Abstract
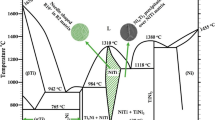
Nowadays, potable water is becoming scarcer, and chemicals components present in wastewater increase corrosion of devices and decrease its lifespan, especially from bearings used in water recovery system. The bearings are subjected to severe corrosion due to harsh environmental conditions from urine composition. 60NiTi alloy which was developed to attend International space station requirements as a resistant material to recycle wastewater to potable water, together DLC film as a solid lubricant, could be new protective material to avoid tribo-corrosion and corrosion from devices under hostile environment. In this work, we compared the tribocorrosion resistance of 60NiTi, also named as NiTi60T and thermally treated, and Ti–6Al–4V alloys with and without diamond-like carbon (DLC) film. The NiTi60T is a promising candidate to be used for the centrifuge bearings to expand their lifespan when in contact with synthetic urine. The DLC film presented high levels of wear resistance, metallic adhesion, and corrosion protection for both tested alloys.















Similar content being viewed by others
References
Dellacorte C, Moore IIIEL (2014) The effect of indenter ball radius on the static load capacity of the superelastic 60NiTi for Rolling element bearings. Nasa/Tm-2014-216627
DellaCorte C (2014) Novel super-elastic materials for advanced bearing applications: NASA Glenn Res Center, Cleveland, OH. https://doi.org/10.4028/www.scientific.net/AST.89.1
Dellacorte C, Wozniak WA (2012) Design and manufacturing considerations for shockproof and corrosion-immune superelastic nickel-titanium bearings for a space station application. Nasa/Tm—2012-216015 1–16
Dellacorte C, Noebe RD, Stanford MK, Padula S (2011) Resilient and Corrosion-Proof Rolling Element Bearings Made From Superelastic Ni-Ti Alloys for Aerospace Mechanism Applications. Nasa Tm-2011-0217105 143–166. https://doi.org/10.1520/STP103887
DellaCorte C, Thomas F, Leak OA (2015) Tribological evaluation of candidate gear materials operating under light loads in highly humid conditions
Santos LV, Trava-Airoldi VJ, Corat EJ et al (2006) DLC cold welding prevention films on a Ti6Al4V alloy for space applications. Surf Coatings Technol 200:2587–2593. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.surfcoat.2005.08.151
Wang J, Huang N, Yang P et al (2004) The effects of amorphous carbon films deposited on polyethylene terephthalate on bacterial adhesion. Biomaterials 25:3163–3170. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biomaterials.2003.10.010
Santos TB, Vieira AA, Paula LO et al (2017) Flexible camphor diamond-like carbon coating on polyurethane to prevent Candida albicans biofilm growth. J Mech Behav Biomed Mater 68:239–246. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jmbbm.2017.02.013
Capote G, Bonetti LF, Santos LV, Corat EJ (2006) Deposition of Adherent DLC Films Using a Low-Cost Enhanced Pulsed-DC PECVD Method. Rev Bras Apl Vacuo 25:209–213
Mendonça RX de, Buzzetti PHM, Silva AL et al (2015) Voltammetric determination of sildenafil citrate and furosemide at composite electrodes of graphite-paraffin for use in samples of pharmaceutical and toxicological Interests. Rev Virtual Química 7:1692–1708. https://doi.org/10.5935/1984-6835.20150096
Tam E, Petrzhik M, Shtansky D (2009) Combination of Instrumented nanoindentation and scanning probe microscopy for adequate mechanical surface testing. J Mater Sci Technol 25:63–68
Ferrari AC, Robertson J (2000) Interpretation of Raman spectra of disordered and amorphous carbon. Phys Rev B 61:14095–14107. https://doi.org/10.1103/PhysRevB.61.14095
Vieira L, Lucas FLCC, Fisssmer SF et al (2014) Surface & coatings technology scratch testing for micro- and nanoscale evaluation of tribocharging in DLC fi lms containing silver nanoparticles using AFM and KPFM techniques. Surf Coatings Technol 260:205–213. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.surfcoat.2014.06.065
Moulder JF, Stickle WF, Sobol PE, Bomben KD (1995) Handbook of X-ray photoelectron spectroscopy. Pelkin-Elmer Corporation, Minneapolis
Rand B, Appleyard SP, Yardim MF (1998) Design and control of structure of advanced carbon materials for enhanced performance. Springer, New York
Database of site. http://www.lasurface.com. Accessed XPS, AES, UPS and ESCA
Kato K, Adachi K (2001) Wear mechanisms. In: Bhushan B (ed) Modern tribology handbook. CRC Press, Boca Raton
Zhang W, Zou F, Li Y et al (2017) Research on tool wear prediction based on Archard agglomeration scavenging theory. Adv Mech Eng 9:1–7. https://doi.org/10.1177/1687814017724086
Li DY, Liu R (1999) The mechanism responsible for high wear resistance of Pseudo-elastic TiNi alloy: a novel tribo-material. Wear 225–229:777–783. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0043-1648(98)00388-3
Orbele TL (1951) Properties influencing wear of metals. J Met 439A:438–446
Acknowledgements
The authors are grateful to the Brazilian agencies FAPESP project number 2017/10491-2, CNPq and Capes for financial support. We would like to also thank, Dr. Christopher DellaCorte Senior Technologist, Tribology, and Rotating Machinery NASA, and Glenn Research Center that provided 60NiTi samples.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Paula, L.O., Sene, A.C., Manfroi, L.A. et al. Tribo-Corrosion and Corrosion Behaviour of Titanium Alloys with and Without DLC Films Immersed in Synthetic Urine. J Bio Tribo Corros 4, 51 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s40735-018-0166-8
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s40735-018-0166-8