Abstract
Background
In recent years, novel anticoagulant drugs have been introduced in the clinical armamentarium and have progressively gained momentum. Although their use is increasing among CKD patients, some skepticism about their risk–benefit ratio still persists. We sought to investigate the safety and effectiveness of rivaroxaban in a cohort of moderate-to-advanced CKD patients.
Methods
This observational, retrospective, longitudinal study involved 347 consecutive CKD stage 3b–4 (according to NKF–KDOQI guidelines) patients enrolled from 8 cardiac outpatient clinics between March 2015 and October 2017. All patients received anticoagulation (100 warfarin vs. 247 rivaroxaban) as part of their non-valvular atrial fibrillation management at the attending physician’s discretion. Clinical effectiveness (defined as the occurrence of ischemic stroke, venous thromboembolism, or transient ischemic attack) and safety (intracranial hemorrhage, gastrointestinal or other bleeding) were assessed separately.
Results
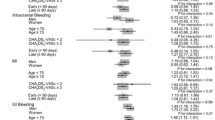
Over a mean follow-up period of 16 ± 0.3 months, 25 stroke episodes (15 hemorrhagic, and 10 ischemic) occurred in 24 warfarin treated patients vs. none in the rivaroxaban arm. There were 5 vs. 0 episodes of deep venous thrombosis and 8 vs. 2 major episodes of bleeding in the warfarin and rivaroxaban groups, respectively. In contrast, the proportion of minor episodes of bleeding was similar between groups.
Conclusion
Rivaroxaban seems a safe and effective therapeutic option in CKD stage 3b–4 patients. However, future randomized controlled trials are needed to definitively establish the role of rivaroxaban in CKD patients.

Similar content being viewed by others
References
Di Lullo L, Ronco C, Cozzolino M et al (2017) Nonvitamin K-dependent oral anticoagulants (NOACs) in chronic kidney disease patients with atrial fibrillation. Thromb Res 155:38–47
Chan KE, Giugliano RP, Patel MR et al (2016) Nonvitamin K anticoagulant agents in patients with advanced chronic kidney disease or on dialysis with AF. J Am Coll Cardiol 67:2888–2899
Bellasi A, Di Lullo L, Melfa G et al. New oral anticoagulants (NOAC) in nephrology. G Ital Nefrol 2016; 33
Lip GYH, Collet JP, Caterina R et al (2017) Antithrombotic therapy in atrial fibrillation associated with valvular heart disease: a joint consensus document from the European Heart Rhythm Association (EHRA) and European Society of Cardiology Working Group on Thrombosis, endorsed by the ESC Working Group on Valvular Heart Disease, Cardiac Arrhythmia Society of Southern Africa (CASSA), Heart Rhythm Society (HRS), Asia Pacific Heart Rhythm Society (APHRS), South African Heart (SA Heart) Association and Sociedad Latinoamericana de Estimulacion Cardiaca y Electrofisiologia (SOLEACE). Europace 19:1757–1758
Camm AJ, Kirchhof P, Lip GY et al (2010) Guidelines for the management of atrial fibrillation: the Task Force for the Management of Atrial Fibrillation of the European Society of Cardiology (ESC). Europace 12:1360–1420
Lin MC, Streja E, Soohoo M et al (2017) Warfarin use and increased mortality in end-stage renal disease. Am J Nephrol 46:249–256
Voskamp PWM, Rookmaaker MB, Verhaar MC et al (2018) Vitamin K antagonist use and mortality in dialysis patients. Nephrol Dial Transplant 33:170–176
Lip GYH, Collet JP, de Caterina R et al. (2017) Antithrombotic therapy in atrial fibrillation associated with valvular heart disease: executive summary of a joint consensus document from the European Heart Rhythm Association (EHRA) and European Society of Cardiology Working Group on Thrombosis, Endorsed by the ESC Working Group on Valvular Heart Disease, Cardiac Arrhythmia Society of Southern Africa (CASSA), Heart Rhythm Society (HRS), Asia Pacific Heart Rhythm Society (APHRS), South African Heart (SA Heart) Association and Sociedad Latinoamericana de Estimulacion Cardiaca y Electrofisiologia (SOLEACE). Thromb Haemost 117:2215–2236
