Abstract
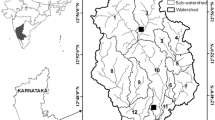
Both natural erosional dynamics and anthropogenic changes have intense effects on the land use/land cover (LULC) of the global earth. These LULC changes have a substantial impact on soil and water. This study focus on impacts of LULC changes on hydrological processes governing the Tons River Basin (TRB). Landsat satellite images based on seven land use classes which were defined for this basin are forest deciduous (FRSD), forest mixed (FRST), mixed crop (RWSW), barren land (BARN), hay (HAY), residential (URBN) and water body (WATR). The LULC (1985–2035) result showed an increase in URBN from 0.29 to 2.81% while the rate of change (RoC) for URBN was calculated to be 8.71%. A continuous reduction was seen in FRSD from 15.57 to 9.77% giving the RoC as − 0.37%. The FRST increased at the RoC of 1.95% from 0.6 to 1.77% while the mixed crop (RWSW) increased from 72.68 to 78.27% at the RoC of 0.77%. The other LULC classes showed similar results. The hydrologic impacts were analyzed by running SWAT for the LULC changes in order to predict the corresponding changes in the hydrologic process. In this consequence SWAT was run for five decades from 1985 to 1995, 1995–2005, 2005–2015 (before baseline scenario) and 2015–2025, 2025–2035 (after baseline scenario) assuming 2015 as a baseline scenario. Evaluation of the impact of LULC changes revealed that there was decrease in surface runoff, from 62.29 to 62.14% and lateral flow from 2.39 to 0.261% for the period of 2015 to 2035. The groundwater flow showed a slight increment from 37.42 to 37.62% while the total water yield increased from 774.74 to 776.74 mm. The simulated results for TRB showed that the hydrological processes in the watershed were minimally influenced by LULC changes. It was concluded that the basin’s LULC change was not pronounced and was minimally affected by natural and artificial changes. The hydrological changes were not correlated with LULC changes. It is recommended that in order to manage the water resources and to properly develop the entire catchment, a rational regulation policy for land use patterns is vitally important in order to assist stakeholders and policy makers.

Source: Hydrosheds-Asia Digital Elevation Model (DEM), Global Rivers and Global Basins







Similar content being viewed by others
References
Abbaspour KC (2012) SWAT-CUP: SWAT calibration and uncertainty programs—a user manual. Swiss Federal Institute of Aquatic Science and Technology. (downloaded on August 2016)
Abbaspour KC (2015) SWAT-CUP: SWAT Calibration and Uncertainty Programs-A User Manual. http://swat.tamu.edu/software/swat-cup/.(downloaded on August 2016)
Abbaspour KC, Yang J, Maximov I, Siber R, Bogner K, Mieleitner J, Zobrist J, Srinivasan R (2007) Modelling hydrology and water quality in the pre-alpine/alpine thur watershed using SWAT. J Hydrol 333(2–4):413–430. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhydrol.2006.09.014
Abbott MB, Bathurst JC, Cunge JA, O’Connell PE, Rasmussen J (1986) An introduction to the European hydrological system—systeme hydrologique Europeen, ‘‘SHE’’, 1: history and philosophy of a physically-based, distributed modelling system. J Hydrol 87(1–2):45–59. https://doi.org/10.1016/0022-1694(86)90114-9
Alamirew CD. 2006. Modeling of Hydrology and Soil Erosion in Upper Awash River Basin. University of Bonn, Institut für Städtebau, Bodenordnung und Kulturtechnik. Ph.D Thesis. p 233
Amin A, Singh SK (2012) Study of urban land use dynamics in Srinagar city using Geo-spatial approach. Bull Environ Sci Res 1:18–24
Arnold JG, Kiniry JR, Srinivasan R, Williams JR, Haney EB, Neitsch SL (2011) Soil and Water Assessment Tool Theoretical Documentation, Version 2009. Texas: Texas Water Resources Institute Technical Report No 365; 2011.(downloaded on May 2016)
