Abstract
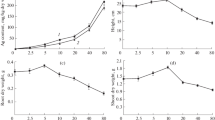
An experiment was conducted to study the effects of silver nanoparticles (AgNPs) on the contents of free amino acids, protein, lipid peroxidation (MDA) and antioxidant enzymes activity, viz., superoxide dismutase (SOD), catalase (CAT), peroxidase (POX) in tomato plants. For this purpose 20 nm size AgNPs in five different concentrations, viz., 0, 25, 50, 75 and 100 mg l−1 were used. The experiments were carried out by high performance liquid chromatography reverse phase (RP-HPLC) with C-18 column. Amino acid analysis by HPLC graphs revealed that all the amino acids except two amino acids, viz, methionine and tryptophan exhibited a linear increase with the increase in concentration of silver nano-particles in tomato plants. The greater increases in amino acids content were observed at 75 and 100 mg l−1 concentrations. Among the different amino acids, greatest increases were observed in glutamine and asparagine, with increases being 8 and 6 times higher than the control. A remarkable decrease in total soluble protein was observed with increase in concentration of AgNPs. Activities of SOD, CAT and POX increased significantly in both shoots and roots of treated tomato plants, though SOD activity declined significantly in the roots at 100 mg l−1 concentration. Also enhanced malondialdehyde content indicated the oxidative stress induced by AgNPs. It seems that the increase in protein degradation, resulting in amino acid contents, and antioxidant enzymes activity are strategies to modulate oxidative stress induced by AgNPs in tomato plants.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Abdul, G. (2010). Toxic effects of heavy metals on plant growth and metal accumulation in maize (Zea mays L.). Iranian Journal of Toxicology, 4, 325–334.
Alia, P., & Saradhi, P. (1991). Proline accumulation under heavy metal stress. Journal of Plant Physiology, 138, 554–558.
Azooz, M. M., Elhamd, M. F. A., & Al- Fredan, M. A. (2012). Biphasic effect of copper on growth, proline, lipid peroxidation and antioxidant enzyme activities of wheat (Triticum aestivum cv. Hasaawi) at early growing stage. Australian Journal of Crop Science, 6, 688–694.
Beauchamp, C., & Fridovich, I. (1971). Superoxide dismutase: improved assays and an assay applicable to acrylamide gels. Analytical Biochemistry, 44, 276–287.
Beers, R. F., & Sizer, I. W, Jr. (1952). A spectrophotometric method for measuring the breakdown of hydrogen peroxide by catalase. Journal of Biological Chemistry, 195, 133–140.
Bieleski, R. L., & Turner, N. A. (1966). Separation and estimation of amino acids in crude plant extracts by thin-layer electrophoresis and chromatography. Analytical Biochemistry, 17, 278–293.
Bowler, C. Van, Montagu, M., & Inzé, D. (1992). Superoxide dismutase and stress tolerance. Annual Review of Plant Physiology, 43, 83–116.
Cavalcanti, F. R., Oliveira, J. T. A., Martins-Miranda, A. S., Vie’gas, R. A., & Silveira, J. A. G. (2004). Superoxide dismutase, catalase and peroxidase activities do not confer protection against oxidative damage in salt– stressed cowpea leaves. New Phytologist, 163, 563–571.
Chaffei, C., Pageau, K., Suzuki, A., Houda, G., Ghorbel, M. H., & Masclaux Daubresse, C. (2004). Cadmium toxicity induced changes in nitrogen management in Lycopersicon esculentum leading to a metabolic safeguard through an amino acid storage strategy. Plant Cell Physiology, 45, 1681–1693.
Chen, X., & Schluesener, H. J. (2008). Nanosilver: a nanoproduct in medical application. Toxicology Letters, 176, 1–12.
Filek, M., Keskinen, R., Hartikainen, H., Szarejko, I., Janiak, A., Miszalski, Z., & Golda, A. (2008). The protective role of selenium in rape seedlings subjected to cadmium stress. Plant Physiology, 165, 833–844.
Gilbert, G. A., Gadush, M. V., Wilson, C., & Madore, M. A. (1998). Amino acid accumulation in sink and source tissues of Coleus blumei Benth during salinity stress. Journal of Experimental Botany, 49, 107–114.
Hall, J. L. (2002). Cellular mechanisms for heavy metal detoxification and tolerance. Journal of Experimental Botany, 53, 1–11.
Kim, S., Lee, S., & Lee, I. (2012). Alteration of phytotoxicity and oxidant stress potential by metal oxide nanoparticles in Cucumis sativus. Water, Air, and Soil Pollution, 223, 2799–2806.
