Abstract
Unsurprisingly, many studies consider CO2 emissions to capture the environment quality needed for testing the augmented environmental Kuznets curve (EKC) hypothesis. However, this is a major limitation of the existing literature because CO2 alone cannot account for environmental pollution. By employing a more comprehensive proxy ecological footprint, this study aims to examine EKC in G20 economies during 1991–2016. To achieve the objective, a second-generation panel data model was implemented, which accounted for the heterogeneity and cross-sectional dependence. The findings reveal that environmental degradation has an inverted N-shaped linkage with economic growth in the selected countries. It is further observed that globalization, renewable energy consumption, and urbanization improve the environmental quality, whereas non-renewable energy consumption mitigates the quality of environment in G20 countries. With these conclusions, it is suggested that policymakers from these countries should emphasize on more renewable energy usage.

Source: Authors’ own calculation based Stata software

Source: Based on authors’ own calculation using Stata software

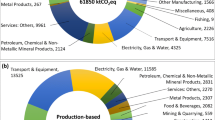
Source: Authors’ own conception
Similar content being viewed by others
Availability of data and materials
The dataset analyzed and used during the current study are available from the corresponding author on reasonable request.
References
Acaravci A, Ozturk I (2010) On the relationship between energy consumption, CO2 emissions and economic growth in Europe. Energy 35(12):5412–5420. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.energy.2010.07.009
Ahmed Z, Zafar MW, Ali Danish S (2020) Linking urbanization, human capital, and the ecological footprint in G7 countries: an empirical analysis. Sustain Cities Soc 55:102064. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scs.2020.102064
Ahmed Z, Zhang B, Cary M (2021) Linking economic globalization, economic growth, financial development, and ecological footprint: evidence from symmetric and asymmetric ARDL. Ecol Ind 121:107060. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ecolind.2020.107060
Akram V, Sahoo PK, Jangam BP (2019) Do shocks to electricity consumption revert to its equilibrium? Evid from Indian States Utilit Policy 61:100977. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jup.2019.100977
Allard A, Takman J, Uddin GS, Ahmed A (2018) The N-shaped environmental kuznets curve: an empirical evaluation using a panel quantile regression approach. Environ Sci Pollut Res 25(6):5848–5861. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-017-0907-0
Alola AA, Bekun FV, Sarkodie SA (2019) Dynamic impact of trade policy, economic growth, fertility rate, renewable and non-renewable energy consumption on ecological footprint in Europe. Sci Total Environ 685:702–709. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2019.05.139
Alper A, Oguz O (2016) The role of renewable energy consumption in economic growth: evidence from asymmetric causality. Renew Sustain Energy Rev 60:953–959. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.rser.2016.01.123
Amin A, Altinoz B, Dogan E (2020) Analyzing the determinants of carbon emissions from transportation in European countries: the role of renewable energy and urbanization. Clean Technol Environ Policy 22(8):1725–1734. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10098-020-01910-2
Ansari MA, Khan NA (2021) Decomposing the trade-environment nexus for high income, upper and lower middle income countries: What do the composition, scale, and technique effect indicate? Ecol Ind 121:107122. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ecolind.2020.107122
Ansari MA, Haider S, Khan NA (2019) Does trade openness affects global carbon dioxide emissions: evidence from the top CO2 emitters. Manag Environm Qual: an Int J 31(1):32–53. https://doi.org/10.1108/MEQ-12-2018-0205
Ansari MA, Ahmad MR, Siddique S, Mansoor K (2020) An environment kuznets curve for ecological footprint: evidence from GCC countries. Carbon Management 11(4):355–368. https://doi.org/10.1080/17583004.2020.1790242
Ansari MA, Haider S, Masood T (2021) Do renewable energy and globalization enhance ecological footprint: an analysis of top renewable energy countries? Environ Sci Pollut Res 28(6):6719–6732. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-020-10786-0
Anser M, Alharthi M, Aziz B, Wasim S (2020) Impact of urbanization, economic growth, and population size on residential carbon emissions in the SAARC countries. Clean Technol Environ Policy. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10098-020-01833-y
Arbulú I, Lozano J, Rey-Maquieira J (2015) Tourism and solid waste generation in Europe: a panel data assessment of the environmental kuznets curve. Waste Manag 46:628–636. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.wasman.2015.04.014