Ashagrie AG, Laat PJM, De, Wit MJM, De, Tu M, Uhlenbrook S (2006) Detecting the influence of land use changes on discharges and floods in the Meuse River Basin—the predictive power of a ninety-year rainfall-runoff relation?. Hydrol Earth Syst Sci 691–701. https://doi.org/10.5194/hess-10-691-2006
Baker TJ, Miller SN (2013) Using the soil and water assessment tool (SWAT) to assess land use impact on water resources in an East African watershed. J Hydrol 486:100–111. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhydrol.2013.01.041
Barthel R, Reichenau TG, Krimly T (2012) Integrated modeling of global change impacts on agriculture and groundwater resources. Water Resour Manag 26(7):1929–1951
Basommi G, Guan Q-F, Cheng D-d, Singh SK (2016) Dynamics of land use change in a mining area: a case study of Nadowli District, Ghana. J Mt Sci 13:633–642
Beven K, Binley A (1992) The Future of distributed models–model calibration & uncertainty prediction. Hydrol Process 6(3):279–298
Cao W, Bowden WB, Davie T, Fenemor A (2006) Multi-variable and multi-site calibration and validation of SWAT in a large mountainous catchment with high spatial variability. Hydrol Process 20(5):1057–1073. https://doi.org/10.1002/hyp.5933
Carpenter SR, Stanley EH, Zanden MJV (2011) State of the World’s freshwater ecosystems: physical, chemical, and biological changes. Annu Rev Environ Resour 36:75–99. https://doi.org/10.1146/annurev-environ-021810-094524
Charlton MB, Arnell NW (2011) Adapting to climate change impacts on water resources in England—an assessment of draft water resources management plans. Global Environ Chang 21(1):238–248. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.gloenvcha.2010.07.012
Chen Z, Chen Y, Li B (2013) Quantifying the effects of climate variability and human activities on runoff for Kaidu river basin in arid region of northwest China. Theor Appl Climatol 111(3–4):537–545
Chen Y, Li J, Xu H (2016) Improving flood forecasting capability of physically based distributed hydrological models by parameter optimization. Hydrol Earth Syst Sci 20(1):375–392. https://doi.org/10.5194/hess-20-375-2016
Choi W, Deal BM (2008) Assessing hydrological impact of potential land use change through hydrological and land use change modeling for the Kishwaukee river basin (USA). J Environ Manage 88:1119–1130. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jenvman.2007.06.001
Conaghan K (2010) Assessing the Hydrologic Implications of Land Use Change for the Upper Neuse River Basin (M.S. Thesis, Nicholas School of the Environment, Duke University). Accessed on 2016
De Girolamo AM, Porto AL (2012) Land use scenario development as a tool for watershed management within the Rio Mannu Basin. Land Use Policy 29(3):691–701. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.landusepol.2011.11.005
Deng X, Shi Q, Zhang Q, Shi C, Yin F (2015) Impacts of land use and land cover changes on surface energy and water balance in the Heihe River Basin of China, 2000–2010. Phys Chem Earth Parts A/B/C 79–82:2–10. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.pce.2015.01.002
Döll P, Portmann FT, Döll P, Eisner S, Strzepek K, Jacobsen M, Boehlert B (2012) Assessment How is the impact of climate change on river flow regimes related to the impact on mean annual runoff ? A global-scale analysis. Environ Res Lett 7(1):1–11. https://doi.org/10.1088/1748-9326/7/1/014037
Du J, Qian L, Rui H, Zuo T, Zheng D, Xu Y, Xu C (2012) Assessing the effects ofurbanization on annual runoff and flood events using an integrated hydrologicalmodeling system for Qinhuai River basin, China. J Hydrol 464–465:127–139. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhydrol.2012.06.057