Kocsy, G., Simon Sarkadi, L., Kovacs, Z., Boldizsar, A., Sovany, C., Kirsch, K., & Galiba, G. (2011). Regulation of free amino acid and polyamine levels during cold acclimation in wheat. Acta Biologica Szegediensis, 55, 91–93.
Kosugi, H., & Kikugawa, K. (1985). Thiobarbituric acid reaction of aldehyes and oxidized lipids in glacial acetic acid. Lipid, 20, 915–920.
Lesko, K., & Simon Sarkadi, L. (2002). Effect of cadmium stress on amino acid and polyamine content of wheat seedlings. Periodica Polytechnica-Chemical Engineering, 46, 65–71.
Li, M., Hu, C. W., Zhu, Q., Chen, L., Kong, Z. M., & Liu, Z. L. (2006). Copper and zinc induction of lipid peroxidation and effects on antioxidant enzyme activities in the microalga Pavlova viridis (Prymnesiophyceae). Chemosphere, 62, 565–572.
Lowry, O. H., Rosebrough, J., Farr, A. L., & Randall, R. J. (1971). Protein measurement with Folinphenol reagent. Journal of Biological Chemistry, 193, 265–275.
Miao, A. J., Schwehr, K. A., Xu, C., Zhang, S. J., Luo, Z. P., Quigg, A., & Santschi, P. H. (2009). The algal toxicity of silver engineered nanoparticles and detoxification by exopolymeric substances. Environmental Pollution, 157, 3034–3041.
Rabe, E. (1990). Stress physiology: The functional significance of the accumulation of nitrogen containing compounds. Journal of Horticultural Sciences, 65, 231–243.
Rai, V. K. (2002). Role of amino acids in plant responses to stresses. Journal of Plant Biology, 45, 81–487.
Rani, G. (2007). Changes in protein profile and amino acids in Cladophora vagabunda (Chlorophyceae) in response to salinity stress. Journal of Applied Phycology, 19, 803–807.
Rastgoo, L., & Alemzadeh, A. (2011). Biochemical responses of Gouan (Aeluropus littoralis) to heavy metals stress. Australian Journal of Crop Science, 5, 375–383.
Saptarshi, S., Duschl, A., & Lopata, A. L. (2013). Interaction of nanoparticles with proteins: Relation to bio-reactivity of the nanoparticle. Journal of Nano biotechnology, 11, 1–12.
Schat, H., Sharma, S. S., & Vooijs, R. (1997). Heavy metal-induced accumulation of free proline in a metal-tolerant and nontolerant ecotype of Silene vulgaris. Physiolia Plantarum, 101, 477–482.
Schickler, H., & Caspi, H. (1999). Response of antioxidant enzymes to nickel and cadmium stress in hyper accumulator plants of the genus Alyssum. Physiologia Plantarum, 105, 39–44.
Sharma, P., Bhatt, D., Zaidi, M. G. H., Pardha Saradhi, P., Khanna, P. K., & Arora, S. (2012). Silver nanoparticle-mediated enhancement in growth and antioxidant status of Brassica juncea. Applied Biochemistry and Biotechnology, 167, 2225–2233.
Singh, S., & Sinha, S. (2005). Accumulation of metals and its effects in Brassica juncea (L.) Czern. (cv. Rohini) grown on various amendments of tannery waste. Ecotoxicology and Environmental Safety, 62, 118–127.
Stroinski, A., & Kozlowska, M. (1997). Cadmium induced oxidative stress in potato tuber. Acta Societatis Botanicorum Poloniae, 66, 189–195.
Yasur, J., & Rani, P. U. (2013). Environmental effects of nanosilver: impact on castor seed germination, seedling growth, and plant physiology. Environmental Science and Pollution Research, 20, 8636–8648.
Zhang, J., Cui, S., Li, J., & Kirkham, M. B. (1995). Protoplasmic factors, antioxidant responses, and chilling resistance in maize. Plant Physiology and Biochemistry, 33, 567–575.
Zhang, H. Y., Jiang, Y. N., He, Z. Y., & Ma, M. (2005). Cadmium accumulation and oxidative burst in garlic (Allium sativum). Journal of Plant Physiology, 162, 977–984.
Zhang, F. Q., Wang, Y. S., Lou, Z. P., & Dong, J. D. (2007). Effect of heavy metal stress on antioxidative enzymes and lipid peroxidation in leaves and roots of two mangrove plant seedlings (Kandelia candel and Bruguiera gymnorrhiza). Chemosphere, 67, 44–50.
Acknowledgments
We are grateful to Mrs. Sepideh Tarbali for her assistance.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Karami Mehrian, S., Heidari, R. & Rahmani, F. Effect of silver nanoparticles on free amino acids content and antioxidant defense system of tomato plants. Ind J Plant Physiol. 20, 257–263 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s40502-015-0171-6
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s40502-015-0171-6