Abstract
This paper aims at estimating the dynamic impact of renewable and non-renewable energy consumption, globalization, urbanization, and economic growth on the environmental quality. Unlike previous study, this study used multi-dimensional indicator of environmental quality that is ecological footprint. Given the importance of renewable energy, a sample of top renewable energy consuming countries has been selected for analysis spanning the period 1991–2016. The analysis is carried out in panel data framework that considers the issues of cross sectional dependence and heterogeneity. The results of cointegration test show the existence of long-run equilibrium relationship among the variables. The long-run elasticity of pooled mean group shows positive impact of economic growth and non-renewable energy consumption on ecological footprint while negative impact is observed in case of renewable energy consumption, globalization and urbanization. The sensitivity of long-run elasticity has been checked with the help of fully modified ordinary least square and dynamic ordinary least square. Based on empirical findings, some policy implication has also been provided.
Similar content being viewed by others
Availability of data and materials
Data will be available upon request.
Notes
assumes government technology, policies, and social preferences continue to evolve in the recent past.
EKC predicts the presence of inverted U-shaped relationship between counry’s growth and environmental degradation. The economic growth generates a more pollution at initial stage but before reaching a threshold level of income; economy moves toward clean environment and people demand better environmental quality.
attractiveness Index of renewable energy country (www.ey.com)
also reveals asymptotic distribution for each seven statistic where for group mean test it is normal
have merits of providing normally distributed estimator.
the cointegrating vectors derived from the DOLS estimation are asymptotically efficients
\( {\Delta z}_{\mathrm{it}}={\delta}_i\ \left({z}_{i,t}-{x}_i\ {y}_{i,t-1}\right)+\sum \limits_{k-0}^{n-1}{\vartheta}_{i\mathrm{k}}\ {\Delta z}_{i,t-1}+\sum \limits_{k-0}^{m-1}{\alpha}_{\mathrm{ik}}\ {\Delta y}_{i,t-k}+{\rho}_i+{\mu}_{\mathrm{it}} \) here, Z indicates dependent variable EF and zi, t − xi yi, t − 1 is magnitude of deviation towards long run equilibrium from short run deviation; δi is adjustment speed; δi signifies short run coefficients; xi is long run coefficients; ρi is time invariant (unobserved) county specific effect; t = 2, 3…T is time period and i = 1, 2, 3…M is cross sectional unit.
References
Ahmad A, Zhao Y, Shahbaz M, Bano S, Zhang Z, Wang S, Liu Y (2016) Carbon emissions, energy consumption and economic growth: an aggregate and disaggregate analysis of the Indian economy. Energy Policy 96:131–143
Ahmed Z, Wang Z, Mahmood F, Hafeez M, Ali N (2019) Does globalization increase the ecological footprint? Empirical evidence from Malaysia. Environ Sci Pollut Res 26(18):18565–18582
Al-mulali U, Weng-Wai C, Sheau-Ting L, Mohammed AH (2015) Investigating the environmental Kuznets curve (EKC) hypothesis by utilizing the ecological footprint as an indicator of environmental degradation. Ecol Indic 48:315–323
Alper A, Oguz O (2016) The role of renewable energy consumption in economic growth: Evidence from asymmetric causality. Renew Sust Energ Rev 60:953–959
Ang JB (2008) Economic development, pollutant emissions and energy consumption in Malaysia. J Policy Model 30:271–278
Ansari MA, Khan NA, Ganaie AA (2019) Does foreign direct investment impede environmental quality in Asian countries? A panel data analysis. OPEC Energy Rev
Ansari MA, Haider S, Khan NA (2020a) Does trade openness affects global carbon dioxide emissions. Manag Environ Qual Int J
Ansari MA, Haider S, Khan NA (2020b) Environmental Kuznets curve revisited: An analysis using ecological and material footprint. Ecol Indic 115:106416
Ansari MA, Ahmad MR, Siddique S, Mansoor K (2020c) An environment Kuznets curve for ecological footprint: evidence from GCC countries. Carbon Manag:1–14
Antweiler W, Copeland BR, Taylor MS (2001) Is free trade good for the environment. Am Econ Rev 91:877–908
