Abstract
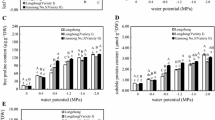
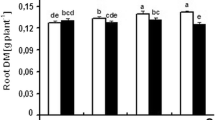
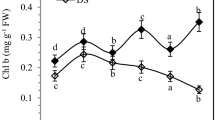
Water deficit can greatly influence plant growth and development. A pot trial was conducted to study the impact of various levels of water deficit on alfalfa (Medicago sativa L.) plants grown in different soil types. The results elucidated that increasing drought level and/or sand proportion in the cultivation soil reduced leaf growth vigor as indicated by declined number of leaves per plant as well as less cumulative leaf biomass, area, specific area, relative water content and degree of succulence with corresponding increase in the cumulative degree of leaf sclerophylly. Leaf anatomical analysis revealed that drought increased leaf thickness and ground tissue thickness but reduced phloem, xylem and whole vascular bundle areas, as well as the number of xylem vessels and rays. In addition, transmission electron microscopic examination of leaves cleared that the shape of chloroplasts was irregular when droughted. Also, stress reduced the number of both chloroplasts per cell and starch grains per chloroplast as well as the area of individual chloroplasts and starch grains. Moreover, severe water deficit resulted in the appearance of plastoglobules within chloroplasts. Concerning pigment fractions, chlorophyll a, b and a + b as well as total pigments and photosystem II activity were all declined in water-unsatisfied plants. Meanwhile, stress enhanced the production of carotenoids and also increased the calculated chlorophyll a/b ratio. The results also showed that water deficit increased glucose, fructose, trehalose, sucrose and total soluble sugars but reduced the amount of polysaccharides and total carbohydrates in alfalfa plants.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Aldesuquy, H. S., Abo-Hamed, S. A., Abbas, M. A., & Elhakeem, A. H. (2012). Role of glycine betaine and salicylic acid in improving growth vigour and physiological aspects of droughted wheat cultivars. Journal of Stress Physiology and Biochemistry, 8, 149–171.
Al-Saied, A. A. (2009). Physiological studies of some polyamines on wheat plants irrigated with waste water (Dissertation, Faculty of Science, Mansoura University, Mansoura).
Andersen, M. N., Asch, F., Wu, Y., Jensen, C. R., Nsted, H., Mogensen, V. O., et al. (2002). Soluble invertase expression is an early target of drought stress during the critical, abortion-sensitive phase of young ovary development in maize. Journal of Plant Physiology, 130, 591–604.
Austin, J. R., Frosta, E., Vidic, P. A., Kesslerc, F., & Staehelina, L. A. (2006). Plastoglobules are lipoprotein subcompartments of the chloroplast that are permanently coupled to thylakoid membranes and contain biosynthetic enzymes. Plant Cell, 18, 1693–1703.
Avramova, V., AbdElgawad, H., Zhang, Z., Fotschki, B., Casadevall, R., Vergauwen, L., et al. (2015). Drought induces distinct growth response, protection, and recovery mechanisms in the maize leaf growth zone. Journal of Plant Physiology, 169, 1382–1396.
Barrs, H. D., & Weatherley, P. E. (1962). A re-examination of the relative turgidity technique for estimating water deficit in leaves. Australian Journal of Biological Sciences, 15, 413–428.
Baum, S. F., Tran, P. N., & Silk, W. K. (2000). Effects of salinity on xylem structure and water use in growing leaves of sorghum. New Phytologist, 146, 119–127.
Beadle, C. L. (1993). Growth analysis. In D. C. Hall, J. M. O. Scurlock, H. R. Bolhar, R. C. Leegod, & S. P. Long (Eds.), Photosynthesis and production in a changing environment: A field and laboratory manual. London: Chapman and Hall.
Chen, Y., Liu, L., Guo, Q., Zhu, Z., & Zhang, L. (2016). Effects of different water management options and fertilizer supply on photosynthesis, fluorescence parameters and water use efficiency of Prunella vulgaris seedlings. Journal of Biological Research, 49, 1–12.