Aşıcı AA, Acar S (2016) Does income growth relocate ecological footprint? Ecol Ind 61:707–714. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ecolind.2015.10.022
Aşıcı AA, Acar S (2018) How does environmental regulation affect production location of non-carbon ecological footprint? J Clean Prod 178:927–936. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jclepro.2018.01.030
Asumadu-Sarkodie S, Yadav P (2019) Achieving a cleaner environment via the environmental Kuznets curve hypothesis: determinants of electricity access and pollution in India. Clean Technol Environ Policy 21(9):1883–1889. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10098-019-01756-3
Aydin C, Esen Ö, Aydin R (2019) Is the ecological footprint related to the kuznets curve a real process or rationalizing the ecological consequences of the affluence? evidence from PSTR approach. Ecol Ind 98:543–555. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ecolind.2018.11.034
Aziz N, Sharif A, Raza A, Jermsittiparsert K (2021) The role of natural resources, globalization, and renewable energy in testing the EKC hypothesis in MINT countries: new evidence from method of moments quantile regression approach. Environ Sci Pollut Res 28(11):13454–13468. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-020-11540-2
Barış-Tüzemen Ö, Tüzemen S, Çelik AK (2020) Does an N-shaped association exist between pollution and ICT in Turkey? ARDL and quantile regression approaches. Environ Sci Pollut Res 27(17):20786–20799. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-020-08513-w
Beckerman W (1992) Economic growth and the environment: whose growth? whose environment? World Dev 20(4):481–496. https://doi.org/10.1016/0305-750X(92)90038-W
Bhat JA (2018) Renewable and non-renewable energy consumption—impact on economic growth and CO2 emissions in five emerging market economies. Environ Sci Pollut Res 25(35):35515–35530. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-018-3523-8
Bilgili F, Ulucak R, Koçak E, İlkay SÇ (2020) Does globalization matter for environmental sustainability? empirical investigation for Turkey by markov regime switching models. Environ Sci Pollut Res 27(1):1087–1100. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-019-06996-w
Caravaggio N (2020) A global empirical re-assessment of the environmental kuznets curve for deforestation. Forest Policy Econ 119:102282. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.forpol.2020.102282
Caviglia-Harris JL, Chambers D, Kahn JR (2009) Taking the “U” out of kuznets: a comprehensive analysis of the EKC and environmental degradation. Ecol Econ 68(4):1149–1159. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ecolecon.2008.08.006
Charfeddine L, Mrabet Z (2017) The impact of economic development and social-political factors on ecological footprint: a panel data analysis for 15 MENA countries. Renew Sustain Energy Rev 76:138–154. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.rser.2017.03.031
Chen J, Xian Q, Zhou J, Li D (2020) Impact of income inequality on CO2 emissions in G20 countries. J Environ Manag 271:110987. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jenvman.2020.110987
Choi I (2001) Unit root tests for panel data. J Int Money Financ 20(2):249–272. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0261-5606(00)00048-6
Coderoni S, Esposti R (2014) Is there a long-term relationship between agricultural GHG emissions and productivity growth? a dynamic panel data approach. Environ Resource Econ 58(2):273–302. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10640-013-9703-6
Danish WZ (2019) Investigation of the ecological footprint’s driving factors: what we learn from the experience of emerging economies. Sustain Cities Soc 49:101626. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scs.2019.101626
Danish UR, Khan SU (2020) Determinants of the ecological footprint: role of renewable energy, natural resources, and urbanization. Sustain Cities Soc 54:101996. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scs.2019.101996
Destek MA, Sinha A (2020) Renewable, non-renewable energy consumption, economic growth, trade openness and ecological footprint: Evidence from organisation for economic co-operation and development countries. J Clean Prod 242:118537. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jclepro.2019.118537
Dinda S (2004) Environmental kuznets curve hypothesis: a survey. Ecol Econ 49(4):431–455. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ecolecon.2004.02.011
Erdoğan S, Yıldırım S, Yıldırım DÇ, Gedikli A (2020) The effects of innovation on sectoral carbon emissions: evidence from G20 countries. J Environ Manag 267:110637. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jenvman.2020.110637
Grossman GM, Krueger AB (1991) Environmental impacts of a North American free trade agreement. Nat Bur Econ Res. https://doi.org/10.3386/w3914
Gyamfi BA, Adedoyin FF, Bein MA, Bekun FV (2021) Environmental implications of N-shaped environmental kuznets curve for E7 countries. Environ Sci Pollut Res 28(25):33072–33082. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-021-12967-x