Apergis N, Payne JE (2014) The causal dynamics between renewable energy, real GDP, emissions and oil prices: evidence from OECD countries. Appl Econ 46:4519–4525
Apergis N, Payne JE (2015) Renewable energy, output, carbon dioxide emissions, and oil prices: evidence from South America. Energy Sour B Econ Plann Policy 10:281–287
Apergis N, Payne JE, Menyah K, Wolde-Rufael Y (2010) On the causal dynamics between emissions, nuclear energy, renewable energy, and economic growth. Ecol Econ Spec Sect Payments Ecosyst Serv Local Glob 69:2255–2260
Aşıcı AA, Acar S (2016) Does income growth relocate ecological footprint. Ecol Indic 61:707–714
Balcilar M, Ozdemir ZA, Ozdemir H, Shahbaz M (2018) The renewable energy consumption and growth in the G-7 countries: evidence from historical decomposition method. Renew Energy 126:594–604
Balsalobre-Lorente D, Shahbaz M, Roubaud D, Farhani S (2018) How economic growth, renewable electricity and natural resources contribute to CO2 emissions. Energy Policy 113:356–367
Bartelmus P (2008) Quantitative eco-nomics: how sustainable are our economies? Springer Science & Business Media
Bhat JA (2018) Renewable and non-renewable energy consumption—impact on economic growth and CO2 emissions in five emerging market economies. Environ Sci Pollut Res
Bhattacharya M, Paramati SR, Ozturk I, Bhattacharya S (2016) The effect of renewable energy consumption on economic growth: evidence from top 38 countries. Appl Energy 162:733–741
Boutabba MA (2014) The impact of financial development, income, energy and trade on carbon emissions: evidence from the Indian economy. Econ Model 40:33–41
BP Global (2018) BP energy outlook | Energy economics | BP
Breusch TS, Pagan AR (1980) The Lagrange multiplier test and its applications to model specification in econometrics. Rev Econ Stud 47(1):239–253
Charfeddine L (2017) The impact of energy consumption and economic development on ecological footprint and CO2 emissions: evidence from a Markov switching equilibrium orrection model. Energy Econ 65:355–374
Charfeddine L, Mrabet Z (2017) The impact of economic development and social-political factors on ecological footprint: a panel data analysis for 15 MENA countries. Renew Sust Energ Rev 76:138–154
Cho C-H, Chu Y-P, Yang H-Y (2014) An environment Kuznets curve for GHG emissions: a panel cointegration analysis. Energy Sour B Econ Plann Policy 9:120–129
Cole MA (2006) Does trade liberalization increase national energy use? Econ Lett 92:108–112
Copeland BR, Taylor MS (2004) Trade, growth, and the environment. J Econ Lit 42:7–71
Destek MA, Aslan A (2017) Renewable and non-renewable energy consumption and economic growth in emerging economies: evidence from bootstrap panel causality. Renew Energy 111:757–763
Destek MA, Sinha A (2020) Renewable, non-renewable energy consumption, economic growth, trade openness and ecological footprint: evidence from organisation for economic co-operation and development countries. J Clean Prod 242:118537
Destek MA, Ulucak R, Dogan E (2018) Analyzing the environmental Kuznets curve for the EU countries: the role of ecological footprint. Environ Sci Pollut Res 25:29387–29396
Dodman D (2009) Blaming cities for climate change? An analysis of urban greenhouse gas emissions inventories. Environ Urban 21(1):185–201
Dogan E, Seker F (2016a) An investigation on the determinants of carbon emissions for OECD countries: empirical evidence from panel models robust to heterogeneity and cross-sectional dependence. Environ Sci Pollut Res 23:14646–14655
Dogan E, Seker F (2016b) The influence of real output, renewable and non-renewable energy, trade and financial development on carbon emissions in the top renewable energy countries. Renew Sust Energ Rev 60:1074–1085
Dreher A (2006) Does globalization affect growth? Evidence from a new index of globalization. Appl Econ 38:1091–1110
Fan Y, Liu L-C, Wu G, Wei Y-M (2006) Analyzing impact factors of CO2 emissions using the STIRPAT model. Environ Impact Assess Rev 26:377–395
Gutierrez L (2003) On the power of panel cointegration tests: a Monte Carlo comparison. Econ Lett 80(1):105–111
Hervieux MS, Darné O (2015) Environmental Kuznets curve and ecological footprint: a time series analysis. Econ Bull 35(1):814–826
Hirschl B (2009) International renewable energy policy—between marginalization and initial approaches. Energy Policy 37(11):4407–4416