Eberhart RC, Kennedy JA (1995) A new optimizer using particle swarm theory. In: Proceedings of the Sixth International Symposium on Micro Machine and Human Science. IEEE Service Center, Piscataway, NJ, Nagoya, Japan. https://doi.org/10.1109/MHS.1995.494215
Ejieji CJ, Amodu MF, Adeogun AG (2016) Prediction of Streamflow of Hadejia-Jama’are-Kamadugu-Yobe River Basin, North Eastern Nigeria, Using SWAT Model. Ethiop Environ Stud Manag 9(2): 209–219
Fan M, Shibata H (2015) Simulation of watershed hydrology and stream water quality under land use and climate change scenarios in Teshio River watershed, northern Japan. Ecol Indic 50:79–89. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ecolind.2014.11.003
Farley KA, Tague C, Grant GE (2011) Vulnerability of water supply from the Oregon Cascades to changing climate: linking science to users and policy. Global Environ Chang 21(1):110–122. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.gloenvcha.2010.09.011
Feldman AD (1981) HEC models for water resources system simulation: theory and experience. Adv Hydrosci 12:297–423. https://doi.org/10.1016/B978-0-12-021812-7.50010-9
Foley JA et al (2005) Global consequences of land use. Science 309:570–574
Gajbhiye S, Singh SK, Sharma SK (2015) Assessing the effects of different land use on water qualify using multi-temporal Landsat data. In: Siddiqui AR SP (ed) Resour Manag Dev Strateg A Geogr Perspect. Pravalika Publications, Allahabad, pp 337–348
García-ruiz JM, López-moreno JI, Vicente-serrano SM, Lasanta T, Beguería S (2011) Earth-science reviews Mediterranean water resources in a global change scenario. Earth Sci Rev 105(3–4):121–139. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.earscirev.2011.01.006
Garg KK, Karlberg L, Barron J, Wani SP, Rockstrom J (2012) Assessing impacts of agricultural water interventions in the Kothapally watershed, Southern India. Hydrol Process 26(3):387–404. https://doi.org/10.1002/hyp.8138
Garg KK, Wani SP, Barron J, Karlberg L, Rockstrom J (2013) Up-scaling potential impacts on water fl ows from agricultural water interventions: opportunities and trade-offs in the Osman. Hydrol Process 27(26):3905–3921. https://doi.org/10.1002/hyp.9516
Gassman PW, Reyes MR, Green CH, Arnold JG (2007) The soil and water assessment tool: historical development, applications, and future research directions. Trans ASABE 50(4):1211–1250
Gebremicael TG, Mohamed YA, Betrie GD, Zaag P, Van Der Teferi E (2013) Trend analysis of runoff and sediment fluxes in the Upper Blue Nile basin: A combined analysis of statistical tests, physically-based models and landuse maps. J Hydrol 482:57–68. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhydrol.2012.12.023
Genxu W, Yu Z, Guimin L, Lin C (2005) Impact of land-use change on hydrological processes in the Maying River basin, China. Sci China Ser D Earth Sci 2006 49(10):1098–1110. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11430-006-1098-6
Getahun YS, Van Lanen HAJ (2015) Assessing the Impacts of land use-cover change on hydrology of Melka Kuntrie Subbasin in Ethiopia, using a conceptual hydrological model. Hydrol Current Res 6:210. https://doi.org/10.4172/2157-7587.1000210
Ghaffari G, Keesstra S, Ghodousi J, Ahmadi H (2010) SWAT-simulated hydrological impact of land-use change in the Zanjanrood Basin, Northwest Iran. Hydrol Process 24(7):892–903. https://doi.org/10.1002/hyp.7530
Gidey E, Dikinya O, Sebego R, Segosebe E, Zenebe A (2017a) Cellular automata and Markov Chain (CA_Markov) model-based predictions of future land use and land cover scenarios (2015–2033) in Raya, northern Ethiopia. Model Earth Syst Environ. https://doi.org/10.1007/s40808-017-0397-6
Gidey E, Dikinya O, Sebego R, Segosebe E, Zenebe A (2017b) Modeling the Spatio-temporal dynamics and evolution of land use and land cover (1984–2015) using remote sensing and GIS in Raya, Northern Ethiopia. Model Earth Syst Environ. https://doi.org/10.1007/s40808-017-0375-z
