Abstract
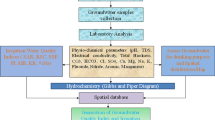
Assessment of the potential zone of groundwater recharge is extremely important for the protection of water quality management in groundwater systems. Groundwater potential areas are identified with the help of RS and GIS techniques. In this study, a standard methodology was used for the determination of groundwater potential areas by using the integration of RS and GIS techniques. The composite maps (geology, geomorphology, lineaments, slope, soils and drainage) were generated using GIS tools. The accurate information to obtain the above parameters can be considered for the identification of the groundwater potential areas. The maps are generated using satellite data (LISS-III IRS-P6) and Survey of India (SOI) toposheet of scale 1:50,000. Then, it was integrated with Arc GIS Software for the evaluation of various geomorphic units and demarked the groundwater availability. The groundwater potential zones are classified into five categories like very poor, poor, moderate, good and excellent. In overall, the study area predominately is occupied with denudation hills and pediment slope and contains the less groundwater potential. This groundwater potential information will be useful for the effective identification of a suitable location for the extraction of groundwater.









Similar content being viewed by others
References
Abdalla F (2012) Mapping of groundwater prospective zones using remote sensing and GIS techniques: a case study from the Central Eastern Desert, Egypt. J Afr Earth Sci 70:817. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jafrearsci.2012.05.003
Baalousha HM, Barth N, Ramasomanana FH et al (2018) Groundwater recharge estimation and its spatial distribution in arid regions using GIS: a case study from Qatar karst aquifer. Model Earth Syst Environ 4:1319–1329. https://doi.org/10.1007/s40808-018-0503-4
Chaudhary BS, Kumar S (2018) Identification of groundwater potential zones using remote sensing and GIS of K–J Watershed, India. J Geol Soc India 91:717–721. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12594-018-0929-3
Czech H, Boswell KC (1953) Morphological analysis of landforms. Macmillan, London
Etikala B, Golla V, Li P, Renati S (2019) Deciphering groundwater potential zones using MIF technique and GIS: a study from Tirupati area, Chittoor district, Andhra Pradesh, India. HydroResearch 1:1–7. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.hydres.2019.04.001
Golla V, Balaji E, Veeranjaneyulu A, Subbarao M, Surekha A, Narasimhlu K (2018) Data sets on delineation of groundwater potential zones identified by geospatial tool in Gudur area, Nellore district, Andhra Pradesh, India. Data Brief 20:1984–1991. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.dib.2018.09.054
Golla V, Rajasekhar M, Balaji E, Harish P (2019) Land use/land cover classification in parts of the Sathyavedu area, Chittoor district (Andhra Pradesh), India by using Remote Sensing and GIS Techniques. J Remote Sens GIS 10(3):18–24
Huggett RJ (2007) Fundamentals of geomorphology, 2nd edn. Routledge Taylor & Francis Group, London and New York
Kishore S, Srivastav SK, Jugran DK (2006) Ground water prospects zonation using remote sensing and GIS—a case study of bata watershed, Sirmaur district, H.P. Symposium of ISPRS Commission IV, Goa, 30
Kkarasu B (2017) Geological, geomorphological and lineament mapping using remote sensing and GIS—a tool for land use planning in Tiruchchirappalli districts of Tamil Nadu. Int J Adv Technol Eng Res 7(6):29–34
Magesh NS, Chandrasekar N, Soundranayagam JP (2010) Delineation of groundwater potential zones in Theni district, Tamil Nadu, using remote sensing, GIS and MIF techniques 2012, China University of Geosciences (Beijing). Geosci Front 3(2):189–196
Nagaraju A, Sreedhar Y, Thejaswi A, Dash P (2016) Integrated approach using remote sensing and GIS for assessment of groundwater quality and hydrogeomorphology in certain parts of Tummalapalle area, Cuddapah district, Andhra Pradesh, South India. Adv Remote Sens 5:83–92. https://doi.org/10.4236/ars.2016.52007
Narendra K, Nageswara Rao K, Swarna Latha P (2013) Integrating remote sensing and GIS for identification of groundwater prospective zones in the Narava basin, Visakhapatnam region, Andhra Pradesh. J Geol Soc India 81:248–260. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12594-013-0028-4
National Remote Sensing Agency (NRSA) (1995) Integrated mission for sustainable development. Guidelines for Field Survey and Mapping, 52
Penck W (1953) Morphological analysis of land forms. Macmillan & Co., London, p 429 (translation by H Czech, KC Boswell of 1924 eds)
Rajasekhar M, Raju G, Raju RS (2019) Assessment of groundwater potential zones in parts of the semi-arid region of Anantapur district, Andhra Pradesh, India using GIS and AHP Approach. Model Earth Syst Environ 1:1. https://doi.org/10.1007/s40808-019-00657-0
Raju RS, Raju G, Rajasekhar M (2019) Identification of groundwater potential zones in Mandavi River basin, Andhra Pradesh, India using remote sensing, GIS and MIF techniques. HydroResearch. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.hydres.2019.09.001
Ramaiah SN, Gopalakrishna GS, Srinivasa Vittala S, Najeeb KM (2012) Morphometric analysis of sub-basins in and around Malur Taluk, Kolar district, Karnataka using remote sensing and GIS techniques. Nat Environ Pollut Technol 11:89–94
Saraf AK, Choudhury PR (1998) Integrated remote sensing and GIS for groundwater exploration and identification of artificial recharge sites. Int J Remote Sens 19:1825–1841. https://doi.org/10.1080/01431169821501
Sarma JL, Translated from the French by VAK (2005) Mapping of the soil cover. Science Publishers, Enfield, ISBN: 9781578083633
Vishwakarma J, Sinha MK, Verma MK, Ahmad I (2014) Application, of remote sensing and GIS in groundwater prospect mapping. IJRET 3(10):549–555
Wood T (1910) The feeding value of mangels. J Agric Sci 3(3):225–232. https://doi.org/10.1017/s0021859600000800
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Golla, V. Delineation of groundwater potential zones in Sathyavedu area, Chittoor District (Andhra Pradesh), South India, using geospatial technologies. Model. Earth Syst. Environ. 6, 895–905 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s40808-020-00726-9
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s40808-020-00726-9