Abstract
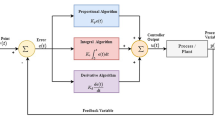
This paper proposes a new adaptive proportional–integral–derivative (PID) control method using predictive control and output recurrent fuzzy wavelet neural network (ORFWNN) for a group of nonlinear digital time-delay dynamic systems. The presented controller, called ORFWNN-APPID controller, is rigorously derived and proved by including an ORFWNN identifier with online parameter learning and identification, and an adaptive ORFWNN-based predictive PID controller to achieve precise setpoints tracking and disturbance rejection. The effectiveness and superiority of the constructed ORFWNN-APPID control approach are well demonstrated by performing numerical simulations on step-like disturbance rejection and precise setpoint tracking of two well-known digital nonlinear processes. The practicability of the presented method is illustrated by carrying out two experimental results on a real PET temperature control process.
















Similar content being viewed by others
References
Garces, F., Becerra, V.M., Kambhampati, C., Warwick, K.: Strategies for Feedback Linearization—A Dynamic Neural Network Approach. Springer, New York (2003)
Spooner, J.T., Maggiore, M., Ordonez, R., Passino, K.M.: Stable Adaptive Control and Estimation for Nonlinear Systems: Neural and Fuzzy Approximation Techniques. Wiley, New York (2002)
Henson, M.A., Seborg, D.E.: Nonlinear Process Control. Prentice Hall PTR, New Jersey (1997)
Maciejowski, J.M.: Predictive Control with Constraints. Prentice Hall, Upper Saddle river (2002)
Huang, S., Tan, K.K., Lee, T.H.: Applied Predictive Control. Springer, New York (2002)
Vega, P., Prada, C., Aleixandre, V.: Self-tuning predictive PID controller. IEE Proc. D Contr. Theory Appl. 138(3), 303–311 (1991)
Yamamoto, T., Omatu, S., Haneda, M.: A design method of self-tuning PID controllers. In: Proceedings of American Control Conference, pp. 3263–3267 (1994)
Miller, R.M., Kwok, K.E., Shan, S.L., Wood, R.K.: Development of a stochastic predictive PID controller. In: Proceedings of American Control Conference, pp. 4204–4208 (1995)
Tsai, C.C., Lu, C.H.: Multivariable self-tuning temperature control for plastic injection molding process. IEEE Trans. Ind. Appl. 34(2), 310–318 (1998)
Yusof, R., Omatu, S.: A multivariable self-tuning PID controllers. Int. J. Contr. 57(6), 1387–1403 (1993)
Yusof, R., Omatu, S., Khalid, M.: Self-tuning PID control: a multivariable derivation and application. Automatica 30(12), 1975–1981 (1994)
Omatu, S., Yusof, R., Sinohara, K., Hotta, M.: Temperature control for heating cylinder by multivariable STC. IEEE Trans. Syst. Contr. Inf. Eng. 5(3), 102–110 (1992). (in Japanese)
Youness, H., Moness, M., Khaled, M.: MPSoCs and multicore microcontrollers for embedded PID control: a detailed study. IEEE Trans. Ind. Inf. 10(4), 2122–2134 (2014)
Yin, J.M., Shin, J.S., Lee, H.H.: On-line tuning PID parameters in an idling engine based on a modified BP neural network by particle swarm optimization. Artif. Life Robot. 14(2), 129–133 (2009)
Han, K.Y., Lee, H.H.: Neuro PID control of power generation using a low temperature gap. Artif. Life Robot. 16(2), 178–184 (2011)
Yu, D.L., Chang, T.K., Yu, D.W.: Fault tolerant control of multivariable processes using auto-tuning PID controller. IEEE Trans. Syst. Man Cybern. B Cybern. 35(1), 32–43 (2005)
Macku, L., Sámek, D.: Two step, PID and model predictive control using artificial neural network applied on semi-batch reactor. WSEAS Trans. Syst. 9(10), 1039–1049 (2010)
Khan, M.A.S.K., Rahman, M.A.: Implementation of a wavelet-based MRPID controller for benchmark thermal system. IEEE Trans. Ind. Electron. 57(12), 4160–4169 (2010)
