 in 1988, 1997, 2008, and 2018. The mean NP, and mean PD profiling results have shown a reverse trend to mean PLAND in said time points. But urban growth has concentrated highly on city center to Zone-4 (0–8 km) in compacting mode and lowly on Zone-4 to Zone-6 (8–12 km) in dispersion mode. Therefore, 0–8 km area requires more emphasis on policy making within sustainable sphere thinking while 8–12 km area relatively needs more attentions for controlling measures for future urban planning.












Similar content being viewed by others
References
Antrop, M. (2000). Changing patterns in the urbanized countryside of Western Europe. Landscape Ecology, 15(3), 257–270. https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1008151109252
Xu, C., Liu, M., Zhang, C., An, S., Yu, W., & Chen, J. M. (2007). The spatiotemporal dynamics of rapid urban growth in the Nanjing metropolitan region of China. Landscape Ecology, 22, 925–937. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10980-007-9079-5
UN. (2018). The World’s Cities in 2018. Department of economic and social affairs, population division. The World’s Cities in 2018—Data Booklet (ST/ESA/ SER.A/417), UN, 1–34. Retrieved from https://digitallibrary.un.org/record/3799524?ln=en.
Alberti, M. (2005). The effects of urban patterns on ecosystem function. International Regional Science Review, 28(2), 168–192. https://doi.org/10.1177/0160017605275160
Shukla, P. R., Skea, J., Buendia, E. C., Masson-Delmotte, V., Pörtner, H.-O., Roberts, D. C., Zhai, P., Slade, R., Connors, S., Van Diemen, R., Ferrat, M., & Malley, J. (2019). Climate change and land: An IPCC special report on climate change, desertification, land degradation, sustainable land management, food security, and greenhouse gas fluxes in terrestrial ecosystems. https://www.ipcc.ch/site/assets/uploads/20. IPCC (AR6). https://doi.org/10.4337/9781784710644
Redman, C. L. (1999). Human dimensions of ecosystem studies. Ecosystems, 2, 296–298.
Xu, G., Jiao, L., Liu, J., Shi, Z., Zeng, C., & Liu, Y. (2019). Understanding urban expansion combining macro patterns and micro dynamics in three Southeast Asian megacities. Science of the Total Environment, 660, 375–383. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2019.01.039
Xu, G., Dong, T., Cobbinah, P. B., Jiao, L., Sumari, N. S., Chai, B., & Liu, Y. (2019). Urban expansion and form changes across African cities with a global outlook: Spatiotemporal analysis of urban land densities. Journal of Cleaner Production, 224, 802–810. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jclepro.2019.03.276
Shukla, A., & Jain, K. (2019). Critical analysis of spatial-temporal morphological characteristic of urban landscape. Arabian Journal of Geosciencesbian Journal of Geoscience, 12(112), 1–14.
Kumar, M., Garg, P. K., & Khare, D. (2008). Monitoring and modelling of urban sprawl using remote sensing and GIS techniques. International journal of Applied earth Observation and Geoinformation, 10, 26–43. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jag.2007.04.002
Gupta, S., Islam, S., & Hasan, M. M. (2018). Analysis of impervious land-cover expansion using remote sensing and GIS: A case study of Sylhet sadar upazila. Applied Geography, 98, 156–165. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apgeog.2018.07.012
Alturk, B., & Konukcu, F. (2019). Modeling land use/land cover change and mapping morphological fragmentation of agricultural lands in Thrace Region/Turkey. Environment, Development and Sustainability. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10668-019-00485-3
Fenta, A. A., Yasuda, H., Haregeweyn, N., Belay, S., Hadush, Z., & Gebremedhin, M. A. (2017). The dynamics of urban expansion and land use/land cover changes using remote sensing and spatial metrics: the case of Mekelle City of northern Ethiopia. International Journal of Remote Sensing, 38(14), 4107–4129. https://doi.org/10.1080/01431161.2017.1317936
Das, T., Chakraborty, S., & Samanta, K. (2016). Urban sprawl and urban growth detection analysis: A comparative study of Kolkata municipal corporation and Haora municipal corporation. International Journal of Geomatics and Geosciences, 7(1), 82–92.
