Abstract
Background
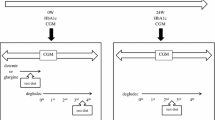
Degludec is a long-acting insulin with a longer duration of action and a greater day-to-day reproducibility of absorption in comparison with previous long-acting insulin formulations. The aim is the definition of the change in insulin needs in patients switching from detemir/glargine to degludec in real-life conditions.
Methods
In this retrospective cohort observational study, all outpatients with either type 1 or type 2 diabetes, starting therapy with degludec insulin—after a prior treatment with either detemir or glargine insulin for at least 6 months—were included.
Results
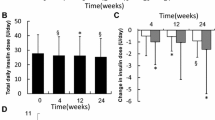
The analysis was performed on 266 patients, 172 and 96 with type 1 and type 2 diabetes, respectively. The equations describing the relationship between baseline and follow-up doses of basal insulin (6 months) were Y = 3.39 + 0.78X and Y = 0.44 + 0.69X, in patients receiving detemir/glargine either once or twice daily, respectively (Y = degludec dose at 6 months and X = basal insulin dose at switch). The corresponding equations for prandial insulin doses were y = 1.83 + 0.83*x and y = 2.85 + 0.80*x for those on pre-switch once or twice-daily basal insulin, respectively. In type 2 diabetes, the switch was associated with a reduction of basal insulin doses only in those with a prior twice-daily treatment with basal insulin. The reduction of prandial insulin reached statistical significance only in patients previously treated with basal insulin once daily.
Conclusions
The present results provide a suggestion for a simple method for the adjustment of basal and prandial insulin doses in type 1 diabetic patients, switching from glargine or detemir to degludec.

Similar content being viewed by others
References
Pettus J, Santos Cavaiola T, Tamborlane WV, Edelman S (2016) The past, present, and future of basal insulins. Diabetes Metab Res Rev 32:478–496
Heise T, Hermanski L, Nosek L, Feldman A, Rasmussen S, Haahr H (2012) Insulin degludec: four times lower pharmacodynamics variability than insulin glargine under steady-state conditions in type 1 diabetes. Diabetes Obes Metab 14:859–864
Heise T, Nosek L, Bøttcher SG, Hastrup H, Haahr H (2012) Ultra-long-acting insulin degludec has a flat and stable glucose-lowering effect in type 2 diabetes. Diabetes Obes Metab 14:944–950
Ratner RE, Gough SC, Mathieu C, Del Prato S, Bode B, Mersebach H, Endahl L, Zinman B (2013) Hypoglycaemia risk with insulin degludec compared with insulin glargine in type 2 and type 1 diabetes: a pre-planned meta-analysis of phase3 trials. Diabetes Obes Metab 15:175–184
Monami M, Mannucci E (2013) Efficacy and safety of degludec insulin: a meta-analysis of randomised trials. Curr Med Res Opin 29:339–342
Vora J, Christensen T, Rana A, Bain SC (2014) Insulin degludec versus insulin glargine in type 1 and type 2 diabetes mellitus: a meta-analysis of endpoints in phase 3a trials. DiabetesTher 5:435–446
Dżygało K, Golicki D, Kowalska A, Szypowska A (2015) The beneficial effect of insulin degludec on nocturnal hypoglycaemia and insulin dose in type 1 diabetic patients: a systematic review and meta-analysis of randomised trials. Acta Diabetol 52:231–238
Birkeland KI, Home PD, Wendisch U, Ratner RE, Johansen T, Endahl LA, Lyby K, Jendle JH, Roberts AP, DeVries JH, Meneghini LF (2011) Insulin degludec in type 1 diabetes: a randomized controlled trial of a new-generation ultra-long-acting insulin compared with insulin glargine. Diabetes Care 34:661–665
Bode BW, Buse JB, Fisher M, Garg SK, Marre M, Merker L, Renard E, Russell-Jones DL, Hansen CT, Rana A, Heller SR, BEGIN® Basal-Bolus Type 1 trial investigators (2013) Insulin degludec improves glycaemic control with lower nocturnal hypoglycaemia risk than insulin glargine in basal-bolus treatment with mealtime insulin aspart in Type 1 diabetes (BEGIN(®) Basal-Bolus Type 1): 2-year results of a randomized clinical trial. Diabet Med 30:1293–1297