Strumiłło, P., Kamiński, W.: Neural Networks and Soft Computing, pp. 107–119. Springer, New York (2003)
Tsai, C.C., Tai, F.C., Chang, Y.L., Tsai, C.T.: Adaptive predictive PID control using fuzzy wavelet neural networks for nonlinear discrete-time time-delay systems. Int. J. Fuzzy Syst. 19(6), 1718–1730 (2017)
Abiyev, R.H., Kaynak, O.: Fuzzy wavelet neural networks for identification and control of dynamic plants-A novel structure and a comparative study. IEEE Trans. Ind. Electron. 55(8), 3133–3140 (2008)
Tsai, C.C., Wu, H.L., Tai, F.C., Chen, Y.S.: Distributed consensus formation control with collision and obstacle avoidance for uncertain networked omnidirectional multi-robot systems using fuzzy wavelet neural networks. Int. J. Fuzzy Syst. 19(5), 1375–1391 (2017)
Lu, C.H.: Design and application of stable predictive controller using recurrent wavelet neural networks. IEEE Trans. Ind. Electr. 56, 3733–3742 (2009)
Tsai, C.C., Chang, Y.L.: Self-tuning PID control using recurrent wavelet neural networks. In: Proceedings of 2012 IEEE International Conference on Systems, Man, and Cybernetics, Soul, Korea, October 14–17 (2012)
El-Sousy, F.F.M., Abuhasel, K.: Self-organizing recurrent fuzzy wavelet neural network-based mixed H2/H∞ adaptive tracking control for uncertain two-axis motion control system. IEEE Trans. Ind. Appl. 52(6), 5139–5155 (2016)
Kuo, C.W., Tsai, C.C.: Quaternion-based adaptive backstepping RFWNN control of quadrotors subject to model uncertainties and disturbances. Int. J. Fuzzy Syst. 20(6), 1745–1755 (2018)
Wang, Y.C., Chien, C.J., Lee, D.T.: An output recurrent fuzzy neural network based iterative learning control for nonlinear systems. In: Proceedings of 2008 IEEE International Conference on Fuzzy Systems (FUZZ 2008), June 1–6, pp. 1563–1569
Rudin, W.: Principles of Mathematical Analysis. McGraw-Hill, New York (1976)
Lu, C.H.: Wavelet fuzzy neural networks for identification and predictive control of dynamic systems. IEEE Trans. Ind. Electron. 58(7), 3046–3058 (2011)
Tsai, C.C., Chang, Y.L.: Self-tuning PID control using recurrent wavelet neural networks. In: Proceedings of IEEE International Conference on Systems, Man, and Cybernetics, October 14–17, pp. 3105–3110 (2012)
Tsai, C.C., Chang, Y.L., Tung, S.L.: Two DOF temperature control using RBFNN for stretch PET blow molding machines. In: Proceedings of IEEE International Conference on Systems, Man, and Cybernetics, October 5–8, pp. 1759–1764 (2014)
Chang, Y.L., Tsai, C.C.: Adaptive predictive PID control using fuzzy wavelet neural networks for nonlinear discrete-time time-delay systems. In: Proceedings of International Conference on Fuzzy Theory and Its Applications, Taichung, Taiwan, November 9–11 (2016)
Tsai, C., Chang, Y.L.: Two degree-of-freedom control using recurrent fuzzy neural networks for a class of nonlinear discrete-time time-delay systems. In: Proceedings of International Conference on Systems Engineering, June 29–July 3, pp. 85–90 (2012)
Tsai, C.T., Tsai, C.C.: Digital command feedforward and PID temperature control for PET stretch blow molding machines. In: Proceedings of 11th Asian Control Conference (ASCC), December 17–20, pp. 1128–1133 (2017)
Acknowledgements
The authors gratefully acknowledge the financial support of the Ministry of Science and Technology (MOST), Republic of China, under Contract MOST 107-2221-E-005-073-MY2.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Tsai, CC., Yu, CC. & Tsai, CT. Adaptive ORFWNN-Based Predictive PID Control. Int. J. Fuzzy Syst. 21, 1544–1559 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s40815-019-00650-w
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s40815-019-00650-w