Abstract
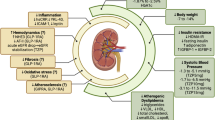
The most common cause of liver disease worldwide is now non-alcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD). NAFLD refers to a spectrum of disease ranging from steatosis to non-alcoholic steatohepatitis, causing cirrhosis, and ultimately hepatocellular carcinoma. However, the impact of NAFLD is not limited to the liver. NAFLD has extra-hepatic consequences, most notably, cardiovascular and renal disease. NAFLD and chronic kidney disease share pathogenic mechanisms including insulin resistance, lipotoxicity, inflammation and oxidative stress. Not surprisingly, there has been a recent surge in efforts to manage NAFLD in an integrated way that not only protects the liver but also delays comorbidities such as chronic kidney disease. This concept of simultaneously addressing the main disease target and comorbidities is key to improve outcomes, as recently demonstrated by clinical trials of SGLT2 inhibitors and GLP1 receptor agonists in diabetes. HIF activators, already marketed in China, also have the potential to protect both liver and kidney, as suggested by preclinical data. This review concisely discusses efforts at identifying common pathogenic pathways between NAFLD and chronic kidney disease with an emphasis on potential paradigm shifts in diagnostic workup and therapeutic management.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Mikolasevic I, Orlic L, Stimac D, Mavrinac V, Ferencic A, Rundic A, Babic V, Milic S (2016) Nonalcoholic fatty liver disease a multisystem disease? Lijec Vjesn 138:353–358
El Hadi H, Di Vincenzo A, Vettor R, Rossato M (2019) Cardio-metabolic disorders in non-alcoholic fatty liver disease. Int J Mol Sci 20:2215
Adams LA, Anstee QM, Tilg H, Targher G (2017) Non-alcoholic fatty liver disease and its relationship with cardiovascular disease and other extrahepatic diseases. Gut 66:1138–1153
Ix JH, Sharma K (2010) Mechanisms linking obesity, chronic kidney disease, and fatty liver disease: the roles of fetuin-A, adiponectin, and AMPK. J Am Soc Nephrol 21:406–412
Sanyal AJ (2019) Past, present and future perspectives in nonalcoholic fatty liver disease. Nat Rev Gastroenterol Hepatol 16:377–386
Han E, Lee YH (2017) Non-alcoholic fatty liver disease: the emerging burden in cardiometabolic and renal diseases. Diabetes Metab J 41:430–437
Jang HR, Kang D, Sinn DH, Gu S, Cho SJ, Lee JE, Huh W, Paik SW, Ryu S, Chang Y, Shafi T, Lazo M, Guallar E, Cho J, Gwak GY (2018) Nonalcoholic fatty liver disease accelerates kidney function decline in patients with chronic kidney disease: a cohort study. Sci Rep 8:4718
Musso G, Gambino R, Tabibian JH, Ekstedt M, Kechagias S, Hamaguchi M, Hultcrantz R, Hagstrom H, Yoon SK, Charatcharoenwitthaya P, George J, Barrera F, Hafliethadottir S, Bjornsson ES, Armstrong MJ, Hopkins LJ, Gao X, Francque S, Verrijken A, Yilmaz Y, Lindor KD, Charlton M, Haring R, Lerch MM, Rettig R, Volzke H, Ryu S, Li G, Wong LL, Machado M, Cortez-Pinto H, Yasui K, Cassader M (2014) Association of non-alcoholic fatty liver disease with chronic kidney disease: a systematic review and meta-analysis. PLoS Med 11:e1001680
Targher G, Chonchol M, Bertolini L, Rodella S, Zenari L, Lippi G, Franchini M, Zoppini G, Muggeo M (2008) Increased risk of CKD among type 2 diabetics with nonalcoholic fatty liver disease. J Am Soc Nephrol 19:1564–1570
Zeina AR, Goldenberg L, Nachtigal A, Hasadia R, Saliba W (2017) Association between nephrolithiasis and fatty liver detected on non-enhanced CT for clinically suspected renal colic. Clin Imaging 43:148–152
Ahn AL, Choi JK, Kim MN, Kim SA, Oh EJ, Kweon HJ, Cho DY (2013) Non-alcoholic fatty liver disease and chronic kidney disease in koreans aged 50 years or older. Korean J Fam Med 34:199–205