Im KS, Pesaran MH, Shin Y (2003) Testing for unit roots in heterogeneous panels. J Econ 115(1):53–74. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0304-4076(03)00092-7
Jena PR (2018) Does trade liberalization create more pollution? Evidence from a panel regression analysis across the states of India. Environ Econ Policy Stud 20(4):861–877. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10018-018-0217-x
Kahia M, Ben Jebli M, Belloumi M (2019) Analysis of the impact of renewable energy consumption and economic growth on carbon dioxide emissions in 12 MENA countries. Clean Technol Environ Policy 21(4):871–885. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10098-019-01676-2
Kasperowicz R, Bilan Y, Štreimikienė D (2020) The renewable energy and economic growth nexus in European countries. Sustain Dev 28(5):1086–1093. https://doi.org/10.1002/sd.2060
Kitzes J, Wackernagel M (2009) Answers to common questions in ecological footprint accounting. Ecol Ind 4(9):812–817. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ecolind.2008.09.014
Kongbuamai N, Bui Q, Yousaf HMAU, Liu Y (2020) The impact of tourism and natural resources on the ecological footprint: a case study of ASEAN countries. Environ Sci Pollut Res 27(16):19251–19264. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-020-08582-x
Kongbuamai N, Bui Q, Nimsai S (2021) The effects of renewable and nonrenewable energy consumption on the ecological footprint: the role of environmental policy in BRICS countries. Environ Sci Pollut Res 28(22):27885–27899. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-021-12551-3
Kumar P, Sahu NC, Ansari MA (2021a) Export potential of climate smart goods in India: evidence from the poisson pseudo maximum likelihood estimator. The Int Trade J 35(3):288–308. https://doi.org/10.1080/08853908.2021.1890652
Kumar P, Sahu NC, Kumar S, Ansari MA (2021b) Impact of climate change on cereal production: evidence from lower-middle-income countries. Environ Sci Pollut Res. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-021-14373-9
Kumar P, Sahu NC, Ansari MA, Kumar S (2021c) Climate change and rice production in India: role of ecological and carbon footprint. J Agribus Develop Emerg Econ. https://doi.org/10.1108/JADEE-06-2021-0152
Leitao J, Ferreira J, Santibanez-Gonzalez E (2021) Green bonds, sustainable development and environmental policy in the European Union carbon market. Bus Strateg Environ 30(4):2077–2090. https://doi.org/10.1002/bse.2733
Levin A, Lin C-F, James Chu C-S (2002) Unit root tests in panel data: asymptotic and finite-sample properties. J Econ 108(1):1–24. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0304-4076(01)00098-7
Luo G, Weng J-H, Zhang Q, Hao Y (2017) A reexamination of the existence of environmental kuznets curve for CO2 emissions: evidence from G20 countries. Nat Hazards 85(2):1023–1042. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11069-016-2618-0
Luo W, Bai H, Jing Q, Liu T, Xu H (2018) Urbanization-induced ecological degradation in Midwestern China: an analysis based on an improved ecological footprint model. Resour Conserv Recycl 137:113–125. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.resconrec.2018.05.015
Ma X, Ahmad N, Oei P-Y (2021) Environmental kuznets curve in France and Germany: role of renewable and nonrenewable energy. Renew Energy 172:88–99. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.renene.2021.03.014
Maddala GS, Wu S (1999) A comparative study of unit root tests with panel data and a new simple test. Oxford Bull Econ Stat 61(S1):631–652. https://doi.org/10.1111/1468-0084.0610s1631
Mark NC, Sul D (2003) Cointegration vector estimation by panel DOLS and long-run money demand. Oxford Bull Econ Stat 65(5):655–680. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1468-0084.2003.00066.x
Markandya A, Golub A, Pedroso-Galinato S (2006) Empirical analysis of national income and SO2 emissions in selected european countries. Environ Res Econ 35(3):221–257. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10640-006-9014-2
Marsiglio S, Ansuategi A, Gallastegui MC (2016) The Environmental kuznets curve and the structural change hypothesis. Environ Res Econ 2(63):265–288. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10640-015-9942-9
McCONNELL KE (1997) Income and the demand for environmental quality. Environ Dev Econ 2(4):383–399. https://doi.org/10.1017/S1355770X9700020X
McDonald GW, Patterson MG (2004) Ecological Footprints and interdependencies of New Zealand regions. Ecol Econ 50(1):49–67. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ecolecon.2004.02.008
Mrabet Z, Alsamara M (2017) Testing the kuznets curve hypothesis for Qatar: a comparison between carbon dioxide and ecological footprint. Renew Sustain Energy Rev 70:1366–1375. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.rser.2016.12.039
