Abstract
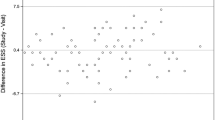
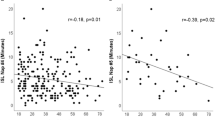
Reliability of mean sleep latency testing (MSLT) over consecutive days in patients with hypersomnia is unknown. We reviewed MSLTs of patients with hypersomnia without cataplexy who underwent our two consecutive MSLT protocol (N = 29). Average MSLs were 10.9 and 10.9 min for day 1 and 2, respectively. Agreement for pathological hypersomnia (defined as MSL ≤8 min) between MSLT days showed k = 0.85 for all (N = 29) and k = 0.76 for those without sleep apnea (N = 20). In patients with subjective complaints of hypersomnia, a single MSLT is sufficient (vs. addition of second day MSLT) in the setting of carefully implemented protocol controlling for potential confounding variables.

Similar content being viewed by others
References
Folkerts M, Rosenthal L, Roehrs T, et al. The reliability of the diagnostic features in patients with narcolepsy. Biol Psychiatry. 1996;40:208–14.
Zwyghuizen-Doorenbos A, Roehrs T, Schaefer M, Roth T. Test–retest reliability of the MSLT. Sleep. 1988;11:562–5.
Goldbart A, Peppard P, Finn L, et al. Narcolepsy and predictors of positive MSLTs in the Wisconsin sleep cohort. Sleep. 2014;37:1043–51.
Trotti LM, Staab BA, Rye DB. Test–retest reliability of the multiple sleep latency test in narcolepsy without cataplexy and idiopathic hypersomnia. J Clin Sleep Med. 2013;9:789–95.
Zorick F, Roehrs T, Koshorek G, et al. Patterns of sleepiness in various disorders of excessive daytime somnolence. Sleep. 1982;5(Suppl 2):S165–74.
Sullivan SS, Kushida CA. Multiple sleep latency test and maintenance of wakefulness test. Chest. 2008;134:854–61.
Mignot E, Lin L, Finn L, et al. Correlates of sleep-onset REM periods during the Multiple Sleep Latency Test in community adults. Brain. 2006;129:1609–23.
Chervin RD, Aldrich MS. Sleep onset REM periods during multiple sleep latency tests in patients evaluated for sleep apnea. Am J Respir Crit Care Med. 2000;161:426–31.
Littner MR, Kushida C, Wise M, et al. Practice parameters for clinical use of the multiple sleep latency test and the maintenance of wakefulness test. Sleep. 2005;28:113–21.
American Academy of Sleep Medicine. International classification of sleep disorders, 3rd edn. Darien: American Academy of Sleep Medicine; 2014.
Acknowledgements
This work was partly supported by National Institutes of Health Grant T32 HL0 69764, granted to Dr. Kwon.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that there is no conflict of interest regarding the publication of this paper.
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Kwon, Y., Kazaglis, L., Cho, Y. et al. Test–retest reliability of two consecutive mean sleep latency tests in patients with hypersomnia. Sleep Biol. Rhythms 15, 337–339 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s41105-017-0116-8
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s41105-017-0116-8