El Azeem HA, el Khalek SA, El-Akabawy H, Naeim H, Khalik HA, Alfifi AA (2013) Association between nonalcoholic fatty liver disease and the incidence of cardiovascular and renal events. J Saudi Heart Assoc 25:239–246
Di Costanzo A, Pacifico L, D'Erasmo L, Polito L, Martino MD, Perla FM, Iezzi L, Chiesa C, Arca M (2019) Nonalcoholic Fatty Liver Disease (NAFLD), but not ıts susceptibility gene variants, ınfluences the decrease of kidney function in overweight/obese children. Int J Mol Sci 20:444
Li L, Liu DW, Yan HY, Wang ZY, Zhao SH, Wang B (2016) Obesity is an independent risk factor for non-alcoholic fatty liver disease: evidence from a meta-analysis of 21 cohort studies. Obes Rev 17:510–519
Lu FB, Hu ED, Xu LM, Chen L, Wu JL, Li H, Chen DZ, Chen YP (2018) The relationship between obesity and the severity of non-alcoholic fatty liver disease: systematic review and meta-analysis. Expert Rev Gastroenterol Hepatol 12:491–502
Anastasio P, Viggiano D, Zacchia M, Altobelli C, Capasso G, Gaspare N (2017) Delay in renal hemodynamic response to a meat meal in severe obesity. Nephron 136:151–157
Fox CS, Larson MG, Leip EP, Culleton B, Wilson PW, Levy D (2004) Predictors of new-onset kidney disease in a community-based population. JAMA 291:844–850
Kramer H, Luke A, Bidani A, Cao G, Cooper R, McGee D (2005) Obesity and prevalent and incident CKD: the hypertension detection and follow-up program. Am J Kidney Dis 46:587–594
Hsu CY, McCulloch CE, Iribarren C, Darbinian J, Go AS (2006) Body mass index and risk for end-stage renal disease. Ann Intern Med 144:21–28
Pacifico L, Bonci E, Andreoli GM, Di Martino M, Gallozzi A, De Luca E, Chiesa C (2016) The ımpact of nonalcoholic fatty liver disease on renal function in children with overweight/obesity. Int J Mol Sci 17:1218
Voith K, Bruderlein FT, Humber LG (1978) Neuroleptics related to butaclamol. Synthesis and some psychopharmacological effects of a series of 3-aryl analogues. J Med Chem 21:694–698
Spoto B, Pisano A, Zoccali C (2016) Insulin resistance in chronic kidney disease: a systematic review. Am J Physiol Renal Physiol 311:F1087–f1108
Friedman SL, Neuschwander-Tetri BA, Rinella M, Sanyal AJ (2018) Mechanisms of NAFLD development and therapeutic strategies. Nat Med 24:908–922
Marcuccilli M, Chonchol M (2016) NAFLD and chronic kidney disease. Int J Mol Sci 17:562
Musso G, Cassader M, Cohney S, Pinach S, Saba F, Gambino R (2015) Emerging liver-kidney interactions in nonalcoholic fatty liver disease. Trends Mol Med 21:645–662
Targher G, Byrne CD (2017) Non-alcoholic fatty liver disease: an emerging driving force in chronic kidney disease. Nature Rev Nephrol 13:297–310
Sanchez-Lozada LG, Andres-Hernando A, Garcia-Arroyo FE, Cicerchi C, Li N, Kuwabara M, Roncal-Jimenez CA, Johnson RJ, Lanaspa MA (2019) Uric acid activates aldose reductase and the polyol pathway for endogenous fructose and fat production causing development of fatty liver in rats. J Biol Chem 294:4272–4281
Takir M, Kostek O, Ozkok A, Elcioglu OC, Bakan A, Erek A, Mutlu HH, Telci O, Semerci A, Odabas AR, Afsar B, Smits G, Sharma S, Johnson RJ, Kanbay M (2015) Lowering uric acid with allopurinol ımproves ınsulin resistance and systemic ınflammation in asymptomatic hyperuricemia. J Investig Med 63:924–929
Kuwabara M, Borghi C, Cicero AFG, Hisatome I, Niwa K, Ohno M, Johnson RJ, Lanaspa MA (2018) Elevated serum uric acid increases risks for developing high LDL cholesterol and hypertriglyceridemia: A five-year cohort study in Japan. Int J Cardiol 261:183–188