Gosain AK, Rao S, Srinivasan R, Reddy NG (2005) Return-flow assessment for irrigation command in the Palleru river basin using SWAT model. Hydrol Process 19(3):673–682. https://doi.org/10.1002/hyp.5622
Gosain AK, Rao S, Basuray D (2006) Climate change impact assessment on hydrology of Indian river basins. Curr Sci 101(3):356–371
Gupta HV, Sorooshian S, Yapo PO (1999) Status of automatic calibration for hydrologic models: comparison with multilevel expert calibration. J Hydrol Eng 4:135–143. https://doi.org/10.1061/(ASCE)1084-0699(1999)4:2(135)
Gyamfi C, Ndambuki JM, Anornu GK, Kifanyi GE (2017) Groundwater recharge modelling in a large scale basin: an example using the SWAT hydrologic model. Model Earth Syst Environ. https://doi.org/10.1007/s40808-017-0383-z
Haregeweyn N, Berhe A, Tsunekawa A, Tsubo M, Meshesha DT (2012) Integrated watershed management as an effective approach to curb land degradation: a case study of the enabered watershed in Northern Ethiopia. Environ Manage 50(6):1219–1233
He M, Hogue TS (2012) Integrating hydrologic modeling and land use projections for evaluation of hydrologic response and regional water supply impacts in semi-arid environments. Environ Earth Sci 65(6):1671–1685
Hornberger GM, Spear RC (1981) An approach to the preliminary-analysis of environmental systems. J Environ Manage 12(1):7–18
Hu X, Lu L, Li X, Wang J, Guo M (2015) Land use/cover change in the middle reaches of the Heihe River Basin over 2000–2011 and its implications for sustainable water resource management. PLoS One 10(6):1–19. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0128960
Huber WC, Dickinson RE, Barnwell TO Jr (1988) Storm water management model, version 4: User’s manual, 600/3–88/001a. US Environmental Protection Agency. Report No. EPA/, Athens
Isik S, Kalin L, Schoonover JE, Srivastava P, Lockaby BG (2012) Modeling effects of changing land use / cover on daily streamflow: An Artificial Neural Network and curve number based hybrid approach. J Hydrol 485:103–112. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhydrol.2012.08.032
Jing Z, Ross M (2015) Hydrologic modeling impacts of post-mining land use changes on streamflow of Peace River, Florida. Chin Geogr Sci 25(6):728–738
Kishor B, Singh SK (2014) Change detection mapping of land use land cover using multidate satellite data. Int J Eng Res Techno 3:2320–2326
Kristian J, Christian J, Mazvimavi D (1998) Assessing the effect of land use change on catchment runoff by combined use of statistical tests and hydrological modelling: Case studies from Zimbabwe. J Hydrol 205(3–4):147–163. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0168-1176(97)00311-9
Krysanova V, White M, Krysanova V, White M (2015) Advances in water resources assessment with SWAT—an overview. Hydrol Sci J 60:771–783. https://doi.org/10.1080/02626667.2015.1029482
Kumar SK, Aier B, Khanduri VP, Gautam P, Singh D, Singh SK (2013) Assessment of soil nutrients (N, P, K) status along with tree diversity In different land use systems at Mokokchung. Nagaland India Sci Technol J 1:42–48
Kumar S, Yadava RN, Singh SK (2014) Assessment of land use around highly populous business centre of Lucknow City using GIS techniques and high resolution Google Earth’s Quickbird satellite data. Bull Environ Sci Res 3:8–14
Kumar N, Singh SK, Srivastava PK, Narsimlu B (2017) SWAT model calibration and uncertainty analysis for streamflow prediction of the Tons river basin, India, using sequential uncertainty fitting (SUFI-2) algorithm. Model Earth Syst Environ. https://doi.org/10.1007/s40808-017-0306-z
Lamine S, Petropoulos GP, Singh SK, Szabó S, Bachari NEI, Srivastava PK, Suman S (2017) Quantifying land use/land cover spatio-temporal landscape pattern dynamics from Hyperion using SVMs classifier and FRAGSTATS®. Geocarto Int 6049:1–17