Mrabet Z, AlSamara M, Hezam Jarallah S (2017) The impact of economic development on environmental degradation in Qatar. Environ Ecol Stat 24(1):7–38. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10651-016-0359-6
Mu L, Fang L, Dou W, Wang C, Qu X, Yu Y (2021) Urbanization-induced spatio-temporal variation of water resources utilization in northwestern China: a spatial panel model based approach. Ecol Ind 125:107457. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ecolind.2021.107457
Nathaniel S, Nwodo O, Sharma G, Shah M (2020) Renewable energy, urbanization, and ecological footprint linkage in CIVETS. Environ Sci Pollut Res 27(16):19616–19629. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-020-08466-0
Okumus I, Erdogan S (2021) Analyzing the tourism development and ecological footprint nexus: evidence from the countries with fastest growing rate of tourism GDP. In: Balsalobre Lorente D, Driha OM, Shahbaz M (eds) Strategies in Sustainable Tourism Economic Growth and Clean Energy. Springer International Publishing, Cham, pp 141–154. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-030-59675-0_8
Pao H-T, Chen C-C (2019) Decoupling strategies: CO2 emissions, energy resources, and economic growth in the group of twenty. J Clean Prod 206:907–919. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jclepro.2018.09.190
Pata UK (2018) Renewable energy consumption, urbanization, financial development, income and CO2 emissions in Turkey: testing EKC hypothesis with structural breaks. J Clean Prod 187:770–779. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jclepro.2018.03.236
Pata UK (2021) Renewable and non-renewable energy consumption, economic complexity, CO2 emissions, and ecological footprint in the USA: testing the EKC hypothesis with a structural break. Environ Sci Pollut Res 28(1):846–861. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-020-10446-3
Pata UK, Caglar AE (2021) Investigating the EKC hypothesis with renewable energy consumption, human capital, globalization and trade openness for China: evidence from augmented ARDL approach with a structural break. Energy 216:119220. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.energy.2020.119220
Pata UK, Yilanci V (2020) Financial development, globalization and ecological footprint in G7: further evidence from threshold cointegration and fractional frequency causality tests. Environ Ecol Stat 27(4):803–825. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10651-020-00467-z
Pedroni P (1999) Critical values for cointegration tests in heterogeneous panels with multiple regressors. Oxford Bull Econ Stat 61(S1):653–670. https://doi.org/10.1111/1468-0084.0610s1653
Pedroni P (2001) Fully modified OLS for heterogeneous cointegrated panels. In: Baltagi BH, Fomby TB, Carter Hill R (eds) Nonstationary Panels, Cointegration, and Dynamic Panels. Emerald Group Publishing Limited, Bingley, pp 93–130. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0731-9053(00)15004-2
Pesaran MH (2007) A simple panel unit root test in the presence of cross-section dependence. J Appl Economet 22(2):265–312. https://doi.org/10.1002/jae.951
Pesaran MH, Shin Y, Smith RJ (2001) Bounds testing approaches to the analysis of level relationships. J Appl Economet 16(3):289–326. https://doi.org/10.1002/jae.616
Pfaff ASP, Chaudhuri S, Nye HLM (2004) Household production and environmental kuznets curves – examining the desirability and feasibility of substitution. Environ Res Econ 27(2):187–200. https://doi.org/10.1023/B:EARE.0000017279.79445.72
Pirlogea C, Cicea C (2012) Econometric perspective of the energy consumption and economic growth relation in European Union. Renew Sustain Energy Rev 16(8):5718–5726. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.rser.2012.06.010
Qiao H, Zheng F, Jiang H, Dong K (2019) The greenhouse effect of the agriculture-economic growth-renewable energy nexus: evidence from G20 countries. Sci Total Environ 671:722–731. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2019.03.336
Qureshi MI, Elashkar EE, Shoukry AM, Aamir A, Mahmood NHN, Rasli AMd, Zaman K (2019) Measuring the ecological footprint of inbound and outbound tourists: Evidence from a panel of 35 countries. Clean Technol Environ Policy 21(10):1949–1967. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10098-019-01720-1
Rafaj P, Amann M, Siri J, Wuester H (2015) Changes in European greenhouse gas and air pollutant emissions: decomposition of determining factors. In: Ometto JP, Bun R, Jonas M, Nahorski Z (eds) Uncertainties in Greenhouse Gas Inventories: Expanding Our Perspective. Springer International Publishing, Cham, pp 27–54. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-319-15901-0_3
Sabir S, Gorus MS (2019) The impact of globalization on ecological footprint: empirical evidence from the South Asian countries. Environ Sci Pollut Res 26(32):33387–33398. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-019-06458-3