Hossain MS (2012) Multivariate granger causality between economic growth, electricity consumption, exports and remittance for the panel of three SAARC countries. Glob J Manag Bus Res 12(4):41–54
Huwart JY, Verdier L (2013) What is the impact of globalisation on the environment? Econ Glob Orig Consequences:112–120
IEA (2013) World energy outlook 2013
Ike GN, Usman O, Alola AA, Sarkodie SA (2020) Environmental quality effects of income, energy prices and trade: the role of renewable energy consumption in G-7 countries. Sci Total Environ 137813
Jalil A, Mahmud SF (2009) Environment Kuznets curve for CO2 emissions: a cointegration analysis for China. Energy Policy 37:5167–5172
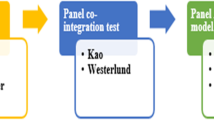
Kao C (1999) Spurious regression and residual-based tests for cointegration in panel data. J Econ 90:1–44
Kaygusuz K, Yüksek Ö, Sari A (2007) Renewable energy sources in the European Union: markets and capacity. Energy Sour B Econ Plann Policy 2(1):19–29
Lau LS, Choong CK, Eng YK (2014) Investigation of the environmental Kuznets curve for carbon emissions in Malaysia: do foreign direct investment and trade matter. Energy Policy 68:490–497
Lee G (2007) Long run equilibrium relationship between inward FDI and productivity. J Econ Dev 32(2):183
Leitão NC (2014) Economic growth, carbon dioxide emissions, renewable energy and globalization. Int J Energy Econ Policy 4:391–399
Liddle B, Lung S (2010) Age-structure, urbanization, and climate change in developed countries: revisiting STIRPAT for disaggregated population and consumption-related environmental impacts. Popul Environ 31:317–343
Mrabet Z, Alsamara M (2017) Testing the Kuznets curve hypothesis for Qatar: a comparison between carbon dioxide and ecological footprint. Renew Sust Energ Rev 70:1366–1375
Nasreen S, Anwar S (2014) Causal relationship between trade openness, economic growth and energy consumption: a panel data analysis of Asian countries. Energy Policy 69:82–91
Ozturk I, Al-Mulali U, Saboori B (2016) Investigating the environmental Kuznets curve hypothesis: the role of tourism and ecological footprint. Environ Sci Pollut Res 23:1916–1928
Pablo-Romero M d P, Sánchez-Braza A (2015) Productive energy use and economic growth: energy, physical and human capital relationships. Energy Econ 49:420–429
Paramati SR, Alam MS, Chen C-F (2017) The effects of tourism on economic growth and CO2 emissions: a comparison between developed and developing economies. J Travel Res 56:712–724
Pedroni P (1999) Critical values for cointegration tests in heterogeneous panels with multiple regressors. Oxf Bull Econ Stat 61:653–670
Pedroni P (2000) Fully modified OLS for heterogeneous cointegrated panels. Adv Econ 15:93–130
Pedroni P (2001) Purchasing power parity tests in cointegrated panels. Rev Econ Stat 83:727–731
Pedroni P (2004) Panel cointegration: asymptotic and finite sample properties of pooled time series tests with an application to the PPP hypothesis. Econ Theory 20:597–625
Pesaran MH (2004) General diagnostic tests for cross section dependence in panels
Pesaran MH (2007) A simple panel unit root test in the presence of cross- section dependence. J Appl Econ 22(2):265–312
Pesaran MH, Smith R (1995) Estimating long-run relationships from dynamic heterogeneous panels. J Econ 68(1):79–113
Rafindadi AA, Usman O (2019) Globalization, energy use, and environmental degradation in South Africa: startling empirical evidence from the Maki-cointegration test. J Environ Manag 244:265–275
REN21 (2017) Renewables 2017. Global Status Report
Sabir S, Gorus MS (2019) The impact of globalization on ecological footprint: empirical evidence from the South Asian countries. Environ Sci Pollut Res 26(32):33387–33398
Sassen S (1991) The Global City. Princeton University Press, New York, London, Tokyo, Princeton
Sebri M, Ben-Salha O (2014) On the causal dynamics between economic growth, renewable energy consumption, CO2 emissions and trade openness: fresh evidence from BRICS countries. Renew Sust Energ Rev 39:14–23
Shafiei S, Salim RA (2014) Non-renewable and renewable energy consumption and CO2 emissions in OECD countries: a comparative analysis. Energy Policy 66:547–556