Legesse D, Vallet-couomb C, Gasse F (1995) Hydrological response of a catchment to climate and land use changes in Tropical Africa: case study South Central Ethiopia. J Hydrol 275(1–2):67–85. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0022-1694(03)00019-2
Li Y, Wang C (2009) Impacts of Urbanization on Surface Runoff of the Dardenne Creek Watershed, St. Charles County, Missouri. Phys Geogr 30(6):556–573
Li Z, Liu W, Zhang X, Zheng F (2009) Impacts of land use change and climate variability on hydrology in an agricultural catchment on the Loess Plateau of China. J Hydrol 377(1–2):35–42. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhydrol.2009.08.007
Lin YP, Verburg PH, Chang CR, Chen HY, Chen MN (2009) Developing and comparing optimal and empirical land-use models for the development of an urbanized watershed forest in Taiwan. Landsc Urban Plan 92(3–4):242–254. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.landurbplan.2009.05.003
Ma X, Xu J, Luo Y, Aggarwal SP, Li J (2009a) Response of hydrological processes to land-cover and climate changes in Kejie watershed, south-west China. Hydrol Process 23(8):1179–1191. https://doi.org/10.1002/hyp.7233
Ma X, Xu J, Luo Y, Aggarwal SP, Li J (2009b) Response of hydrological processes to land-cover and climate changes in Kejie watershed, south-west China. Hydrol Process. https://doi.org/10.1002/hyp.7233
Maetens W, Vanmaercke M, Poesen J, Jankauskas B, Jankauskiene G, Ionita I (2012) Effects of land use on annual runoff and soil loss in Europe and the Mediterranean: a meta-analysis of plot data. Prog Phys Geogr 36:597–651
Makwana JJ, Tiwari MK (2017) Hydrological stream flow modelling using soil and water assessment tool (SWAT) and neural networks (NNs) for the Limkheda watershed, Gujarat, India M.K. Model Earth Syst Environ 3:635. https://doi.org/10.1007/s40808-017-0323-y
Mango LM, Melesse AM, Mcclain ME, Gann D, Setegn SG (2011) Land use and climate change impacts on the hydrology of the upper Mara River Basin, Kenya: results of a modeling study to support better resource management. Hydrol Earth Syst Sci 15:2245–2258. https://doi.org/10.5194/hess-15-2245-2011
Marhaento H, Booij MJ, Rientjes THM, Hoekstra AY (2016) Attribution of changes in the water balance of a tropical catchment to land use change using the SWAT model. Hydrol Process 2017:1–12. https://doi.org/10.1002/hyp.11167
Metzger JC, Landschreiber L, Gröngröft A, Eschenbach A (2014) Soil evaporation under different types of land use in southern African savanna ecosystems. J Plant Nutr Soil Sci 177(3):468–475. https://doi.org/10.1002/jpln.201300257
Molina-navarro E, Trolle D, Martínez-pérez S, Sastre-merlín A, Jeppesen E (2014) Hydrological and water quality impact assessment of a Mediterranean limno-reservoir under climate change and land use management scenarios. J Hydrol 509:354–366. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhydrol.2013.11.053
Morán-tejeda E, Ceballos-barbancho A, Llorente-pinto JM (2010) Hydrological response of Mediterranean headwaters to climate oscillations and land-cover changes: the mountains of Duero River basin (Central Spain). Global Planet Change 72:39–49. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.gloplacha.2010.03.003
Morán-tejeda E, Zabalza J, Rahman K, Gago-silva A, López-moreno JI, Vicente-serrano S, Lehmann A, Tague CL, Beniston M (2015) Hydrological impacts of climate and land-use changes in a mountain watershed: uncertainty estimation based on model comparison. Ecohydrology 8(8):1396–1416. https://doi.org/10.1002/eco.1590
Moriasi DN, Arnold JG, Van Liew MW, Bingner RL, Harmel RD, Veith TL (2007) Model evaluation guidelines for systematic quantification of accuracy in watershed simulations. Trans ASABE 50:885–900