DaMatta, F. M., & Ramalho, J. D. C. (2006). Impacts of drought and temperature stress on coffee physiology and production: A review. Brazilian Journal of Plant Physiology, 18, 55–81.
Devi, P. (2007). Principles and methods in plant molecular biology, biochemistry and genetics (4th ed.). India: Agrobios.
Djanaguiraman, M., & Ramadass, R. (2004). Effect of salinity on chlorophyll content of rice genotypes. Agricultural Science Digest, 24, 178–181.
Edwards, C., Read, J., & Sanson, G. (2000). Characterizing sclerophylly: Some mechanical properties of leaves from heath and forest. Oecologia, 123, 158–167.
Elhakeem, A. H. (2008). Control of growth and productivity of droughted wheat cultivars by glycine betaine and salicylic acid (Dissertation, Faculty of Science, Mansoura University, Mansoura).
El-Sawy, O. E. (2009). Protective effects of polyamines on wheat plants irrigated by seawater (Dissertation, Faculty of Science, Mansoura University, Mansoura).
Fu, L., Bounelis, P., Dey, N., Browne, B. L., Marchase, R. B., & Bedwell, D. M. (1995). Posttranslational modification of phosphoglucomutase is regulated by galactose induction and glucose repression in Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Journal of Bacteriology, 177, 3087–3094.
Garg, A. K., Kim, J. K., Owens, T. G., Ranwala, A. P., Choi, Y. D., Kochian, L. V., et al. (2002). Trehalose accumulation in rice plants confers high tolerance levels to different abiotic stresses. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences, 99, 15898–15903.
Gianessi, L. P. (2009). The benefits of insecticide use: Alfalfa. Washington, DC: Crop Life Foundation.
Hameed, M., Ashraf, M., & Naz, N. (2009). Anatomical adaptations to salinity in cogon grass [Imperata cylindrica (L.) Raeuschel] from the Salt Range. Pakistan. Plant Soil, 322, 229–238.
Hamidi, H., & Safarnejad, A. (2010). Effect of drought stress on alfalfa cultivars (Medicago sativa L.) in germination stage. American-Eurasian Journal of Agricultural and Environmental Sciences, 8, 705–709.
Havaux, M. (2014). Carotenoid oxidation products as stress signals in plants. Plant Journal, 79, 597–606.
Hu, Y., Fromm, J., & Schmidhalter, U. (2005). Effect of salinity on tissue architecture in expanding wheat leaves. Planta, 220, 838–848.
Hülskamp, M., Schwab, B., Grini, P., & Schwarz, H. (2010). Transmission electron microscopy (TEM) of plant tissues. Cold Spring Harbor Protocols. https://doi.org/10.1101/pdb.prot4958.
Jaleel, A. C., Azooz, M. M., & Panneerselvam, R. (2009). Treatment with different sodium salts alters growth and photosynthetic pigment constituents in Withania somnifera. Global Journal of Molecular Sciences, 4, 6–9.
Jaleel, A. C., Manivannan, P., Sankar, B., Kishorekumar, A., Gopi, R., Somasundaram, R., et al. (2007). Water deficit stress mitigation by calcium chloride in Catharanthus roseus: Effects on oxidative stress, proline metabolism and indole alkaloid accumulation. Colloids and Surfaces B: Biointerfaces, 60, 110–116.
Jamei, R., Heidari, R., Khara, J., & Zare, S. (2008). The interaction effects of flooding and kinetin on growth criteria, chlorophyll content and 5-aminolevulinic acid dehydratase activity in corn seedlings. Turkish Journal of Biology, 32, 253–257.
Kim, J., Mahe, A., Brangeon, J., & Prioul, J. L. (2000). A maize vacuolar invertase, IVR2, is induced by water stress: Organ/tissue specificity and diurnal modulation of expression. Journal of Plant Physiology, 124, 71–84.
Kissimon, J. (1999). Analysis of the photosynthetic pigment composition. In International workshop and training course on microalgal biology and biotechnology, Mosonmagyarouar (pp. 13–26).