Anees, M. M., Sajjad, S., & Joshi, P. K. (2019). Characterizing urban area dynamics in historic city of Kurukshetra, India, using remote sensing and spatial metric tools. Geocarto International, 34(14), 1584–1607. https://doi.org/10.1080/10106049.2018.1499819
Radhakrishnan, N., & Kumar, S. (2014). Analysis of urban sprawl pattern in Tiruchirappalli City using applications of remote sensing and GIS. Arabian Journal of Science and Engineering. https://doi.org/10.1007/s13369-014-1099-2
Sudhira, H. S., Ramachandra, T. V., & Jagadish, K. S. (2004). Urban sprawl: Metrics, dynamics and modelling using GIS. International Journal of Applied Earth Observation and Geoinformation, 5(1), 29–39. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jag.2003.08.002
Jiao, L. (2017). Urban land density function: A new method to characterize urban expansion. Landscape and Urban Planning, 139, 26–39. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.landurbplan.2015.02.017
Shikary, C., & Rudra, S. (2020). Measuring urban land use change and sprawl using geospatial techniques: A study on Purulia Municipality, West Bengal, India. Journal of the Indian Society of Remote Sensing. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12524-020-01212-6
Ozturk, D. (2017). Assessment of urban sprawl using Shannon’s entropy and fractal analysis: A case study of Atakum, Ilkadim and Canik (Samsun, Turkey). Journal of Environmental Engineering and Landscape Management, 25(3), 264–276. https://doi.org/10.3846/16486897.2016.1233881
Liu, M., Hu, Y. M., & Li, C. L. (2017). Landscape metrics for three-dimensional urban building pattern recognition. Applied Geography, 87, 66–72. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apgeog.2017.07.011
Chettry, V., & Surawar, M. (2021). Assessment of urban sprawl characteristics in Indian cities using remote sensing: Case studies of Patna, Ranchi, and Srinagar. Environment, Development and Sustainability. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10668-020-01149-3
Naikoo, M. W., Rihan, M., Ishtiaque, M., & Shahfahad, A. (2020). Analyses of land use land cover (LULC) change and built-up expansion in the suburb of a metropolitan city: Spatio-temporal analysis of Delhi NCR using landsat datasets. Journal of Urban Management, 9(3), 347–359. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jum.2020.05.004
Pathak, C., Chandra, S., Maurya, G., Rathore, A., Sarif, M. O., & Gupta, R. D. (2020). The effects of land indices on thermal state in surface urban heat island formation: A case study on Agra City in India using remote sensing data (1992–2019). Earth Systems and Environment. https://doi.org/10.1007/s41748-020-00172-8
Chaturvedi, R. (2014). Application of remote sensing and GIS in land use/land covers mapping in Allahabad District. International Journal of Advanced Information in Engineering Technology, 4(4), 1–9.
Srivastava, S. K., & Gupta, R. D. (2003). Monitoring of changes in land use/land cover using multi-sensor satellite data. In 6th International Conference on GIS/GPS/RS: Map India 2003. New Delhi.
Singh, A., Singh, S., Kumar, P., & Khanduri, K. (2013). Land use and land cover change detection: A comparative approach using post classification change matrix and discriminate function change detection methodology of Allahabad City. International Journal of Current Engineering and Technology, 33(1), 142–148.
Kumar, V., & Agrawal, S. (2019). Agricultural land use change analysis using remote sensing and GIS: A case study of Allahabad, India. In ISPRS—International Archives of the Photogrammetry, Remote Sensing and Spatial Information Sciences (Vol. XLII-3/W6, pp. 397–402). New Delhi. https://doi.org/10.5194/isprs-archives-xlii-3-w6-397-2019
MoHUA. (2015). Smart Citie: Ministry of Housing and Urban Affairs Reports, Government of India. New Delhi, India. Retrieved from http://www.mhupa.gov.in/Default.aspx?ReturnUrl=%2F
PNN. (2019). Prayag Kumbh. Prayagraj Nagar Nigam, Government of Uttar Pradesh. Retrieved October 22, 2019, from allahabadmc.gov.in/kumbh_mela.html
Nanda, M. K. (2018). Climatic classification. In D. K. Khan (Ed.), Environmental science (pp. 1–16).