Moriasi DN, Gitau MW, Pai N, Daggupati P (2015) Hydrologic and water quality models: performance measures and evaluation criteria. Trans ASABE 58(6):1763–1785. https://doi.org/10.13031/trans.58.10715
Murty PS, Pandey A, Suryavanshi S (2014) Application of Semi distributed hydrological model for basin level water balance of the Ken basin of Central India. Hydrol Process 28(13):4119–4129. https://doi.org/10.1002/hyp.9950
Mustak SK, Baghmar NK, Singh SK (2015) Prediction of industrial land use using linear regression and MOLA techniques: a case study of Siltara industrial belt. Landsc Environ 9:59–70
Mustak SK, Baghmar NK, Singh SK (2016) Land suitability modeling for arhar pulse through analytic hierarchy process using remote sensing and GIS: a case study of Seonath Basin. Bull Environ Sci Res 4:6–17
Nash JE, Sutcliffe J (1970) River flow forecasting through conceptual models: part I—a discussion of principles. J Hydrol 10:282–290
Neitsch SL, Arnold JG, Kiniry JR, Williams JR (2005) Soil and Water Assessment Tool Theoretical Documentation. Ver. 2005. Temple, Tex., USDA–ARS Grassland Soil and Water. Research Laboratory, and Texas A&M University, Blackland Research and Extension Center, 2005
Niraula R, Meixner T, Norman LM (2015) Determining the importance of model calibration for forecasting absolute/relative changes in streamflow from LULC and climate changes. J Hydrol 522:439–451. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhydrol.2015.01.007
Niu J, Sivakumar B (2014) Study of runoff response to land use change in the East River basin in South China. Stoch Env Res Risk Assess 28(4):857–865
Nugroho P, Marsono D, Sudira P, Suryatmojo H (2013) Impact of land-use changes on water balance. Proced Environ Sci 17:256–262
Nyssen J, Clymans W, Descheemaeker K, Poesen J, Vandecasteele I et al (2010) Impact of soil and water conservation measures on catchment hydrological response–a case in north Ethiopia. Hydrol Process 24(13):78–87. https://doi.org/10.1002/hyp.7628
Olang LO (2011) Effects of land cover change on flood peak discharges and runoff volumes: model estimates for the Nyando River Basin, Kenya. Hydrol Process 25(1):80–89. https://doi.org/10.1002/hyp.7821
Perrin J (2014) Assessing water availability in a semi-arid watershed of southern India using a semi-distributed model. J Hydrol 460–461:143–155. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhydrol.2012.07.002
Poff NL, Zimmerman JKH (2010) Ecological responses to altered flow regimes: a literature review to inform the science and management of environmental flows. Freshwater Biol 55(1):194–205. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1365-2427.2009.0227
Portela R, Rademacher I (2001) A dynamic model of patterns of deforestation and their effect on the ability of the Brazilian Amazonia to provide ecosystem services. Ecol Model 143(1–2):115–146
Prasad BKV (2012) Water for sustainable water resources management in watershed for sustainable water resources management in watershed
Rolls RJ, Catherine Leigh C, Sheldon F (2012) Mechanistic effects of low-flow hydrology on riverine ecosystems: ecological principles and consequences of alteration. Freshwater Sci 31(4):1163–1186
Santhi C, Arnold JG. Williams JR. Dugas WA, Srinivasan R. Hauck LM (2001a) Validation of the SWAT model on a large river basin with point and nonpoint sources. J Am Water Resou Assoc 37(5):1169–1188
Santhi C, Arnold JG, Williams JR, Dugas WA, Srinivasan R, Hauck LM (2001b) Validation of the SWAT model on a large river basin with point and nonpoint sources. J Am Water Resour Assoc 37:1169–1188. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1752-1688.2001.tb03630.x