Jensen T, Niwa K, Hisatome I, Kanbay M, Andres-Hernando A, Roncal-Jimenez CA, Sato Y, Garcia G, Ohno M, Lanaspa MA, Johnson RJ, Kuwabara M (2018) Increased serum uric acid over five years is a risk factor for developing fatty liver. Sci Rep 8:11735
Kanbay M, Jensen T, Solak Y, Le M, Roncal-Jimenez C, Rivard C, Lanaspa MA, Nakagawa T, Johnson RJ (2016) Uric acid in metabolic syndrome: From an innocent bystander to a central player. Eur J Intern Med 29:3–8
Sato Y, Feig DI, Stack AG, Kang DH, Lanaspa MA, Ejaz AA, Sanchez-Lozada LG, Kuwabara M, Borghi C, Johnson RJ (2019) The case for uric acid-lowering treatment in patients with hyperuricaemia and CKD. Nature Rev Nephrol 15:767–775
Kanbay M, Afsar B, Covic A (2011) Uric acid as a cardiometabolic risk factor: to be or not to be. Contrib Nephrol 171:62–67
Pal D, Dasgupta S, Kundu R, Maitra S, Das G, Mukhopadhyay S, Ray S, Majumdar SS, Bhattacharya S (2012) Fetuin-A acts as an endogenous ligand of TLR4 to promote lipid-induced insulin resistance. Nat Med 18:1279–1285
Agarwal S, Chattopadhyay M, Mukherjee S, Dasgupta S, Mukhopadhyay S, Bhattacharya S (2017) Fetuin-A downregulates adiponectin through Wnt-PPARgamma pathway in lipid induced inflamed adipocyte. Biochim Biophys Acta Mol Basis Dis 1863:174–181
Chowdhry S, Nazmy MH, Meakin PJ, Dinkova-Kostova AT, Walsh SV, Tsujita T, Dillon JF, Ashford ML, Hayes JD (2010) Loss of Nrf2 markedly exacerbates nonalcoholic steatohepatitis. Free Radic Biol Med 48:357–371
Camer D, Yu Y, Szabo A, Dinh CH, Wang H, Cheng L, Huang XF (2015) Bardoxolone methyl prevents insulin resistance and the development of hepatic steatosis in mice fed a high-fat diet. Mol Cell Endocrinol 412:36–43
Kuro OM (2019) The Klotho proteins in health and disease. Nat Rev Nephrol 15:27–44
Fernandez-Fernandez B, Izquierdo MC, Valino-Rivas L, Nastou D, Sanz AB, Ortiz A, Sanchez-Nino MD (2018) Albumin downregulates Klotho in tubular cells. Nephrol Dial Transplant 33:1712–1722
Navarro-Gonzalez JF, Sanchez-Nino MD, Donate-Correa J, Martin-Nunez E, Ferri C, Perez-Delgado N, Gorriz JL, Martinez-Castelao A, Ortiz A, Mora-Fernandez C (2018) Effects of pentoxifylline on soluble klotho concentrations and renal tubular cell expression in diabetic kidney disease. Diabetes Care 41:1817–1820
Kanbay M, Vervloet M, Cozzolino M, Siriopol D, Covic A, Goldsmith D, Solak Y (2017) Novel Faces of Fibroblast Growth Factor 23 (FGF23): iron deficiency, inflammation, insulin resistance, left ventricular hypertrophy, proteinuria and acute kidney injury. Calcif Tissue Int 100:217–228
Rao Z, Landry T, Li P, Bunner W, Laing BT, Yuan Y, Huang H (2019) Administration of alpha klotho reduces liver and adipose lipid accumulation in obese mice. Heliyon 5:e01494
Dongiovanni P, Crudele A, Panera N, Romito I, Meroni M, De Stefanis C, Palma A, Comparcola D, Fracanzani AL, Miele L, Valenti L, Nobili V, Alisi A (2019) beta-Klotho gene variation is associated with liver damage in children with NAFLD. J Hepatol 72:411–419
Capalbo O, Giuliani S, Ferrero-Fernandez A, Casciato P, Musso CG (2019) Kidney-liver pathophysiological crosstalk: its characteristics and importance. Int Urol Nephrol 51:2203–2207
Hirata T, Tomita K, Kawai T, Yokoyama H, Shimada A, Kikuchi M, Hirose H, Ebinuma H, Irie J, Ojiro K, Oikawa Y, Saito H, Itoh H, Hibi T (2013) Effect of telmisartan or losartan for treatment of nonalcoholic fatty liver disease: fatty liver protection trial by Telmisartan or Losartan Study (FANTASY). Int J Endocrinol 2013:587140
Musso G, Cassader M, Cohney S, De Michieli F, Pinach S, Saba F, Gambino R (2016) Fatty liver and chronic kidney disease: novel mechanistic insights and therapeutic opportunities. Diabetes Care 39:1830–1845