Krasensky, J., & Jonak, C. (2011). Drought, salt, and temperature stress-induced metabolic rearrangements and regulatory networks. Journal of Experimental Botany. https://doi.org/10.1093/jxb/err460.
Kwon, M. Y., & Woo, S. Y. (2015). Plants’ responses to drought and shade environments. African Journal of Biotechnology, 15, 29–31.
Laurentin, A., & Edwards, C. A. (2003). A microtiter modification anthrone-sulfuric acid colorimetric assay for glucose-basehydrates. Analytical Biochemistry, 315, 143–145.
Lemoine, R. (2000). Sucrose transporters in plants: Update on function and structure. Biochimica et Biophysica Acta, 1465, 246–262.
Liu, F., Christian, R. J., & Mathias, N. A. (2004). Drought stress effect on carbohydrate concentration in soybean leaves and pods during early reproductive development: Its implication in altering pod set. Field Crop Research, 86, 1–13.
Liu, S. C., Jin, J. Q., Ma, J. Q., Yao, M. Z., Ma, C. L., Li, C. F., et al. (2016). Transcriptomic analysis of tea plant responding to drought stress and recovery. PLoS ONE. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0147306.
Mahalingam, R., & Fedoroff, N. (2003). Stress response, cell death and signalling: The many faces of reactive oxygen species. Physiologia Plantarum, 119, 56–68.
Maiti, R., Satya, P., Rajkumar, D., & Ramaswamy, A. (2012). Crop plant anatomy (pp. 15–17). Wallingford: CAB International.
Manivannan, P., Jaleel, C. A., Sankar, B., Kishorekumar, A., Somasundaram, R., Lakshmanan, G. M., et al. (2007). Growth biochemical modifications and proline metabolism in Helianthus annuus L. as induced by drought stress. Colloids and Surfaces B: Biointerfaces, 59, 141–149.
McElroy, J. S., & Kopsell, D. A. (2009). Physiological role of carotenoids and other antioxidants in plants and application to turf grass stress management. New Zealand Journal of Crop and Horticultural Science, 37, 327–333.
Mekki, B., Hussien, H., & Salem, H. (2015). Role of glutathione, ascorbic acid and α-tocopherol in alleviation of drought stress in cotton plants. International Journal of ChemTech Research, 8, 1573–1581.
Mickky, B. M. (2010). Mitigatory effect of kinetin and spermine on seawater-stressed wheat (Triticum aestivum) plants (Dissertation, Faculty of Science, Mansoura University, Mansoura).
Mickky, B. M. (2012). Biotechnological aspects of economic maximization and characterization of medically-active phytochemicals from Medicago sativa plants (Dissertation, Faculty of Science, Mansoura University, Mansoura).
Mickky, B. M. (2016). Could sodium benzoate enhance broad bean salinity tolerance? I. Seedling vigor, membrane features, antioxidant enzymes and osmolytes. Journal of Chemical, Biological and Physical Sciences, 6, 313–328.
Munne-Bosch, S., & Alegre, L. (2004). Die and let live: Leaf senescence contributes to plant survival under drought stress. Functional Plant Biology, 31, 203–216.
Munns, R. (2002). Comparative physiology of salt and water stress. Plant and Cell Physiology, 25, 239–250.
Munns, R., Guo, J. M., Passioura, J. B., & Cramer, G. R. (2000). Leaf water status controls day-time but not daily rates of leaf expansion in salt-treated barley. Australian Journal of Plant Physiology, 27, 949–957.
Netondo, G. W., Onyango, J. C., & Beck, E. (2004). Sorghum and salinity. II. Gas exchange and chlorophyll fluorescence of sorghum under salt stress. Crop Sciences, 44, 806–811.
Parés, J., Arizaleta, M., Sanabria, M. E., & García, Y. G. (2008). Effect of salinity levels on the stomatal density, stomatal index and leaf thickness of Carica papaya L. Acta Botánica Venezuelica, 31, 27–34.
Rosa, M., Prado, C., Podazza, G., Interdonato, R., González, J. A., Hilal, M., et al. (2009). Soluble sugars-metabolism, sensing and abiotic stress: A complex network in the life of plants. Plant Signaling and Behavior, 4, 388–393.