Davies MJ, Gross JL, Ono Y, Sasaki T, Bantwal G, Gall MA, Niemeyer M, Seino H, BEGIN BB T1 Study Group (2014) Efficacy and safety of insulin degludec given as part of basal-bolus treatment with mealtime insulin aspart in type 1 diabetes: a 26-week randomized, open-label, treat-to-target non-inferiority trial. Diabetes Obes Metab 16:922–930
Kalra S (2013) Insulin degludec: a significant advancement in ultralong-acting Basal insulin. Diabetes Ther 4:167–173
Kaku K, Wolden ML, Hyllested-Winge J, Nørtoft E (2017) Insulin degludec in clinical practice: a review of Japanese real-world data. Diabetes Ther 8:189–195
Galasso S, Facchinetti A, Bonora BM, Mariano V, Boscari F, Cipponeri E, Maran A, Avogaro A, Fadini GP, Bruttomesso D (2016) Switching from twice-daily glargine or detemir to once-daily degludec improves glucose control in type 1 diabetes. An observational study. Nutr Metab Cardiovasc Dis 26:1112–1119
Heller S, Buse J, Fisher M, Garg S, Marre M, Merker L, Renard E, Russell-Jones D, Philotheou A, Francisco AM, Pei H, Bode B, BEGIN Basal-Bolus Type 1 Trial Investigators (2012) Insulin degludec, an ultra-longacting basal insulin, versus insulin glargine in basal-bolus treatment with mealtime insulin aspart in type 1 diabetes (BEGIN Basal-Bolus Type 1): a phase 3, randomised, open-label, treat-to-target non-inferiority trial. Lancet 379:1489–1497
Mathieu C, Hollander P, Miranda-Palma B, Cooper J, Franek E, Russell-Jones D, Larsen J, Tamer SC, Bain SC, NN1250-3770 (BEGIN: Flex T1) Trial Investigators (2013) Efficacy and safety of insulin degludec in a flexible dosing regimen vs insulin glargine in patients with type 1 diabetes (BEGIN: Flex T1): a 26-week randomized, treat-to-target trial with a 26-week extension. J Clin Endocrinol Metab 98:1154–1162
Meneghini L, Atkin SL, Gough SC, Raz I, Blonde L, Shestakova M, Bain S, Johansen T, Begtrup K, Birkeland KI, NN1250-3668 (BEGIN FLEX) Trial Investigators (2013) The efficacy and safety of insulin degludec given in variable once-daily dosing intervals compared with insulin glargine and insulin degludec dosed at the same time daily: a 26-week, randomized, open-label, parallel-group, treat-to-target trial in individuals with type 2 diabetes. Diabetes Care 36:858–864
Zinman B, Philis-Tsimikas A, Cariou B, Handelsman Y, Rodbard HW, Johansen T, Endahl L, Mathieu C, NN1250-3579 (BEGIN Once Long) Trial Investigators (2012) Insulin degludec versus insulin glargine in insulin-naive patients with type 2 diabetes: a 1-year, randomized, treat-to-target trial (BEGIN Once Long). Diabetes Care 35:2464–2471
Komuro M, Inoue G, Tabata M, Yamada Y, Atsuda K, Matsubara H, Irie J, Uchida J, Nakajima C, Izumi H, Shimada M, Yamada S (2015) Insulin degludec requires lower bolus insulin doses than does insulin glargine in Japanese diabetic patients with insulin-dependent state. J Diabetes Sci Technol 9:632–638
Simon AC, Schopman JE, Hoekstra JB, Abu-Hanna A, Gerdes VE, Peek N, Holleman F (2015) Factors that drive insulin-dosing decisions of diabetes care providers: a vignette-based study in the Netherlands. Diabet Med 32:69–77
Goldman J, Kapitza C, Pettus J, Heise T (2017) Understanding how pharmacokinetic and pharmacodynamic differences of basal analog insulins influence clinical practice. Curr Med Res Opin 33:1821–1831 (Epub ahead of print)
Heise T, Hövelmann U, Nosek L, Hermanski L, Bøttcher SG, Haahr H (2015) Comparison of the pharmacokinetic and pharmacodynamic profiles of insulin degludec and insulin glargin. Expert Opin Drug Metab Toxicol 11:1193–1201
Porcellati F, Rossetti P, Busciantella NR, Marzotti S, Lucidi P, Luzio S, Owens DR, Bolli GB, Fanelli CG (2007) Comparison of pharmacokinetics and dynamics of the long-acting insulin analogs glargine and detemir at steady state in type 1 diabetes: a double-blind, randomized, crossover study. Diabetes Care 30:2447–2452