Santra P, Das SB (2013) Modeling runoff from an agricultural watershed of western catchment of Chilika lake through ArcSWAT. J Hydro-Environ Res 7(4):261–269. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jher.2013.04.005
Singh A, Imtiyaz M (2012) Application of process based hydrological model for simulating stream flow in an agricultural water shed of India. In: India Water Week 2012—Water Energy and Food Security Call for Solutions, New Delhi, India
Singh SK, Singh CK, Mukherjee S (2010) Impact of land-use and land-cover change on groundwater quality in the Lower Shiwalik hills: a remote sensing and GIS based approach. Cent Eur J Geosci 2:124–131
Singh SK, Kumar KS, Aier B, Kanduri VP, Ahirwar S (2012) Plant community characteristics and soil status in different land use systems in Dimapur district, Nagaland, India. For Res Pap 73:305–312
Singh SK, Srivastava K, Gupta M, Thakur K, Mukherjee S (2014) Appraisal of land use/land cover of mangrove forest ecosystem using support vector machine. Environ Earth Sci 71:2245–2255
Singh SK, Mustak S, Srivastava PK, Szabó S, Islam T (2015) Predicting spatial and decadal LULC changes through cellular automata markov chain models using earth observation datasets and geo-information. Environ Process 2(1):61–78
Singh SK, Srivastava PK, Szabó S, Petropoulos GP, Gupta M, Islam T (2017a) Landscape transform and spatial metrics for mapping spatiotemporal land cover dynamics using earth observation data-sets. Geocarto Int 32(2):113–127. https://doi.org/10.1080/10106049.2015.1130084
Singh SK, Basommi BP, Mustak SK, Srivastava PK, Szabo S (2017b) Modelling of land use land cover change using earth observation data-sets of Tons River Basin, Madhya Pradesh, India. Geocarto Int. https://doi.org/10.1080/10106049.2017.1343390
Srinivasan R, Ramanarayanan TS, Arnold JG, Bednarz ST (1998) Large area hydrological modeling and assessment part II: model application. J Am Water Resou Assoc 34:91–101.https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1752-1688.tb05962.x
Srinivasan R, Zhang X, Arnold J (2010) SWAT ungauged: hydrological budget and crop yield predictions in the Upper Mississippi River Basin. T ASABE 53(5):1533–1546
Sterling SM, Ducharne A, Polcher J (2012) The impact of global land-cover change on the terrestrial water cycle. Nat Cli Change:385–390. https://doi.org/10.1038/nclimate1690
Suliman AHA, Jajarmizadeh M, Harun S, Zaurah I, Darus M (2015) Comparison of semi-distributed, GIS-based hydrological models for the prediction of streamflow in a large catchment. Water Resour Manag 29(9):3095–3110
Tripathi MP, Raghuwanshi NS, Rao GP (2006) Effect of watershed subdivision on simulation of water. Hydrol Process 20(5):1137–1156. https://doi.org/10.1002/hyp.5927
US Department of Agriculture (USDA) (2011) AGNPS. Retrieved October 24, 2010 from http://www.ars.usda.gov/research/ docs.htm?docid = 5199
Verburg PH, Veldkamp A, Bouma J (1999) Land-use change under conditions of high population pressure: the case of Java. Glob Environ Change 9(4):303–312
Vilaysane B, Takara K, Luo P, Akkharath I (2015) Hydrological stream flow modelling for calibration and uncertainty analysis using SWAT model in the Xedone river basin, Lao PDR. Proced Environ Sci 28:380–390. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.proenv.2015.07.047
Wang S, Kang S, Zhang L, Li F (2008) Modelling hydrological response to different land-use and climate change scenarios in the Zamu River basin of northwest China. Hydrol Process 22(14):2502–2510
Wang G, Yang H, Wang L, Xu Z, Xue B (2014) Using the SWAT model to assess impacts of land use changes on runoff generation in headwaters. Hydrol Process 28(3):1032–1042. https://doi.org/10.1002/hyp.9645
Webb BW, Clack PD, Walling DE (2003) Water-air temperature relationships in a Devon river system and the role of flow. Hydrol Process 17:3069–3084