Rahtu-Korpela L, Karsikas S, Horkko S, Blanco Sequeiros R, Lammentausta E, Makela KA, Herzig KH, Walkinshaw G, Kivirikko KI, Myllyharju J, Serpi R, Koivunen P (2014) HIF prolyl 4-hydroxylase-2 inhibition improves glucose and lipid metabolism and protects against obesity and metabolic dysfunction. Diabetes 63:3324–3333
Armstrong MJ, Houlihan DD, Rowe IA, Clausen WH, Elbrond B, Gough SC, Tomlinson JW, Newsome PN (2013) Safety and efficacy of liraglutide in patients with type 2 diabetes and elevated liver enzymes: individual patient data meta-analysis of the LEAD program. Aliment Pharmacol Ther 37:234–242
Sarafidis P, Ferro CJ, Morales E, Ortiz A, Malyszko J, Hojs R, Khazim K, Ekart R, Valdivielso J, Fouque D, London GM, Massy Z, Ruggenenti P, Porrini E, Wiecek A, Zoccali C, Mallamaci F, Hornum M (2019) SGLT-2 inhibitors and GLP-1 receptor agonists for nephroprotection and cardioprotection in patients with diabetes mellitus and chronic kidney disease. A consensus statement by the EURECA-m and the DIABESITY working groups of the ERA-EDTA. Nephrol Dial Transplant 34:208–230
Fernandez-Fernandez B, Fernandez-Prado R, Gorriz JL, Martinez-Castelao A, Navarro-Gonzalez JF, Porrini E, Soler MJ, Ortiz A (2019) Canagliflozin and Renal Events in Diabetes with Established Nephropathy Clinical Evaluation and Study of Diabetic Nephropathy with Atrasentan: what was learned about the treatment of diabetic kidney disease with canagliflozin and atrasentan? Clin Kidney J 12:313–321
Sanchez-Nino MD, Bozic M, Cordoba-Lanus E, Valcheva P, Gracia O, Ibarz M, Fernandez E, Navarro-Gonzalez JF, Ortiz A, Valdivielso JM (2012) Beyond proteinuria: VDR activation reduces renal inflammation in experimental diabetic nephropathy. Am J Physiol Renal Physiol 302:F647–657
Chen N, Hao C, Peng X, Lin H, Yin A, Hao L, Tao Y, Liang X, Liu Z, Xing C, Chen J, Luo L, Zuo L, Liao Y, Liu BC, Leong R, Wang C, Liu C, Neff T, Szczech L, Yu KP (2019) Roxadustat for anemia in patients with kidney disease not receiving dialysis. N Engl J Med 381:1001–1010
Provenzano R, Besarab A, Sun CH, Diamond SA, Durham JH, Cangiano JL, Aiello JR, Novak JE, Lee T, Leong R, Roberts BK, Saikali KG, Hemmerich S, Szczech LA, Yu KH, Neff TB (2016) Oral hypoxia-inducible factor prolyl hydroxylase inhibitor roxadustat (FG-4592) for the treatment of anemia in patients with CKD. Clin J Am Soc Nephrol 11(6):982–991. https://doi.org/10.2215/CJN.06890615
Saito H, Tanaka T, Sugahara M, Tanaka S, Fukui K, Wakashima T, Nangaku M (2019) Inhibition of prolyl hydroxylase domain (PHD) by JTZ-951 reduces obesity-related diseases in the liver, white adipose tissue, and kidney in mice with a high-fat diet. Lab Invest 99:1217–1232
Adinolfi LE, Ingrosso D, Cesaro G, Cimmino A, D'Antò M, Capasso R, Zappia V, Ruggiero G (2005) Hyperhomocysteinemia and the MTHFR C677T polymorphism promote steatosis and fibrosis in chronic hepatitis C patients. Hepatology 41:995–1003
Zampino R, Ingrosso D, Durante-Mangoni E, Capasso R, Tripodi MF, Restivo L, Zappia V, Ruggiero G, Adinolfi LE (2008) Microsomal triglyceride transfer protein (MTP) -493G/T gene polymorphism contributes to fat liver accumulation in HCV genotype 3 infected patients. J Viral Hepat 15:740–746
Zampino R, Macera M, Cirillo G, Pafundi PC, Rinaldi L, Coppola N, Pisaturo M, Adinolfi LE, Miraglia Del Giudice E, Ingrosso D, Capasso R (2018) No effect of MTP polymorphisms on PNPLA3 in HCV-correlated steatosis. Infez Med 26:244–248
Byrne CD, Targher G (2020) NAFLD as a driver of chronic kidney disease. J Hepatol 72:785–801
Sinn DH, Kang D, Jang HR, Gu S, Cho SJ, Paik SW, Ryu S, Chang Y, Lazo M, Guallar E, Cho J, Gwak GY (2017) Development of chronic kidney disease in patients with non-alcoholic fatty liver disease: a cohort study. J Hepatol 67:1274–1280