Shahbaz M, Loganathan N, Zeshan M, Zaman K (2015a) Does renewable energy consumption add in economic growth? An application of auto-regressive distributed lag model in Pakistan. Renew Sust Energ Rev 44:576–585
Shahbaz M, Mallick H, Mahalik MK, Loganathan N (2015b) Does globalization impede environmental quality in India. Ecol Indic 52:379–393
Shahbaz M, Khan S, Ali A, Bhattacharya M (2016a) The impact of globalization on Co2 emissions in China. Singap Econ Rev 62:929–957
Shahbaz M, Mallick H, Mahalik MK, Sadorsky P (2016b) The role of globalization on the recent evolution of energy demand in India: Implications for sustainable development. Energy Econ 55:52–68
Shahbaz M, Solarin SA, Ozturk I (2016c) Environmental Kuznets Curve hypothesis and the role of globalization in selected African countries. Ecol Indic 67:623–636
Shahbaz M, Destek M, Polemis M (2018a) Do foreign capital and financial development affect clean energy consumption and carbon emissions? Evidence from BRICS and Next-11 Countries
Shahbaz M, Haouas I, Sbia R, Ozturk I (2018b) Financial development-environmental degradation nexus in the United Arab Emirates: the importance of growth, globalization and structural breaks
Shahbaz M, Lahiani A, Abosedra S, Hammoudeh S (2018c) The role of globalization in energy consumption: a quantile cointegrating regression approach. Energy Econ 71:161–170
Shahbaz M, Shahzad SJH, Mahalik MK (2018d) Is globalization detrimental to CO2 emissions in Japan? New Threshold Analysis. Environ Model Assess 23:557–568
Shahbaz M, Shahzad SJH, Mahalik MK, Sadorsky P (2018e) How strong is the causal relationship between globalization and energy consumption in developed economies? A country-specific time-series and panel analysis. Appl Econ 50:1479–1494
Sinha A, Shahbaz M (2018) Estimation of environmental Kuznets curve for CO2 emission: role of renewable energy generation in India. Renew Energy 119:703–711
Tiba S, Omri A (2017) Literature survey on the relationships between energy, environment and economic growth. Renew Sust Energ Rev 69:1129–1146
Tietenberg TH, Folmer H (2005) The international yearbook of environmental and resource economics 2004/2005: a survey of current issues. Edward Elgar Publishing
Usman O, Olanipekun IO, Iorember PT, Abu-Goodman M (2020a) Modelling environmental degradation in South Africa: the effects of energy consumption, democracy, and globalization using innovation accounting tests. Environ Sci Pollut Res 27(8):8334–8349
Usman O, Alola AA, Sarkodie SA (2020b) Assessment of the role of renewable energy consumption and trade policy on environmental degradation using innovation accounting: evidence from the US. Renew Energy 150:266–277
Wackernagel, M., Rees, W., 1998. Our ecological footprint: reducing human impact on the earth. New Society Publishers.
Weisz H, Steinberger JK (2010) Reducing energy and material flows in cities. Curr Opin Environ Sustain 2(3):185–192
WEO (2018) World Energy Outlook:2018
Westerlund J (2007) Testing for error correction in panel data. Oxf Bull Econ Stat 69:709–748
York R, Rosa EA, Dietz T (2003) STIRPAT, IPAT and ImPACT: analytic tools for unpacking the driving forces of environmental impacts. Ecol Econ 46:351–365
Zeb R, Salar L, Awan U, Zaman K, Shahbaz M (2014) Causal links between renewable energy, environmental degradation and economic growth in selected SAARC countries: Progress towards green economy. Renew Energy 71:123–132
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
All three authors have contributed equally. MAA made the analysis part while SH compiled introduction and literature review, and the overall formatting of the paper has been done by TM. All authors have read and approved the manuscript.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Competing interests
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Ethics approval and conset to participate
Not applicable
Conset for publication
Not applicable
Additional information
Responsible editor: Nicholas Apergis
Publisher’s note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Ansari, M.A., Haider, S. & Masood, T. Do renewable energy and globalization enhance ecological footprint: an analysis of top renewable energy countries?. Environ Sci Pollut Res 28, 6719–6732 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-020-10786-0
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-020-10786-0