Roussos, P. A., Tsantili, E., & Pontikis, C. A. (2005). Responses of jojoba explants to different salinity levels during the proliferation stage in vitro. Indian Crop Production, 23, 65–72.
Sadasivam, S., & Manickam, A. (1996). Biochemical methods (2nd ed.). New Delhi: New Age International (P) Limited.
Sam, O., Ramirez, C., Coronado, M. J., Testillano, P. S., & Risueno, M. C. (2003). Changes in tomato leaves induced by NaCl stress: Leaf organization and cell ultrastructure. Biologia Plantarum, 47, 361–366.
Sankar, B., Karthishwaran, K., & Somasundaram, R. (2013). Leaf anatomical changes in peanut plants in relation to drought stress with or without paclobutrazol and abscisic acid. Journal of Phytology, 5, 25–29.
Scott, N., & Greenberg, B. (1995). Measurement of photosynthetic activity in plant cell fractions. In: C. A. Goldman (Ed.), Tested studies for laboratory teaching (Vol. 16). Proceedings of the 16th workshop/conference of the association for biology laboratory education (ABLE) (pp. 71–80).
Shah, S. H. (2007). Effects of salt stress on mustard as affected by gibberellic acid application. General and Applied Plant Physiology, 33, 97–106.
Shani, U., & Ben-Gal, A. (2005). Long-term response of grapevines to salinity: Osmotic effects and ion toxicity. American Journal of Enology and Viticulture, 56, 148–154.
Shanmugam, S., Kumar, T. S., & Selvam, K. P. (2010). Laboratory handbook on biochemistry. New Delhi: PHI Learning Private Limited.
Shao, R., Xin, L., Mao, J., Li, L., Kang, G., & Yang, Q. (2015). Physiological, ultrastructural and proteomic responses in the leaf of maize seedlings to polyethylene glycol-stimulated severe water deficiency. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 16, 21606–21625.
Small, E. (2011). Alfalfa and relatives: Evolution and classification of Medicago. Ottawa: National Research Council of Canada.
Smethurst, C. F., Gill, W. M., & Shabala, S. (2009). Using excised leaves to screen lucerne for salt tolerance: Physiological and cytological evidence. Plant Signaling and Behavior, 4, 39–41.
VandenLangenberg, K. M., Bethke, P. C., & Nienhuis, J. (2012). Patterns of fructose, glucose, and sucrose accumulation in snap and dry bean (Phaseolus vulgaris) pods. Journal of Hortsciences, 47, 874–878.
Welch, M. E., & Rieseberg, L. H. (2002). Habitat divergence between a homoploid hybrid sunflower species, Helianthus paradoxus (Asteraceae), and its progenitors. American Journal of Botany, 89, 472–479.
Witkoswski, E. T. F., & Lamont, B. B. (1991). Leaf specific mass confounds leaf density and thickness. Oecologia, 84, 362–370.
Xian-Zheng, Z. (1992). Research methods of crop physiology (pp. 148–150). Beijing: China Agricultural Press.
Younis, M. E., El-Shahaby, O. A., Nemat-Alla, M. M., & El-Bastawisy, Z. M. (2003). Kinetin alleviates the influence of water logging and salinity on growth and affects the production of plant growth regulators in Vigna sinensis and Zea mays. Agronomie, 23, 277–285.
Zhu, J. K. (2002). Salt and drought stress signal transduction in plants. Annual Review of Plant Biology, 53, 247–273.
Zlatev, Z. S., & Yordanov, I. T. (2005). Effects of soil drought on photosynthesis and chlorophyll fluorescence in bean plants. Bulgarian Journal of Plant Physiology, 30, 3–18.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Mickky, B.M., Abbas, M.A. & El-Shhaby, O.A. Alterations in photosynthetic capacity and morpho-histological features of leaf in alfalfa plants subjected to water deficit-stress in different soil types. Ind J Plant Physiol. 23, 426–443 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s40502-018-0383-7
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s40502-018-0383-7