Heidbuchel H, Dagres N, Antz M, Kuck KH, Lazure P, Murray S, Carrera C, Hindricks G, Vahanian A (2018) European Society of Cardiology (ESC) and European Heart Rhythm Association (EHRA). Europace. https://doi.org/10.1093/europace/euy039
Bansal VK, Herzog CA, Sarnak MJ et al (2017) Oral anticoagulants to prevent stroke in nonvalvular atrial fibrillation in Patients with CKD Stage 5D: an NKF-KDOQI controversies report. Am J Kidney Dis 70:859–868
Tan J, Bae S, Segal JB et al (2017) Treatment of atrial fibrillation with warfarin among older adults with end stage renal disease. J Nephrol 30:831–839
Genovesi S, Rebora P, Gallieni M et al (2017) Effect of oral anticoagulant therapy on mortality in end-stage renal disease patients with atrial fibrillation: a prospective study. J Nephrol 30:573–581
Bansilal S, Bloomgarden Z, Halperin JL et al (2015) Efficacy and safety of rivaroxaban in patients with diabetes and nonvalvular atrial fibrillation: the rivaroxaban once-daily, oral, direct factor Xa inhibition compared with vitamin K antagonism for prevention of stroke and embolism trial in atrial fibrillation (ROCKET AF trial). Am Heart J 170:675–682 e678
Huang HY, Lin SY, Cheng SH et al (2018) Effectiveness and safety of different rivaroxaban dosage regimens in patients with non-valvular atrial fibrillation: a nationwide, population-based cohort study. Sci Rep 8:3451
Di Lullo L, Rivera R, Barbera V et al (2016) Sudden cardiac death and chronic kidney disease: from pathophysiology to treatment strategies. Int J Cardiol 217:16–27
Bansal N, Zelnick LR, Alonso A et al (2017) eGFR and Albuminuria in relation to risk of incident atrial fibrillation: a meta-analysis of the jackson heart study, the multi-ethnic study of atherosclerosis, and the cardiovascular health study. Clin J Am Soc Nephrol 12:1386–1398
Losito A, Nunzi E, Pittavini L et al (2018) Cardiovascular morbidity and long term mortality associated with in hospital small increases of serum creatinine. J Nephrol 31:71–77
Losito A, Zampi I, Pittavini L et al (2017) Association of reduced kidney function with cardiovascular disease and mortality in elderly patients: comparison between the new Berlin initiative study (BIS1) and the MDRD study equations. J Nephrol 30:81–86
Gibertoni D, Mandreoli M, Rucci P et al (2016) Excess mortality attributable to chronic kidney disease. Results from the PIRP project. J Nephrol 29:663–671
Olesen JB, Lip GY, Kamper AL et al (2012) Stroke and bleeding in atrial fibrillation with chronic kidney disease. N Engl J Med 367:625–635
Capodanno D, Angiolillo DJ (2012) Antithrombotic therapy in patients with chronic kidney disease. Circulation 125:2649–2661
Camm AJ, Amarenco P, Haas S et al (2016) XANTUS: a real-world, prospective, observational study of patients treated with rivaroxaban for stroke prevention in atrial fibrillation. Eur Heart J 37:1145–1153
Martinez BK, Sood NA, Bunz TJ et al. Effectiveness and safety of apixaban, dabigatran, and rivaroxaban versus warfarin in frail patients with nonvalvular atrial fibrillation. J Am Heart Assoc 2018; 7
Vimalesvaran K, Dockrill SJ, Gorog DA (2018) Role of rivaroxaban in the management of atrial fibrillation: insights from clinical practice. Vasc Health Risk Manag 14:13–21
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Ethical approval
All procedures performed in studies involving human participants were in accordance with the ethical standards of the institutional and/or national research committee and with the 1964 Helsinki declaration and its later amendments or comparable ethical standards.
Informed consent
Informed consent was obtained from all individual participants included in the study.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Di Lullo, L., Tripepi, G., Ronco, C. et al. Safety and effectiveness of rivaroxaban and warfarin in moderate-to-advanced CKD: real world data. J Nephrol 31, 751–756 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s40620-018-0501-7
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s40620-018-0501-7