IMD. (2010). Allahabad climatological table (period: 1981–2010). Indian Meteorological Department, Government of India. Retrieved October 22, 2019, from http://www.imd.gov.in/section/climate/extreme/allahabad2.htm
Sarif, M. O., Rimal, B., & Stork, N. E. (2020). Assessment of changes in land use/land cover and land surface temperatures and their impact on surface urban heat island phenomena in the Kathmandu Valley (1988–2018). ISPRS International Journal of Geo-Information, 9(12), 1–29. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijgi9120726
Dissanayake, D., Morimoto, T., Murayama, Y., & Ranagalage, M. (2019). Impact of landscape structure on the variation of land surface temperature in sub-Saharan region: A case study of Addis Ababa using landsat data. Sustainability, 11(8), 1–18. https://doi.org/10.3390/su11082257
Fonji, S. F., & Taff, G. N. (2014). Using satellite data to monitor land-use land-cover change in North-eastern Latvia. Springerplus, 3(61), 1–15.
Rousta, I., Sarif, M. O., Gupta, R. D., Olafsson, H., Ranagalage, M., Murayama, Y., Zhang, H., & Mushore, T. D. (2018). Spatiotemporal analysis of land use/land cover and its effects on surface urban heat island using landsat data: A case study of Metropolitan City Tehran (1988–2018). Sustainability, 10(12), 1–25. https://doi.org/10.3390/su10124433
Patel, S. K., Verma, P., & Sinsh, G. S. (2019). Agricultural growth and land use land cover change in peri-urban India. Environmental Monitoring and Assessment, 191(600), 1–17.
Sarif, M. O., & Gupta, R. D. (2021). Spatiotemporal mapping of Land Use/Land Cover dynamics using Remote Sensing and GIS approach: a case study of Prayagraj City, India (1988–2018). Environment Development Sustainability. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10668-021-01475-0
Pal, S., & Ziaul, S. (2017). Detection of land use and land cover change and land surface temperature in English Bazar urban centre. The Egyptian Journal of Remote Sensing and Space Sciences, 20(1), 125–145. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ejrs.2016.11.003
Ranagalage, M., Murayama, Y., Dissanayake, D., & Simwanda, M. (2019). The Impacts of landscape changes on annual mean land surface temperature in the Tropical Mountain City of Sri Lanka: A case study of Nuwara Eliya (1996–2017). Sustainability, 11(19), 1–27. https://doi.org/10.3390/su11195517
Ranagalage, M., Wang, R., Gunarathna, M. H. J. P., Dissanayake, D., Murayama, Y., & Simwanda, M. (2019). Spatial forecasting of the landscape in rapidly urbanizing hill stations of South Asia: A case study of Nuwara Eliya, Sri Lanka (1996–2037). Remote Sensing, 11(15), 1–31. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs11151743
Chettry, V., & Surawar, M. (2020). Urban sprawl assessment in Raipur and Bhubaneswar urban agglomerations from 1991 to 2018 using geoinformatics. Arabian Journal of Geosciences, 13(667), 1–17. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12517-020-05693-0
Bhatta, B. (2010). Analysis of urban growth and sprawl from remote sensing data. Springer. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-642-05299-6
Polsbyt, D. D., & Poppertt, R. D. (1991). The third criterion: Compactness as a procedural safeguard against Partisan Gerrymandering. Yale Law & Policy Review, 9(301), 301–353.
Hagen-Zanker, A. (2006). Map comparison methods that simultaneously address overlap and structure. Journal of Geographical Systems, 8(2), 165–185. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10109-006-0024-y
Luck, M., & Wu, J. (2002). A gradient analysis of urban landscape pattern: A case study from the from the Phoenix metropolitan region, Arizona, USA. Landscape Ecology, 17, 327–339. https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1020512723753.