Welde K, Gebremariam B (2017) Effect of land use land cover dynamics on hydrological response of watershed: case study of Tekeze dam watershed, northern Ethiopia. Int Soil Water Conserv Res 5(2017):1–16. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.iswcr.2017.03.002
Wijesekara GN, Gupta A, Valeo C, Hasbani J, Qiao Y, Delaney P, Marceau DJ (2012) Assessing the impact of future land-use changes on hydrological processes in the Elbow river watershed in southern Alberta, Canada. J Hydrol 412–413:220–232. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhydrol.2011.04.018
Woldesenbet TA, Elagib NA, Ribbe L, Heinrich J (2017) Hydrological responses to land use/cover changes in the source region of the Upper Blue Nile Basin, Ethiopia. Sci Total Environ 575(2017):724–741. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2016.09.124
Yan B, Fang NF, Zhang PC, Shi ZH (2013) Impacts of land use change on watershed streamflow and sediment yield: An assessment using hydrologic modelling and partial least squares regression. J Hydrol 484:26–37. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhydrol.2013.01.008
Yang XL, Ren LL, Singh VP et al (2012) Impacts of land use and land cover changes on evapotranspiration and runoff at Shalamulun River watershed, China. Hydrol Res 43(1–2):23–37. https://doi.org/10.2166/nh.2011.120
Ye X, Zhang Q, Liu J, Li X, Xu C (2013) Distinguishing the relative impacts of climate change and human activities on variation of streamflow in the Poyang Lake catchment. J Hydrol 494:83–95. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhydrol.2013.04.036
Young RA, Onstad C, Bosch D, Anderson W (1989) AGNPS: a nonpoint-source pollution model for evaluating agricultural watersheds. J Soil Water Cons 44:168–173
Yu W, Zang S, Wu C, Liu W, Na X (2011) Analyzing and modeling land use land cover change (LUCC) in the Daqing. Appl Geogr 31:600–608. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apgeog.2010.11.019
Zhang YK, Schilling KE (2006) Increasing streamflow and baseflow in Mississippi River since the 1940s: Effect of land use change. J Hydrol 324(1–4):412–422. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhydrol.2005.09.033
Zhang C, Zhang B, Li W, Liu M (2014) Response of stream fl ow to climate change and human activity in Xitiaoxi river basin in China. Hydrol Process 28(1):43–50
Zhou H, Xiong D, Yang Z (2008) Effects of land use change on ecosystem service value in Yuanmou dry-hot valley. Trans Chin Soc Agric Eng 24(3):135–138
Zhou F, Xu Y, Chen Y, Xu C, Gao Y, Du J (2013) Hydrological response to urbanization at different spatio-temporal scales simulated by coupling of CLUE-S and the SWAT model in the Yangtze River Delta region. J Hydrol 485:113–125. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhydrol.2012.12.040
ISWSCR2004-08.pdf. Accessed 8 Sept 2005
Acknowledgements
The corresponding author is thankful to University Grant Commission (UGC), New Delhi, India for sponsoring major research project (MRP) [Grant No. 42–74/2013 (SR)] to carry out this research work. Authors also express their sincere thanks to Prof. R Srinivasan, Departments of Ecosystem Sciences and Management and Biological and Agricultural Engineering at Texas A&M University. Dr. Srinivasan is one of the developers of Soil and Water Assessment Tool (SWAT) for his constructive remarks on the first draft of the paper.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Kumar, N., Singh, S.K., Singh, V.G. et al. Investigation of impacts of land use/land cover change on water availability of Tons River Basin, Madhya Pradesh, India. Model. Earth Syst. Environ. 4, 295–310 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s40808-018-0425-1
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s40808-018-0425-1