Shimoda S, Sato M, Sekigami T, Motoshima H, Yoshimura R, Fukuda K, Matsuo Y, Noda H, Okubo M, Ichimori S, Fujisawa K, Fukunaga M, Araki E, Kumamoto Insulin Degludec Observational (KIDUNA) Study Group (2016) A 1-year, prospective, observational study of Japanese outpatients with type 1 and type 2 diabetes switching from insulin glargine or detemir to insulin degludec in basal-bolus insulin therapy (Kumamoto Insulin Degludec Observational study). J Diabetes Investig 7:703–710
Kusunoki Y, Katsuno T, Miyakoshi K, Ikawa T, Nakae R, Ochi F, Tokuda M, Akagami T, Murai K, Miuchi M, Hamaguchi T, Miyagawa J, Namba M (2013) Effects of switching from insulin glargine or detemir to insulin degludec in patients with type 1 diabetes mellitus. Diabetes Ther 4:461–472
Bohn B, Zimmermann A, Wagner C, Merger S, Dunstheimer D, Kopp F, Gollisch K, Zindel V, Holl RW, DPV DPV (2017) Real-life experience of patientsstarting insulindegludec. A multicenteranalysis of 1064 subjects from the German/Austrian DPV registry. Diabetes Res Clin Pract 129:52–58
Dornhorst A, Lüddeke HJ, Sreenan S (2007) Safety and efficacy of insulin detemir in clinical practice: 14-week follow-up data from type 1 and type 2 diabetes patients in the PREDICTIVE European cohort. Int J Clin Pract 61:523–528
Porcellati F, Rossetti P, Busciantella NR, Marzotti S, Lucidi P, Luzio S, Owens DR, Bolli GB, Fanelli CG (2007) Comparison of pharmacokinetics and dynamics of the long-acting insulin analogs glargine and detemir at steady state in type 1 diabetes: a double-blind, randomized, crossover study. Diabetes Care 30:2447–2452
Urakami T, Kuwabara R, Habu M, Komiya K, Nagano N et al (2012) Comparison of the injection frequencies employed and basal-to-total insulin dose ratios obtained when glargine and detemir are used in children with type 1 diabetes mellitus treated by basal-bolus therapy. Diabetol Int 3:75–79
Funding
This research was performed independently of any funding, as part of the institutional activity of the investigators.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
CL, AS, ID, and LP were involved in each of the following points: (1) data collection, (2) writing manuscript, and (3) manuscript revision. MM and EM were involved in each of the following points: (1) design; (2) analysis; (3) writing manuscript; and (4) Manuscript revision.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
All the authors approved the final version of this manuscript. Dr. Edoardo Mannucci is the person who takes full responsibility for the work as a whole, including the study design, access to data, and the decision to submit and publish the manuscript
Conflict of interest
The authors have no relevant conflicts of interest to declare with the exception of MM and EM: Dr. Matteo Monami (MM) and Prof. Edoardo Mannucci (EM) have received grant/speaking fees from Astra, Boehringer, MSD, Takeda, Jannsen, Sanofi, Nobonordisk, and Lilly.
Ethical approval
All procedures followed were in accordance with the ethical standards of the responsible committee on human experimentation (institutional and national) and with the Helsinki Declaration of 1975, as revised in 2008.
Informed consent
Informed consent was obtained from all patients for being included in the study.
Human and animal rights
This article does not contain any studies with animal subjects.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Lualdi, C., Silverii, A., Dicembrini, I. et al. Adjustment of insulin doses when switching from glargine 100 U/ml or detemir to degludec: an observational study. J Endocrinol Invest 42, 319–326 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s40618-018-0920-2
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s40618-018-0920-2