Herold, M., Couclelis, H., & Clarke, K. C. (2005). The role of spatial metrics in the analysis and modeling of urban land use change. Computers, Environment and Urban Systems, 29(4), 369–399. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.compenvurbsys.2003.12.001
Krajewski, P. (2017). Assessing change in a high-value landscape: Case study of the municipality of Sobotka, Poland. Polish Journal of Environmental Studies, 26(6), 2603–2610. https://doi.org/10.15244/pjoes/70896
Turok, I., & Borel-saladin, J. M. (2014). Is urbanisation in South Africa on a sustainable trajectory? Development Southern Africa, 31(5), 675–691. https://doi.org/10.1080/0376835X.2014.937524
Gumma, M. K., Mohammad, I., Nedumaran, S., Whitbread, A., & Lagerkvist, C. J. (2017). Urban sprawl and adverse impacts on agricultural land: A case study on Hyderabad, India. Remote Sensing, 9(11), 1–16. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs9111136
Singh, P., Kikon, N., & Verma, P. (2017). Impact of land use change and urbanization on urban heat island in Lucknow city, Central India: A remote sensing based estimate. Sustainable Cities and Society, 32, 100–114. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scs.2017.02.018
Shahfahad, A., Kumari, B., Tayyab, M., Hang, H. T., Khan, M. F., & Rahman, A. (2019). Assessment of public open spaces (POS) and landscape quality based on per capita POS index in Delhi, India. SN Applied Sciences. https://doi.org/10.1007/s42452-019-0372-0
Chakraborti, S., Banerjee, A., Sannigrahi, S., Pramanik, S., Maiti, A., & Jha, S. (2019). Assessing the dynamic relationship among land use pattern and land surface temperature: A spatial regression approach. Asian Geographer. https://doi.org/10.1080/10225706.2019.1623054
Mengistu, D. A., & Salami, A. T. (2007). Application of remote sensing and GIS inland use/land cover mapping and change detection in a part of south western Nigeria. African Journal of Environmental Science and Technology, 1(5), 99–109.
Sharma, R., Chakraborty, A., & Joshi, P. K. (2015). Geospatial quantification and analysis of environmental changes in urbanizing city of Kolkata (India). Environmental Monitoring and Assessment, 187(1), 1–12. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10661-014-4206-7
Angel, S., Franco, S. A., Liu, Y., & Blei, A. M. (2020). The shape compactness of urban footprints. Progress in Planning, 139, 3–5. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.progress.2018.12.001
Nagendra, H., Bai, X., Brondizio, E. S., & Lwasa, S. (2018). The urban south and the predicament of global sustainability. Nature Sustainability, 1, 341–349.
Wang, C., Wang, Y., Wang, R., & Zheng, P. (2018). Modeling and evaluating land-use land-cover change for urban planning and sustainability: A case study of Dongying city, China. Journal of Cleaner, 172, 1529–1534.
Acknowledgements
The authors are very thankful to the USGS portal for freely availing the long periods (1988–2018) satellite Landsat datasets. Md. Omar Sarif is grateful to UGC for providing a financial assistantship through Maulana Azad National Fellowship for Minority Students (MANF) scheme by the Ministry of Minority Affairs, Government of India for pursuing his Ph.D. research work (Award Letter No. F1-17.1/2017-18/MANF-2017-18-WES-84175/(SA-III/Website)). Authors are also very thankful to Editor-in-Chief and blind reviewers for their valuable comments and suggestions.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
The topic has Conceptualized by M.O.S. and R.D.G.; Methodology, M.O.S., and R.D.G.; Validation, M.O.S.; Formal Analysis, M.O.S.; Investigation, M.O.S.; Resources, M.O.S., and R.D.G.; Data Curation, M.O.S., and R.D.G.; Writing-Original Draft Preparation, M.O.S.; Writing-Review & Editing, M.O.S., and R.D.G.; Visualization, M.O.S.; Supervising, R.D.G.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary Information
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Sarif, M.O., Gupta, R.D. Comparative evaluation between Shannon's entropy and spatial metrics in exploring the spatiotemporal dynamics of urban morphology: a case study of Prayagraj City, India (1988–2018). Spat. Inf. Res. 29, 961–979 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s41324-021-00406-5
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s41324-021-00406-5