Sarkodie SA (2018) The invisible hand and EKC hypothesis: What are the drivers of environmental degradation and pollution in Africa? Environ Sci Pollut Res 25(22):21993–22022. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-018-2347-x
Selden TM, Song D (1994) Environmental quality and development: is there a kuznets curve for air pollution emissions? J Environ Econ Manag 27(2):147–162. https://doi.org/10.1006/jeem.1994.1031
Sharif A, Baris-Tuzemen O, Uzuner G, Ozturk I, Sinha A (2020) Revisiting the role of renewable and non-renewable energy consumption on Turkey’s ecological footprint: evidence from quantile ARDL approach. Sustain Cities Soc 57:102138. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scs.2020.102138
Shekhawat KK, Yadav AK, Sanu MS, Kumar P (2021) Key drivers of consumption-based carbon emissions: empirical evidence from SAARC countries. Environ Sci Pollut Res. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-021-17413-6
Sheraz M, Deyi X, Ahmed J, Ullah S, Ullah A (2021) Moderating the effect of globalization on financial development, energy consumption, human capital, and carbon emissions: evidence from G20 countries. Environ Sci Pollut Res 28(26):35126–35144. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-021-13116-0
Ulucak R, Bilgili F (2018) A reinvestigation of EKC model by ecological footprint measurement for high, middle and low income countries. J Clean Prod 188:144–157. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jclepro.2018.03.191
Usman M, Makhdum MSA, Kousar R (2021) Does financial inclusion, renewable and non-renewable energy utilization accelerate ecological footprints and economic growth? fresh evidence from 15 highest emitting countries. Sustain Cities Soc 65:102590. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scs.2020.102590
Villanthenkodath MA, Arakkal MF (2020) Exploring the existence of environmental kuznets curve in the midst of financial development, openness, and foreign direct investment in New Zealand: insights from ARDL bound test. Environ Sci Pollut Res 27(29):36511–36527. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-020-09664-6
Wang Y, Kang L, Wu X, Xiao Y (2013) Estimating the environmental kuznets curve for ecological footprint at the global level: a spatial econometric approach. Ecol Ind 34:15–21. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ecolind.2013.03.021
Wang N, Zhu H, Guo Y, Peng C (2018) The heterogeneous effect of democracy, political globalization, and urbanization on PM2.5 concentrations in G20 countries: evidence from panel quantile regression. J Clean Prod 194:54–68. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jclepro.2018.05.092
Weisz H, Steinberger JK (2010) Reducing energy and material flows in cities. Curr Opin Environ Sustain 2(3):185–192. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cosust.2010.05.010
Westerlund J (2005) New simple tests for panel cointegration. Economet Rev 24(3):297–316. https://doi.org/10.1080/07474930500243019
Wiedmann TO, Schandl H, Lenzen M, Moran D, Suh S, West J, Kanemoto K (2015) The material footprint of nations. Proc Natl Acad Sci 112(20):6271–6276. https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.1220362110
Yilanci V, Pata UK (2020) Investigating the EKC hypothesis for China: the role of economic complexity on ecological footprint. Environ Sci Pollut Res 27(26):32683–32694. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-020-09434-4
Bartelmus P (2008). Quantitative Eco-nomics: How sustainable are our economies? Springer Science and Business Media
EB-20-V40-I3-P190.pdf. (n.d.). Retrieved September 4, 2021, from http://www.accessecon.com/Pubs/EB/2020/Volume40/EB-20-V40-I3-P190.pdf
Niu H, Li H. (n.d.). An Empirical Study on Economic Growth and Carbon Emissions of G20 Group
Spurious regression and residual-based tests for cointegration in panel data—ScienceDirect. (n.d.). Retrieved September 4, 2021, from https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S0304407698000232
United Nations Climate Change Conference 2021. https://enb.iisd.org/Glasgow-Climate-Change-Conference-COP26
Wackernagel M, Rees W (1998) Our ecological footprint: reducing human impact on the earth. New Society Publishers
Acknowledgements
The authors gratefully acknowledge the valuable suggestions received from the five anonymous referees on the earlier draft of this paper, which substantially improved the paper. All errors are our own.
Funding
No funding was received to conduct this research.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Ansari, M.A., Haider, S., Kumar, P. et al. Main determinants for ecological footprint: an econometric perspective from G20 countries. Energ. Ecol. Environ. 7, 250–267 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s40974-022-00240-x
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s40974-022-00240-x
Keywords
- Ecological footprint
- Economic growth
- Renewable energy
- Environmental kuznets curve
- Globalization
- Cross-sectional dependency