Yeung MW, Wong GL, Choi KC, Luk AO, Kwok R, Shu SS, Chan AW, Lau ESH, Ma RCW, Chan HL, Chan JC, Wong VW, Kong AP (2017) Advanced liver fibrosis but not steatosis is independently associated with albuminuria in Chinese patients with type 2 diabetes. J Hepatol. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhep.2017.09.020
Yasui K, Sumida Y, Mori Y, Mitsuyoshi H, Minami M, Itoh Y, Kanemasa K, Matsubara H, Okanoue T, Yoshikawa T (2011) Nonalcoholic steatohepatitis and increased risk of chronic kidney disease. Metabolism 60:735–739
Targher G, Pichiri I, Zoppini G, Trombetta M, Bonora E (2012) Increased prevalence of chronic kidney disease in patients with Type 1 diabetes and non-alcoholic fatty liver. Diabetic Med 29:220–226
Arase Y, Suzuki F, Kobayashi M, Suzuki Y, Kawamura Y, Matsumoto N, Akuta N, Kobayashi M, Sezaki H, Saito S, Hosaka T, Ikeda K, Kumada H, Ohmoto Y, Amakawa K, Tsuji H, Hsieh SD, Kato K, Tanabe M, Ogawa K, Hara S, Kobayashi T (2011) The development of chronic kidney disease in Japanese patients with non-alcoholic fatty liver disease. Internal Med (Tokyo, Japan) 50:1081–1087
Hwang ST, Cho YK, Yun JW, Park JH, Kim HJ, Park DI, Sohn CI, Jeon WK, Kim BI, Rhee EJ, Oh KW, Lee WY, Jin W (2010) Impact of non-alcoholic fatty liver disease on microalbuminuria in patients with prediabetes and diabetes. Internal Med J 40:437–442
Chang Y, Ryu S, Sung E, Woo HY, Oh E, Cha K, Jung E, Kim WS (2008) Nonalcoholic fatty liver disease predicts chronic kidney disease in nonhypertensive and nondiabetic Korean men. Metabolism 57:569–576
Mikolasevic I, Racki S, Bubic I, Jelic I, Stimac D, Orlic L (2013) Chronic kidney disease and nonalcoholic Fatty liver disease proven by transient elastography. Kidney Blood Pressure Res 37:305–310
Targher G, Mantovani A, Pichiri I, Mingolla L, Cavalieri V, Mantovani W, Pancheri S, Trombetta M, Zoppini G, Chonchol M, Byrne CD, Bonora E (2014) Nonalcoholic fatty liver disease is independently associated with an increased incidence of chronic kidney disease in patients with type 1 diabetes. Diabetes Care 37:1729–1736
Acknowledgements
MK gratefully acknowledge use of the services and facilities of the Koç University Research Center for Translational Medicine (KUTTAM), funded by the Presidency of Turkey, Presidency of Strategy and Budget. The content is solely the responsibility of the authors and does not necessarily represent the official views of the Presidency of Strategy and Budget.”AO research is supported by FIS PI19/00815, DTS18/00032, ERA-PerMed-JTC2018 (KIDNEY ATTACK AC18/00064 and PERSTIGAN AC18/00071, ISCIII-RETIC REDinREN RD016/0009 FEDER funds, Fundacion Renal Iñigo Álvarez de Toledo (FRIAT).
Funding
This study was not funded by any grant.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
All authors contributed to: (1) substantial contributions to conception and design, or acquisition of data, or analysis and interpretation of data, (2) drafting the article or revising it critically for important intellectual content, and, (3) final approval of the version to be published.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
All authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Ethical approval
This article does not contain any studies with human participants or animals performed by any of the authors.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Kanbay, M., Bulbul, M.C., Copur, S. et al. Therapeutic implications of shared mechanisms in non-alcoholic fatty liver disease and chronic kidney disease. J Nephrol 34, 649–659 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s40620-020-00751-y
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s40620-020-00751-y